Mechanistic Analysis of Fluid Dynamics and Multifactorial Impact Mechanisms in Inhaled Pharmaceutical Deposition for Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
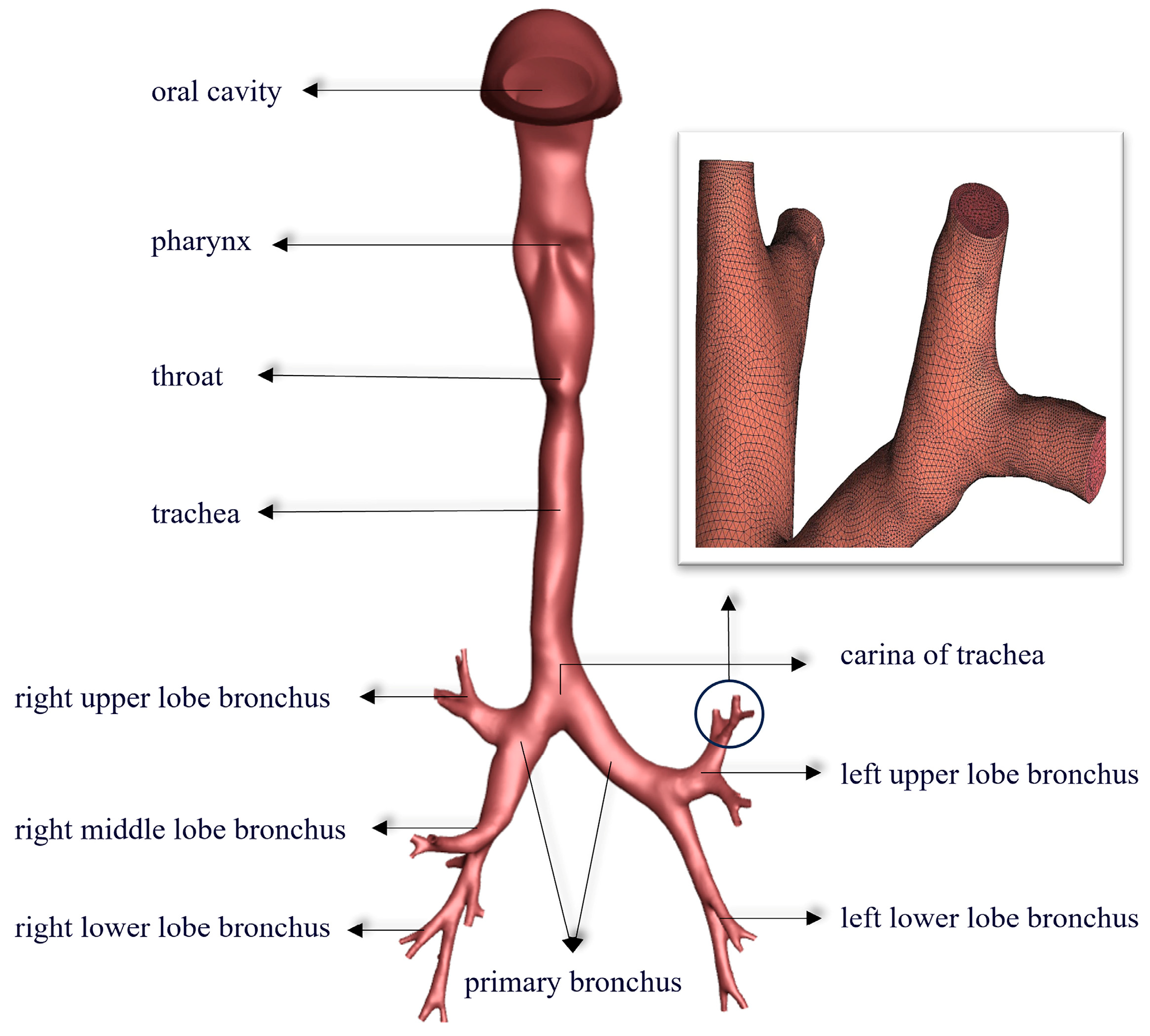
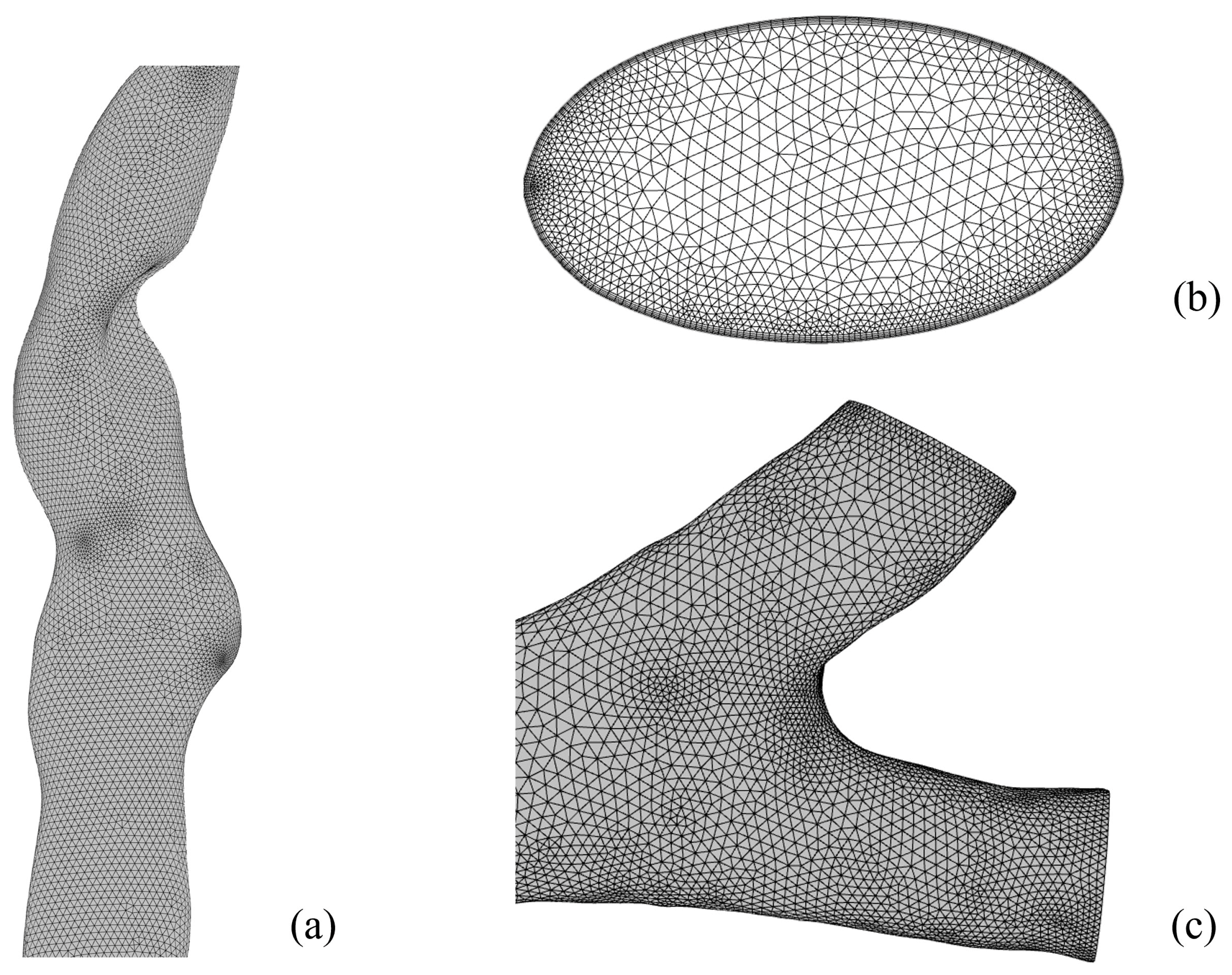
2.1. Establish a 3D Model of the Human Respiratory Tract
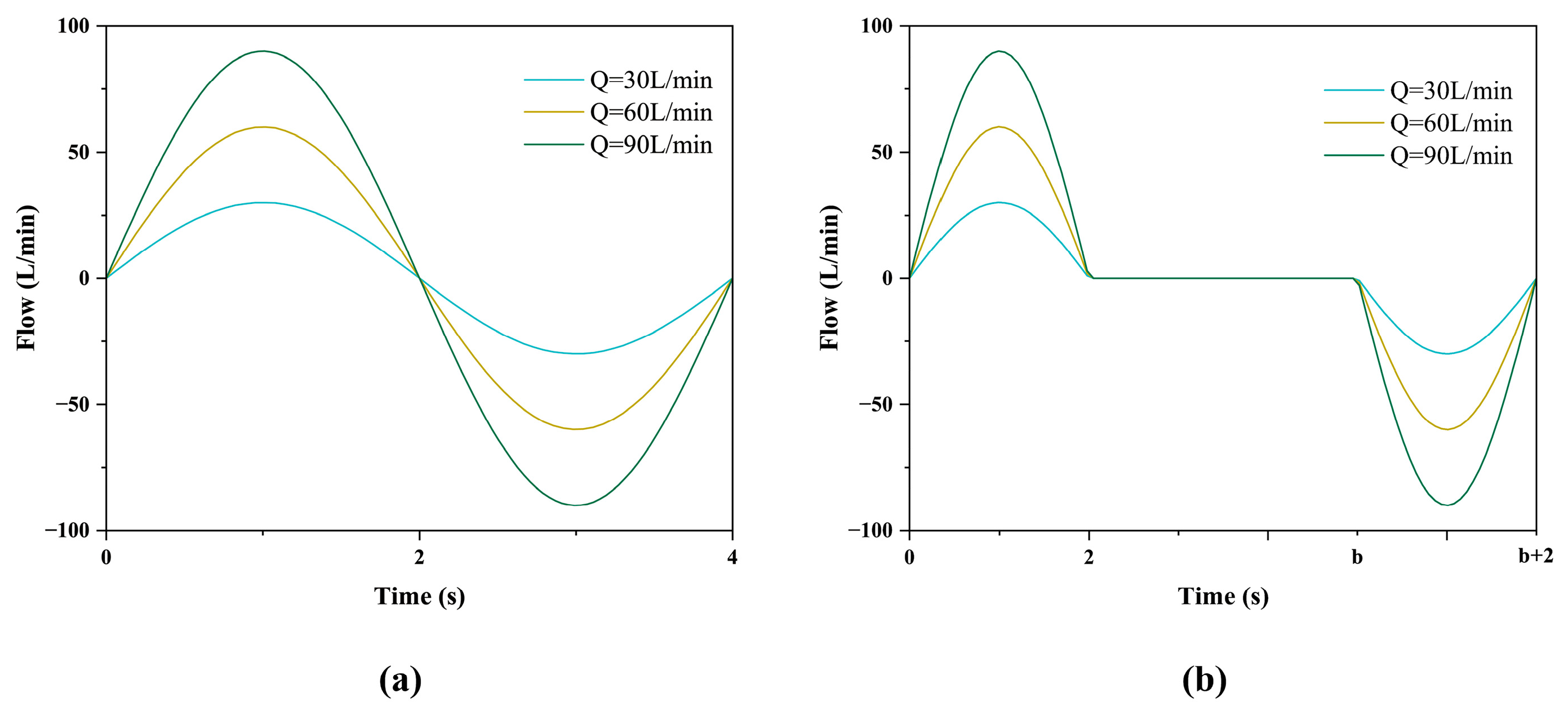
2.2. Boundary Conditions
2.3. Preferred Simulation Model
2.3.1. General Fluid Field Model
2.3.2. Discrete Phase Model
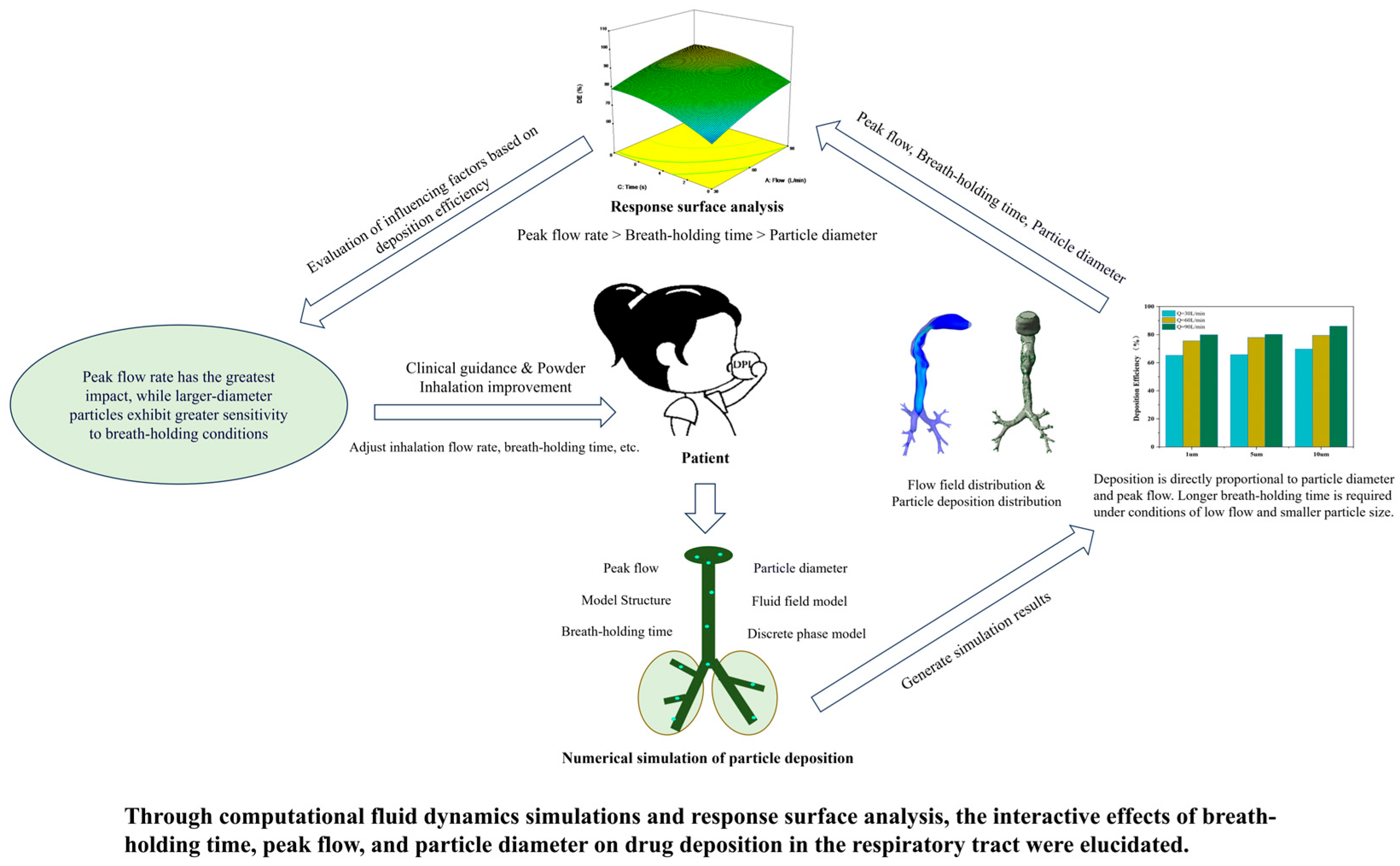
3. Results
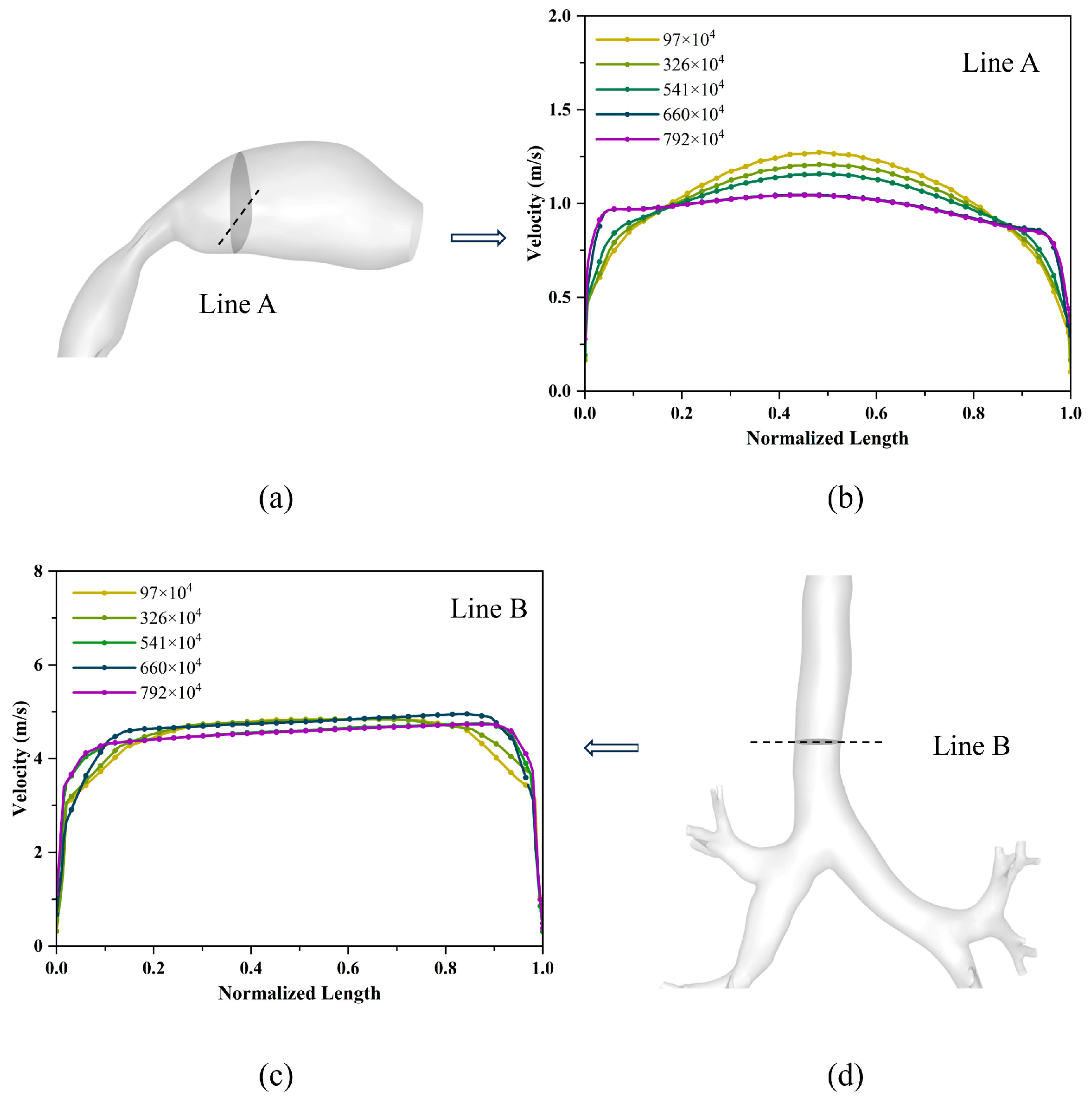
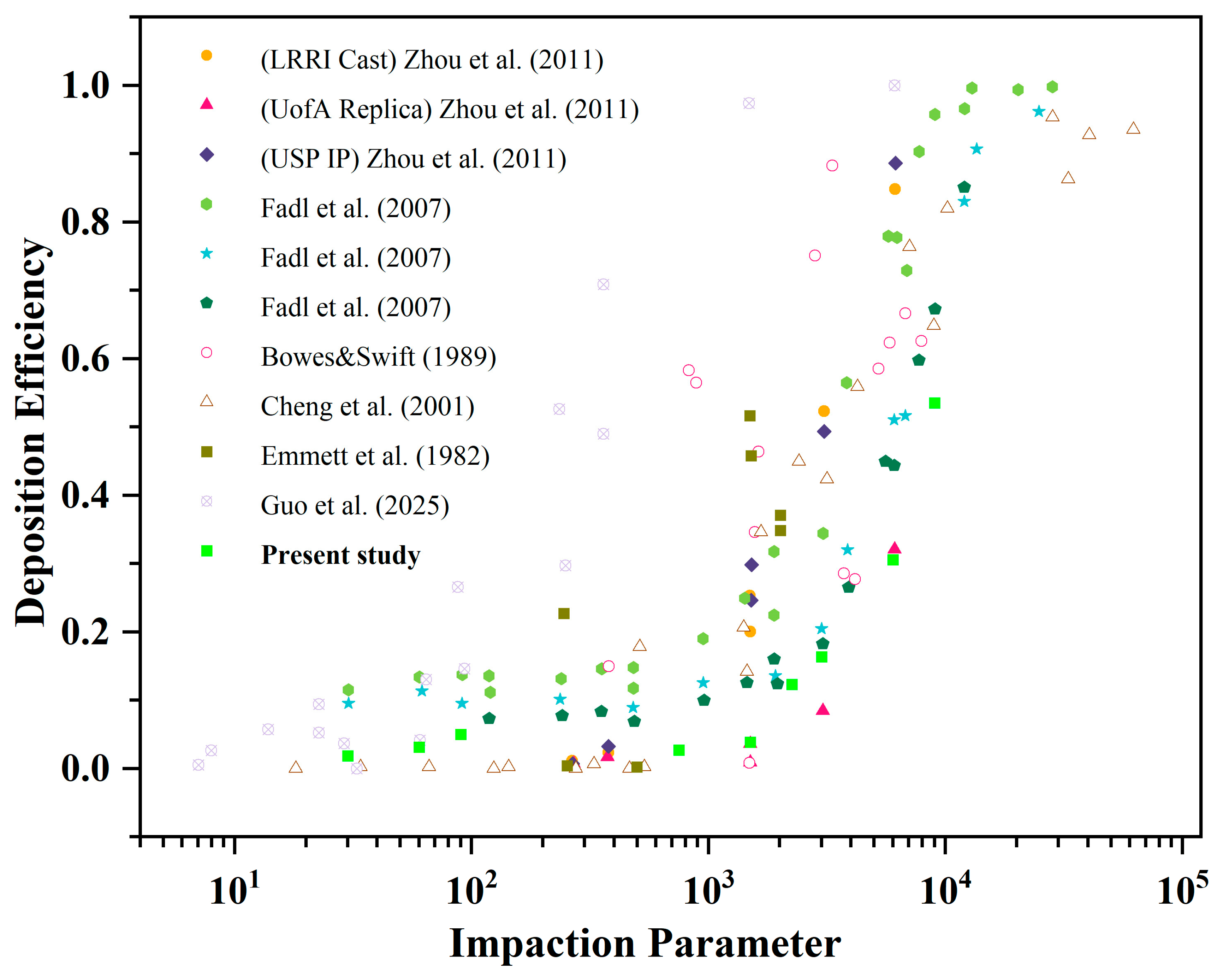
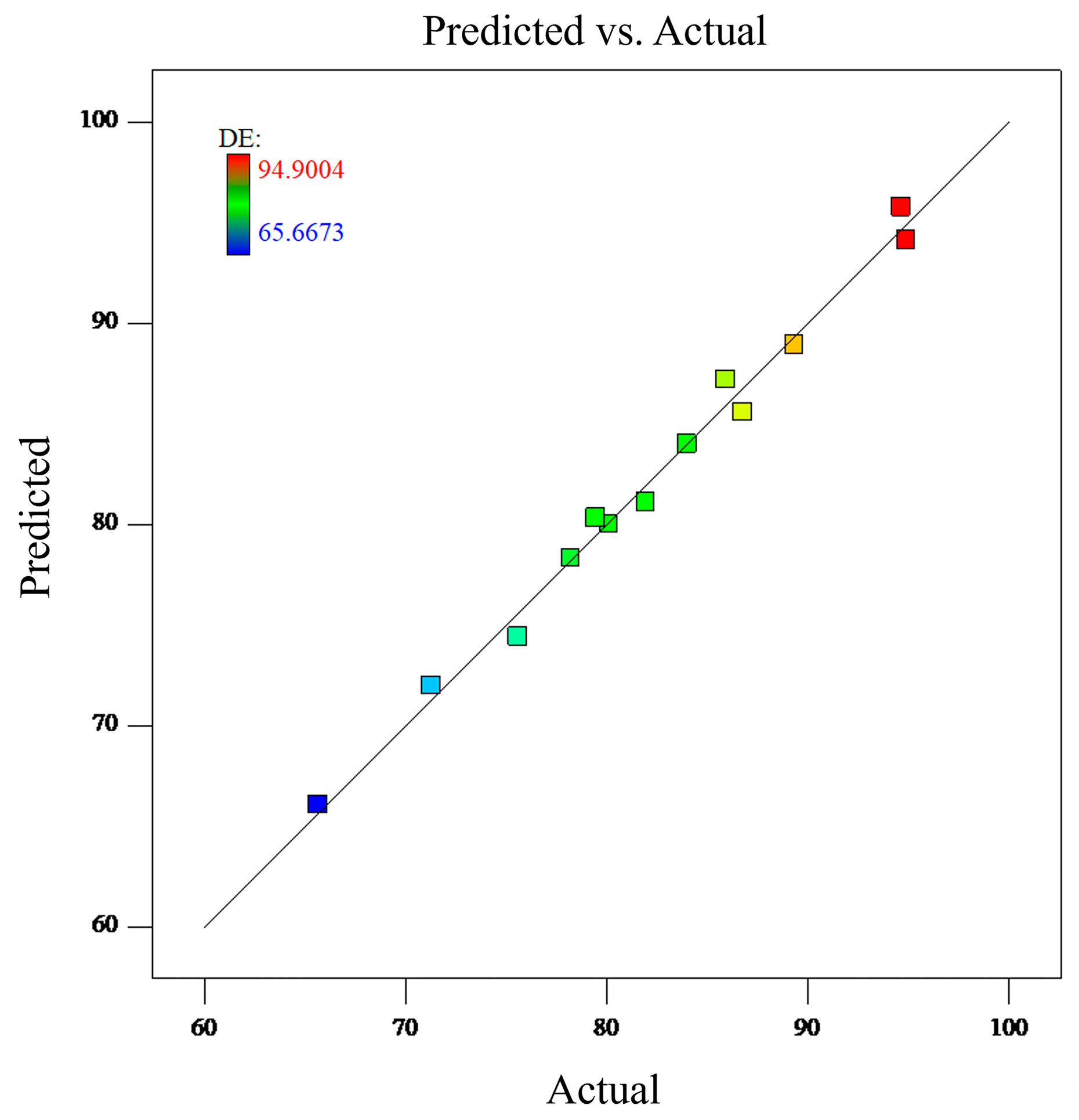
3.1. Model Validation
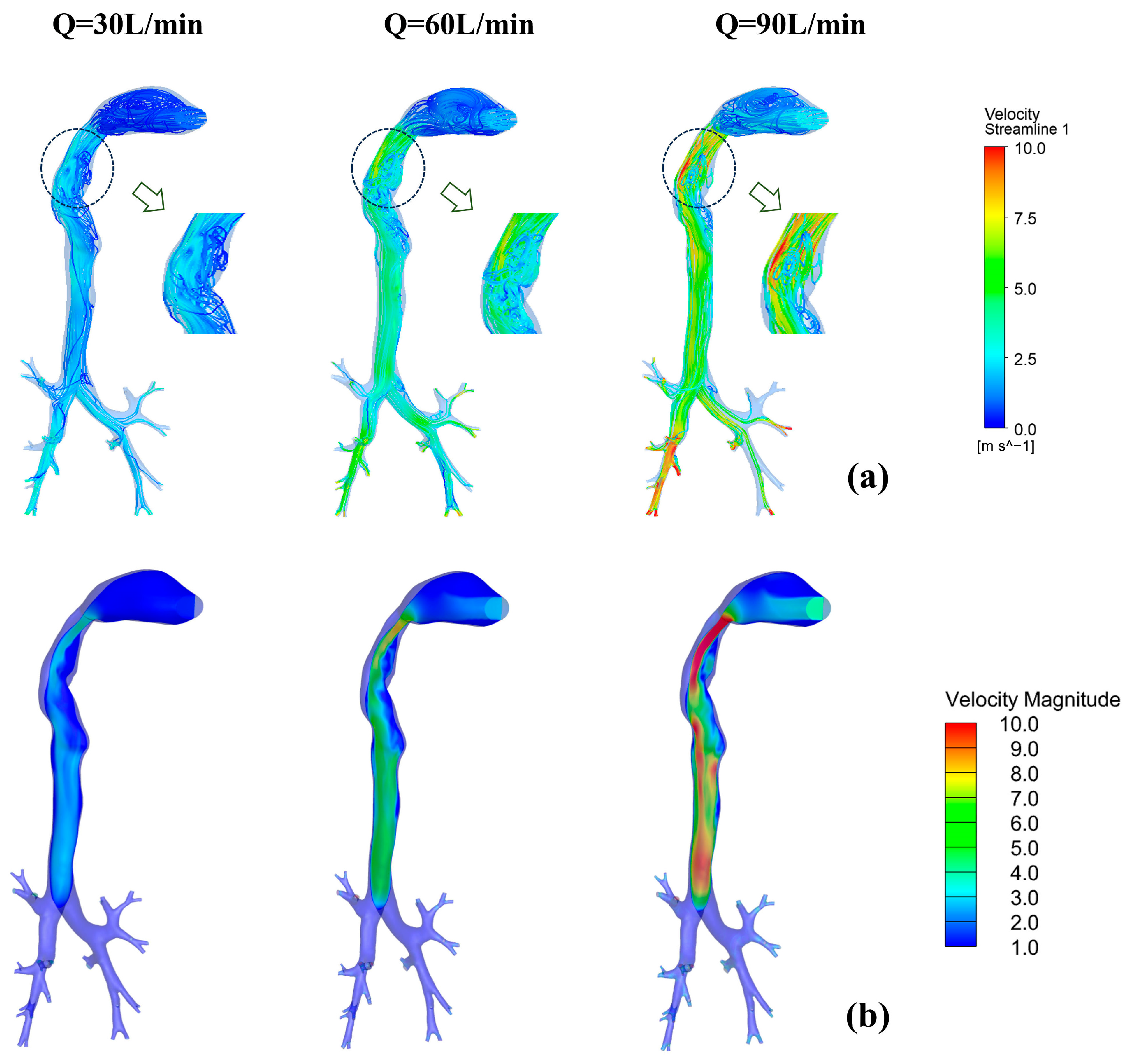
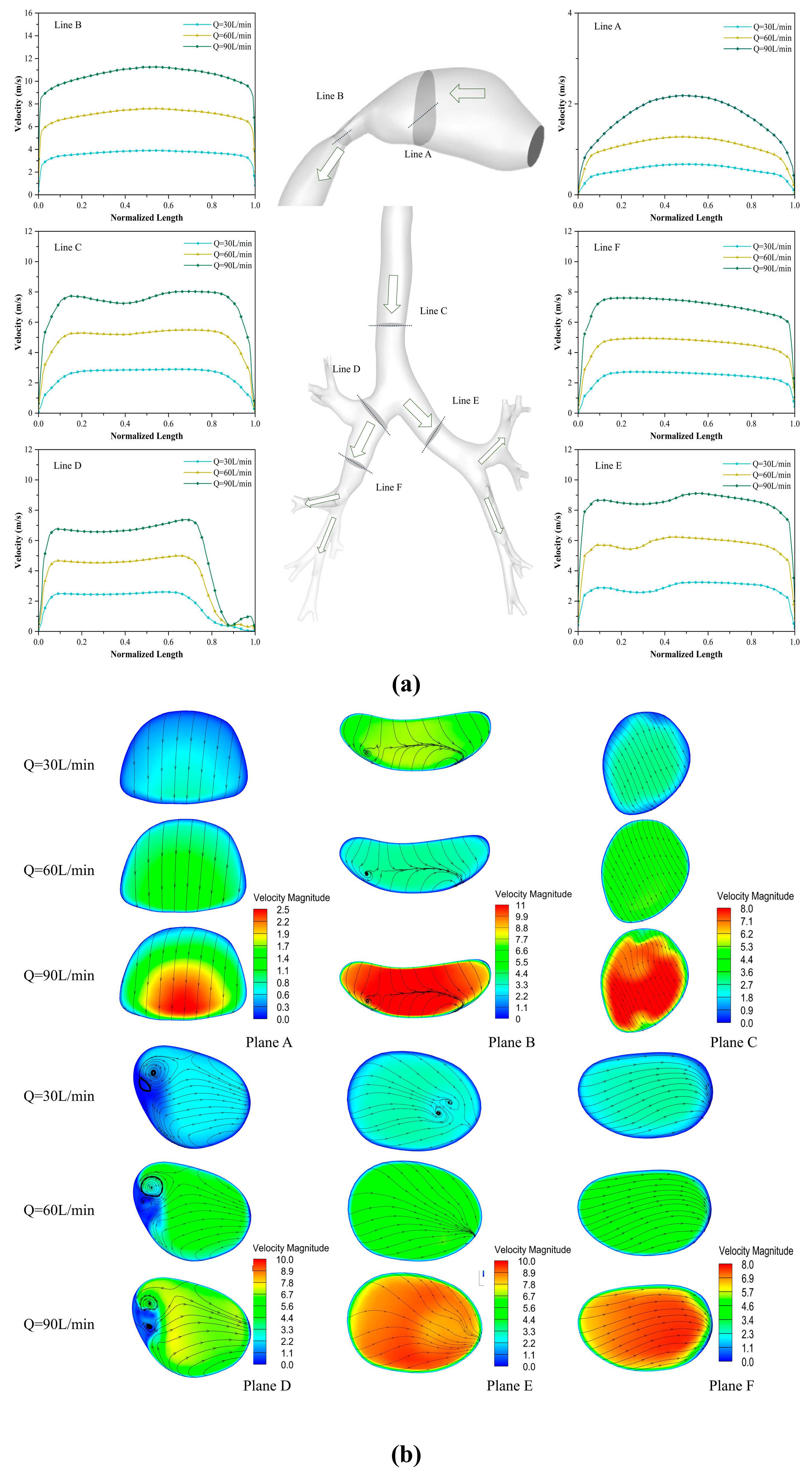
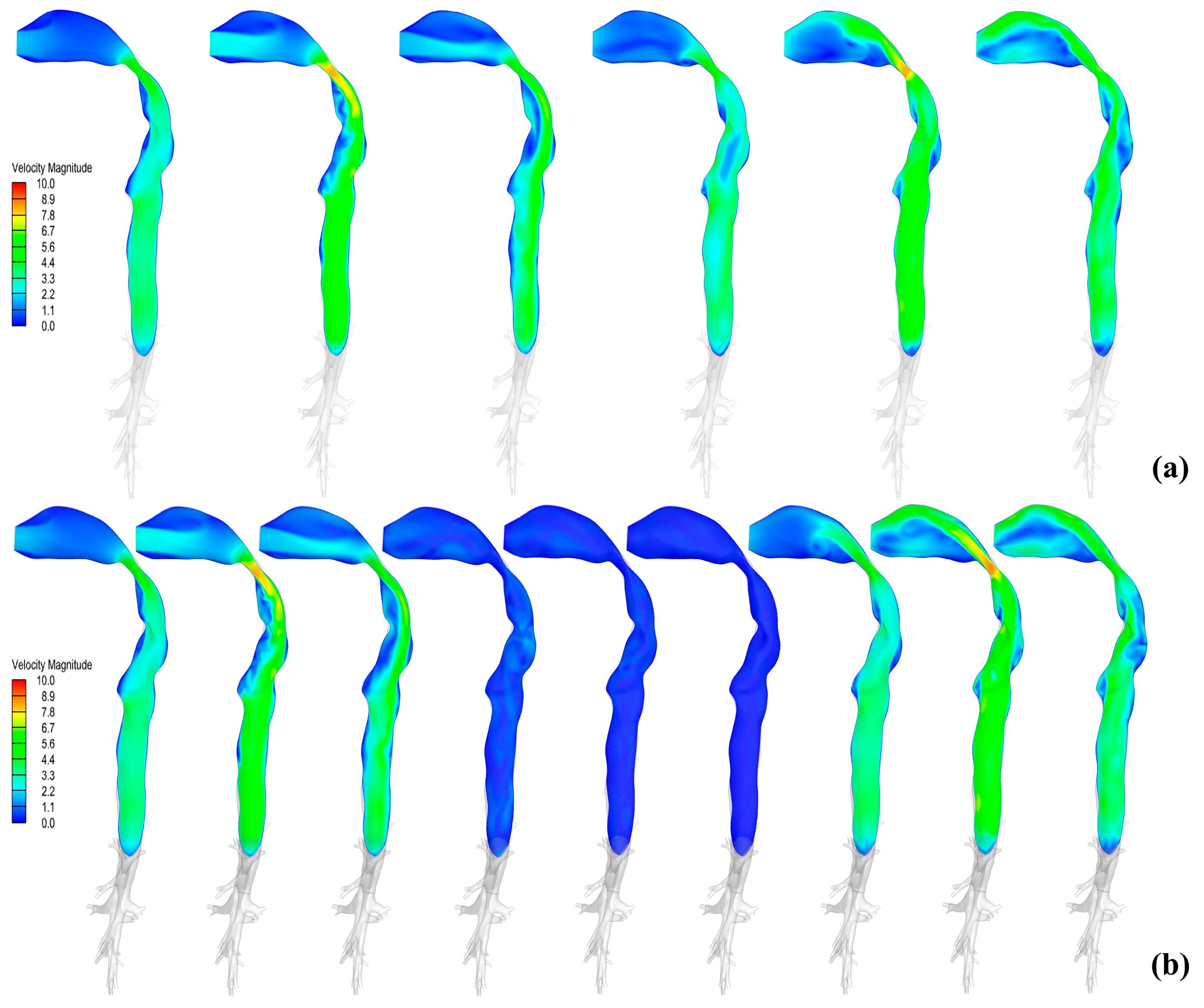
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Flow Field
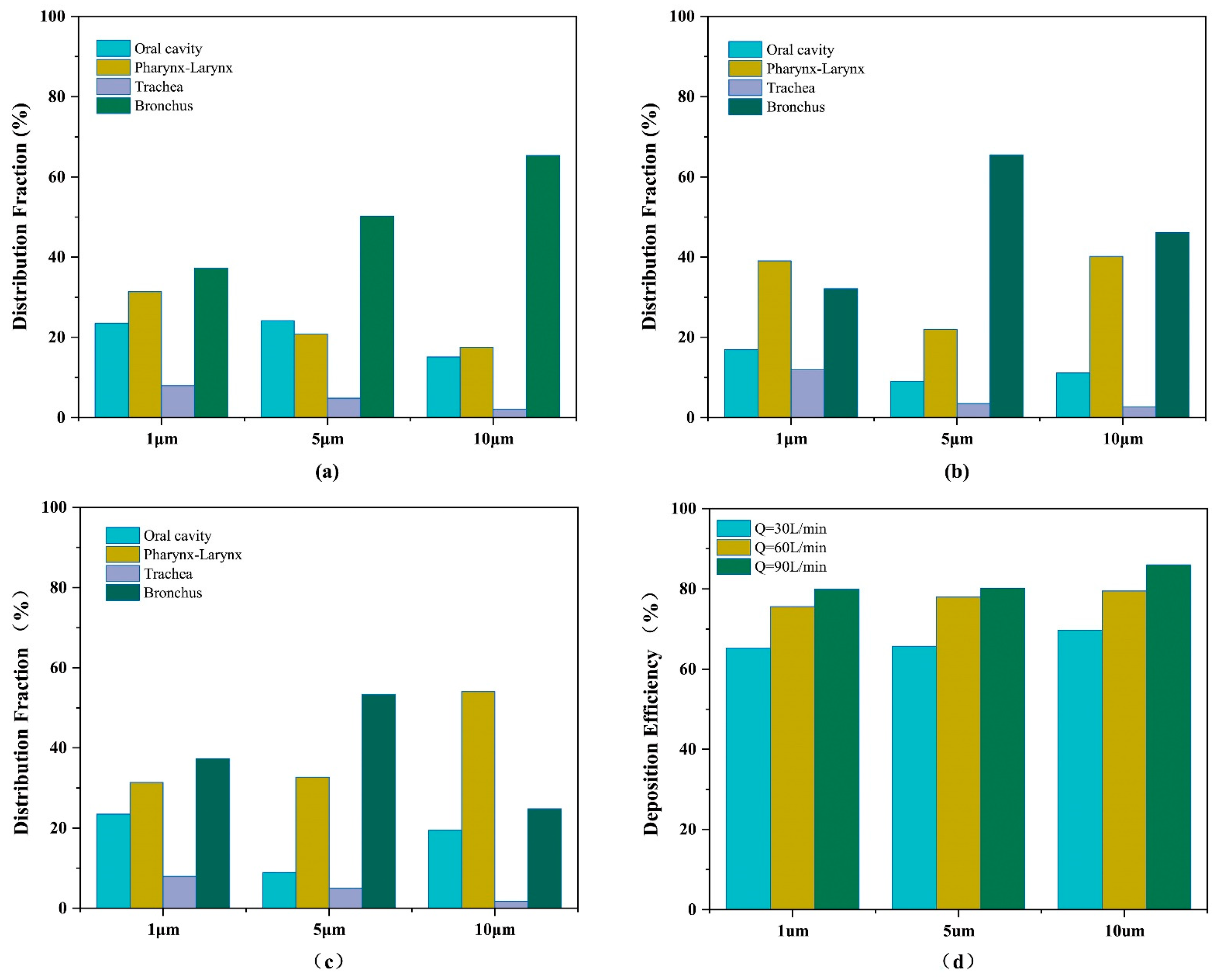
3.3. Pattern of Particle Distribution
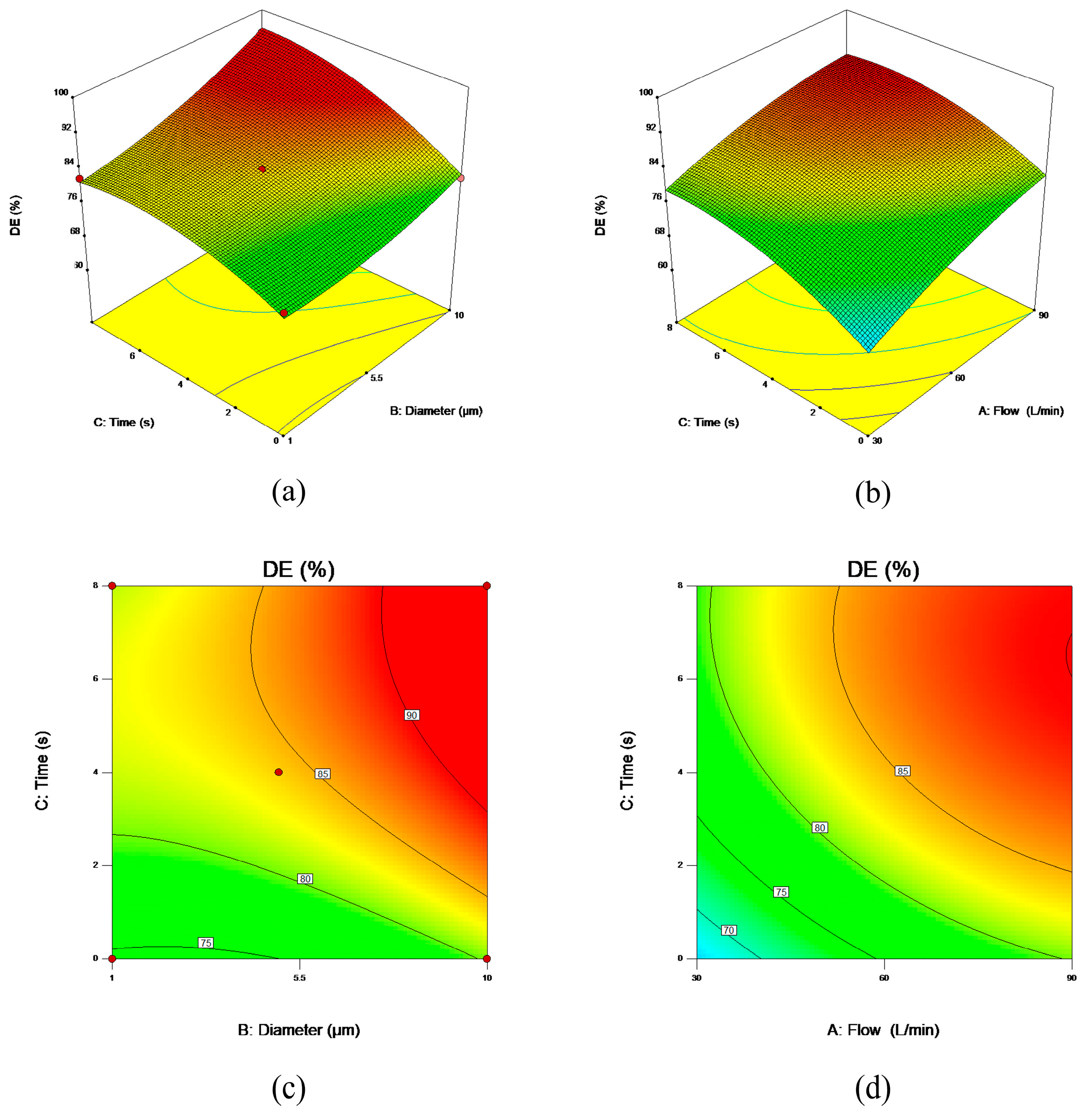
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DPM | Discrete Phase Model |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| BBD | Box-Behnken Design |
| DF | Deposition Fraction |
| DE | Deposition Efficiency |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
References
