Deep Learning-Based Fine-Tuning Approach of Coarse Registration for Ear–Nose–Throat (ENT) Surgical Navigation Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Develop a novel surface registration protocol that integrates deep-learning methodologies with conventional model registration techniques to enhance accuracy in surgical navigation systems while maintaining existing clinical workflows.
- Design a specialized deep-learning model architecture capable of processing sparse point clouds and predicting precise refinements for optimized registration.
- Validate the proposed method within existing surgical navigation workflows through phantom-based studies, assessing both SRE and TRE to demonstrate improved accuracy.
2. Materials and Methods
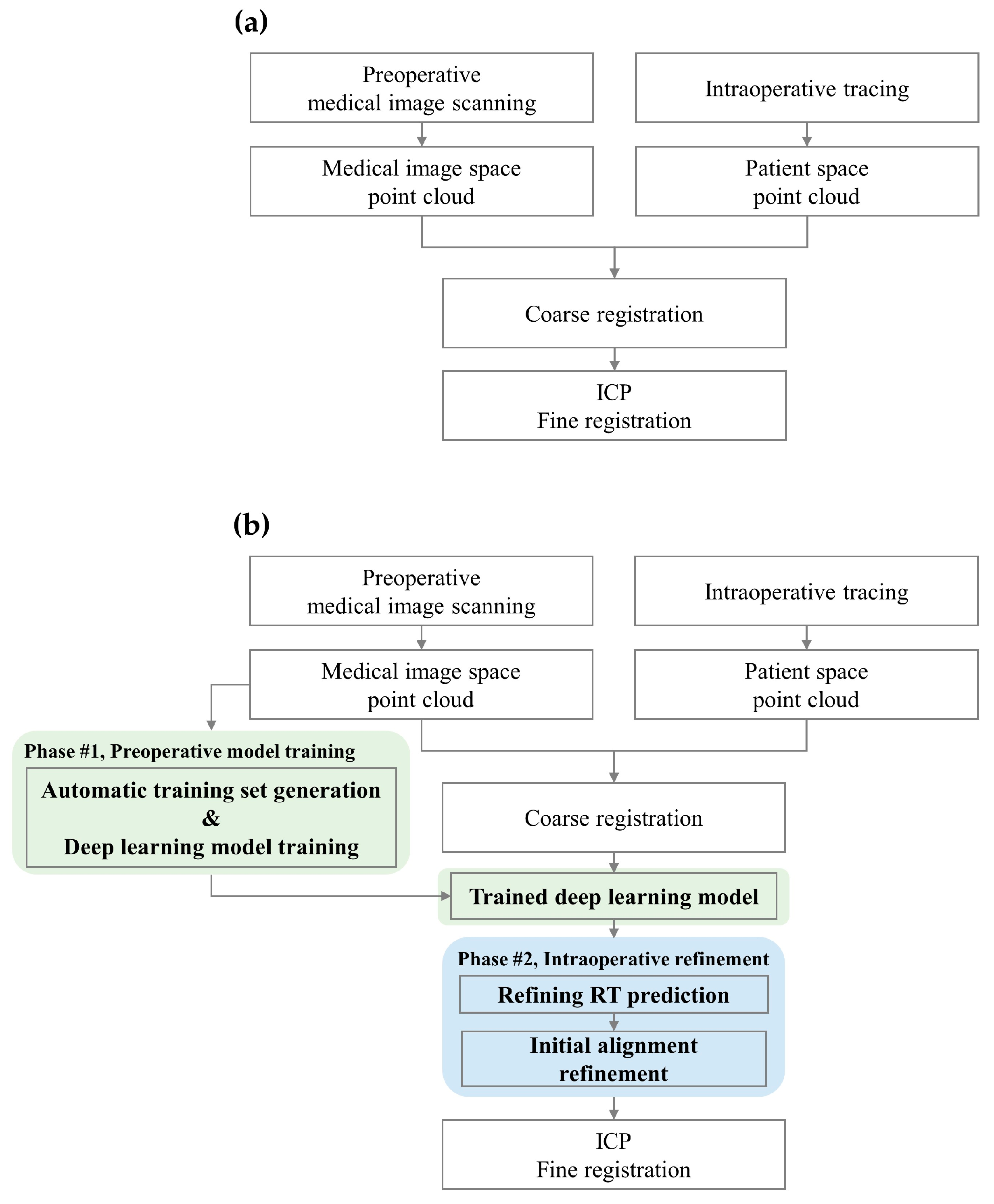
2.1. Conventional Surface Registration Process
2.1.1. Medical Image and Patient Space Point Cloud Acquisition
2.1.2. Coarse Registration
2.1.3. ICP Fine Registration
2.2. Proposed Surface Registration Protocol
2.2.1. Automatic Training Set Generation
- Standardization of point cloud data
- Identification of anatomical landmarks and candidate points generation
- Generation of unique landmark combinations and coarse registration
2.2.2. Deep-Learning Model
- Problem statement
- Encoder architecture
- Decoder architecture
- Iterative refinement process
- Loss functions
- Hyperparameters and optimizer
2.2.3. Refining RT Prediction and Initial Alignment Refinement
- Landmark types and coordinate systems
- Patient’s anatomical landmarks: These landmarks, identified in the patient space, incorporate localization errors.
