Press-Fit Placement of a Rectangular Block Implant in the Resorbed Alveolar Ridge: Surgical and Biomechanical Considerations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manufacture
2.2. Experimental Subjects
2.2.1. Ex Vivo Animal Placements (×3)
2.2.2. In Vivo Animal Placements (×12)
2.2.3. Human Placements (×2)
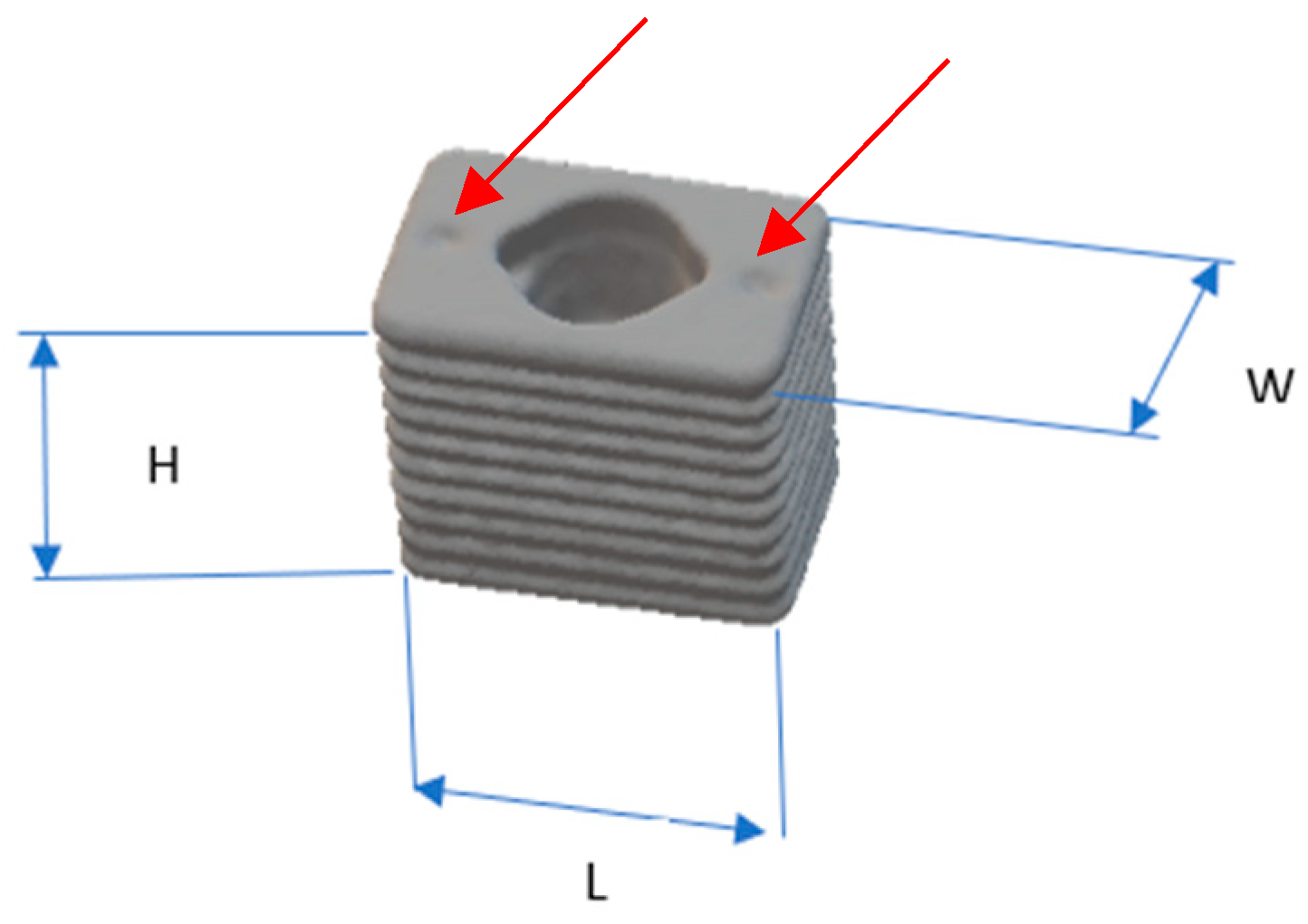
2.3. Implants
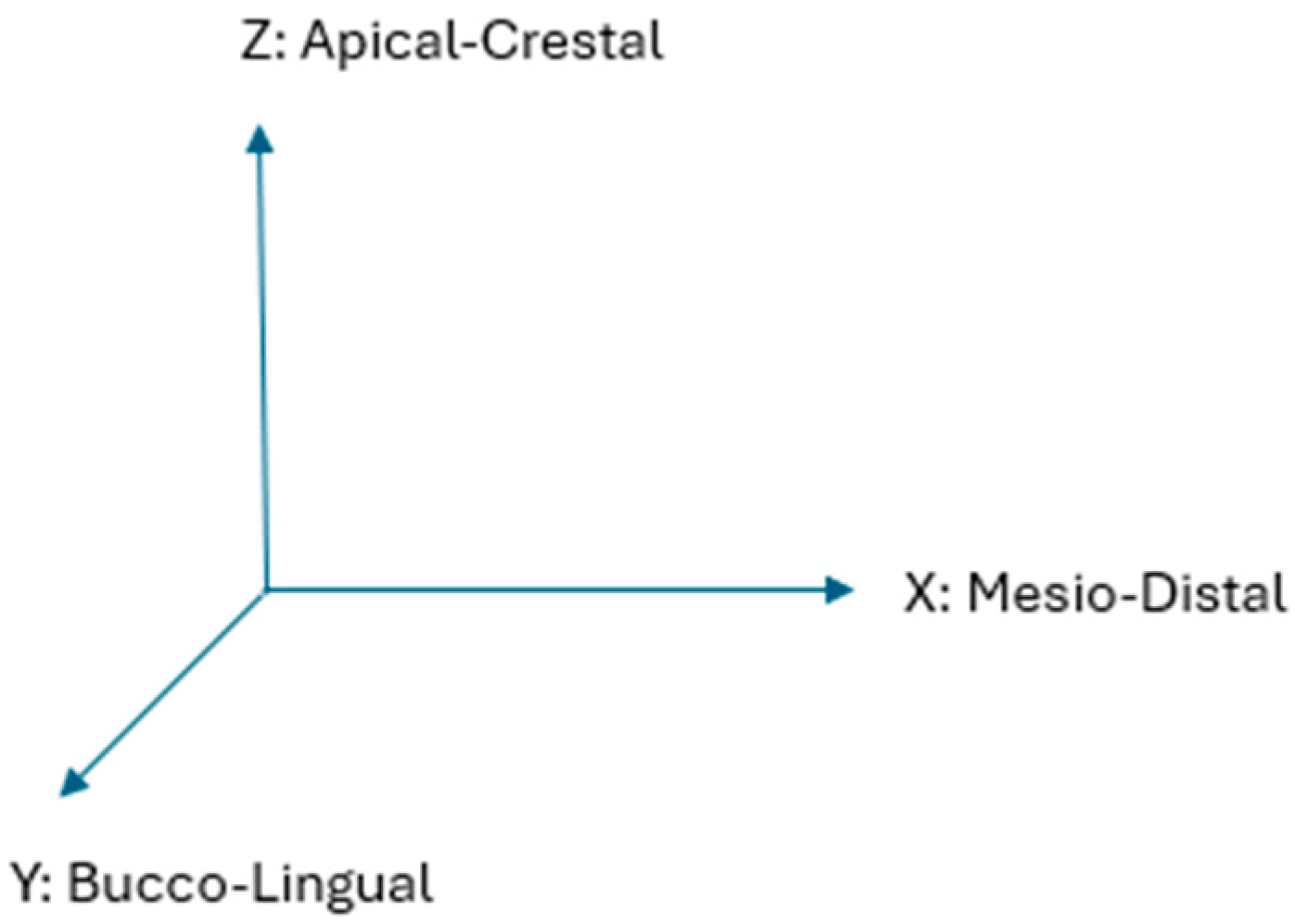
2.4. Site Assessment
2.5. Flap Design
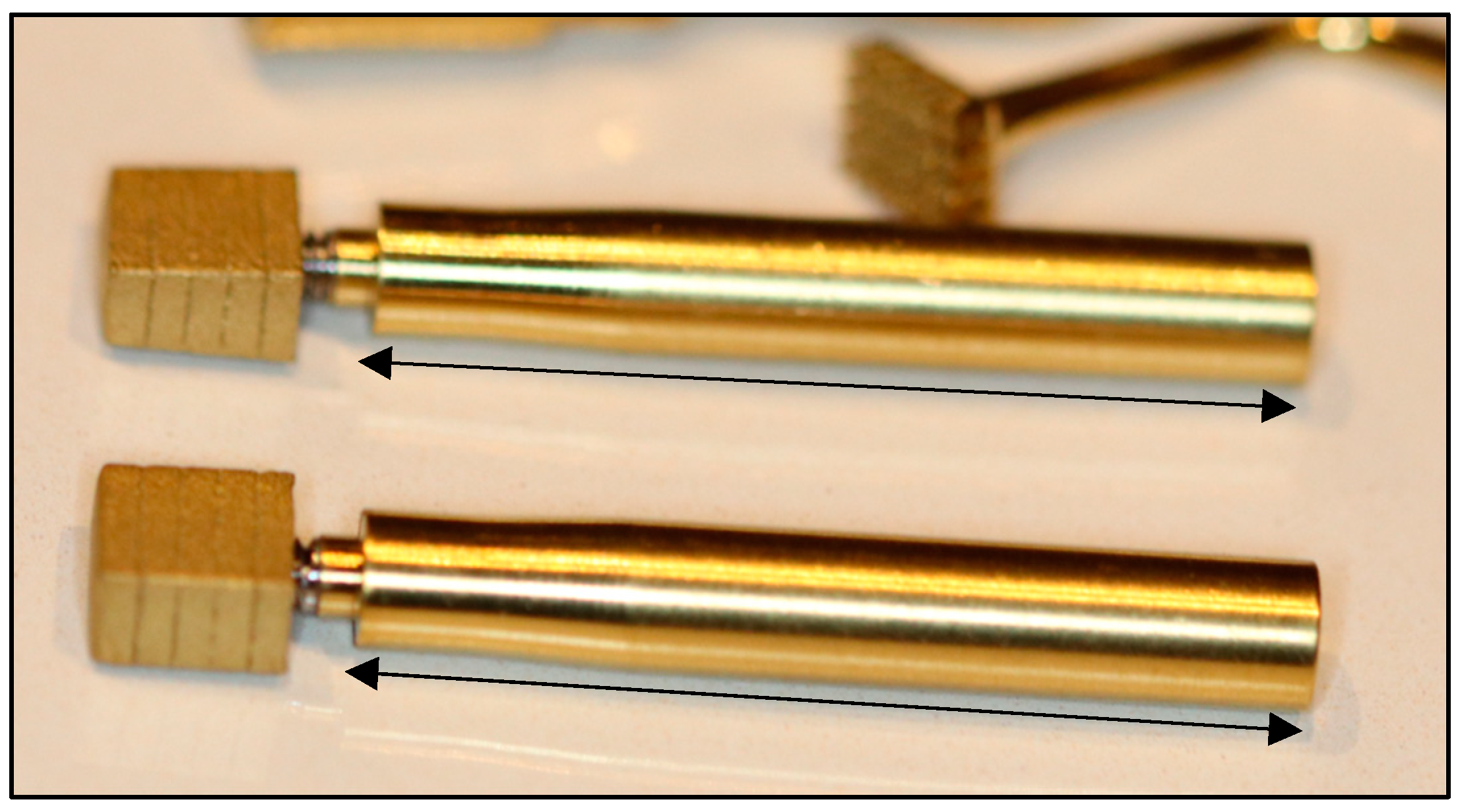
2.6. Rectangular Osteotomy Construction
2.7. Implant Placement and the Trial-Fit Gauge
2.8. Primary Stability
2.9. Radiography
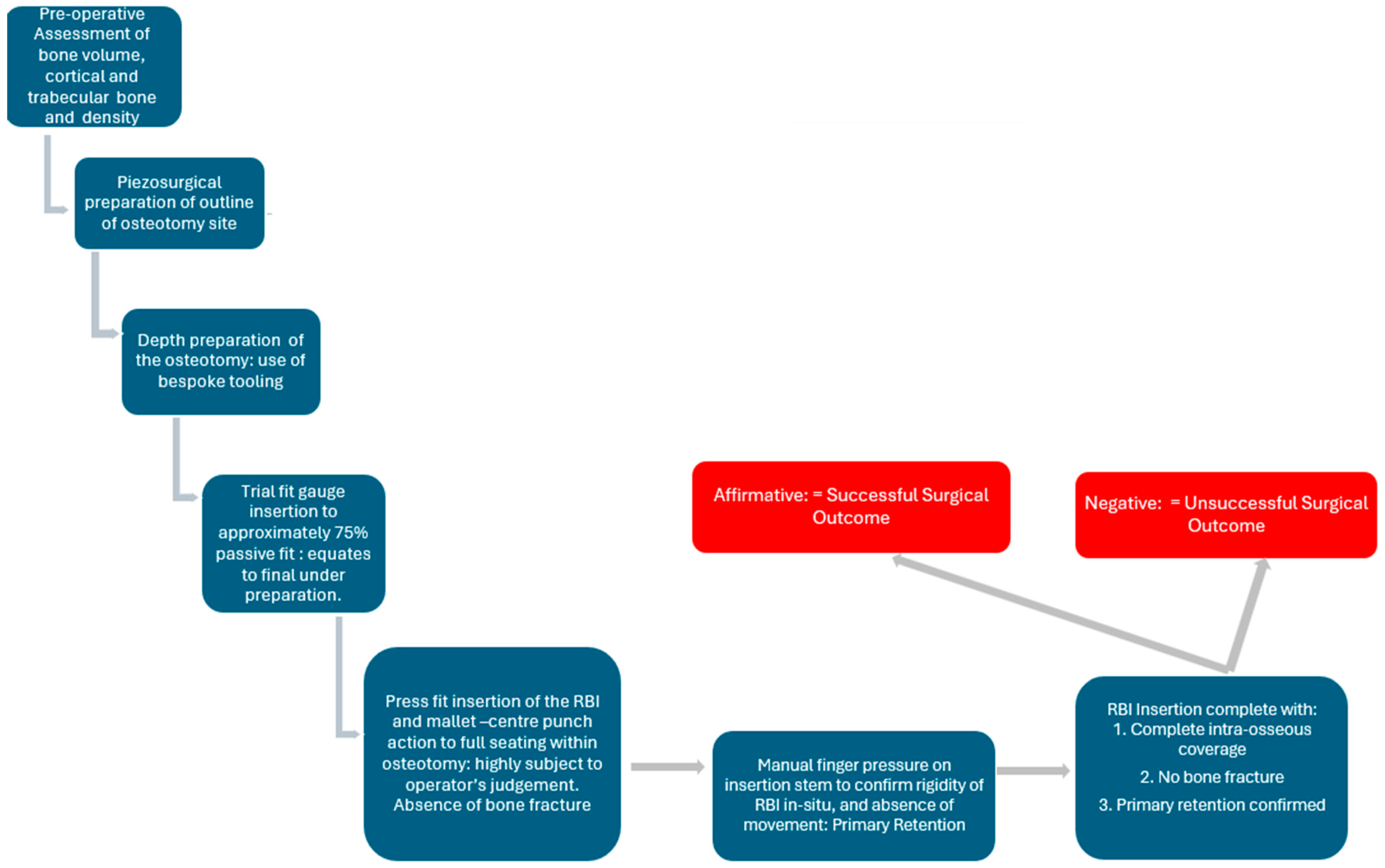
2.10. Surgical Protocol Summary
3. Results
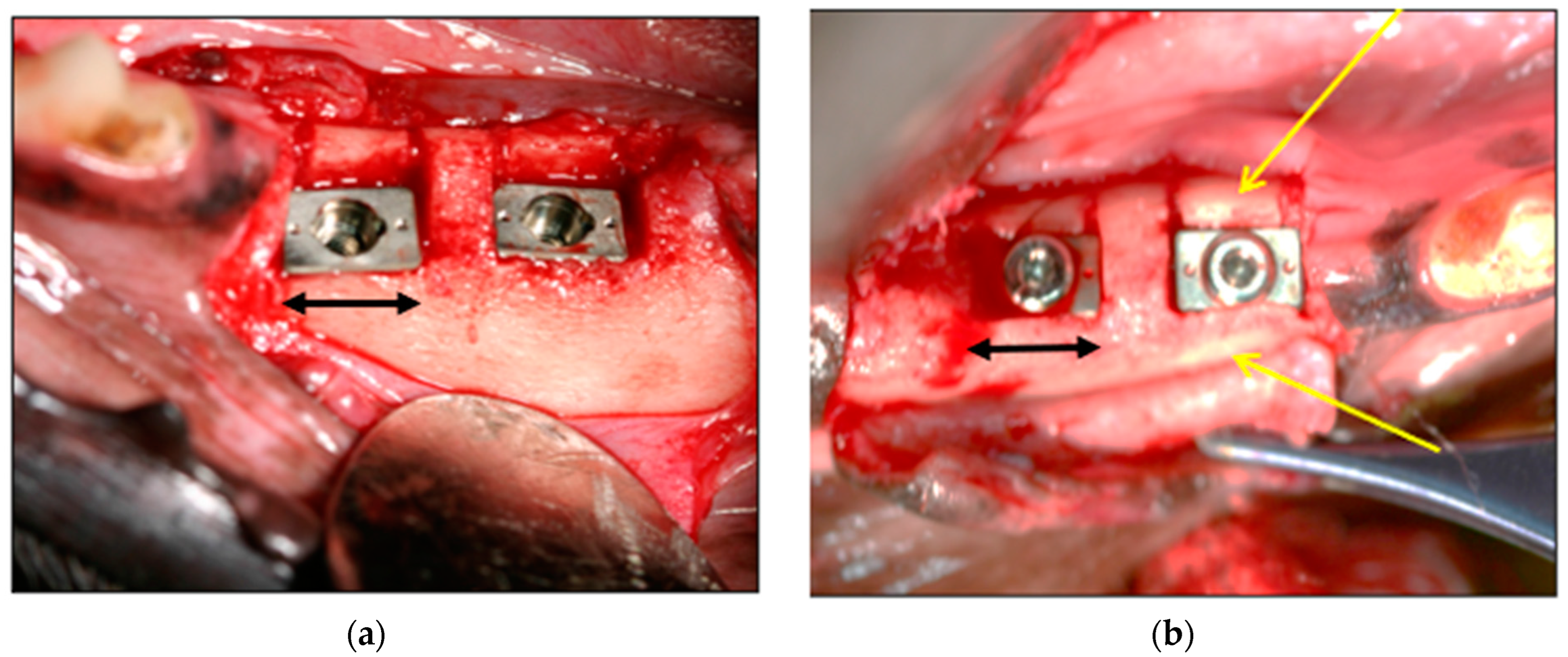
3.1. Ex Vivo Animal Placements
3.2. In Vivo Animal Placements
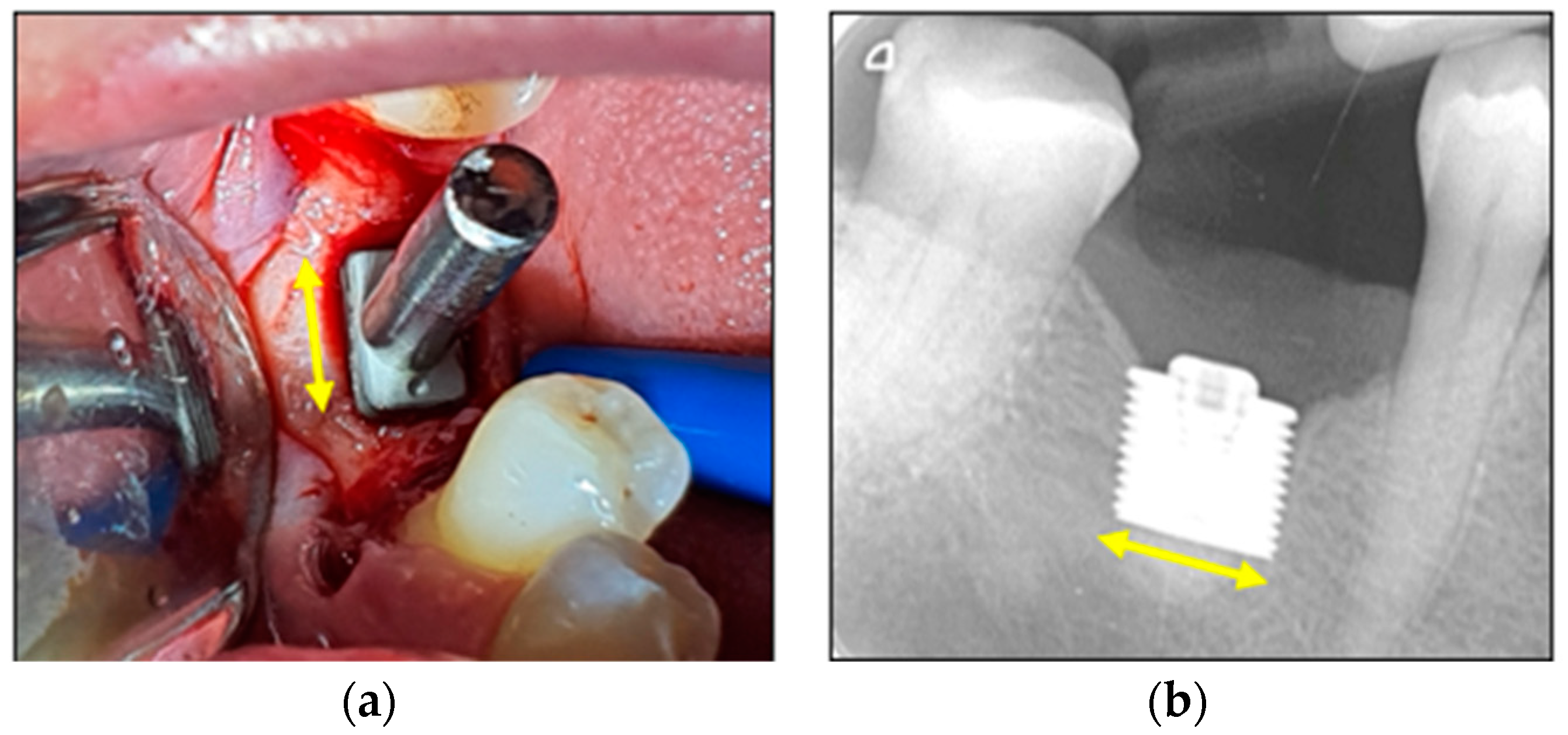
3.3. Human Placements
3.3.1. Clinical Images
3.3.2. Statiscal Significance
4. Discussion
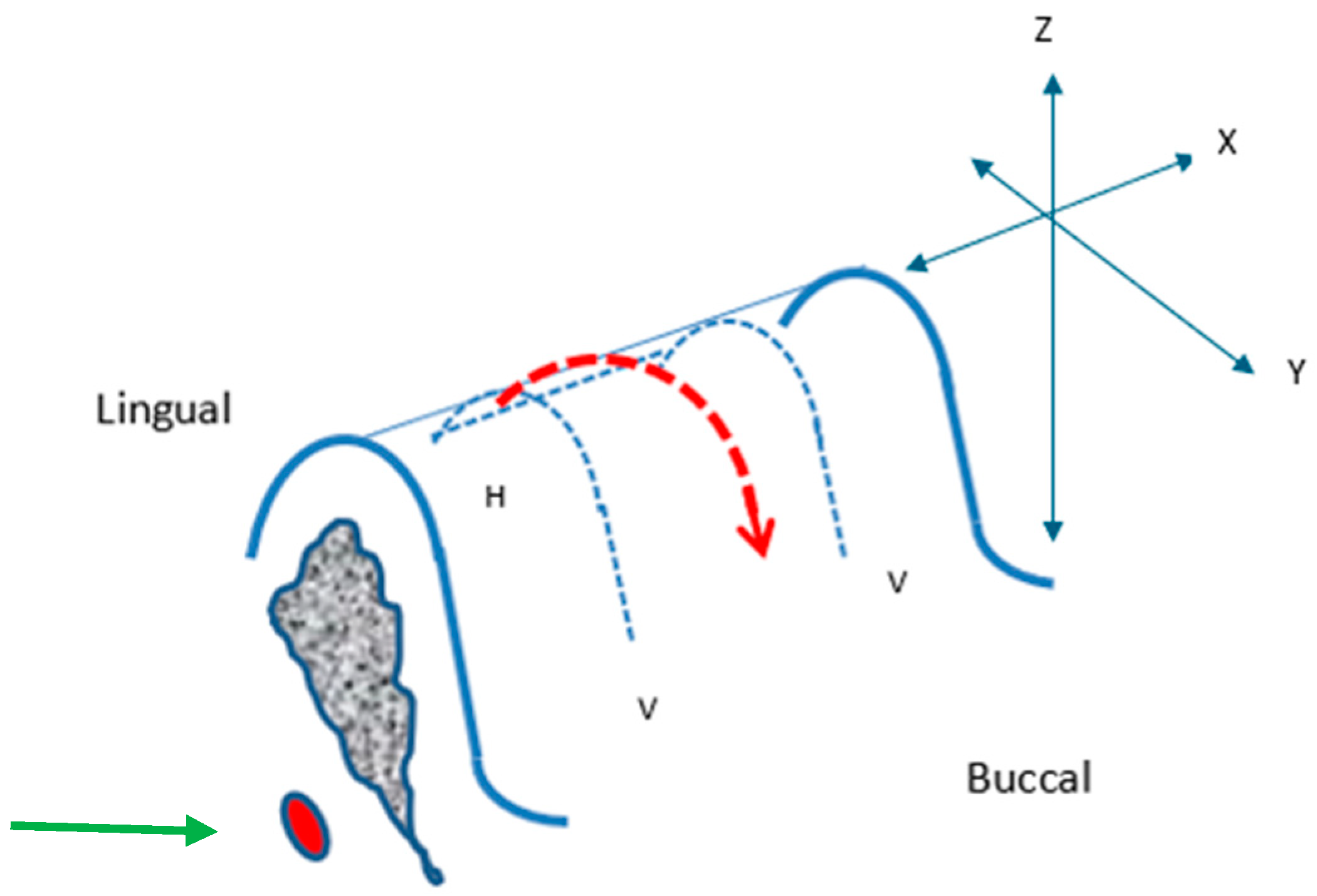
4.1. RBI Geometry
4.2. Cylindrical Implant Geometry
4.3. Geometry Comparison
4.4. Factors Influencing Press-Fit Placement
4.4.1. The Press-Fit Action Limitations
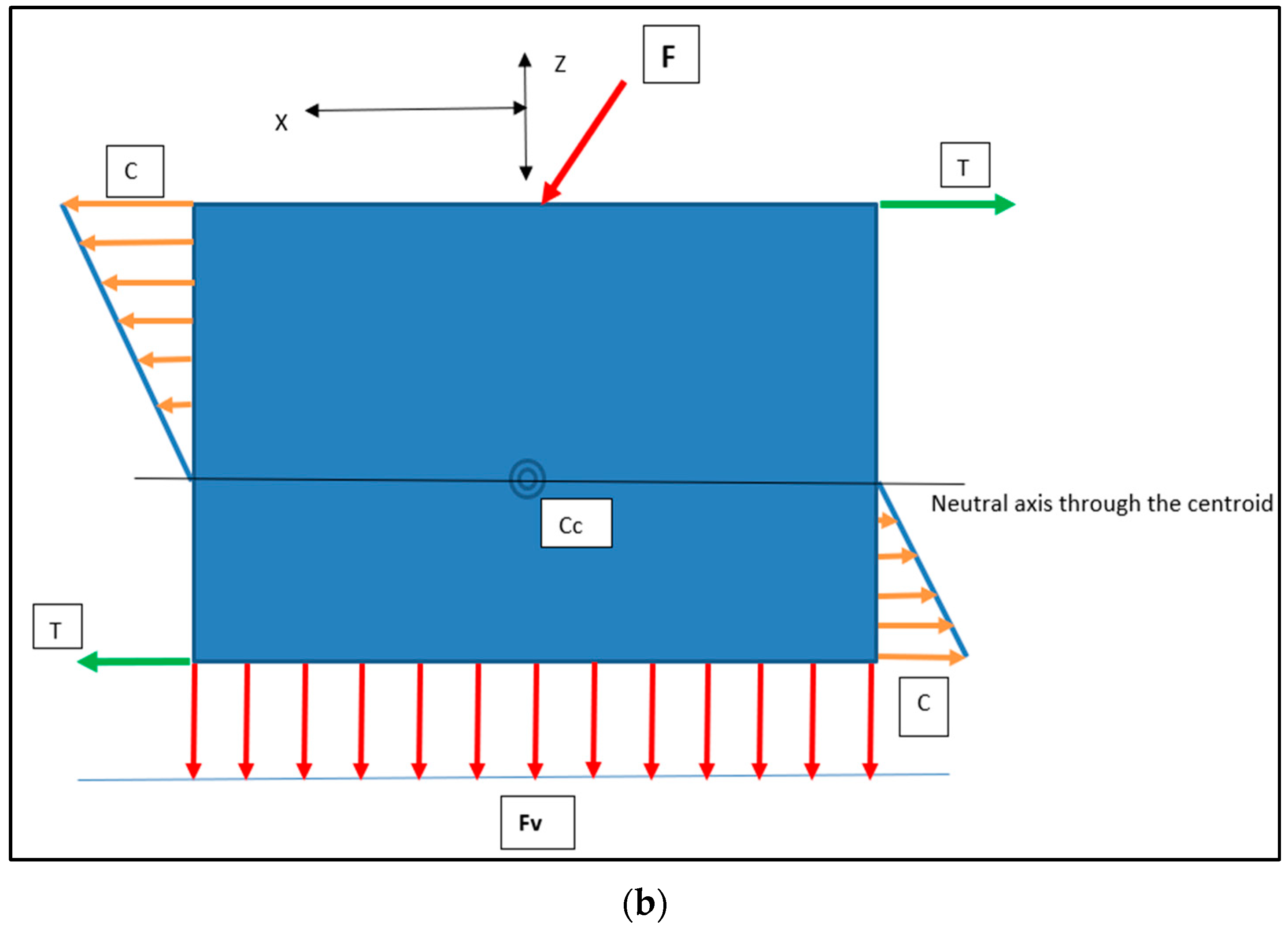
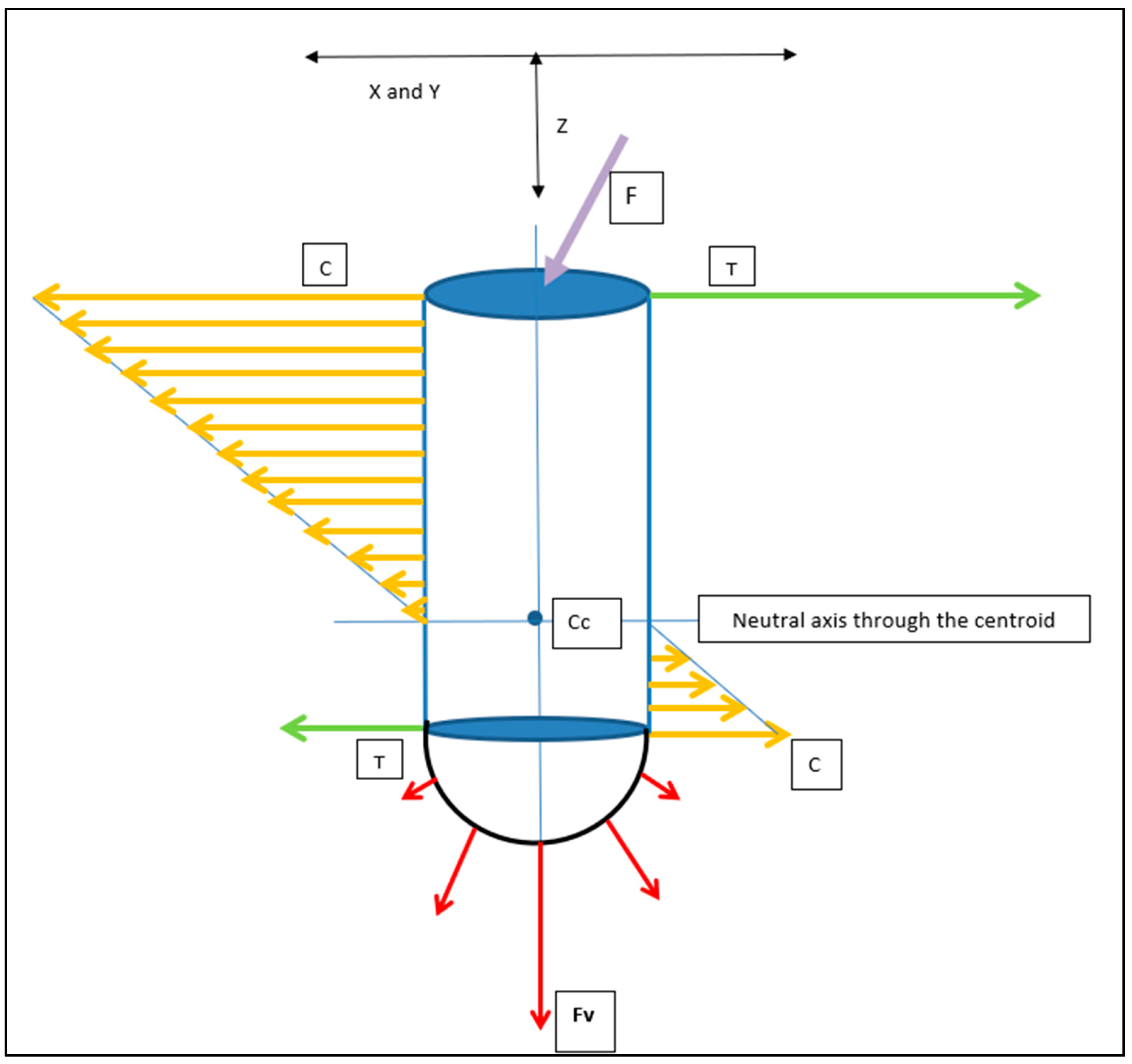
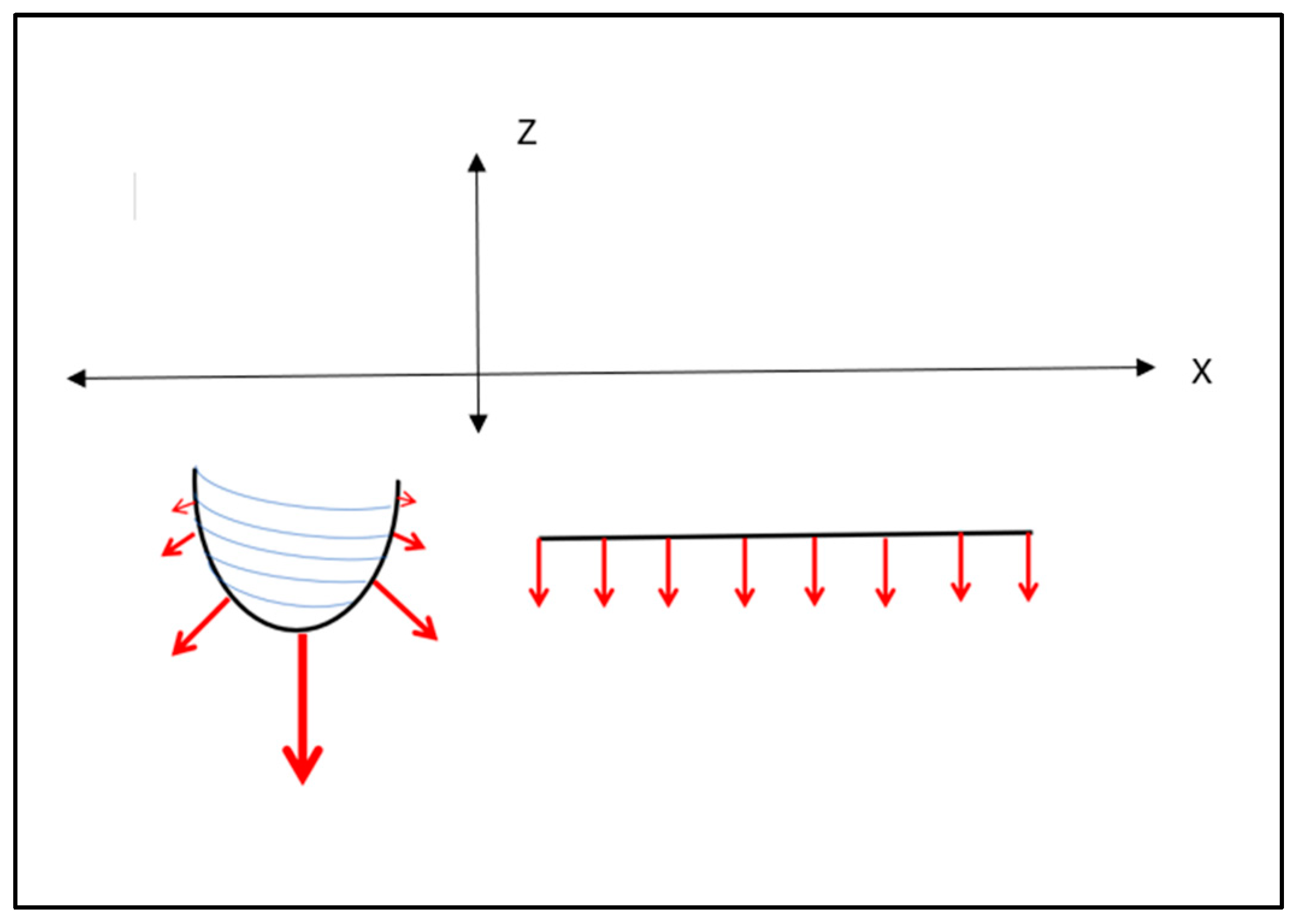
4.4.2. Press-Fit Stress Patterns and the RBI
4.5. Piezosurgery
4.6. Future Research
4.6.1. Graeter Sample Sized Studies
4.6.2. Primary Stability
4.6.3. Titanium Surface Modifications
