Towards Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Non-Cellular Treatments for EB
3. Cellular Therapies for EB
3.1. Ex Vivo Strategies to Treat EB
3.2. MSC Treatments for EB
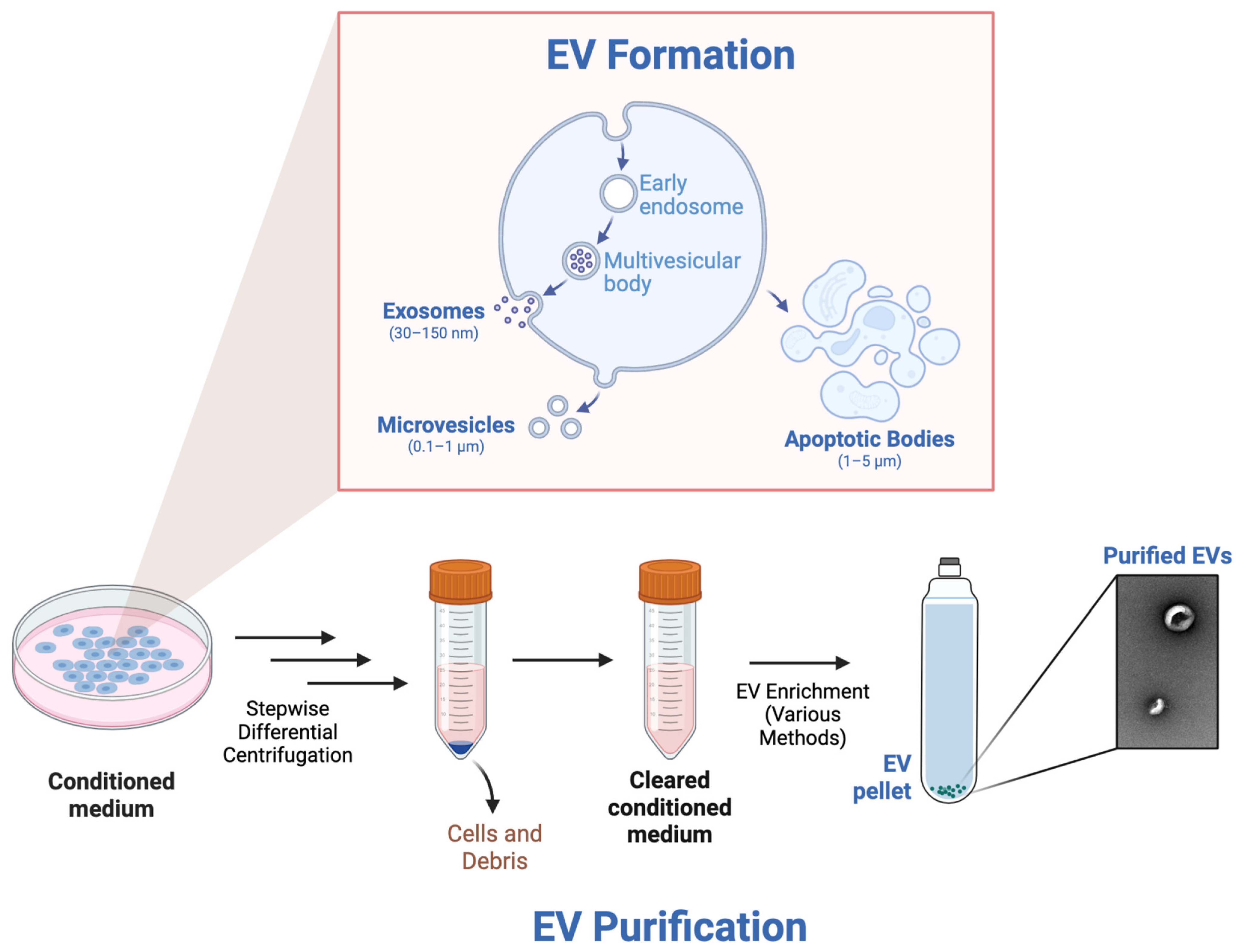
4. EVs to Treat EB
4.1. Advancements in MSC EVs to Treat EB
4.2. Challenges and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EB | Epidermolysis bullosa |
| RDEB | Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa |
| C7 | Type VII col |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| SEC | Size-exclusion chromatography |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cell |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
References
- Fine, J.-D.; Mellerio, J.E. Extracutaneous Manifestations and Complications of Inherited Epidermolysis Bullosa: Part I. Epithelial Associated Tissues. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Bauer, J.W.; Bodemer, C.; Bolling, M.C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Diem, A.; Fine, J.-D.; Heagerty, A.; Hovnanian, A.; Marinkovich, M.P.; et al. Consensus Reclassification of Inherited Epidermolysis Bullosa and Other Disorders with Skin Fragility. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkuma, S. Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa: A Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Fine, J.-D.; Harper, N.; Has, C.; Magin, T.M.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Marshall, J.F.; McGrath, J.A.; et al. Epidermolysis Bullosa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2020, 6, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Lucas, E.; Gorell, E.; Chiou, A.; Lu, Y.; Gillon, J.; Patel, D.; Rudin, D. A Systematic Literature Review of the Disease Burden in Patients with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soro, L.; Bartus, C.; Purcell, S. Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2015, 8, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Amat-Samaranch, V.; Agut-Busquet, E.; Vilarrasa, E.; Puig, L. New Perspectives on the Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211055920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, E.; Lara-Corrales, I.; Mellerio, J.; Martinez, A.; Schultz, G.; Burrell, R.; Goodman, L.; Coutts, P.; Wagner, J.; Allen, U.; et al. A Consensus Approach to Wound Care in Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA FDA Approves First Topical Gene Therapy for Treatment of Wounds in Patients with Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-topical-gene-therapy-treatment-wounds-patients-dystrophic-epidermolysis-bullosa (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Payne, A.S. Topical Gene Therapy for Epidermolysis Bullosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2281–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, S.V.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Bağcı, I.S.; Agostini, B.; Chen, H.; Feeney, G.; Steimer, M.; Kapadia, B.; Sridhar, K.; Sanchez, L.Q.; et al. Trial of Beremagene Geperpavec (B-VEC) for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.; Sathe, N.C.; Tsuchiya, A. Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Dosing & Administration. Available online: https://www.vyjuvek.com/starting-vyjuvek/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Bruckner, A.L.; Losow, M.; Wisk, J.; Patel, N.; Reha, A.; Lagast, H.; Gault, J.; Gershkowitz, J.; Kopelan, B.; Hund, M.; et al. The Challenges of Living with and Managing Epidermolysis Bullosa: Insights from Patients and Caregivers. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymakers, A.J.N.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Mostaghimi, A.; Feldman, W.B. Estimated Spending on Beremagene Geperpavec for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travagin, C. Chiesi Global Rare Diseases Receives FDA Approval for FILSUVEZ® (Birch Triterpenes) Topical Gel for the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa. Available online: https://chiesirarediseases.com/media/fda-approval-for-filsuvez-topical-gel (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Ebeling, S.; Naumann, K.; Pollok, S.; Wardecki, T.; Vidal-y-Sy, S.; Nascimento, J.M.; Boerries, M.; Schmidt, G.; Brandner, J.M.; Merfort, I. From a Traditional Medicinal Plant to a Rational Drug: Understanding the Clinically Proven Wound Healing Efficacy of Birch Bark Extract. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.S.; Sprecher, E.; Fernandez, M.F.; Schauer, F.; Bodemer, C.; Cunningham, T.; Löwe, S.; Davis, C.; Sumeray, M.; Bruckner, A.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Oleogel-S10 (Birch Triterpenes) for Epidermolysis Bullosa: Results from the Phase III Randomized Double-Blind Phase of the EASE Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.V.; Harris, A.G.; Su, J.C.; Orchard, D.; Warren, L.J.; McManus, H.; Murrell, D.F. The Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI): Grading Disease Severity and Assessing Responsiveness to Clinical Change in Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shesteen, H. Amryt’s Rare Skin Disease (Epidermolysis Bullosa) Treatment Rejected by FDA. Available online: https://www.biospace.com/fda-declines-approval-for-epidermolysis-bullosa-treatment (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- FILSUVEZ® (Birch Triterpenes) Topical Gel | Prescribing FILSUVEZ. Available online: https://www.filsuvez.com/hcp/dosage-and-administration/prescribing-filsuvez (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Niti, A.; Koliakos, G.; Michopoulou, A. Stem Cell Therapies for Epidermolysis Bullosa Treatment. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.; Rothoeft, T.; Teig, N.; Bauer, J.W.; Pellegrini, G.; De Rosa, L.; Scaglione, D.; Reichelt, J.; Klausegger, A.; Kneisz, D.; et al. Regeneration of the Entire Human Epidermis by Transgenic Stem Cells. Nature 2017, 551, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueckelhaus, M.; Rothoeft, T.; Rosa, L.D.; Yeni, B.; Ohmann, T.; Maier, C.; Eitner, L.; Metze, D.; Losi, L.; Seconetti, A.S.; et al. Transgenic Epidermal Cultures for Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa—5-Year Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinkovich, M.P.; Tang, J.Y. Gene Therapy for Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siprashvili, Z.; Nguyen, N.T.; Gorell, E.S.; Loutit, K.; Khuu, P.; Furukawa, L.K.; Lorenz, H.P.; Leung, T.H.; Keene, D.R.; Rieger, K.E.; et al. Safety and Wound Outcomes Following Genetically Corrected Autologous Epidermal Grafts in Patients With Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. JAMA 2016, 316, 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.Y.; Nazaroff, J.; Iwummadu, C.V.; Harris, N.; Gorell, E.S.; Fulchand, S.; Bailey, I.; McCarthy, D.; Siprashvili, Z.; Marinkovich, M.P.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Gene-Corrected Autologous Keratinocyte Grafts for Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little Abeona Gets Big Setback with FDA Clinical Hold on Pivotal Phase 3 | Fierce Biotech. Available online: https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/little-abeona-gets-a-big-setback-fda-clinical-hold-pivotal-phase-3 (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Dunleavy, K. FDA Rejects Abeona’ Therapeutics’ Topical Gene Therapy Pz-Cel. Available online: https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/another-delay-abeonas-topical-gene-therapy-pz-cel-fda-sends-out-crl (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- U.S. FDA Approves ZEVASKYNTM (Prademagene Zamikeracel), the First and Only Cell-Based Gene Therapy for Patients with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB). Available online: https://investors.abeonatherapeutics.com/press-releases/detail/303/u-s-fda-approves-zevaskyn-prademagene-zamikeracel (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Abeona Therapeutics, Inc. VIITAL: A Phase 3 Study of EB-101 for the Treatment of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB); Clinicaltrials.gov: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2022.