- Reference anatomical landmarks: These are the ground truth points serving as a common reference for alignment, assumed to be precise in the medical image coordinate system.
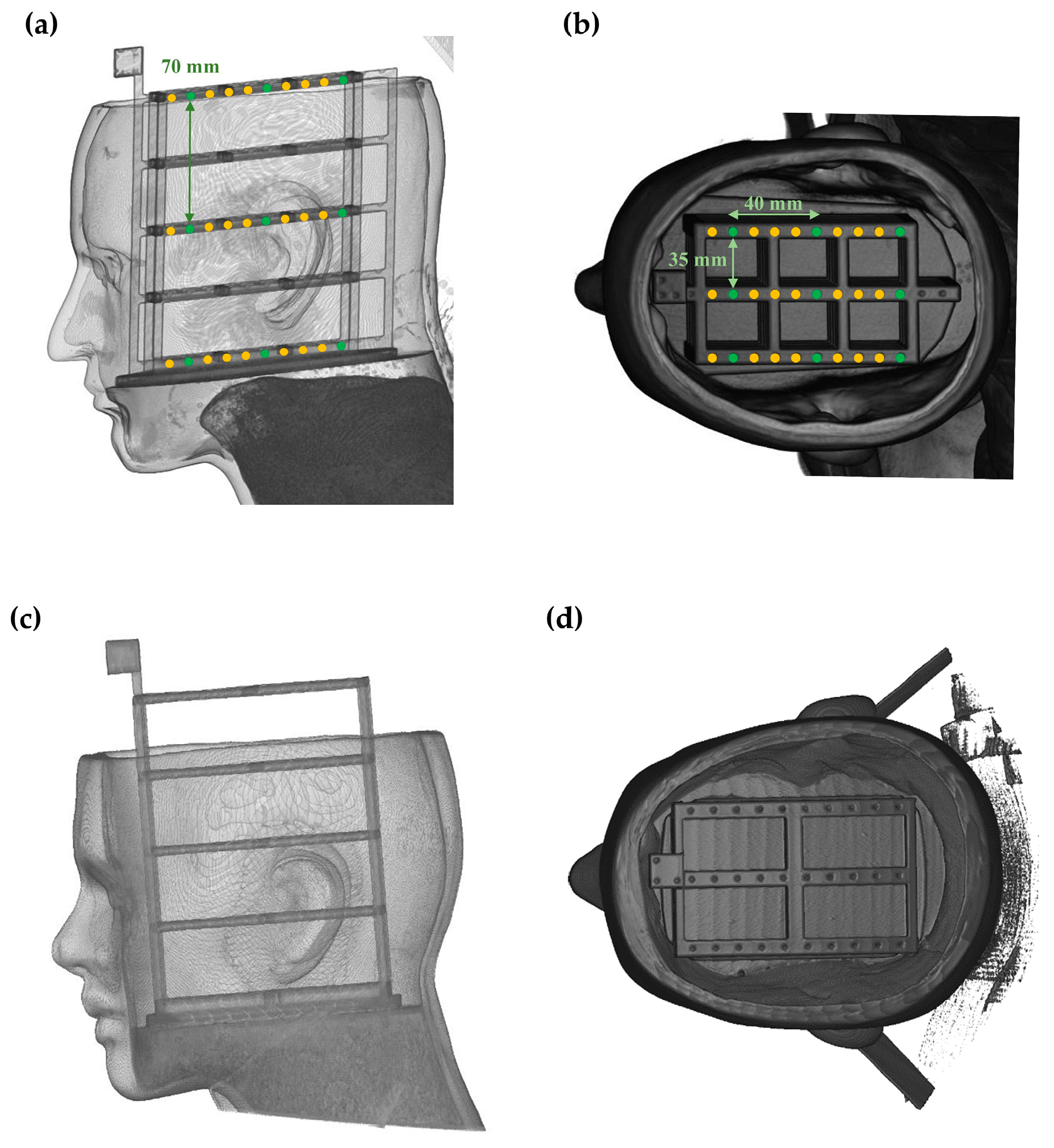
2.3. Phantom-Based Validation Study
3. Results
4. Discussion
- Presence of respiratory apparatus: Endotracheal tubes and other respiratory support devices can obstruct access to the lower face, limiting point cloud acquisition.
