Measuring the Impact of Large Language Models on Academic Success and Quality of Life Among Students with Visual Disability: An Assistive Technology Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Large Language Models and Accessibility in Education
2.2. Trust in AI and Assistive Technologies
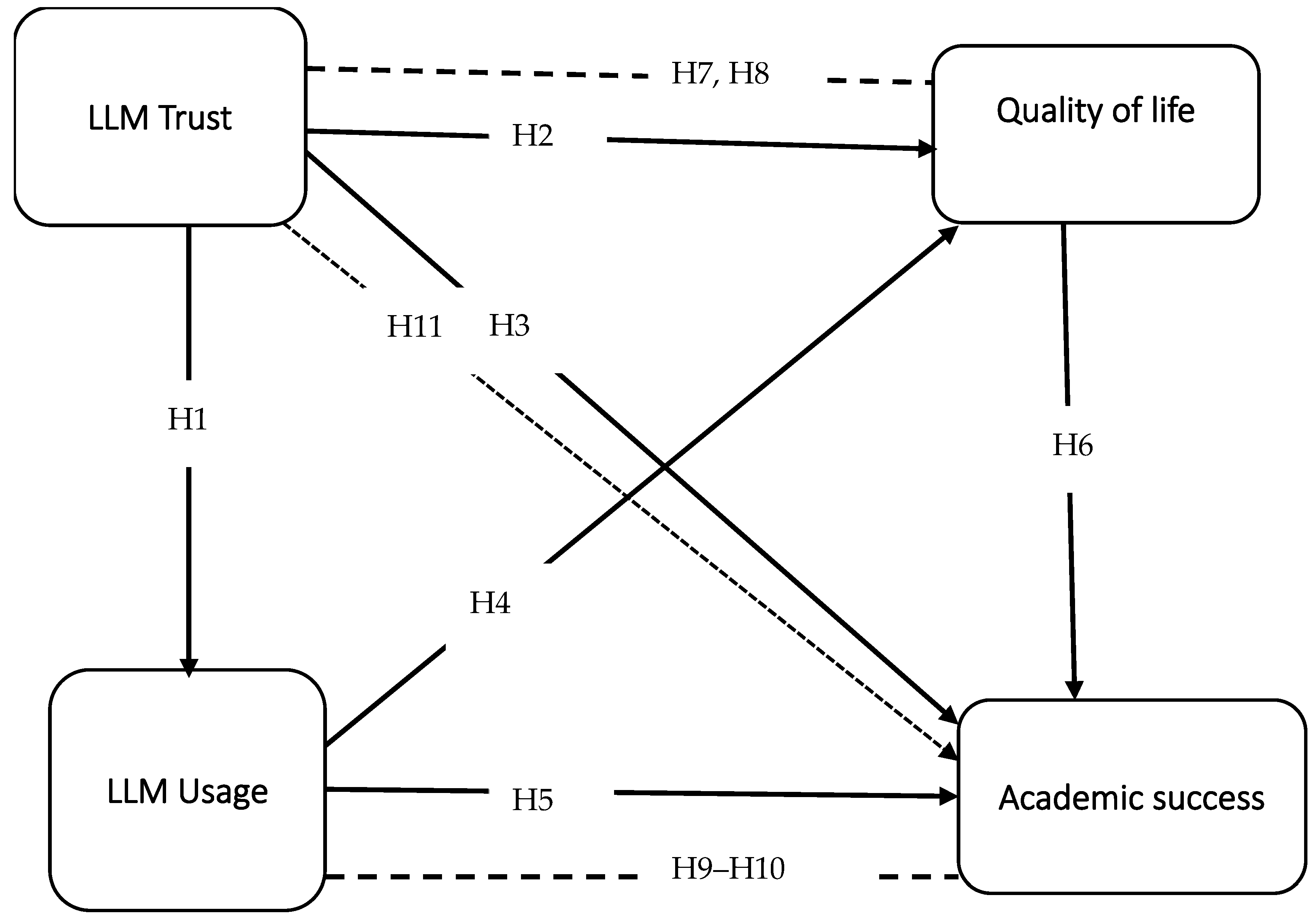
- H1: Trust in LLMs positively predicts LLMs usage.