- Lwin, S.M.; Syed, F.; Di, W.-L.; Kadiyirire, T.; Liu, L.; Guy, A.; Petrova, A.; Abdul-Wahab, A.; Reid, F.; Phillips, R.; et al. Safety and Early Efficacy Outcomes for Lentiviral Fibroblast Gene Therapy in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e126243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautz, D. 3 min ABEO: ZevaskynTM Approved by FDA. Raising Valuation to $11…. Available online: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/abeo-zevaskyn-approved-fda-raising-100500085.html (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Badiavas, E.V.; Abedi, M.; Butmarc, J.; Falanga, V.; Quesenberry, P. Participation of Bone Marrow Derived Cells in Cutaneous Wound Healing. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 196, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolar, J.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Riddle, M.; McElmurry, R.T.; Osborn, M.; Xia, L.; Lund, T.; Slattery, C.; Uitto, J.; Christiano, A.M.; et al. Amelioration of Epidermolysis Bullosa by Transfer of Wild-Type Bone Marrow Cells. Blood 2009, 113, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iinuma, S.; Aikawa, E.; Tamai, K.; Fujita, R.; Kikuchi, Y.; Chino, T.; Kikuta, J.; McGrath, J.A.; Uitto, J.; Ishii, M.; et al. Transplanted Bone Marrow–Derived Circulating PDGFRα+ Cells Restore Type VII Collagen in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Mouse Skin Graft. J. Immunol. Author Choice 2015, 194, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustin, M.; Mahadewi, A.; Danarti, R. Bone Marrow Transplantation and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Epidermolysis Bullosa: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2024, 41, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Systemic Therapy for a Genetic Skin Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiał-Wysocka, A.; Kot, M.; Majka, M. The Pros and Cons of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.R.; West, C.C.; Hardy, W.R.; James, A.W.; Park, T.S.; Nguyen, A.; Tawonsawatruk, T.; Lazzari, L.; Soo, C.; Péault, B. Natural History of Mesenchymal Stem Cells, from Vessel Walls to Culture Vessels. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1353–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiritsi, D.; Dieter, K.; Niebergall-Roth, E.; Fluhr, S.; Daniele, C.; Esterlechner, J.; Sadeghi, S.; Ballikaya, S.; Erdinger, L.; Schauer, F.; et al. Clinical Trial of ABCB5+ Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e151922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrum, J.A.; Ong, J.F.; Karp, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Immune Evasive, Not Immune Privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bahr, L.; Batsis, I.; Moll, G.; Hägg, M.; Szakos, A.; Sundberg, B.; Uzunel, M.; Ringden, O.; Le Blanc, K. Analysis of Tissues Following Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Humans Indicates Limited Long-Term Engraftment and No Ectopic Tissue Formation. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, M.B.; Neculachi, C.A.; Fenyo, I.M.; Vacaru, A.-M.; Publik, M.A.; Simionescu, M.; Burlacu, A. Short Lifespan of Syngeneic Transplanted MSC Is a Consequence of in Vivo Apoptosis and Immune Cell Recruitment in Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.S.; Kuncewicz, T.M.; Karp, J.M. Beyond Hit-and-Run: Stem Cells Leave a Lasting Memory. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.D.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; Badiavas, E.V. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers and Therapeutics in Dermatology: A Focus on Exosomes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, E.R.; Oropallo, A.R.; Grande, D.A.; Kirsner, R.S.; Badiavas, E.V. Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Tools for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clos-Sansalvador, M.; Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Roura, S.; Franquesa, M.; Borràs, F.E. Commonly Used Methods for Extracellular Vesicles’ Enrichment: Implications in Downstream Analyses and Use. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Fernandez-Rhodes, M.; Law, A.; Peacock, B.; Lewis, M.P.; Davies, O.G. Comparison of Extracellular Vesicle Isolation Processes for Therapeutic Applications. J. Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231174609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Wolfram, J. Immunogenicity of Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhao, F.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Song, J. Loss of Interactions between P53 and Survivin Gene in Mesenchymal Stem Cells after Spontaneous Transformation in Vitro. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Jeyaram, A.; Born, L.J.; Chang, K.-H.; Abadchi, S.N.; Hsu, A.T.W.; Solomon, T.; Aranda, A.; Stewart, S.; He, X.; et al. Impact of Storage Conditions and Duration on Function of Native and Cargo-Loaded Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, A.; Alini, M.; Baghaban Eslaminejad, M.; Hosseini, S. Engineering Strategies for Customizing Extracellular Vesicle Uptake in a Therapeutic Context. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/17/12/2085 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Mahmoudi, M.; Taghavi-Farahabadi, M.; Rezaei, N.; Hashemi, S.M. Comparison of the Effects of Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes with Conditioned Media on Neutrophil Function and Apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MSC-Derived Exosome Promotes M2 Polarization and Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing-He-2019-Stem Cells International-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1155/2019/7132708 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Favaro, E.; Carpanetto, A.; Caorsi, C.; Giovarelli, M.; Angelini, C.; Cavallo-Perin, P.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G.; Zanone, M.M. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Derived Extracellular Vesicles Induce Regulatory Dendritic Cells in Type 1 Diabetic Patients. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microvesicles from Human Adipose Stem Cells Promote Wound Healing by Optimizing Cellular Functions via AKT and ERK Signaling Pathways | Stem Cell Research & Therapy. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13287-019-1152-x (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Stavely, R.; Nurgali, K. The Emerging Antioxidant Paradigm of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 985–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concise Review: Intercellular Communication Via Organelle Transfer in the Biology and Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cells | Stem Cells | Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/stmcls/article-abstract/37/1/14/6423871 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Narauskaitė, D.; Vydmantaitė, G.; Rusteikaitė, J.; Sampath, R.; Rudaitytė, A.; Stašytė, G.; Aparicio Calvente, M.I.; Jekabsone, A. Extracellular Vesicles in Skin Wound Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitema, L.; Phillips, T.; Alexeev, V.; Igoucheva, O. Immunological Mechanisms Underlying Progression of Chronic Wounds in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.D.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; Candanedo, A.; Guzman, W.; Garcia-Contreras, M.; Badiavas, E.V. Dual Mechanism of Type VII Collagen Transfer by Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles to Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Fibroblasts. Biochimie 2018, 155, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Wang, Y.; Lou, P.; Liu, S.; Zhou, P.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. Extracellular Vesicles as Advanced Therapeutics for the Resolution of Organ Fibrosis: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1042983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, R.; Bernardis, C.; Pleshkov, A.; Jessop, N.; Miller, C.; Skye, J.; O’Brien, V.; Veerkamp, M.; da Rocha, A.C.F.; Cornwall, R. Hand Surgery and Hand Therapy Clinical Practice Guideline for Epidermolysis Bullosa. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bağcı, C.; Sever-Bahcekapili, M.; Belder, N.; Bennett, A.P.S.; Erdener, Ş.E.; Dalkara, T. Overview of Extracellular Vesicle Characterization Techniques and Introduction to Combined Reflectance and Fluorescence Confocal Microscopy to Distinguish Extracellular Vesicle Subpopulations. Neurophotonics 2022, 9, 021903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.Y.; Kee, L.T.; Al-Masawa, M.E.; Lee, Q.H.; Subramaniam, T.; Kok, D.