Label-Free Optical Technologies for Middle-Ear Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Label-Free Optical Techniques
2.1. Autofluorescence Imaging
2.2. Diffuse Reflectance Imaging
2.3. Raman Spectroscopy
2.4. SWIR Imaging
2.5. Optical Coherence Tomography
3. Applications in Disease Diagnosis and Visualization
3.1. Ex Vivo Application
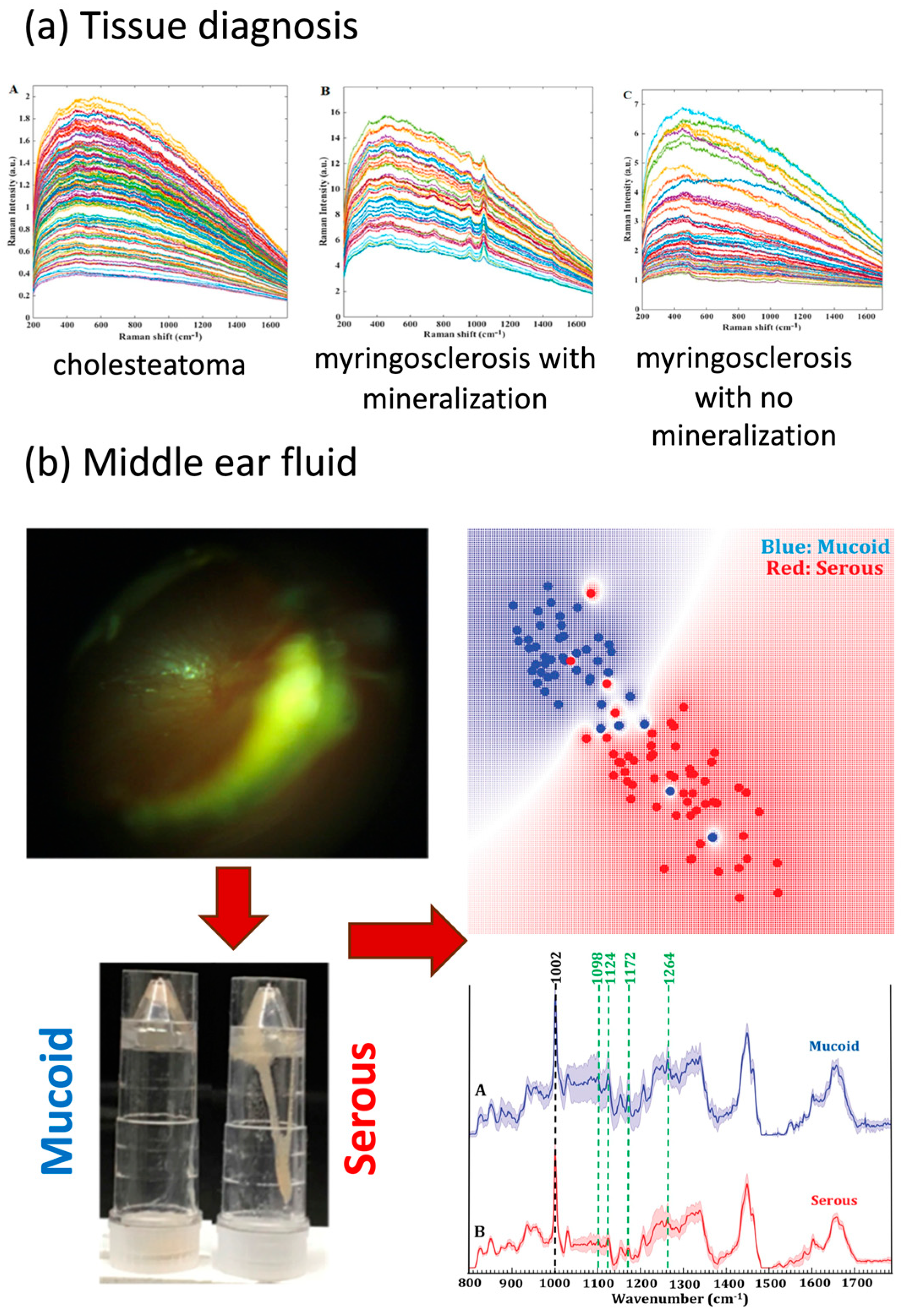
3.1.1. Tissue Diagnosis
3.1.2. Middle-Ear Fluid
3.1.3. Tympanic Membrane Visualization
3.2. In Vivo Application
3.2.1. Tissue Differentiation and Visualization of Tympanic Membrane
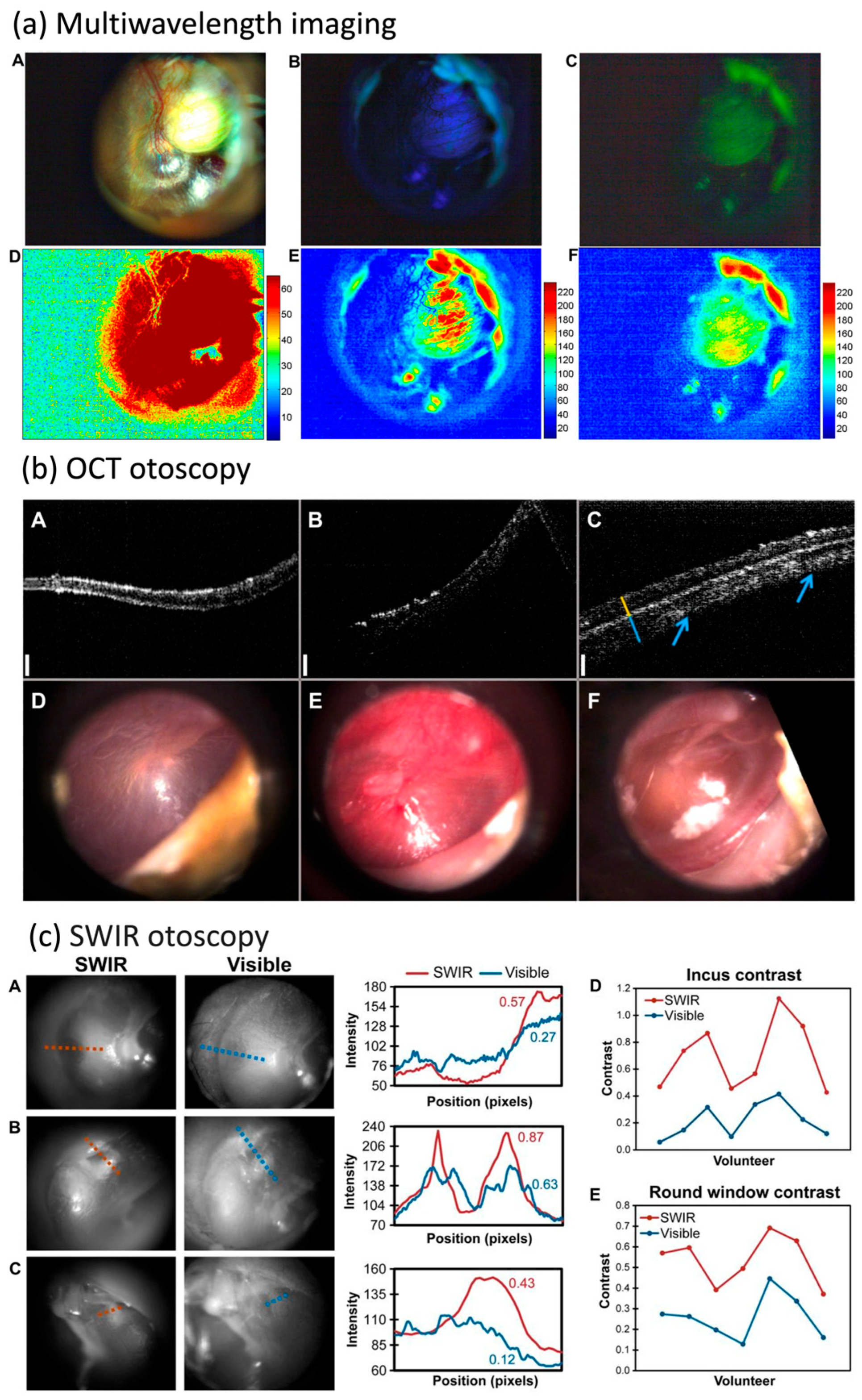
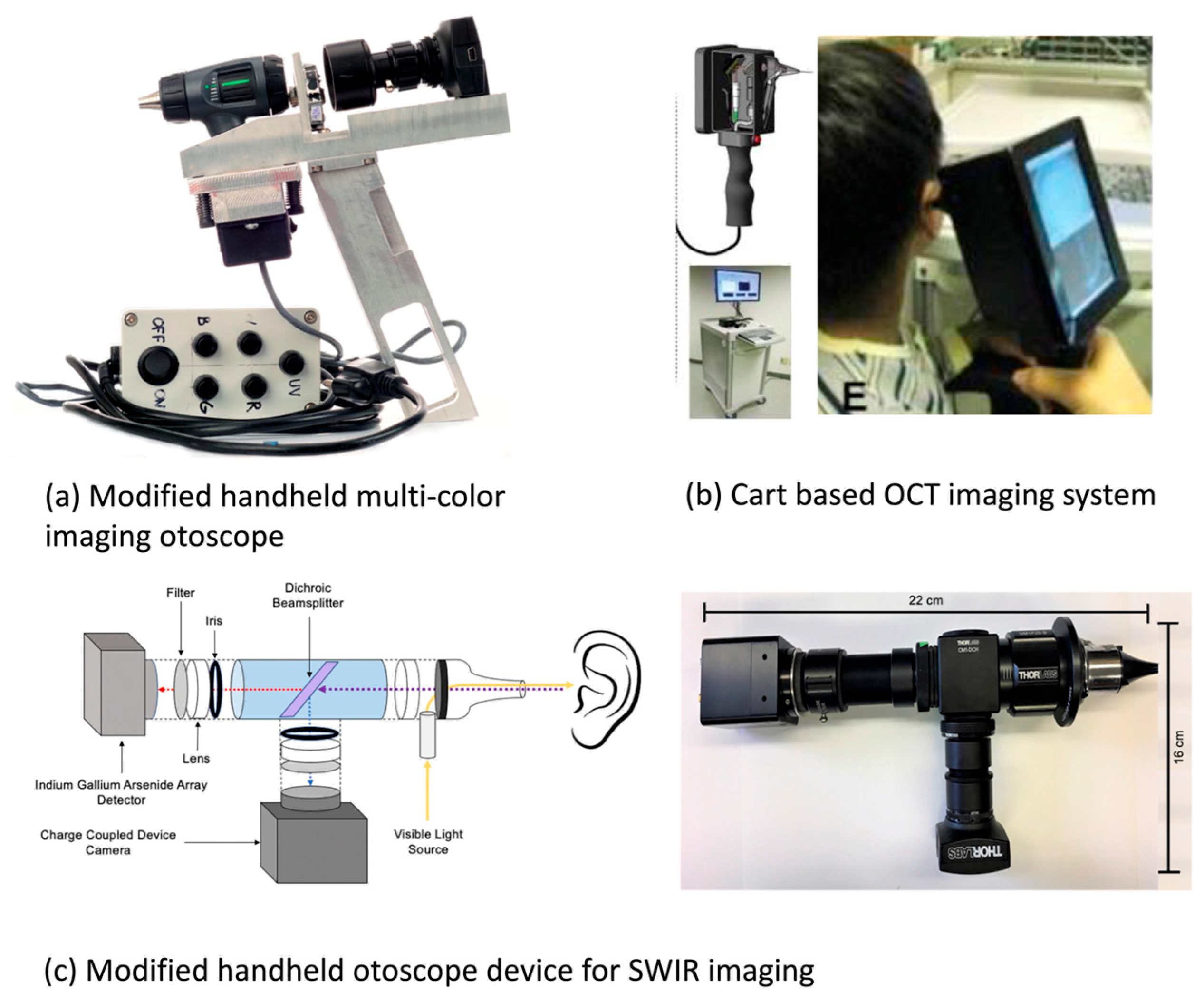
3.2.2. Otitis Media
4. Emerging Opportunities
4.1. Bacteria Identification
4.2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Opportunities
5. Clinical Translational Considerations
5.1. Integration with Clinical Devices: Practical Considerations
5.2. Quality Control of Spectroscopy and Imaging Data
5.3. Clinical Adoption
5.4. Regulatory Challenges
5.5. Democratization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orosco, R.K.; Tsien, R.Y.; Nguyen, Q.T. Fluorescence Imaging in Surgery. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 6, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Owen, V.; Shonde, A.; Kaye, P.; Hawkey, C.; Ragunath, K. White light endoscopy, narrow band imaging and chromoendoscopy with magnification in diagnosing colorectal neoplasia. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 1, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.E.I.; Maria, P.L.S.; Wijesinghe, P.; Kennedy, B.F.; Allardyce, B.J.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Atlas, M.D.; Dilley, R.J. Optical Coherence Tomography of the Tympanic Membrane and Middle Ear: A Review. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, J.G.; Pitris, C.; Boppart, S.A.; Brezinski, M.E. Optical Coherence Tomography: An Emerging Technology for Biomedical Imaging and Optical Biopsy. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zysk, A.M.; Nguyen, F.T.; Oldenburg, A.L.; Marks, D.L.; Boppart, S.A. Optical coherence tomography: A review of clinical development from bench to bedside. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 051403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, R.; Simpson, H.M.; Duberman, J.; Hill, G.C.; Ogawa, M.; Regino, C.; Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Toxicity of Organic Fluorophores Used in Molecular Imaging: Literature Review. Mol. Imaging 2009, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Isomäki, A.; Hirvonen, T.; Aarnisalo, A.; Jero, J.; Pyykkö, I. Label-free visualization of cholesteatoma in the mastoid and tympanic membrane using CARS microscopy. J. Otol. 2016, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Paidi, S.K.; Kang, J.W.; Spegazzini, N.; Dasari, R.R.; Valdez, T.A.; Barman, I. Discerning the differential molecular pathology of proliferative middle ear lesions using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisotzky, E.L.; Rosenthal, J.