Mechanical Design, Control, and Laboratory Test of a Two-Degrees-of-Freedom Elbow Prosthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
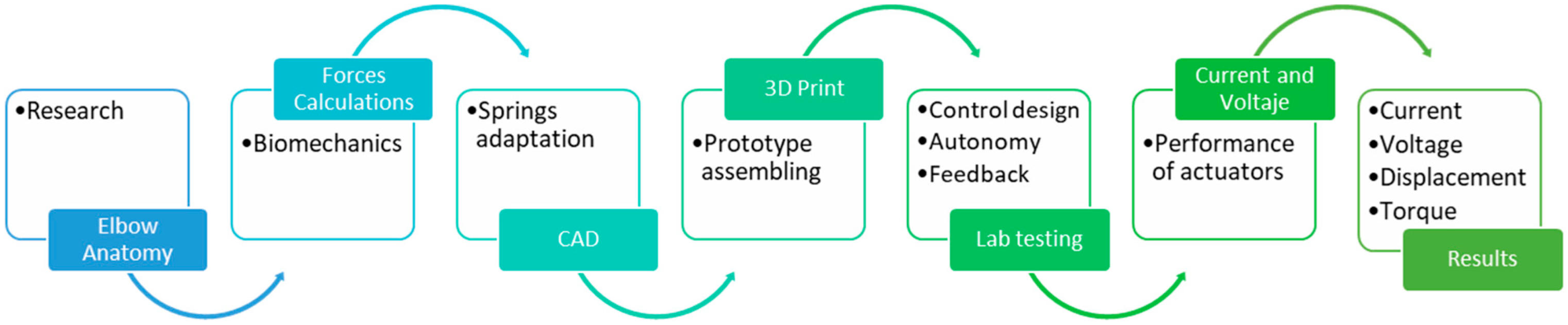
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Prosthesis Design
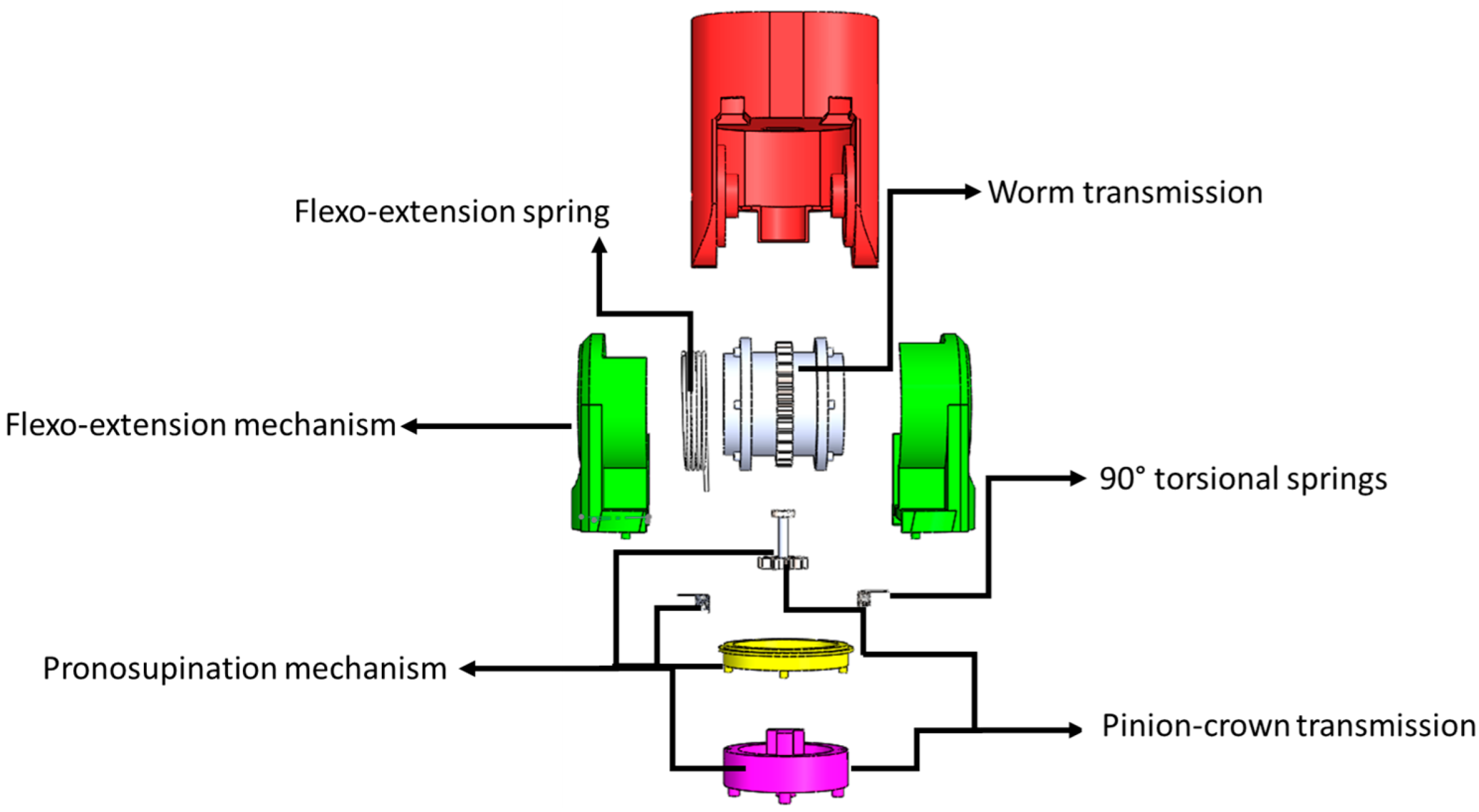
2.2. Mechanical Design
Drives for Movements
2.3. Kinematics
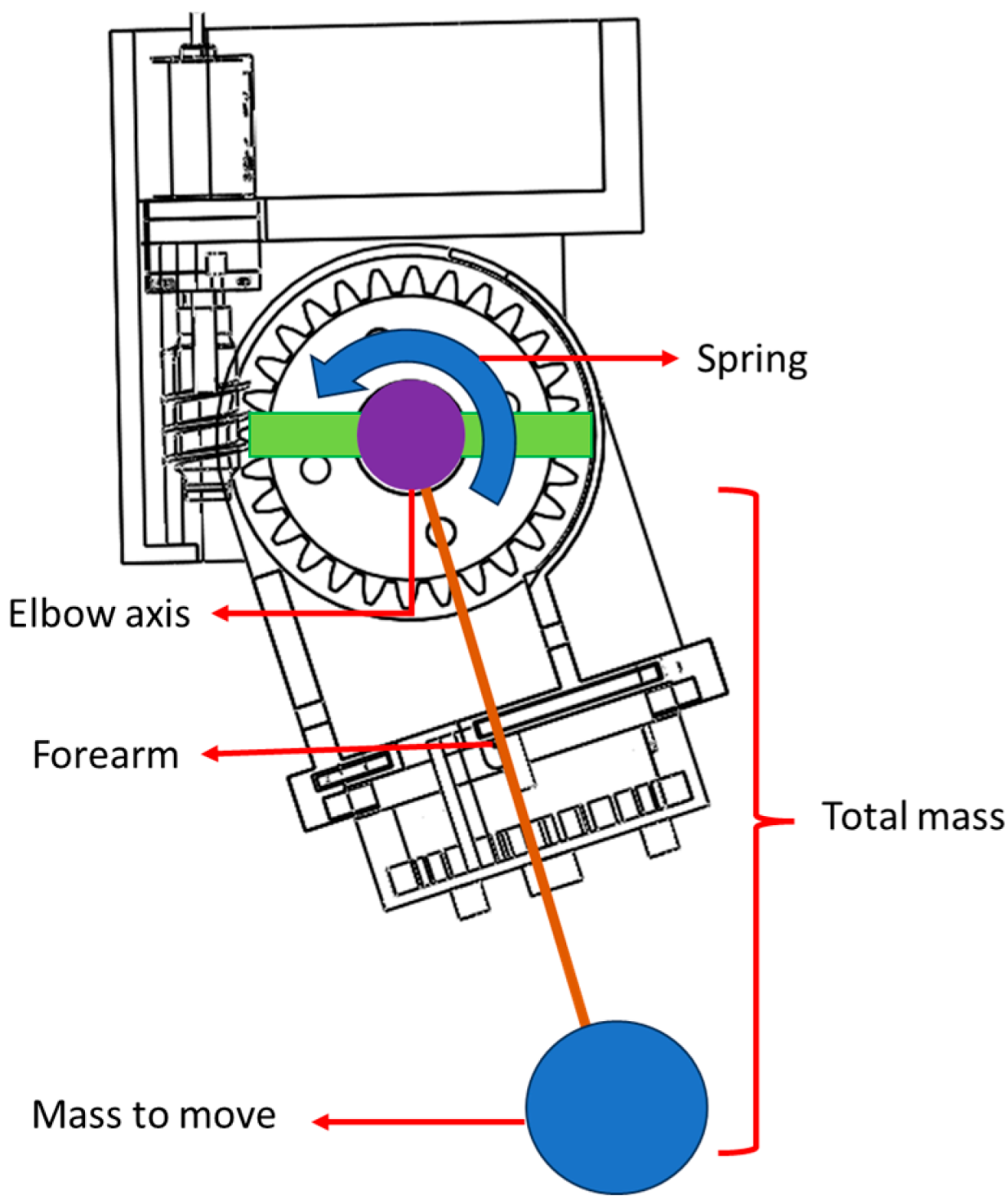
2.4. Mechanical Parameters Determined
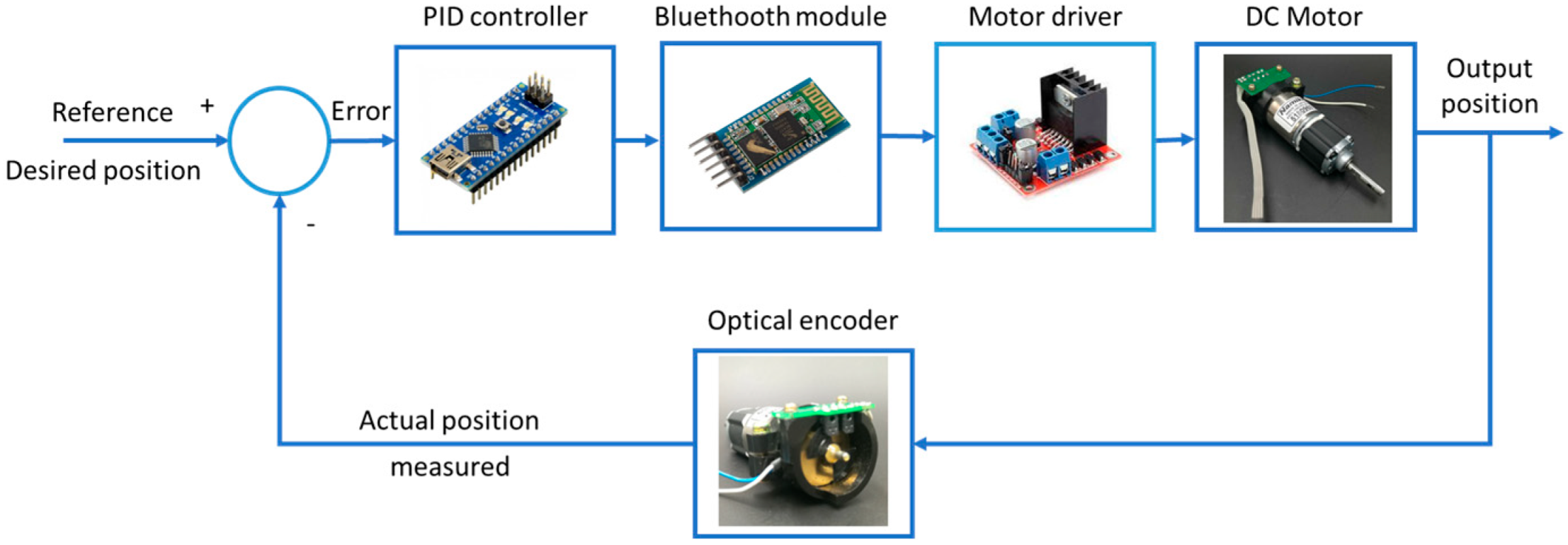
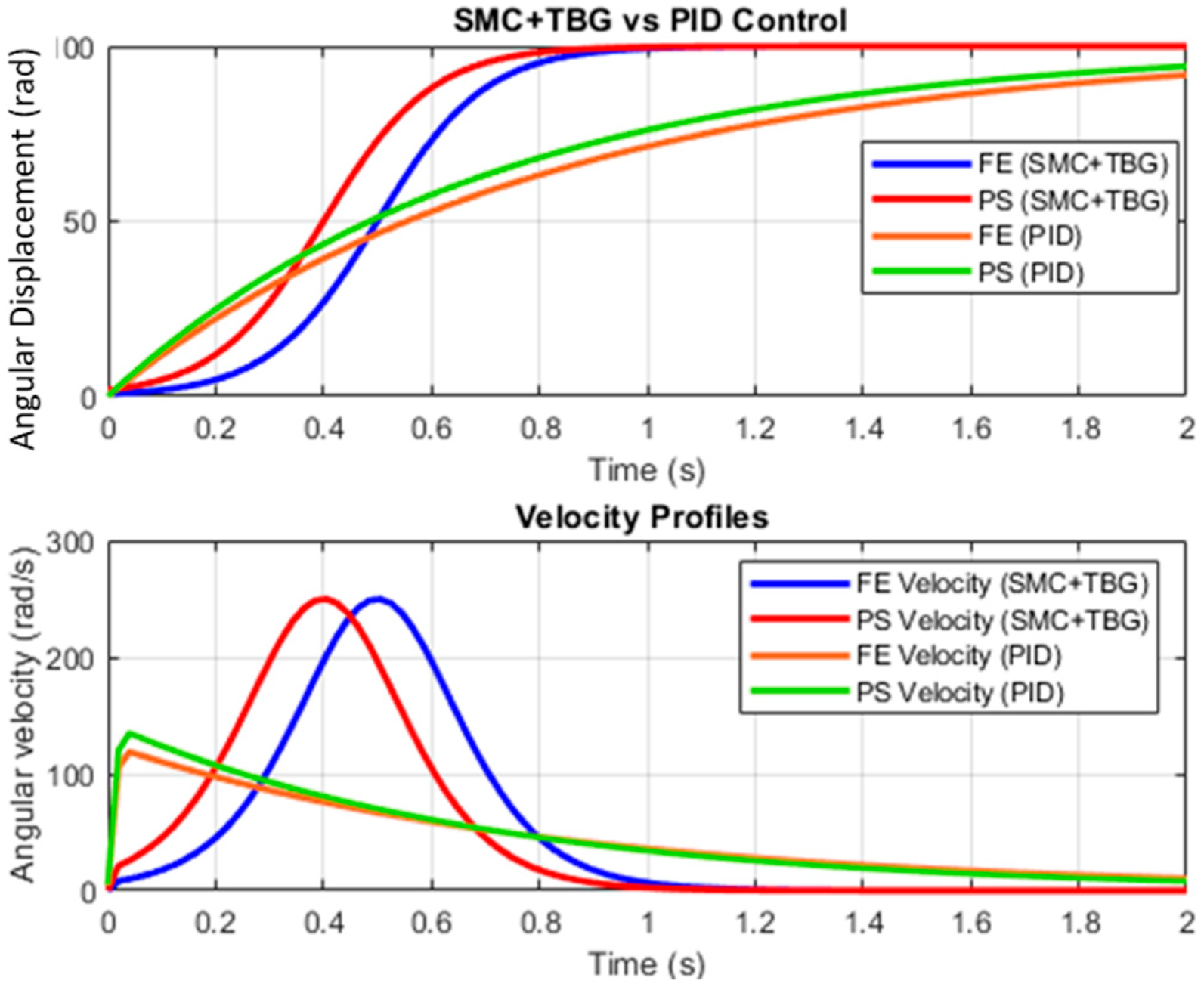
2.5. Control Strategies
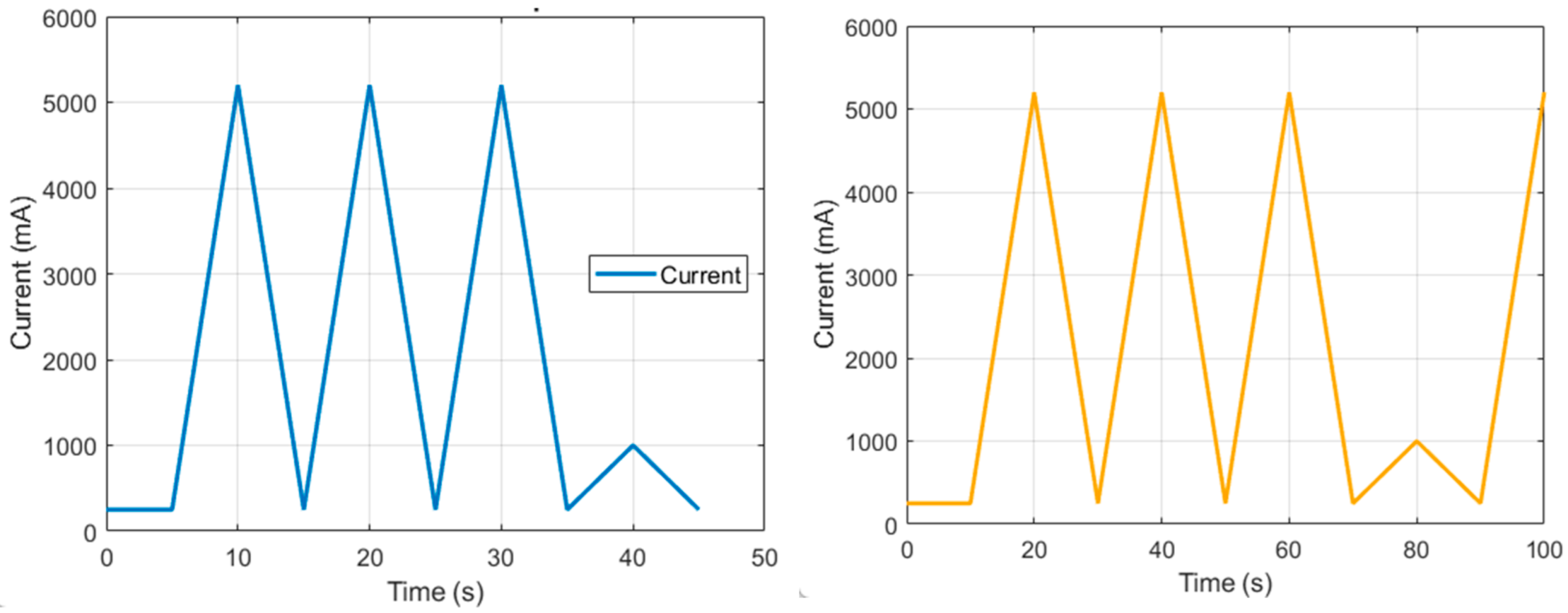
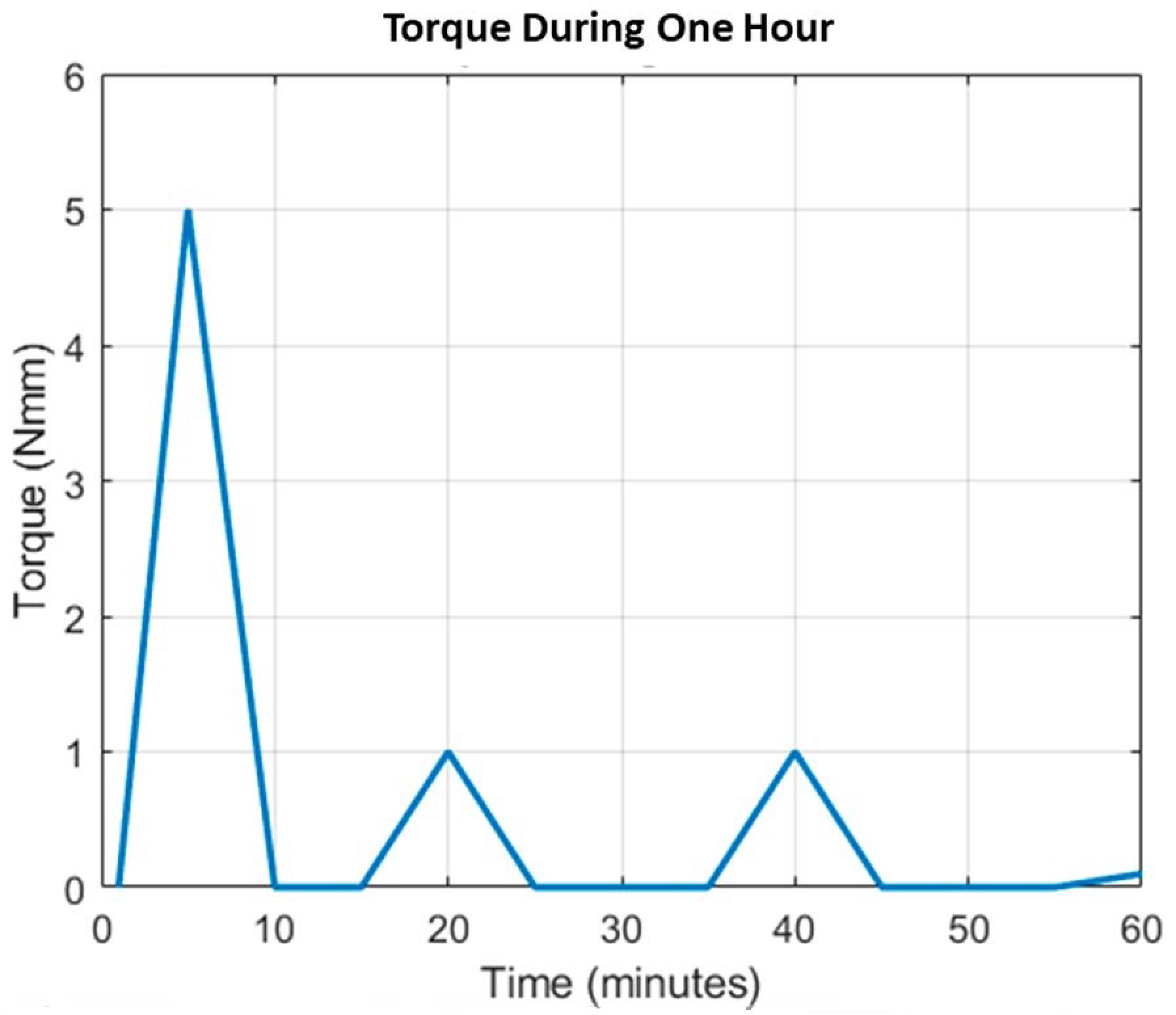
2.6. Autonomy of the Prototype
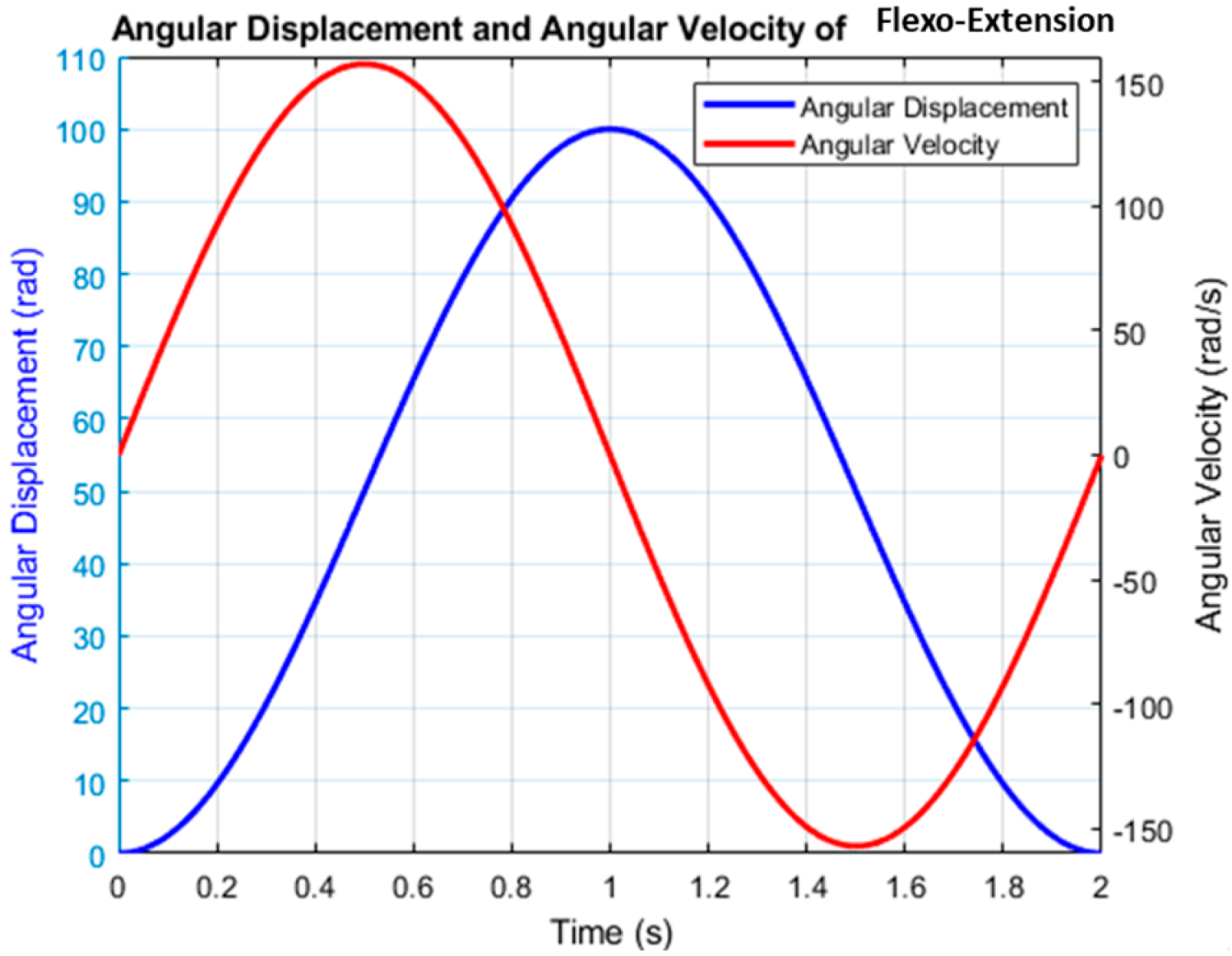
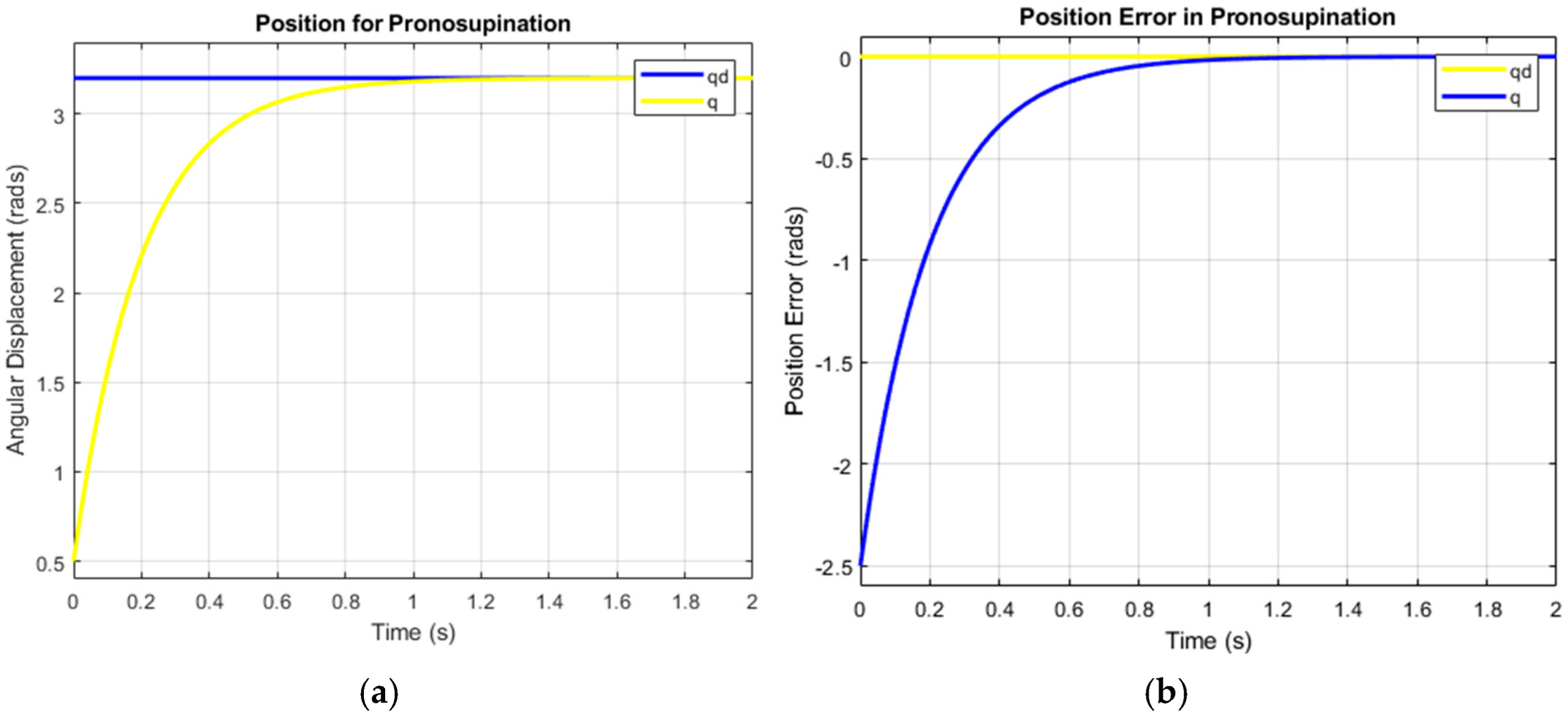
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronyms | Definition |
| PID | Proportional–integral–derivative control strategy |
| DOF | Degrees of freedom |
| SMC | Sliding mode control |
| TBG | Time base generator |
| PWM | Pulse width modulation |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| Symbol | Definition |
| τ | Torque |
| k | Stiffness constant |
| Λ | Constant that weights the position vector |
| q | Position |
| N | Gears |
| L | Lagrangian of the system |
| θ | Angle |
| α | Angle |
