Automatic Osteoporosis Screening System Using Radiomics and Deep Learning from Low-Dose Chest CT Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
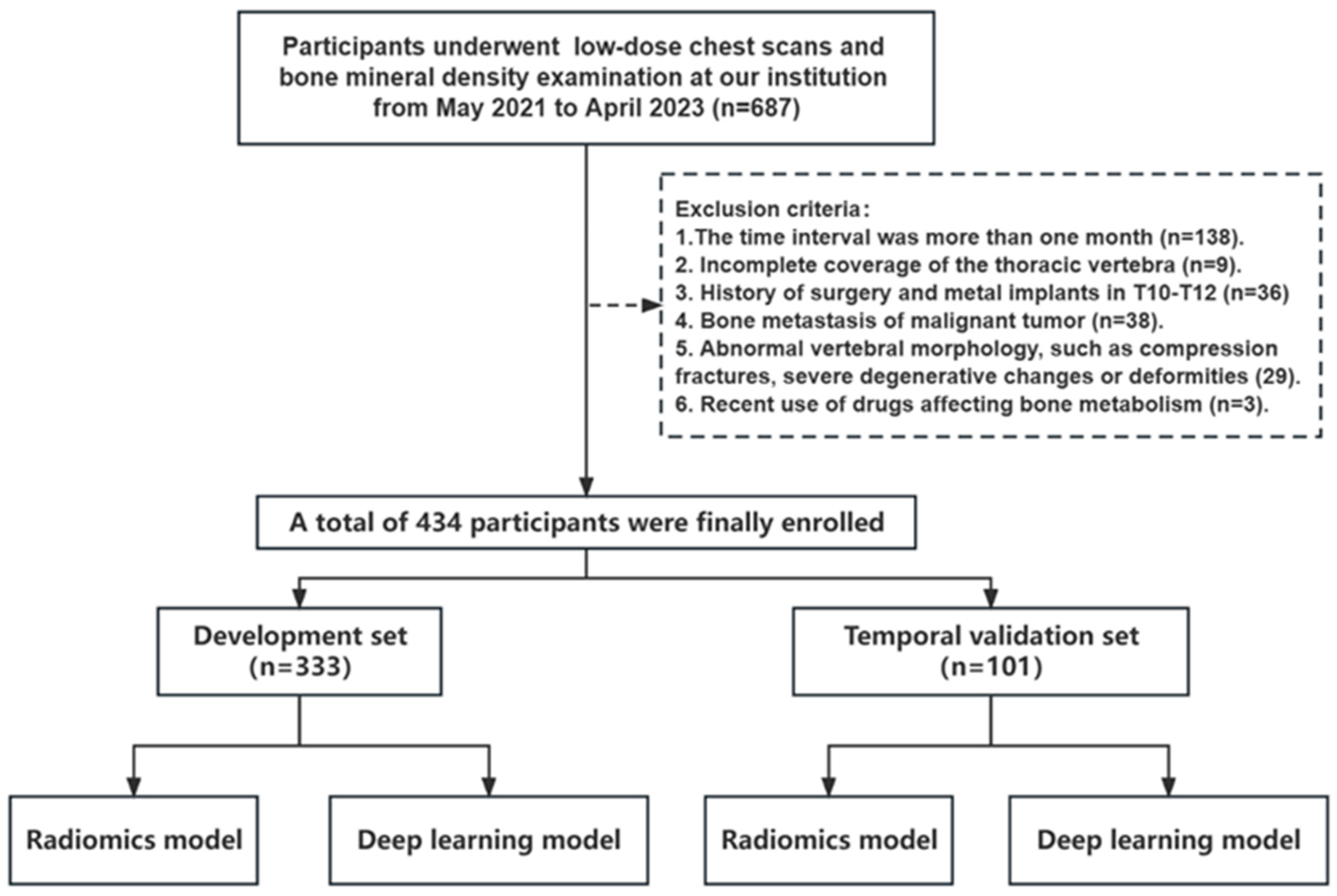
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisition and BMD Assessment
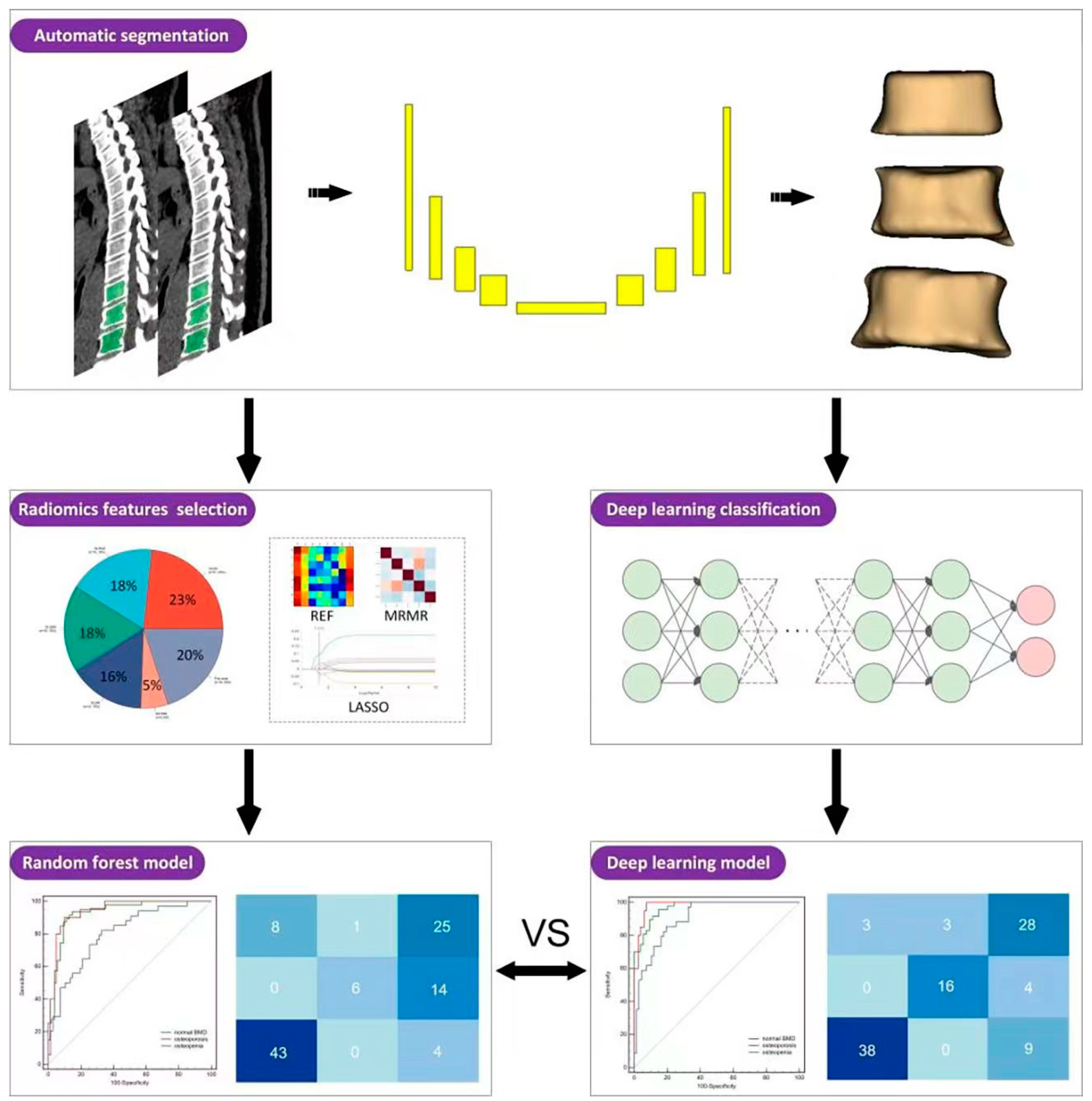
2.3. TVCB Auto-Segmentation Framework and VOI Delineation
2.4. Radiomics Model Construction
2.4.1. Radiomics Features Extraction
2.4.2. Features Selection and Model Construction
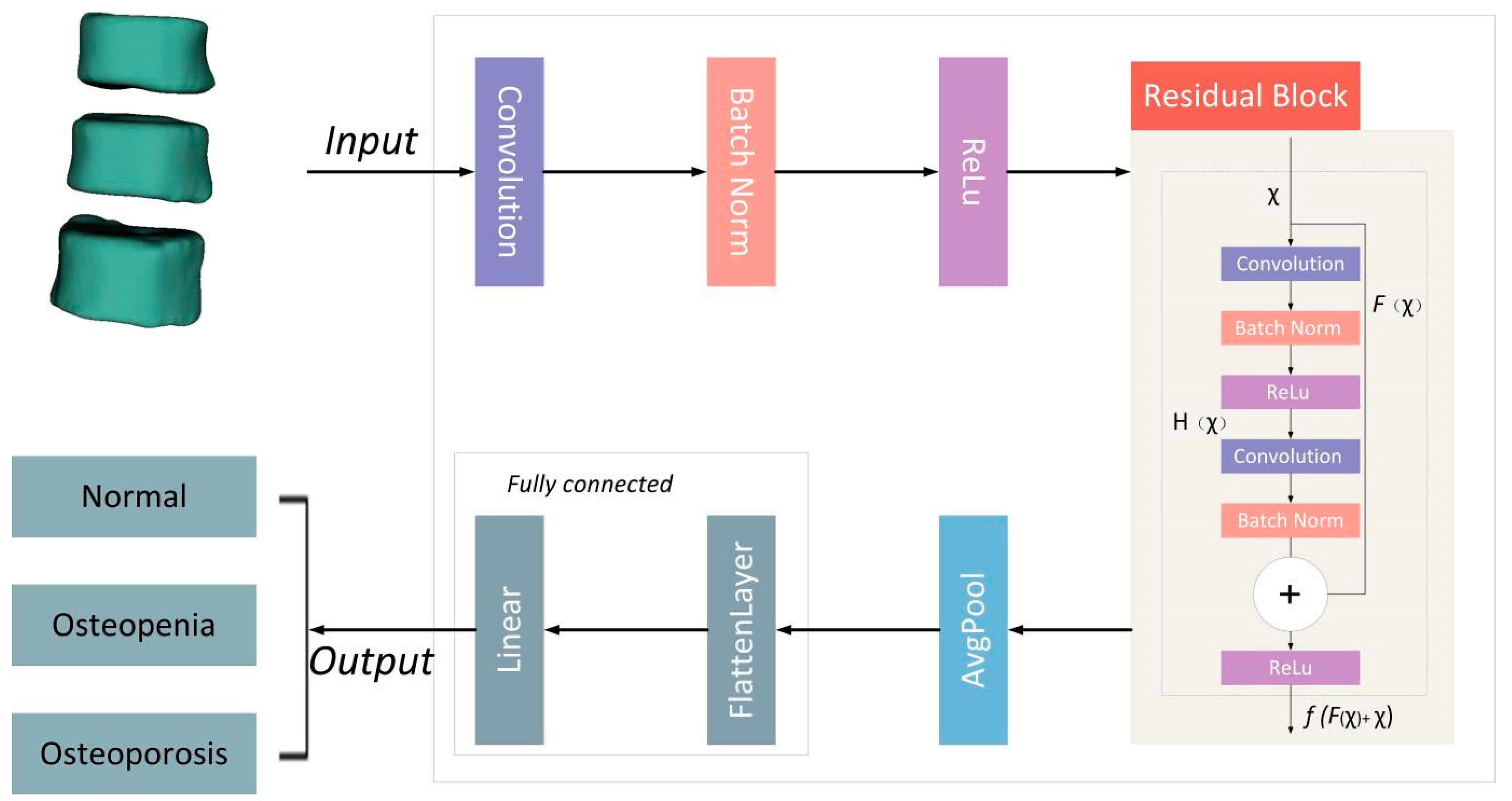
2.5. Deep Learning Network Construction
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Demographics
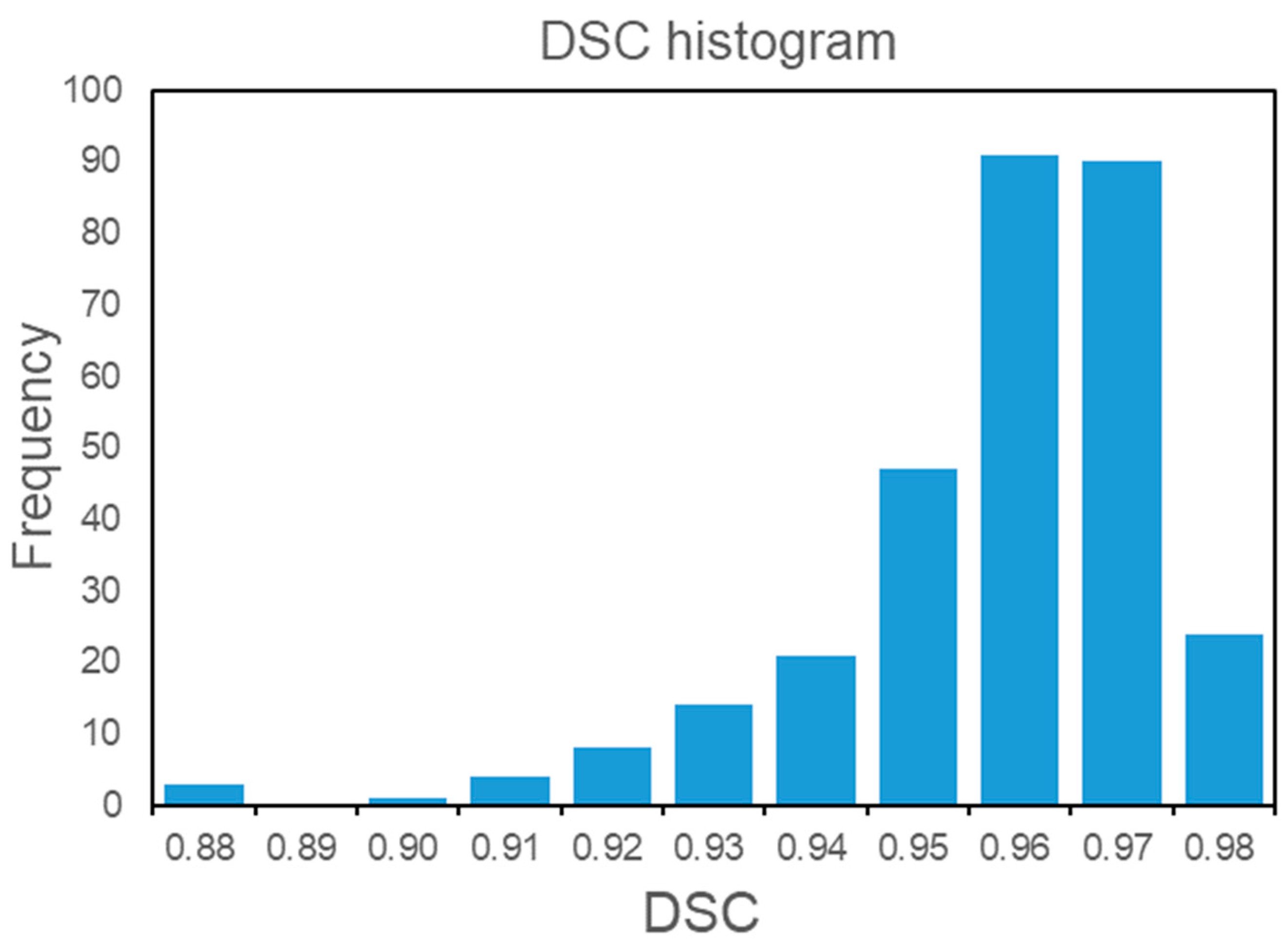
3.2. Automatic Segmentation Model
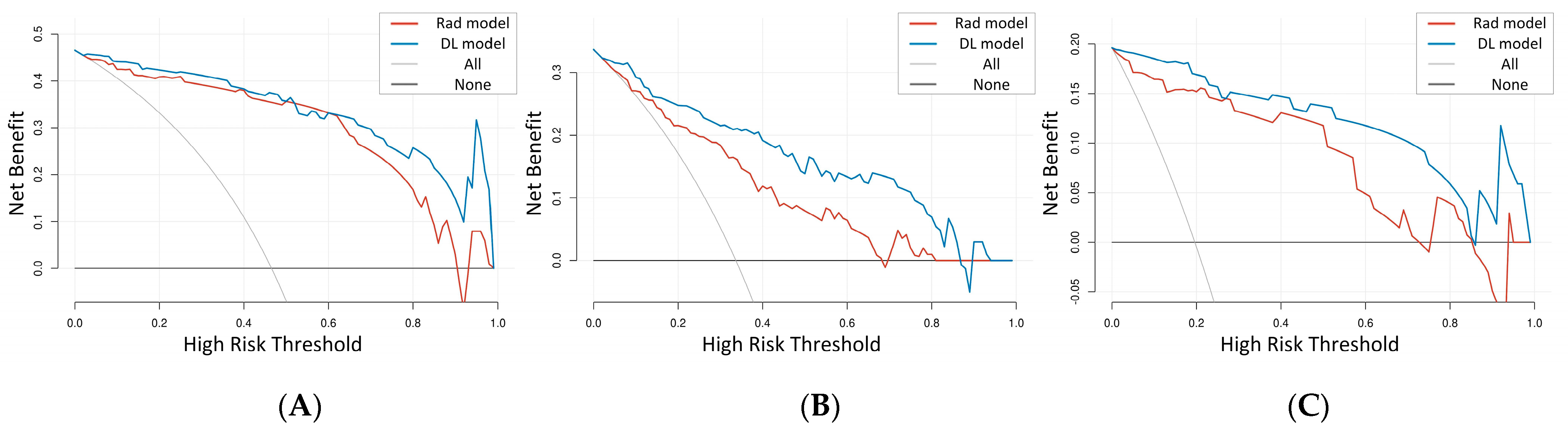
3.3. The Comparison of the Rad Model and DL Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruenewald, L.D.; Koch, V.; Martin, S.S.; Yel, I.; Eichler, K.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Lenga, L.; Wichmann, J.L.; Alizadeh, L.S.; Albrecht, M.H.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of quantitative dual-energy CT-based volumetric bone mineral density assessment for the prediction of osteoporosis-associated fractures. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3076–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Huang, J.; He, L.; Xi, F. Simple immunosensor for ultrasensitive electrochemical determination of biomarker of the bone metabolism in human serum. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 940795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Real, Á.; Valero, C.; Olmos, J.M.; Hernández, J.L.; Riancho, J.A. Pharmacogenetics of Osteoporosis: A Pathway Analysis of the Genetic Influence on the Effects of Antiresorptive Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, L.; Winzenberg, T.M.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, M.; Palmer, A.J. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010–2050. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liao, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; He, L.; Ji, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fan, W.; Nie, Z.; et al. Opportunistic osteoporosis screening using chest CT with artificial intelligence. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Chung, M.J.; Hwang, H.S.; Moon, J.W.; Lee, K.S. Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction-Applied Ultra-Low-Dose CT with Radiography-Comparable Radiation Dose: Usefulness for Lung Nodule Detection. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, M.; Lei, M.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, J. Diagnostic accuracy of ultra-low-dose CT compared to standard-dose CT for identification of non-displaced fractures of the shoulder, knee, ankle, and wrist. Insights Into Imaging 2023, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Baum, S.L.; Eapen, G.A.; Ettinger, D.S.; Hou, L.; Jackman, D.M.; Klippenstein, D.; Kumar, R.; Lackner, R.P.; et al. Lung Cancer Screening, Version 3.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2018, 16, 412–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; Sicks, J.D. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Li, P. Lung nodules assessment in ultra-low-dose CT with iterative reconstruction compared to conventional dose CT. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, D.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, Y. Feasibility study of using one-tenth mSv radiation dose in young children chest CT with 80 kVp and model-based iterative reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiazi, R.; Abbas, E.; Famiyeh, P.; Rezaie, A.; Kwan, J.Y.Y.; Patel, T.; Bratman, S.V.; Tadic, T.; Liu, F.F.; Haibe-Kains, B. The impact of the variation of imaging parameters on