- Rhee, C.K.; Chau, N.Q.; Yunus, F.; Matsunaga, K.; Perng, D. On behalf the COPD Assembly of the APSR. Management of COPD in Asia: A position statement of the Asian Pacific Society of Respirology. Respirology 2019, 24, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, H.I.; Chablani, L. A comprehensive overview of dry powder inhalers for pulmonary drug delivery: Challenges, advances, optimization techniques, and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bera, H.; Shi, C.; Zhang, L.; Cun, D.; Yang, M. Pharmaceutical strategies to extend pulmonary exposure of inhaled medicines. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2565–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Ni, R.; Zhou, J.; Mao, S. Recent advances in controlled pulmonary drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heenan, A.F.; Matida, E.; Pollard, A.; Finlay, W.H. Experimental measurements and computational modeling of the flow field in an idealized human oropharynx. Exp. Fluids 2003, 35, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahookhosh, K.; Yaqoubi, S.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Aminfar, H. Experimental investigation of aerosol deposition through a realistic respiratory airway replica: An evaluation for MDI and DPI performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, W.M.; Ghazali, N.N.N.; Khor, C.Y.; Badruddin, I.A.; Zainon, M.Z.; Yazid, A.A.; Ibrahim, N.B.; Razi, R.M. Computational fluid dynamics modelling of human upper airway: A review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yin, Y.; Saha, G.; Francis, I.; Saha, S.C. A Comprehensive Numerical Study on the Transport and Deposition of Nasal Sprayed Pharmaceutical Aerosols in a Nasal-To-Lung Respiratory Tract Model. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2024, 42, 2400004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintermann, A.; Schröder, W. Simulation of aerosol particle deposition in the upper human tracheobronchial tract. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2017, 63, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiasadegh, M.; Emdad, H.; Ahmadi, G.; Abouali, O. Transient numerical simulation of airflow and fibrous particles in a human upper airway model. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 140, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, B.; Owen, T.P.; Kuempel, E.D.; Jarabek, A.M. Dosimetry of inhaled elongate mineral particles in the respiratory tract: The impact of shape factor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 361, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piemjaiswang, R.; Shiratori, S.; Chaiwatanarat, T.; Piumsomboon, P.; Chalermsinsuwan, B. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of full breathing cycle for aerosol deposition in trachea: Effect of breathing frequency. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, E.R. Geometric and Dimensional Airway Models of Conductive, Transitory and Respiratory Zones of the Human Lung. In Morphometry of the Human Lung; Weibel, E.R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1963; pp. 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Horsfield, K.; Cumming, G. Morphology of the bronchial tree in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1968, 34, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadafi, H.; Monshi Tousi, N.; De Backer, W.; De Backer, J. Validation of computational fluid dynamics models for airway deposition with SPECT data of the same population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, S.; Rahai, H.; Lopez, S.; Shin, J.; Jafari, B. Evaluation of human obstructive sleep apnea using computational fluid dynamics. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, S.; Zhao, J.; Ye, Y. Study on the coal dust deposition fraction and site in the upper respiratory tract under different particle sizes and labor intensities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglu, D.; Karaman, A. A Numerical Simulation of the Airflow and Aerosol Particle Deposition in a Realistic Airway Model of a Healthy Adult. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 3130–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lixing, Z.; Zhenbo, T.; Ya, Z.; Aibing, Y. Numerical study on the deposition distribution and mechanism of inhaled drug particles in various regions of the realistic inhaler-airway model. Powder Technol. 