| τC | Control torque vector applied to the robot’s joints. |
| Kp | Proportional gain matrix. |
| Kd | Proportional derivative gain matrix |
| e = q − qr | Posotion error |
| e˙= q˙ − q˙r | Joint velocity error |
| G(q) | Gravity torque |
References
- Cerero, R.H.; Miguel, C.R.T.S.; Torres, C.T. Modelo Industrial de una Prótesis de Codo de Dos Grados de Libertad; Diseño Industrial MX/E/2023/089633, 14 de diciembre de 2023; Instituto Politécnico Nacional: Mexico City, Mexico, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cerero, R.; Torres San Miguel, C.R.; Leal-Naranjo, J.A.; Ceccarelli, M. Design and Analysis of 2 DOF Elbow Prosthesis. In Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics. RAAD 2021; Zeghloul, S., Laribi, M.A., Sandoval, J., Eds.; Mechanisms and Machine Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 102, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerero, R.H.; Miguel, C.R.T.S.; Naranjo, J.A.L. Control of a 2 DOF Elbow Prosthesis prototype. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2307, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Morasso, P.G.; Sanguineti, V.; Kaneko, M. Bio-Mimetic Trajectory Generation of Robots via Artificial Potential Field with Time Base Generator. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2002, 32, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng-Guan, L.; Chang, J.Y. Enhanced Design of an Adaptive Anthropomorphic Finger through Integration of Modular Soft Actuators and Kinematic Modeling. Robotics 2024, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucan, P.; Gherman, B.; Major, K.; Vaida, C.; Major, Z.; Plitea, N.; Carbone, G.; Pisla, D. Fuzzy Logic-Based Risk Assessment of a Parallel Robot for Elbow and Wrist Rehabilitation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliolini, G.; Lanni, C.; Tomassi, L.; Ortiz, J. Eight-Bar Elbow Joint Exoskeleton Mechanism. Robotics 2024, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Liu, G.; Meng, Q.; Xu, X.; Qin, L.; Yu, H. Bionic Design of a Novel Portable Hand-Elbow Coordinate Exoskeleton for Activities of Daily Living. Electronics 2023, 12, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maung, M.M.; Latt, M.M.; Nwe, C.M. DC Motor Angular Position Control Using PID Controller with Friction Compensation. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2018, 8, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriyono, H.; Alanro, F.F.; Supardi, A. Development of DC Motor Speed Control