Implementation of a Conditional Latent Diffusion-Based Generative Model to Synthetically Create Unlabeled Histopathological Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Description of the Dataset
3.2. Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network (VQ-GAN)
3.3. VQ-GAN Hyperparameters
3.4. The Conditional Latent Diffusion Model (cLDM)
3.5. Information Maximization-Based Clustering
3.6. cLDM Hyperparameters
4. Results
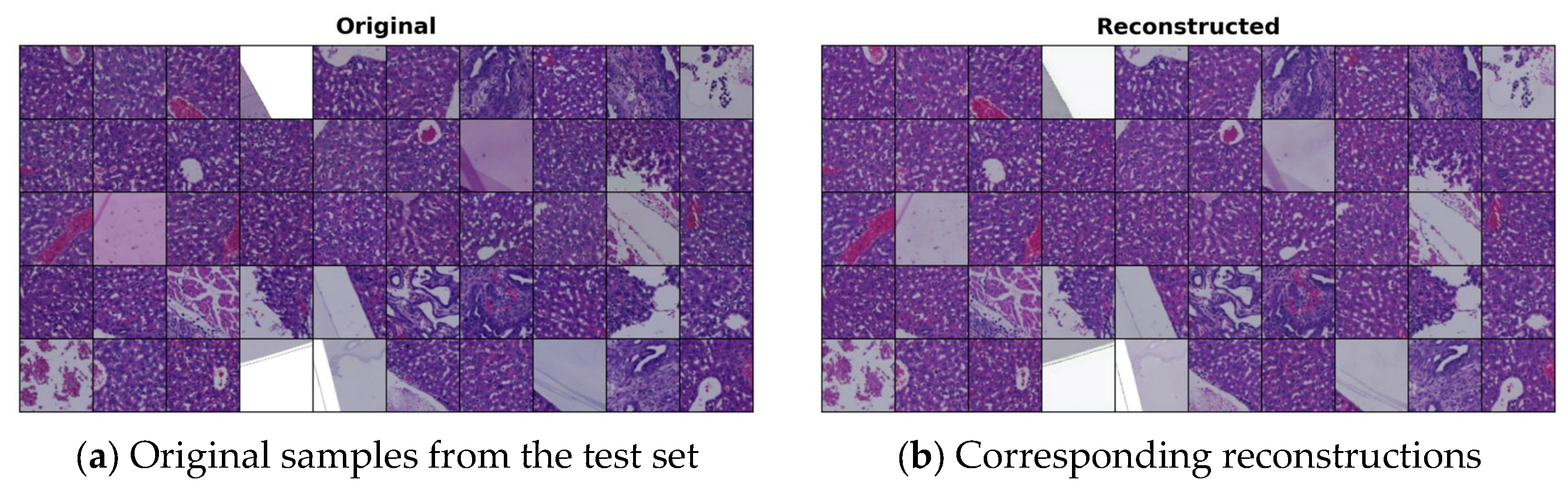
4.1. VQ-GAN Reconstructions
4.2. Cluster Validation
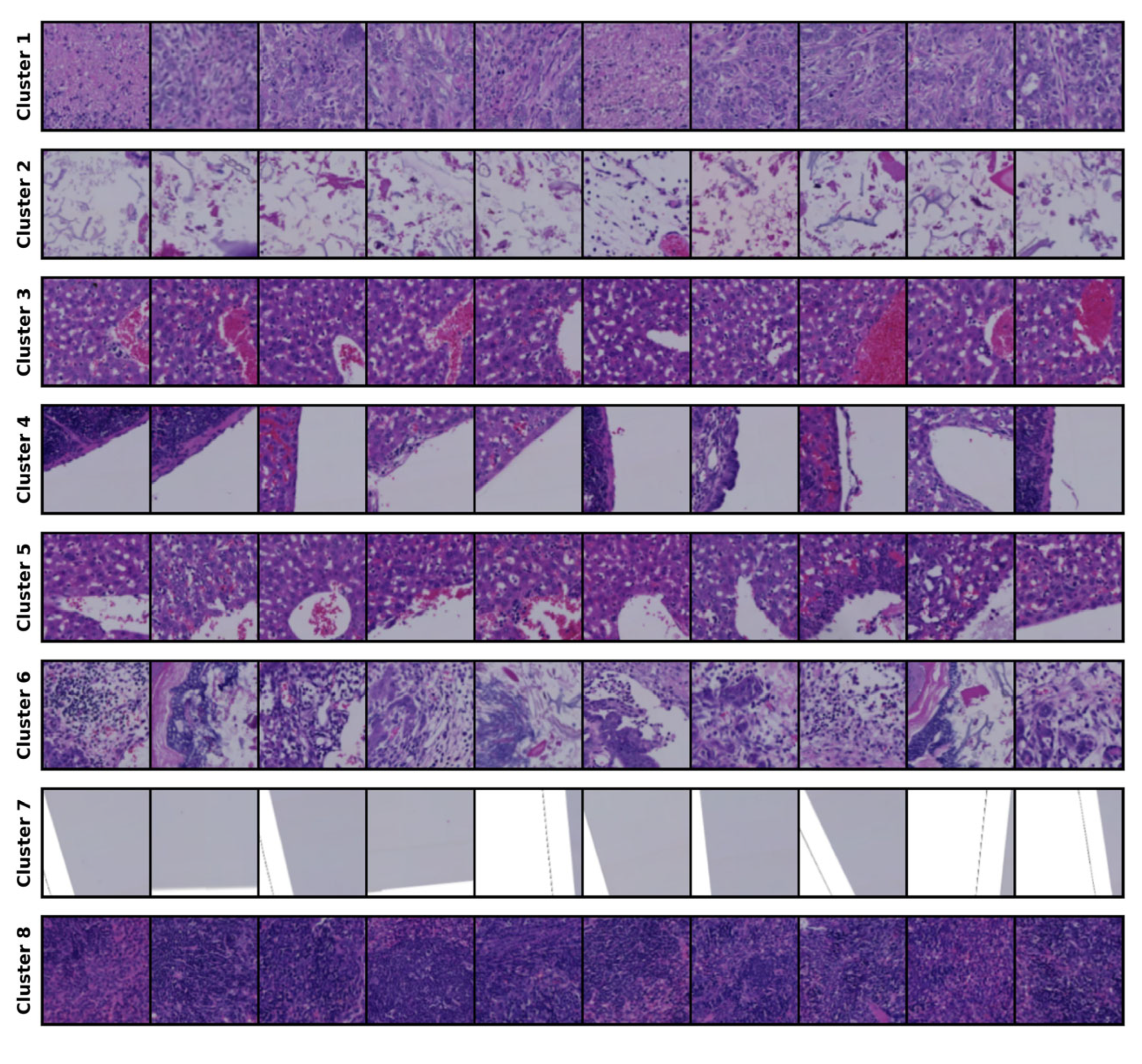
4.3. Clustering Results
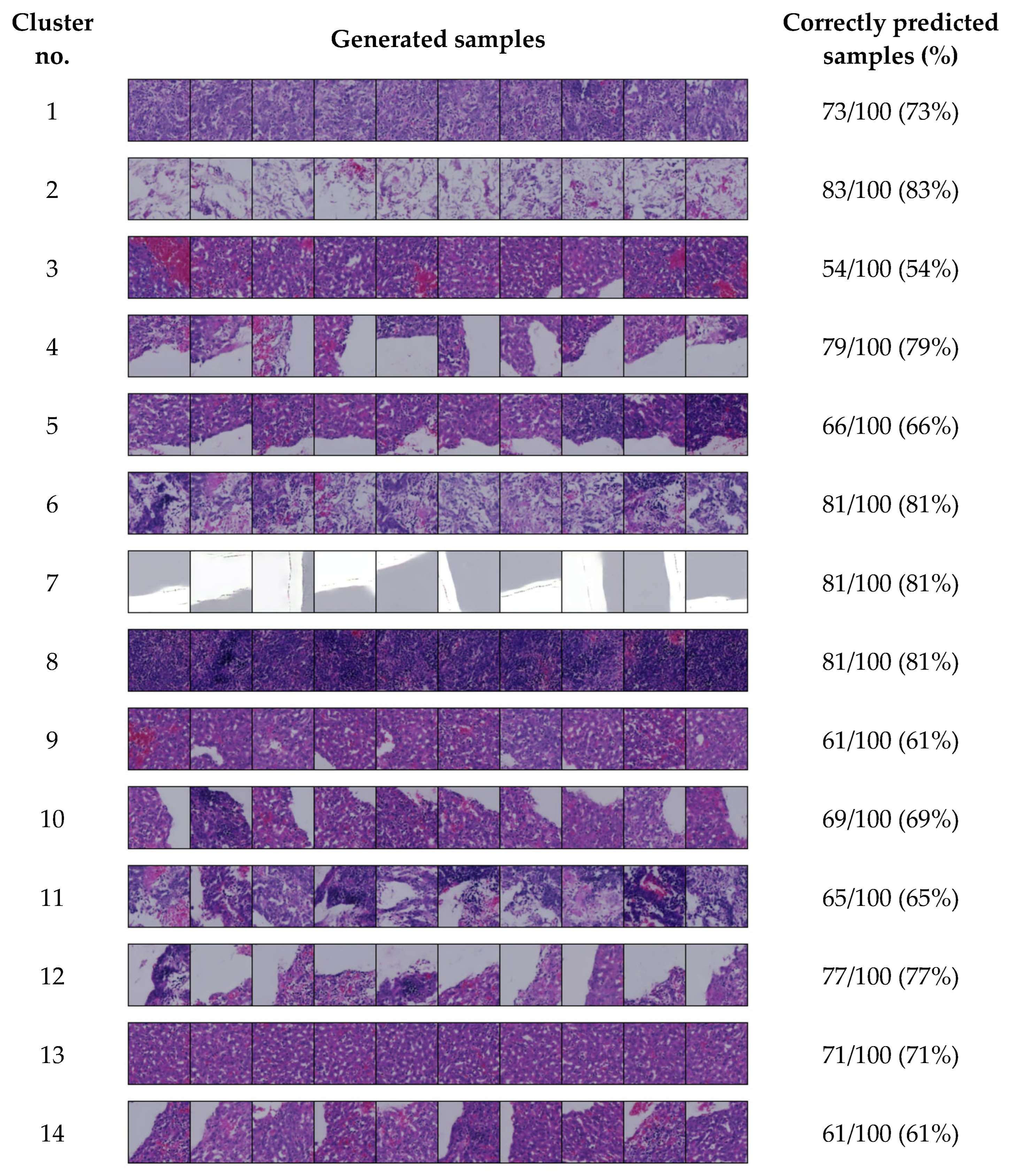
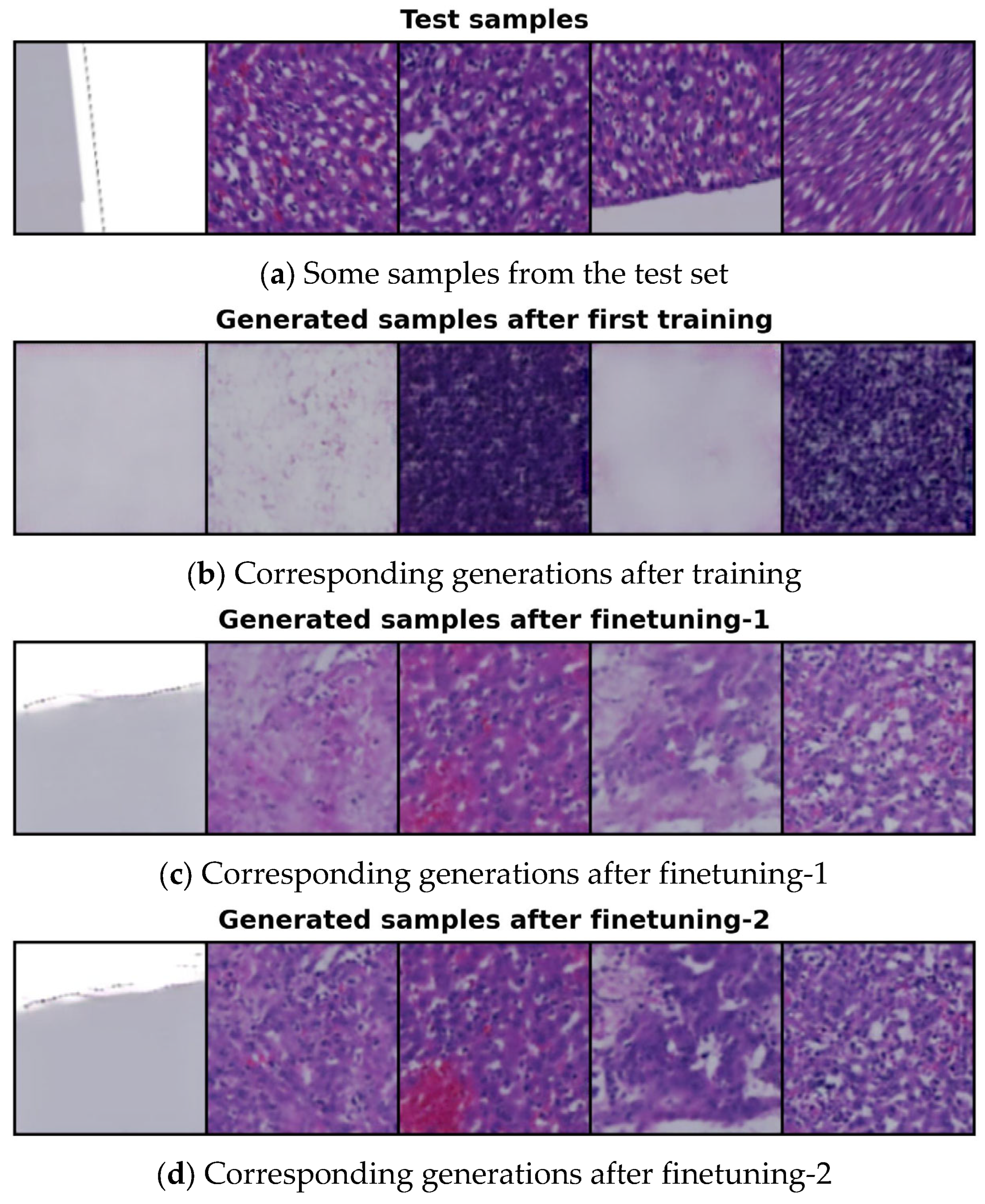
4.4. Generated Image Evaluation
4.5. Conditional Image Sampling Using the 14-Cluster Set
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VQ-GAN | Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network |
| GAI | Generative Artificial Intelligence |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| VAE | Variational Autoencoder |
| LDM | Latent Diffusion Model |
| DDPM | Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model |
| cLDM | Conditional Latent Diffusion Model |
| HE | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| VQ | Vector Quantization |
| VQ-VAE | Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder |
| LPIPS | Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| MI | Mutual Information |
| CH index | Calinski–Harabasz index |
| MR index | McClain–Rao index |
| SSIM | Structural Similarity Index Measure |
| MS-SSIM | Multi-Scale Structural Similarity Index Measure |
References
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, D.; Cao, J. Generative adversarial networks (GANs): Challenges, solutions, and future directions. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.Q.; Dhariwal, P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models are optimally adaptive to unknown low dimensionality. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.18784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovanu, S.; Munteanu, D.; Sîrbu, C. Impact on Classification Process Generated by Corrupted Features. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, D.; Moldovanu, S.; Miron, M. The Explanation and Sensitivity of AI Algorithms Supplied with Synthetic Medical Data. Electronics 2025, 14, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letafati, M.; Ali, S.; Latva-Aho, M. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models for hardware-impaired communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21–24 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Podell, D.; English, Z.; Lacey, K.; Blattmann, A.; Dockhorn, T.; Müller, J.; Penna, J.; Rombach, R. Improving latent diffusion models for high-resolution image synthesis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Gould, S.; Zheng, L. High-fidelity guided image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.F.; Lyu, S.; Vinaroz, M.; Park, M. Differentially private latent diffusion models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.15759. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Cui, S.; Meng, C.; Wu, W.; Lyu, M.R. On the robustness of latent diffusion models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.08257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Pu, Y.; Ni, Z.; Wang, C.; Vasu, M.; Song, S.; Huang, G.; Shi, H. Smooth diffusion: Crafting smooth latent spaces in diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Di Federico, G.; Durlofsky, L.J. Latent diffusion models for parameterization and data assimilation of facies-based geomodels. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.14815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Cola-diff: Conditional latent diffusion model for multi-model mri synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, X. Are conditional latent diffusion models effective for image restoration? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.09324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Parikh, M.H.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, J.X. Conditional neural field latent diffusion model for generating spatiotemporal turbulence. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jaitly, N.; Susskind, J.M. Kaleido diffusion: Improving conditional diffusion models with autoregressive latent modeling. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.21048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, B.; Williams, E.C.; Pederson, R.; Underkoffler, C.; Panjwani, Z.; Wang-Henderson, M.; Mardirossian, N.; Katcher, M.H.; Strater, Z.; Grandjean, J.M.; et al. Latent diffusion for conditional generation of molecules. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Abnar, S.; Gu, J.; Schwing, A.; Susskind, J.M.; Bautista, M.A. Diffusion probabilistic fields. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khader, F.; Müller-Fanzes, G.; Tayebi Arasteh, S.; Han, T.; Haarburger, C.; Schulze-Hagen, M.; Schad, P.; Engelhardt, S.; Baeßler, B.; Foersch, S.; et al. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models for 3d medical image generation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, S.U.H.; Ghanaat, A.; Kahmaan, J.; Ayx, I.; Papavassiliu, T.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Engelhardt, S. Investigating data memorization in 3d latent diffusion models for medical image synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, S.U.H.; Seyfarth, M.; Ayx, I.; Papavassiliu, T.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Siepmann, R.M.; Laqua, F.C.; Kahmann, J.; Frey, N.; Baeßler, B.; et al. Unconditional latent diffusion models memorize patient imaging data: Implications for openly sharing synthetic data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01054. [Google Scholar]
- Nafi, A.A.N.; Hossain, M.A.; Rifat, R.H.; Zaman, M.M.U.; Ahsan, M.M.; Raman, S. Diffusion-based approaches in medical image generation and analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.16860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.L.U.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, H.; Yan, R.; Raman, S.S.; Terzopoulos, D.; Sung, K. Med-cDiff: Conditional medical image generation with diffusion models. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Tirunagari, S.; Zia, T.; Windridge, D. A latent diffusion approach to visual attribution in medical imaging. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Xing, H.; Wu, X. Medical image generation based on latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Innovation (ICAII), Wuhan, China, 22–24 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pinaya, W.H.L.; Tudosiu, P.D.; Dafflon, J.; Da Costa, P.F.; Fernandez, V.; Nachev, P.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J. Brain imaging generation with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, Singapore, 22 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Fanzes, G.; Niehues, J.M.; Khader, F.; Arasteh, S.T.; Haarburger, C.; Kuhl, C.; Wang, T.; Han, T.; Nolte, T.; Nebelung, S.; et al. A multimodal comparison of latent denoising diffusion probabilistic models and generative adversarial networks for medical image synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; He, J.; Gupta, M.; Delp, E.J.; Zhu, F. Diffusion model with clustering-based