A Language Vision Model Approach for Automated Tumor Contouring in Radiation Oncology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
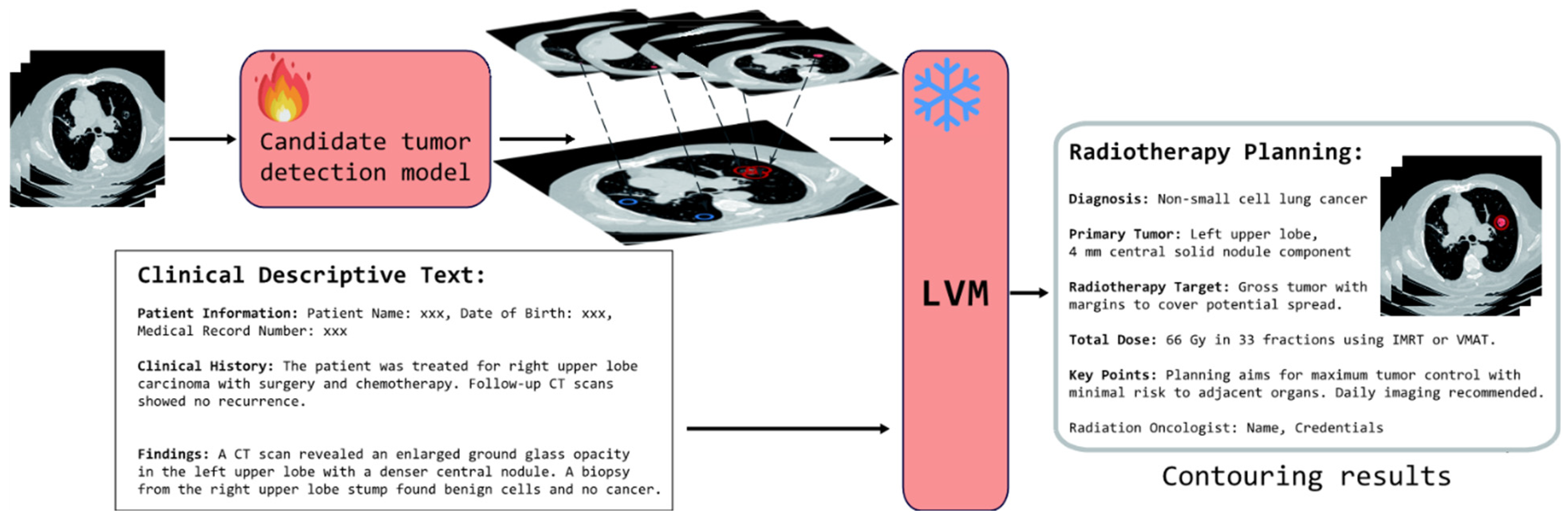
3. Methods
3.1. Candidate Tumor Detection Model
3.1.1. Architecture
3.1.2. Loss Functions
3.2. False Positive Reduction Model
3.2.1. Experiment Design
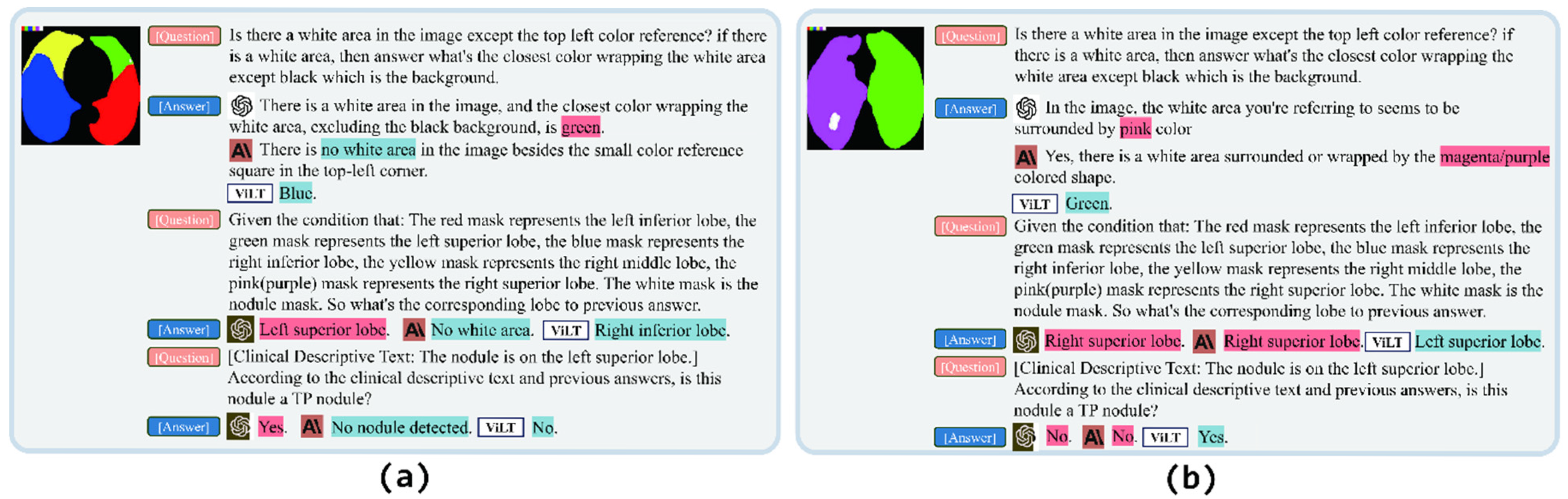
3.2.2. Medical Language Vision Prompt Methods
3.3. Dataset and Preprocessing
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
5. Case Study
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vyas, A.; Kumar, K.; Sharma, A.; Verma, D.; Bhatia, D.; Wahi, N.; Yadav, A.K. Advancing the frontier of artificial intelligence on emerging technologies to redefine cancer diagnosis and care. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 191, 110178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, A.; Veluswamy, R.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. The global burden of lung cancer: Current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodor, J.N.; Boumber, Y.; Borghaei, H. Biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibition in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer 2020, 126, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Yu, X.; Holmes, J.; Feng, H.; Dai, H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Generalizable and promptable artificial intelligence model to augment clinical delineation in radiation oncology. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 2187–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, W.; Ngoma, T.; Zietman, A.; Mayr, N.; Elzawawy, A.; Winningham, T.A.; Balogun, O.; Enwerem-Bromson, N.; Ntizimira, C.; Olopade, O.I.; et al. Closing the cancer divide through Ubuntu: Information and communication technology-powered models for global radiation oncology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 94, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addai, B.W.; Ngwa, W. COVID-19 and cancer in Africa. Science 2021, 371, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, A.; Hu, Z.; Wang, L. Accurate pulmonary nodule detection in computed tomography images using deep convolutional neural networks. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Proceedings of the MICCAI 2017: 20th International Conference, Quebec, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; Proceedings, Part III 20; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 559–567. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Kim, D.R.; Xie, X. Automated pulmonary nodule detection using 3D deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 523–526. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Xie, X. Deeplung: Deep 3d dual path nets for automated pulmonary nodule detection and classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 673–681. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Song, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, W. A deep learning approach for automatic tumor delineation in stereotactic radiotherapy for nonsmall cell lung cancer using diagnostic PET-CT and planning CT. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1235461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Litjens, G.; Gerke, P.; Jacobs, C.; Van Riel, S.J.; Wille, M.M.W.; Naqibullah, M.; S’anchez, C.I.; Van Ginneken, B. Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: False positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Chen, H.; Yu, L.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.-A. Multilevel contextual 3-D CNNs for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 64, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Feng, D.; Fulham, M.; Cai, W. Knowledge-based collaborative deep learning for benign-malignant lung nodule classification on chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shu, P.; Zhong, A.; Yang, L.; Ju, C.; Wu, Z.; Ma, C.