Using PID Based on Arduino and Matlab for Laboratory Trainer. J. Nas. Tek. Elektro 2024, 13, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, Z.; Maqbool, H.F.; Ashraf, M.I.; Malik, D.J.; Abdeen, Z.U.; Ali, W.; Taborri, J.; Rossi, S. Towards Prosthesis Control: Identification of Locomotion Activities through EEG-Based Measurements. Robotics 2024, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa, A.-I.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Davis, S. Design, Kinematics and Controlling a Novel Soft Robot Arm with Parallel Motion. Robotics 2018, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishay, P.L.; Wilgus, J.; Chen, R.; Valenzuela, D.; Medina, V.; Tan, C.; Ittner, T.; Caldera, M.; Rubalcava, C.; Safarian, S.; et al. Controlling a Below-the-Elbow Prosthetic Arm Using the Infinity Foot Controller. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 1206–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Wu, G.; Song, H.; Li, L.; Hou, W.; Wang, X. Prosthetic Elbow Flexion and Extension Sense Rebuilt by Electrotactile Feedback: A Preliminary Study. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 226, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M. Investigations on Upper Limb Prosthesis Control with an Active Elbow. Doctoral Dissertation, Université Pierre et Marie Curie Paris VI, Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Merad, M.; de Montalivet, É.; Touillet, A.; Martinet, N.; Roby-Brami, A.; Jarrassé, N. Can We Achieve Intuitive Prosthetic Elbow Control Based on Healthy Upper Limb Motor Strategies? Front. Neurorobotics 2018, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milazzo, G.; Lemerle, S.; Grioli, G.; Bicchi, A.; Catalano, M.G. Design, Characterization, and Validation of a Variable Stiffness Prosthetic Elbow. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 41, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrey, B.F.; Askew, L.J.; Chao, E.Y. A Biomechanical Study of Normal Functional Elbow Motion. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1981, 63, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Chen, J. Design and Passive Training Control of Elbow Rehabilitation Robot. Electronics 2021, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, L.D.F.; Castañeda, E.C.; Laribi, M.A.; Carbone, G. Design and Analysis of VARONE a Novel Passive Upper-Limb Exercising Device. Robotics 2024, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ibadi, A.; Abbas, K.A.; Al-Atwani, M.; Al-Fahaam, H. Design, Implementation, and