The Role of Eye Movements in the Process of Silicone Oil Emulsification After Vitreoretinal Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Working Fluids and Eye Model Filling Protocol
2.3. Simulation of Eye Movements
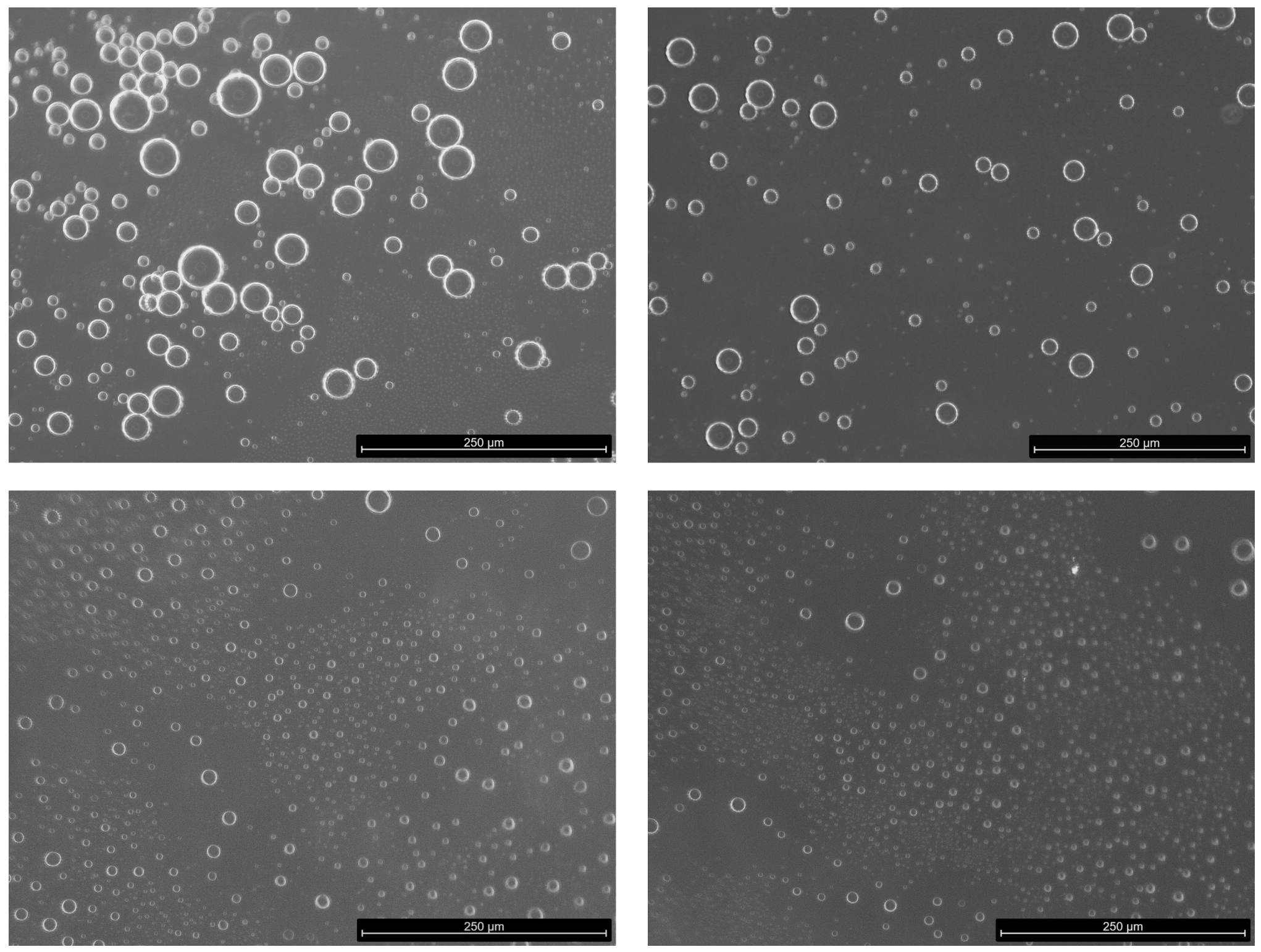
2.4. Microscope Image Acquisition
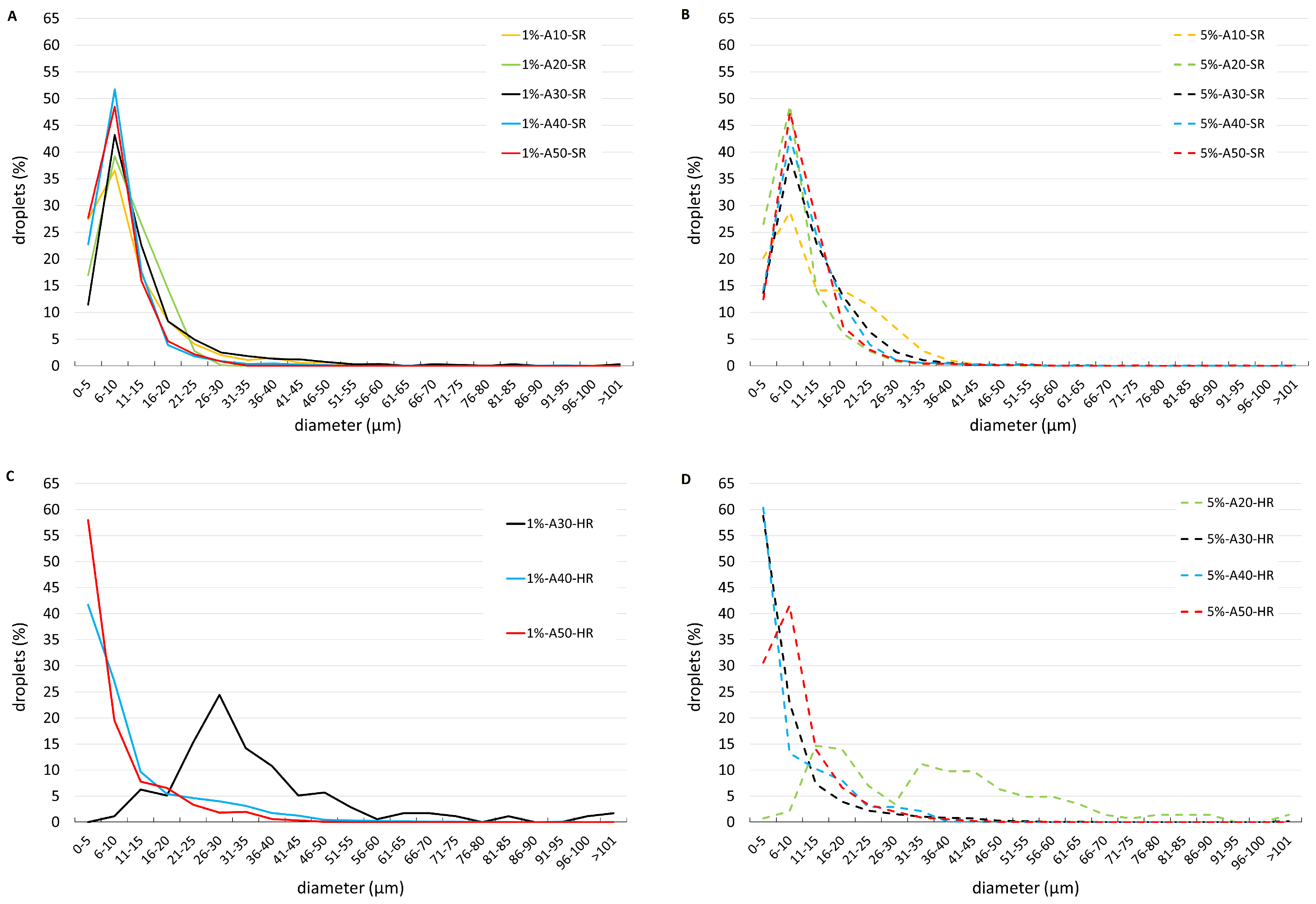
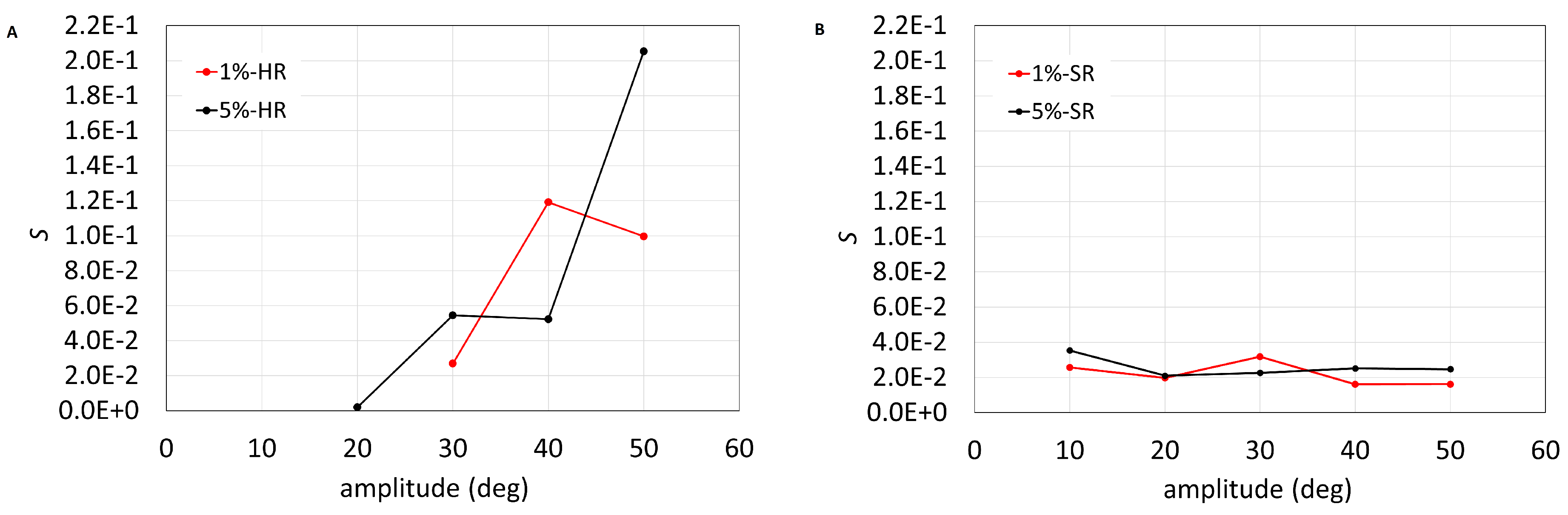
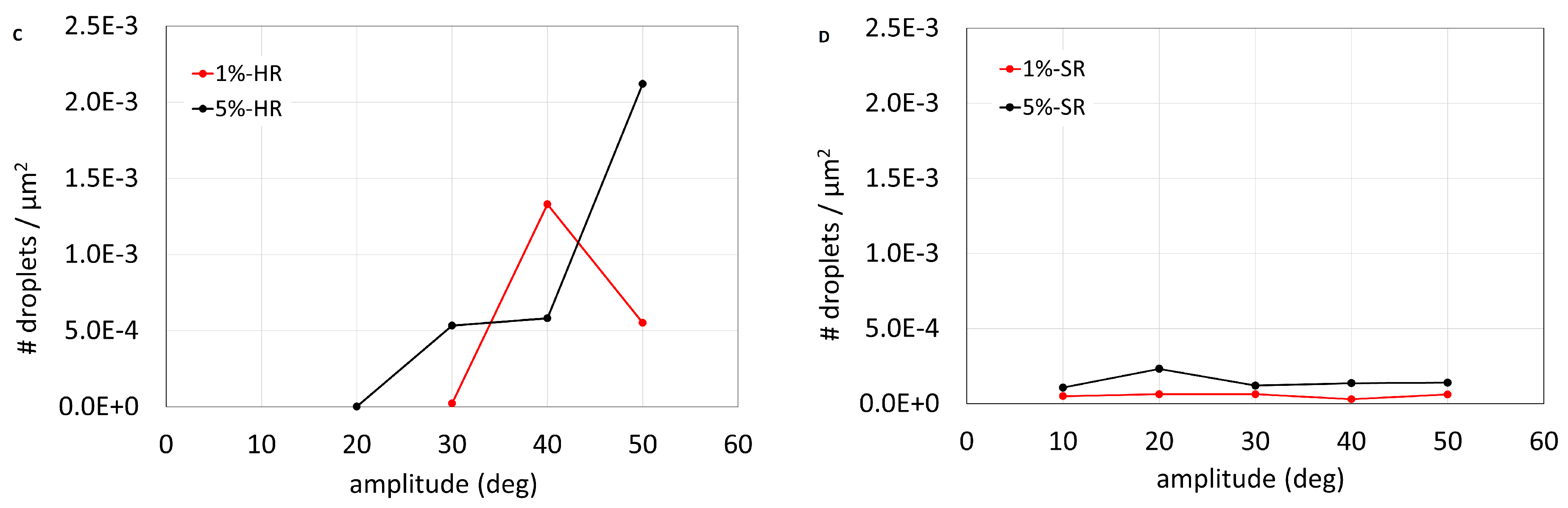
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romano, M.R.; Ferrara, M.; Nepita, I.; D’Amato Tothova, J.; Giacometti Schieroni, A.; Reami, D.; Mendichi, R.; Liggieri, L.; Repetto, R. Biocompatibility of intraocular liquid tamponade agents: An update. Eye 2021, 35, 2699–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, M.; Coco, G.; Sorrentino, T.; Jasani, K.M.; Moussa, G.; Morescalchi, F.; Dhawahir-Scala, F.; Semeraro, F.; Steel, D.H.; Romano, V.; et al. Retinal and corneal changes associated with intraocular silicone oil tamponade. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Russo, A.; Morescalchi, F.; Gambicorti, E.; Vezzoli, S.; Parmeggiani, F.; Romano, M.R.; Costagliola, C. Comparative assessment of intraocular inflammation following standard or heavy silicone oil tamponade: A prospective study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, e97–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenkummer, H.; Kampik, A.; Thierfelder, S. Emulsification of silicone oils with specific physicochemical characteristics. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1991, 229, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartov, E.; Pennarola, F.; Savion, N.; Naveh, N.; Treister, G. A quantitative in vitro model for silicone oil emulsification. Role of blood constituents. Retina 1992, 12, S23–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savion, N.; Alhalel, A.; Treister, G.; Bartov, E. Role of blood components in ocular silicone oil emulsification. Studies on an in vitro model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 2694–2699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nepita, I.; Repetto, R.; Pralits, J.O.; Romano, M.R.; Ravera, F.; Santini, E.; Liggieri, L. The Role of Endogenous Proteins on the Emulsification of Silicone Oils Used in Vitreoretinal Surgery. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2915010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Y. Biofunctionalization of gelatin microcarrier with oxidized hyaluronic acid for corneal keratocyte cultivation. Colloids Surfaces Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.K.; Cheung, N.; Wong, D. Factors Influencing the Shear Rate Acting on Silicone Oil to Cause Silicone Oil Emulsification. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 7451–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.K.; Williams, R.L.; Wong, D. Flow behavior of heavy silicone oil during eye movements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 8453–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Snead, M.; Alexander, P.; Ian Wilson, D. Assessing bulk emulsification at the silicone oil–saline solution interface in a 3D model of the eye. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 99, e209–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Tsai, J.H.; Snead, M.P.; Alexander, P.; Wilson, D.I. Stability of the interface between two immiscible liquids in a model eye subject to saccadic motion. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 051004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouali, O.; Modareszadeh, A.; Ghaffariyeh, A.; Tu, J. Numerical simulation of the fluid dynamics in vitreous cavity due to saccadic eye movement. Med. Eng. Phys. 2012, 34, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modarreszadeh, A.; Abouali, O. Numerical simulation for unsteady motions of the human vitreous humor as a viscoelastic substance in linear and non-linear regimes. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2014, 204, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, R. An analytical model of the dynamics of the liquefied vitreous induced by saccadic eye movements. Meccanica 2006, 41, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, R.; Siggers, J.; Stocchino, A. Mathematical model of flow in the vitreous humor induced by saccadic eye rotations: Effect of geometry. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2010, 9, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Pimenta, F.; Alves, M.A.; Oliveira, M.S. Flow dynamics of vitreous humour during saccadic eye movements. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, J.; Emdad, H.; Abouali, O. Numerical simulation of the fluid dynamics in a 3D spherical model of partially liquefied vitreous due to eye movements under planar interface conditions. J. Comput. Appl. Mech. 2019, 50, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Bayat, J.; Emdad, H.; Abouali, O. Numerical investigation of partially liquefied vitreous dynamics as two-phase viscoelastic-Newtonian fluid flow in a planar cavity due to oscillatory motion. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2020, 127, 103259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, A.; Repetto, R.; Siggers, J.H.; Stocchino, A. Investigation of the motion of a viscous fluid in the vitreous cavity induced by eye rotations and implications for drug delivery. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, R.; Stocchino, A.; Cafferata, C. Experimental investigation of vitreous humour motion within a human eye model. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocchino, A.; Repetto, R.; Cafferata, C. Eye rotation induced dynamics of a Newtonian fluid within the vitreous cavity: The effect of the chamber shape. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirelli, M.; Bergamin, O.; Landau, K.; Boesiger, P.; Luechinger, R. Vitreous deformation during eye movement. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, T.; Querzoli, G.; Pasqualitto, G.; Iossa, M.; Placentino, L.; Repetto, R.; Stocchino, A.; Ripandelli, G. Ultrasound imaging velocimetry of the human vitreous. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 99, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, K.; Pralits, J.O.; Romano, M.R.; Beenakker, J.W.M.; Shamonin, D.P.; Repetto, R. Equilibrium shape of the aqueous humor-vitreous substitute interface in vitrectomized eyes. J. Model. Ophthalmol. 2017, 1, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, T.; Querzoli, G.; Badas, M.G.; Angius, F.; Telani, S.; Ripandelli, G. Computational Fluid Dynamics of Intraocular Silicone Oil Tamponade. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, K.; Pralits, J.O.; Repetto, R.; Romano, M.R. A model for the linear stability of the interface between aqueous humor and vitreous substitutes after vitreoretinal surgery. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, P.; Zankl, M.; Schlattl, H.; Vaz, P. Dose conversion coefficients for monoenergetic electrons incident on a realistic human eye model with different lens cell populations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, D.; Smith, G. Optics of the Human Eye; Butterworth Heinemann: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Atchison, D.A.; Jones, C.E.; Schmid, K.L.; Pritchard, N.; Pope, J.M.; Strugnell, W.E.; Riley, R.A. Eye shape in emmetropia and myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3380–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdam, A.M.; Goldberg, R.A.; Ugradar, S. In vivo measurement of the human vitreous chamber volume using computed tomography imaging of 100 eyes. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W. The Neurobiology of Saccadic Eye Movements ed RH Wurtz and ME Goldberg; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, M.R.; Cuomo, F.; Massarotti, N.; Mauro, A.; Salahudeen, M.; Costagliola, C.; Ambrosone, L. Temperature effect on rheological behavior of silicone oils. a model for the viscous heating. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 7048–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics, 6th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 305–361. [Google Scholar]
- Möbius, D.; Miller, R. Proteins at Liquid Interfaces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Fautsch, M.P.; Johnson, D.H.; Second ARVO/Pfizer Research Institute Working Group. Aqueous humor outflow: What do we know? Where will it lead us? Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4181–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, W.D. The Theory of Emulsification, V. J. Phys. Chem. 1913, 17, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soós, J.; Resch, M.D.; Berkó, S.; Kovács, A.; Katona, G.; Facskó, A.; Csányi, E.; Budai-Szűcs, M. Comparison of hydrophilic ophthalmic media on silicone oil emulsification. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.I.; Te Water Naude, A.D.; Snead, M.P. Refinements in the use of silicone oil as an intraocular tamponade. Eye 2024, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenkummer, H.P.; Kampik, A.; Thierfelder, S. Experimental evaluation of in vitro stability of purified polydimethylsiloxanes (silicone oil) in viscosity ranges from 1000 to 5000 centistokes. Retina 1992, 12, S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.K.; Cheung, N.; Chan, W.S.C.; Wong, D. Quantifying silicone oil emulsification in patients: Are we only seeing the tip of the iceberg? Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zong, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, H.; Deng, G.; Xu, G. Silicone oil emulsification after vitrectomy for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 6940625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morescalchi, F.; Costagliola, C.; Duse, S.; Gambicorti, E.; Parolini, B.; Arcidiacono, B.; Romano, M.R.; Semeraro, F. Heavy silicone oil and intraocular inflammation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 574825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaria, R.; Kon, C.; Bunce, C.; Sethi, C.; Limb, G.; Khaw, P.; Aylward, G.; Charteris, D. Silicone oil concentrates fibrogenic growth factors in the retro-oil fluid. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, L.; Asaria, R.H.; Alexander, R.; Luthert, P.; Charteris, D.G. Immunopathology of intraocular silicone oil: Enucleated eyes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.R.; Ferrara, M.; Coco-Martin, R.M.; Rickmann, A.; Spitzer, M.S.; Steel, D.H.; Pastor, J.C. Intraocular emulsion of silicone oil (ITEMS) grading system: An evidence-based expert-led consensus. Retina 2023, 43, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichhpujani, P.; Jindal, A.; Katz, L.J. Silicone oil induced glaucoma: A review. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 247, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.B.; Papakostas, T.D.; Vavvas, D.G. Complications of emulsified silicone oil after retinal detachment repair. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 29, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Errera, M.H.; Liyanage, S.E.; Elgohary, M.; Day, A.C.; Wickham, L.; Patel, P.J.; Sahel, J.A.; Paques, M.; Ezra, E.; Sullivan, P.M. Using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging to identify the presence of retinal silicone oil emulsification after silicone oil tamponade. Retina 2013, 33, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odrobina, D.; Laudańska-Olszewska, I. Analysis of the time and location of the silicone oil emulsification by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography after silicone oil tamponade. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 372045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Lois, N. Perfluorocarbons and Semifluorinated Alkanes. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2000, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.R.; Ferrara, M.; Gatto, C.; Ferrari, B.; Giurgola, L.; Tóthová, J.D.A. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Perfluorocarbons for Intraocular Use by Cytotoxicity Test in Vitro in Cell Lines and Human Donor Retina Ex Vivo. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgalas, I.; Ladas, I.; Tservakis, I.; Taliantzis, S.; Gotzaridis, E.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Koutsandrea, C. Perfluorocarbon Liquids in Vitreoretinal Surgery: A Review of Applications and Toxicity. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, H.; Stappler, T.; Wong, D. Heavy tamponade 1: A review of indications, use, and complications. Eye 2008, 22, 1342–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, T.T.; Tzekov, R.T.; Stein, L.; Ravi, N.; Kaushal, S. Vitreous substitutes: A comprehensive review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2011, 56, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Wakili, P.; Januschowski, K.; Heinz, W.R.; Engelhard, M.; Menz, H.; Szurman, P. Safety and Performance Assessment of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Vitreous Substitutes in Patients with Phthisis Bulbi. Acta Ophthalmol. 2023, 101, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, A.; Lappe-Osthege, M.; Talamo, S.; Gais, S.; Kimmig, H.; Helmchen, C. Eye movements during REM sleep and imagination of visual scenes. Neuroreport 2010, 21, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Injection | Saccadic Rot. (SR) | Harmonic Rot. (HR) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin Conc. (%) | Amplitude (Deg) | Amplitude (Deg) | Amplitude (Deg) |
| 0 | 0 | 40 | 40 |
| 1 | 0 | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 | 30, 40, 50 |
| 5 | 0 | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 | 20, 30, 40, 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nepita, I.; Brusati, C.; Liggieri, L.; Ravera, F.; Ferrara, M.; Stocchino, A.; Romano, M.R.; Santini, E.; Repetto, R. The Role of Eye Movements in the Process of Silicone Oil Emulsification After Vitreoretinal Surgery. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111081
Nepita I, Brusati C, Liggieri L, Ravera F, Ferrara M, Stocchino A, Romano MR, Santini E, Repetto R. The Role of Eye Movements in the Process of Silicone Oil Emulsification After Vitreoretinal Surgery. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(11):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111081
Chicago/Turabian StyleNepita, Irene, Camilla Brusati, Libero Liggieri, Francesca Ravera, Mariantonia Ferrara, Alessandro Stocchino, Mario R. Romano, Eva Santini, and Rodolfo Repetto. 2024. "The Role of Eye Movements in the Process of Silicone Oil Emulsification After Vitreoretinal Surgery" Bioengineering 11, no. 11: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111081
APA StyleNepita, I., Brusati, C., Liggieri, L., Ravera, F., Ferrara, M., Stocchino, A., Romano, M. R., Santini, E., & Repetto, R. (2024). The Role of Eye Movements in the Process of Silicone Oil Emulsification After Vitreoretinal Surgery. Bioengineering, 11(11), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111081








