Variability in Alignment and Bone Resections in Robotically Balanced Total Knee Arthroplasties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analyses
2.4. Patient Characteristics
3. Results
3.1. Target Alignments and Resection Magnitudes by Demographics
3.2. Target Alignments Compared by Preoperative Alignment Category
3.3. Target Resection Magnitudes Compared by Preoperative Alignment Category
3.4. Metric Variability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonios, J.K.; Korber, S.; Sivasundaram, L.; Mayfield, C.; Kang, H.P.; Oakes, D.A.; Heckmann, N.D. Trends in computer navigation and robotic assistance for total knee arthroplasty in the United States: An analysis of patient and hospital factors. Arthroplast. Today 2019, 5, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendich, I.; Kapadia, M.; Alpaugh, K.; Diane, A.; Vigdorchik, J.; Westrich, G. Trends of Utilization and 90-Day Complication Rates for Computer-Assisted Navigation and Robotic Assistance for Total Knee Arthroplasty in the United States From 2010 to 2018. Arthroplast. Today 2021, 11, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Mart, J.-P.; Goh, E.L. The current state of robotics in total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmakers, D.A.; Dorling, I.M.; Heymans, M.J.; Kort, N.P.; Boonen, B.; Van Rhijn, L.W.; Schotanus, M.G. Computer-based pre- and intra-operative planning modalities for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A comprehensive review. J. Orthop. Exp. Innov. 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, B.; Konan, S.; Huq, S.S.; Tahmassebi, J.; Haddad, F.S. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty has a learning curve of seven cases for integration into the surgical workflow but no learning curve effect for accuracy of implant positioning. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sires, J.D.; Craik, J.D.; Wilson, C.J. Accuracy of Bone Resection in MAKO Total Knee Robotic-Assisted Surgery. J. Knee Surg. 2021, 34, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sires, J.D.; Wilson, C.J. CT Validation of Intraoperative Implant Position and Knee Alignment as Determined by the MAKO Total Knee Arthroplasty System. J. Knee Surg. 2021, 34, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savov, P.; Tuecking, L.R.; Windhagen, H.; Ehmig, J.; Ettinger, M. Imageless robotic handpiece-assisted total knee arthroplasty: A learning curve analysis of surgical time and alignment accuracy. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2021, 141, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diquattro, E.; Prill, R.; Salzmann, M.; Traina, F.; Becker, R. High three-dimensional accuracy of component placement and lower limb alignment using a robotic arm-assisted system and gap-balancing instrument in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2024, 32, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicat, C.S.; Chow, J.C.; Kaper, B.; Mitra, R.; Xie, J.; Schwarzkopf, R. Component placement accuracy in two generations of handheld robotics-assisted knee arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2021, 141, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambianchi, F.; Matveitchouk, N.; Pavesi, M.; Clemenza, S.; Cuoghi Costantini, R.; Marcovigi, A.; Seracchioli, S.; Catani, F. Small deviations between planned and performed bone cuts using a CT-based robotic-arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty system. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2024, 32, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimani, S.J.; Bhimani, R.; Smith, A.; Eccles, C.; Smith, L.; Malkani, A. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty demonstrates decreased postoperative pain and opioid usage compared to conventional total knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. Open 2020, 1, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, B.; Konan, S.; Tahmassebi, J.; Pietrzak, J.R.T.; Haddad, F.S. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study. Bone Joint J. 2018, 100-b, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, R.C.; Sodhi, N.; Khlopas, A.; Sultan, A.A.; Harwin, S.F.; Malkani, A.L.; Mont, M.A. Patient Satisfaction Outcomes after Robotic Arm-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Short-Term Evaluation. J. Knee Surg. 2017, 30, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziri, Q.; Cusson, B.C.; Chaudhri, M.; Shah, N.V.; Sastry, A. Making the transition from traditional to robotic-arm assisted TKA: What to expect? A single-surgeon comparative-analysis of the first-40 consecutive cases. J. Orthop. 2019, 16, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, C.L.; Jimenez, C.; Erickson, J.; Anderson, M.B.; Pelt, C.E. Lessons Learned from Selective Soft-Tissue Release for Gap Balancing in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Joint Surg. 2013, 95, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigdorchik, J.M.; Wakelin, E.A.; Koenig, J.A.; Ponder, C.E.; Plaskos, C.; DeClaire, J.H.; Lawrence, J.M.; Keggi, J.M. Impact of Component Alignment and Soft Tissue Release on 2-Year Outcomes in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 2035–2040.e2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampp, E.L.; Sodhi, N.; Scholl, L.; Deren, M.E.; Yenna, Z.; Westrich, G.; Mont, M.A. Less iatrogenic soft-tissue damage utilizing robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty when compared with a manual approach. Bone Joint Res. 2019, 8, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, B.; Konan, S.; Pietrzak, J.R.T.; Haddad, F.S. Iatrogenic Bone and Soft Tissue Trauma in Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared With Conventional Jig-Based Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Cohort Study and Validation of a New Classification System. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopas, A.; Chughtai, M.; Hampp, E.L.; Scholl, L.Y.; Prieto, M.; Chang, T.-C.; Chang, T.C.; Abbasi, A.; Bhowmik-Stoker, M.; Otto, J.; et al. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Demonstrated Soft Tissue Protection. Surg. Technol. Int. 2017, 30, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karasavvidis, T.; Pagan Moldenhauer, C.A.; Haddad, F.S.; Hirschmann, M.T.; Pagnano, M.W.; Vigdorchik, J.M. Current Concepts in Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S29–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatrov, J.; Battelier, C.; Sappey-Marinier, E.; Gunst, S.; Servien, E.; Lustig, S. Functional Alignment Philosophy in Total Knee Arthroplasty—Rationale and technique for the varus morphotype using a CT based robotic platform and individualized planning. SICOT J. 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risitano, S.; Cacciola, G.; Sabatini, L.; Capella, M.; Bosco, F.; Giustra, F.; Massè, A.; Vaishya, R. Restricted kinematic alignment in primary total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review of radiographic and clinical data. J. Orthop. 2022, 33, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnock de Grave, P.; Luyckx, T.; Claeys, K.; Tampere, T.; Kellens, J.; Müller, J.; Gunst, P. Higher satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty using restricted inverse kinematic alignment compared to adjusted mechanical alignment. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pailhé, R. Total knee arthroplasty: Latest robotics implantation techniques. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2021, 107, 102780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M. The MAKO robotic-arm knee arthroplasty system. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2021, 141, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calliess, T.; Ettinger, M.; Savov, P.; Karkosch, R.; Windhagen, H. Individualized alignment in total knee arthroplasty using image-based robotic assistance. Orthopäde 2018, 47, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.C.; Conditt, M.A.; Verstraete, M.A. Achieving a Balanced Knee in Robotic TKA. Sensors 2021, 21, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Mitterer, J.A.; Vallant, S.M.; Simon, S.; Hanak-Hammerl, F.; Schwarz, G.M.; Klasan, A.; Hofstaetter, J.G. Gender-specific distribution of knee morphology according to CPAK and functional phenotype classification: Analysis of 8739 osteoarthritic knees prior to total knee arthroplasty using artificial intelligence. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 4220–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.W.; Esposito, C.I.; Wood, D. Individualized Functional Knee Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Robotic-assisted Technique. Tech. Orthop. 