conditioning for food image generation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, P.A.; Van Dalen, S.; Martin, K.C.; Lennerz, J.; Yip, S.; Farahani, H.; Bashashati, A. A morphology focused diffusion probabilistic model for synthesis of histopathology images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Harb, R.; Pock, T.; Müller, H. Diffusion-based generation of histopathological whole slide images at a gigapixel scale. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yellapragada, S.; Graikos, A.; Prasanna, P.; Kurc, T.; Saltz, J.; Samaras, D. PathLDM: Text conditioned latent diffusion model for histopathology. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI): 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreu, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Konblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Jeyaseelan, L.; Li, Q.; Chiang, J.N.; Wu, Z.; Ding, X. Embracing Imperfect Datasets: A Review of Deep Learning Solutions for Medical Image Segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumman, M.I.; Ono, N.; Ohuchida, K.; Arasteh Altaf-Ul-Amin, M.D.; Huang, M.; Kanaya, S. Information maximization-based clustering of histopathology images using deep learning. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, P.; Rombach, R.; Ommer, B. Taming transformers for high-resolution image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Oord, A.; Vinyals, O.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Neural discrete representation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/2969033.2969125 (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Li, C.; Wand, M. Precomputed real-time texture synthesis with Markovian generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Miyato, T.; Tokui, S.; Matsumoto, E.; Sugiyama, M. Learning discrete representations via information maximizing self-augmented training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, H.; Gao, X.; Wu, J. Understanding of internal clustering validation measures. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Sydney, Australia, 13–17 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saitta, S.; Raphael, B.; Smith, I.F.C. A comprehensive validity index for clustering. Intell. Data Anal. 2008, 12, 529–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, Z.; Azeem, M.F.; Ahmed, W.; Babu, A.V. Quantitative evaluation of performance and validity indices for clustering the web navigational sessions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1507.03340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, N.; Julio, O.; Berzal, F. Evaluation metrics for unsupervised learning algorithms. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.05667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A. Clustering Algorithms, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 97–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Bovik, A.C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.; Neher, P.; Schüffler, P.; Xiao, S.; Almeida, S.D.; Ulrich, C.; Muckenhuber, A.; Braren, R.; Götz, M.; Kleesiek, J.; et al. Enhanced Diagnostic Fidelity in Pathology Whole Slide Image Compression via Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban, M.T.; Baur, C.; Navab, N.; Albarqouni, S. StainGAN: Stain Style Transfer for Digital Histological Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Li, X. Stain Style Transfer of Histopathology Images Via Structure-Preserved Generative Learning. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Medical Image Reconstruction, Lima, Peru, 8 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen, M.; Klemens, M.A.; Baltruschat, I.M.; Truong, T.; Lenga, M. Similarity and Quality Metrics for MR Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.08431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Codebook size | 128 |
| Codebook vector dimension | 16 |
| Latent space resolution | 32 × 32 |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Epochs | 20 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Activation function | SiLU |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 16 |
| Activation function | SiLU |
| Timesteps | 1000 |
| Noise scheduler | Linear |
| U-Net bottleneck resolution | 8 × 8 |
| Learning rate (cLDM training) | 0.003 |
| Optimizer (cLDM training) | Adadelta |
| Epochs (cLDM training) | 600 |
| Learning rate (cLDM finetuning-1) | 0.0001 |
| Optimizer (cLDM finetuing-1) | Adam |
| Epochs (cLDM finetuning-1) | 130 |
| Learning rate (cLDM finetuning-2) | 0.003 |
| Optimizer (cLDM finetuing-2) | Adadelta |
| Epochs (cLDM finetuning-2) | 70 |
| No. of Clusters | CH Index | C Index | Dunn Index | Hartigan Index | MR Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2142.54026 | 0.12234 | 0.00441 | 0.65763 | 0.54631 |
| 11 | 2866.86433 | 0.10477 | 0.00477 | 1.05432 | 0.49791 |
| 12 | 1865.81774 | 0.12042 | 0.00463 | 0.72021 | 0.55443 |
