Dynamic Virtual Simulation with Real-Time Haptic Feedback for Robotic Internal Mammary Artery Harvesting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surgical Anatomy and Motion Constraints
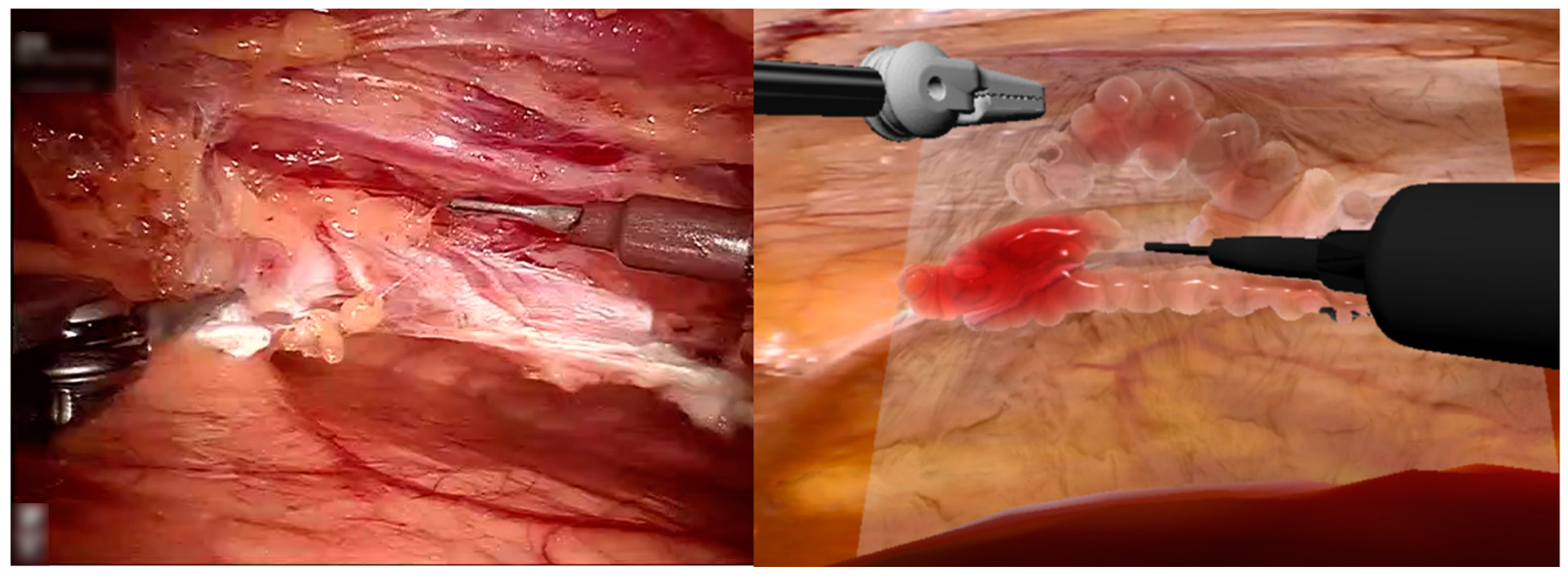
2.2. Images and Processing
2.3. Biomechanical Framework for Dynamic Thoracic Wall Simulation
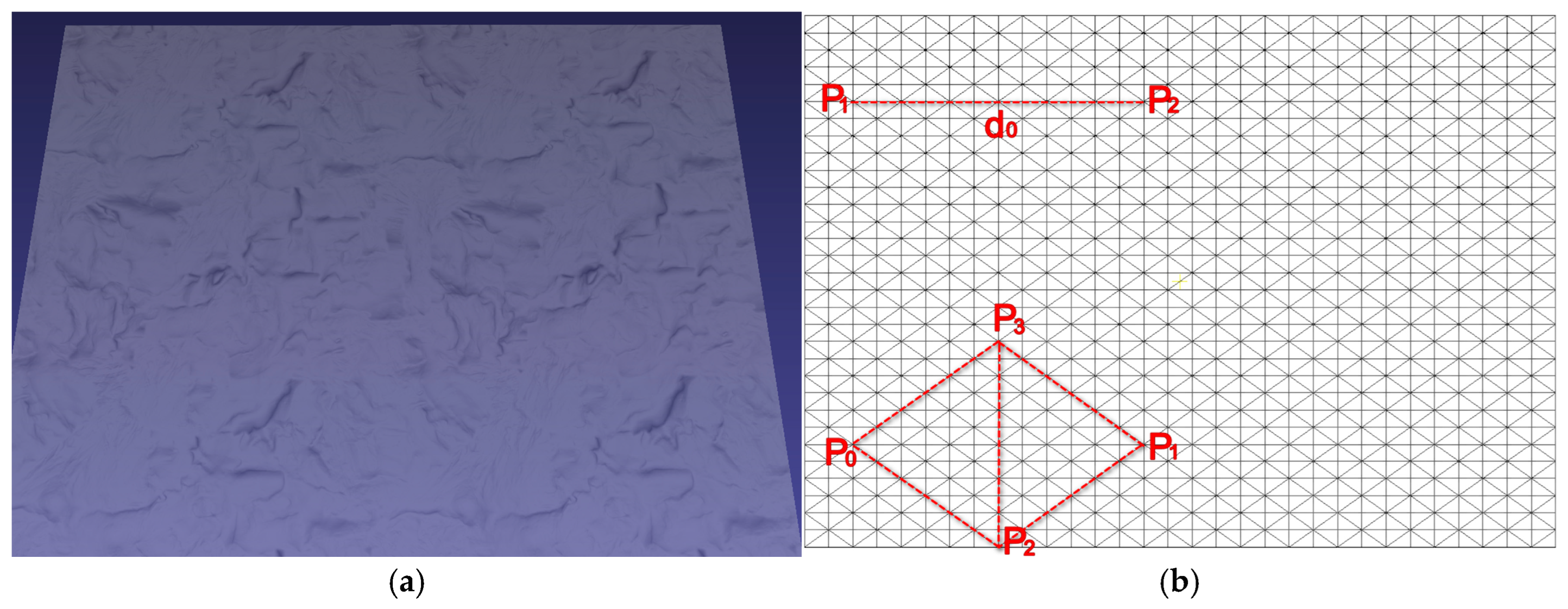
2.3.1. Fascia Superficialis Simulation
2.3.2. Multi-Resolution IMA Vessel Simulation
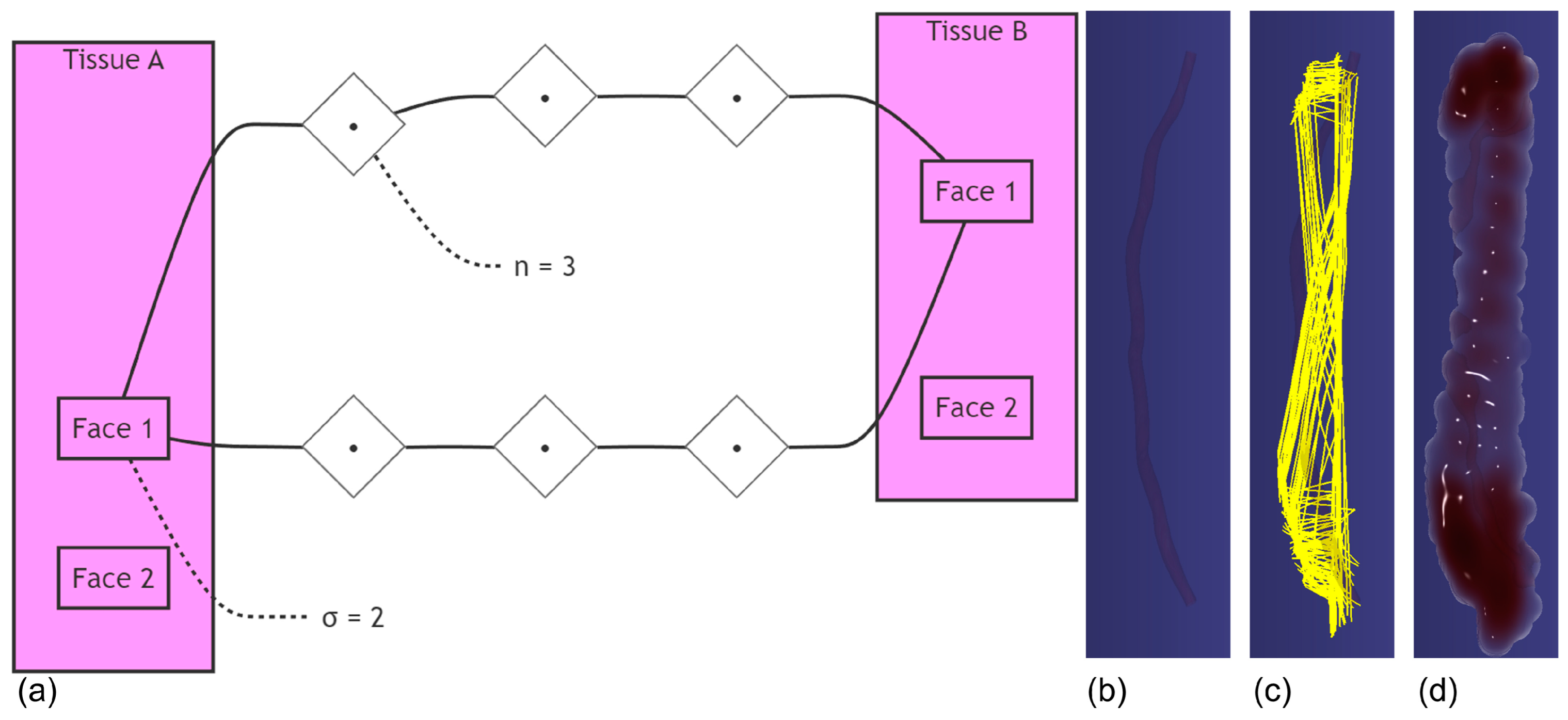
2.3.3. Connective Tissue Modeling
2.3.4. Bidirectional Coupling of IMA and Adipose Tissue
2.4. Interactive Haptic-Enabled Surgical Manipulation and Cutting
2.4.1. Topology-Preserving Cutting Method
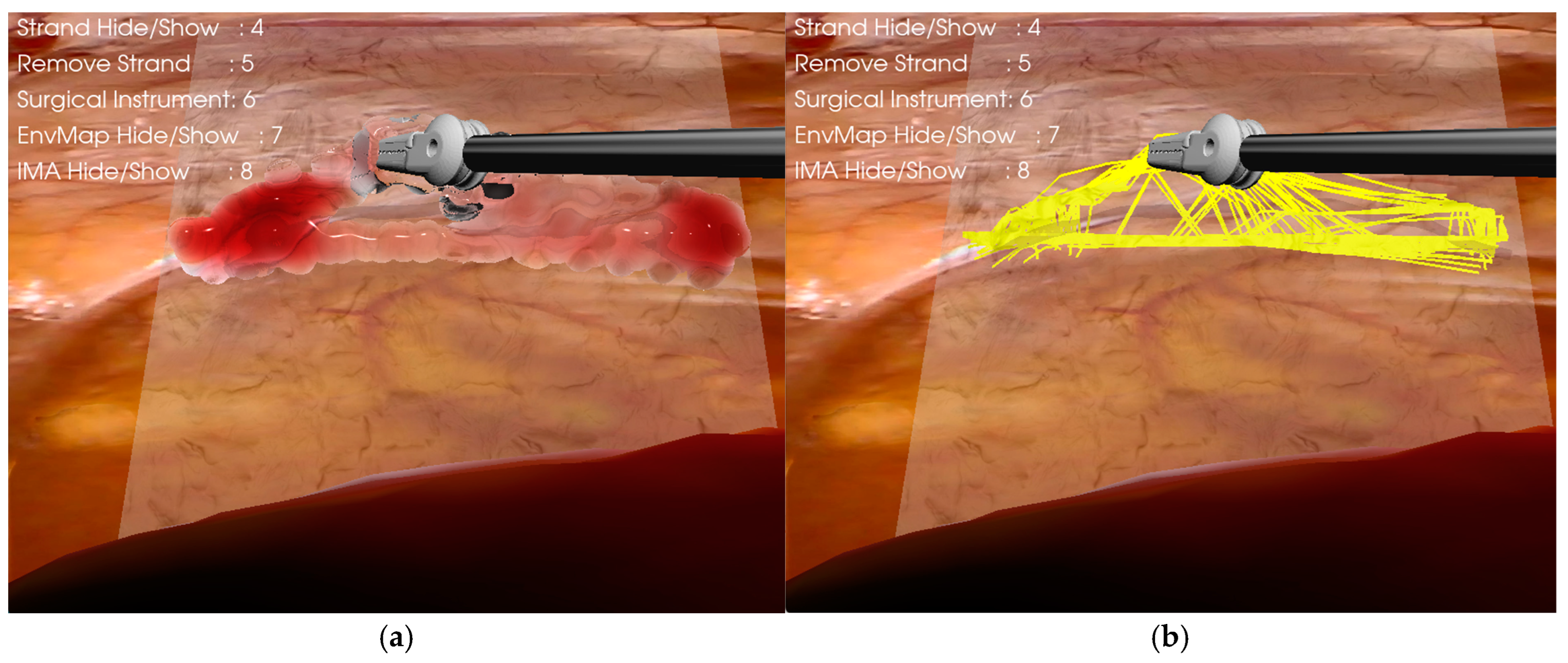
2.4.2. Connective Tissue Surgical Cutting Simulation
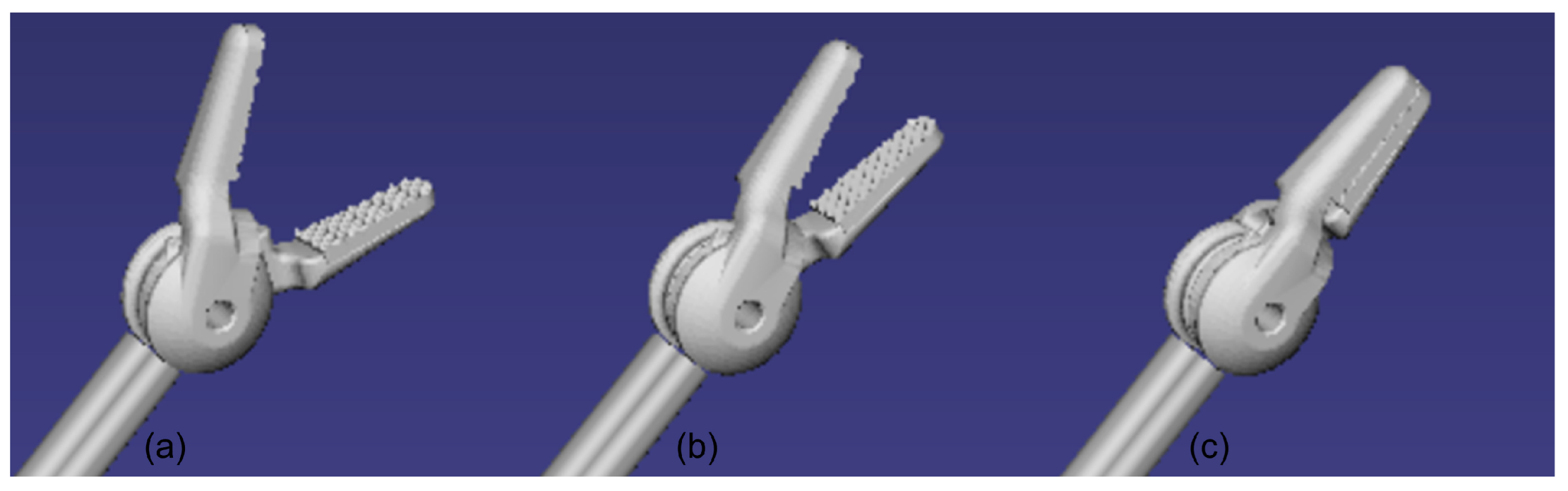
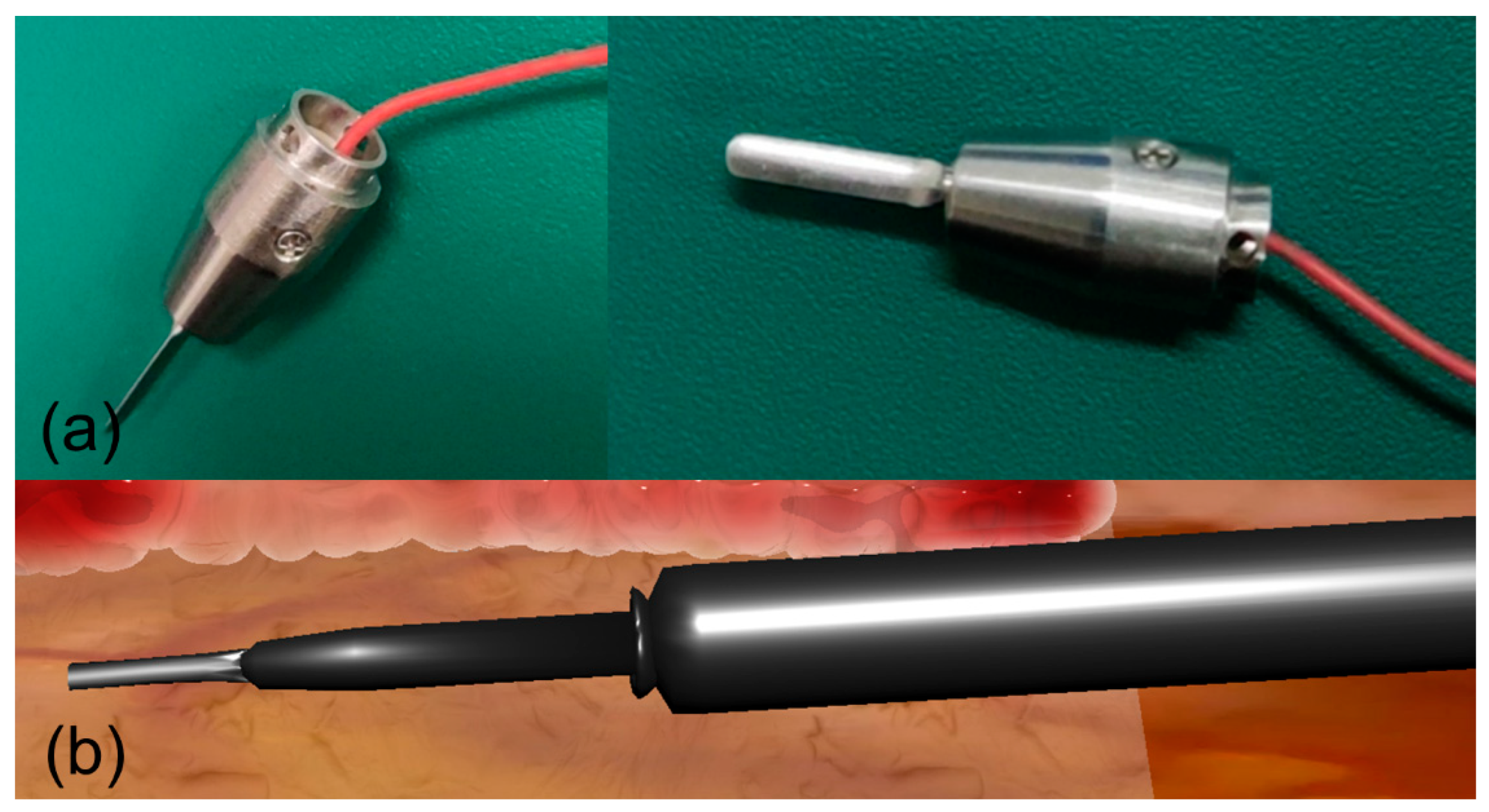
2.4.3. Kinematic Modeling of Surgical Instrument Motion
