Accuracy of Dental Implant Placement with Dynamic Navigation—Investigation of the Influence of Two Different Optical Reference Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Structure
- Interocclusal gaps in the maxillary and/or mandibular posterior regions.
- Free-end situations in the maxillary and/or mandibular posterior regions.
- The extraction must have taken place at least 3 months ago. Only early implantations (3–6 months post-extraction) and late implantations (>6 months post-extraction) are performed.
- The marker tray used as a reference point must be tooth-supported. Therefore, there must be at least 6 remaining teeth in the jaw to be implanted.
- The patient must demonstrate good oral hygiene and compliance.
- A pre-implant hygiene phase and pre-treatments must be completed.
- The patient’s declaration of consent must be available.
- Persons under 18 or persons without legal capacity.
- Untreated acute periodontitis with pocket depths > 4 mm.
- Heavy smokers (more than 10 cigarettes/day).
- Taking bisphosphonates.
- Pregnant women.
- Alcohol and drug addicts.
- Patients with an infectious disease such as hepatitis or HIV/AIDS.
- Patients with severe diabetes mellitus.
- Immediate implantations.
- Width of the gap in the mesiodistal direction for single-tooth gaps < 7.1 mm.
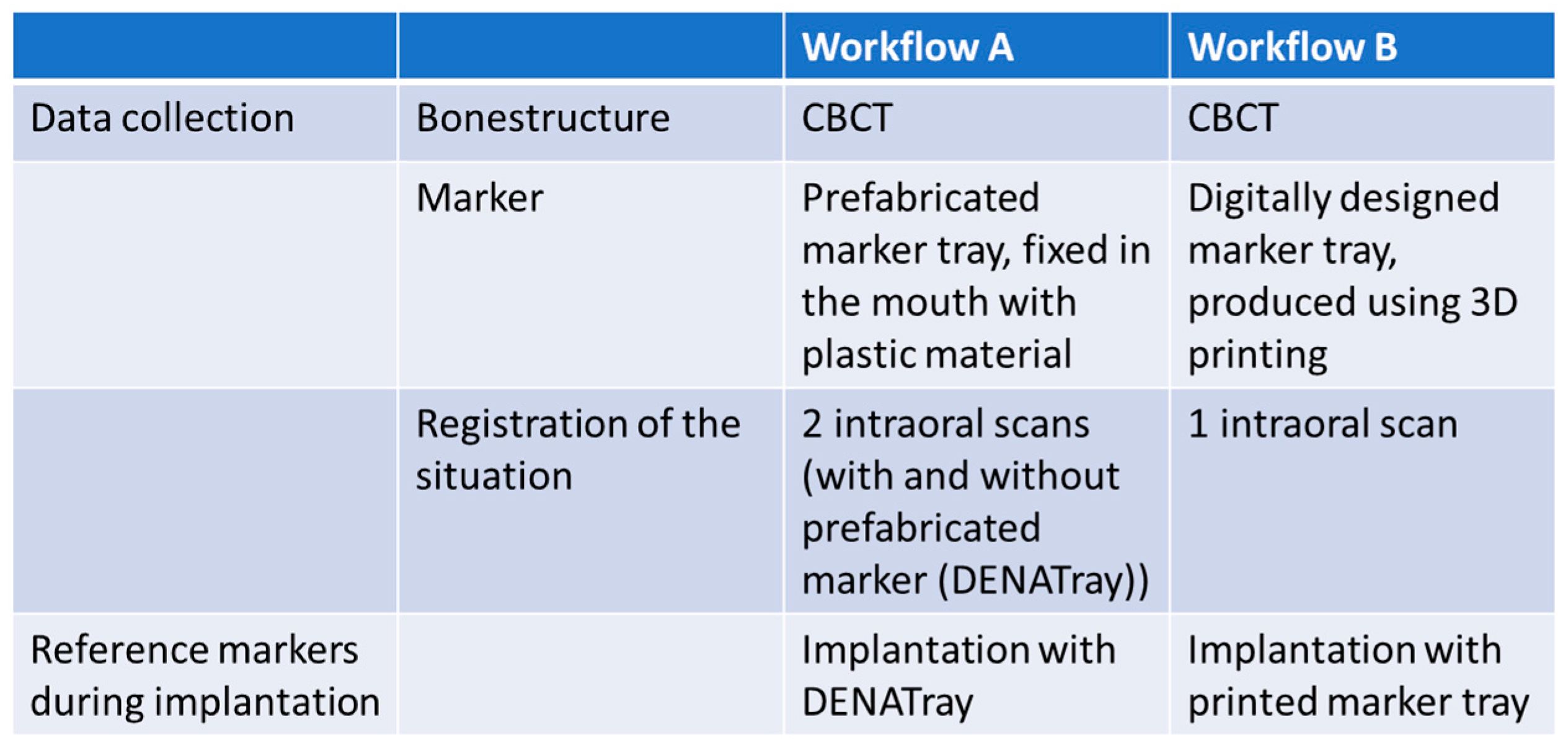
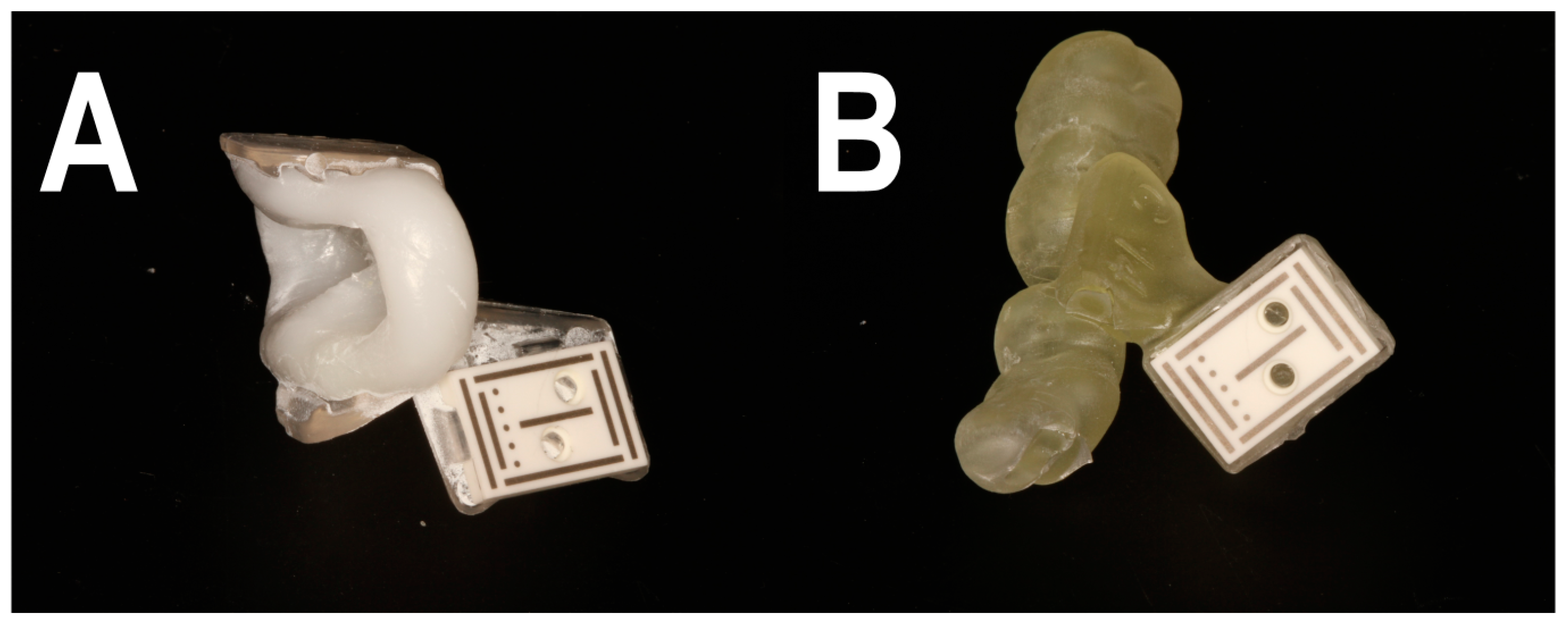
2.2. Workflow A
2.3. Workflow B
2.4. Randomization
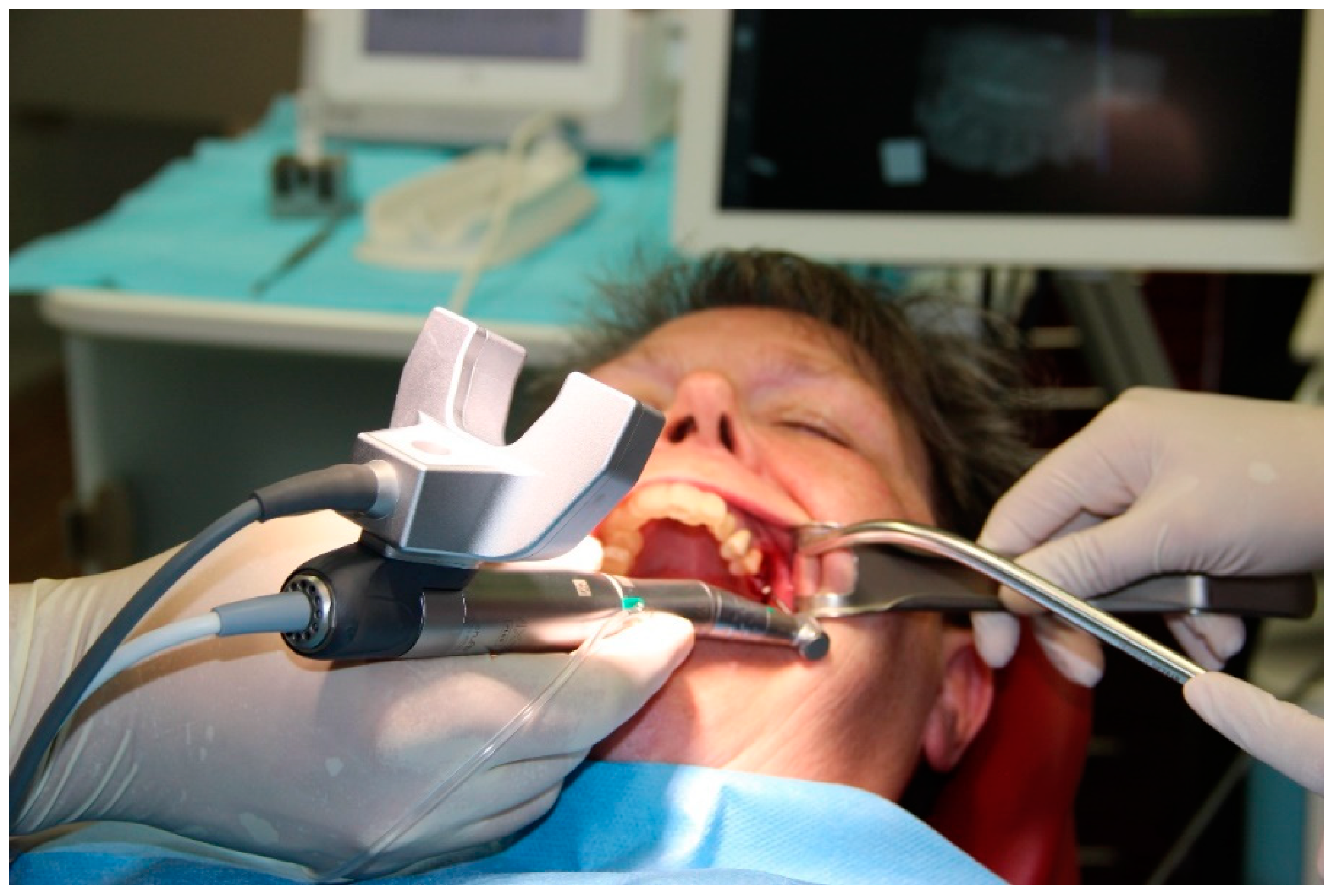
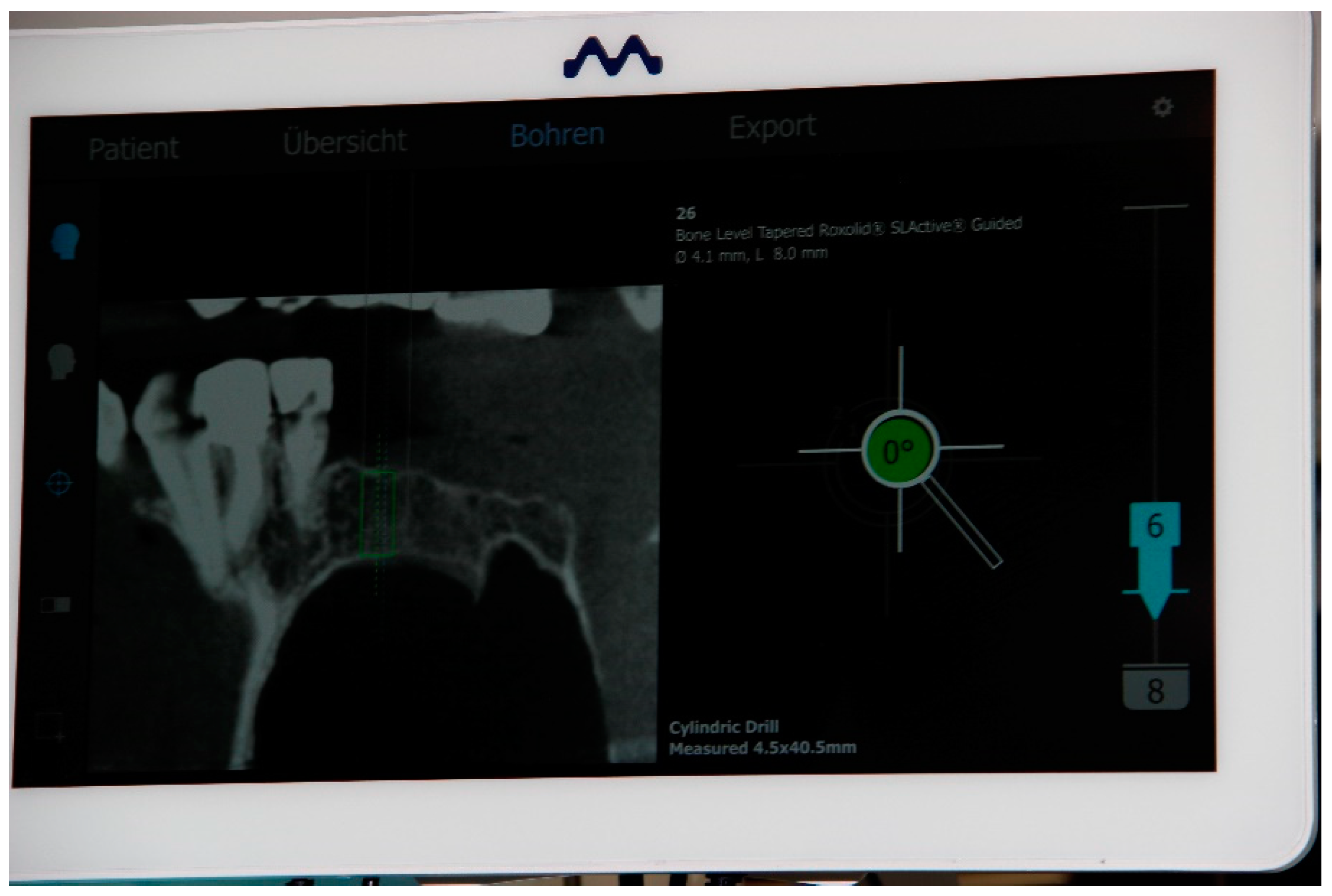
2.5. Registration of the Implant Position
- Three-dimensional deviation: the three-dimensional deviation of the center points between the planning and the clinically achieved positions of the implants measured at the implant shoulder and the implant apex (corresponds to the Euclidean distance);
- Apicocoronal deviation: includes the difference in height, i.e., the spatial offset in the vertical direction, measured at the center of the implant shoulder;
- Axial deviation: angular deviation of the implant axes from the implant planning and clinically achieved implant positions;
- Two-dimensional deviation: the two-dimensional deviation in the mesiodistal and buccolingual directions measured at the implant shoulder and the implant axis.
2.6. Sample Size
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Result
