Innovative Compact Vibrational System with Custom GUI for Modulating Trunk Proprioception Using Individualized Vibration Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
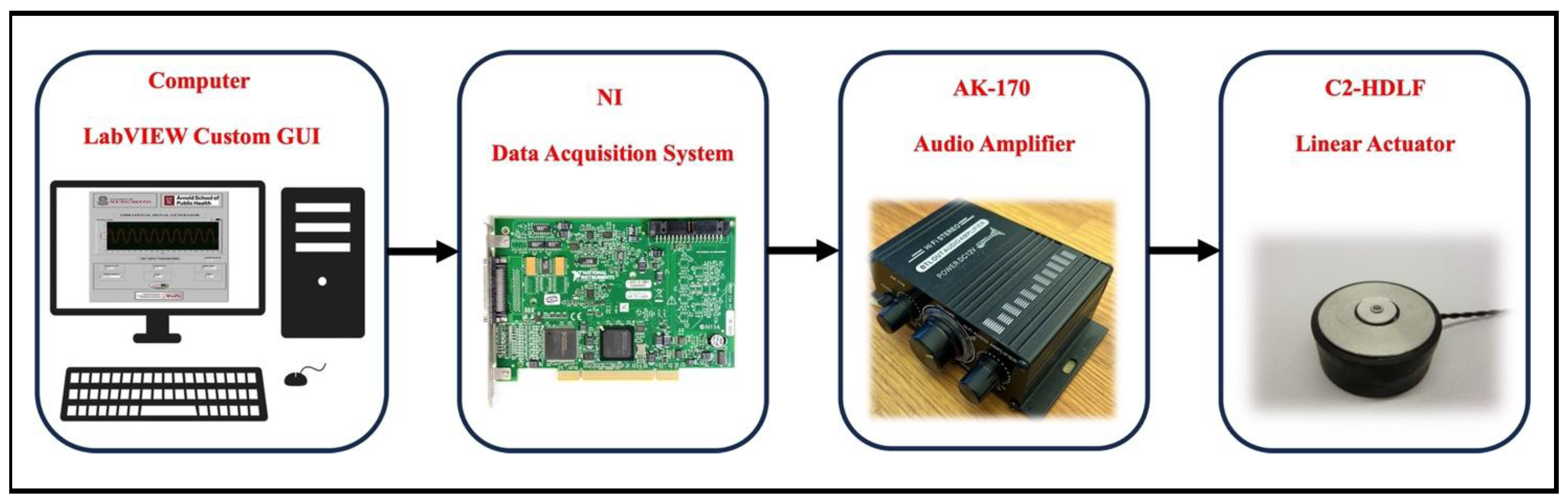
2. Materials and Methods
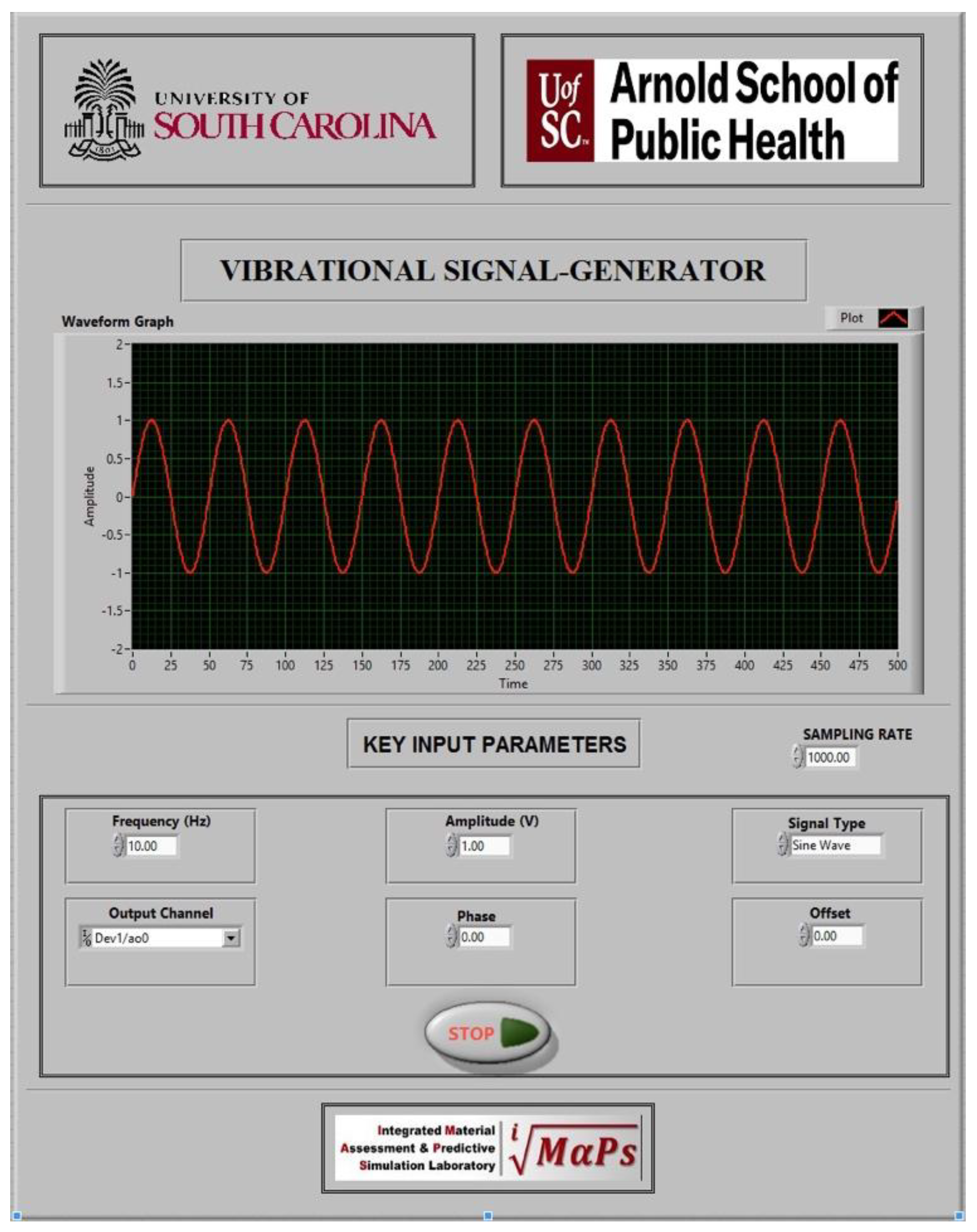
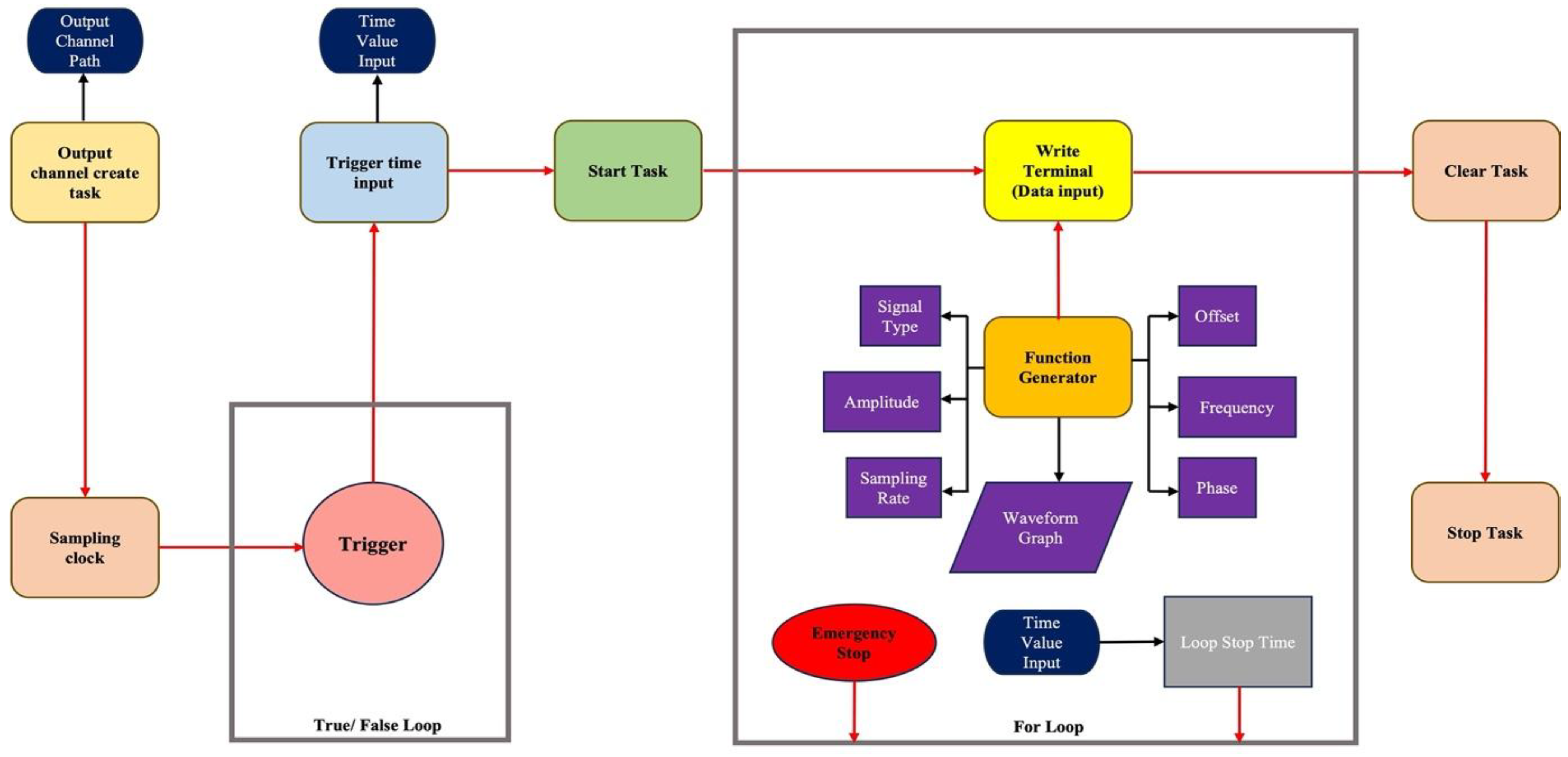
2.1. Custom LabVIEW Graphical User Interface (GUI)
2.2. NI Data Acquisition System
2.3. Signal Amplifier
2.4. Linear Actuators
3. Experimental Test Capabilities
3.1. Linear Experimental Setup for Inducing Proprioceptive Alteration in the Lumbopelvic Region
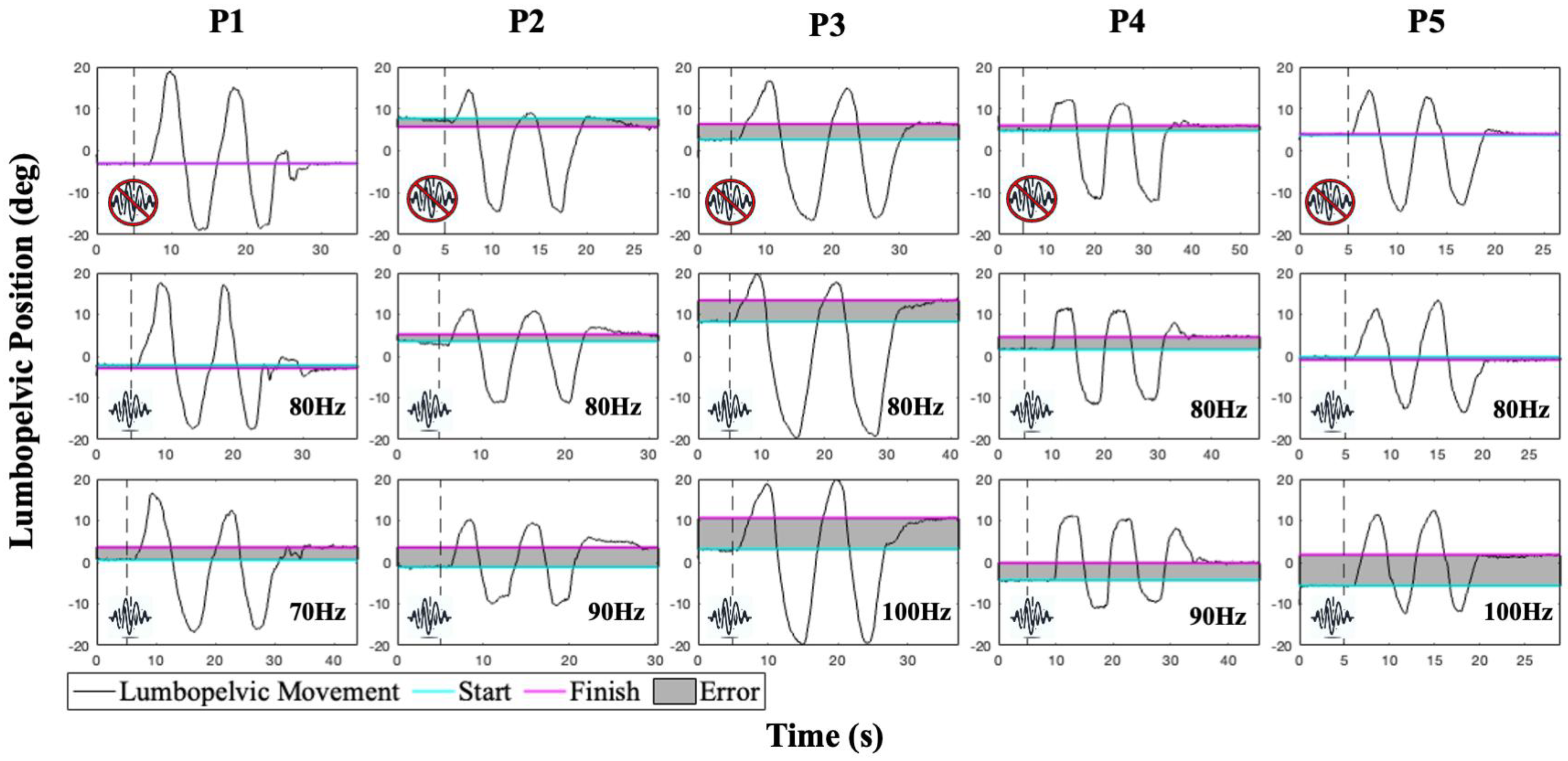
3.2. Linear Active Joint Reposition Error Testing Paradigm
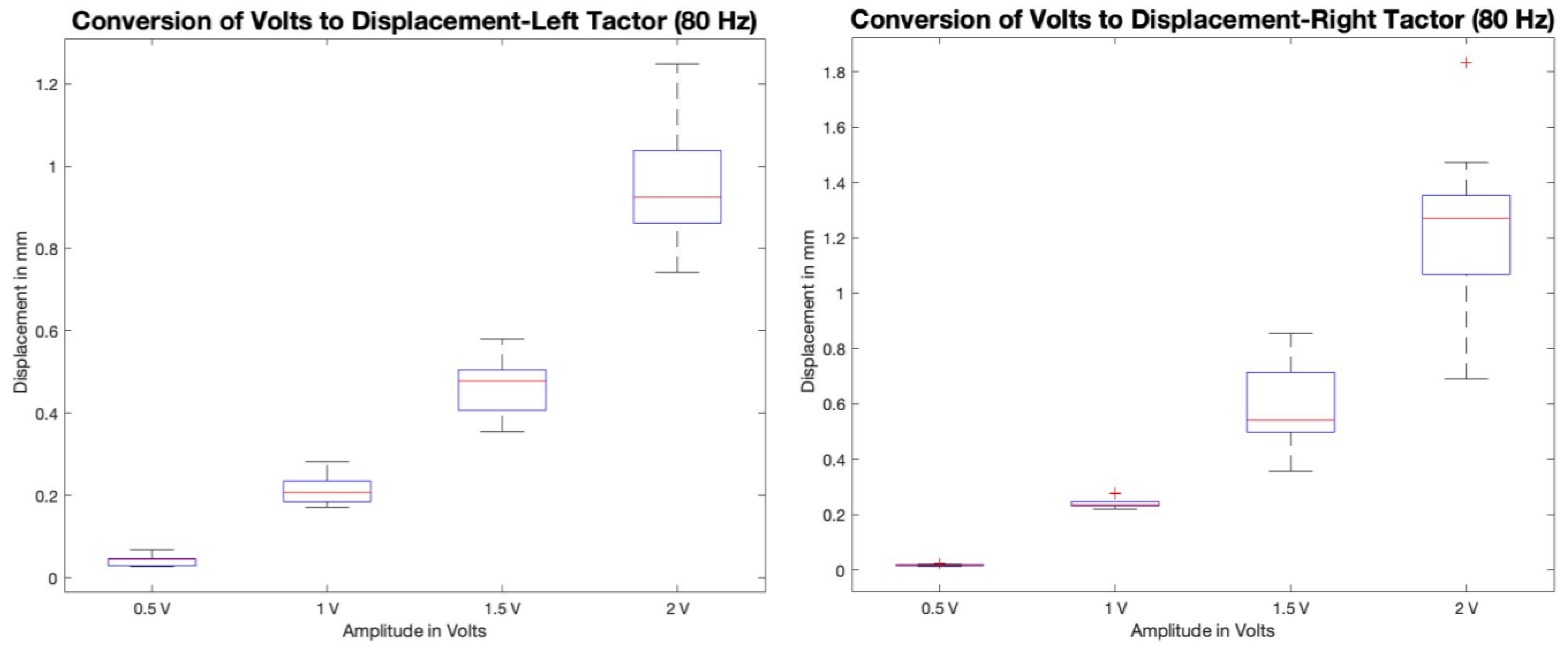
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proske, U. Kinesthesia: The role of muscle receptors. Muscle Nerve 2006, 34, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S.C. The proprioceptive senses: Their roles in signaling body shape, body position and movement, and muscle force. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1651–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S.C. Kinesthetic Senses. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1157–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerulli, G.; Benoit, D.L.; Caraffa, A.; Ponteggia, F. Proprioceptive training and prevention of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in soccer. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2001, 31, 655–660, discussion 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargo, L.; Robinson, K.J.; Games, K.E. Prevention of Knee and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries Through the Use of Neuromuscular and Proprioceptive Training: An Evidence-Based Review. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 1171–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K. Comparison of maximum strength, proprioceptive, dynamic balance, maximum joint angle between two groups classified through the ankle instability instrument. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2022, 34, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Sun, W. Effects of fatigue on balance and ankle proprioception during drop landing among individuals with and without chronic ankle instability. J. Biomech. 2023, 146, 111431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relph, N.; Herrington, L.; Tyson, S. The effects of ACL injury on knee proprioception: A meta-analysis. Physiotherapy 2014, 100, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumagne, S.; Cordo, P.; Lysens, R.; Verschueren, S.; Swinnen, S. The role of paraspinal muscle spindles in lumbosacral position sense in individuals with and without low back pain. Spine 2000, 25, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumagne, S.; Cordo, P.; Verschueren, S. Proprioceptive weighting changes in persons with low back pain and elderly persons during upright standing. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 366, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumagne, S.; Lysens, R.; Spaepen, A. Lumbosacral repositioning accuracy in standing posture: A combined electrogoniometric and videographic evaluation. Clin. Biomech. 1999, 14, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.H.; Mousavi, S.J.; Kiers, H.; Ferreira, P.; Refshauge, K.; van Dieën, J. Is There a Relationship Between Lumbar Proprioception and Low Back Pain? A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 120–136.e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielska, I.A.; Wang, X.; Lee, R.; Johnson, A.P. The health economics of ankle and foot sprains and fractures: A systematic review of English-language published papers. Part 1: Overview and critical appraisal. Foot 2019, 39, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieleman, J.L.; Cao, J.; Chapin, A.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, A.; Horst, C.; Kaldjian, A.; Matyasz, T.; Scott, K.W.; et al. US Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996–2016. JAMA 2020, 323, 863–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, M.M.; Marshall, S.W.; Lund, J.L.; Pate, V.; Spang, J.T. Cost of Outpatient Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Among Commercially Insured Patients in the United States, 2005–2013. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2017, 5, 2325967116684776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; March, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Blyth, F.M.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R.; Hoy, D. Global low back pain prevalence and years lived with disability from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, D.J.; Kyberd, P.J.; Fergusson, C.M.; Dodd, C.A. Proprioception after rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. An objective indication of the need for surgery? J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1993, 75, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amonoo-Kuofi, H.S. The density of muscle spindles in the medial, intermediate and lateral columns of human intrinsic postvertebral muscles. J. Anat. 1983, 136, 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, D.; Buxton, D.F.; Nitz, A. A comparison of spindle concentrations in large and small muscles acting in parallel combinations. J. Morphol. 1984, 180, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Ordaz, A.; Zlomislic, V.; Allen, R.T.; Garfin, S.R.; Schuepbach, R.; Farshad, M.; Schenk, S.; Ward, S.R.; Shahidi, B. Paraspinal Muscle Health is Related to Fibrogenic, Adipogenic, and Myogenic Gene Expression in Patients with Lumbar Spine Pathology. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.D.; Woodham, M.A.; Woodham, A.W. The role of the lumbar multifidus in chronic low back pain: A review. PM&R 2010, 2, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, P.; Holm, A.K.; Hansson, T.; Holm, S. Rapid atrophy of the lumbar multifidus follows experimental disc or nerve root injury. Spine 2006, 31, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhoseinpoor, T.; Taghipour, M.; Dadgoo, M.; Sanjari, M.A.; Takamjani, I.E.; Kazemnejad, A.; Khoshamooz, Y.; Hides, J. Alteration of lumbar muscle morphology and composition in relation to low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2022, 22, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yan, B.