Improved Dipole Source Localization from Simultaneous MEG-EEG Data by Combining a Global Optimization Algorithm with a Local Parameter Search: A Brain Phantom Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Physical Head Phantom
2.2. Computational Head Phantom
2.3. EEG and MEG Data Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses of Dipole Localization Algorithm Parameter Estimates
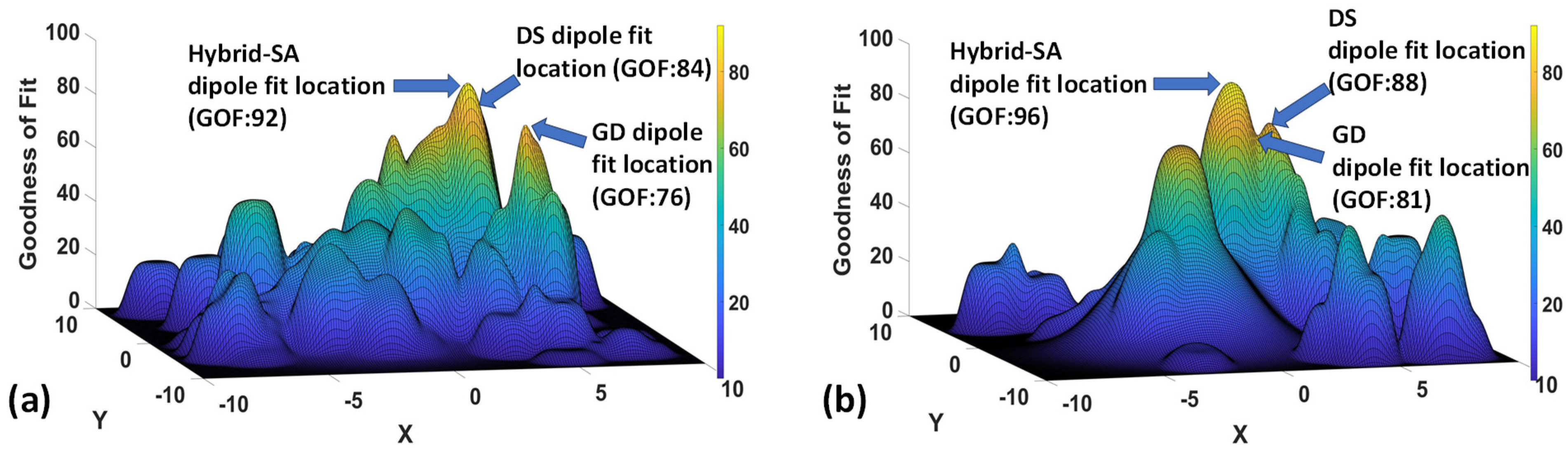
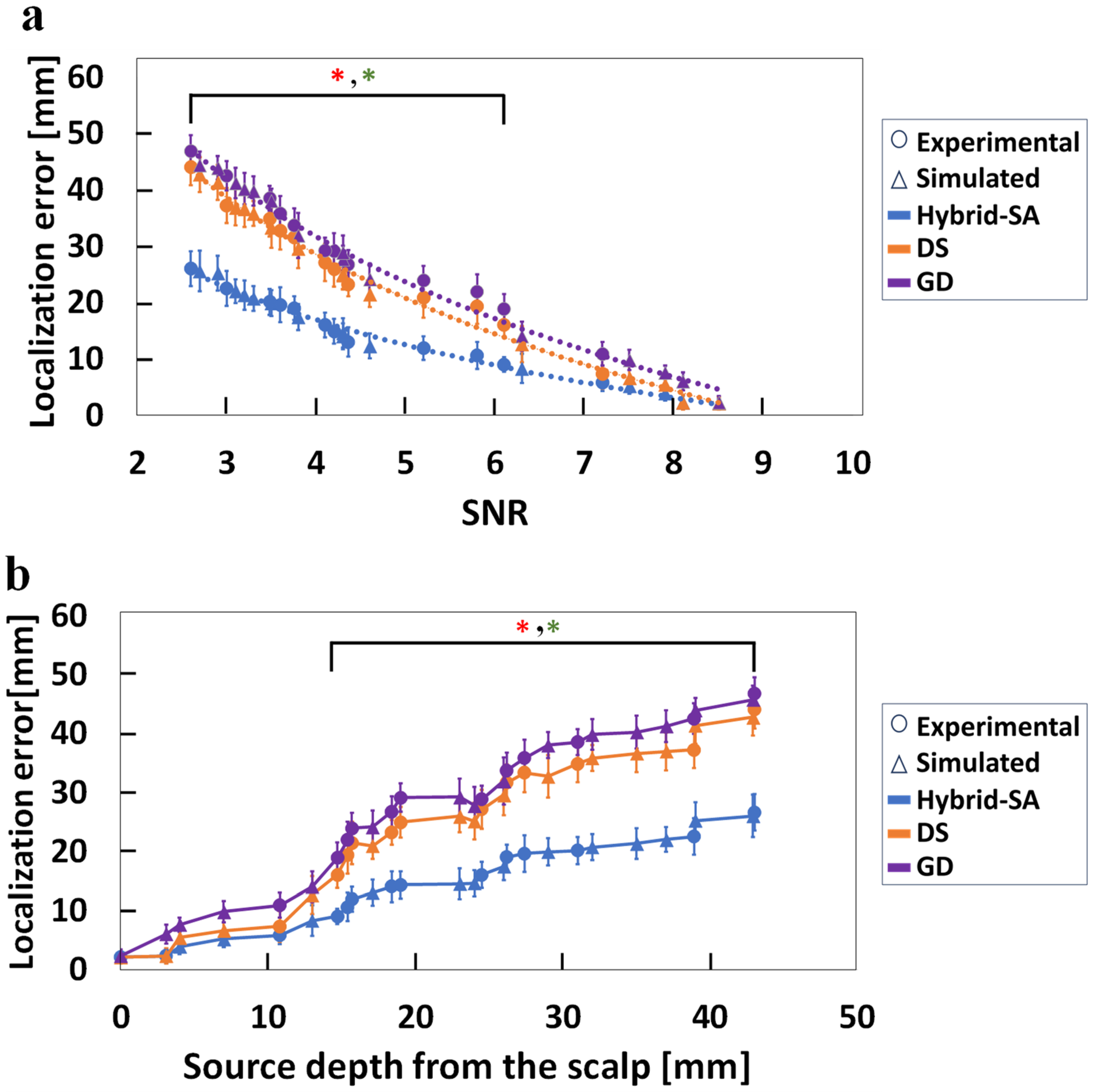
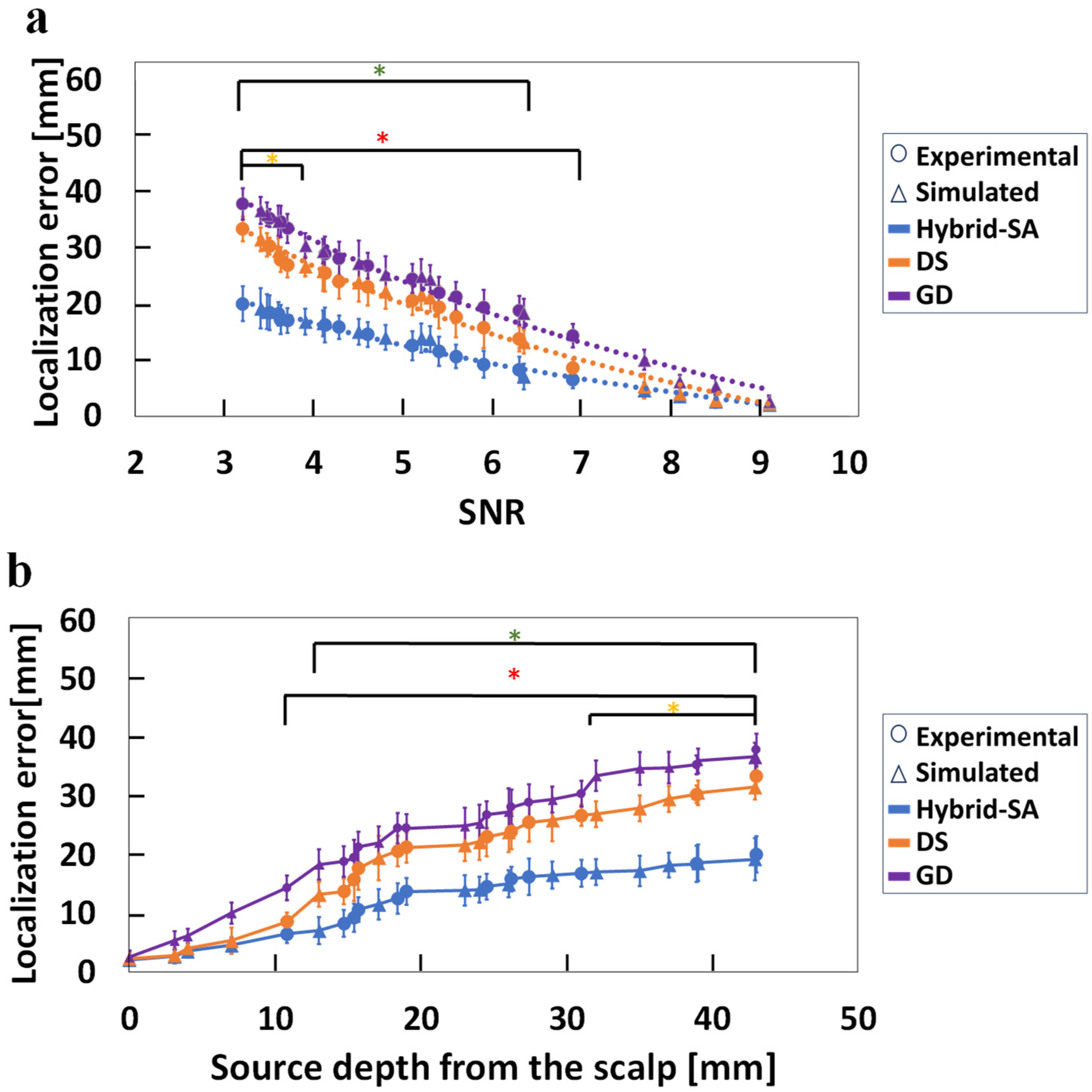
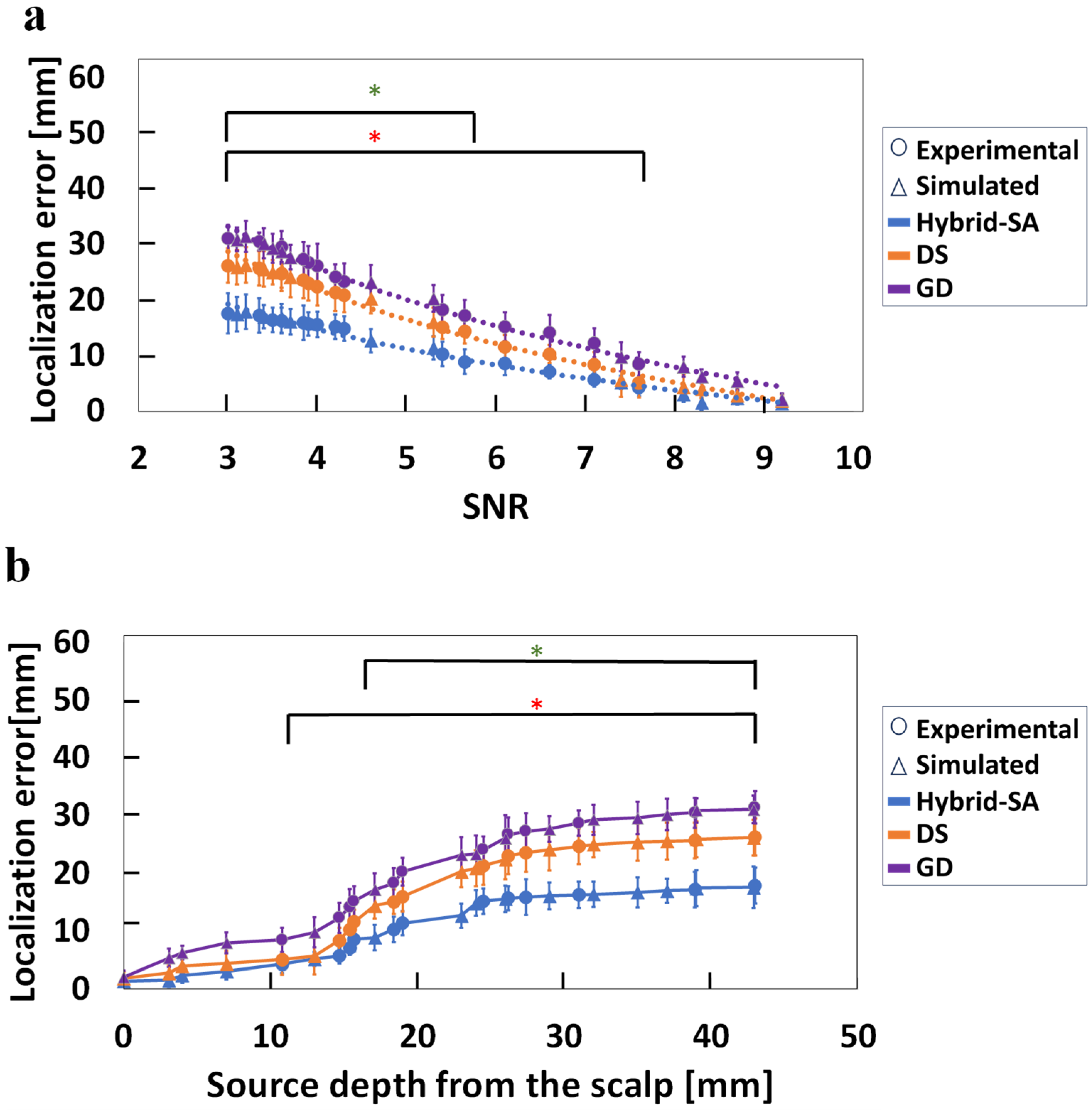
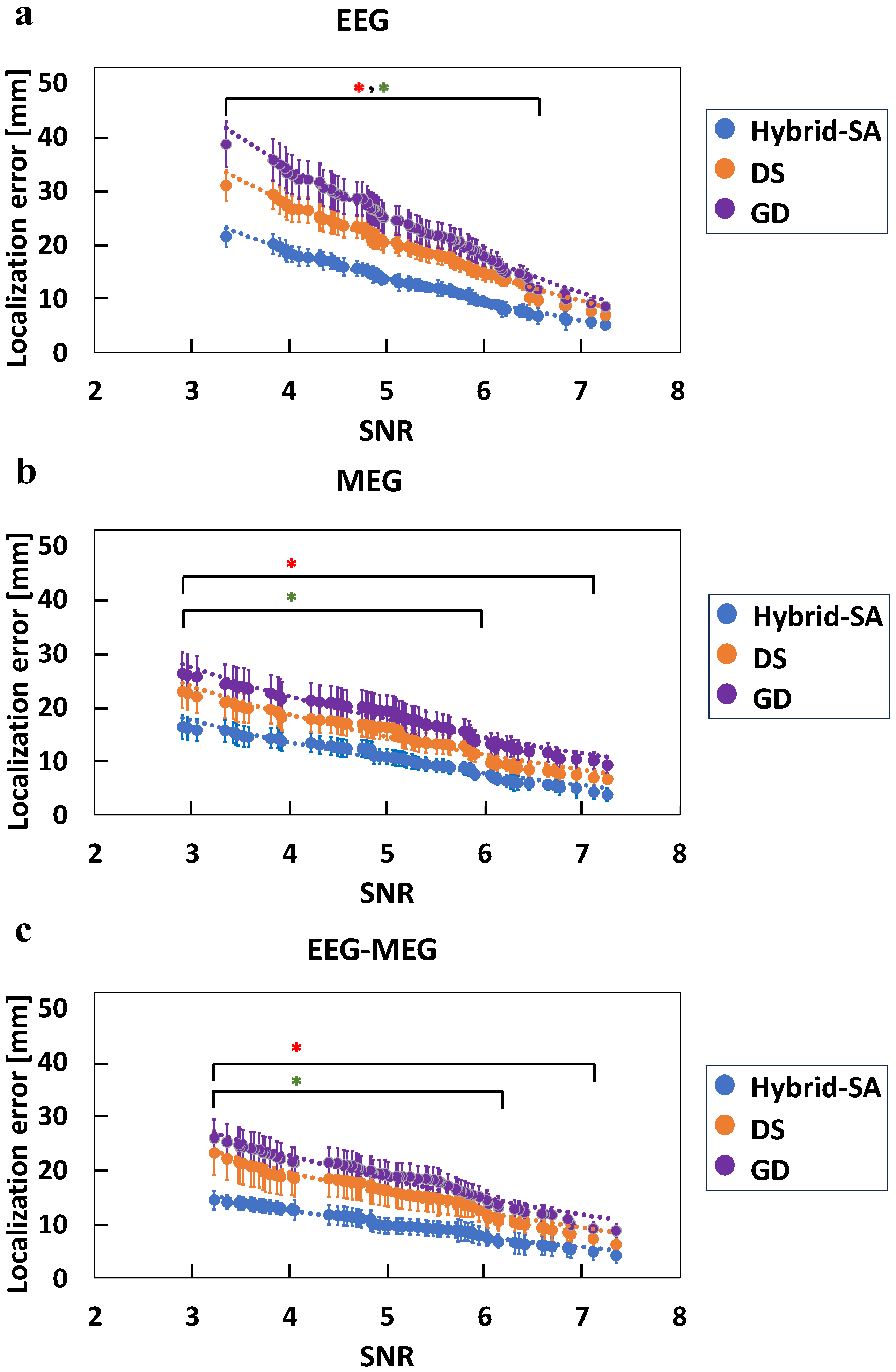
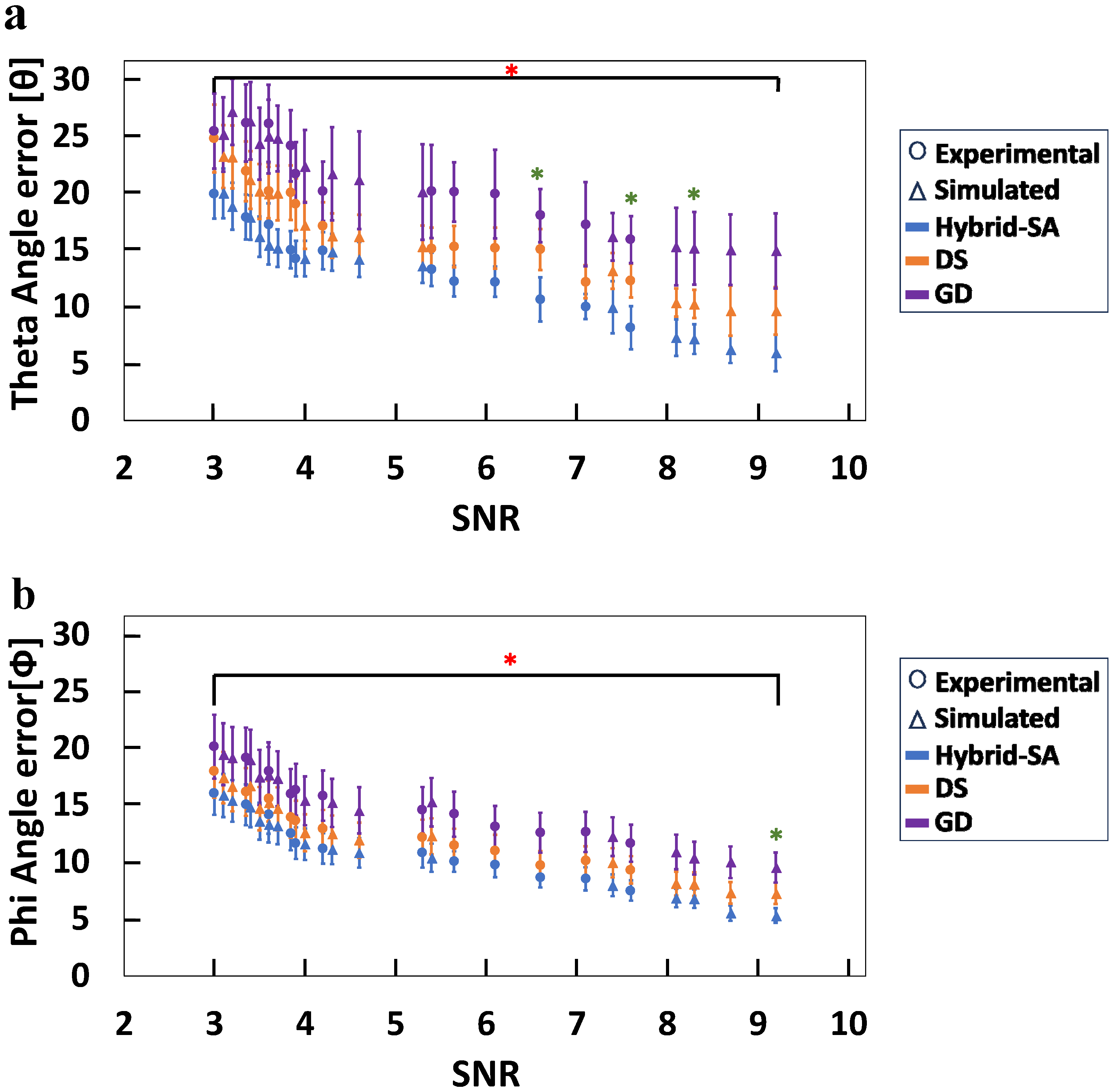
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mégevand, P.; Seeck, M. Electroencephalography, magnetoencephalography and source localization: Their value in epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Sohrabpour, A.; Brown, E.; Liu, Z. Electrophysiological Source Imaging: A Noninvasive Window to Brain Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 20, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona-Vargas, D.I.; Lopez-Arevalo, I.; Gutiérrez, D. Multicompare Tests of the Performance of Different Metaheuristics in EEG Dipole Source Localization. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 524367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazis, D.; Adler, A. MEG Source Localization via Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grech, R.; Cassar, T.; Muscat, J.; Camilleri, K.P.; Fabri, S.G.; Zervakis, M.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Sakkalis, V.; Vanrumste, B. Review on solving the inverse problem in EEG source analysis. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2008, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, D.; Singh, M.; Don, M. Spatio-temporal EEG source localization using simulated annealing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 44, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, Z.A.; Makeig, S. Effects of Forward Model Errors on EEG Source Localization. Brain Topogr. 2013, 26, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Ying, L.; Lingyue, W.; Ning, Y.; Shuo, Y. EEG Dipole Source Localization using Deep Neural Network. Int. J. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadirov, R.; Lyakhov, P.; Nagornov, N. Survey of Optimization Algorithms in Modern Neural Networks. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, H.P. The Levenberg-Marquardt Method for Nonlinear Least Squares Curve-Fitting Problems. 2013. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:5708656 (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Coffman, B.A.; Salisbury, D.F. MEG Methods: A Primer of Basic MEG Analysis. In Neuroimaging in Schizophrenia; Kubicki, M., Shenton, M.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medani, T.; Garcia-Prieto, J.; Tadel, F.; Antonakakis, M.; Erdbrügger, T.; Höltershinken, M.; Mead, W.; Schrader, S.; Joshi, A.; Engwer, C.; et al. Brainstorm-DUNEuro: An integrated and user-friendly Finite Element Method for modeling electromagnetic brain activity. Neuroimage 2023, 267, 119851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaye, D.; Chaimatanan, S.; Mongeau, M. Simulated annealing: From basics to applications. In Handbook of Metaheuristics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Baldominos, A.; Ramón-Lozano, C. Optimizing EEG energy-based seizure detection using genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Donostia, Spain, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 2338–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Luo, A.; Li, X.; Kruggel, F. A comparative study of global optimization approaches to MEG source localization. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2003, 80, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Li, Y.; Yao, D. A feasibility study of EEG dipole source localization using particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, 2–5 September 2005; Volume 1, pp. 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekihara, K.; Haneishi, H.; Ohyama, N. Details of simulated annealing algorithm to estimate parameters of multiple current dipoles using biomagnetic data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1992, 11, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, J.; Cardenas, V.A.; Fein, G. Equivalent dipole parameter estimation using simulated annealing. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Potentials Sect. 1994, 92, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Uitert, R.; Johnson, C. Can a spherical model substitute for a realistic head model in forward and inverse MEG simulations? Proc. BIOMAG 2002, 25, 52–68. [Google Scholar]