2021, 37, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Graaf, V.A.; Chen, D.B.; Allom, R.J.; Wood, J.A.; MacDessi, S.J. Functional alignment in total knee arthroplasty best achieves balanced gaps and minimal bone resections: An analysis comparing mechanical, kinematic and functional alignment strategies. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 5118–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowalla, C.; Langer, S.; Lenze, U.; Lazic, I.; Hirschmann, M.T.; Hinterwimmer, F.; Von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Pohlig, F. Postoperative full leg radiographs exhibit less residual coronal varus deformity compared to intraoperative measurements in robotic arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty with the MAKO™ system. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 3912–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
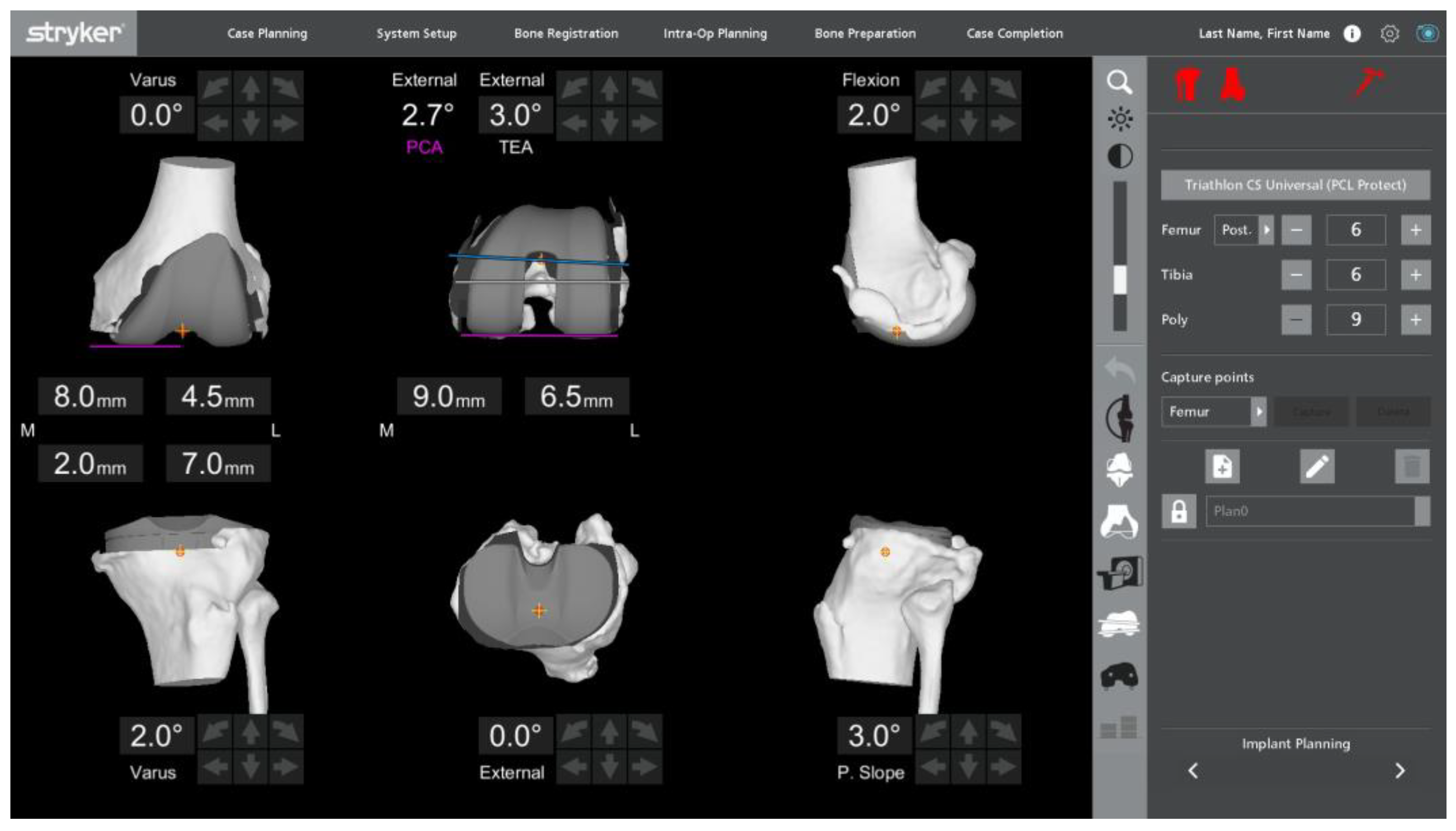

| Varus (n = 191) | Neutral (n = 189) | Valgus (n = 104) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | Range | M ± SD | Range | M ± SD | Range | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 67.9 ± 8.9 | 45–94 | 67.7 ± 8.9 | 42–88 | 67 ± 8.6 | 45–85 | 0.716 |
| Male—no. (%) | 71 (37.2) | - | 52 (27.5) | - | 17 (16.3) | - | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.4 ± 5.5 | 18.2–46.2 | 32.7 ± 5.3 | 20.8–46.1 | 31.7 ± 5.8 | 20.5–47.5 | 0.064 |
| Preop Dx | 0.585 | ||||||
| OA | 189 (99.0) | - | 187 (98.9) | - | 103 (99.0) | - | |
| Trauma | 2 (1.0) | - | 1 (0.5) | - | - | - | |
| RA | - | - | 1 (0.5) | - | 1 (1.0) | - | |
| Race—no. (%) | 0.031 | ||||||
| White | 96 (50.3) | - | 99 (52.4) | - | 52 (50.0) | - | |
| Black | 29 (15.2) | - | 35 (18.5) | - | 18 (17.3) | - | |
| Asian | 20 (10.5) | - | 19 (10.1) | - | 1 (1.0) | - | |
| Other | 46 (24.1) | - | 36 (19.0) | - | 33 (31.7) | - | |
| Smoking—no. (%) | 0.069 | ||||||
| Current | 6 (3.1) | - | 8 (4.2) | - | 2 (1.9) | - | |
| Former | 38 (19.9) | - | 58 (30.7) | - | 34 (32.7) | - | |
| Never | 144 (75.4) | - | 120 (63.5) | - | 64 (61.5) | - | |
| N/A | 3 (1.6) | - | 3 (1.6) | - | 4 (3.8) | - | |
| ASA Class—no. (%) | 0.751 | ||||||
| 1 | 6 (3.1) | - | 5 (2.6) | - | 3 (2.9) | - | |
| 2 | 109 (57.1) | - | 107 (56.6) | - | 67 (64.4) | - | |
| 3 | 75 (39.3) | - | 76 (40.2) | - | 34 (32.7) | - | |
| 4 | 1 (0.5) | - | - | - | - | - | |
| N/A | - | - | 1 (0.5) | - | - | - | |
| Varus (n = 191) | Neutral (n = 189) | Valgus (n = 104) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | Range | M ± SD | Range | M ± SD | Range | p-Value | |
| Preoperative aHKA (degrees) 1 | * 4.9 ± 2.2 | 2.1–12.8 | 0.2 ± 1.1 | −2.0–2.0 | * −4.7 ± 2.1 | −12.5–−2.1 | <0.001 |
| Planned coronal alignment (degrees) 1 | |||||||
| Limb | * 3.0 ± 1.7 | −2.0–6.2 | 0.9 ± 1.4 | −4.0–4.4 | −1.3 ± 1.4 | −4.5–2.2 | <0.001 |
| Distal femur | 0.8 ± 1.2 | −3.5–4 | −0.3 ± 1.2 | −4.5–2.5 | −1.4 ± 1.2 | −4.5–2.0 | <0.001 |
