Enhanced U-Net-Based Deep Learning Model for Automated Segmentation of Organoid Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
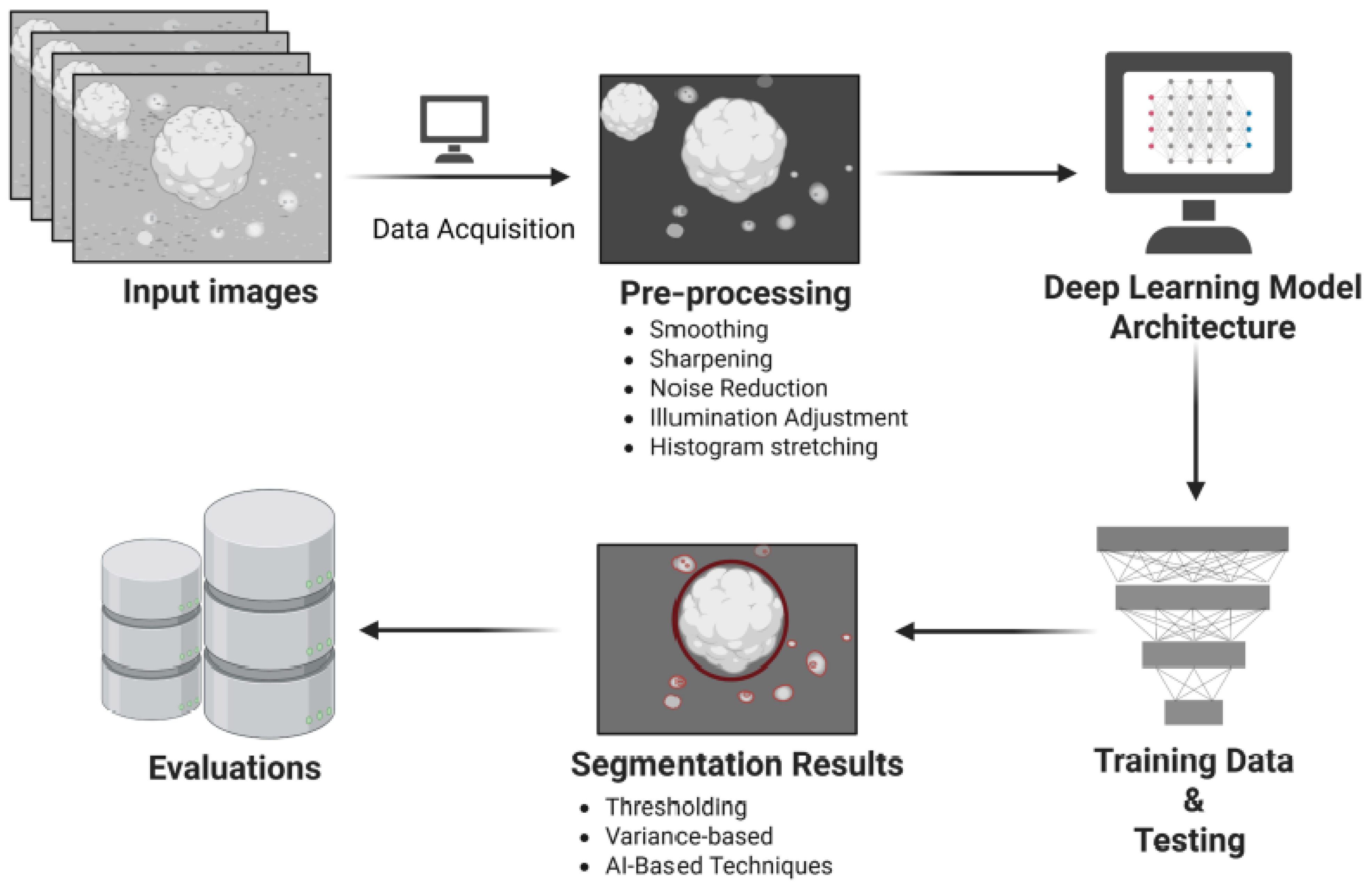
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Culture
2.2. Brain Organoid Generation
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Deep-Learning Model Architecture
2.5. Image Preprocessing
2.6. Training of CNN Segmentation Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
- Accuracy: the ratio of correctly classified pixels to the total number of pixels,
- Dice Similarity Coefficient: a measure of spatial overlap between prediction and ground truth,
- Jaccard Index: the proportion of correctly predicted pixels relative to the union of prediction and ground truth,
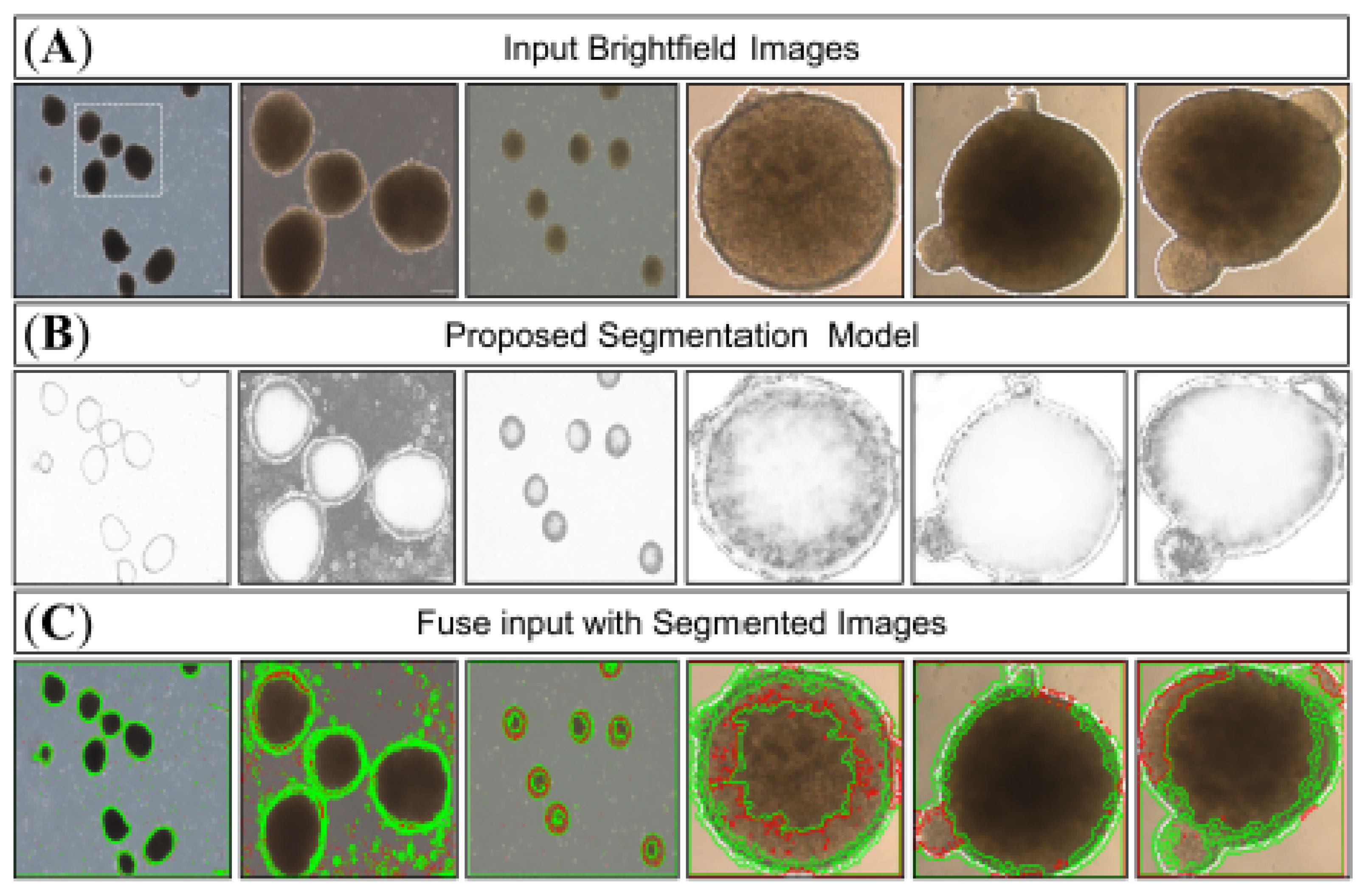
3.2. Model Testing
3.3. Comparative Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaker, M.R.; Kahtan, A.; Prasad, R.; Lee, J.-H.; Pietrogrande, G.; Leeson, H.C.; Sun, W.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Slonchak, A. Neural Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Like Protein 2 Is Expressed in Human Oligodendroglial Cell Types. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 803061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, M.R.; Aguado, J.; Chaggar, H.K.; Wolvetang, E.J. Klotho inhibits neuronal senescence in human brain organoids. npj Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, M.R.; Slonchak, A.; Al-mhanawi, B.; Morrison, S.D.; Sng, J.D.J.; Cooper-White, J.; Khromykh, A.A.; Wolvetang, E.J. Choroid plexus defects in Down syndrome brain organoids enhance neurotropism of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shin, H.; Shaker, M.R.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, N.; Kang, M.; Cho, S.; Kwak, T.H.; et al. Production of human spinal-cord organoids recapitulating neural-tube morphogenesis. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shaker, M.R.; Park, S.