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cao, P. Correlation between the fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscles and disc degeneration and the underlying mechanism. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvin-Figuière, S.; Romaiguère, P.; Roll, J.P. Relations between the directions of vibration-induced kinesthetic illusions and the pattern of activation of antagonist muscles. Brain Res. 2000, 881, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilhodes, J.C.; Roll, J.P.; Tardy-Gervet, M.F. Perceptual and motor effects of agonist-antagonist muscle vibration in man. Exp. Brain Res. 1986, 61, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, J.P.; Vedel, J.P. Kinaesthetic role of muscle afferents in man, studied by tendon vibration and microneurography. Exp. Brain Res. 1982, 47, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, J.P.; Vedel, J.P.; Ribot, E. Alteration of proprioceptive messages induced by tendon vibration in man: A microneurographic study. Exp. Brain Res. 1989, 76, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romaiguère, P.; Anton, J.L.; Roth, M.; Casini, L.; Roll, J.P. Motor and parietal cortical areas both underlie kinaesthesia. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 2003, 16, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, M.M.; Gilhodes, J.C.; Roll, J.P. Vibration-induced postural posteffects. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.F.; Prochazka, A. Movement illusions evoked by ensemble cutaneous input from the dorsum of the human hand. J. Physiol. 1996, 496 Pt 3, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.F.; Refshauge, K.M.; Todd, G.; Gandevia, S.C. Cutaneous receptors contribute to kinesthesia at the index finger, elbow, and knee. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, G. On muscle vibration in man; an amplitude-dependent inhibition, inversely related to muscle length. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1971, 83, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, G.; Hagbarth, K.E.; Torebjörk, E. Exteroceptive vibration-induced finger flexion reflex in man. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1978, 41, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, M.A.; Bouchard, E.; Lauzier, L.; Mecheri, H.; Bégin, W.; Lavallière, M.; Massé-Alarie, H.; da Silva, R.A.; Beaulieu, L.D. Distinctive phases and variability of vibration-induced postural reactions highlighted by center of pressure analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, J.R.; Levine, M.S. Changes in apparent body orientation and sensory localization induced by vibration of postural muscles: Vibratory myesthetic illusions. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1979, 50, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goossens, N.; Janssens, L.; Caeyenberghs, K.; Albouy, G.; Brumagne, S. Differences in brain processing of proprioception related to postural control in patients with recurrent non-specific low back pain and healthy controls. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.A.; Abboud, J.; Nougarou, F.; Normand, M.C.; Descarreaux, M. The Effects of Vibration and Muscle Fatigue on Trunk Sensorimotor Control in Low Back Pain Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumagne, S.; Lysens, R.; Swinnen, S.; Verschueren, S. Effect of paraspinal muscle vibration on position sense of the lumbosacral spine. Spine 1999, 24, 1328–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiers, H.; Brumagne, S.; van Dieën, J.; Vanhees, L. Test-retest reliability of muscle vibration effects on postural sway. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willigenburg, N.W.; Kingma, I.; Hoozemans, M.J.; van Dieen, J.H. Precision control of trunk movement in low back pain patients. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2013, 32, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin-Figuière, S.; Romaiguère, P.; Gilhodes, J.C.; Roll, J.P. Antagonist motor responses correlate with kinesthetic illusions induced by tendon vibration. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 124, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willigenburg, N.W.; Kingma, I.; van Dieën, J.H. Center of pressure trajectories, trunk kinematics and trunk muscle activation during unstable sitting in low back pain patients. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Taylor, J.L.; Seizova-Cajic, T. Muscle Vibration-Induced Illusions: Review of Contributing Factors, Taxonomy of Illusions and User’s Guide. Multisens. Res. 2017, 30, 25–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Clemente, F.; Cipriani, C. The preload force affects the perception threshold of muscle vibration-induced movement illusions. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidoni, E.; Fusco, G.; Leonardis, D.; Frisoli, A.; Bergamasco, M.; Aglioti, S.M. Illusory movements induced by tendon vibration in right- and left-handed people. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumagne, S.; Lysens, R.; Spaepen, A. Lumbosacral position sense during pelvic tilting in men and women without low back pain: Test development and reliability assessment. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1999, 29, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokouhyan, S.M.; Davoudi, M.; Hoviattalab, M.; Abedi, M.; Bervis, S.; Parnianpour, M.; Brumagne, S.; Khalaf, K. Linear and Non-linear Dynamic Methods Toward Investigating Proprioception Impairment in Non-specific Low Back Pain Patients. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 584952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.A.; Normand, M.C.; Descarreaux, M. Trunk isometric force production parameters during erector spinae muscle vibration at different frequencies. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliam, J.R.; Mandal, D.; Wattananon, P.; Banerjee, S.; Herter, T.M.; Silfies, S.P. Vibration-Induced Alteration in Trunk Extensor Muscle Proprioception as a Model for Impaired Trunk Control in Low Back Pain. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Participant Demographics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | |
| Age (years) | 26 | 23 | 22 | 33 | 31 |
| Sex | F | M | F | M | F |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.9 | 25.6 | 19.0 | 23.6 | 23.6 |
| AROM (degrees) | 28.4 (0.8) | 27.2 (0.2) | 33.8 (2.1) | 47.5 (0.3) | 42.5 (1.4) |
| Mean (SD) Absolute Error with AJRE Testing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | |
| Baseline | 1.0 (1.1) | 1.9 (1.0) | 4.4 (0.6) | 1.1 (0.8) | 1.5 (1.1) |
| 70 Hz | 2.2 (0.7) | 3.8 (4.5) | 7.2 (3.1) | 1.2 (1.5) | 1.8 (0.9) |
| 80 Hz | 1.6 (1.9) | 2.0 (1.8) | 6.0 (3.9) | 1.3 (0.9) | 1.5 (0.6) |
| 90 Hz | 1.7 (1.3) | 4.9 (2.1) | 6.4 (6.0) | 3.0 (2.5) | 1.7 (0.7) |
| 100 Hz | 1.2 (2.0) | 1.2 (1.2) | 8.6 (3.2) | 2.7 (1.7) | 2.4 (0.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandal, D.; Gilliam, J.R.; Silfies, S.P.; Banerjee, S. Innovative Compact Vibrational System with Custom GUI for Modulating Trunk Proprioception Using Individualized Vibration Parameters. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101088
Mandal D, Gilliam JR, Silfies SP, Banerjee S. Innovative Compact Vibrational System with Custom GUI for Modulating Trunk Proprioception Using Individualized Vibration Parameters. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101088
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandal, Debdyuti, John R. Gilliam, Sheri P. Silfies, and Sourav Banerjee. 2025. "Innovative Compact Vibrational System with Custom GUI for Modulating Trunk Proprioception Using Individualized Vibration Parameters" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101088
APA StyleMandal, D., Gilliam, J. R., Silfies, S. P., & Banerjee, S. (2025). Innovative Compact Vibrational System with Custom GUI for Modulating Trunk Proprioception Using Individualized Vibration Parameters. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101088