- Mobility of the mandible: Due to its range of motion and the fact that it is not rigidly attached to the skull, the mandible can introduce variability in the geometry of the lower face during point cloud acquisition.
- Patient breathing: Respiratory motion can result in subtle but significant changes in facial geometry, especially in the mid and lower face regions.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cleary, K.; Peters, T.M. Image-guided interventions: Technology review and clinical applications. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 12, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, B.S.; Armijo, P.R.; Krause, C.; Choudhury, S.A.; Oleynikov, D. Review of emerging surgical robotic technology. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 1636–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrory, B.; LaGrange, C.A.; Hallbeck, M.S. Quality and safety of minimally invasive surgery: Past, present, and future. Biomed. Eng. Comput. Biol. 2014, 6, BECB-S10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.; Gharde, P.; Tayade, H.; Patil, M.; Reddy, L.S.; Surya, D.; Srivani Reddy, L.; Surya, D., Jr. Advancements in robotic surgery: A comprehensive overview of current utilizations and upcoming frontiers. Cureus 2023, 15, e50415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, U.; Jendrewski, C.; Bartels, M. Navigation in surgery. Langenbeck Arch. Surg. 2013, 398, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarmehr, I.; Stokbro, K.; Bell, R.B.; Thygesen, T. Surgical navigation: A systematic review of indications treatments and outcomes in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1987–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Rahman, S.U.; Ullah, S.; Gulati, K. Medical image registration in image guided surgery: Issues, challenges and research opportunities. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Jaw, F.S.; Lo, W.C.; Fang, K.M.; Cheng, P.W. Three-dimensional analysis of the accuracy of optic and electromagnetic navigation systems using surface registration in live endoscopic sinus surgery. Rhinology 2016, 54, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongen, M.A.; Willems, P.W. Current accuracy of surface matching compared to adhesive markers in patient-to-image registration. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, G.; Mühling, J.; Marmulla, R. Image-to-patient registration techniques in head surgery. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; Beache, G.M.; Gimel’farb, G.; Suri, J.S.; El-Baz, A.S. State-of-the-art medical image registration methodologies: A survey. In Multi Modality State-of-the-Art Medical Image Segmentation and Registration Methodologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 235–280. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Yao, X.; Xu, X. A robust automated surface-matching registration method for neuronavigation. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 2755–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, M.; Song, Z. A new markerless patient-to-image registration method using a portable 3D scanner. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, Z.; Tian, Z.; Ai, D.; Song, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. An incremental registration method for endoscopic sinus and skull base surgery navigation: From phantom study to clinical trials. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Tao, W. Evaluation of the ICP algorithm in 3D point cloud registration. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 68030–68048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, J.; Fei, B.; Liu, J.; Cheung, Y.M.; Ye, X.; Engelhardt, K.; Zhang, J. A robust automated markerless registration framework for neurosurgery navigation. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2015, 11, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. Pointcnn: Convolution on x-transformed points. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 820–830. [Google Scholar]