4.6.4. Forces Distributions under Differing Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elani, H.W.; Starr, J.R.; Da Silva, J.D.; Gallucia, G.O. Trends in dental implant use in the U.S., 1999–2016 and Projections to 2026. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstunov, L. Classification of the alveolar ridge width: Implant-driven treatment considerations for the horizontally deficient alveolar ridges. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Wu, C.; Shao, M. Simultaneous implant placement with autogenous onlay bone grafts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2021, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, F.; Ahmed, H.B.; Crespi, R.; Romanos, G.E. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2013, 5, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lioubavina-Hack, N.; Lang, N.P.; Karring, T. Significance of primary stability for osseointegration of dental implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarce, C.J.; Kan, J.Y.K.; Rungcharassaeng, K. Clinical complications of osseo-integrated implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 537–552. [Google Scholar]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Custodio, A.L.N.; Ramos, B. Mandibular fractures associated with endosteal implants. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 13, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, X.; Huang, R.; Liu, R.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Placement accuracy and primary stability of implants in the esthetic zone using dynamic and static computer-assisted navigation: A retrospective case-control study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 131, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varcellotti, T. Technological characteristics and clinical indications of piezo-electric bone surgery. Minerva Stomatol. 2004, 53, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanivahid, P.; Heidari, M. Design parameters of dental implants: A review. Rev. Int. Métodos Numér. Cálc. Diseño Ing. 2022, 38, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Carlo, L.; Pasqualini, M.; Shulman, M.; Rossi, F.; Comola, G.; Manenti, P.; Candotto, V.; Lauritano, D.; Zampetti, P. Endosseous distal extension (EDE) blade implant technique useful to provide stable pillars in the ipotrophic lower posterior sector: 22 years statistical survey. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419838092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memè, L.; Mummolo, S.; Strappa, E.M.; Fabrizio Bambini, F.; Gallusi, G. A New Wedge-Shape Dental Implants for Narrow Bone Ridge: REX Piezoimplant, a Case Report With 12 Months of Follow-Up. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2022, 16, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, I.R. Surgical aids to prosthodontics, including osseointegrated implants. In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2nd ed.; Pedlar, J., Frame, J.W., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 145–165. [Google Scholar]
