Characterization of a Novel POx-Based Adhesive Powder for Obliterating Dead Spaces After Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
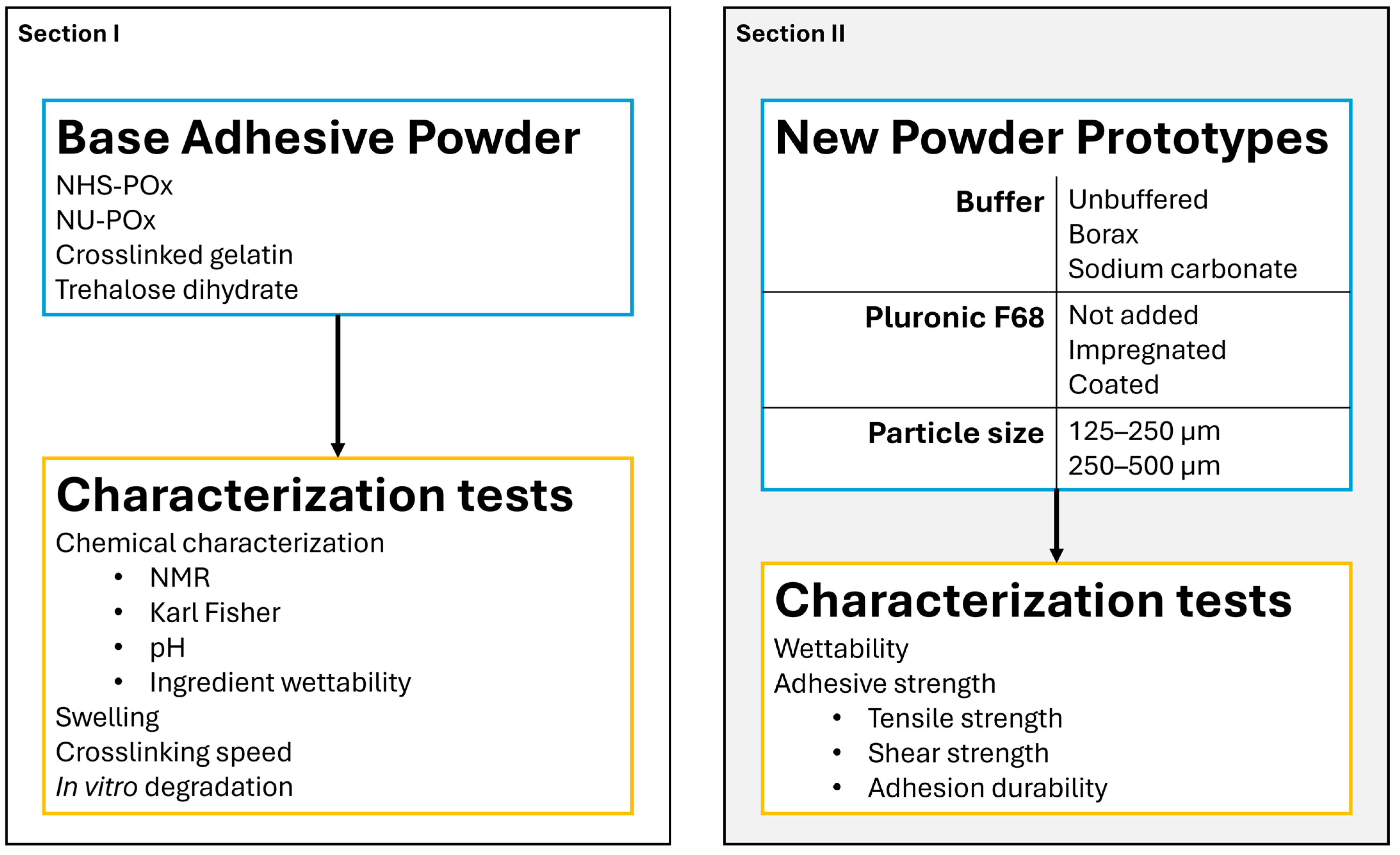
2.1. Study Outline
2.2. Materials
2.3. Preparation of Adhesive Powder
2.4. Chemical Analysis
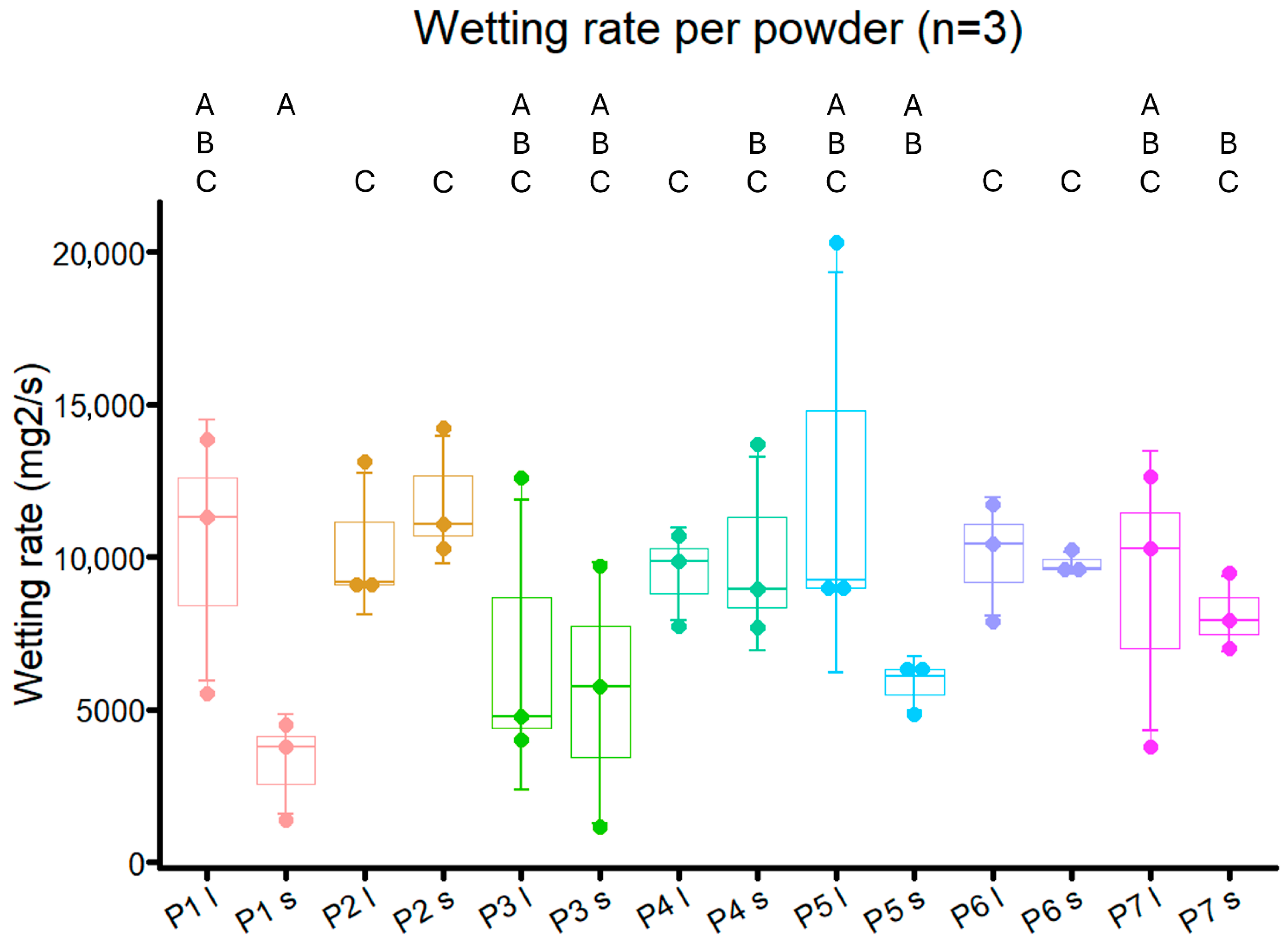
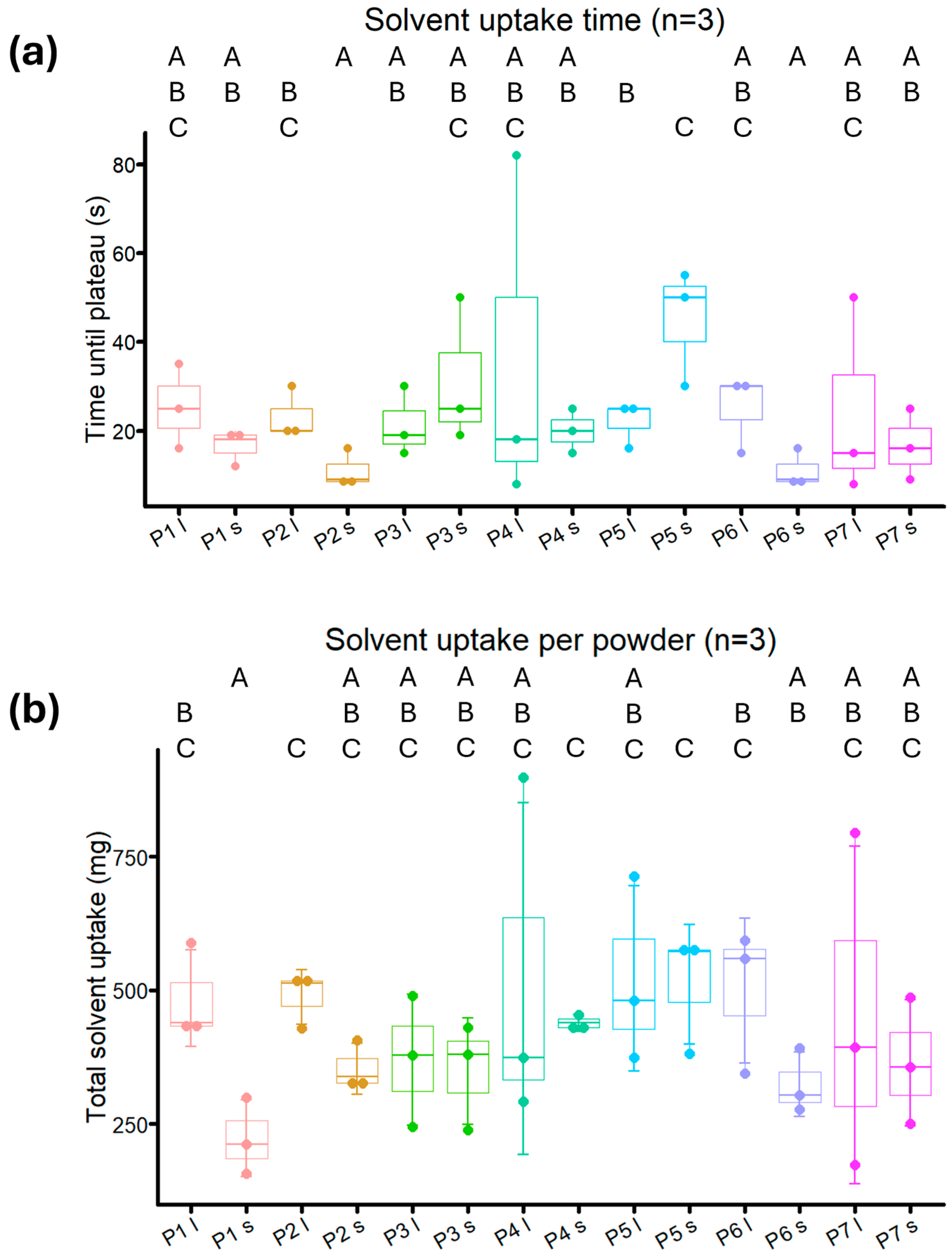
2.5. Wettability Tests
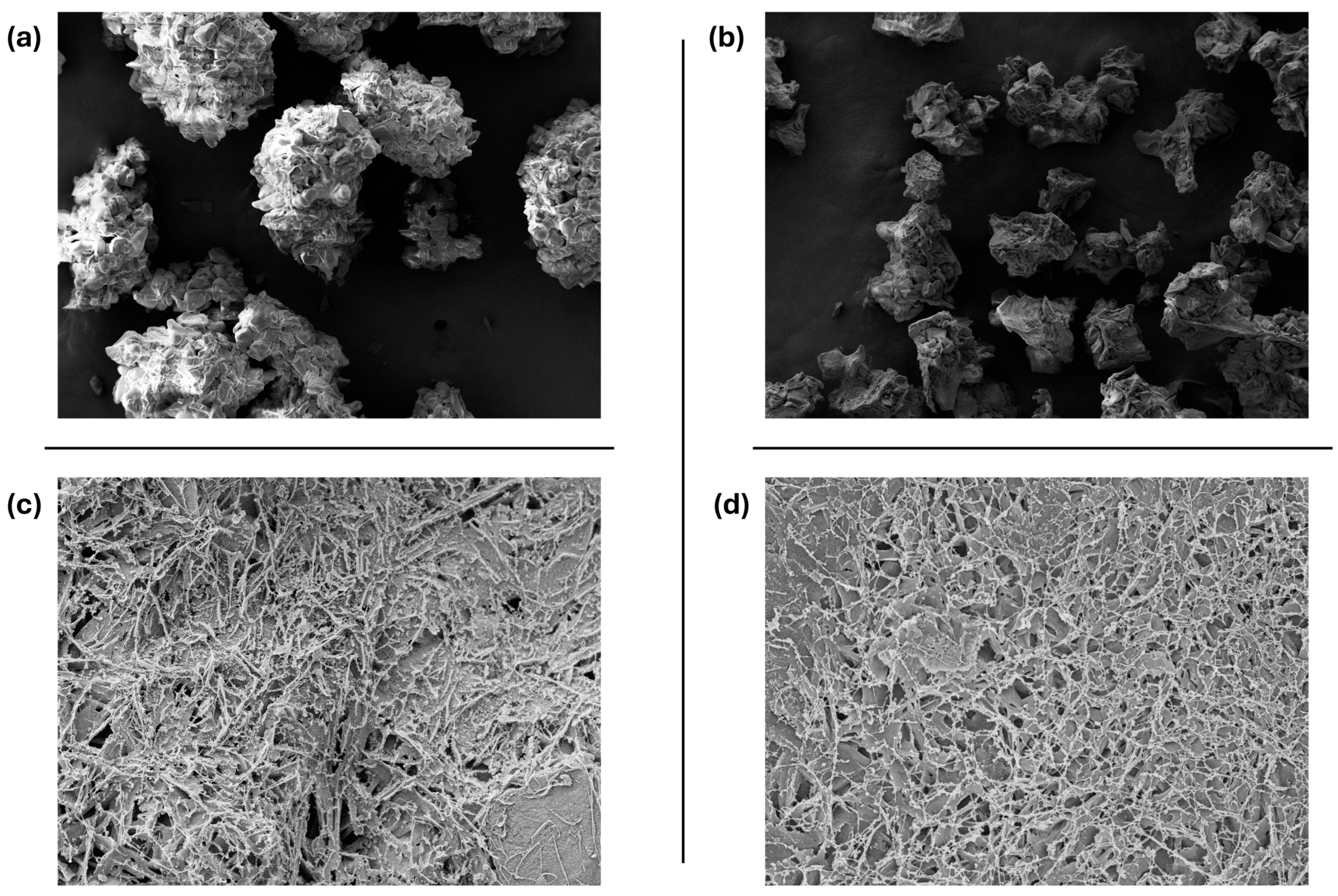
2.6. SEM Imaging
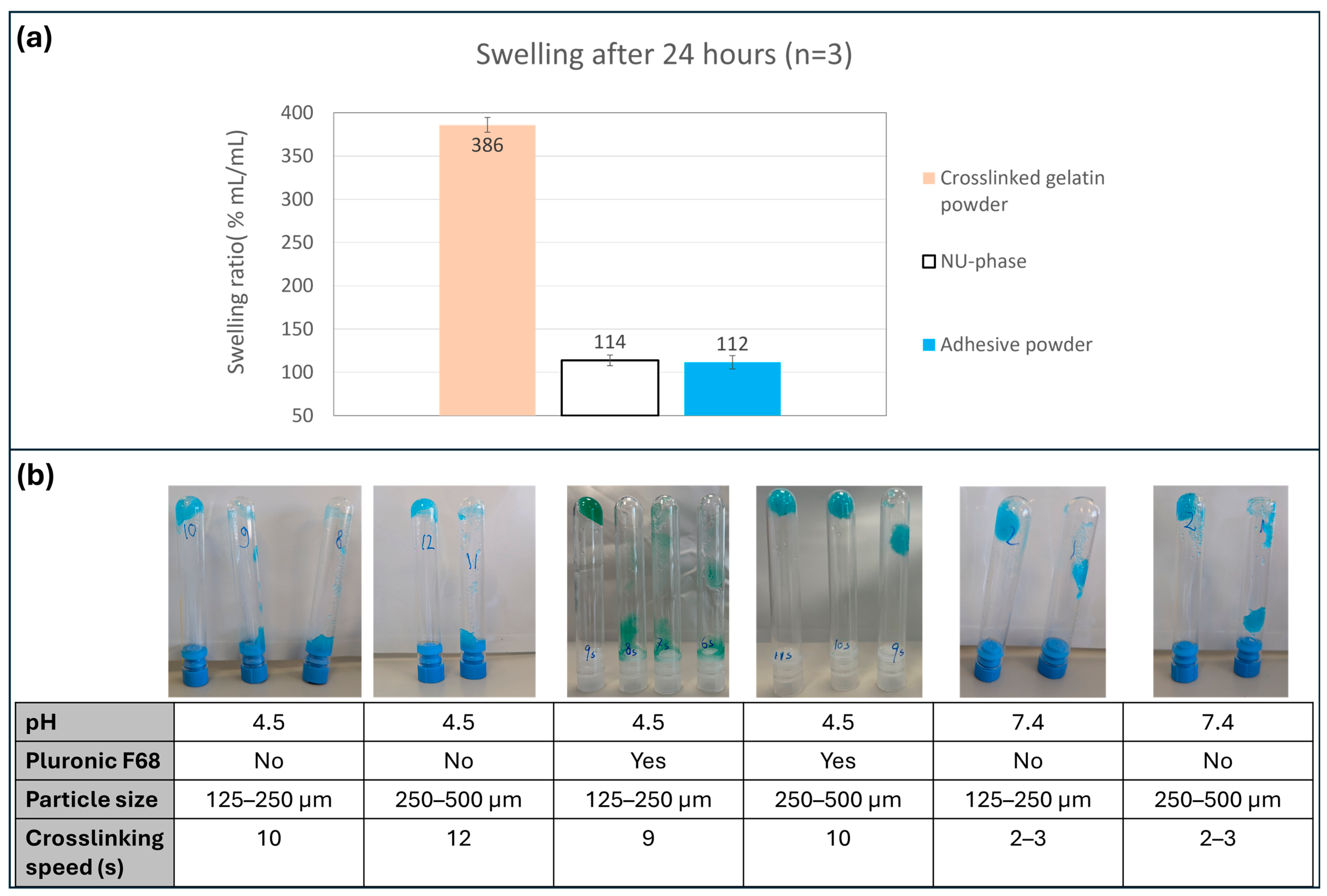
2.7. Swelling Measurement
2.8. Crosslinking Speed Measurement
2.9. In Vitro Degradation Measurements
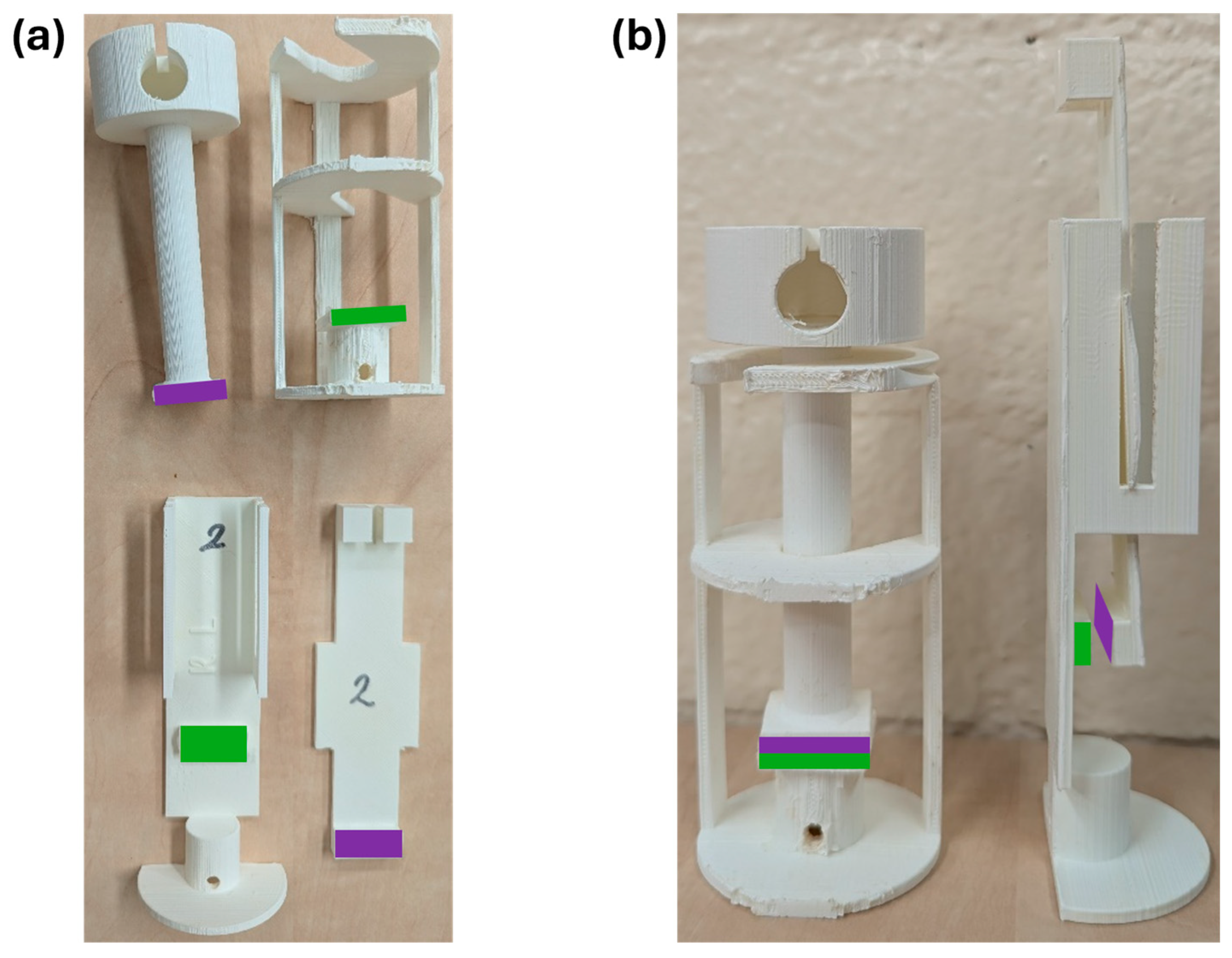
2.10. Adhesive Strength Measurements
2.10.1. Treatment and Characterization of Collagen Sheets
2.10.2. Tensile Strength
2.10.3. Shear Strength
2.10.4. Adhesion Durability
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
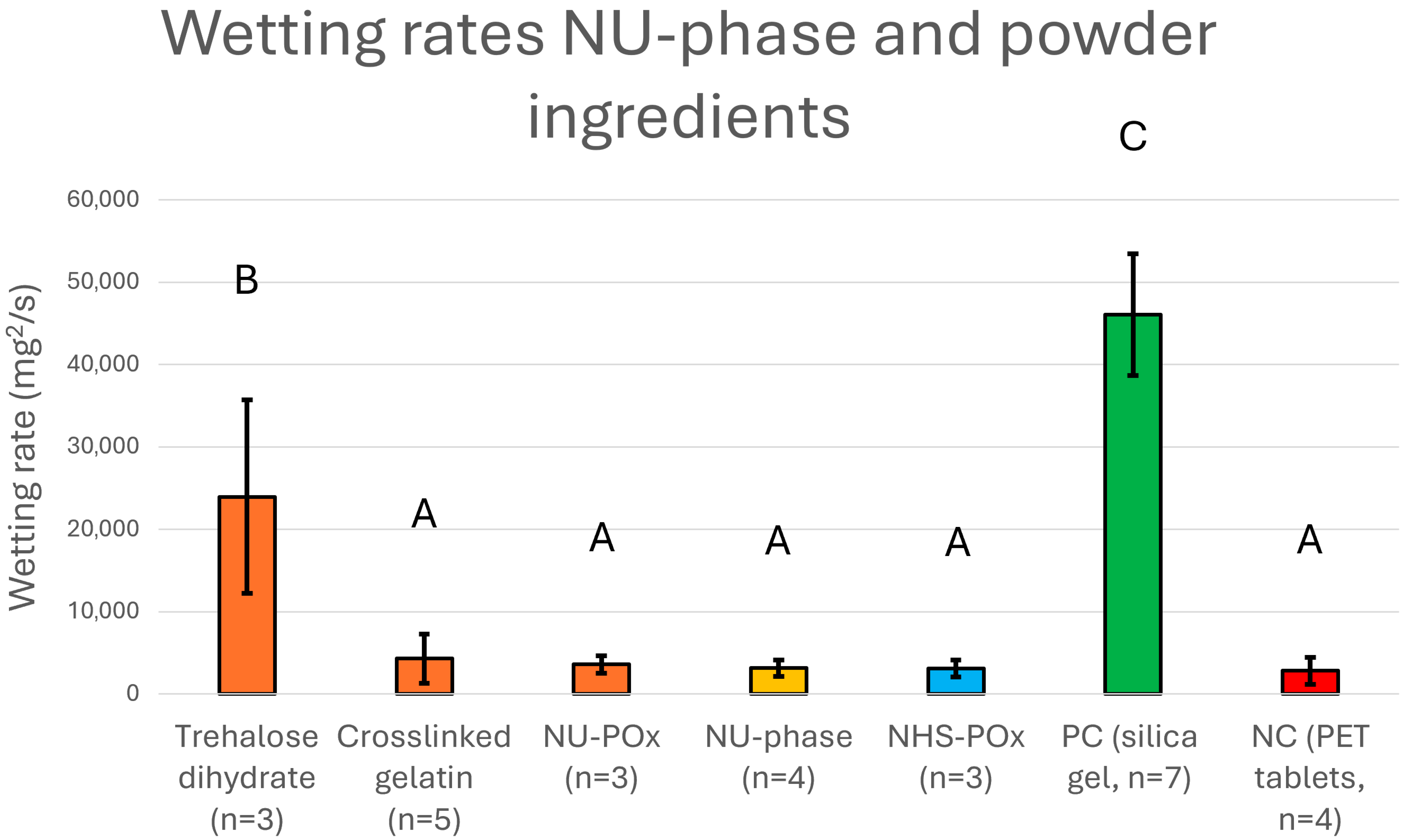
3.1. Chemical Characteristics of Ingredients, NU-Phase, and Powder
3.2. SEM Imaging
3.3. Swelling Measurement
3.4. Crosslinking Speed Measurement
3.5. In Vitro Degradation Measurement
3.6. Creation of Powder Prototypes
3.7. Wettability Measurement
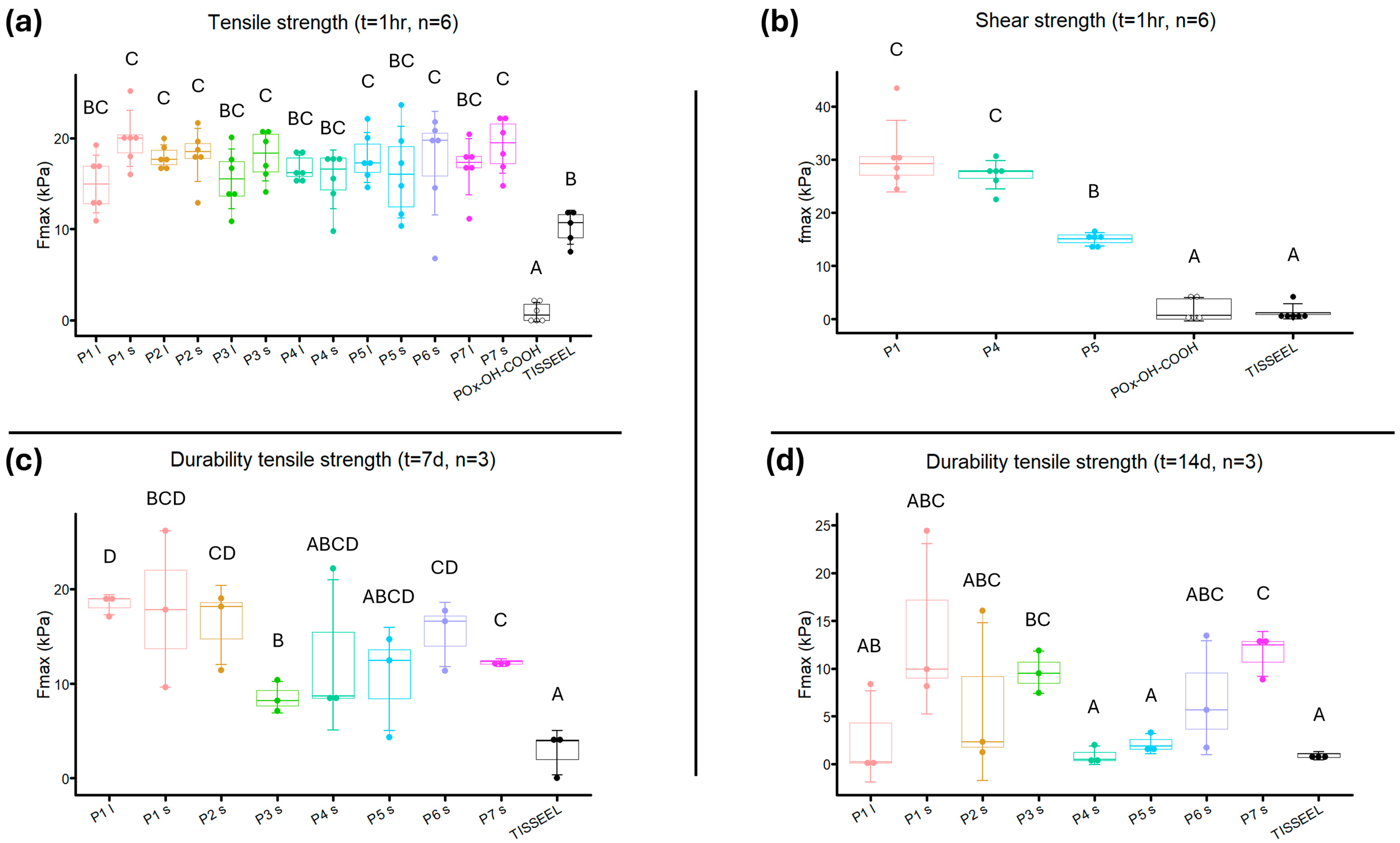
3.8. Adhesive Strength Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Future Directives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| NHS-POx | N-Hydroxysuccinimide-poly(2-oxazoline) |
| NHS-ester | N-Hydroxysuccinimide-ester |
| NU-POx | Nucleophilicly activated poly(2-oxazoline) |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| POx-OH-COOH | poly(2-oxazoline)-acid |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Kuroi, K.; Shimozuma, K.; Taguchi, T.; Imai, H.; Yamashiro, H.; Ohsumi, S.; Saito, S. Pathophysiology of Seroma in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer 2005, 12, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampathraju, S.; Rodrigues, G. Seroma Formation after Mastectomy: Pathogenesis and Prevention. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 1, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, J.M.; Nickerson, T.P.; Thiels, C.A.; Saint-Cyr, M.; Farley, D.R. Prevention of Postoperative Seromas With Dead Space Obliteration. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 29, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, L.; Bosmans, J.W.A.M.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Vissers, Y.L.J.; Beets, G.L.; van Bastelaar, J. A systematic review of seroma formation following drain-free mastectomy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, H.; Kargar, S.; Jafari-Nedooshan, J.; Dehghan, H.; Akhavan-Tafti, Y.; Heiranizadeh, N.; Neshan, M. Using Drain-Free Flap Fixation Techniques Versus Traditional Wound Closure With Drain Placement to Prevent Seroma Formation and Its Complications in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Mastectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast. Aesthetic Nurs. 2022, 42, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Lin, S.F.; Hung, C.F.; Chou, P. Risk of infection is associated more with drain duration than daily drainage volume in prosthesis-based breast reconstruction: A cohort study. Medicine 2016, 95, e5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Basu, S.; Shukla, V.K. Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery: What we have learned in the last two decades. J. Breast Cancer 2012, 15, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiraju, G.K.; Prospero, M.R.; Tobias, F.; Malek, A.J.; Reiche, E.; Broyles, J.M. Understanding the Impacts of Surgical Drains on Postoperative Pain and Quality of Life. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2025, 13, e6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumville, J.C.; Coulthard, P.; Worthington, H.V.; Riley, P.; Patel, N.; Darcey, J.; Esposito, M.; van der Elst, M.; van Waes, O.J. Tissue adhesives for closure of surgical incisions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD004287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajirian, A.L.; Goldberg, D.J. A review of sutures and other skin closure materials. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2010, 12, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Bao, G.; Li, J.; Ma, Z.; Bao, G.; Li, J. Multifaceted Design and Emerging Applications of Tissue Adhesives. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Chen, S. Recent Advances in Tissue Adhesives for Clinical Medicine. Polymers 2020, 12, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Huang, D.W.; Chou, Y.Y.; An, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.S.; Chen, P.H.; Tzeng, Y.S. Comparative Evaluation of Tissue Adhesives and Sutures in the Management of Facial Laceration Wounds in Children. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musham, A.; Samuel, E.M.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Elamurugan, T.P.; Manwar, A.S. Comparison of Tissue Adhesive Glue with Subcuticular Absorbable Suture for Skin Closure Following Thyroid Surgery: A single-blinded randomised controlled trial. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2023, 23, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotnitz, W.D. Fibrin Sealant: The Only Approved Hemostat, Sealant, and Adhesive-a Laboratory and Clinical Perspective. ISRN Surg. 2014, 2014, 203943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaze, L.; Le Dem, N.; Bubenheim, M.; Tsilividis, B.; Mezghani, J.; Schwartz, L.; Francois, A.; Ertaud, J.Y.; Bagot d’Arc, M.; Scotte, M. Tensile strength of biological fibrin sealants: A comparative study. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 176, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, W.; Banerjee, A. Release of glutaraldehyde from an albumin-glutaraldehyde tissue adhesive causes significant in vitro and in vivo toxicity. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 79, 1522–1528; discussion 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, K.; Tonar, Z.; Matejka, V.M.; Martinca, T.; Jonak, M.; Rokosny, S.; Pirk, J. Tissue reaction to three different types of tissue glues in an experimental aorta dissection model: A quantitative approach. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 133, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Imoto, K.; Uchida, K.; Takanashi, Y. Aortic root necrosis after surgical treatment using gelatin-resorcinol-formaldehyde (GRF) glue in patients with acute type A aortic dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 12, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Inci, I.; Kirsebom, H.; Galaev, I.Y.; Mattiasson, B.; Piskin, E. Gelatin cryogels crosslinked with oxidized dextran and containing freshly formed hydroxyapatite as potential bone tissue-engineering scaffolds. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.; Alhomrani, M.; Alamri, A.S.; Alsanie, W.F.; Nainwal, P.; Kimothi, V.; Deepak, A.; Sargsyan, A.S. Unveiling the versatility of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels: A comprehensive journey into biomedical applications. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantigua, D.; Nguyen, M.A.; Wu, X.; Suvarnapathaki, S.; Kwon, S.; Gavin, W.; Camci-Unal, G. Synthesis and characterization of photocrosslinkable albumin-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9242–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Soman, D.; Payanam, U.; Laurent, A.; Labarre, D.; Jayakrishnan, A. A novel injectable tissue adhesive based on oxidized dextran and chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Park, C.-W.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, W.-K. Postoperative Cervical Cord Compression Induced by Hydrogel Dural Sealant (DuraSeal®). Korean J. Spine 2013, 10, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavaraja, D.; De Lacy, P.; Hussain, R.; Redfern, R.M. Postoperative Cervical Cord Compression Induced by Hydrogel (DuraSeal): A possible complication. SPINE 2010, 35, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, P.T.M.; van der Ven, L.G.J.; van Benthem, R.; Esteves, A.C.C.; de With, G. Water Swelling Behavior of Poly(ethylene glycol)-Based Polyurethane Networks. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerman, M.A.; Van der Laan, H.L.; Bender, J.C.M.E.; Hoogenboom, R.; Jansen, J.A.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.; Van Hest, J.C.M. Synthesis of pH- and thermoresponsive poly(2-n-propyl-2-oxazoline) based copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronek, J.; Minarcikova, A.; Kronekova, Z.; Majercikova, M.; Strasser, P.; Teasdale, I. Poly(2-isopropenyl-2-oxazoline) as a Versatile Functional Polymer for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Mooney, D. Polymeric Tissue Adhesives. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11336–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelmansky, R.; McAlvin, B.J.; Nyska, A.; Dohlman, J.C.; Chiang, H.H.; Hashimoto, M.; Kohane, D.S.; Mizrahi, B. Strong tissue glue with tunable elasticity. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerman, M.; Roozen, E.; Franssen, G.M.; Bender, J.; Hoogenboom, R.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.; Laverman, P.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Felix Lanao, R.P. Degradation and excretion of NHS-ester functionalized poly(2-oxazoline)s. Materialia 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerman, M.A.; Roozen, E.; Sanchez-Fernandez, M.J.; Keereweer, A.R.; Felix Lanao, R.P.; Bender, J.; Hoogenboom, R.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.; Jansen, J.A.; Van Goor, H.; et al. Next Generation Hemostatic Materials Based on NHS-Ester Functionalized Poly(2-oxazoline)s. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerman, M. Development of Poly(2-Oxazoline) Based Hemostatic Materials. Available online: https://repository.ubn.ru.nl/bitstream/handle/2066/177085/177085.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Roozen, E.A.; Warlé, M.C.; Lomme, R.M.L.M.; Félix Lanao, R.P.; van Goor, H. New polyoxazoline loaded patches for hemostasis in experimental liver resection. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, B.P.; Li, W.W.L.; Roozen, E.A.; van Dort, D.I.M.; Evers, J.; van der Heijden, E.; van der Heide, S.M.; van Goor, H.; Verhagen, A. Sealing effectiveness of a novel NHS-POx based patch: Experiments in a dynamic ex vivo porcine lung. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 3580–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Erk, M.; Lomme, R.; Sánchez-Fernández, M.J.; van Oirschot, B.A.J.A.; Félix Lanao, R.P.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G.; van Goor, H. Novel alendronate and NHS-ester functionalized poly(2-oxazoline)s bone adhesive barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration: Prototype selection and experimental model comparison. Materialia 2022, 24, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, M.J.; Peerlings, M.; Felix Lanao, R.P.; Bender, J.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G. Bone-adhesive barrier membranes based on alendronate-functionalized poly(2-oxazoline)s. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5848–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poos, S.E.M.; van Erk, M.; van Oirschot, B.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G.; Félix Lanao, R.P.; van Goor, H.; van den Beucken, J. Evaluation of bone adhesive barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration: An experimental study in rats. Eur. Cells Mater. 2025, 51, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K. Raplixa: A Review in Improving Surgical Haemostasis. Clin. Drug Investig. 2015, 35, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, S.C. Unlocking Trehalose’s versatility: A comprehensive Journey from biosynthesis to therapeutic applications. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J.; Van Dijck, J. Bioresorbable Sealing Powder. WO2022148725A1, 14 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tantipanjaporn, A.; Wong, M.K. Development and Recent Advances in Lysine and N-Terminal Bioconjugation for Peptides and Proteins. Molecules 2023, 28, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Oh, S.-C. Gelation of Gelatin Solution. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1982, 47, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Kirdponpattara, S.; Phisalaphong, M.; Newby, B.M. Applicability of Washburn capillary rise for determining contact angles of powders/porous materials. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2013, 397, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaine, J.E.; Mucalo, M.R. Measurements of the wettability of catalyst support materials using the Washburn capillary rise technique. Powder Technol. 