-H.; Sun, W. Transcriptional Signature of Valproic Acid-Induced Neural Tube Defects in Human Spinal Cord Organoids. Int. J. Stem Cells 2023, 16, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mhanawi, B.; Marti, M.B.; Morrison, S.D.; Gupta, P.; Alani, M.; Noakes, P.G.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Shaker, M.R. Protocol for generating embedding-free brain organoids enriched with oligodendrocytes. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M.R.; Hunter, Z.L.; Wolvetang, E.J. Robust and Highly Reproducible Generation of Cortical Brain Organoids for Modelling Brain Neuronal Senescence In Vitro. JoVE 2022, 183, e63714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H. Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids. Cell 2016, 165, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Guo, N.; Li, Q. Deep Learning-Based Image Segmentation on Multimodal Medical Imaging. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2019, 3, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, H.; Bhupendra, S. Segmentation of Microscopic Images: A Survey. Conference. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Systems, Signal Processing and Computing Technologies, Nagpur, India, 9–11 January 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L. Discriminative low-rank preserving projection for dimensionality reduction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 85, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ding, H.; Liu, C. Segmentation of cell images based on improved deep learning approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 110189–110202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, F.; Cisneros, M.T.; Cervantes, J.; Martinez, J.; Debeir, O. Detection of biological cells in phase-contrast microscopy images. In Proceedings of the Fifth Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligent MICAI, Mexico City, Mexico, 13–17 November 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lai, Z.; Ou, W.