- H2: Trust in LLMs positively predicts quality of life.
- H3: Trust in LLMs positively predicts academic success.
2.3. Academic Success and Quality of Life with LLM-Supported Learning
- H4: LLM usage positively predicts quality of life.
- H5: LLM usage positively predicts academic success.
- H6: Quality of life positively predicts academic success.
- H7: Trust in LLMs indirectly predicts academic success via quality of life.
- H8: Trust in LLMs indirectly predicts quality of life via LLM usage.
- H9 Trust in LLMs indirectly predicts academic success via quality of life.
- H10 Trust in LLMs indirectly predicts academic success via LLM usage.
- H11 Trust in LLMs indirectly predicts academic success via LLM usage and quality of life.
3. Methods
3.1. The Study Developed Scale
3.2. Population and Sample Size
3.3. Testing Common Method Variance (CMV)
3.4. Ethical Approvals
4. Data Analysis and Study Findings
4.1. Measurement Model Assessment
4.2. Structural Model Findings
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitas, R.J. Inclusive Education with AI: Supporting Special Needs and Tackling Language Barriers. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paice, A.; Biallas, M.; Andrushevich, A. Assistive and Inclusive Technology Design for People with Disabilities (Special Needs). In Human-Technology Interaction: Interdisciplinary Approaches and Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 329–347. [Google Scholar]
- Giansanti, D.; Pirrera, A. Integrating AI and Assistive Technologies in Healthcare: Insights from a Narrative Review of Reviews. Healthcare 2025, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S. Digital Horizons in Special Education: Pioneering Transformational Technologies for Individuals with Visual Impairments. In Educating for Societal Transitions; Blue Rose Publishers: Noida, India, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.K.S. A Review of Utilizing Natural Language Processing and AI For Advanced Data Visualization in Real-Time Analytics. Glob. Manag. J. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, A.J. Intelligent Systems For Disabilities Technology For A More Inclusive Life; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, C.; Mohler, E.; Mcfarland, J.; Hand, C.; Rudman, D.L.; Fitzgeorge, B.; Stone, M. Research Practices to Foster Accessibility for, and the Inclusivity of, Older Adults With Vision Loss: Examples From a Critical Participatory Study. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2025, 24, 16094069251316214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.C.; Chang, C.I.; Choi, I.C.; Lam, L.C. Country Landscape of Large Language Models Development: A Review. Preprints 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gupta, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Liu, C.H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Verdoliva, L.; Hu, S. Detecting Multimedia Generated by Large AI Models: A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A Comprehensive Review on Background, Applications, Key Challenges, Bias, Ethics, Limitations and Future Scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Saini, A.; Barad, H. Artificial Intelligence in Governance: Recent Trends, Risks, Challenges, Innovative Frameworks and Future Directions. In AI & SOCIETY; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Weygand, Z. The Blind in French Society from the Middle Ages to the Century of Louis Braille; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, B. The Blind Advantage: How Going Blind Made Me a Stronger Principal and How Including Children with Disabilities Made Our School Better for Everyone; Harvard Education Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- French, K. Perkins School for the Blind; Arcadia Publishing: Mount Pleasant, SC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Trent, J.W. The Manliest Man: Samuel G. Howe and the Contours of Nineteenth-Century American Reform; University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, M.D.; Feng, X.; Dyo, V. Revolutionising Higher Education: Unleashing the Potential of Large Language Models for Strategic Transformation. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 67738–67757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, M. Developing AI Applications With Large Language Models; Maria Johnsen: Trondheim, Norway, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Nagar, D.K. AI-Based Language Translation and Interpretation Services: Improving Accessibility for Visually Impaired Students. In Transforming Learning: The Power of Educational Technology; BlueRose Publisher: Noida, India, 2024; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhaie Ahooie, N. Enhancing Access to Medical Literature Through an LLM-Based Browser Extension 2024; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, D.S. AI-Powered Adaptive Education for Disabled Learners. In Advances in Accessibility and Sustainability; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Puspitasari, F.D.; Zheng, S.; Zheng, J.; Lee, L.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Hong, C.S.; Zhang, C. Sora as an AGI World Model? A Complete Survey on Text-to-Video Generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05131. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Shokeen, R.; Raj, R. Artificial Intelligence: Solutions in Special Education. In Transforming Special Education Through Artificial Intelligence; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 459–520. [Google Scholar]
- Lata, P. Towards Equitable Learning: Exploring Artificial Intelligence in Inclusive Education. Int’l JL Mgmt. Human. 2024, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Patel, H.; Rajput, D.S.; Bansal, N. Empowering Inclusive Education: Leveraging AI-ML and Innovative Tech Stacks to Support Students with Learning Disabilities in Higher Education. In Applied Assistive Technologies and Informatics for Students with Disabilities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 255–275. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, S.; Kamran, F.; Anis, F. Beyond Accommodation: Artificial Intelligence’s Role in Reimagining Inclusive Classrooms. Int. J. Soc. Sci. 2024, 2, 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.; Bose, U.; Cross, J. BEYOND SIGHT: Transforming Visual Content into Accessible Learning Content for the Blind. In Proceedings of the EDULEARN24 Proceedings, Palma, Spain, 1–3 July 2024; IATED: Valencia, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Alqahtani, L.; Albooq, A.; Ainousah, A. A Survey on Security and Privacy of Large Multimodal Deep Learning Models: Teaching and Learning Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2024 21st Learning and Technology Conference (L&T), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 15–16 January 2024; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, H. The Impact of Hallucinated Information in Large Language Models on Student Learning Outcomes: A Critical Examination of Misinformation Risks in AI-Assisted Education. Nat. Rev. AI Res. Theor. Comput. Complex. 2024, 9, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A.; Mohanty, A. Educational Technology: Exploring the Convergence of Technology and Pedagogy through Mobility, Interactivity, AI, and Learning Tools. Comput. Educ. 2023, 10, 2283282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R. Impact. AI: Democratizing AI Through K-12 Artificial Intelligence Education; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abubaker, N.M.; Kashani, S.M.; Alshalwy, A.M.; Garib, A. Reshaping Higher Education in MENA with Generative AI: A Systematic Review. In Emerging Technologies Transforming Higher Education: Instructional Design and Student Success; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 231–256. [Google Scholar]