-C.; Hilsmann, A.; Eisert, P.; Uecker, F.C. A multispectral 3D-Endoscope for Cholesteatoma Removal. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 6, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Farrell, J.; Ye, S.; Ahmad, I.; Valdez, T.A. Imaging guidance for cholesteatoma surgery using tissue autofluorescence. J. Biomed. Opt. 2023, 28, 066003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzian, P.; Lange, B.; Penxová, Z.; Leichtle, A.; Miura, Y.; Bruchhage, K.-L.; Brinkmann, R. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) of human middle ear tissue samples. In Translational Bio-Photonics: Diagnostics and Therapeutics III; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023; pp. 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.A.; Valdez, T.A.; Bruns, O.T.; Bawendi, M.G. Using the shortwave infrared to image middle ear pathologies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9989–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Zhang, C.; Kang, J.W.; Desai, P.M.; Dasari, R.R.; Barman, I.; Valdez, T.A. Differential diagnosis of otitis media with effusion using label-free Raman spectroscopy: A pilot study. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitris, C.; Saunders, K.T.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Brezinski, M.E. High-Resolution Imaging of the Middle Ear with Optical Coherence Tomography: A feasibility study. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2001, 127, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Tu, H.; Chaney, E.J.; Stewart, C.N.; Boppart, S.A. Non-invasive optical interferometry for the assessment of biofilm growth in the middle ear. Biomed. Opt. Express 2010, 1, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, T.A.; Spegazzini, N.; Pandey, R.; Longo, K.; Grindle, C.; Peterson, D.; Barman, I. Multi-color reflectance imaging of middle ear pathology in vivo. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3277–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, T.A.; Pandey, R.; Spegazzini, N.; Longo, K.; Roehm, C.; Dasari, R.R.; Barman, I. Multiwavelength Fluorescence Otoscope for Video-Rate Chemical Imaging of Middle Ear Pathology. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10454–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.T.; Thao, M.L.T.; Quynh, L.B.M.; Khuong, C.P.N.; Quang, L.H. Application of Multispectral Imaging in the Human Tympanic Membrane. J. Health Eng. 2020, 2020, 6219845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisotzky, E.L.; Rosenthal, J.