Fabrication Method for Shape-Controlled 3D Tissue Using High-Porosity Porous Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
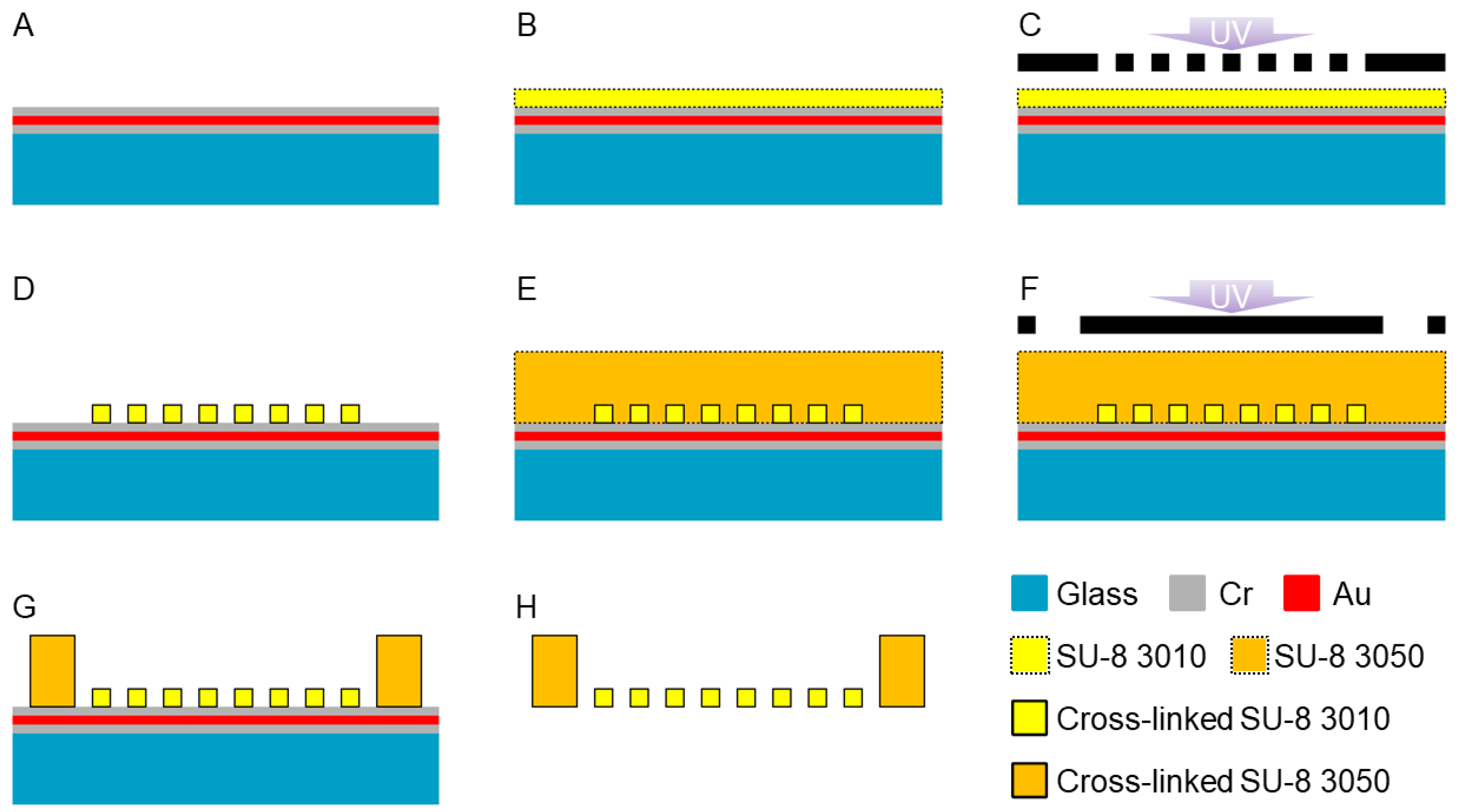
2.1. Design and Fabrication Method for HPPS
2.2. Cell Culture
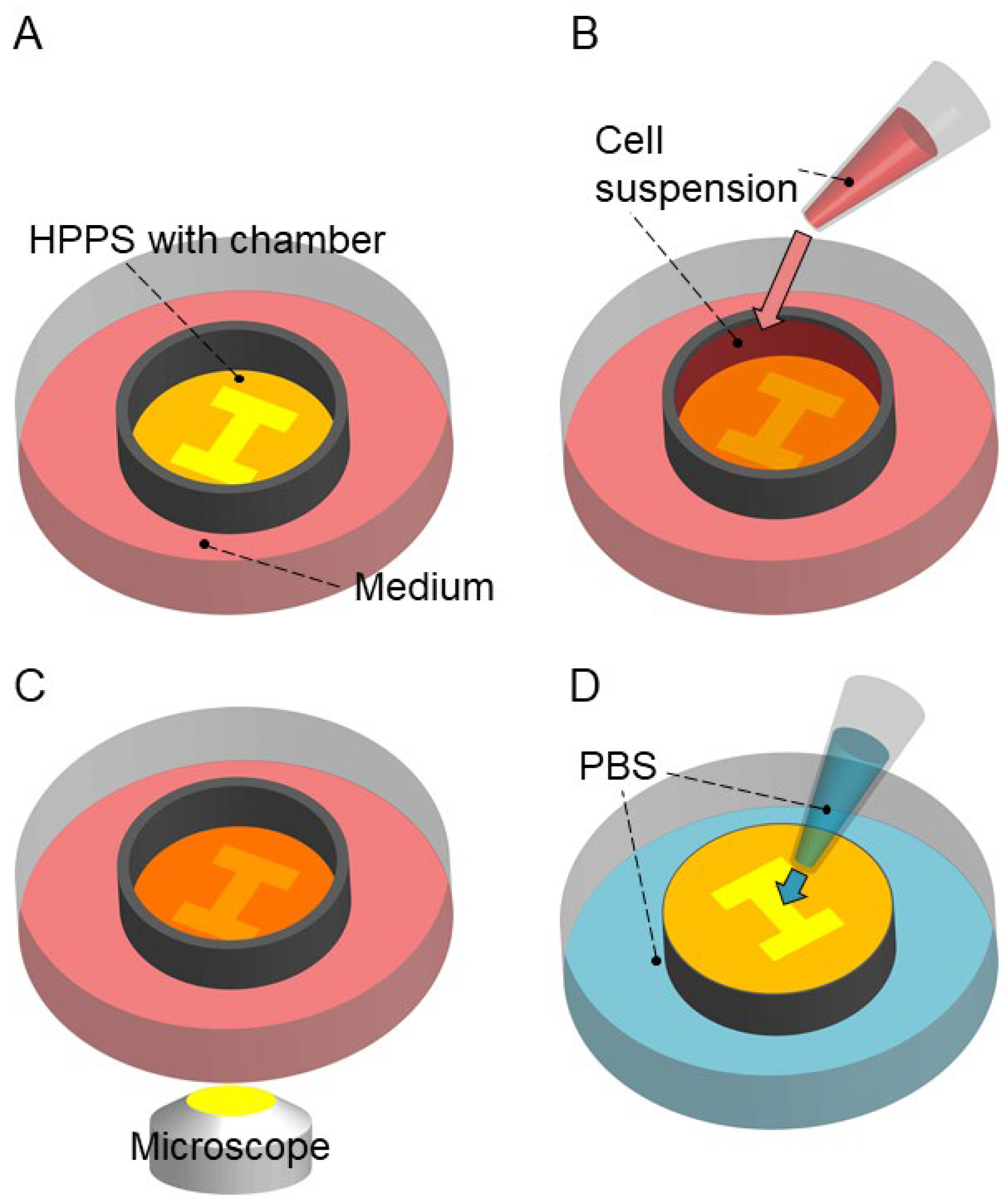
2.3. Tissue Cultivation and Releasing
2.4. Microscopy and Image Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
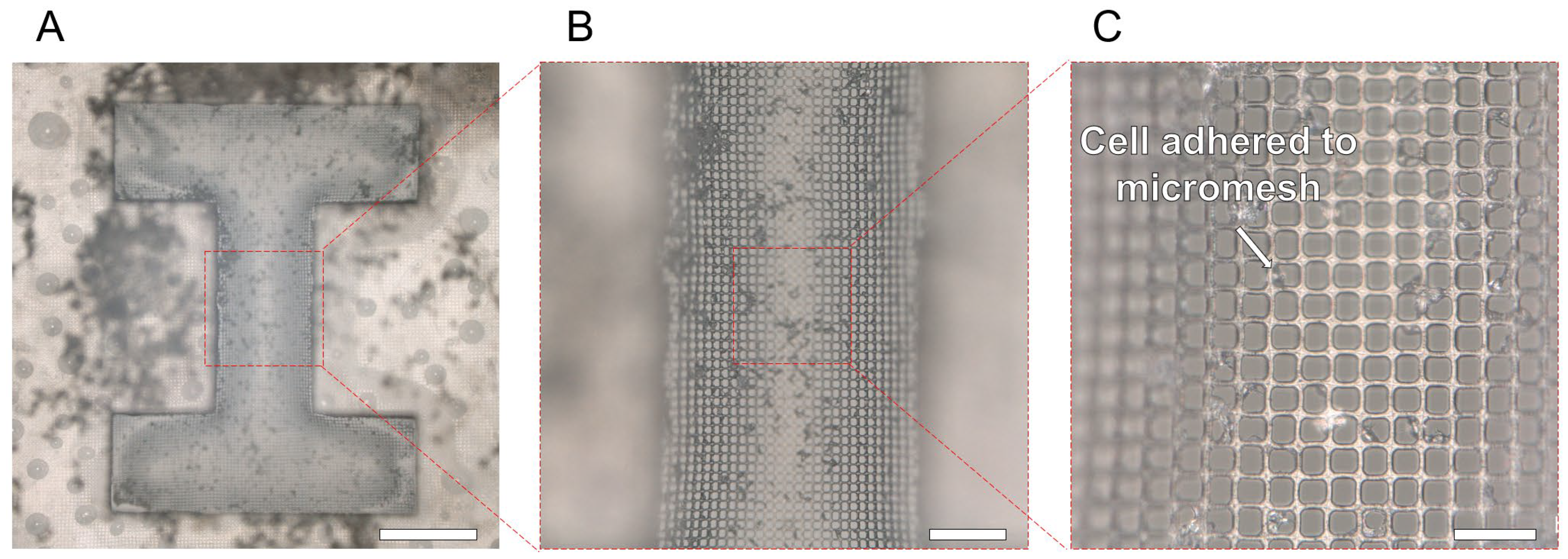
3.1. Fabrication of HPPS
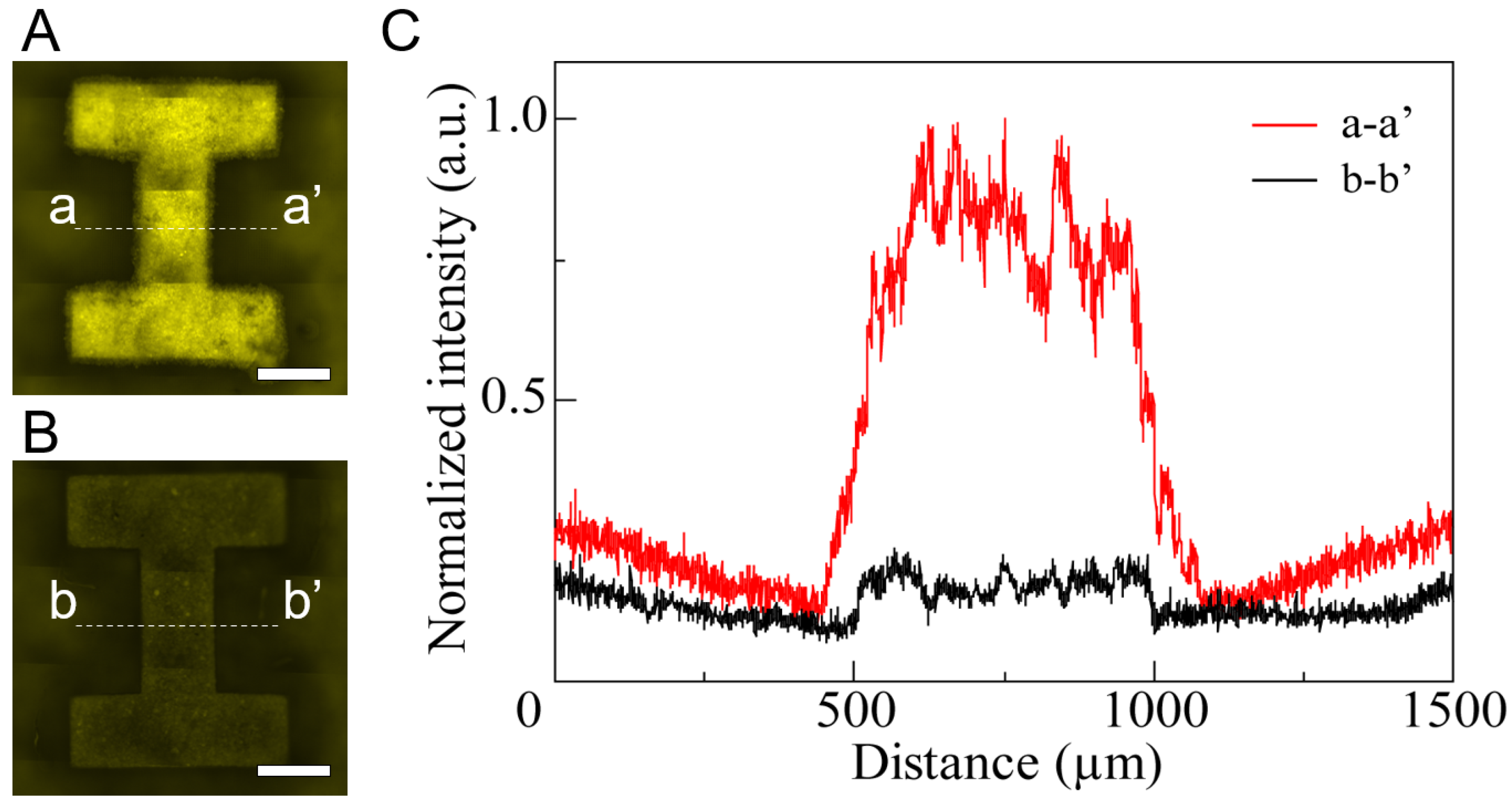
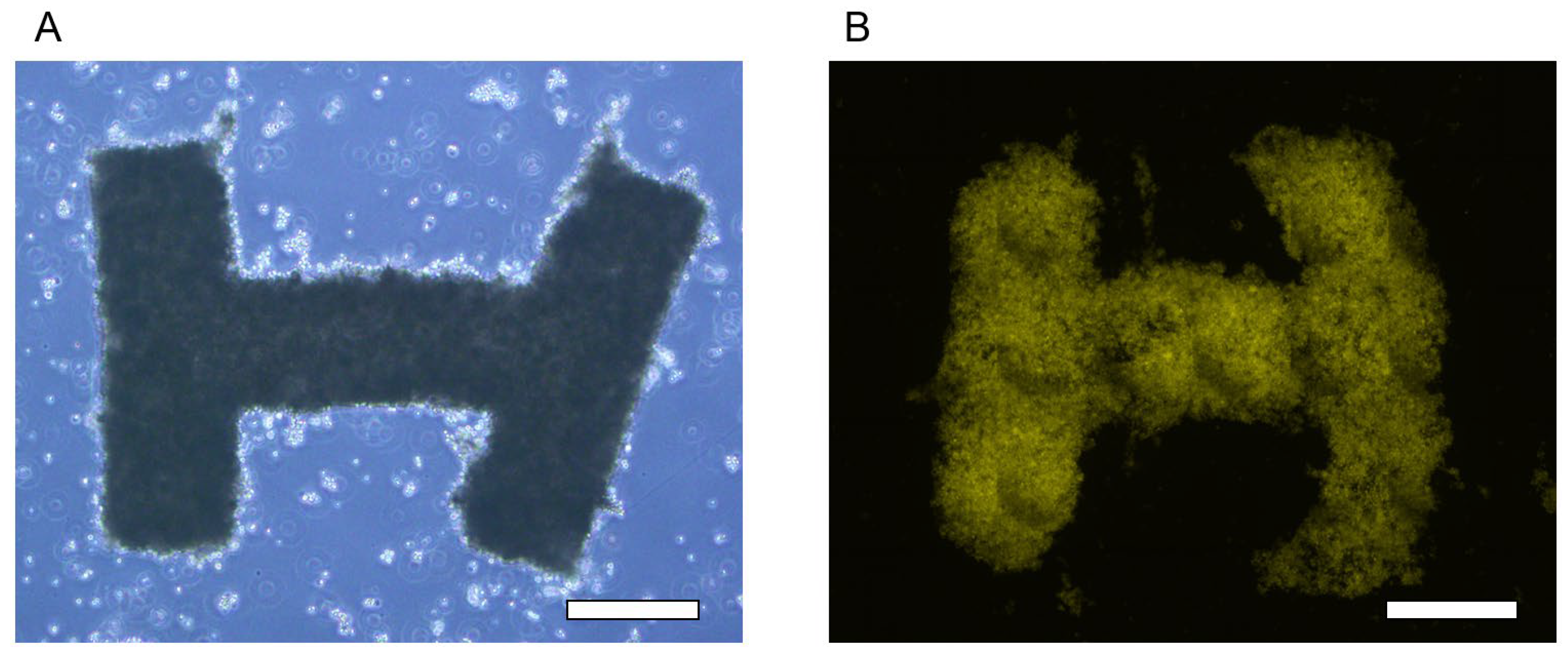
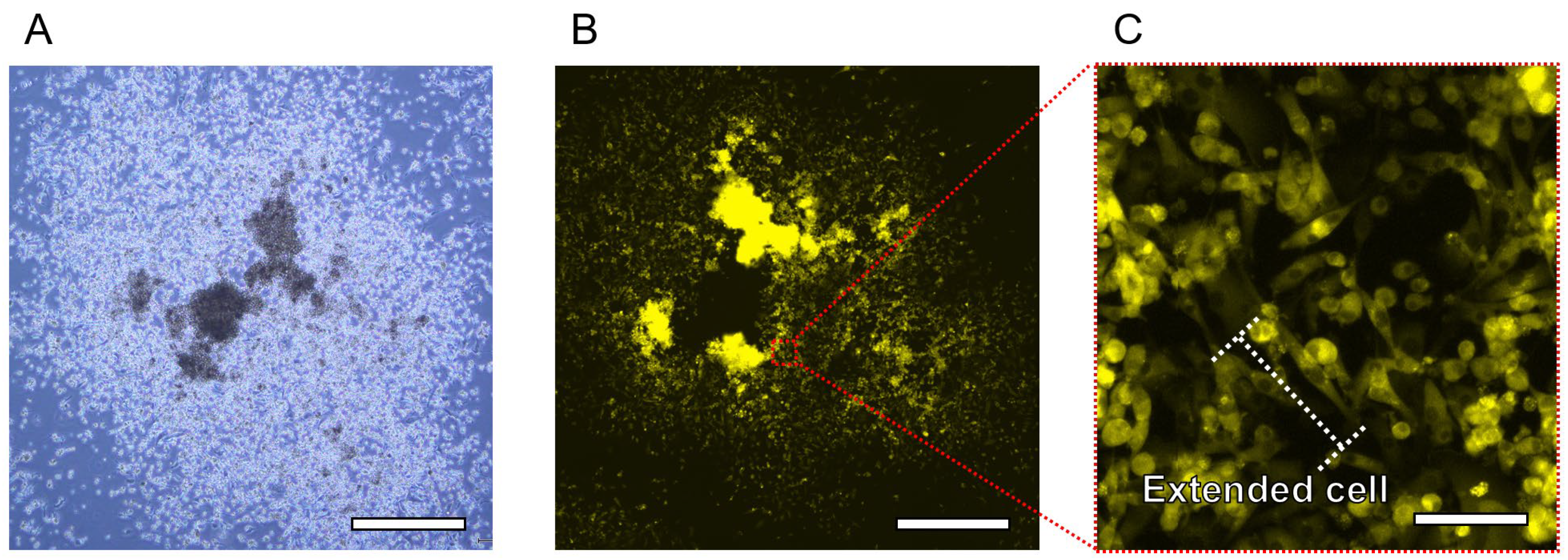
3.2. Tissue Cultivation and Releasing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holland, I.; Logan, J.; Shi, J.; McCormick, C.; Liu, D.; Shu, W. 3D Biofabrication for Tubular Tissue Engineering. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galpayage Dona, K.N.U.; Ramirez, S.H.; Andrews, A.M. A Next-Generation 3D Tissue-Engineered Model of the Human Brain Microvasculature to Study the Blood-Brain Barrier. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaicharoenaudomrung, N.; Kunhorm, P.; Noisa, P. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Systems as an in Vitro Platform for Cancer and Stem Cell Modeling. World J. Stem Cells 2019, 11, 1065–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, H.A.; Moss, S.M.; Hoying, J.B. Vascularized Tissue Organoids. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoya, T.; Anada, T.; Shiwaku, Y.