2025, 449, 120402. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Sun, B. Interactive response analysis of transportation and deposition of engineered aerosol particle in airway. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 709, 136022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerti, M.; Balogh, Z.; Kelemen, K.; Varga, J.T. The relationship between exercise capacity and different functional markers in pulmonary rehabilitation for COPD. COPD 2018, 13, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, A.; Balásházy, I.; Tomisa, G.; Farkas, Á. Significance of breath-hold time in dry powder aerosol drug therapy of COPD patients. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabe, R.; Rafee, R.; Valipour, M.S.; Ahmadi, G. Investigation of airflow at different activity conditions in a realistic model of human upper respiratory tract. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 24, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshaghi, S.; Khaleghi, H.; Maddahian, R. Prediction of Transport and Deposition of Porous Particles in the Respiratory System Using Eulerian–Lagrangian Approach. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2024, 40, e3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ma, H.; Liu, G.; Cui, X.; Xu, Q. Dust transport law and deposition characteristic in coal workers’ respiratory tract based on CFD simulations. Powder Technol. 2023, 427, 118760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.; Kuntz, M.; Langtry, R. Ten years of industrial experience with the SST turbulence model. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 4, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Cheng, Y.-S. Comparison of Deposition in the USP and Physical Mouth–Throat Models with Solid and Liquid Particles. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2011, 24, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sung Cheng, Y. Effects of MDI spray angle on aerosol penetration efficiency through an oral airway cast. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, S.M.; Swift, D.L. Deposition of Inhaled Particles in the Oral Airway During Oronasal Breathing. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1989, 11, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Fu, C.S.; Yazzie, D.; Zhou, Y. Respiratory Deposition Patterns of Salbutamol pMDI with CFC and HFA-134a Formulations in a Human Airway Replica. J. Aerosol Med. 2001, 14, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, P.C.; Aitken, R.J.; Hannan, W.J. Measurements of the total and regional deposition of inhaled particles in the human respiratory tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 1982, 13, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Hu, T.; Ma, D. Computational investigation of flow characteristics and particle deposition patterns in a realistic human airway model under different breathing conditions. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2023, 314, 104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsalanloo, A.; Abbasalizadeh, M.; Khalilian, M.; Saniee, Y.; Ramezanpour, A.; Islam, M.S. A computational approach to understand the breathing dynamics and pharmaceutical aerosol transport in a realistic airways. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| level | (A) Peak Flow Rate (L/min) | (B) Particle Diameter (μm) | (C) Breath-Holding Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 30 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 60 | 5 | 4 |
| 1 | 90 | 10 | 8 |
| Case No. | A(L/min) | B(μm) | C(s) | DE(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90 | 5 | 0 | 80.1205 |
| 2 | 90 | 1 | 4 | 85.9185 |
| 3 | 60 | 1 | 8 | 81.9384 |
| 4 | 60 | 5 | 4 | 84.0030 |
| 5 | 30 | 5 | 0 | 65.6673 |
| 6 | 90 | 5 | 8 | 89.3506 |
| 7 | 60 | 1 | 0 | 75.5906 |
| 8 | 30 | 10 | 4 | 86.7918 |
| 9 | 60 | 10 | 0 | 79.4711 |
| 10 | 30 | 5 | 8 | 78.2122 |
| 11 | 60 | 10 | 8 | 94.6443 |
| 12 | 30 | 1 | 4 | 71.3084 |
| 13 | 30 | 10 | 4 | 94.9004 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F Value | Pr > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 986.28 | 9 | 95.59 | 33.64 | 0.0074 |
| A-flow | 281.19 | 1 | 281.19 | 98.97 | 0.0022 |
| B-diameter | 210.66 | 1 | 210.66 | 74.14 | 0.0033 |