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reda, R.; Zanza, A.; Cicconetti, A.; Bhandi, S.; Guarnieri, R.; Testarelli, L.; Di Nardo, D. A Systematic Review of Cementation Techniques to Minimize Cement Excess in Cement-Retained Implant Restorations. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnutenhaus, S.; Edelmann, C.; Rudolph, H.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Luthardt, R.G. 3D accuracy of implant positions in template-guided implant placement as a function of the remaining teeth and the surgical procedure: A retrospective study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, M.; Poli, P.P.; Maiorana, C. Accuracy of computer-aided template-guided oral implant placement: A prospective clinical study. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2014, 44, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaivani, G.; Balaji, V.R.; Manikandan, D.; Rohini, G. Expectation and reality of guided implant surgery protocol using computer-assisted static and dynamic navigation system at present scenario: Evidence-based literature review. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2020, 24, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Barootchi, S.; Salomó-Coll, O.; Wang, H.L. Advantages and disadvantages of implant navigation surgery. A systematic review. Ann. Anat. 2019, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmaseb, A.; Wu, V.; Wismeijer, D.; Coucke, W.; Evans, C. The accuracy of static computer-aided implant surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 16), 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmaseb, A.; Wismeijer, D.; Coucke, W.; Derksen, W. Computer technology applications in surgical implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2014, 29, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, W.; Liu, C.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y. Accuracy of different types of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing surgical guides for dental implant placement. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8442–8449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vercruyssen, M.; Cox, C.; Coucke, W.; Naert, I.; Jacobs, R.; Quirynen, M. A randomized clinical trial comparing guided implant surgery (bone- or mucosa-supported) with mental navigation or the use of a pilot-drill template. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjelvold, B.; Mahmood, D.J.H.; Wennerberg, A. Accuracy of surgical guides from 2 different desktop 3D printers for computed tomography-guided surgery. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henprasert, P.; Dawson, D.V.; El-Kerdani, T.; Song, X.; Couso-Queiruga, E.; Holloway, J.A. Comparison of the Accuracy of Implant Position Using Surgical Guides Fabricated by Additive and Subtractive Techniques. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieralli, S.; Spies, B.C.; Hromadnik, V.; Nicic, R.; Beuer, F.; Wesemann, C. How Accurate Is Oral Implant Installation Using Surgical Guides Printed from a Degradable and Steam-Sterilized Biopolymer? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, S.; Payer, M.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Lambrecht, J.T.; Filippi, A. Technical accuracy of printed surgical templates for guided implant surgery with the coDiagnostiX™ software. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 1), e177–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Huan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, C.; Li, J. In Vitro Experimental Study of the Effect of Adjusting the Guide Sleeve Height and Using a Visual Direction-Indicating Guide on Implantation Accuracy. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarico, M.; Martinolli, M.; Kim, Y.; Cocchi, F.; Meloni, S.M.; Alushi, A.; Xhanari, E. Accuracy of Computer-Assisted Template-Based Implant Placement Using Two Different Surgical Templates Designed with or without Metallic Sleeves: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnutenhaus, S.; Edelmann, C.; Rudolph, H.; Luthardt, R.G. Retrospective study to determine the accuracy of template-guided implant placement using a novel nonradiologic evaluation method. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 121, e72–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haese, J.; Ackhurst, J.; Wismeijer, D.; De Bruyn, H.; Tahmaseb, A. Current state of the art of computer-guided implant surgery. Periodontology 2000 2017, 73, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruyssen, M.; Fortin, T.; Widmann, G.; Jacobs, R.; Quirynen, M. Different techniques of static/dynamic guided implant surgery: Modalities and indications. Periodontology 2000 2014, 66, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brief, J.; Edinger, D.; Hassfeld, S.; Eggers, G. Accuracy of image-guided implantology. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Westendorff, C.; Gomez-Roman, G.; Reinert, S. Accuracy of navigation-guided socket drilling before implant installation compared to the conventional free-hand method in a synthetic edentulous lower jaw model. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, F.J.; Baethge, C.; Swennen, G.; Rosahl, S. Navigated vs. conventional implant insertion for maxillary single tooth replacement. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.T. A Novel Application of Dynamic Navigation System in Socket Shield Technique. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 45, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.S.; Emery, R.W. Static or Dynamic Navigation for Implant Placement-Choosing the Method of Guidance. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorba-García, A.; Figueiredo, R.; González-Barnadas, A.; Camps-Font, O.; Valmaseda-Castellón, E. Accuracy and the role of experience in dynamic computer guided dental implant surgery: An in-vitro study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2019, 24, e76–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, G.; Bellini, P.; Cavallini, P.F.; Ferri, A.; Zacchino, A.; Taraschi, V.; Marchetti, C.; Consolo, U. Dynamic Navigation in Dental Implantology: The Influence of Surgical Experience on Implant Placement Accuracy and Operating Time. An in Vitro Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y. Accuracy of dynamic navigation compared to static surgical guide for dental implant placement. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R.E.; Schneider, D.; Ganeles, J.; Wismeijer, D.; Zwahlen, M.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Tahmaseb, A. Computer technology applications in surgical implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wangrao, K.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Yao, Y. Quantification of image artifacts from navigation markers in dynamic guided implant surgery and the effect on registration performance in different clinical scenarios. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnutenhaus, S.; Knipper, A.; Wetzel, M.; Edelmann, C.; Luthardt, R. Accuracy of Computer-Assisted Dynamic Navigation as a Function of Different Intraoral Reference Systems: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, A.; Pulijala, Y. The application of virtual reality and augmented reality in Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, M.W.H.; Beuer, F.; Schwitalla, A.; Bruhnke, M.; Herklotz, I. Dynamic