- Muravchik, C.H.; Nehorai, A. EEG/MEC error bounds for a static dipole source with a realistic head model. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffin, B.N.; Schomer, D.L.; Ives, J.R.; Blume, H. Experimental tests of EEG source localization accuracy in realistically shaped head models. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 2288–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolander, H.; Moran, J.E.; Nagesh, V.; Mason, K.M.; Bowyer, S.M.; Barkley, G.L.; Tepley, N. MEG localization errors associated with a realistic cortical model. In Proceedings of the Biomag 2002: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Biomagnetism, Jena, Germany, 10–14 August 2002; pp. 743–745. [Google Scholar]
- McNay, D.; Michielssen, E.; Rogers, R.; Taylor, S.; Akhtari, M.; Sutherling, W. Multiple source localization using genetic algorithms. J. Neurosci. Methods 1996, 64, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona-Vargas, D.; Murphy, P.; Lowery, C.L.; Eswaran, H. Genetic algorithms for dipole location of fetal magnetocardiography. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 904–907. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.S.; Mosher, J.C. Genetic algorithms for minimal source reconstructions. In Proceedings of the 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1–3 November 1993; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 335–338. [Google Scholar]
- Scherg, M.; Bast, T.; Berg, P. Multiple source analysis of interictal spikes: Goals, requirements, and clinical value. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 16, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, C.; Sanchez-Quesada, F.; Sancho, M.; Hidalgo, I.; Ortiz, T. A genetic algorithm approach for localization of deep sources in MEG. Phys. Scr. 2005, 2005, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytsar, R.; Pun, T. EEG source reconstruction using global optimization approaches: Genetic algorithms versus simulated annealing. Int. J. Tomogr. Stat. 2010, 14, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, Ü.; Vorwerk, J.; Dümpelmann, M.; Küpper, P.; Kugel, H.; Heers, M.; Wellmer, J.; Kellinghaus, C.; Haueisen, J.; Rampp, S.; et al. Combined EEG/MEG can outperform single modality EEG or MEG source reconstruction in presurgical epilepsy diagnosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.-H.; Vorwerk, J.; Wolters, C.H.; Knösche, T.R. Influence of the head model on EEG and MEG source connectivity analyses. Neuroimage 2015, 110, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmutoglu, M.A.; Rupp, A.; Baumgärtner, U. Simultaneous EEG/MEG yields complementary information of nociceptive evoked responses. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 143, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittau, F.; Grova, C.; Moeller, F.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. Patterns of altered functional connectivity in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneef, Z.; Lenartowicz, A.; Yeh, H.J.; Levin, H.S.; Engel, J., Jr.; Stern, J.M. Functional connectivity of hippocampal networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chang, F.; Peng, D.; Xie, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, W. The morphological characteristics of hippocampus and thalamus in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostergard, T.A.; Miller, J.P. Surgery for epilepsy in the primary motor cortex: A critical review. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 91, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, S.; Rollo, M.J.; Kim, K.; Johnson, J.A.; Kalamangalam, G.P.; Aazhang, B.; Tandon, N. The interictal mesial temporal lobe epilepsy network. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrabpour, A.; He, B. Exploring the extent of source imaging: Recent advances in noninvasive electromagnetic brain imaging. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 18, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, R.; Emura, T.; Nakata, O.; Nakashima, T.; Asai, M.; Kagitani-Shimono, K.; Kishima, H.; Hirata, M. Fully-automated spike detection and dipole analysis of epileptic MEG using deep learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 2879–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razorenova, A.; Yavich, N.; Malovichko, M.; Fedorov, M.; Koshev, N.; Dylov, D.V. Deep learning for non-invasive cortical potential imaging. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Clinical Neuroimaging, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.; Kashyap, R.; Rahamatkar, S. Chapter 10—A study of deep learning approach for the classification of electroencephalogram (EEG) brain signals. In Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for EDGE Computing; Pandey, R., Khatri, S.K., Singh, N.K., Verma, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Wagner, M.; Wischmann, H.