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, R. Structured optimal graph based sparse feature extraction for semi-supervised learning. Signal Process. 2020, 170, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havaei, M.; Davy, A.; Warde-Farley, D.; Biard, A.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.; Pal, C.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Larochelle, H. Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Bartlett, J.; Zhang, T.; Lu, W.; Qiu, Z.; Duan, J. U-net vs. transformer: Is u-net outdated in medical image registration? In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. Ce-net: Context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wu, P.; Jiang, M.; Huang, Q.; Hoeppner, D.J.; Metaxas, D.N. Attentive neural cell instance segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 55, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, D.R.; Yong, W.X.; Yapeter, J.; Subburaj, K.; Chandramohanadas, R. A deep learning approach to the screening of malaria infection: Automated and rapid cell counting, object detection and instance segmentation using Mask R-CNN. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 88, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumevska, B.; Bosman, A.; McKernan, R.; Schmidt, U.; Peura, T. Derivation of human embryonic stem cell line Genea022. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 16, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hunter, Z.L.; Leeson, H.C.; Shaker, M.R.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Vadlamudi, L. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell lines from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of three drug resistant and three drug responsive epilepsy patients. Stem Cell Res. 2021, 56, 102564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Revah, O.; Yoon, S.-J.; Narazaki, G.; Pașca, S.P. Engineering brain assembloids to interrogate human neural circuits. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarap, A.F. Deep learning using rectified linear units (relu). arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08375. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelbode, T.; Bertels, J.; Berman, M.; Vandermeulen, D.; Maes, F.; Bisschops, R.; Blaschko, M.B. Optimization for medical image segmentation: Theory and practice when evaluating with dice score or jaccard index. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vania, M.; Mureja, D.; Lee, D. Automatic spine segmentation from CT images using convolutional neural network via redundant generation of class labels. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2019, 6, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, R.M.; Saeedi, P.; Au, J.; Havelock, J. Trophectoderm segmentation in human embryo images via inceptioned U-Net. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 62, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asvadi, A.; Karami, M.; Baleghi, Y. Efficient object tracking using optimized K-means segmentation and radial basis function neural networks. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol 2011, 4, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Altulea, A.H.; Jalab, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.W. Fractional Hölder mean-based image segmentation for mouse behavior analysis in conditional place preference test. Signal Image Video Process. 2020, 14, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arxiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Kim, T.K.; Han, Y.D.; Kim, K.-A.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.S. Development of a deep learning based image processing tool for enhanced organoid analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Luan, Z.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, G. RDAU-Net: Based on a Residual Convolutional Neural Network with DFP and CBAM for Brain Tumor Segmentation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 805263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.M.; Schuster, B.; Kashaf, S.S.; Liu, P.; Ben-Yishay, R.; Ishay-Ronen, D.; Izumchenko, E.; Shen, L.; Weber, C.R.; Bielski, M.; et al. OrganoID: A versatile deep learning platform for tracking and analysis of single-organoid dynamics. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



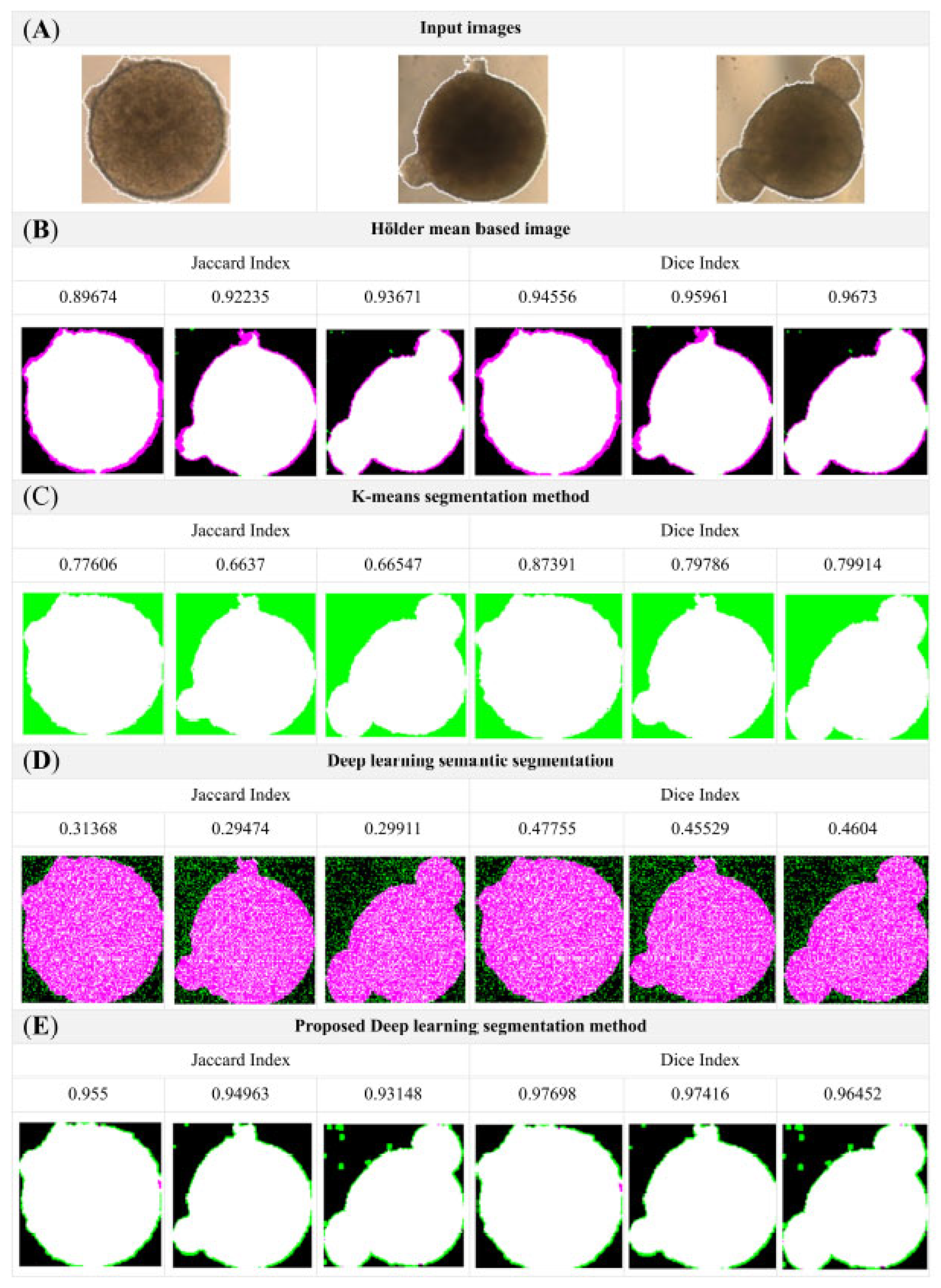
| Methods | Accuracy | Dice Similarity Coefficient | Jaccard Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hölder mean-based image [23] | 0.9198 ± 0.001 | 0.9456 ± 0.001 | 0.8967 ± 0.002 |
| K-means segmentation method [24] | 0.776 ± 0.002 | 0.8739 ± 0.002 | 0.7761 ± 0.0011 |
| Deep-learning semantic segmentation [25] | 0.9198 ± 0.002 | 0.4776 ± 0.003 | 0.4137 ± 0.002 |
| Proposal Model | 0.9815 ± 0.007 * | 0.9718 ± 0.007 * | 0.94537 ± 0.012 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alani, M.; Jalab, H.A.; Pars, S.; Al-mhanawi, B.; Taha, R.Z.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Shaker, M.R. Enhanced U-Net-Based Deep Learning Model for Automated Segmentation of Organoid Images. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111216
Alani M, Jalab HA, Pars S, Al-mhanawi B, Taha RZ, Wolvetang EJ, Shaker MR. Enhanced U-Net-Based Deep Learning Model for Automated Segmentation of Organoid Images. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111216
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlani, Maath, Hamid A. Jalab, Selin Pars, Bahaa Al-mhanawi, Rowaida Z. Taha, Ernst J. Wolvetang, and Mohammed R. Shaker. 2025. "Enhanced U-Net-Based Deep Learning Model for Automated Segmentation of Organoid Images" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111216
APA StyleAlani, M., Jalab, H. A., Pars, S., Al-mhanawi, B., Taha, R. Z., Wolvetang, E. J., & Shaker, M. R. (2025). Enhanced U-Net-Based Deep Learning Model for Automated Segmentation of Organoid Images. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111216