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X. Scalable Production of Extracellular Vesicles and Its Therapeutic Values: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Zickler, A.M.; El Andaloussi, S. Dosing Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindle, J.; Williams, A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Patil, K.; Khatkar, P.; Osgood, Q.; Nelson, C.; Routenberg, D.A.; Howard, M.; et al. hTERT-Immortalized Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Large-Scale Manufacturing, Cargo Profiling, and Functional Effects in Retinal Epithelial Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler-Botija, C.; Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Munizaga-Larroudé, M.; Gálvez-Montón, C.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Roura, S. Mechanisms Governing the Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Scoping Review of Preclinical Evidence. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C.Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy Designation; FDA: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2021.
- Commissioner, O. of the Rare Pediatric Disease Designation and Priority Review Voucher Programs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/industry/medical-products-rare-diseases-and-conditions/rare-pediatric-disease-designation-and-priority-review-voucher-programs (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Aegle Therapeutics. A Safety Study of the Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Wounds; Clinicaltrials.gov: Miami, FL, USA, 2025.
- Yang, Z.; Shi, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; et al. Large-Scale Generation of Functional mRNA-Encapsulating Exosomes via Cellular Nanoporation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ianni, E.; Obuchi, W.; Breyne, K.; Breakefield, X.O. Extracellular Vesicles for the Delivery of Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2025, 3, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, J.; Kwak, K.J.; Tong, Y.; Estania, A.P.; Cao, J.; Hsu, W.-H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Intradermally Delivered mRNA-Encapsulating Extracellular Vesicles for Collagen-Replacement Therapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkasy, O.M.; Nordin, J.Z.; Hagey, D.W.; de Jong, O.G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Systems: Why and How? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchin, R.; Troyer, Z.; Witwer, K.; Morris, K.V. Extracellular Vesicles: The next Generation in Gene Therapy Delivery. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Modality | Example | Immuno-modulatory | Functional Col7 | Shelf-Stable | Acellular | Scalability | Ease of Admin. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo Gene Therapy | Modified HSV-1 vector | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | Medium | High (Topical) |
| Autologous Ex Vivo Gene Therapy | AAV-modified keratinocytes | × | ✓ | × | × | Low | Low (Transplant) |
| Allogeneic MSC Therapy | Dermal ABCB5+ MSCs | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | Low | Medium (IV infusion) |
| Small Molecule | Birch bark triterpenes | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | High | High (Topical) |
| Allogeneic Extracellular Vesicles | Bone marrow-derived MSC EVs | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Medium | High (Topical) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandoval, A.G.W.; Badiavas, E.V. Towards Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060574
Sandoval AGW, Badiavas EV. Towards Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060574
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandoval, Aaron Gabriel W., and Evangelos V. Badiavas. 2025. "Towards Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060574
APA StyleSandoval, A. G. W., & Badiavas, E. V. (2025). Towards Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Epidermolysis Bullosa. Bioengineering, 12(6), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060574