the robustness of Computed Tomography radiomic features: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Meng, M.; Bi, L.; Kim, J.; Feng, D.D.; Song, S. Prediction of 5-year progression-free survival in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma with pretreatment PET/CT using multi-modality deep learning-based radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 899351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shen, D. Deformable MR Prostate Segmentation via Deep Feature Learning and Sparse Patch Matching. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Hua, Y.; Cao, G.; Hu, J.; Cui, W.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Rong, T.; Liu, B. Differential diagnosis of benign and malignant vertebral compression fractures: Comparison and correlation of radiomics and deep learning frameworks based on spinal CT and clinical characteristics. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 165, 110899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Gu, D.; Qi, P.; Cao, X.; Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Qu, G.; Wang, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Evaluation of an automated intracranial aneurysm detection and rupture analysis approach using cascade detection and classification networks. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2022, 102, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Lin, N.; Yu, S.; Sha, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, A.; Niu, Y. Automated Prediction of Early Recurrence in Advanced Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Deep Learning and Multi-parametric MRI-based Radiomics Nomogram. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, A.; Innanje, A.; Zheng, M.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; et al. uRP: An integrated research platform for one-stop analysis of medical images. Front. Radiol. 2023, 3, 1153784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, K.; Lang, T.; Khosla, S.; Qin, L.; Zysset, P.; Leslie, W.D.; Shepherd, J.A.; Shousboe, J.T. Clinical Use of Quantitative Computed Tomography-Based Advanced Techniques in the Management of Osteoporosis in Adults: The 2015 ISCD Official Positions-Part III. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaia, E.; Grisi, G.; Baratella, E.; Cuttin, R.; Poillucci, G.; Kus, S.; Cova, M.A. Diagnostic imaging costs before and after digital tomosynthesis implementation in patient management after detection of suspected thoracic lesions on chest radiography. Insights Into Imaging 2014, 5, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Budoff, M.J.; Malpeso, J.M.; Zeb, I.; Gao, Y.L.; Li, D.; Choi, T.Y.; Dailing, C.A.; Mao, S.S. Measurement of phantomless thoracic bone mineral density on coronary artery calcium CT scans acquired with various CT scanner models. Radiology 2013, 267, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Kanafi, A.R.; Acharya, U.R.; Khadem, N.; Mohammadi, A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Huo, J.; Sun, X.; Sun, X.; Ai, S.T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C. Using radiomic features of lumbar spine CT images to differentiate osteoporosis from normal bone density. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Li, Y.T.; Kuo, P.C.; Cheng, S.J.; Chung, Y.H.; Kuo, D.P.; Chen, C.Y. Automatic segmentation and radiomic texture analysis for osteoporosis screening using chest low-dose computed tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 5097–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, S.; He, Y.; Gao, H.; Yan, L.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Shen, H.; Luo, M.; et al. Prediction of osteoporosis using radiomics analysis derived from single source dual energy CT. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.I.; Moon, M.H.; Lee, E.J.; Hong, S.S.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, K.A.; Park, S.B.; et al. Low-Tube-Voltage CT Urography Using Low-Concentration-Iodine Contrast Media and Iterative Reconstruction: A Multi-Institutional Randomized Controlled Trial for Comparison with Conventional CT Urography. Korean J. Radiol. 2018, 19, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takafuji, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Ishida, M.; Goto, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Nagasawa, N.; Sakuma, H. Myocardial Coverage and Radiation Dose in Dynamic Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Using Third-Generation Dual-Source CT. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, N.M. The Rising Utilization of Opportunistic CT Screening and Machine Learning in Bone Mineral Density. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2023, 74, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Zhou, J.Y.; Xu, X.T.; Guo, J.; Han, M.F.; Gao, Y.Z.; Du, H.; Stahl, J.N.; Maltz, J.S. Deep learning-based auto-segmentation of clinical target volumes for radiotherapy treatment of cervical cancer. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yin, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Zeng, M. Establishment and validation of a radiological-radiomics model for predicting high-grade patterns of lung adenocarcinoma less than or equal to 3 cm. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 964322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shi, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Cui, D.; Cheng, X.; Lu, Y. Automatic opportunistic osteoporosis screening using low-dose chest computed tomography scans obtained for lung cancer screening. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4107–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, R.; Pastor-Juan, M.D.R.; Canales-Vázquez, J.; Castro-García, M.; Villas, M.V.; Mansilla Legorburo, F.; Sabater, S. Radiomics of CT Features May Be Nonreproducible and Redundant: Influence of CT Acquisition Parameters. Radiology 2018, 288, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astaraki, M.; Yang, G.; Zakko, Y.; Toma-Dasu, I.; Smedby, Ö.; Wang, C. A Comparative Study of Radiomics and Deep-Learning Based Methods for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy Prediction in Low Dose CT Images. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, E.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, K.; Yu, H.J.; Yuan, H.; Lang, N.; Su, M.Y. Differential diagnosis of benign and malignant vertebral fracture on CT using deep learning. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9612–9619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, G.; Chung, C.Y.; Moore, B.E., 2nd. Ankle Fracture Detection Utilizing a Convolutional Neural Network Ensemble Implemented with a Small Sample, De Novo Training, and Multiview Incorporation. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, K.; Qian, T.; Jiang, T.; et al. Molecular subtyping of diffuse gliomas using magnetic resonance imaging: Comparison and correlation between radiomics and deep learning. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Development Set | Temporal Validation Set | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| All (n) | 333 | 101 | |
| Male (n) | 170 | 57 | |
| Female (n) | 163 | 44 | 0.404 |
| All (years) | 62.89 ± 11.55 | 60.76 ± 10.41 | 0.098 |
| Male (years) | 65.37 ± 10.37 | 62.60 ± 9.14 | 0.073 |
| Female (years) | 60.30 ± 12.17 | 58.39 ± 11.54 | 0.350 |
| Osteoporosis (n) | 84 | 20 | |
| Osteopenia (n) | 134 | 34 | |
| Normal BMD (n) | 115 | 47 | 0.094 |
| Category | DSC | VD (cm3) |
|---|---|---|
| All | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.50 (0.17, 0.69) |