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Suzuki, O. An Oxygen-Permeable Spheroid Culture Chip (Oxy Chip) Promotes Osteoblastic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 232, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, Y. Next-Generation Regenerative Medicine: Organogenesis from Stem Cells in 3D Culture. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lo, K.; Payne, G.F.; Bentley, W.E. Chip Modularity Enables Molecular Information Access from Organ-on-Chip Devices with Quality Control. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 295, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Huang, S.-B.; Cui, Z.; Cui, Z.; Lee, G.-B. Development of Perfusion-Based Micro 3-D Cell Culture Platform and Its Application for High Throughput Drug Testing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, F.; Weltin, A.; Marzioch, J.; Urban, G.A.; Kieninger, J. Zero-Consumption Clark-Type Microsensor for Oxygen Monitoring in Cell Culture and Organ-on-Chip Systems. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Onoe, H.; Takeuchi, S. Biohybrid Robot Powered by an Antagonistic Pair of Skeletal Muscle Tissues. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Onoe, H.; Takeuchi, S. Biohybrid Robot with Skeletal Muscle Tissue Covered with a Collagen Structure for Moving in Air. APL Bioeng. 2020, 4, 026101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, R.D.; Bashir, R.; Arora, N.; Dar, R.D.; Gillette, M.U.; Griffith, L.G.; Kemp, M.L.; Kinlaw, K.; Levin, M.; Martin, A.C.; et al. Perspective: The Promise of Multi-Cellular Engineered Living Systems. APL Bioeng. 