| 13 | 2836.22720 | 0.09131 | 0.00424 | 1.22610 | 0.46335 |
| 14 | 3367.74211 | 0.07645 | 0.00548 | 1.47801 | 0.41643 |
| 15 | 2027.82944 | 0.10489 | 0.00424 | 1.04494 | 0.51414 |
| 16 | 2603.28507 | 0.08615 | 0.00490 | 1.36384 | 0.45223 |
| No. of Clusters | SSIM | MS-SSIM | LPIPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.7814 | 0.2138 | 0.5008 |
| 11 | 0.7835 | 0.2130 | 0.5003 |
| 12 | 0.7801 | 0.2168 | 0.5032 |
| 13 | 0.7865 | 0.2161 | 0.4987 |
| 14 | 0.7988 | 0.2196 | 0.4923 |
| 15 | 0.7889 | 0.2152 | 0.4980 |
| 16 | 0.7908 | 0.2186 | 0.4939 |
| Cluster No. | Description from Expert |
|---|---|
| 1 | Tissue with high cancer cell density |
| 2 | Tissue with low cell density |
| 3 | Liver parenchyma with red blood cells |
| 4 | Tissue with large voids |
| 5 | Tumor area with voids |
| 6 | Tumor with abundant stromal components |
| 7 | Surrounding empty space |
| 8 | Tissue with high cell density |
| 9 | Tissue containing small voids |
| 10 | Boundary of tissue containing red blood cells |
| 11 | Voids within the tissue |
| 12 | Boundary between tissue and empty space |
| 13 | Normal liver parenchyma |
| 14 | Edge of the liver |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rumman, M.I.; Ono, N.; Ohuchida, K.; Nasution, A.K.; Alqaaf, M.; Altaf-Ul-Amin, M.; Kanaya, S. Implementation of a Conditional Latent Diffusion-Based Generative Model to Synthetically Create Unlabeled Histopathological Images. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070764
Rumman MI, Ono N, Ohuchida K, Nasution AK, Alqaaf M, Altaf-Ul-Amin M, Kanaya S. Implementation of a Conditional Latent Diffusion-Based Generative Model to Synthetically Create Unlabeled Histopathological Images. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070764
Chicago/Turabian StyleRumman, Mahfujul Islam, Naoaki Ono, Kenoki Ohuchida, Ahmad Kamal Nasution, Muhammad Alqaaf, Md. Altaf-Ul-Amin, and Shigehiko Kanaya. 2025. "Implementation of a Conditional Latent Diffusion-Based Generative Model to Synthetically Create Unlabeled Histopathological Images" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070764
APA StyleRumman, M. I., Ono, N., Ohuchida, K., Nasution, A. K., Alqaaf, M., Altaf-Ul-Amin, M., & Kanaya, S. (2025). Implementation of a Conditional Latent Diffusion-Based Generative Model to Synthetically Create Unlabeled Histopathological Images. Bioengineering, 12(7), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070764