| Osteoporosis | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.44 (0.09, 0.68) |
| Osteopenia | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.53 (0.19, 0.63) |
| Normal BMD | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.50 (0.18, 0.80) |
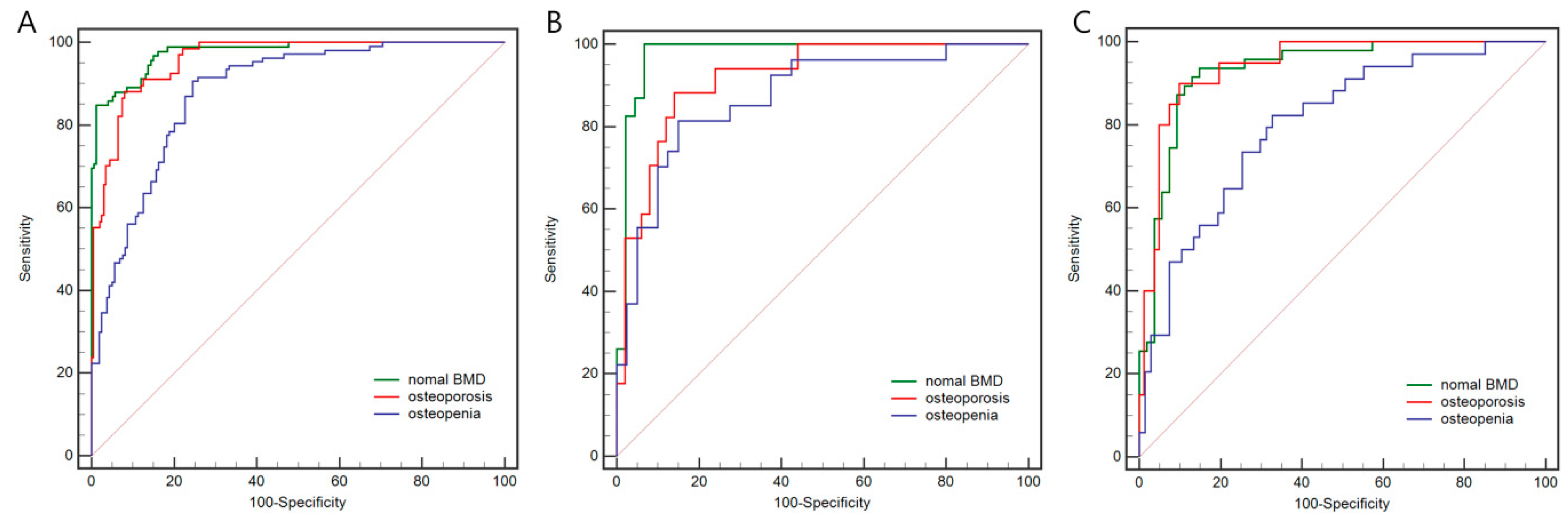
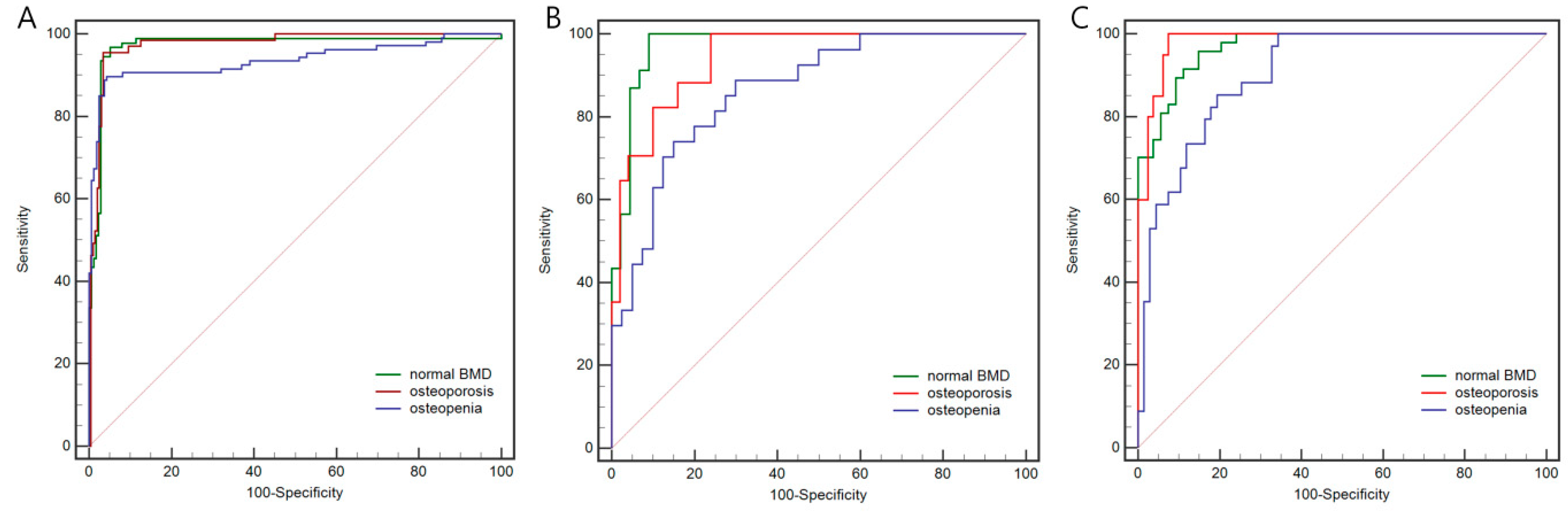
| Model | Set | Category | AUC | 95%CI | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rad Model | Internal training set | Osteoporosis | 0.959 | 0.927–0.979 | 88.1 | 92.0 | 88.9 | |
| Osteopenia | 0.881 | 0.835–0.917 | 90.7 | 75.5 | 67.3 | |||
| Normal BMD | 0.977 | 0.95–0.991 | 84.8 | 98.9 | 96.3 | |||
| Overall | 79.0 | |||||||
| Internal test set | Osteoporosis | 0.919 | 0.826–0.971 | 88.2 | 86.0 | 71.4 | ||
| Osteopenia | 0.873 | 0.769–0.942 | 81.5 | 85.0 | 60.0 | |||
| Normal BMD | 0.976 | 0.906–0.998 | 100.0 | 93.2 | 90.0 | |||
| Overall | 70.2 | |||||||
| Temporal validation set | Osteoporosis | 0.943 | 0.878–0.979 | 90.0 | 90.1 | 85.7 | ||
| Osteopenia | 0.801 | 0.709–0.874 | 82.4 | 67.2 | 58.1 | |||
| Normal BMD | 0.932 | 0.864–0.972 | 93.6 | 85.2 | 84.3 | |||
| Overall | 73.3 | |||||||
| DL Model | Internal training set | Osteoporosis | 0.975 | 0.948–0.990 | 95.5 | 96.5 | 87.7 | |
| Osteopenia | 0.936 | 0.900–0.962 | 89.7 | 95.6 | 93.2 | |||
| Normal BMD | 0.972 | 0.944–0.988 | 96.7 | 94.8 | 95.6 | |||
| Overall | 92.5 | |||||||
| Internal test set | Osteoporosis | 0.942 | 0.857–0.985 | 100.0 | 76.0 | 75.0 | ||
| Osteopenia | 0.866 | 0.760–0.937 | 74.1 | 85.0 | 71.4 | |||
| Normal BMD | 0.972 | 0.900–0.997 | 100.0 | 90.9 | 87.0 | |||
| Overall | 77.6 | |||||||
| Temporal validation set | Osteoporosis | 0.983 | 0.935–0.998 | 100.0 | 92.6 | 84.2 | ||
| Osteopenia | 0.906 | 0.831–0.955 | 85.3 | 80.6 | 68.3 | |||
| Normal BMD | 0.969 | 0.914–0.993 | 95.7 | 85.2 | 92.7 | |||