-C.; Wege, U.; Hilsmann, A.; Eisert, P.; Uecker, F.C. Surgical Guidance for Removal of Cholesteatoma Using a Multispectral 3D-Endoscope. Sensors 2020, 20, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalilian, H.R.; Rubinstein, M.; Wu, E.C.; Naemi, K.; Zardouz, S.; Karimi, K.; Wong, B.J.F. Optical Coherence Tomography of Cholesteatoma. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovi, C.; Luchena, A.; Bivona, R.; Borsetto, D.; Creber, N.; Danesi, G. Il colesteatoma ricorrente nella chirurgia dell’orecchio medio: Lezioni imparate e prospettive future. Una narrative review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2023, 43 (Suppl. S1), S48–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, M.; Peebo, M.; Öberg, P.; Lundquist, P.G.; Strömberg, T. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of the human tympanic membrane in otitis media. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, T.A.; Carr, J.A.; Kavanagh, K.R.; Schwartz, M.; Blake, D.; Bruns, O.; Bawendi, M. Initial findings of shortwave infrared otoscopy in a pediatric population. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 114, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, R.G.; Młyńczak, M.C.; Zarabanda, D.; Solis-Pazmino, P.; Huland, D.M.; Ahmad, I.N.; Singh, S.P.; Valdez, T.A. Shortwave infrared otoscopy for diagnosis of middle ear effusions: A machine-learning-based approach. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, G.L.; Shelton, R.L.; Nolan, R.M.; Nguyen, C.T.; Novak, M.A.; Hill, M.C.; McCormick, D.T.; Boppart, S.A. Noninvasive depth-resolved optical measurements of the tympanic membrane and middle ear for differentiating otitis media. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E276–E282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Jung, W.; Kim, J.; Chaney, E.J.; Novak, M.; Stewart, C.N.; Boppart, S.A. Noninvasive in vivo optical detection of biofilm in the human middle ear. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9529–9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubler, Z.; Shemonski, N.D.; Shelton, R.L.; Monroy, G.L.; Nolan, R.M.; Boppart, S.A. Real-time automated thickness measurement of the in vivo human tympanic membrane using optical coherence tomography. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2015, 5, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.L.; Jung, W.; Sayegh, S.I.; McCormick, D.T.; Kim, J.; Boppart, S.A. Optical coherence tomography for advanced screening in the primary care office. J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Cho, N.H.; Jeon, M.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, J.H.; Boppart, S.A.; Jung, W.; Kim, J. Optical assessment of the in vivo tympanic membrane status using a handheld optical coherence tomography-based otoscope. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018, 138, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, T.C.; Lew, H.M.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, M.K.; Hwang, J.Y. Intelligent smartphone-based multimode imaging otoscope for the mobile diagnosis of otitis media. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 7765–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, A.; Sriraman, R.; Sindhuja, P.; Mohideen, K.; Parameswar, R.; Haris, K.M. Autofluorescence based diagnostic techniques for oral cancer. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7 (Suppl. S2), S374–S377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Long, F.; Tang, F.; Jing, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, L.; Ma, J.; Fei, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; et al. Autofluorescence Imaging and Spectroscopy of Human Lung Cancer. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepah, Y.J.; Akhtar, A.; Sadiq, M.A.; Hafeez, Y.; Nasir, H.; Perez, B.; Mawji, N.; Dean, D.J.; Ferraz, D.; Nguyen, Q.D. Fundus autofluorescence imaging: Fundamentals and clinical relevance. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 28, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladurner, R.; Lerchenberger, M.; Al Arabi, N.; Gallwas, J.K.S.; Stepp, H.; Hallfeldt, K.K.J. Parathyroid Autofluorescence—How Does It Affect Parathyroid and Thyroid Surgery? A 5 Year Experience. Molecules 2019, 24, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, F.T.; Zysk, A.M.; Chaney, E.J.; Kotynek, J.G.; Oliphant, U.J.; Bellafiore, F.J.; Rowland, K.M.; Johnson, P.A.; Boppart, S.A. Intraoperative Evaluation of Breast Tumor Margins with Optical Coherence Tomography. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 8790–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tearney, G.J.; Brezinski, M.E.; Southern, J.F.; Bouma, B.E.; Boppart, S.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Optical biopsy in human gastrointestinal tissue using optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 1800–1804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brezinski, M.E.; Tearney, G.J.; Bouma, B.E.; Boppart, S.A.; Hee, M.R.; Swanson, E.A.; Southern, J.F.; Fujimoto, J.G. Imaging of coronary artery microstructure (in vitro) with optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 77, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.G.; Boppart, S.A.; Tearney, G.J.; Bouma, B.E.; Pitris, C.; Brezinski, M.E. High resolution in vivo intra-arterial imaging with optical coherence tomography. Heart 1999, 82, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, M.L.; Wollstein, G.; Ishikawa, H.; Kagemann, L.; Xu, J.; Folio, L.S.; Schuman, J.S. Optical Coherence Tomography: History, Current Status, and Laboratory Work. Investig. Ophtalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 