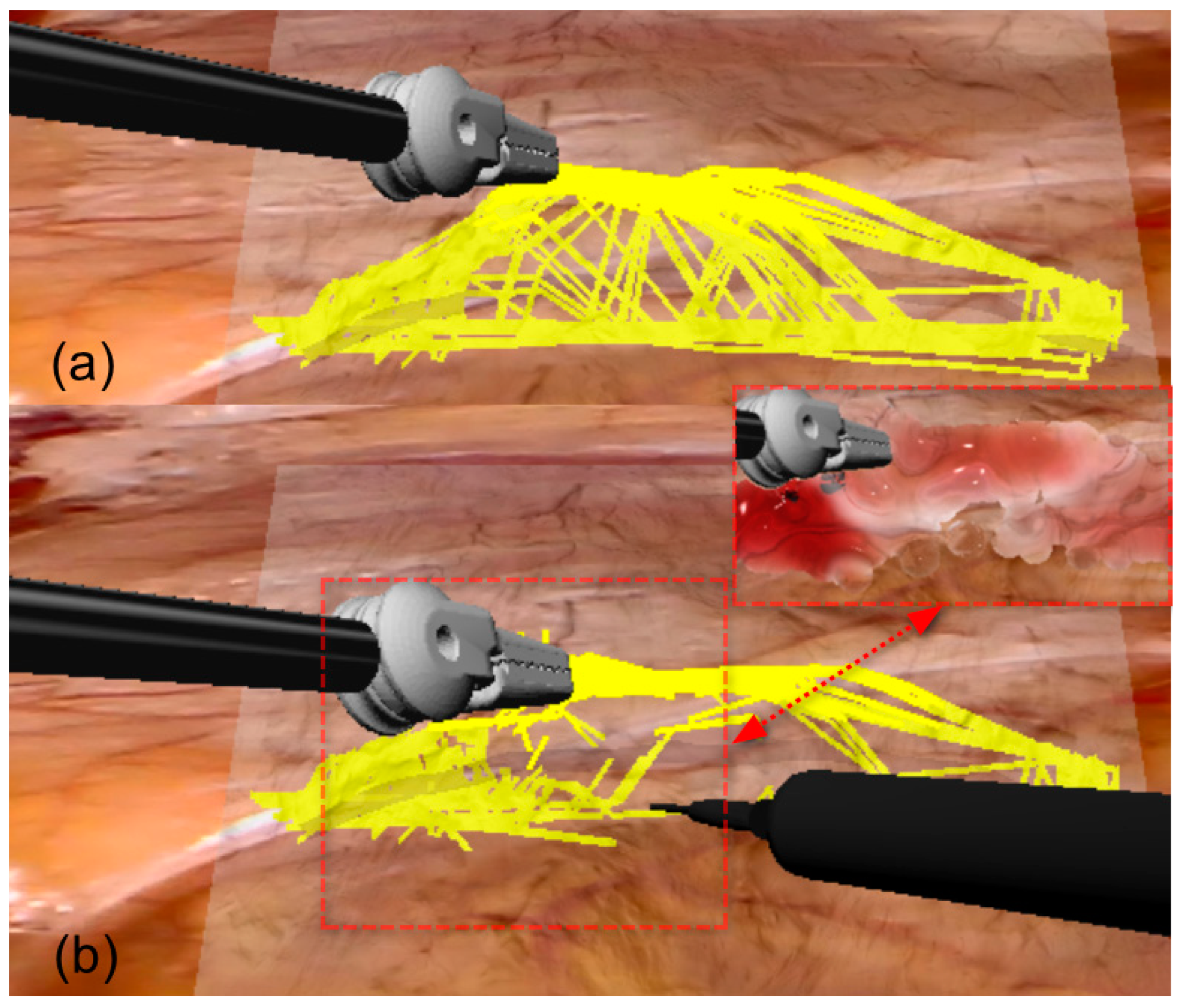
2.4.4. Force Feedback Modeling for Electrosurgical Simulation
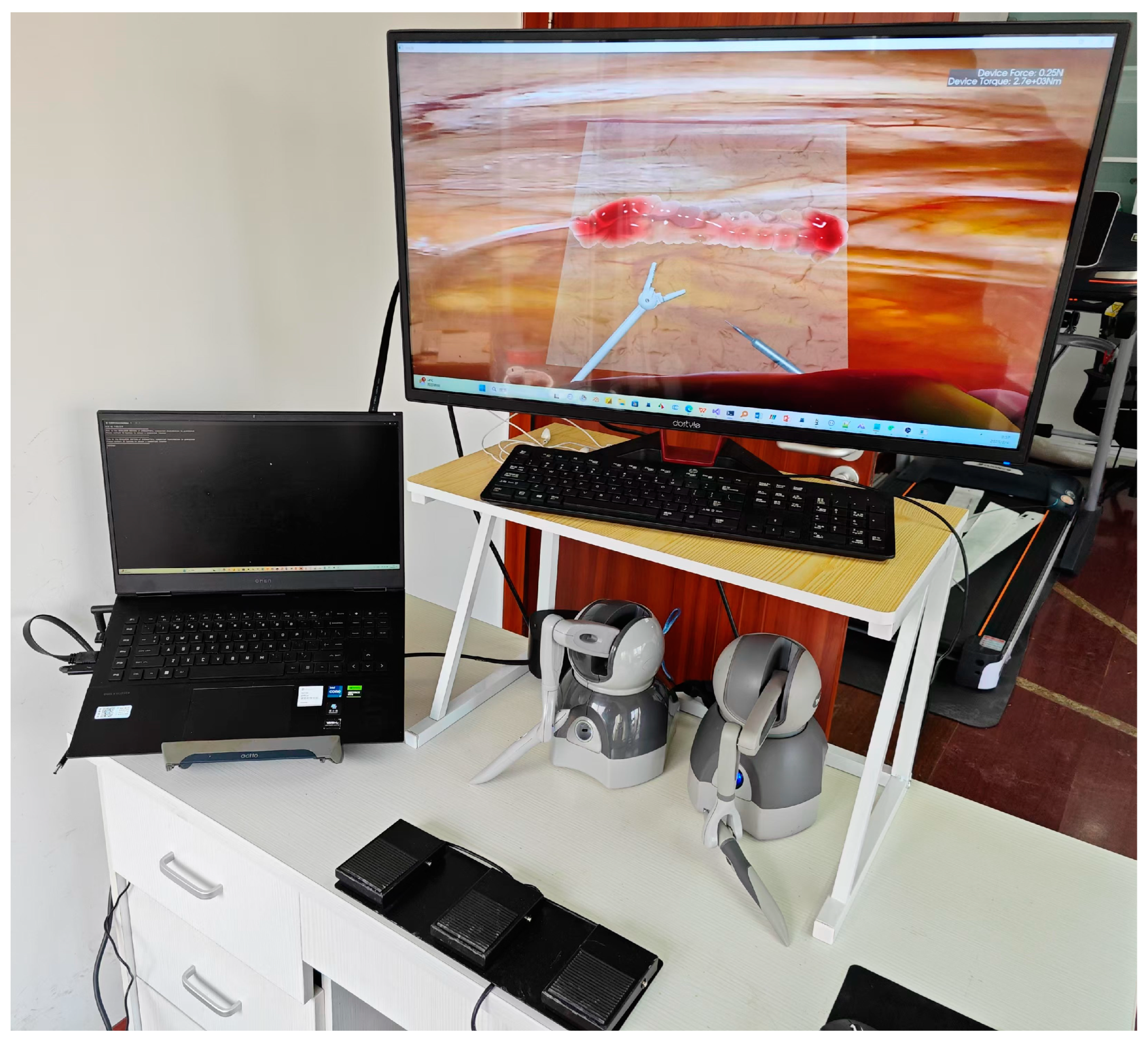
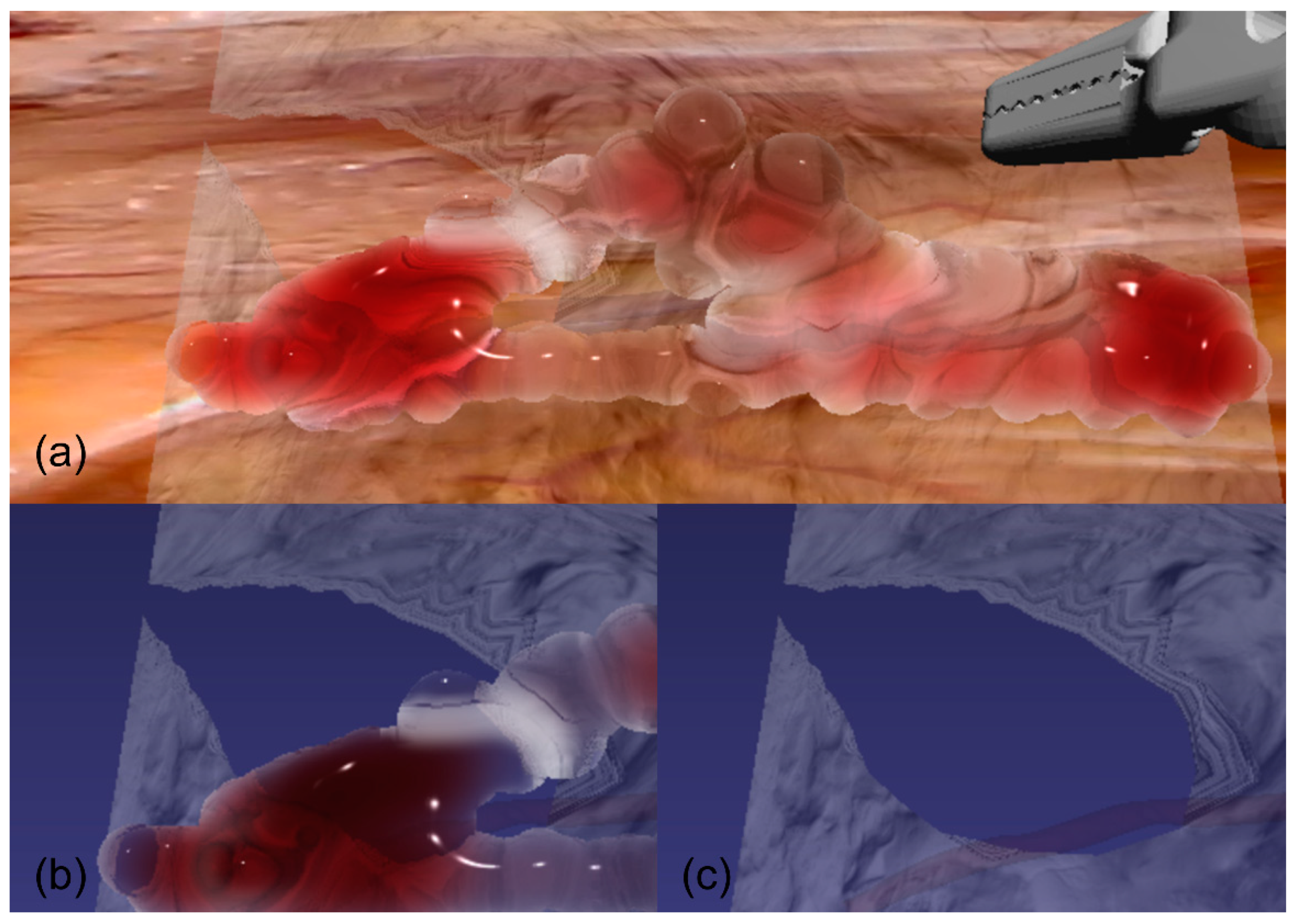
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Hemli, J.M.; Patel, N.C. Robotic Cardiac Surgery. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 100, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, H.U.H.; Lakhter, V.; Ahmed, M.; O’ Murchu, B.; Chatterjee, S. Radial Artery Versus Saphenous Vein Grafts in Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Literature Review. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonatti, J.; Wallner, S.; Winkler, B.; Grabenwöger, M. Robotic totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass grafting: Current status and future prospects. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, W.L.; Iyengar, A.; Han, J.J.; Mays, J.C.; Helmers, M.; Kelly, J.J.; Wang, X.; Ghoreishi, M.; Taylor, B.S.; Atluri, P.; et al. The learning curve of robotic coronary arterial bypass surgery: A report from the STS database. J. Card. Surg. 2021, 36, 4178–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdis, M.; Chu, M.W.; Schlachta, C.; Kiaii, B. Evaluation of robotic cardiac surgery simulation training: A randomized controlled trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 151, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trehan, K.; Kemp, C.D.; Yang, S.C. Simulation in cardiothoracic surgical training: Where do we stand? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Wolff, G.; Wernly, B.; Bruno, R.R.; Franz, M.; Schulze, P.C.; Silva, J.N.A.; Silva, J.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kelm, M. Virtual and Augmented Reality in Cardiovascular Care: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelargos, P.E.; Nagasawa, D.T.; Lagman, C.; Tenn, S.; Demos, J.V.; Lee, S.J.; Bui, T.T.; Barnette, N.E.; Bhatt, N.S.; Ung, N.; et al. Utilizing virtual and augmented reality for educational and clinical enhancements in neurosurgery. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 35, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, S.A.; Lumens, J.; Trayanova, N.A. Computational models in cardiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, C.J.; Haouchine, N.; Kong, S.H.; Soares, R.V.; Cazier, D.; Cotin, S. Handling topological changes during elastic registration. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, F.; Duriez, C.; Delingette, H.; Allard, J.; Gilles, B.; Marchesseau, S.; Talbot, H.; Courtecuisse, H.; Bousquet, G.; Peterlik, I.; et al. SOFA: A multi-model framework for interactive physical simulation. Soft Tissue Biomech. Model. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2012, 11, 283–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Kong, D.; Xu, X. A Liver Electrosurgery Simulator Developed by Unity Engine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Signal and Image Processing, Suzhou, China, 20–22 August 2021; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Wang, M.; Cui, Y. Simulation ready anatomy model generation pipeline for virtual surgery. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2021, 32, e1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Scheirich, H.; Jadhav, S.; Enquobahrie, A.; Paniagua, B.; Wilson, A.; Bray, A.; Sankaranarayanan, G.; Clipp, R.B. The interactive medical simulation toolkit (iMSTK): An open source platform for surgical simulation. Front. Virtual Real. 2023, 4, 1130156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, A.M. Haptic feedback in robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2009, 19, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacchierotti, C.; Prattichizzo, D.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Cutaneous feedback of fingertip deformation and vibration for palpation in robotic surgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Li, W.; Brown, R.; Ma, N.; Kerfoot, E.; Wang, Y.; Murrey, B.; Myronenko, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, D.; et al. Monai: An open-source framework for deep learning in healthcare. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.02701. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Shadden, S.C. Learning Whole Heart Mesh Generation From Patient Images for Computational Simulations. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Updegrove, A.; Wilson, N.M.; Merkow, J.; Lan, H.; Marsden, A.L.; Shadden, S.C. SimVascular: An open source pipeline for cardiovascular