-A.; Köhler, T.; Theißen, A.; Drenckhahn, R.; Buchner, H. Improving source reconstructions by combining bioelectric and biomagnetic data. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 107, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnazaee, M.F.; Wittevrongel, B.; Khachatryan, E.; Libert, A.; Carrette, E.; Dauwe, I.; Meurs, A.; Boon, P.; Van Roost, D.; Van Hulle, M.M. Localization of deep brain activity with scalp and subdural EEG. NeuroImage 2020, 223, 117344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, T.J.; Kynor, D.B.; Bieszczad, J.; Audette, W.E.; Kobylarz, E.J.; Diamond, S.G. Creation of a human head phantom for testing of electroencephalography equipment and techniques. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2628–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobashsher, A.; Abbosh, A. Three-dimensional human head phantom with realistic electrical properties and anatomy. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunold, A.; Funke, M.; Eichardt, R.; Stenroos, M.; Haueisen, J. EEG and MEG: Sensitivity to epileptic spike activity as function of source orientation and depth. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, C.H.; Köstler, H.; Möller, C.; Härdtlein, J.; Grasedyck, L.; Hackbusch, W. Numerical mathematics of the subtraction method for the modeling of a current dipole in EEG source reconstruction using finite element head models. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2008, 30, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Park, B.-K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Reed, M.P.; Rupp, J.D.; Hoff, C.N.; Hu, J. A statistical skull geometry model for children 0–3 years old. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thigpen, N.N.; Kappenman, E.S.; Keil, A. Assessing the internal consistency of the event-related potential: An example analysis. Psychophysiology 2017, 54, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Mouraux, A.; Hu, Y.; Iannetti, G.D. A novel approach for enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio and detecting automatically event-related potentials (ERPs) in single trials. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FieldTrip Toolbox. Creating a BEM Volume Conduction Model of the Head for Source Reconstruction of EEG Data—FieldTrip Toolbox. Available online: https://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_bem/ (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Vorwerk, J.; Oostenveld, R.; Piastra, M.C.; Magyari, L.; Wolters, C.H. The FieldTrip-SimBio pipeline for EEG forward solutions. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatoi, M.A.; Kamel, N.; Faye, I.; Malik, A.S.; Bornot, J.M.; Begum, T. BEM based solution of forward problem for brain source estimation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications (ICSIPA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Gramfort, A.; Papadopoulo, T.; Olivi, E.; Clerc, M. Forward field computation with OpenMEEG. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 923703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, F.; Roehri, N.; Giusiano, B.; Lagarde, S.; Carron, R.; Scavarda, D.; Bartolomei, F. The ictal signature of thalamus and basal ganglia in focal epilepsy: A SEEG study. Neurology 2021, 96, e280–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikara, R.K.; Jahromi, S.; Tamilia, E.; Madsen, J.R.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Pearl, P.L.; Papadelis, C. Electromagnetic source imaging predicts surgical outcome in children with focal cortical dysplasia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2023, 153, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Moreno, A.; Aurtenetxe, S.; Lopez-Garcia, M.-E.; del Pozo, F.; Maestu, F.; Nevado, A. Signal-to-noise ratio of the MEG signal after preprocessing. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 222, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Davey, C.; Poulsen, C.; Luu, P.; Turovets, S.; Anderson, E.; Li, K.; Tucker, D. EEG source localization: Sensor density and head surface coverage. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 256, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.; Jones, R.; Bones, P.J.; Carroll, G. Enhancement of deep epileptiform activity in the EEG via 3-D adaptive spatial filtering. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 46, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cleophas, T.; Zwinderman, A. Non-parametric Tests for Three or More Samples (Friedman and Kruskal-Wallis). In Clinical Data Analysis on a Pocket Calculator; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.H.; Lim, K.H. Review of second-order optimization techniques in artificial neural networks backpropagation. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Escalona-Vargas, D.I.; López-Arévalo, I.; Gutiérrez, D. On the performance of metahuristic algorithms in the solution of the EEG inverse problem. In Proceedings of the 2011 Third World Congress on Nature and Biologically Inspired Computing, Salamanca, Spain, 19–21 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran, C.; Ramachandran, M.; Ramu, K.; Prasanth, V.; Mathivanan, G. Application of simulated annealing in various field. Mater. Charact. 2022, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, A.; Barnes, G.R. A quantitative assessment of the sensitivity of Whole-Head MEG to activity in the adult human cortex. NeuroImage 2002, 16, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizenga, H.; Van Zuijen, T.; Heslenfeld, D.J.; Molenaar, P. Simultaneous MEG and EEG source analysis. Phys. Med. Biol. 2001, 46, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, C.-H.; Jung, H.-K.; Fujimaki, N. Anatomically constrained dipole adjustment (ANACONDA) for accurate MEG/EEG focal source localizations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramantani, G.; Boor, R.; Paetau, R.; Ille, N.; Feneberg, R.; Rupp, A.; Boppel, T.; Scherg, M.; Rating, D.; Bast, T. MEG versus EEG: Influence of background activity on interictal spike detection. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 23, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rere, L.M.R.; Fanany, M.I.; Arymurthy, A.M. Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Deep Learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 72, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
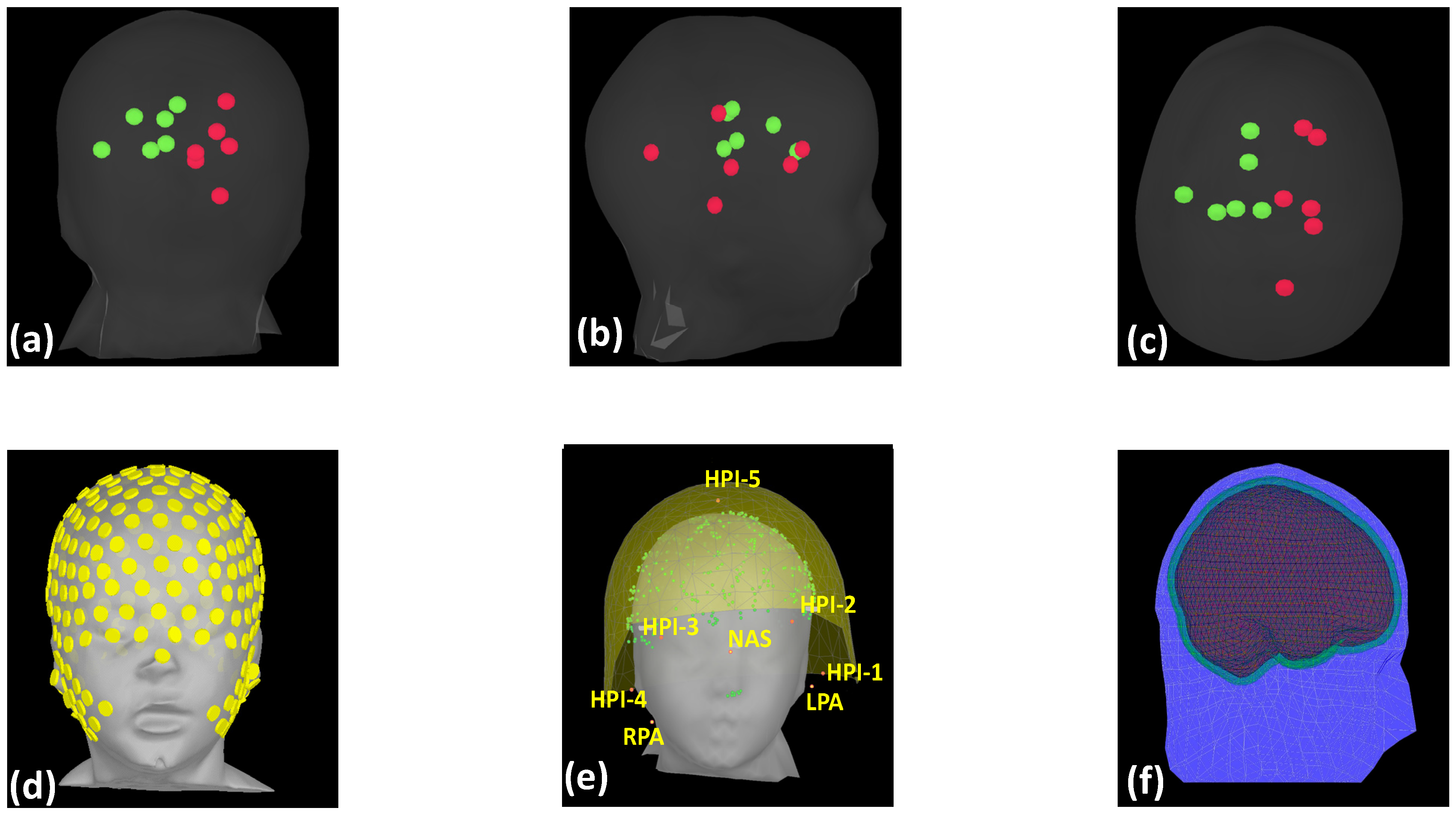
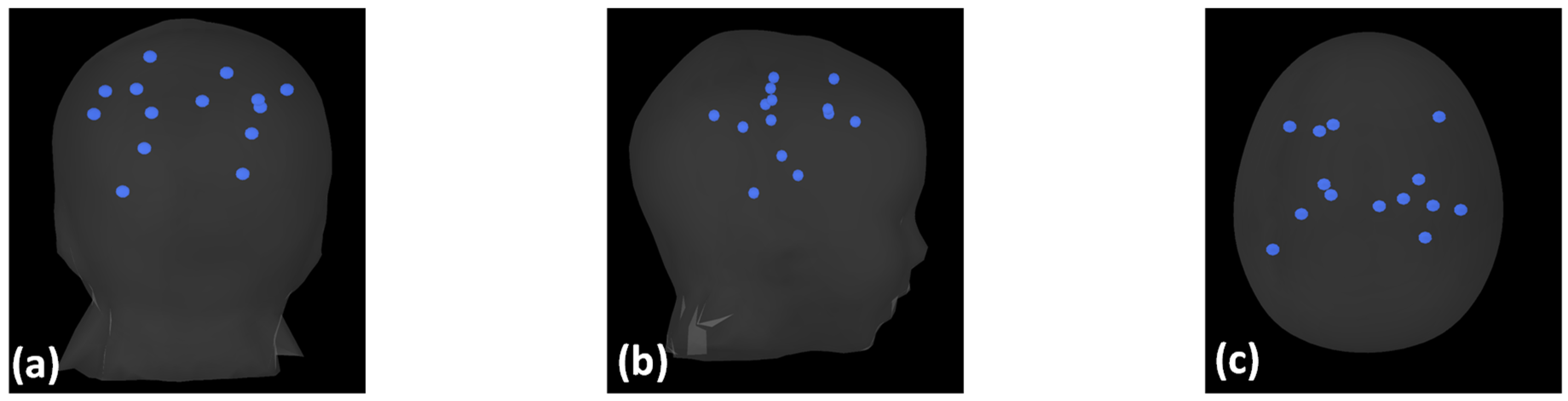
| Tissue Type | Tissue Layer Thickness in mm | Conductivity in S/m |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | 2.76 mm | 0.330 |
| Skull | 4.16 mm | 0.004 |
| Scalp | 3.90 mm | 0.330 |
| Source | [x y z] Location in mm in SCS System | Theta (θ) Value in Degrees | Phi (φ) Value in Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right 1 | [8.62, −21.4, 0.63] | 112 | 36 |
| Right 2 | [−36.76, −5.14, 45.82] | 68 | 186 |
| Right 3 | [−0.27, −18.41, 12.01] | 31 | 107 |
| Right 4 | [10.66, −5.30, 28.83] | 47 | 78 |
| Right 5 | [56.09, −16.60, 33.42] | 48 | 112 |
| Right 6 | [47.54, −23.29, 27.32] | 135 | 84 |
| Left 1 | [13.39, 27.66, 53.16] | 112 | 26 |
| Left 2 | [7.68, 18.73, 35.37] | 32 | 121 |
| Left 3 | [16.92, 4.60, 59.22] | 36 | 48 |
| Left 4 | [15.76, 44.49, 33.32] | 68 | 53 |
| Left 5 | [40.31, 11.13, 44.68] | 73 | 191 |