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; et al. Radiology-llama2: Best-in-class large language model for radiology. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.06419. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Holmes, J.; Shu, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, N.; Zhu, D.; Liu, W. Radonc-gpt: A large language model for radiation oncology. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.10160. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Huang, J.; Yeung, J.; Blaes, A.; Johnson, S.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, R. Cancerllm: A large language model in cancer domain. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.10459. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Hooshangnejad, H.; Ngwa, W.; Ding, K. Opportunities and challenges in lung cancer care in the era of large language models and vision language models. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2025, 14, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenAI; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Dong, L.; Wang, W.; Hao, Y.; Singhal, S.; Ma, S.; Lv, T.; Cui, L.; Mohammed, O.K.; Patra, B.; et al. Language is not all you need: Aligning perception with language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.14045. [Google Scholar]
- Alayrac, J.-B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 23716–23736. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Yin, S.; Qi, W.; Wang, X.; Tang, Z.; Duan, N. Visual chatgpt: Talking, drawing and editing with visual foundation models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.04671. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Lei, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Lin, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Can gpt-4v (ision) serve medical applications? case studies on gpt-4v for multimodal medical diagnosis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.09909. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Yang, D.; Sun, N.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Automated pulmonary nodule detection in CT images using deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, A.; Fujita, H.; Yamamuro, O.; Tamaki, T. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in PET/CT images: Ensemble false-positive reduction using a convolutional neural network technique. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, Z. An attentive and adaptive 3D CNN for automatic pulmonary nodule detection in CT image. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 211, 118672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, H.; Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Weng, X.; Su, Z.; Yang, J. 3D ARCNN: An Asymmetric Residual CNN for False Positive Reduction in Pulmonary Nodule. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2023, 23, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C. Controlling False-Positives in Automatic Lung Nodule Detection by Adding 3D Cuboid Attention to a Convolutional Neural Network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 85, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshangnejad, H.; Feng, X.; Huang, G.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q.; Ding, K. EXACT-Net: EHR-guided lung tumor auto-segmentation for non-small cell lung cancer radiotherapy. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14099. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghir, J.; Naguib, M.; Bjelogrlic, M.; Névéol, A.; Tannier, X.; Lovis, C. Prompt engineering paradigms for medical applications: Scoping review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e60501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.; Singh, A.K.; Saha, S.; Jain, V.; Mondal, S.; Chadha, A. A systematic survey of prompt engineering in large language models: Techniques and applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.07927. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, S.; Beirami, A.; He, B.; Zhang, G.; Liao, R.; Qin, Y.; Tresp, V.; Torr, P. A systematic survey of prompt engineering on vision-language foundation models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.12980. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Luan, Z.; Chen, B. Soft prompt generation for domain generalization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 434–450. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Doll’ar, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Proceedings of the MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; proceedings, part III 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Armato, S.G., III; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Name of the Conference the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems—Volume 1, Montreal, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, C.; Xie, X. Automatic pulmonary lobe segmentation using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 1225–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Kim, I. Vilt: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5583–5594. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Chiang, W.-L.; Sheng, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xing, E.P.; et al. Judging llm-as-a-judge with mt-bench and chatbot arena. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 46595–46623. [Google Scholar]


| Method | FDR ↓ | Average FP/Scan ↓ | Sen ↑ | Spe ↑ | F1-Score ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidates | 0.787 | 6.214 | - | - | - |
| Candidates + Unet-3D [35] | 0.696 | 3.357 | 0.872 | 0.460 | 0.366 |
| Candidates + ViLT [39] | 0.773 | 3.036 | 0.532 | 0.511 | 0.318 |
| Candidates + Claude 3 Sonnet | 0.556 | 1.964 | 0.936 | 0.684 | 0.603 |
| Candidates + GPT-4V (Ours) | 0.511 | 1.714 | 0.979 | 0.724 | 0.652 |
| Methods and Metrics | Choice and Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Vision Input | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Leave Time to Think | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Conceal Medical Intent | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| A Series of Guiding Questions | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Vision Instructions | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Highlighting Areas of Interest | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| FDR ↓ | 0.615 | 0.546 | 0.667 | 0.715 | 0.639 | 0.762 | 0.511 |
| Average FP/Scan ↓ | 2.286 | 1.893 | 2.607 | 4.036 | 1.393 | 1.607 | 1.714 |
| Sen ↑ | 0.833 | 0.917 | 0.766 | 0.954 | 0.468 | 0.298 | 0.979 |
| Spe ↑ | 0.630 | 0.695 | 0.580 | 0.362 | 0.776 | 0.741 | 0.724 |
| F1-score ↑ | 0.527 | 0.607 | 0.464 | 0.439 | 0.407 | 0.265 | 0.652 |
| Reject Rate ↓ | - | - | - | 0.575 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Hooshangnejad, H.; Feng, X.; Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q.; Ngwa, W.; Ding, K. A Language Vision Model Approach for Automated Tumor Contouring in Radiation Oncology. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080835
Luo Y, Hooshangnejad H, Feng X, Huang G, Chen X, Zhang R, Chen Q, Ngwa W, Ding K. A Language Vision Model Approach for Automated Tumor Contouring in Radiation Oncology. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(8):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yi, Hamed Hooshangnejad, Xue Feng, Gaofeng Huang, Xiaojian Chen, Rui Zhang, Quan Chen, Wil Ngwa, and Kai Ding. 2025. "A Language Vision Model Approach for Automated Tumor Contouring in Radiation Oncology" Bioengineering 12, no. 8: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080835
APA StyleLuo, Y., Hooshangnejad, H., Feng, X., Huang, G., Chen, X., Zhang, R., Chen, Q., Ngwa, W., & Ding, K. (2025). A Language Vision Model Approach for Automated Tumor Contouring in Radiation Oncology. Bioengineering, 12(8), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080835