Kinematics of a Twisting Robot Continuum Arm Inspired by Human Forearm Movements. Robotics 2022, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Wang, M.; Cao, G.; Wang, Q.; Liao, Y. PID Sliding Mode Control of PMSM Based on Improved Terminal Sliding Mode Reaching Law. Energies 2025, 18, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, O.; Wafa, M.; Shalaby, R. Reinforcement Learning-Enhanced Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Nonlinear Systems. Complex Intell. Syst. 2025, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Marchand, C.; Richer, F.; Touillet, A.; Martinet, N.; Paysant, J.; Morel, G.; Jarrasse, N. Simultaneous Control of 2DOF Upper-Limb Prosthesis with Body Compensations-Based Control: A Multiple Cases Study. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Islam, M.; Rashid, M.; Mounis, S.; Ahsan, M.M.; Ahad, M.T.; Siddique, Z.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Mahmud, M.A.P. Investigation of 2DOF PID Controller for Physio-Therapeutic Application for Elbow Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Naranjo, J.A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Miguel, C.R.T.-S.; Aguilar-Perez, L.A.; Urriolagoitia-Sosa, G.; Urriolagoitia-Calderón, G. Multi-objective optimization of a parallel manipulator for the design of a prosthetic arm using genetic algorithms. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 15, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Naranjo, J.A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Torres-San Miguel, C.R. Mechanical Design of a Prosthetic Human Arm and its Dynamic Simulation. In Advances in Robot Design and Intelligent Control. RAAD 2016; Rodić, A., Borangiu, T., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Naranjo, J.-A.; Miguel, C.-R.T.-S.; Ceccarelli, M.; Rostro-Gonzalez, H. Mechanical Design and Assessment of a Low-Cost 7-DOF Prosthetic Arm for Shoulder Disarticulation. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2018, 2018, 4357602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

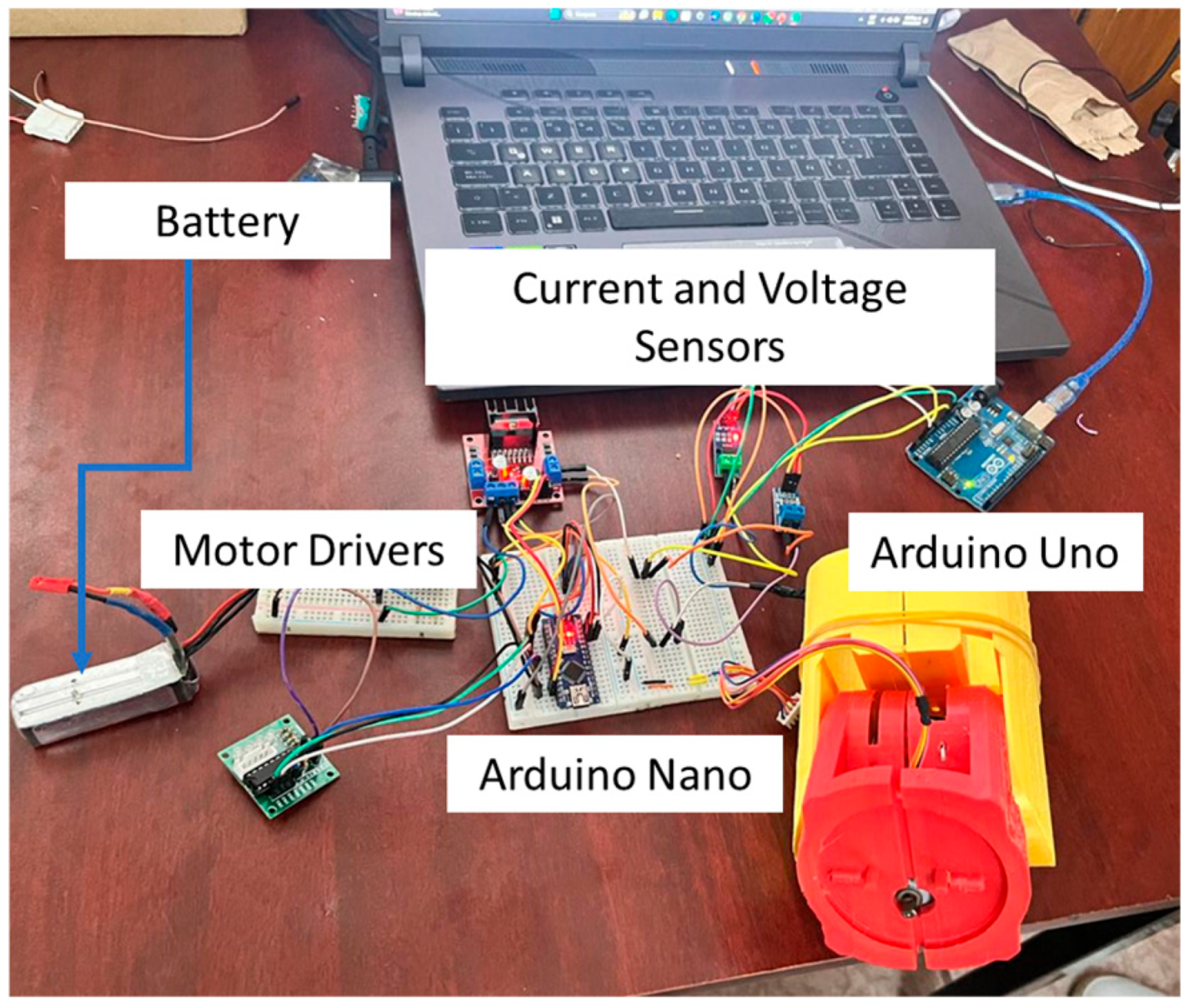

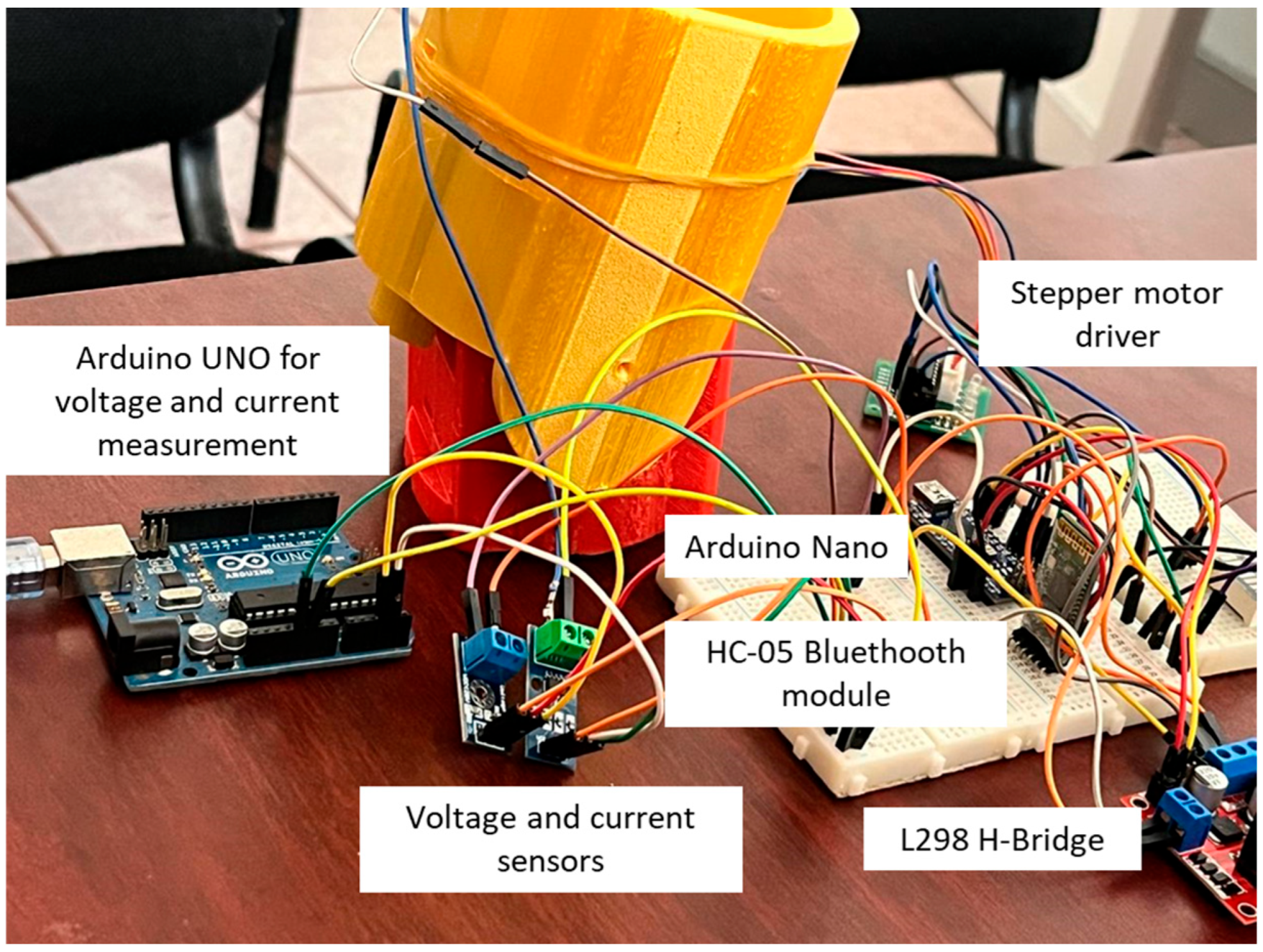


| Link | θi (Joint Angle) | Di (Displacement Along z2) | ai (Length of the Link Along ×2) | αi (Angle Between Zi and Zi + i) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Flexo-extension) | 0 | |||
