An Interpretable System for Screening the Severity Level of Retinopathy in Premature Infants Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. DATA Preparation and Preprocessing
2.2. Disease Classification Criteria
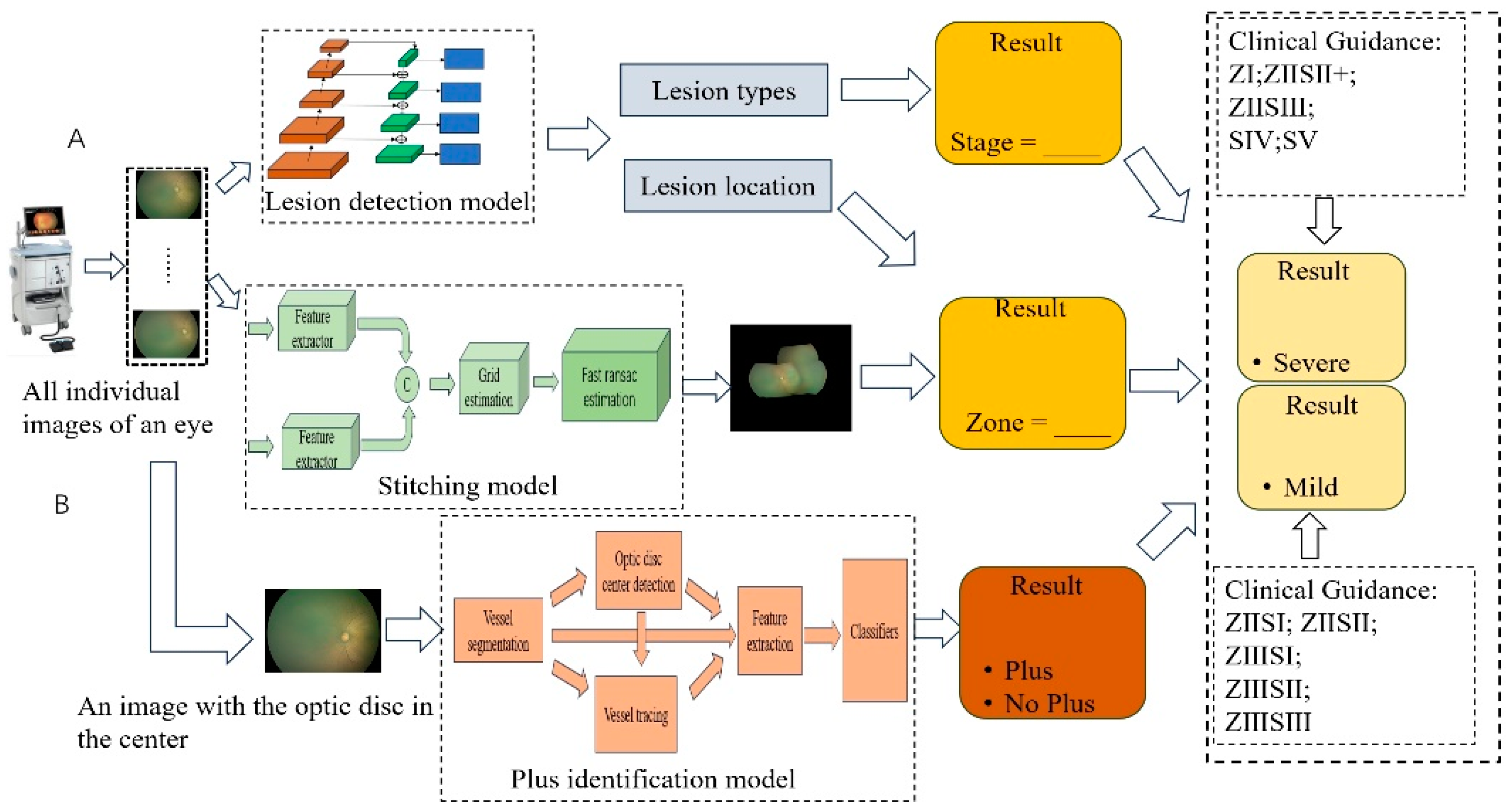
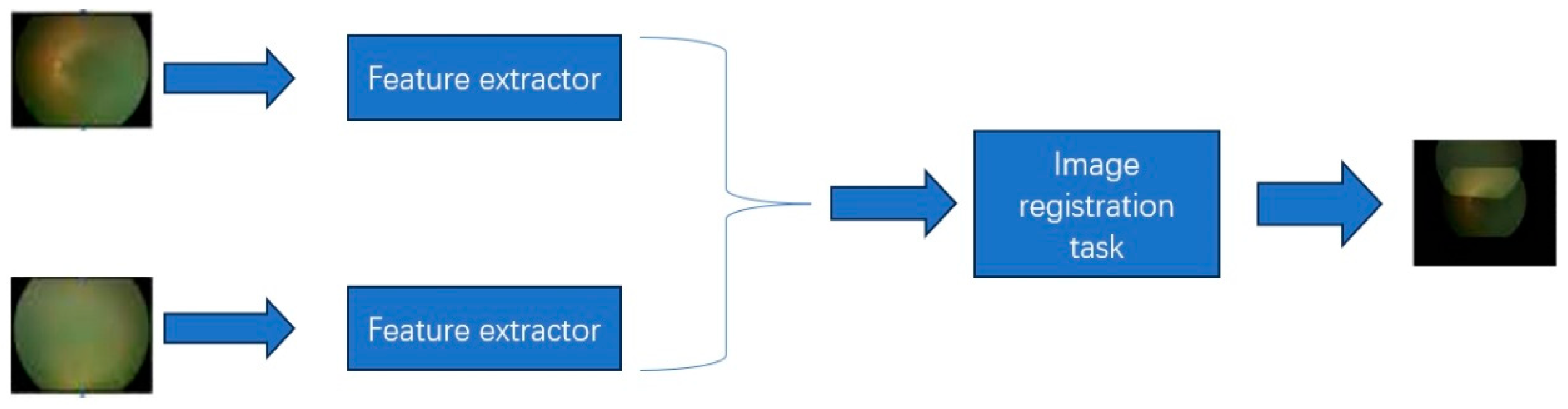
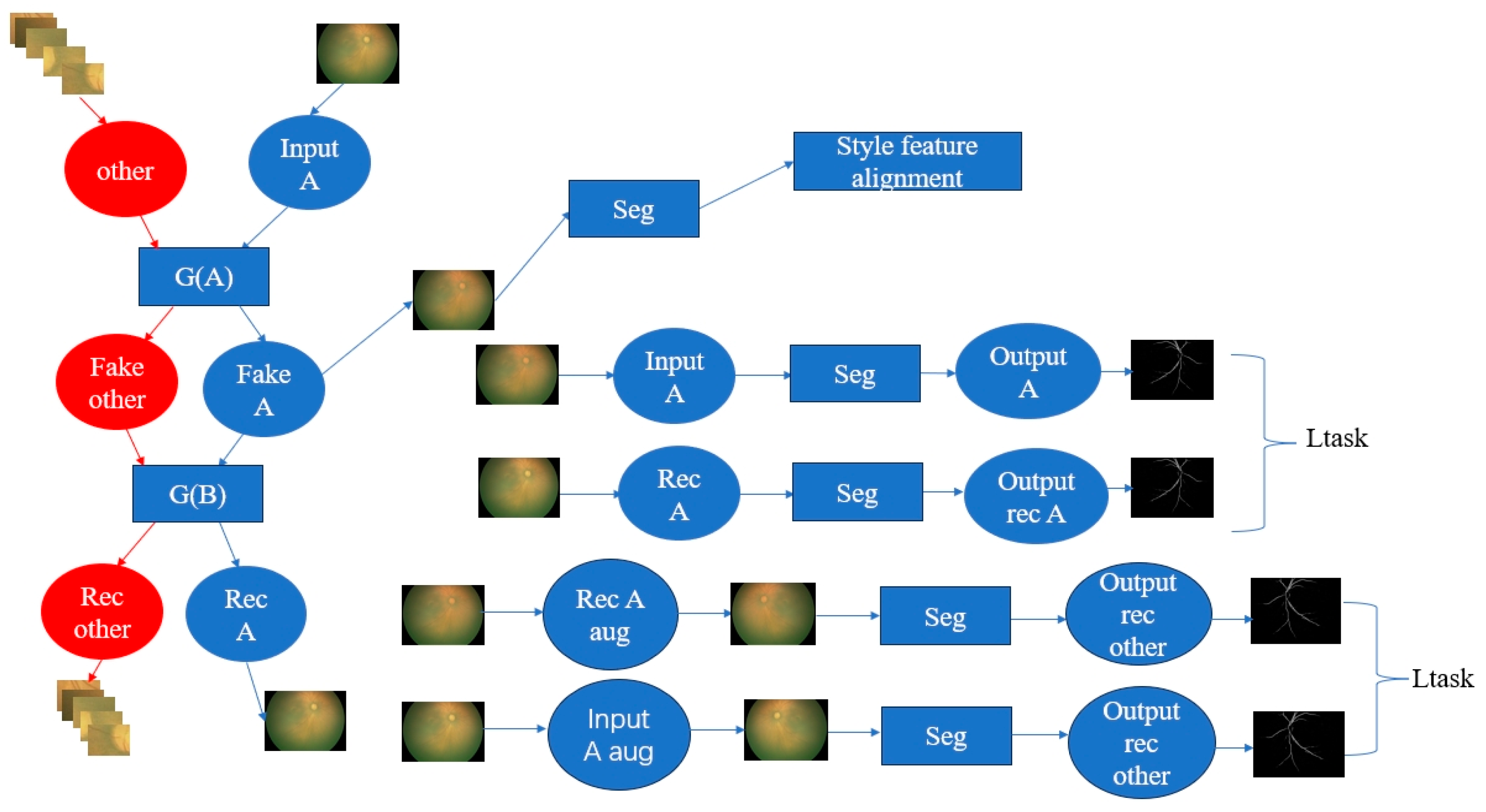
2.3. The Interpretable ROP Assessment System
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
2.5. Experiments Setting
3. Results
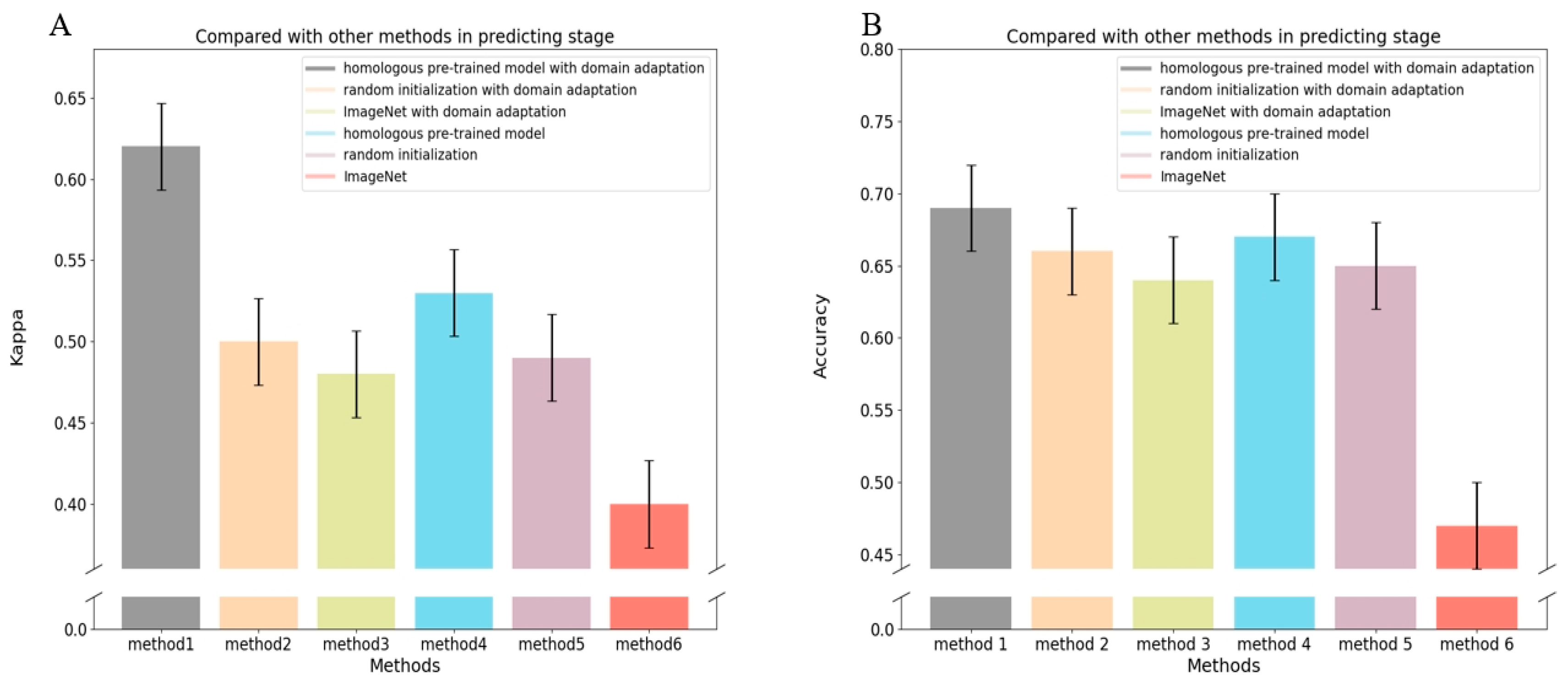
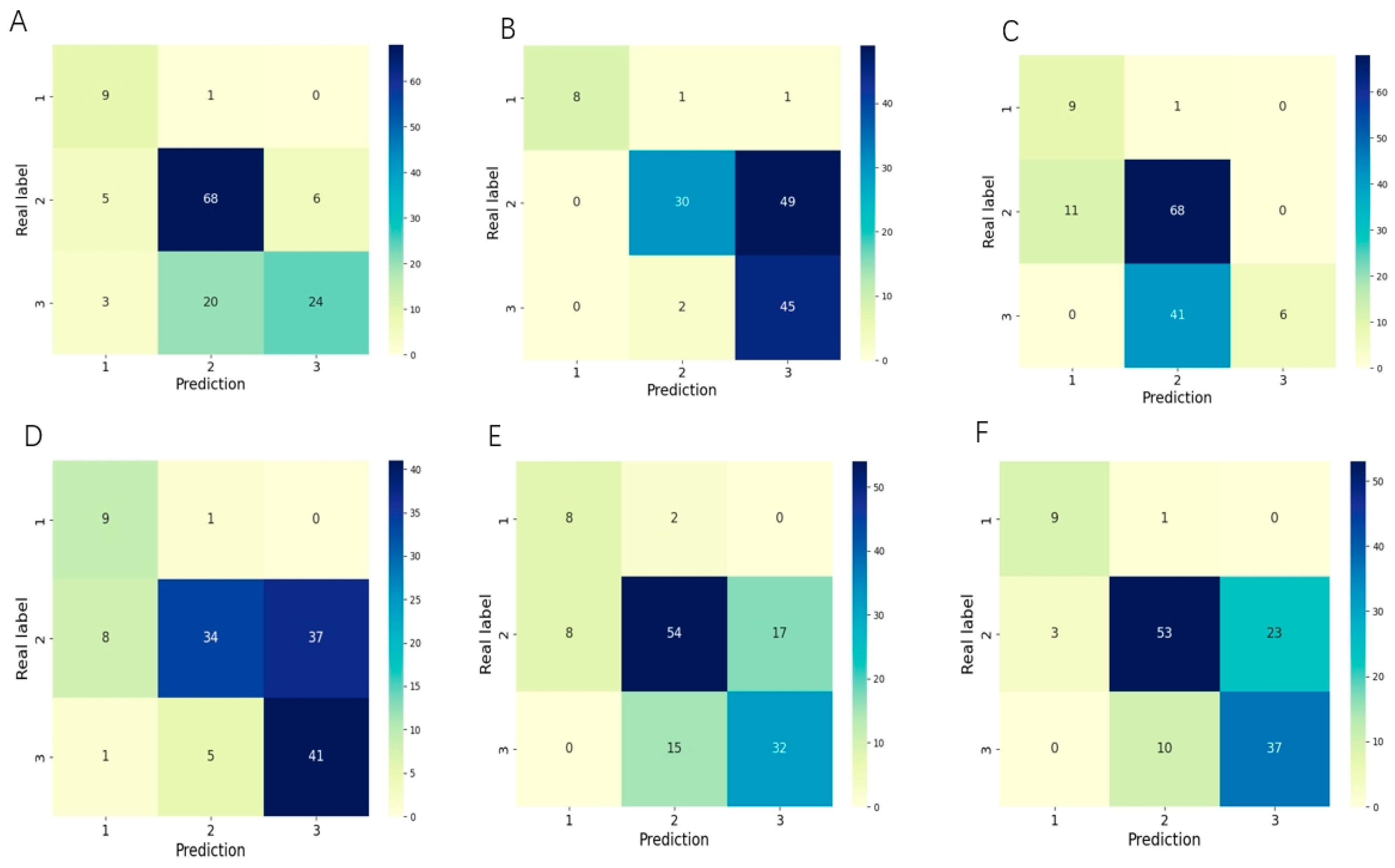
3.1. Evaluation of the Performance for Classifying the Stage of ROP
3.2. Evaluation of the Performance for Classifying the Zone of ROP
3.3. Evaluation of the Performance of the ROP Plus Disease Prediction
3.4. Evaluation of the Performance of the Severity of ROP
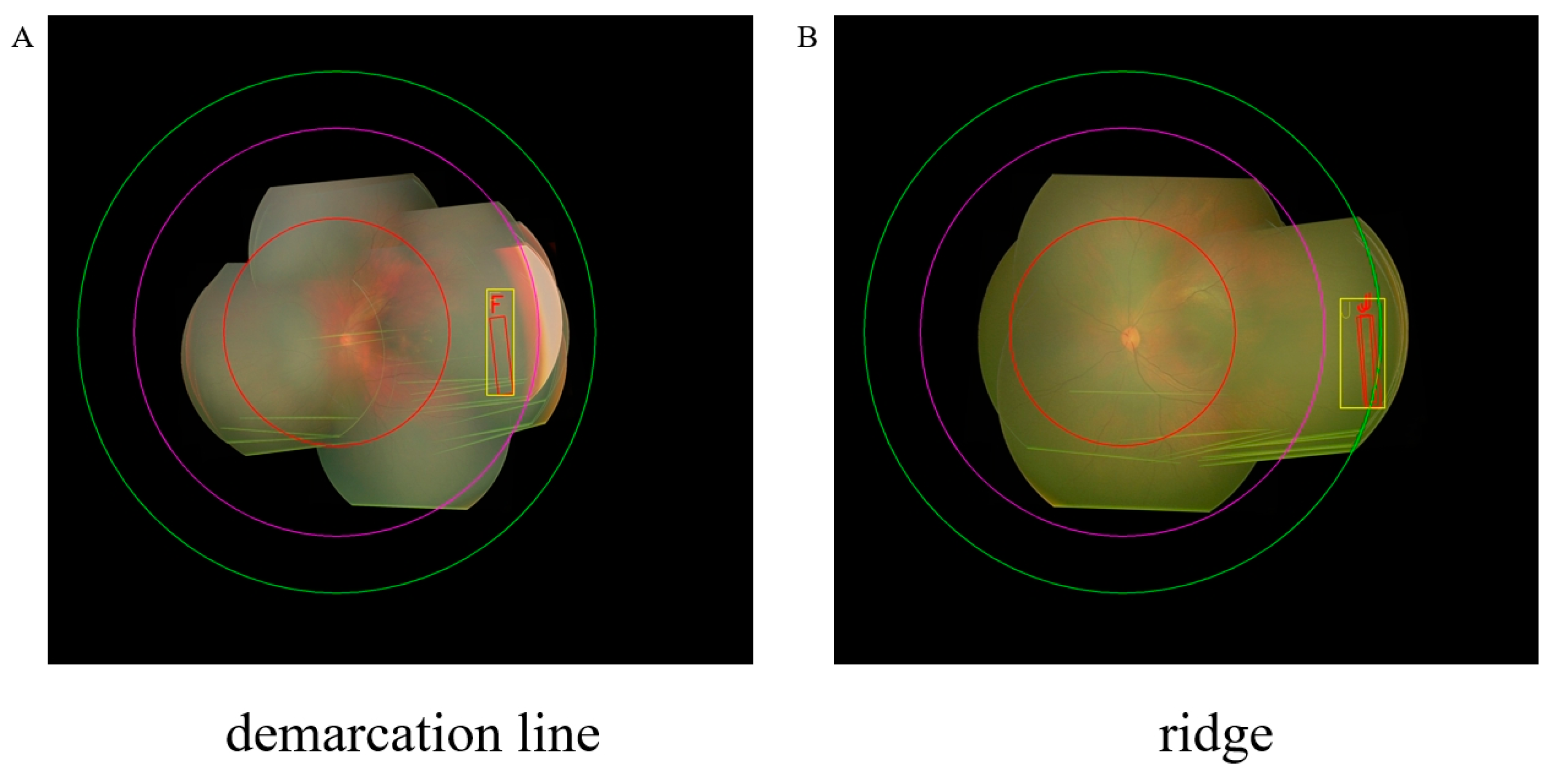
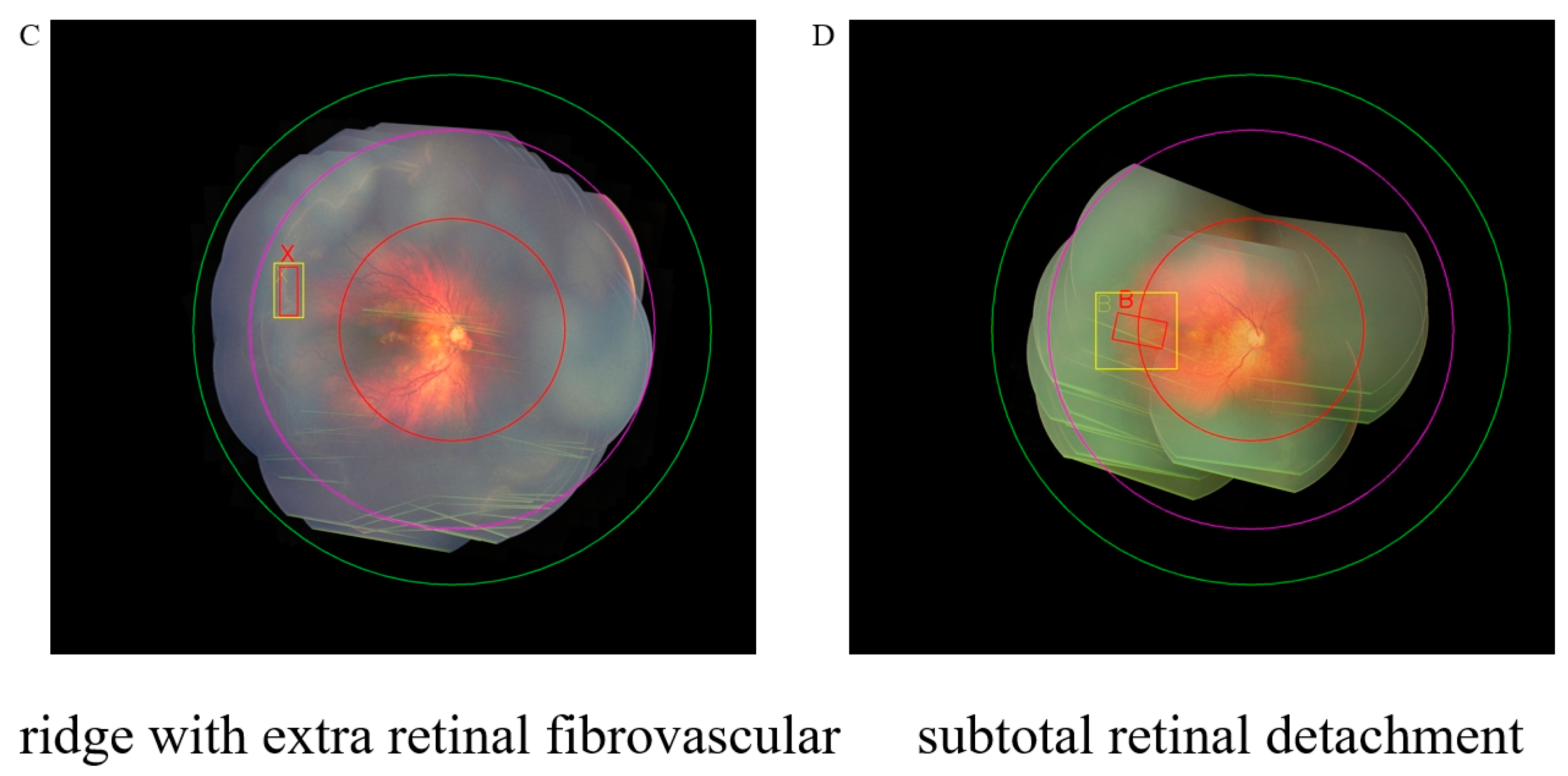
3.5. Visualization of Our Method
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Global, regional and national burden of retinopathy of prematurity among childhood and adolescent: A spatiotemporal analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2024, 8, e002267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Nguyen, K.-H.; Donovan, T.; Edirippulige, S.; Armfield, N.R. A cost-minimisation analysis comparing alternative telemedicine screening approaches for retinopathy of prematurity. J. Telemed. Telecare 2023, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Donovan, T.; Armfield, N.; A Gole, G. Retinopathy of prematurity: The high cost of screening regional and remote infants. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 46, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, M.I.; Russ, R.; Brennan, K.A.; Williams, C.J.; Berrones, D.; Patel, B.; Martinez-Castellanos, M.A.; Fernandes, A.; Hubbard, G.B.; Chan, R.P.; et al. The Economic Model of Retinopathy of Prematurity (EcROP) Screening and Treatment: Mexico and the United States. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2016, 168, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, H.B.; Gordillo, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.S.; Hubbard, G.B., III; Olsen, T.W. The societal burden of blindness secondary to retinopathy of prematurity in Lima, Peru. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.; Hellström, A.; Hallberg, B.; Wallin, A.; Gustafson, P.; Tornqvist, K.; Håkansson, S.; Holmström, G. Prevalence of severe visual disability among preterm children with retinopathy of prematurity and association with adherence to best practice guidelines. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e186801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, W.V. Early Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Final results of the Early Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity (ETROP) randomized trial. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2004, 102, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, M.F.; Quinn, G.E.; Fielder, A.R.; Ostmo, S.R.; Chan, R.P.; Berrocal, A.; Binenbaum, G.; Blair, M.; Campbell, J.P.; Capone, A.; et al. International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity, Third Edition. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e51–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.J.; Wu, S.H.; Cheng, M.Q.; Huang, H.; Liang, J.Y.; Li, C.Q.; Guo, H.L.; He, D.N.; Liu, Y.H.; Xiao, H.; et al. Integration of artificial intelligence decision aids to reduce workload and enhance efficiency in thyroid nodule management. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2313674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, J.; Ehrenfeld, J.M.; Miller, B.J. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Health Care Delivery. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Xie, L.; Luo, X.; Zheng, M.; Tian, R.; et al. A fundus image dataset for intelligent retinopathy of prematurity system. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenice, E.K.; Kara, C.; Erdaş, B. Automated detection of type 1 ROP, type 2 ROP and A-ROP based on deep learning. Eye 2024, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhao, X.; Tang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tian, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Ntentakis, D.P.; et al. Automated detection of nine infantile fundus diseases and conditions in retinal images using a deep learning system. EPMA J. 2024, 15, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Geng, L.; Yu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Xiang, D.; Chen, F.; et al. Automatic staging for retinopathy of prematurity with deep feature fusion and ordinal classification strategy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Basanta, H.; Kang, E.Y.