- Unberath, M.; Gao, C.; Hu, Y.; Judish, M.; Taylor, R.H.; Armand, M.; Grupp, R. The impact of machine learning on 2d/3d registration for image-guided interventions: A systematic review and perspective. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 716007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Pena, R.M.G.; Ruiz, G.O.; Ali, S. A comprehensive survey on recent deep learning-based methods applied to surgical data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.01435. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, H.; Sim, T. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for Automated Coarse Registration (ACR) of Image-Guided Surgical Navigation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 115884–115894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorensen, W.E.; Cline, H.E. Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques—SIGGRAPH ’87, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27–31 July 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, K.S.; Huang, T.S.; Blostein, S.D. Least-squares fitting of two 3-D point sets. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, 9, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, R.R.; Joskowicz, L.; Shoshan, Y. Fiducial Optimization for Minimal Target Registration Error in Image-Guided Neurosurgery. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 31, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerdeman, P.A.; Willems, P.W.; Noordmans, H.J.; Tulleken, C.A.; van der Sprenkel, J.W. Application accuracy in frameless image-guided neurosurgery: A comparison study of three patient-to-image registration methods. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, A.; Guigou, C.; Leclerc, S.; Lalande, A.; Bozorg Grayeli, A. Image-to-patient registration in computer-assisted surgery of head and neck: State-of-the-art, perspectives, and challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omara, A.; Wang, M.; Fan, Y.; Song, Z. Anatomical landmarks for point-matching registration in image-guided neurosurgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. MRCAS 2014, 10, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, A.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, N.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. Comparison Study of Extraction Accuracy of 3D Facial Anatomical Landmarks Based on Non-Rigid Registration of Face Template. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagertun, J.; Harder, S.; Rosengren, A.; Moeller, C.; Werge, T.; Paulsen, R.R.; Hansen, T.F. 3D facial landmarks: Inter-operator variability of manual annotation. BMC Med. Imaging 2014, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabanas, M.; Luboz, V.; Payan, Y. Patient specific finite element model of the face soft tissues for computer-assisted maxillofacial surgery. Med. Image Anal. 2003, 7, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccetti, M.; Delnevo, G.; Casini, L.; Cappiello, G. Is bigger always better? A controversial journey to the center of machine learning design, with uses and misuses of big data for predicting water meter failures. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar]