| 2 (Pronosupination) | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Cerero, R.; Flores-Campos, J.A.; Mojica-Martínez, J.J.; Casarez-Duran, A.A.; Guerrero-Hernández, L.A.; Torres-SanMiguel, C.R. Mechanical Design, Control, and Laboratory Test of a Two-Degrees-of-Freedom Elbow Prosthesis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070695
Hernández-Cerero R, Flores-Campos JA, Mojica-Martínez JJ, Casarez-Duran AA, Guerrero-Hernández LA, Torres-SanMiguel CR. Mechanical Design, Control, and Laboratory Test of a Two-Degrees-of-Freedom Elbow Prosthesis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070695
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Cerero, Ramsés, Juan Alejandro Flores-Campos, José Juan Mojica-Martínez, Adolfo Angel Casarez-Duran, Luis Angel Guerrero-Hernández, and Christopher René Torres-SanMiguel. 2025. "Mechanical Design, Control, and Laboratory Test of a Two-Degrees-of-Freedom Elbow Prosthesis" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070695
APA StyleHernández-Cerero, R., Flores-Campos, J. A., Mojica-Martínez, J. J., Casarez-Duran, A. A., Guerrero-Hernández, L. A., & Torres-SanMiguel, C. R. (2025). Mechanical Design, Control, and Laboratory Test of a Two-Degrees-of-Freedom Elbow Prosthesis. Bioengineering, 12(7), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070695