navigation for dental implant placement in single-tooth gaps: A preclinical pilot investigation. J. Dent. 2022, 125, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnutenhaus, S.; Edelmann, C.; Knipper, A.; Luthardt, R.G. Accuracy of Dynamic Computer-Assisted Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical and In Vitro Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivovics, M.; Takács, A.; Pénzes, D.; Németh, O.; Mijiritsky, E. Accuracy of dental implant placement using augmented reality-based navigation, static computer assisted implant surgery, and the free-hand method: An in vitro study. J. Dent. 2022, 119, 104070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Guasch, J.; Bofarull-Ballus, A.; Giralt-Hernando, M.; Hernandez-Alfaro, F.; Gargallo-Albiol, J. Dynamic Implant Surgery-An Accurate Alternative to Stereolithographic Guides-Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaemsuwan, S.; Arunjaroensuk, S.; Kaboosaya, B.; Subbalekha, K.; Mattheos, N.; Pimkhaokham, A. Comparison of the accuracy of implant position among freehand implant placement, static and dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery in fully edentulous patients: A non-randomized prospective study. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, G.; Ferri, A.; Del Fabbro, M.; Prati, C.; Gandolfi, M.G.; Marchetti, C. Dynamic Navigation in Implant Dentistry: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2021, 36, e121–e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, C.A.; Arısan, V. Accuracy of dental implant placement via dynamic navigation or the freehand method: A split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.S.; Emery, R.W.; Cullum, D.R.; Sheikh, A. Implant Placement Is More Accurate Using Dynamic Navigation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.S.; Emery, R.W.; Lank, K.; Ryan, J. Implant Placement Accuracy Using Dynamic Navigation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewsiri, D.; Panmekiate, S.; Subbalekha, K.; Mattheos, N.; Pimkhaokham, A. The accuracy of static vs. dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery in single tooth space: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, G.; Taraschi, V.; Andrea, Z.; Ferri, A.; Marchetti, C. Dynamic navigation: A prospective clinical trial to evaluate the accuracy of implant placement. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2019, 22, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; DeGroot, B.S.; Lipton, D.I.; Mandelaris, G.A. Accuracy of a Dynamic Dental Implant Navigation System in a Private Practice. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; Mandelaris, G.A.; Franchina, A.; Pranno, N.; Pagliarulo, M.; Cera, F.; Maltese, F.; Angelis, F.; Carlo, S.D. Accuracy of Dynamic Navigation System Workflow for Implant Supported Full Arch Prosthesis: A Case Series. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, L.V.; Mandelaris, G.A.; DeGroot, B.S.; Gambarini, G.; De Angelis, F.; Di Carlo, S. Accuracy of a Novel Trace-Registration Method for Dynamic Navigation Surgery. Int. J. Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2020, 40, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimarj, P.; Subbalekha, K.; Dhanesuan, K.; Siriwatana, K.; Mattheos, N.; Pimkhaokham, A. Comparison of the accuracy of implant position for two-implants supported fixed dental prosthesis using static and dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorba-García, A.; González-Barnadas, A.; Camps-Font, O.; Figueiredo, R.; Valmaseda-Castellón, E. Accuracy assessment of dynamic computer-aided implant placement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 2479–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.M.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, J.X.; Zhang, C.N.; Shi, J.Y.; Lai, H.C. Accuracy of dynamic navigation in implant surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Role of Dynamic Navigation Systems in Enhancing the Accuracy of Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forna, N.; Agop-Forna, D. Esthetic aspects in implant-prosthetic rehabilitation. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2019, 92, S6–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hooft, J.; Kielenstijn, G.; Liebregts, J.; Baan, F.; Meijer, G.; D’Haese, J.; Bronkhorst, E.; Verhamme, L. Intraoral Scanning as an Alternative to Evaluate the Accuracy of Dental Implant Placements in Partially Edentate Situations: A Prospective Clinical Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchina, A.; Stefanelli, L.V.; Maltese, F.; Mandelaris, G.A.; Vantaggiato, A.; Pagliarulo, M.; Pranno, N.; Brauner, E.; Angelis, F.; Carlo, S.D. Validation of an Intra-Oral Scan Method Versus Cone Beam Computed Tomography Superimposition to Assess the Accuracy between Planned and Achieved Dental Implants: A Randomized