2015, 276, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Modeling of stimuli-responsive hydrogels: A transient analysis. In The Mechanics of Hydrogels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 223–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Fu, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, D.A. A mussel-inspired double-crosslinked tissue adhesive intended for internal medical use. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooren, M.F.; Van der Veen, J.; Muller, D.E.; Herstig, D.T.; De Vries, H.H.; Ribbels, R.S.R. Tissue-Adhesive Sealant Device. WO2019066657A3, 1 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM F2258-24; Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Tissue Adhesives in Tension. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008; Volume F2558, pp. 1–5.
- Baxter. TISSEEL Instructions for Use. December 2019; p. 1–10. Available online: https://baxterpi.com/pi-pdf/Tisseel_PI.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- ASTM F2255-05; Strength Properties of Tissue Adhesives in Lap-Shear by Tension Loading. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008; Volume F2255, pp. 1–6.
- Piepho, H.P. Letters in Mean Comparisons: What They Do and Don’t Mean. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda de Oliveira, G.; Kim, M.; Santos, C.S.; Limani, N.; Chung, T.D.; Tetteh, E.B.; Schuhmann, W. Controlling surface wetting in high-alkaline electrolytes for single facet Pt oxygen evolution electrocatalytic activity mapping by scanning electrochemical cell microscopy. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 16331–16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, É.; Erdélyi, K.; Szendrö, I.; Vargha-Butler, E.I. Adsorption and Wetting Properties of Pluronic Block Copolymers on Hydrophobic Surfaces Studied by Optical Waveguide Lightmode Spectroscopy and Dynamic Tensiometric Method. J. Adhes. 2010, 80, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loerting, T.; Tautermann, C.; Kroemer, R.T.; Kohl, I.; Hallbrucker, A.; Mayer, E.; Liedl, K.R. On the Surprising Kinetic Stability of Carbonic Acid (H2CO3). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M.A.; Elbadawy, H.M.; Shaker, M.A. Improved solubility, dissolution, and oral bioavailability for atorvastatin-Pluronic(R) solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Castillo-Santaella, T.; Yang, Y.; Martinez-Gonzalez, I.; Galvez-Ruiz, M.J.; Cabrerizo-Vilchez, M.A.; Holgado-Terriza, J.A.; Selles-Galiana, F.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Effect of Hyaluronic Acid and Pluronic-F68 on the Surface Properties of Foam as a Delivery System for Polidocanol in Sclerotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brette, M.M.; Holm, A.H.; Drozdov, A.D.; Christiansen, J.d.C. Pure Hydrolysis of Polyamides: A Comparative Study. Chemistry 2023, 6, 13–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Tu, W.; Chen, X.; Zhan, C.G. Reaction pathways and free energy profiles for spontaneous hydrolysis of urea and tetramethylurea: Unexpected substituent effects. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 7595–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chauhan, H.; Ambechada, J.K. Biodegradation of Plastics: The role of biosurfactant-producing bacteria in environmental remediation. J. Adv. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 6, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Ding, Y.; Qian, Z.; Wang, W.; Mao, Z.; Ding, Y. Sequential-Crosslinking Fibrin Glue for Rapid and Reinforced Hemostasis. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Ariens, R.A.S. Fibrinogen splice variation and cross-linking: Effects on fibrin structure/function and role of fibrinogen gamma’ as thrombomobulin II. Matrix Biol. 2017, 60–61, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, J.P.; Shuman, H.; Ledger, R.E.; Lee, S.; Weisel, J.W. The elasticity of an individual fibrin fiber in a clot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9133–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, V.; Becker, M.L. Degradable Adhesives for Surgery and Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3009–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.Y.; Hwang, S.K.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, C.S. Progress of tissue adhesives based on proteins and synthetic polymers. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, L.; Golaszewska, K.; Malkowska, J.; Golebiewska, M.; Kaczynska, J.; Gromadka, B.; Matak, D. Safety and performance of surgical adhesives. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Qing, X.; Xia, H.; Hao, S.; Zhu, H.; He, Y.; Mao, H.; Gu, Z. Injectable Hydrogel Based on Modified Gelatin and Sodium Alginate for Soft-Tissue Adhesive. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 744099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Hou, X.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, X. Rapid Gelling Chitosan/Polylysine Hydrogel with Enhanced Bulk Cohesive and Interfacial Adhesive Force: Mimicking Features of Epineurial Matrix for Peripheral Nerve Anastomosis. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Nie, J.; Yang, D. Dextran and gelatin based photocrosslinkable tissue adhesive. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, G.M.; Yang, K.; Pereira, M.J.N.; Liu, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Karp, J.M.; Artzi, N.; Lee, Y. Overcoming the translational barriers of tissue adhesives. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazly, T.M.; Baker, A.B.; Naber, J.R.; Bon, A.; Van Vliet, K.J.; Edelman, E.R. Augmentation of postswelling surgical sealant potential of adhesive hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 95, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatridis, J.C.; Wu, J.; Yandow, J.A.; Langevin, H.M. Subcutaneous tissue mechanical behavior is linear and viscoelastic under uniaxial tension. Connect. Tissue Res. 2003, 44, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardo, A.; Bonaldi, L.; Stecco, C.; Fontanella, C.G. Biomechanical properties of the human superficial fascia: Site-specific variability and anisotropy of abdominal and thoracic regions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 157, 106637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, K.; Okamoto, S.; Asaba, T.; Ogusu, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yamada, Y. Young’s moduli of subcutaneous tissues and muscles under different loads at the gluteal region calculated using ultrasonography. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2022, 34, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, B.; Stefanescu, C.F.; Yang, C.; Lawlor, M.W.; Ko, D.