| Proximal tibia | 2.2 ± 1.1 | −1.0–5.1 | 1.2 ± 1.2 | −1.0–4.0 | 0.1 ± 1.0 | −2.0–3.5 | <0.001 |
| Planned transverse rotation (degrees) 2 | |||||||
| Femoral TEA | * 2.4 ± 1.8 | −3.0–6.0 | * 2.1 ± 1.8 | −3.9–6.5 | * 0.5 ± 2.0 | −5.2–5.0 | <0.001 |
| Femoral PCA | * 5.0 ± 2.0 | −0.8–9.5 | * 4.8 ± 2.1 | −0.6–9.9 | * 3.7 ± 2.0 | −0.3–10.0 | <0.001 |
| Planned sagittal alignment (degrees) | |||||||
| Femoral flexion 3 | 3.9 ± 1.4 | 0.0–7.5 | 4 ± 1.5 | 0.5–8.0 | 4.1 ± 1.5 | 0.0–8.0 | 0.614 |
| Tibial slope 4 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 2.0–5.5 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 2.0–5.8 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 2.0–5.5 | 0.357 |
| Distal femur resection (mm) | |||||||
| Lateral | 5.5 ± 1.5 | 0.5–9.5 | 4.6 ± 1.5 | 1.0–8.5 | 3.4 ± 1.4 | 0.5–7.0 | <0.001 |
| Medial | * 7.1 ± 1.7 | 1.5–11.0 | 7.3 ± 1.2 | 4.0–10.0 | 7.3 ± 1.2 | 4.5–11.0 | 0.431 |
| Posterior femur resection (mm) | |||||||
| Lateral | * 5.8 ± 1.7 | 0.5–10.0 | * 5.6 ± 1.8 | 1.5–11.5 | * 5.7 ± 1.7 | 1.5–9.5 | 0.429 |
| Medial | 10.0 ± 1.5 | 6.0–13.5 | 9.5 ± 1.5 | 4.0–14.5 | 8.6 ± 1.4 | 5.5–12.5 | <0.001 |
| Tibia resection (mm) | |||||||
| Lateral | 6.3 ± 1.2 | 2.0–10.0 | 6.3 ± 1.2 | 2.5–10.0 | 5.6 ± 1.5 | 2.0–10.0 | <0.001 |
| Medial | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 0.5–8.0 | 4.6 ± 1.3 | 1.0–9.0 | 4.9 ± 1.4 | 1.0–7.5 | <0.001 |
| Sum of extension resections (mm) | |||||||
| Lateral | * 11.9 ± 1.9 | 6.5–17.5 | * 10.8 ± 1.8 | 6.0–15.5 | * 9.0 ± 1.8 | 4.5–14.0 | <0.001 |
| Medial | * 10.9 ± 2.2 | 3.5–17.5 | * 11.9 ± 1.7 | 7.0–16 | 12.2 ± 1.5 | 8.0–16.5 | <0.001 |
| Sum of flexion resections (mm) | |||||||
| Lateral | * 12.1 ± 1.9 | 5.5–17.5 | * 11.9 ± 1.9 | 6.0–17.0 | * 11.3 ± 1.9 | 6.5–16.0 | 0.001 |
| Medial | * 13.8 ± 1.7 | 8.0–17.0 | * 14.0 ± 1.6 | 8.5–19.0 | * 13.5 ± 1.6 | 9.5–18.0 | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hepinstall, M.S.; Di Gangi, C.; Oakley, C.; Sybert, M.; Meere, P.A.; Meftah, M. Variability in Alignment and Bone Resections in Robotically Balanced Total Knee Arthroplasties. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080845
Hepinstall MS, Di Gangi C, Oakley C, Sybert M, Meere PA, Meftah M. Variability in Alignment and Bone Resections in Robotically Balanced Total Knee Arthroplasties. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080845
Chicago/Turabian StyleHepinstall, Matthew S., Catherine Di Gangi, Christian Oakley, Michael Sybert, Patrick A. Meere, and Morteza Meftah. 2024. "Variability in Alignment and Bone Resections in Robotically Balanced Total Knee Arthroplasties" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080845
APA StyleHepinstall, M. S., Di Gangi, C., Oakley, C., Sybert, M., Meere, P. A., & Meftah, M. (2024). Variability in Alignment and Bone Resections in Robotically Balanced Total Knee Arthroplasties. Bioengineering, 11(8), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080845