| C-time | 243.47 | 1 | 243.47 | 85.69 | 0.0027 |
| AB | 11.02 | 1 | 11.02 | 3.88 | 0.1435 |
| AC | 2.75 | 1 | 2.75 | 0.97 | 0.3980 |
| BC | 19.29 | 1 | 19.29 | 6.79 | 0.0800 |
| A2 | 8.46 | 1 | 8.46 | 2.98 | 0.1830 |
| B2 | 9.85 | 1 | 9.85 | 3.47 | 0.1595 |
| C2 | 32.01 | 1 | 32.01 | 11.27 | 0.0439 |
| Residual | 8.52 | 3 | 2.84 | ||
| Cor total | 868.80 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, F.; Ma, S.; Hu, T. Mechanistic Analysis of Fluid Dynamics and Multifactorial Impact Mechanisms in Inhaled Pharmaceutical Deposition for Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060643
Hu F, Ma S, Hu T. Mechanistic Analysis of Fluid Dynamics and Multifactorial Impact Mechanisms in Inhaled Pharmaceutical Deposition for Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060643
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Fuli, Songhua Ma, and Tianliang Hu. 2025. "Mechanistic Analysis of Fluid Dynamics and Multifactorial Impact Mechanisms in Inhaled Pharmaceutical Deposition for Chronic Respiratory Diseases" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060643
APA StyleHu, F., Ma, S., & Hu, T. (2025). Mechanistic Analysis of Fluid Dynamics and Multifactorial Impact Mechanisms in Inhaled Pharmaceutical Deposition for Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Bioengineering, 12(6), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060643