In Vitro Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjerven, H.; Olsen-Bergem, H.; Rønold, H.J.; Riis, U.H.; Ellingsen, J.E. Comparison of postoperative intraoral scan versus cone beam computerised tomography to measure accuracy of guided implant placement-A prospective clinical study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holberg, C.; Steinhäuser, S.; Geis, P.; Rudzki-Janson, I. Cone-beam computed tomography in orthodontics: Benefits and limitations. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2005, 66, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.; Abdulmajeed, A.; Carrico, C.K.; Deeb, G.R.; Bencharit, S. Accuracy and precision of 3D-printed implant surgical guides with different implant systems: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, Z.; Song, L.; Kuo, C.L.; Shafer, D.M. Clinical Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Guided Implant Surgery-A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2018, 18, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, A.; Hardi, E.; Cavalcante, B.G.N.; Szabo, B.; Kispelyi, B.; Joob-Fancsaly, A.; Mikulas, K.; Varga, G.; Hegyi, P.; Kivovics, M. Advancing accuracy in guided implant placement: A comprehensive meta-analysis: Meta-Analysis evaluation of the accuracy of available implant placement Methods. J. Dent. 2023, 139, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group Distribution (Number of Patients) | Group A | 12 | |
| Group B | 15 | ||
| Group distribution (number of patients) | Group A | Women | 7 |
| Men | 5 | ||
| Group B | Women | 7 | |
| Men | 8 | ||
| Group distribution (number of patients) | 20–30 years | 3 | |
| 30–40 years | 4 | ||
| 40–50 years | 7 | ||
| 50–60 years | 4 | ||
| 60–70 years | 7 | ||
| 70–80 years | 2 | ||
| Positions of the implants (number of each position) | Regio 16 | 1 |
| Regio 23 | 1 | |
| Regio 24 | 1 | |
| Regio 25 | 6 | |
| Regio 35 | 1 | |
| Regio 36 | 7 | |
| Regio 45 | 4 | |
| Regio 46 | 6 | |
| Distribution of upper/lower jaw (number of respective jaws) | OK | 9 |
| UK | 18 | |
| Implant distribution (number of implants in each case) | Straumann BLT Length 8.0 mm Diameter 3.3 mm | 2 |
| Straumann BLT Length 8.0 mm Diameter 4.1 mm | 2 | |
| Straumann BLT Length 10.0 mm Diameter 3.3 mm | 7 | |
| Straumann BLT Length 10.0 mm Diameter 4.1 mm | 11 | |
| Straumann BLT Length 10.0 mm Diameter 4.8 mm | 2 | |
| Straumann BLT Length 12.0 mm Diameter 3.3 mm | 1 | |