- Aladi, C.C. IT Higher Education Teachers and Trust in AI-Enabled Ed-Tech: Implications for Adoption of AI in Higher Education. In Proceedings of the 2024 Computers and People Research Conference, Murfreesboro, TN, USA, 29 May–1 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chellappa, R.; Niiler, E. Can We Trust AI? JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chalkiadakis, A.; Seremetaki, A.; Kanellou, A.; Kallishi, M.; Morfopoulou, A.; Moraitaki, M.; Mastrokoukou, S. Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality on Educational Inclusion: A Systematic Review of Technologies Supporting Students with Disabilities. J. Educ. 2024, 14, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.; Bali, A.; Sharma, P.; Chadha, S.; Sharma, B. Empowering Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Supporting Students with Disabilities. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Microelectronics, Automation, Computing and Communications Systems (ICMACC), Hyderabad, India, 19–21 December 2024; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, H.; Jelani, S.A.K.; Najla, S. Revolutionizing Inclusion: AI in Adaptive Learning for Students with Disabilities. Mod. Stud. J. 2022, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Paliszkiewicz, J.; Gołuchowski, J. Trust and Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Syst. 2024, 1, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Afroogh, S.; Akbari, A.; Malone, E.; Kargar, M.; Alambeigi, H. Trust in AI: Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions. J. AI Res. 2024, 11, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küper, A.; Krämer, N.J. Psychological Traits and Appropriate Reliance: Factors Shaping Trust in AI. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2025, 41, 4115–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, A.R.; Advincula, W.D. Creating Tactile Educational Materials for the Visually Impaired and Blind Students Using AI Cloud Computing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darji, H. AI-Powered Digital Platform for Religious Literature. In Advances in Accessibility and Sustainability; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Vayadande, K.; Bohri, M.; Chawala, M.; Kulkarni, A.M.; Mursal, A. The Rise of AI-Generated News Videos: A Detailed Review. In How Machine Learning is Innovating Today’s World: A Concise Technical Guide; Wiley-Scrivener: Austin, TX, USA, 2024; pp. 423–451. [Google Scholar]
- Julio, C. Evaluation of Speech Recognition, Text-to-Speech, and Generative Text Artificial Intelligence for English as Foreign Language Learning Speaking Practices. Ph.D. Thesis, Tokyo Denki University, Tokyo, Japan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Geethanjali, K.S.; Umashankar, N. Enhancing Educational Outcomes with Explainable AI: Bridging Transparency and Trust in Learning Systems. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Emerging Systems and Intelligent Computing (ESIC), Bhubaneswar, India, 8–9 February 2025; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, R. Undergraduate Educational Experiences: The Academic Success of College Students with Blindness and Visual Impairments. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kaliappan, S.; Anand, A.S.; Saha, K.; Karkar, R. Exploring the Role of LLMs for Supporting Older Adults: Opportunities and Concerns. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.08123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X. Exploring Engagement, Self-Efficacy, and Anxiety in Large Language Model EFL Learning: A Latent Profile Analysis of Chinese University Students. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2024, 41, 7815–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study; Pesudovs, K.; Lansingh, V.C.; Kempen, J.H.; Tapply, I.; Fernandes, A.G.