| Left 6 | [52.03, 10.55, 27.39] | 116 | 118 |
| Source | [x, y, z] Location in mm in SCS System | Theta (θ) Value in Degrees | Phi (φ) Value in Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | [50.68, 26.54, 65.3] | 108 | 78 |
| S2 | [55.24, 20.18, 82.11] | 56 | 113 |
| S3 | [53.44, 41.38, 63.12] | 24 | 57 |
| S4 | [−15.87, 51.26, 69.33] | 124 | 63 |
| S5 | [5.30, −43.02, 78.15] | 146 | 119 |
| S6 | [12.60, −14.18, 85.23] | 171 | 138 |
| S7 | [7.65, −29.41, 71.78] | 21 | 54 |
| S8 | [57.01, −33.96, 54.12] | 59 | 78 |
| S9 | [14.14, 21.36, 62.13] | 112 | 91 |
| S10 | [1.21, 34.98, 21.68] | 74 | 162 |
| S11 | [4.41, 41.26, 44.73] | 82 | 49 |
| S12 | [−11.27, −25.57, 58.12] | 61 | 36 |
| S13 | [29.12, −23.44, 45.47] | 38 | 87 |
| S14 | [7.77, −2.51, 70.69] | 45 | 76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bastola, S.; Jahromi, S.; Chikara, R.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Ottensmeyer, M.P.; De Novi, G.; Papadelis, C.; Alexandrakis, G. Improved Dipole Source Localization from Simultaneous MEG-EEG Data by Combining a Global Optimization Algorithm with a Local Parameter Search: A Brain Phantom Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090897
Bastola S, Jahromi S, Chikara R, Stufflebeam SM, Ottensmeyer MP, De Novi G, Papadelis C, Alexandrakis G. Improved Dipole Source Localization from Simultaneous MEG-EEG Data by Combining a Global Optimization Algorithm with a Local Parameter Search: A Brain Phantom Study. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(9):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090897
Chicago/Turabian StyleBastola, Subrat, Saeed Jahromi, Rupesh Chikara, Steven M. Stufflebeam, Mark P. Ottensmeyer, Gianluca De Novi, Christos Papadelis, and George Alexandrakis. 2024. "Improved Dipole Source Localization from Simultaneous MEG-EEG Data by Combining a Global Optimization Algorithm with a Local Parameter Search: A Brain Phantom Study" Bioengineering 11, no. 9: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090897
APA StyleBastola, S., Jahromi, S., Chikara, R., Stufflebeam, S. M., Ottensmeyer, M. P., De Novi, G., Papadelis, C., & Alexandrakis, G. (2024). Improved Dipole Source Localization from Simultaneous MEG-EEG Data by Combining a Global Optimization Algorithm with a Local Parameter Search: A Brain Phantom Study. Bioengineering, 11(9), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090897