| Overall | 81.2 |
| Authors(methods) | Key Findings | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xue et al. (Radiomics) [23] | Detecting abnormal BMD | 0.944 | 95.8 | - | - |
| Detecting osteoporosis | 0.866 | 83.3 | - | - | |
| Chen et al. (Radiomics) [24] | Detecting abnormal BMD | 0.960 | 93.0 | 89.0 | 91.0 |
| Detecting osteoporosis | 0.980 | 95.0 | 93.0 | 94.0 | |
| Wang et al. (Radiomics) [25] | Detecting osteoporosis | 0.914 | 90.7 | 75.0 | 89.8 |
| Ours (Radiomics) | Detecting abnormal BMD | 0.932 | 93.6 | 85.2 | 73.3 |
| Detecting osteopenia | 0.801 | 82.4 | 67.5 | ||
| Detecting osteoporosis | 0.943 | 90.0 | 90.1 | ||
| Yang et al. (Deep learning) [5] | Detecting osteopenia | 0.831 | 73.6 | 80.5 | - |
| Detecting osteoporosis | 0.972 | 95.6 | 88.0 | ||
| Ours (Deep learning) | Detecting abnormal BMD | 0.969 | 95.7 | 85.2 | 81.2 |
| Detecting Osteopenia | 0.906 | 85.3 | 80.6 | ||
| Detecting osteoporosis | 0.983 | 100 | 92.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W. Automatic Osteoporosis Screening System Using Radiomics and Deep Learning from Low-Dose Chest CT Images. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010050
Tong X, Wang S, Zhang J, Fan Y, Liu Y, Wei W. Automatic Osteoporosis Screening System Using Radiomics and Deep Learning from Low-Dose Chest CT Images. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Xiaoyu, Shigeng Wang, Jingyi Zhang, Yong Fan, Yijun Liu, and Wei Wei. 2024. "Automatic Osteoporosis Screening System Using Radiomics and Deep Learning from Low-Dose Chest CT Images" Bioengineering 11, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010050
APA StyleTong, X., Wang, S., Zhang, J., Fan, Y., Liu, Y., & Wei, W. (2024). Automatic Osteoporosis Screening System Using Radiomics and Deep Learning from Low-Dose Chest CT Images. Bioengineering, 11(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010050