simulation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczkodaj, W.W.; Kakiashvili, T.; Szymańska, A.; Montero-Marin, J.; Araya, R.; Garcia-Campayo, J.; Rutkowski, K.; Strzałka, D. How to reduce the number of rating scale items without predictability loss? Scientometrics 2017, 111, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




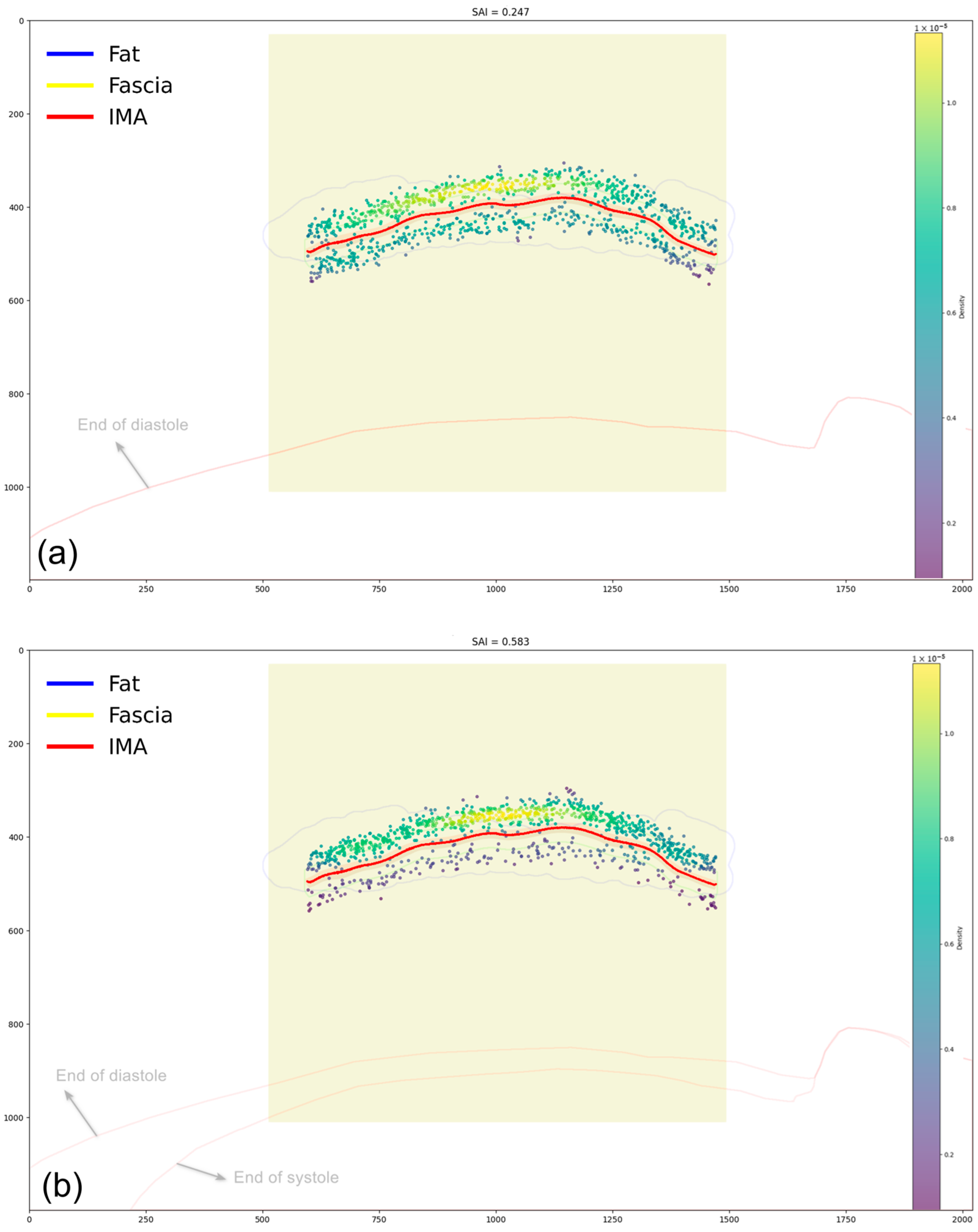

| Trial No. | Dynamic Group SAI | Static Group SAI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.583 | 0.247 |
| 2 | 0.621 | 0.268 |
| 3 | 0.545 | 0.221 |
| 4 | 0.602 | 0.285 |
| 5 | 0.568 | 0.238 |
| 6 | 0.634 | 0.276 |
| 7 | 0.592 | 0.212 |
| 8 | 0.551 | 0.257 |
| 9 | 0.615 | 0.228 |
| 10 | 0.577 | 0.243 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.589 ± 0.029 | 0.248 ± 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Ren, T.; Cheng, N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Virtual Simulation with Real-Time Haptic Feedback for Robotic Internal Mammary Artery Harvesting. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030285
Wang S, Ren T, Cheng N, Wang R, Zhang L. Dynamic Virtual Simulation with Real-Time Haptic Feedback for Robotic Internal Mammary Artery Harvesting. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(3):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030285
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuo, Tong Ren, Nan Cheng, Rong Wang, and Li Zhang. 2025. "Dynamic Virtual Simulation with Real-Time Haptic Feedback for Robotic Internal Mammary Artery Harvesting" Bioengineering 12, no. 3: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030285
APA StyleWang, S., Ren, T., Cheng, N., Wang, R., & Zhang, L. (2025). Dynamic Virtual Simulation with Real-Time Haptic Feedback for Robotic Internal Mammary Artery Harvesting. Bioengineering, 12(3), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030285