- Sarode, V.; Li, X.; Goforth, H.; Aoki, Y.; Srivatsan, R.A.; Lucey, S.; Choset, H. Pcrnet: Point cloud registration network using pointnet encoding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.07906. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Solomon, J.M. Prnet: Self-supervised learning for partial-to-partial registration. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. A Point Set Generation Network for 3D Object Reconstruction from A Single Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Gojcic, Z.; Zhou, C.F.; Wegner, J.D.; Wieser, A. The perfect match: 3D point cloud matching with smoothed densities. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5540–5549. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, K.; Cherukuri, A.K.; Vincent, D.R.; Garg, A.; Chen, B.Y. An efficient implementation of artificial neural networks with K-fold cross-validation for process optimization. J. Internet Technol. 2019, 20, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, T.; Palivela, H.; Tiwari, S. Optimization and fine-tuning of DenseNet model for classification of COVID-19 cases in medical imaging. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiotti, A.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Dos Santos, D.M. Evaluation of the Shore A Hardness of Silicone for Facial Prosthesis as to the Effect of Storage Period and Chemical Disinfection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herregodts, S.; Verhaeghe, M.; De Coninck, B.; Forward, M.; Verstraete, M.A.; Victor, J.; De Baets, P. An improved method for assessing the technical accuracy of optical tracking systems for orthopaedic surgical navigation. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2021, 17, e2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, A.; Krishnan, R.; Wolff, R.; Hermann, E.; Zimmermann, M.; Seifert, V. Laser surface scanning for patient registration in intracranial image-guided surgery. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Geer, A.F.; de Koning, S.B.; van Alphen, M.J.A.; Van der Mierden, S.; Zuur, C.L.; Van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Loeve, A.J.; van Veen, R.L.; Karakullukcu, M.B. Registration methods for surgical navigation of the mandible: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.K. What is the proper way to apply the multiple comparison test? Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 71, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liang, B.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; He, J. An iterative closest points algorithm for registration of 3D laser scanner point clouds with geometric features. Sensors 2017, 17, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobek, S.L. Applications of navigation for orthognathic surgery. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 26, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paydarfar, J.A.; Wu, X.; Halter, R.J. Initial experience with image-guided surgical navigation in transoral surgery. Head Neck 2019, 41, E1–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miga, M.I.; Sinha, T.K.; Cash, D.M.; Galloway, R.L.; Weil, R.J. Cortical surface registration for image-guided neurosurgery using laser-range scanning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.N.; Song, Z.J. Properties of the target registration error for surface matching in neuronavigation. Comput. Aided Surg. 2011, 16, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.H.; Cai, J.X.; Liu, Z.N.; Mu, T.J.; Martin, R.R.; Hu, S.M. Pct: Point cloud transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Peng, Y.; Xu, K. Geometric transformer for fast and robust point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11143–11152. [Google Scholar]