- Birdi, H.; Schulte, J.; Kovacs, A.; Weed, M.; Chuang, S.K. Crown-to-implant ratios of short-length implants. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 36, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazelakis, E.; Judge, R.B.; Palamara, J.E.A.; Nazir, M. The biomechanical profile of an osseo-integrated rectangular block implant: A pilot in-vivo strain analysis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deporter, D.; Todescan, R.; Caudry, S. Simplifying management of the posterior maxilla using short, porous surfaced dental implants and simultaneous indirect sinus elevation. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2000, 20, 477–486. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, N.E.; Höhn, J.-C.; Rothstock, S.; Damm, N.B.; Morlock, M.M. The influence of bone damage on press-fit mechanics. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, N.B.; Morlock, M.; Bishop, N.E. Friction coefficient and effective interference at the implant-bone interface. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3517–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berahmani, S.; Janssen, D.; van Kessel, S.; Wolfson, D.; de Waal Malefijt, M.; Buma, P.; Verdonschot, N. An experimental study to investigate biomechanical aspects of the initial stability of press-fit implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 42, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisardi, G.; Barone, S.; Razionale, A.V.; Paoli, A.; Frisardi, F.; Tullio, A.; Lumbau, A.; Chessa, G. Biomechanics of the press-fit phenomenon in dental implantology: An image-based finite element analysis. Head Face Med. 2012, 8, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.S.; Schilling, C.; Thomas, M.; Grupp, T.M.; Giurea, A.; Wyers, C.; van den Bergh, J.; Verdonschot, N.; Janssen, D. The effect of different interference fits on the primary fixation of a cementless femoral component during experimental testing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 113, 104189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, A.N.; Carniel, E.L.; Pavan, P.G. Dental implants press-fit phenomena: Biomechanical analysis considering bone inelastic response. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.J.; Jinnah, R.H.; Wilson, V.D.; Hungerford, D.S. The initial stability of uncemented acetabular components. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1992, 74, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazelakis, E. The Rectangular Block Implant: A Novel Implant Design for the Posterior Atrophic Ridge. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gazelakis, E.; Judge, R.B.; Joseph E A Palamara, J.E.A. The biomechanical profile of an osseo-integrated rectangular block implant: A pilot in-vivo experimental study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32, 1274–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Orangee, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Government, Canberra, Australia. National Health and Medical Research Council. 2023. Available online: https://www.nhmrc.gov.au/research-policy/ethics/national-statement-ethical-conduct-human-research (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- ISO 14801: 2016; Dentistry Implants—Dynamic Loading Test for Endosseous Dental Implants. International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/sist/76926102-25bb-46ce-932cd911ba96db92/iso-14801-2016 (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Cehreli, M.; Duyck, J.; De Cooman, M.; Puers, R.; Naert, I. Implant design and interface force transfer. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Kadir, M.R.; Hansen, U.; Klabunde, R.; Lucas, D.; Amis, A. Finite element modelling of primary hip stem stability: The effect of interference fit. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degidi, M.; Daprile, G.; Piattelli, A. Determination of primary stability: A comparison of the surgeon’s perception and objective measurements. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 558–561. [Google Scholar]
- Rues, S.; Schmitter, M.; Kappel, S.; Sonntag, R.; Philippe, K.; Nadorf, J. Effect of bone quality and quantity on the primary stability of dental implants in a simulated bi-cortical placement. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Cambridge. Mechanical Properties of Bone. Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science (DoITPoMS). 2024. Available online: https://www.doitpoms.ac.uk/tlplib/bones/bone_mechanical.php (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Meredith, N.; Alleyne, D.; Cawley, P. Quantitative determination of the stability of the implant-tissue interface using resonance frequency analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1996, 7, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1998, 11, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Atieh, M.A.; Alsabeeha, N.H.M.; Payne, A.G.T.; de Silva, R.K.; Schwass, D.S.; Duncan, W.J. The prognostic accuracy of resonance frequency analysis in predicting failure risk of immediately restored implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neldam, C.A.; Pinholt, E.S. State of the Art of Short Dental Implants: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Medina, P.; Sundaram, P.A.; Diffoot-Carlo, N. Titanium Oxide: A Bioactive Factor in Osteoblast Differentiation. Int. J. Dent. 2015, 2015, 357653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozelskaya, A.I.; Verzunova, K.N.; Akimchenko, I.O.; Frueh, J.; Petrov, V.I.; Slepchenko, G.B.; Bakina, O.V.; Lerner, M.I.; Brizhan, L.K.; Davydov, D.V.; et al. Antibacterial Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Biomedical Applications Fabricated via Micro-Arc Oxidation. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazelakis, E.; Judge, R.B.; Palamara, J.E.A.; Subramanian, S.; Nazir, M. Press-Fit Placement of a Rectangular Block Implant in the Resorbed Alveolar Ridge: Surgical and Biomechanical Considerations. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060532
Gazelakis E, Judge RB, Palamara JEA, Subramanian S, Nazir M. Press-Fit Placement of a Rectangular Block Implant in the Resorbed Alveolar Ridge: Surgical and Biomechanical Considerations. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060532
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazelakis, Efthimios, Roy B. Judge, Joseph E. A. Palamara, Shiva Subramanian, and Mohsin Nazir. 2024. "Press-Fit Placement of a Rectangular Block Implant in the Resorbed Alveolar Ridge: Surgical and Biomechanical Considerations" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060532
APA StyleGazelakis, E., Judge, R. B., Palamara, J. E. A., Subramanian, S., & Nazir, M. (2024). Press-Fit Placement of a Rectangular Block Implant in the Resorbed Alveolar Ridge: Surgical and Biomechanical Considerations. Bioengineering, 11(6), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060532