-C.; Chen, K.-J.; Hwang, Y.-S.; Lai, C.-C.; Campbell, J.P.; Chiang, M.F.; Chan, R.V.P.; Kusaka, S.; et al. Automated detection of early-stage ROP using a deep convolutional neural network. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 105, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Ju, R.; Yi, Z. Automated Analysis for Retinopathy of Prematurity by Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Lu, W.; Deng, Q.-Q.; Chen, C.; Shen, Y. Automated identification of retinopathy of prematurity by image-based deep learning. Eye Vis. 2020, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.P.; Kim, S.J.; Brown, J.M.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Chiang, M.F.; Sonmez, K.; Schelonka, R.; Jonas, K.; et al. Evaluation of a deep learning–derived quantitative retinopathy of prematurity severity scale. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.; Brown, J.M.; Gupta, K.; Campbell, J.P.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Dy, J.; Erdogmus, D.; Ioannidis, S.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Monitoring disease progression with a quantitative severity scale for retinopathy of prematurity using deep learning. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Vadloori, S.; Chu, H.-C.; Kang, E.Y.-C.; Wu, W.-C.; Kusaka, S.; Fukushima, Y. Deep learning models for automated diagnosis of retinopathy of prematurity in preterm infants. Electronics 2020, 9, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, W.; Shi, F.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. ADS-Net: Attention-awareness and deep supervision based network for automatic detection of retinopathy of prematurity. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 4087–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ju, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhong, J.; Yi, Z. Automated retinopathy of prematurity screening using deep neural networks. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qiao, W.; Guo, W.; Cai, Y. Applying novel self-supervised learning for early detection of retinopathy of prematurity. Electron. Lett. 2024, 60, e13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redd, T.K.; Campbell, J.P.; Brown, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Dy, J.; Erdogmus, D.; Ioannidis, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; et al. Evaluation of a deep learning image assessment system for detecting severe retinopathy of prematurity. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 103, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Mo, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lin, Z.; et al. Development and validation of a deep learning model to predict the occurrence and severity of retinopathy of prematurity. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2217447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Jordan, B.K.; Scottoline, B.; Ostmo, S.R.; Coyner, A.S.; Singh, P.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Erdogmus, D.; Chan, R.P.; Chiang, M.F.; et al. Oxygenation Fluctuations Associated with Severe Retinopathy of Prematurity: Insights from a Multimodal Deep Learning Approach. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2024, 4, 100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Alizadehsani, R.; Cifci, M.A.; Kausar, S.; Rehman, R.; Mahanta, P.; Bora, P.K.; Almasri, A.; Alkhawaldeh, R.S.; Hussain, S.; et al. A review of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in healthcare. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 118, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, V. Enhancing Transparency and Understanding in AI Decision-Making Processes. Iconic Res. Eng. J. 2024, 8, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Mahapatra, A.; Singal, A.; Goel, D.; Huang, K.; Scardapane, S.; Spinelli, I.; Mahmud, M.; Hussain, A. Interpreting black-box models: A review on explainable artificial intelligence. Cogn. Comput. 2023, 16, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J. Early diagnosis and quantitative analysis of stages in retinopathy of prematurity based on deep convolutional neural networks. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Huang, Q.; Ma, T.; Ju, L.; Ge, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P. Development and validation of a semi-supervised deep learning model for automatic retinopathy of prematurity staging. iScience 2024, 27, 108516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Le, D.; Abtahi, M.; Dadzie, A.K.; Rossi, A.; Rahimi, M.; Son, T.; Ostmo, S.; Campbell, J.P.; Chan, R.V.P.; et al. Assessing spectral effectiveness in color fundus photography for deep learning classification of retinopathy of prematurity. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, 076001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, J.; Zhang, M.; Lin, J.-W.; Zhang, G.; Gong, W.; Cen, L.-P.; Lu, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, D.; et al. Automated explainable multidimensional deep learning platform of retinal images for retinopathy of prematurity screening. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e218758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Lei, B. Attention-guided deep multi-instance learning for staging retinopathy of prematurity. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1025–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Lei, B. Early detection of retinopathy of prematurity stage using deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2019: Computer-Aided Diagnosis 2019, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–20 February 2019; Volume 10950, pp. 758–764. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, J.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lei, B. Dual-branch Feature Interaction Network with Structure Information Learning for Retinopathy of Prematurity Classification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Istanbul, Turkiye, 5–8 December 2023; pp. 1230–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, W.; Shi, F.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, K.; Chen, X. Automatic zoning for retinopathy of prematurity with a key area location system. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 15, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, W.; Shi, F.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. Automatic zoning for retinopathy of prematurity with semi-supervised feature calibration adversarial learning. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 1968–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lei, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, J.; et al. A deep learning framework for identifying zone I in RetCam images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 103530–103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Patel, H.; Paul, K.; Azad, S. Deep learning-assisted retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) screening. ACM Trans. Comput. Health 2023, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Niyas, P.; Vinekar, A.; John, R. A deep learning framework for the detection of Plus disease in retinal fundus images of preterm infants. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, K.L.; Sreelekha, G.; Sathidevi, P.S.; Mohanachandran, P.; Vinekar, A. A computer-aided diagnosis system for plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity with structure adaptive segmentation and vessel based features. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 74, 72–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VMR, S. Computer Aided Diagnostics in Prediction of Plus and Pre Plus Diseases of ROP in Neonatal Fundus Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Recent Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Ubiquitous Communication, and Computational Intelligence (RAEEUCCI), Chennai, India, 17–19 April 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Simkin, S.; Lai, C.; Dai, S. Deep learning algorithm for automated diagnosis of retinopathy of prematurity plus disease. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Lao, J.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Sun, M.; Shen, L. Automated diagnosis and quantitative analysis of plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity based on deep convolutional neural networks. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, E339–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, V.M.; Tian, P.; Yildiz, I.; Brown, J.M.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Dy, J.; Ioannidis, S.; Erdogmus, D.; Ostmo, S.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity: Convolutional neural network performance using a combined neural network and feature extraction approach. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, A.; Orge, F.; Douglass, M.; Can, B.; Monteoliva, G.; Fried, E.; Schbib, V.; Saidman, G.; Peña, B.; Ulacia, S.; et al. Image harmonization and deep learning automated classification of plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity. J. Med. Imaging 2023, 10, 061107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemshi, K.M.; Sreelekha, G.; Sathidevi, P.; Mohanachandran, P.; Vinekar, A. Plus disease classification in Retinopathy of Prematurity using transform based features. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 861–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Dong, W.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Yi, Z. GFF-Net: Graph-based feature fusion network for diagnosing plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 25259–25281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovitz, S.; Lifshitz-Assaf, H.; Levina, N. To engage or not to engage with AI for critical judgments: How professionals deal with opacity when using AI for medical diagnosis. Organ. Sci. 2022, 33, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, B.; Kudina, O. What is morally at stake when using algorithms to make medical diagnoses? Expanding the discussion beyond risks and harms. Theor. Med. Bioeth. 2021, 42, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Ruddy, J. Improving patient-provider relationships to improve health care. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, W.; Sun, L.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Jin, Y.; Sun, W.; Yan, W.; Li, J.; et al. RDLR: A Robust Deep Learning-Based Image Registration Method for Pediatric Retinal Images. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open mmlab detection toolbox and benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.; Zhmoginov, A.; Sandler, M. Cyclegan, a master of steganography. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.02950. [Google Scholar]




| Data | Stage I Lesion | Stage II Lesion | Stage III Lesion | Stage IV Lesion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| training data | 77 | 177 | 39 | 36 |
| validation data | 11 | 35 | 10 | 10 |
| Methods | Acc | Kappa |
|---|---|---|
| our system | 0.69 | 0.62 |
| clinical doctor A | 0.57 | 0.52 |
| clinical doctor B | 0.37 | 0.28 |
| clinical doctor X | 0.47 | 0.47 |
| clinical doctor Y | 0.51 | 0.45 |
| clinical doctor Z | 0.45 | 0.36 |
| Methods | Acc | Kappa |
|---|---|---|
| our system | 0.74 | 0.55 |