- Yew, Z.J.; Lee, G.H. Regtr: End-to-end point cloud correspondences with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6677–6686. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Rajkumar, R. Point-gnn: Graph neural network for 3d object detection in a point cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1711–1719. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Suo, S.; Ma, W.C.; Pokrovsky, A.; Urtasun, R. Deep Parametric Continuous Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2589–2597. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Tang, H.; Yang, S.; Han, S. FlatFormer: Flattened Window Attention for Efficient Point Cloud Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 1200–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Ma, J.; Chen, G.; An, P. Feature interactive representation for point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5530–5539. [Google Scholar]
- Yew, Z.J.; Lee, G.H. Rpm-net: Robust point matching using learned features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11824–11833. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Ye, N.; Liu, S.; Zeng, B.; Liu, S. FINet: Dual branches feature interaction for partial-to-partial point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Event, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2848–2856. [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth, B.A.; Davis, G.W.; Schlosser, R.J. Comparison of laser versus surface-touch registration for image-guided sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. 2005, 19, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



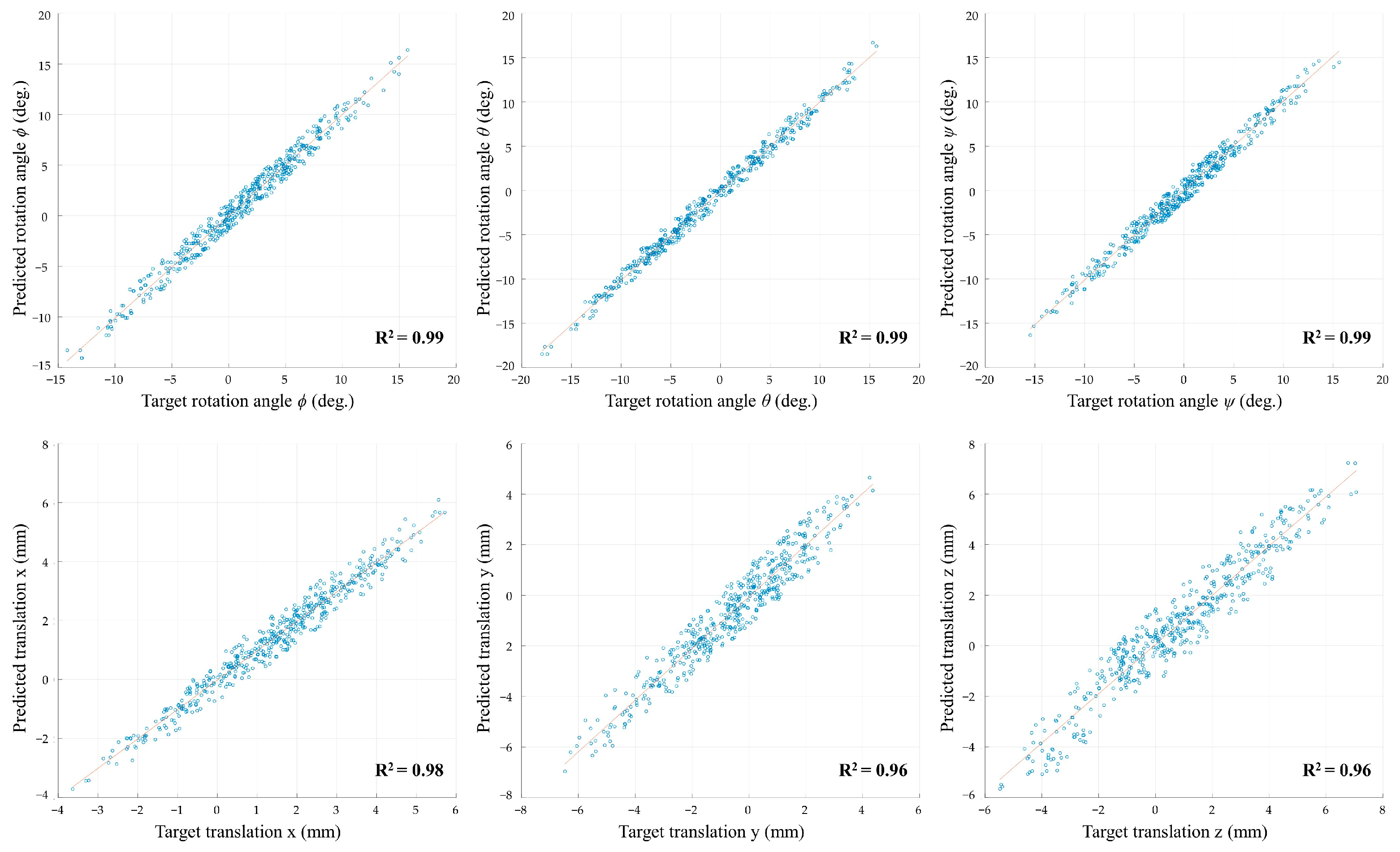



| Fold Number | Rotation Angle RMSE (deg.) | Translation RMSE (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rx | Ry | Rz | Tx | Ty | Tz | |
| 1 | 0.989 | 0.726 | 1.089 | 0.334 | 0.695 | 0.753 |
| 2 | 0.976 | 0.837 | 1.114 | 0.566 | 0.683 | 0.619 |
| 3 | 1.067 | 0.850 | 1.043 | 0.520 | 0.774 | 0.715 |
| 4 | 1.105 | 0.812 | 1.118 | 0.365 | 0.695 | 0.715 |
| 5 | 1.051 | 0.810 | 1.105 | 0.610 | 0.641 | 0.732 |
| Average | 1.037 | 0.807 | 1.094 | 0.479 | 0.698 | 0.706 |
| Standard Deviation (SD) | 0.054 | 0.048 | 0.031 | 0.123 | 0.048 | 0.052 |
| Model 1 (Conventional) | Model 2 (Yoo and Sim [23]) | Proposed | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Average | SD | Min | Max | Average | SD | Min | Max | Average | SD | |
| SRE (mm) | 0.482 | 0.596 | 0.534 | 0.025 | 0.492 | 0.595 | 0.544 | 0.026 | 0.482 | 0.545 | 0.517 | 0.025 |
| Model Name | TRE by Target Region (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Front | Middle | Back | |
| Model 1 (Conventional) | 1.865 ± 0.994 | 2.315 ± 0.929 | 3.308 ± 1.403 |
| Model 2 (Yoo and Sim [23]) | 1.738 ± 0.848 | 2.216 ± 0.784 | 3.239 ± 1.321 |
| Proposed | 1.220 ± 0.177 a,b | 1.591 ± 0.207 a,b | 1.986 ± 0.260 a,b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Choi, A.; Mun, J.H. Deep Learning-Based Fine-Tuning Approach of Coarse Registration for Ear–Nose–Throat (ENT) Surgical Navigation Systems. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090941
Lee D, Choi A, Mun JH. Deep Learning-Based Fine-Tuning Approach of Coarse Registration for Ear–Nose–Throat (ENT) Surgical Navigation Systems. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(9):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090941
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dongjun, Ahnryul Choi, and Joung Hwan Mun. 2024. "Deep Learning-Based Fine-Tuning Approach of Coarse Registration for Ear–Nose–Throat (ENT) Surgical Navigation Systems" Bioengineering 11, no. 9: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090941
APA StyleLee, D., Choi, A., & Mun, J. H. (2024). Deep Learning-Based Fine-Tuning Approach of Coarse Registration for Ear–Nose–Throat (ENT) Surgical Navigation Systems. Bioengineering, 11(9), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090941