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Arrigo, A.; Leveziel, N.; Resnikoff, S.; et al. Global Estimates on the Number of People Blind or Visually Impaired by Cataract: A Meta-Analysis from 2000 to 2020. Eye 2024, 38, 2156–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappolt-Schlichtmann, G.; Daley, S.G.; Rose, L.T. A Research Reader in Universal Design for Learning; ERIC: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, T.A.; Khan, A.; Hallock, H.; Beltrão, G.; Sousa, S. A Systematic Literature Review of User Trust in AI-Enabled Systems: An HCI Perspective. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2024, 40, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalos, A.C. Connecting the Quality of Life Theory to Health, Well-Being and Education; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bright, D.J. An Integrative Review of the Potential of Wireless Assistive Technologies and Internet of Things (IoT) to Improve Accessibility to Education for Students with Disabilities. Assist. Technol. 2022, 34, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenduri, G.; Kaluri, R.; Rajput, D.S.; Lakshmanna, K.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Mahmud, M.; Brown, D.J. From Assistive Technologies to Metaverse—Technologies in Inclusive Higher Education for Students with Specific Learning Difficulties: A Review. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 11, 64907–64927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Batanero, J.M.; Montenegro-Rueda, M.; Fernández-Cerero, J.; García-Martínez, I. Assistive Technology for the Inclusion of Students with Disabilities: A Systematic Review. Educ. Rev. 2022, 70, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrab, M.; Al-Shihi, H.; Khan, A.I. An Empirical Analysis of Mobile Learning (m-Learning) Awareness and Acceptance in Higher Education. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computing and Network Communications (CoCoNet), Anaheim, CA, USA, 16–19 February 2015; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Owusu-Acheaw, M.; Larson, A.G. Use of Social Media and Its Impact on Academic Performance of Tertiary Institution Students: A Study of Students of Koforidua Polytechnic, Ghana. J. Educ. Pract. 2015, 6, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Elshaer, I.A.; AlNajdi, S.M.; Salem, M.A. Sustainable AI Solutions for Empowering Visually Impaired Students: The Role of Assistive Technologies in Academic Success. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.A.; Moustafa, M.A.; Elrayah, M.; Elshaer, I.A. Optimizing Quality of Life of Vulnerable Students: The Impact of Physical Fitness, Self-Esteem, and Academic Performance: A Case Study of Saudi Arabia Universities. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Duro, E.S.; Veltri, G.A.; Golino, H.; Stella, M. Measuring and Identifying Factors of Individuals’ Trust in Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.21028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.; Xu, X. Consumer Acceptance and Use of Information Technology: Extending the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, E.D.; Emmons, R.A.; Larsen, R.J.; Griffin, S. The Satisfaction with Life Scale. J. Personal. Assess. 1985, 49, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KSA Census Saudi Arabia’s Fifth Housing and Population Census Is Approved to Commence on May 9, 2022 (Shawwal 8, 1443). Available online: https://www.stats.gov.sa/w/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%87%D9%8A%D8%A6%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%85%D8%A9-%D9%84%D9%84%D8%A5%D8%AD%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%A1-%D8%A8%D8%AF%D8%A1-%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%AD%D9%84%D8%A9-%D8%AA%D8%AD%D8%AF%D9%8A%D8%AB-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%88%D9%8A%D9%86-%D9%84 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.J.; Brown, B.K. Method Variance in Organizational Behavior and Human Resources Research: Effects on Correlations, Path Coefficients, and Hypothesis Testing. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1994, 57, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reio, T.G., Jr. The Threat of Common Method Variance Bias to Theory Building. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2010, 9, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Alamer, A. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) in Second Language and Education Research: Guidelines Using an Applied Example. Res. Methods Appl. Linguist. 2022, 1, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. In Handbook of Market Research; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 587–632. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. The Partial Least Squares Approach to Structural Equation Modeling. In Modern Methods for Business Research; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 1998; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Mitchell, R.; Gudergan, S.P. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling in HRM Research. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2020, 31, 1617–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, R.; Veale, M.; Van Kleek, M.; Shadbolt, N. “It’s Reducing a Human Being to a Percentage”: Perceptions of Justice in Algorithmic Decisions. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 21–26 April 2018; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdaus, M.M.; Abdelguerfi, M.; Ioup, E.; Niles, K.N.; Pathak, K.; Sloan, S. Towards Trustworthy AI: A Review of Ethical and Robust Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.13934. [Google Scholar]
- Bong, W.K.; Chen, W. Increasing Faculty’s Competence in Digital Accessibility for Inclusive Education: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2024, 28, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senjam, S.S.; Manna, S.; Bascaran, C. Smartphones-Based Assistive Technology: Accessibility Features and Apps for People with Visual Impairment, and Its Usage, Challenges, and Usability Testing. Clin. Optom. 2021, 13, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Kasneci, G.; et al. ChatGPT for Good? On Opportunities and Challenges of Large Language Models for Education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommel, J.; Sagl, V.; Depping, A.E.; Johanson, C.; Miller, M.K.; Mandryk, R.L. Recognizing Affiliation: Using Behavioural Traces to Predict the Quality of Social Interactions in Online Games. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Mittal, P.; Kumar, M.; Bhardwaj, V. The Role of Large Language Models in Personalized Learning: A Systematic Review of Educational Impact. Discov. Sustain. 2025, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Cui, S.; Khanna, K.; Knieling, V.; Duggal, Y.N.; Shao, M. Investigation of the Gender-Specific Discourse about Online Learning during COVID-19 on Twitter Using Sentiment Analysis, Subjectivity Analysis, and Toxicity Analysis. Computers 2023, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosch-Villaronga, E.; Poulsen, A.; Søraa, R.A.; Custers, B.H.M. A Little Bird Told Me Your Gender: Gender Inferences in Social Media. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FL | α | C.R. | AVE | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Language Model Trust | 0.934 | 0.935 | 0.687 | ||
| Trust_1 | 0.741 | 2.069 | |||
| Trust_2 | 0.813 | 2.472 | |||
| Trust_3 | 0.869 | 2.163 | |||
| Trust_4 | 0.864 | 2.644 | |||
| Trust_5 | 0.867 | 3.094 | |||
| Trust_6 | 0.870 | 3.076 | |||
| Trust_7 | 0.861 | 3.128 | |||
| Trust_8 | 0.732 | 1.909 | |||
| Large Language Model Usage | 0.852 | 0.858 | 0.772 | ||
| Usage_1 | 0.905 | 2.350 | |||
| Usage_2 | 0.876 | 2.115 | |||
| Usage_3 | 0.854 | 1.936 | |||
| Quality of life | 0.859 | 0.879 | 0.640 | ||
| QoL_1 | 0.861 | 2.403 | |||