| clinical doctor A | 0.61 | 0.51 |
| clinical doctor B | 0.61 | 0.42 |
| clinical doctor X | 0.62 | 0.54 |
| clinical doctor Y | 0.68 | 0.59 |
| clinical doctor Z | 0.73 | 0.64 |
| Methods | Acc | F1 |
|---|---|---|
| our system | 0.96 | 0.7 |
| clinical doctor A | 0.92 | 0.52 |
| clinical doctor B | 0.93 | 0.64 |
| clinical doctor X | 0.91 | 0.65 |
| clinical doctor Y | 0.94 | 0.67 |
| clinical doctor Z | 0.9 | 0.58 |
| Methods | Acc | F1 |
|---|---|---|
| I-ROP ASSIST with domain adaptation | 0.96 | 0.7 |
| I-ROP ASSIST | 0.92 | 0.35 |
| Methods | AUC (95%CI) | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
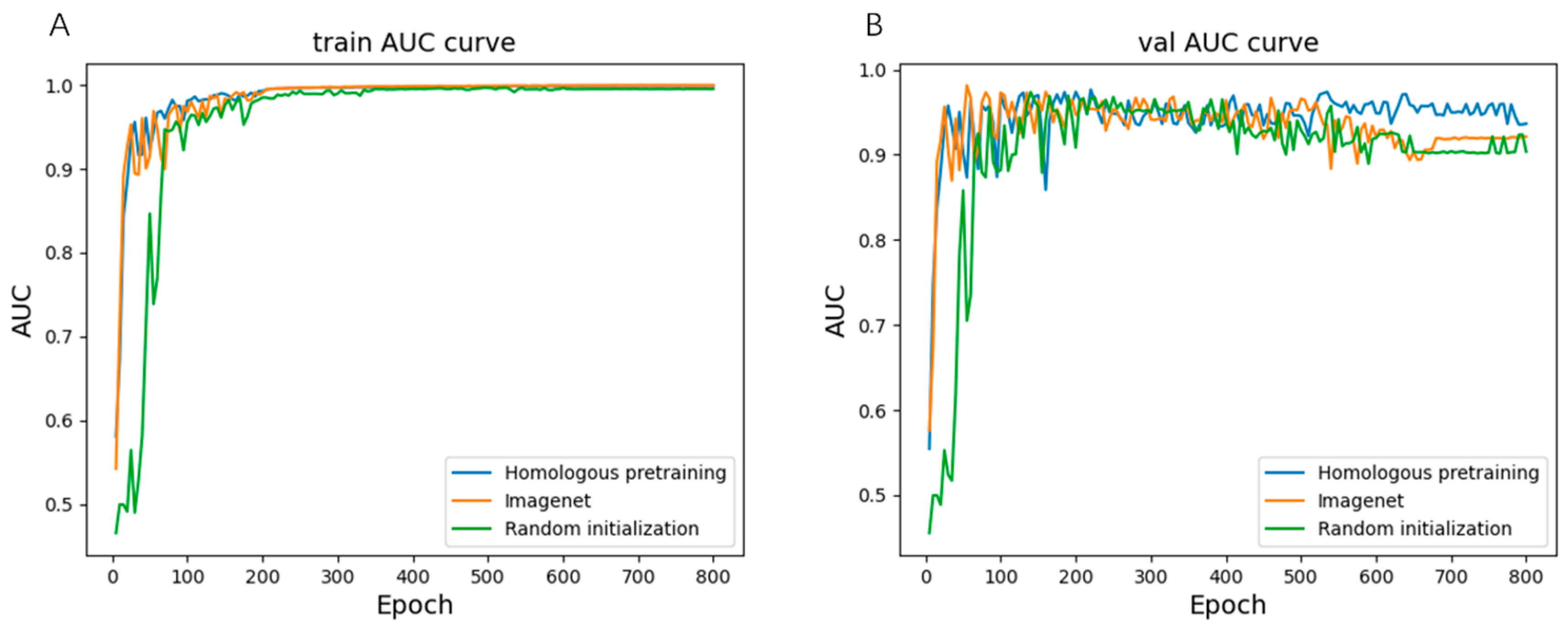
| domain adaptation with homologous pretrain | 0.95 (0.90–0.98) | 1 | 0.7 |
| domain adaptation with random initialization | 0.92 (0.86–0.96) | 1 | 0.43 |
| domain adaptation with ImageNet | 0.93 (0.88–0.98) | 1 | 0.45 |
| homologous pretrain | 0.93 (0.88–0.98) | 1 | 0.68 |
| random initialization | 0.92 (0.87–0.97) | 1 | 0.54 |
| ImageNet | 0.88 (0.81–0.94) | 1 | 0.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Jin, Y.; Sun, W.; Yan, W.; et al. An Interpretable System for Screening the Severity Level of Retinopathy in Premature Infants Using Deep Learning. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080792
Yang W, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Sun L, Huang L, Li S, Luo X, Jin Y, Sun W, Yan W, et al. An Interpretable System for Screening the Severity Level of Retinopathy in Premature Infants Using Deep Learning. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080792
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wenhan, Hao Zhou, Yun Zhang, Limei Sun, Li Huang, Songshan Li, Xiaoling Luo, Yili Jin, Wei Sun, Wenjia Yan, and et al. 2024. "An Interpretable System for Screening the Severity Level of Retinopathy in Premature Infants Using Deep Learning" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080792
APA StyleYang, W., Zhou, H., Zhang, Y., Sun, L., Huang, L., Li, S., Luo, X., Jin, Y., Sun, W., Yan, W., Li, J., Deng, J., Xie, Z., He, Y., & Ding, X. (2024). An Interpretable System for Screening the Severity Level of Retinopathy in Premature Infants Using Deep Learning. Bioengineering, 11(8), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080792