2018, 2, 040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.; Przyborski, S. Advances in 3D Cell Culture Technologies Enabling Tissue-like Structures to Be Created in Vitro. J. Anat. 2015, 227, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, T. Techniques for Fabrication and Construction of Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2013, 8, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Q.L.; Choong, C. Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: Role of Porosity and Pore Size. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarvarti, S.K. Track-Etch Membranes Enabled Nano-/Microtechnology: A Review. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Mochida, J.; Sakai, D.; Nakai, T.; Nishimura, K.; Kawada, H.; Hotta, T. Upregulation of the Viability of Nucleus Pulposus Cells by Bone Marrow-Derived Stromal Cells: Significance of Direct Cell-to-Cell Contact in Coculture System. Spine 2004, 29, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, H.W.; Smith, L.A.; Williams, R.J.; Przyborski, S.A. Applications of Novel Bioreactor Technology to Enhance the Viability and Function of Cultured Cells and Tissues. Interface Focus 2020, 10, 20190090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, I.; Haag, M.; Ugbode, C.; Tams, D.; Rattray, M.; Przyborski, S.; Bithell, A.; Whalley, B.J. Neuronal-Glial Populations Form Functional Networks in a Biocompatible 3D Scaffold. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 609, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Kook, Y.-M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, H.; Koh, W.-G. A Three-Dimensional Co-Culture of HepG2 Spheroids and Fibroblasts Using Double-Layered Fibrous Scaffolds Incorporated with Hydrogel Micropatterns. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61005–61011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabionet, M.; Yeste, M.; Puig, T.; Ciurana, J. Electrospinning PCL Scaffolds Manufacture for Three-Dimensional Breast Cancer Cell Culture. Polymers 2017, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Fu, J.; He, Y. Rapid Assembling Organ Prototypes with Controllable Cell-Laden Multi-Scale Sheets. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2019, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoe, H.; Okitsu, T.; Itou, A.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Gojo, R.; Kiriya, D.; Sato, K.; Miura, S.; Iwanaga, S.; Kuribayashi-Shigetomi, K.; et al. Metre-Long Cell-Laden Microfibres Exhibit Tissue Morphologies and Functions. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurashina, Y.; Sato, R.; Onoe, H. Microfiber-Shaped Building-Block Tissues with Endothelial Networks for Constructing Macroscopic Tissue Assembly. APL Bioeng. 2019, 3, 046101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokomizo, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Takeuchi, S. Temporal Observation of Adipocyte Microfiber Using Anchoring Device. Micromachines 2019, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennema, E.; Rivron, N.; Rouwkema, J.; Van Blitterswijk, C.; De Boer, J. Spheroid Culture as a Tool for Creating 3D Complex Tissues. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Ikeuchi, M.; Noguchi, H.; Yagi, T.; Hayashi, S. Spheroid Formation and Evaluation of Hepatic Cells in a Three-Dimensional Culture Device. Cell Med. 2015, 8, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshksayan, K.; Kashaninejad, N.; Warkiani, M.E.; Lock, J.G.; Moghadas, H.; Firoozabadi, B.; Saidi, M.S.; Nguyen, N.-T. Spheroids-on-a-Chip: Recent Advances and Design Considerations in Microfluidic Platforms for Spheroid Formation and Culture. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivron, N.C.; Vrij, E.J.; Rouwkema, J.; Le Gac, S.; Van Den Berg, A.; Truckenmüller, R.K.; Van Blitterswijk, C.A. Tissue Deformation Spatially Modulates VEGF Signaling and Angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6886–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, O.; Misun, P.M.; Fluri, D.A.; Hengstler, J.G.; Hierlemann, A. Reconfigurable Microfluidic Hanging Drop Network for Multi-Tissue Interaction and Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture: The Missing Link in Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benwood, C.; Chrenek, J.; Kirsch, R.L.; Masri, N.Z.; Richards, H.; Teetzen, K.; Willerth, S.M. Natural Biomaterials and Their Use as Bioinks for Printing Tissues. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddon, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C. Osteochondral Tissue Repair in Osteoarthritic Joints: Clinical Challenges and Opportunities in Tissue Engineering. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Starly, B.; Daly, A.C.; Burdick, J.A.; Groll, J.; Skeldon, G.; Shu, W.; Sakai, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Nishikawa, M.; et al. The Bioprinting Roadmap. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülow, A.; Schäfer, B.; Beier, J.P. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting in Soft Tissue Engineering for Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Inoue, M.; Okonogi, A.; Kotera, H.; Suzuki, T. Correlation between Cells-on-Chips Materials and Cell Adhesion/Proliferation Focused on Material’s Surface Free Energy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 565, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, E.; Salerno, S.; Barbieri, G.; De Bartolo, L.; Drioli, E.; Bader, A. Mass Transfer and Metabolic Reactions in Hepatocyte Spheroids Cultured in Rotating Wall Gas-Permeable Membrane System. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, P.B.; Vyas, R.; Wadhwa, M.; Verma, S. Progress in Deep-UV Photoresists. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2002, 25, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huh, D.; Leslie, D.C.; Matthews, B.D.; Fraser, J.P.; Jurek, S.; Hamilton, G.A.; Thorneloe, K.S.; McAlexander, M.A.; Ingber, D.E. A Human Disease Model of Drug Toxicity–Induced Pulmonary Edema in a Lung-on-a-Chip