2425–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froom, J.; Culpepper, L.; Grob, P.; Bartelds, A.; Bowers, P.; Bridges-Webb, C.; Grava-Gubins, I.; Green, L.; Lion, J.; Somaini, B. Diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of acute otitis media: Report from International Primary Care Network. BMJ 1990, 300, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searight, F.T.; Singh, R.; Peterson, D.C. Otitis Media with Effusion. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538293/ (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Maquelin, K.; Choo-Smith, L.-P.; van Vreeswijk, T.; Endtz, H.P.; Smith, B.; Bennett, R.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J. Raman Spectroscopic Method for Identification of Clinically Relevant Microorganisms Growing on Solid Culture Medium. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, O.D.; Wakeman, C.A.; Pence, I.J.; O’Brien, C.M.; Werkhaven, J.A.; Skaar, E.P.; Mahadevan-Jansen, A. Characterization of bacteria causing acute otitis media using Raman microspectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Monroy, G.L.; You, S.; Shelton, R.L.; Nolan, R.M.; Tu, H.; Chaney, E.J.; Boppart, S.A. Rapid diagnosis and differentiation of microbial pathogens in otitis media with a combined Raman spectroscopy and low-coherence interferometry probe: Toward in vivo implementation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.K.; Zaki, F.R.; Fitzgerald, S.T.; Sudhir, K.; Monroy, G.L.; Choi, H.; Won, J.; Mahadevan-Jansen, A.; Boppart, S.A. Differentiation of otitis media-causing bacteria and biofilms via Raman spectroscopy and optical coherence tomography. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 869761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowson, M.G.; Ranisau, J.; Eskander, A.; Babier, A.; Xu, B.; Kahmke, R.R.; Chen, J.M.; Chan, T.C.Y. A contemporary review of machine learning in otolaryngology–head and neck surgery. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroğlu, O.; Eroğlu, Y.; Yıldırım, M.; Karlıdag, T.; Çınar, A.; Akyiğit, A.; Kaygusuz, I.; Yıldırım, H.; Keleş, E.; Yalçın, Ş. Comparison of Computed Tomography-Based Artificial Intelligence Modeling and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Diagnosis of Cholesteatoma. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2023, 19, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.-R.; Crossland, G.; Patel, H.; Wong, E.; Kong, K.; Gunasekera, H.; Richards, B.; Caffery, L.; Perry, C.; Sacks, R.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Computer-vision Algorithm to Triage Otoscopic Images from Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Children. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, D.; Chau, J. Otoscopic diagnosis using computer vision: An automated machine learning approach. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscaino, M.; Maass, J.C.; Delano, P.H.; Torrente, M.; Stott, C.; Cheein, F.A. Computer-aided diagnosis of external and middle ear conditions: A machine learning approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscaino, M.; Talamilla, M.; Maass, J.C.; Henríquez, P.; Délano, P.H.; Cheein, C.A.; Cheein, F.A. Color Dependence Analysis in a CNN-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Middle and External Ear Diseases. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, O.; Yildirim, M. Automatic detection of eardrum otoendoscopic images in patients with otitis media using hybrid-based deep models. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, G.L.; Won, J.; Dsouza, R.; Pande, P.; Hill, M.C.; Porter, R.G.; Novak, M.A.; Spillman, D.R.; Boppart, S.A. Automated classification platform for the identification of otitis media using optical coherence tomography. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroy, G.L.; Won, J.; Shi, J.; Hill, M.C.; Porter, R.G.; Novak, M.A.; Hong, W.; Khampang, P.; Kerschner, J.E.; Spillman, D.R.; et al. Automated classification of otitis media with OCT: Augmenting pediatric image datasets with gold-standard animal model data. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 3601–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Application Setting | Application Area | Technology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ex vivo | Middle-ear tissue diagnosis | Raman spectroscopy | [7,8] |
| Autofluorescence imaging | [9,10,11] | ||
| Middle-ear fluid detection and differentiation | SWIR imaging | [12] | |
| Raman spectroscopy | [13] | ||
| Tympanic membrane visualization | OCT | [14,15] | |
| SWIR imaging | [12] | ||
| In vivo | Tissue differentiation and visualization of tympanic membrane | Multicolor or multispectral autofluorescence imaging | [16,17,18,19] |
| SWIR imaging | [12] | ||
| OCT | [20,21] | ||
| Otitis media | DRS | [22] | |
| SWIR | [23,24] | ||
| OCT | [25,26,27,28,29] | ||
| Multimodal | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Pandey, R.; Valdez, T.A. Label-Free Optical Technologies for Middle-Ear Diseases. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020104
Zhou Z, Pandey R, Valdez TA. Label-Free Optical Technologies for Middle-Ear Diseases. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zeyi, Rishikesh Pandey, and Tulio A. Valdez. 2024. "Label-Free Optical Technologies for Middle-Ear Diseases" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020104
APA StyleZhou, Z., Pandey, R., & Valdez, T. A. (2024). Label-Free Optical Technologies for Middle-Ear Diseases. Bioengineering, 11(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020104