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. Elasticity and safety of alkoxyethyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesives. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.R.; Mooney, D.J. Biomaterials to Mimic and Heal Connective Tissues. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1806695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, A.J.; Griffin, M.A.; Sen, S.; Bonnemann, C.G.; Sweeney, H.L.; Discher, D.E. Myotubes differentiate optimally on substrates with tissue-like stiffness: Pathological implications for soft or stiff microenvironments. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, B.; Gao, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Pan, S. Substrate Stiffness of Bone Microenvironment Controls Functions of Pre-Osteoblasts and Fibroblasts In Vitro. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehlmann, B.; Bonham, C.A.; Zucal, I.; Prantl, L.; Gurtner, G.C. Mechanotransduction in Wound Healing and Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Varela, C.E.; Nabzdyk, C.S.; Mao, X.; Padera, R.F.; Roche, E.T.; Zhao, X. Dry double-sided tape for adhesion of wet tissues and devices. Nature 2019, 575, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehnpfennig, L.; Ritter, M.; Montagna, G.; Handschin, T.M.; Ling, B.M.; Oberhauser, I.; Levy, J.; Schaefer, K.M.; Maggi, N.; Soysal, S.D.; et al. The impact of delayed wound healing on patient-reported outcomes after breast cancer surgery. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2022, 75, 4125–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, T.Y.; Lin, K.J.; Chang, H.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Huang, C.U.; Lin, X.Y.; Tsai, F.C.; Tsai, C.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, F.Y.; et al. Early identification of delayed wound healing in complex diabetic foot ulcers treated with a dermal regeneration template: A novel clinical target and its risk factors. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, J.P.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. The impact of psychological stress on wound healing: Methods and mechanisms. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2011, 31, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.; Shoham, Y.; Monstrey, S.; Hoeksema, H.; Goverman, J.; Hickerson, W.; Mataro, I.; Singer, A.J. Burn Care in the Era of Rapid Enzymatic Debridement: Challenging the Dogma that Healing Beyond 21 Days Results in Hypertrophic Scarring. Open Dermatol. J. 2021, 15, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Elwood, E.; Jones, G.; Barrick, R.; Feng, J. Decreasing expander breast infection: A new drain care protocol. Can. J. Plast. Surg. 2009, 17, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, N.; Shitreet, S.; Abraham, E.; Stanley, B.; Edelman, E.R.; Artzi, N. Natural tissue microenvironmental conditions modulate adhesive material performance. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15402–15409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nippi Collagen NA Inc. Types of Collagen. Available online: https://nippicollagen.com/why-trumarine-collagen/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Eckes, S.; Braun, J.; Wack, J.S.; Ritz, U.; Nickel, D.; Schmitz, K. Rose Bengal Crosslinking to Stabilize Collagen Sheets and Generate Modulated Collagen Laminates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charney, R.; Takahashi, S.; Zhao, M.; Sonnenblick, E.; Eng, C. Collagen loss in the stunned myocardium. Circulation 1992, 85, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baino, F.; Yamaguchi, S. The Use of Simulated Body Fluid (SBF) for Assessing Materials Bioactivity in the Context of Tissue Engineering: Review and Challenges. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Erk, M.; Félix Lanao, R.; Calon, N.; Tropper, J.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G.; van Goor, H. Cellular viability of fibroblasts, osteoblasts and osteoclasts in response to bone adhesive alendronate-functionalized poly(2-oxazoline). Polym. Test. 2024, 131, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădescu, A.; Pârâu, A.; Pană, I.; Cotruț, C.M.; Constantin, L.R.; Braic, V.; Vrânceanu, D.M. In Vitro Activity Assays of Sputtered HAp Coatings with SiC Addition in Various Simulated Biological Fluids. Coatings 2019, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchy, T.; Bartos, M.; Sedlacek, R.; Supova, M.; Zaloudkova, M.; Martynkova, G.S.; Foltan, R. Various Simulated Body Fluids Lead to Significant Differences in Collagen Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Materials 2021, 14, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, B.P.; Vos, S.; Li, W.W.L.; van der Heijden, E.; van Goor, H.; Verhagen, A.; Ten Broek, R.P.G. Biocompatibility of a novel lung sealant based on functionalized polyoxazolines in an ovine model of parenchymal lung injury. J. Thorac. Dis. 2025, 17, 2140–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Prototype | Buffer Added to Powder | Pluronic F68 Added to Powder |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | No | No |
| P2 | No | Impregnated |
| P3 | Borax | No |
| P4 | Borax | Impregnated |
| P5 | Sodium carbonate | Impregnated |
| P6 | No | Coated |
| P7 | Borax | Coated |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poos, S.E.M.; Lomme, R.M.L.M.; Roozen, E.A.; Bender, J.C.M.E.; van Goor, H.; Ten Broek, R.P.G. Characterization of a Novel POx-Based Adhesive Powder for Obliterating Dead Spaces After Surgery. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101011
Poos SEM, Lomme RMLM, Roozen EA, Bender JCME, van Goor H, Ten Broek RPG. Characterization of a Novel POx-Based Adhesive Powder for Obliterating Dead Spaces After Surgery. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101011
Chicago/Turabian StylePoos, Steven E. M., Roger M. L. M. Lomme, Edwin A. Roozen, Johan C. M. E. Bender, Harry van Goor, and Richard P. G. Ten Broek. 2025. "Characterization of a Novel POx-Based Adhesive Powder for Obliterating Dead Spaces After Surgery" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101011
APA StylePoos, S. E. M., Lomme, R. M. L. M., Roozen, E. A., Bender, J. C. M. E., van Goor, H., & Ten Broek, R. P. G. (2025). Characterization of a Novel POx-Based Adhesive Powder for Obliterating Dead Spaces After Surgery. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101011