Microdevice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 159ra147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Nagata, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Sugahara, K.; Miura, S.; Takeuchi, S. Microfluidic System for Applying Shear Flow to Endothelial Cells on Culture Insert with Collagen Vitrigel Membrane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Li, D.J.; Pham, L.K.; Wong, B.G.; Hui, E.E. Microfabrication of High-Resolution Porous Membranes for Cell Culture. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennemeyer, M.; Walther, F.; Kerstan, S.; Schürzinger, K.; Gigler, A.M.; Stark, R.W. Cell Proliferation Assays on Plasma Activated SU-8. Microelectron. Eng. 2008, 85, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, T. Integration Method of Microchannel and Vertical Micromesh Structure for Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Using Inclined Exposure and Inclined Oxygen Ashing. Micromachines 2018, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, M.B.; Sung, J.H.; Yang, J.; Yu, C.; Yu, J.; March, J.C.; Shuler, M.L. On Chip Porous Polymer Membranes for Integration of Gastrointestinal Tract Epithelium with Microfluidic ‘Body-on-a-Chip’ Devices. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torizal, F.G.; Lau, Q.Y.; Ibuki, M.; Kawai, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Minami, M.; Michiue, T.; Horiguchi, I.; Nishikawa, M.; Sakai, Y. A Miniature Dialysis-Culture Device Allows High-Density Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Expansion from Growth Factor Accumulation. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornoff, D.M.; Wang, Y.; Proctor, A.; Shah, A.S.; Allbritton, N.L. Co-Fabrication of Chitosan and Epoxy Photoresist to Form Microwell Arrays with Permeable Hydrogel Bottoms. Biomaterials 2016, 74, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Designed (μm) | Measured (μm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pore (Top) | 14 | 14.87 ± 1.83 |
| Pore (Back) | 15.51 ± 0.75 | |
| Lattice (Top) | 3 | 2.24 ± 0.10 |
| Lattice (Back) | 1.72 ± 0.04 | |
| Thickness (Micromesh) | 10 | 9.96 ± 0.92 |
| Thickness (Microchamber) | >200 | 555.26 ± 11.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueno, H.; Yamamura, S. Fabrication Method for Shape-Controlled 3D Tissue Using High-Porosity Porous Structure. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020160
Ueno H, Yamamura S. Fabrication Method for Shape-Controlled 3D Tissue Using High-Porosity Porous Structure. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020160
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeno, Hidetaka, and Shohei Yamamura. 2024. "Fabrication Method for Shape-Controlled 3D Tissue Using High-Porosity Porous Structure" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020160
APA StyleUeno, H., & Yamamura, S. (2024). Fabrication Method for Shape-Controlled 3D Tissue Using High-Porosity Porous Structure. Bioengineering, 11(2), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020160