| Straumann BLT Length 12.0 mm Diameter 4.1 mm | 2 |
| Group A N = 12 Patients/12 Implants | Group B N = 15 Patients/15 Implants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium (SD) | 95% CI | Min– Max | Medium (SD) | 95% CI | Min– Max | |
| Deviations at the implant shoulder (mm) | ||||||
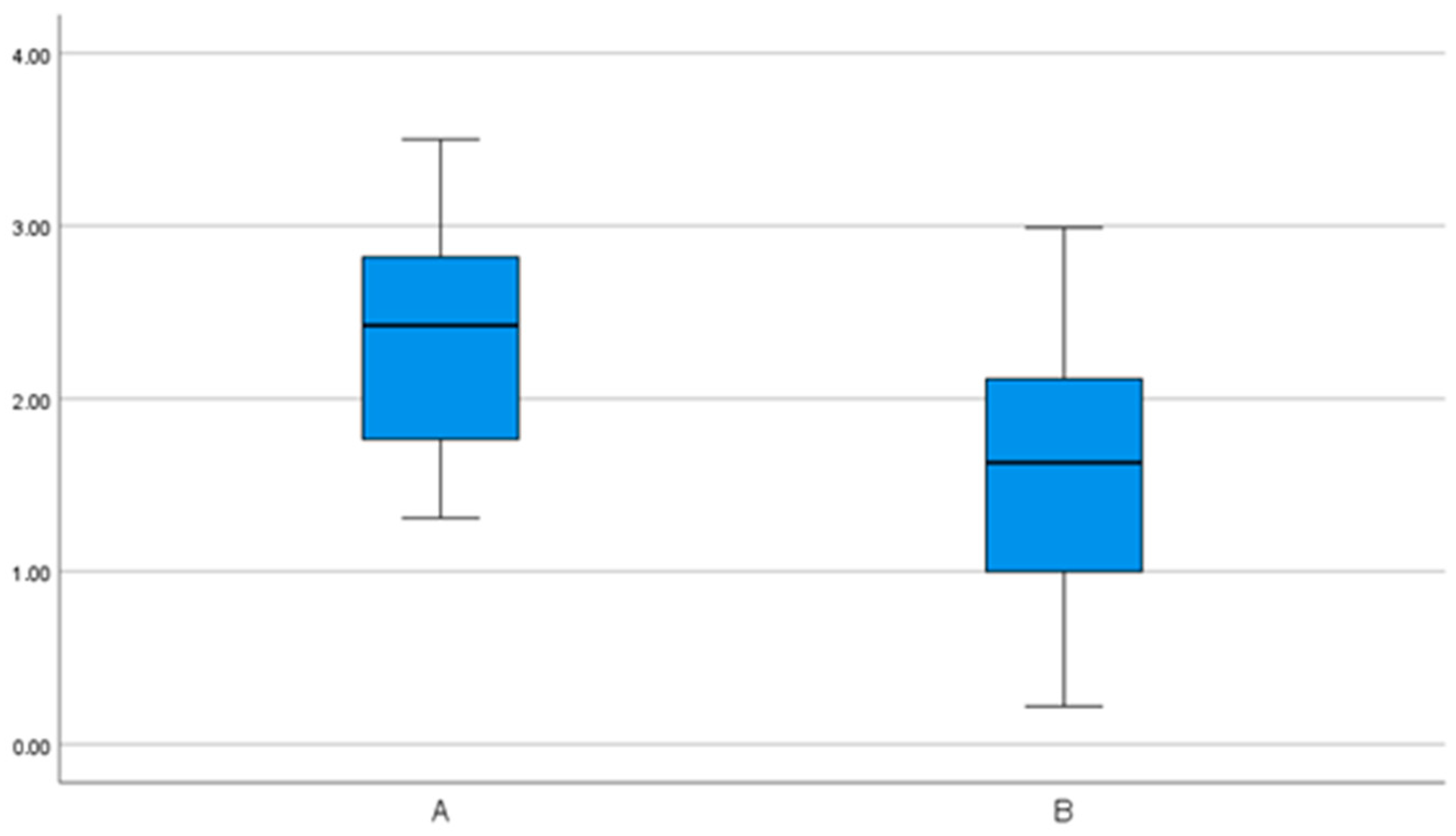
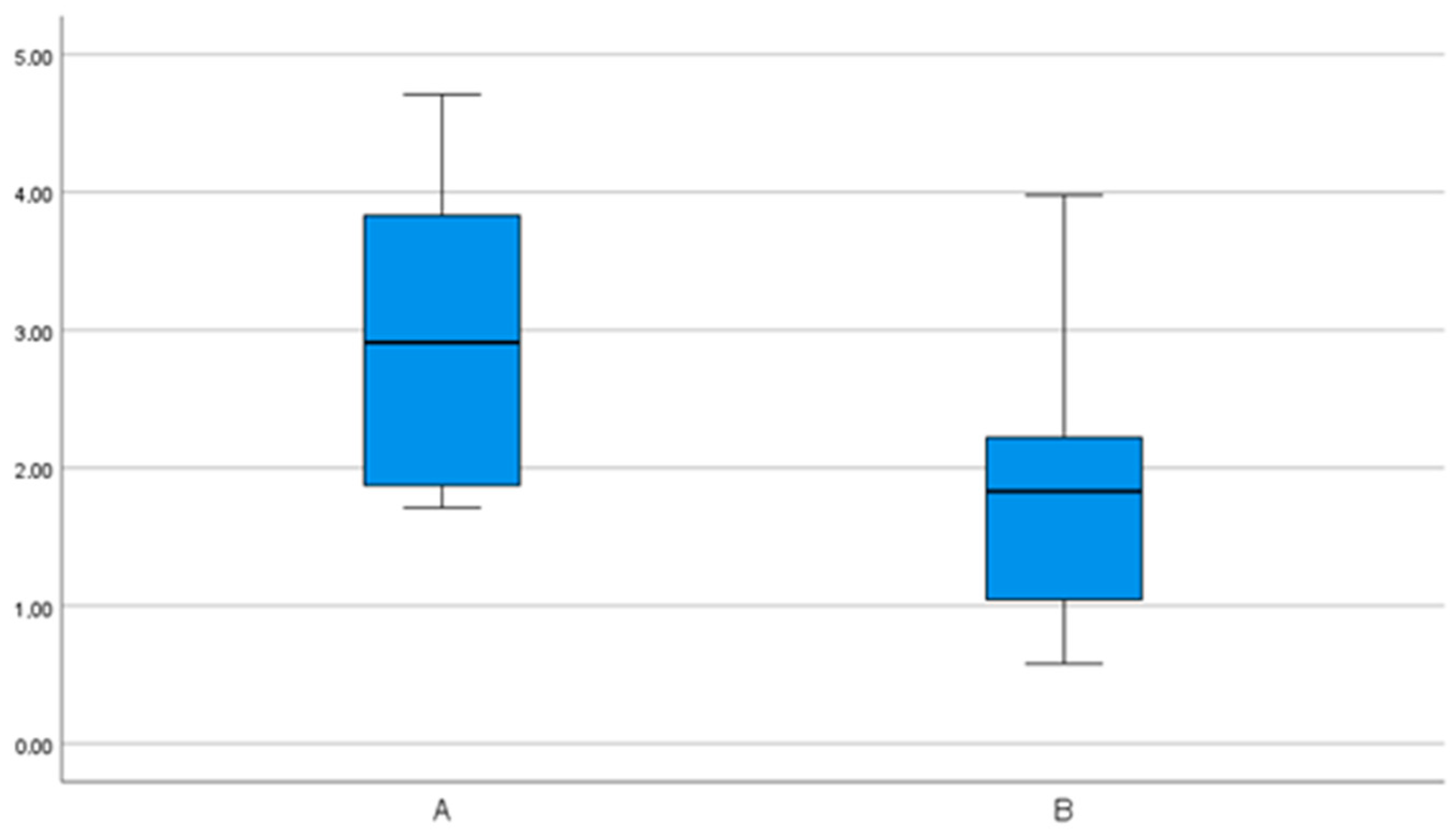
| 3D | 2.35 (0.7) | 1.92– 2.78 | 1.31– 3.5 | 1.62 (0.8) | 1.2– 2.05 | 0.22– 2.99 |
| Mesiodistal | 0.17 (1.7) | −0.9– 1.2 | −2.8– 2.7 | 0.6 (0.8) | 0.2– 1.04 | −0.6– 2.4 |
| Buccolingual | −0.1 (1.0) | −0.8– 0.5 | −1.3– 1.8 | −0.5 (0.7) | −0.93– −0.1 | −2.0– 0.9 |
| Apicocoronal | −1.3 (0.9) | −1.9– −0.8 | −2.3– 1.0 | −0.74 (1.0) | −1.3– −0.2 | −2.1– 0.8 |
| Deviations at the implant tip (mm) | ||||||
| 3D | 3.0 (1.1) | 2.3– 3.7 | 1.7– 4.7 | 1.8 (0.9) | 1.3– 2.3 | 0.6– 4.0 |
| Mesiodistal | 0.1 (2.5) | −1.6– 1.7 | −3.4– 4.3 | 0.7 (1.1) | 0.1– 1.24 | −0.7– 3.3 |
| Buccolingual | −0.3 (1.5) | −1.2– 0.7 | −2.9– 2.2 | −0.6 (0.8) | −1.1– −0.1 | −2.1– 0.7 |
| Apicocoronal | −1.3 (0.8) | −1.8– −0.7 | −2.3– 1.0 | −0.7 (1.0) | −1.3– −0.2 | −2.1– 0.8 |
| Angular deviations (°) | 6.3 (3.7) | 4.0– 8.7 | 0.4– 13.9 | 2.7 (2.0) | 1.6– 3.9 | 0.7– 8.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knipper, A.; Kuhn, K.; Luthardt, R.G.; Schnutenhaus, S. Accuracy of Dental Implant Placement with Dynamic Navigation—Investigation of the Influence of Two Different Optical Reference Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020155
Knipper A, Kuhn K, Luthardt RG, Schnutenhaus S. Accuracy of Dental Implant Placement with Dynamic Navigation—Investigation of the Influence of Two Different Optical Reference Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020155
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnipper, Anne, Katharina Kuhn, Ralph G. Luthardt, and Sigmar Schnutenhaus. 2024. "Accuracy of Dental Implant Placement with Dynamic Navigation—Investigation of the Influence of Two Different Optical Reference Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020155
APA StyleKnipper, A., Kuhn, K., Luthardt, R. G., & Schnutenhaus, S. (2024). Accuracy of Dental Implant Placement with Dynamic Navigation—Investigation of the Influence of Two Different Optical Reference Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Bioengineering, 11(2), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020155