| QoL_2 | 0.822 | 2.236 | |||
| QoL_3 | 0.847 | 2.217 | |||
| QoL_4 | 0.747 | 2.036 | |||
| QoL_5 | 0.710 | 1.877 | |||
| Academic success | 0.863 | 0.868 | 0.784 | ||
| Acd_Prfmnc_1 | 0.880 | 2.034 | |||
| Acd_Prfmnc_2 | 0.910 | 2.783 | |||
| Acd_Prfmnc_3 | 0.866 | 2.209 | |||
| Academic Success | LLM Trust | LLM Usage | Quality of Life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Success | 0.886 | |||
| LLM Trust | 0.725 | 0.829 | ||
| LLM Usage | 0.521 | 0.613 | 0.879 | |
| Quality of Life | 0.470 | 0.422 | 0.450 | 0.800 |
| Academic Success | LLM Trust | LLM Usage | Quality of Life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Success | ||||
| LLM Trust | 0.803 | |||
| LLM Usage | 0.602 | 0.683 | ||
| Quality of Life | 0.532 | 0.464 | 0.515 |
| Academic Success | LLM Trust | LLM Usage | Quality of Life | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acd_Prfmnc_1 | 0.880 | 0.708 | 0.494 | 0.440 |
| Acd_Prfmnc_2 | 0.910 | 0.618 | 0.426 | 0.397 |
| Acd_Prfmnc_3 | 0.866 | 0.589 | 0.458 | 0.408 |
| QoL_1 | 0.426 | 0.395 | 0.451 | 0.861 |
| QoL_2 | 0.376 | 0.311 | 0.330 | 0.822 |
| QoL_3 | 0.461 | 0.375 | 0.399 | 0.847 |
| QoL_4 | 0.265 | 0.281 | 0.324 | 0.747 |
| QoL_5 | 0.309 | 0.302 | 0.262 | 0.710 |
| Trust_1 | 0.615 | 0.741 | 0.554 | 0.329 |
| Trust_2 | 0.629 | 0.813 | 0.576 | 0.349 |
| Trust_3 | 0.548 | 0.869 | 0.549 | 0.324 |
| Trust_4 | 0.601 | 0.864 | 0.443 | 0.364 |
| Trust_5 | 0.607 | 0.867 | 0.508 | 0.409 |
| Trust_6 | 0.557 | 0.870 | 0.566 | 0.367 |
| Trust_7 | 0.605 | 0.861 | 0.481 | 0.335 |
| Trust_8 | 0.639 | 0.732 | 0.359 | 0.308 |
| Usage_1 | 0.512 | 0.572 | 0.905 | 0.423 |
| Usage_2 | 0.462 | 0.526 | 0.876 | 0.379 |
| Usage_3 | 0.391 | 0.515 | 0.854 | 0.382 |
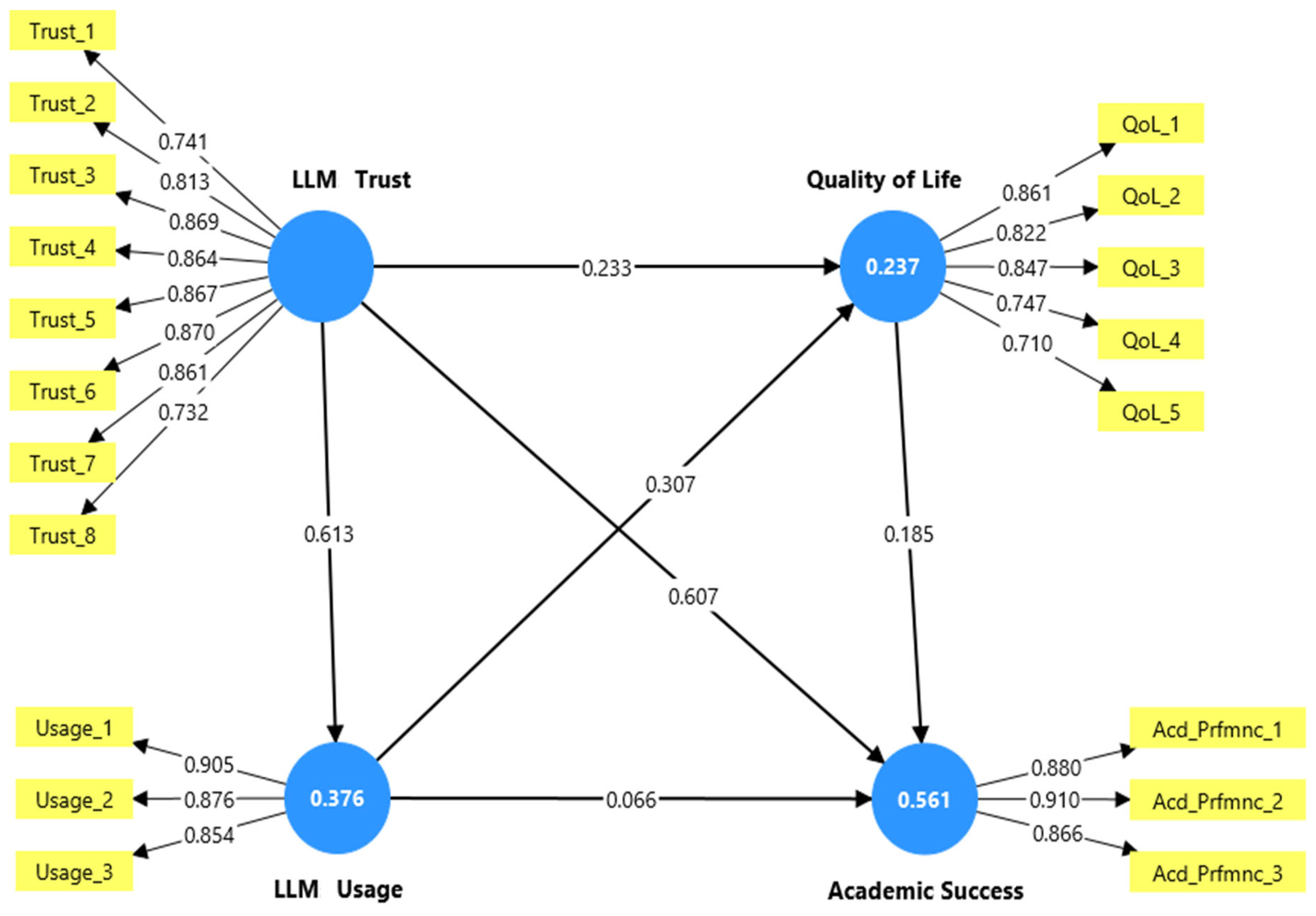
| Hypotheses | β | T | p | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLM Trust -> LLM Usage | 0.613 | 10.895 | 0.000 | H1: Supported |
| LLM Trust -> Quality of Life | 0.233 | 3.745 | 0.000 | H2: Supported |
| LLM Trust -> Academic Success | 0.607 | 14.001 | 0.000 | H3: Supported |
| LLM Usage -> Quality of Life | 0.307 | 4.893 | 0.000 | H4: Supported |
| LLM Usage -> Academic Success | 0.066 | 1.652 | 0.099 | H5: Rejected |
| Quality of Life -> Academic Success | 0.185 | 5.535 | 0.000 | H6: Supported |
| Specific indirect effects | ||||
| LLM Trust -> Quality of Life -> Academic Success | 0.043 | 2.713 | 0.007 | H7: Supported |
| LLM Trust -> LLM Usage -> Academic Success | 0.040 | 1.499 | 0.134 | H8: Rejected |
| LLM Usage -> Quality of Life -> Academic Success | 0.057 | 3.496 | 0.000 | H9: Supported |
| LLM Trust -> LLM Usage -> Quality of Life | 0.188 | 4.554 | 0.000 | H10: Supported |
| LLM Trust -> LLM Usage -> Quality of Life -> Academic Success | 0.035 | 3.392 | 0.001 | H11: Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elshaer, I.A.; AlNajdi, S.M.; Salem, M.A. Measuring the Impact of Large Language Models on Academic Success and Quality of Life Among Students with Visual Disability: An Assistive Technology Perspective. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101056
Elshaer IA, AlNajdi SM, Salem MA. Measuring the Impact of Large Language Models on Academic Success and Quality of Life Among Students with Visual Disability: An Assistive Technology Perspective. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101056
Chicago/Turabian StyleElshaer, Ibrahim A., Sameer M. AlNajdi, and Mostafa A. Salem. 2025. "Measuring the Impact of Large Language Models on Academic Success and Quality of Life Among Students with Visual Disability: An Assistive Technology Perspective" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101056
APA StyleElshaer, I. A., AlNajdi, S. M., & Salem, M. A. (2025). Measuring the Impact of Large Language Models on Academic Success and Quality of Life Among Students with Visual Disability: An Assistive Technology Perspective. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101056









