Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio May Predict Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury from the MIMIC Database: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Data Pre-Processing
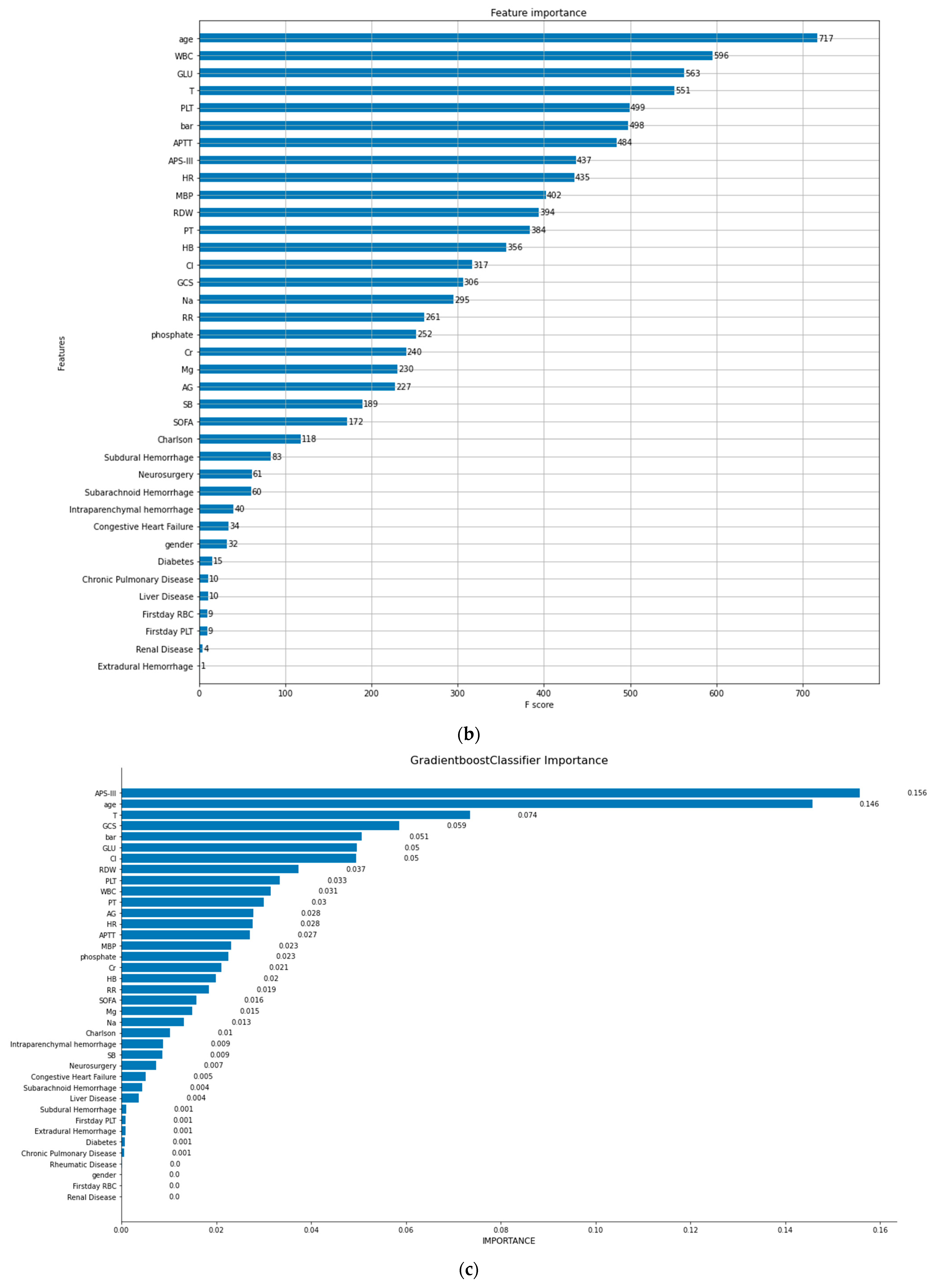
3.2. BAR Importance Ranks High among All Included Factors Affecting In-Hospital Mortality in TBI Patients
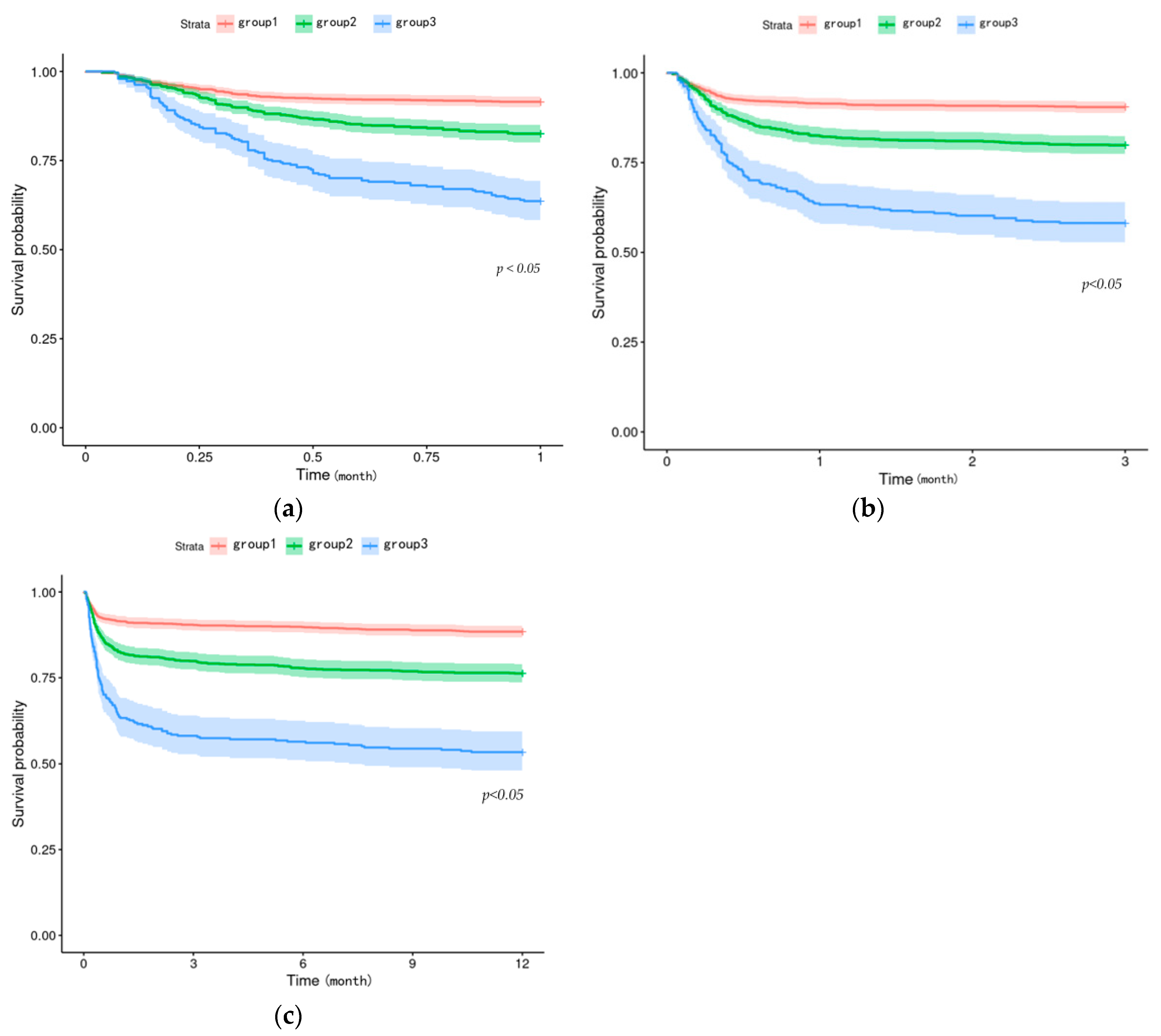
3.3. High-BAR Group Mortality Is Significantly Higher than That of Low-BAR Group
3.4. BAR-Increased Group of TBI Patients Has a Higher Death Risk
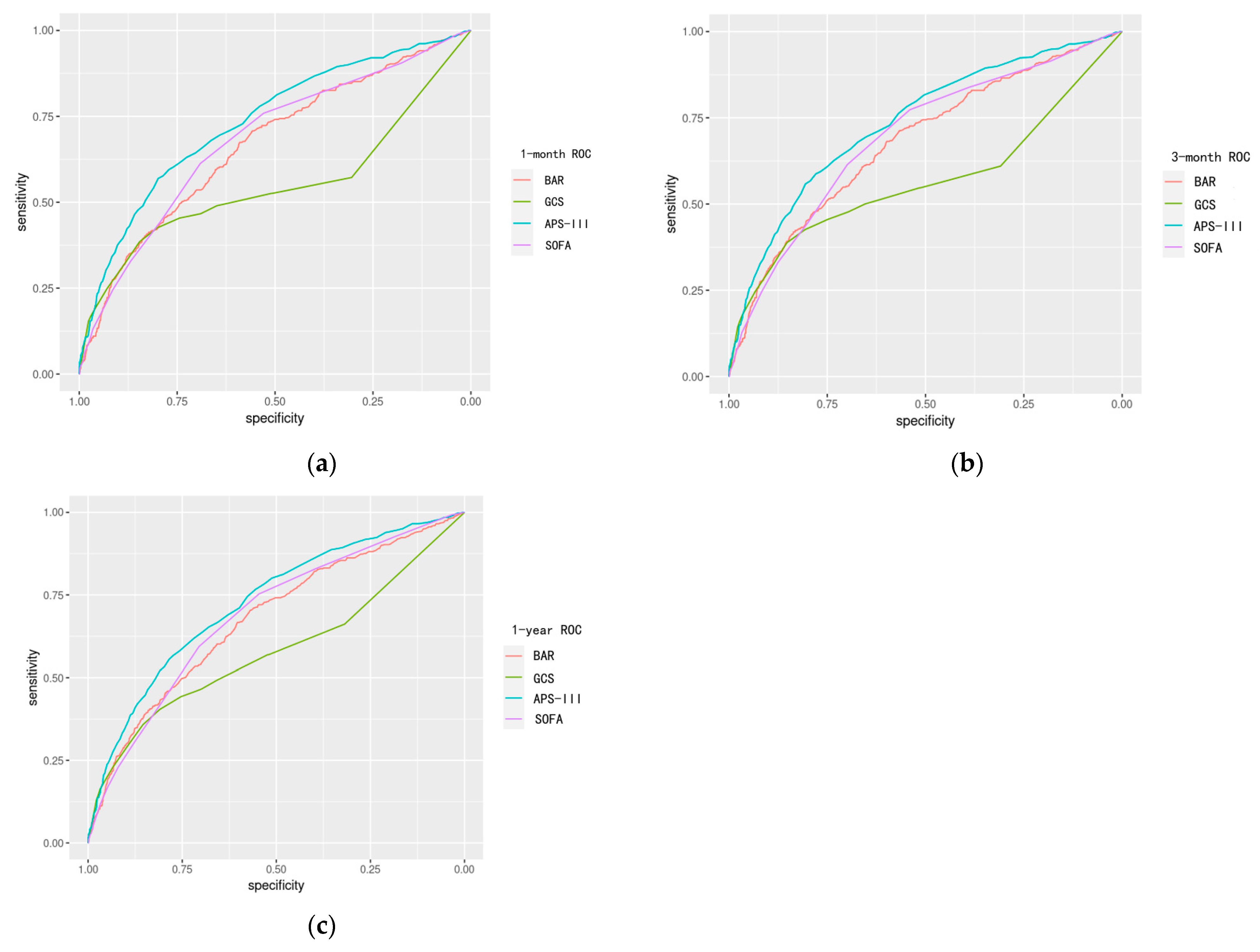
3.5. Prognostic Effectiveness of BAR Is as Good as SOFA Score in TBI Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Among all considered variables, BAR stands out as highly important, significantly contributing to the mortality rates of patients with TBI.
- Stratifying patients by BAR levels reveals a marked disparity in mortality across the strata, with individuals in the high-BAR group facing a considerably higher risk of all-cause mortality compared to those in the low-BAR group.
- For predicting all-cause mortality in TBI patients, BAR outperforms the GCS score, performs comparably to the SOFA score, and falls slightly behind the APS-III score in independent predictive ability.
- The BAR ratio emerges as a potentially strong predictor of mortality in patients with TBI.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mollayeva, T.; Mollayeva, S.; Colantonio, A. Traumatic brain injury: Sex, gender and intersecting vulnerabilities. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Åkerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capizzi, A.; Woo, J.; Verduzco-Gutierrez, M. Traumatic Brain Injury: An Overview of Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Medical Management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, M.; Struchen, M.A.; Yablon, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Nick, T.G. Comparison of indices of traumatic brain injury severity: Glasgow Coma Scale, length of coma and post-traumatic amnesia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Liraz-Zaltsman, S.; Shohami, E.; Gordevičius, J.; Kerševičiūtė, I.; Sherman, E.; Bahado-Singh, R.O.; Graham, S.F. The longitudinal biochemical profiling of TBI in a drop weight model of TBI. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaith, H.S.; Nawar, A.A.; Gabra, M.D.; Abdelrahman, M.E.; Nafady, M.H.; Bahbah, E.I.; Ebada, M.A.; Ashraf, G.M.; Negida, A.; Barreto, G.E. A Literature Review of Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarkers. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 4141–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shen, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, C.; Ma, X. Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio in Predicting Long-Term Mortality in Patients Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: An Analysis of the MIMIC-III Database. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 801708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Guo, C.; Zheng, L.; Yuan, M. Association between blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and in-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis in intensive care: A retrospective analysis of the fourth-generation Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care database. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.W.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Bulgarelli, L.; Shen, L.; Gayles, A.; Shammout, A.; Horng, S.; Pollard, T.J.; Hao, S.; Moody, B.; Gow, B.; et al. MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luwei, L. Application of Machine Learning and Data Mining in Medicine: Opportunities and Considerations. In Machine Learning and Data Mining Annual Volume 2023; Marco Antonio, A.-F., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023; p. Ch. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, K.; Aihara, H.; Nakai, T.; Morishita, A.; Tohma, Y.; Kohmura, E. Machine Learning to Predict In-Hospital Morbidity and Mortality after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Parimputation: From Imputation and Null-Imputation to Partially Imputation. IEEE Intell. Inform. Bull. 2008, 9, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Camp, R.L.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Rimm, D.L. X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In Proceedings of the Ijcai, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; pp. 1137–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, B.J.; Kitamura, F. Magician’s Corner: 9. Performance Metrics for Machine Learning Models. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e200126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, M.A.; Oratz, M.; Schreiber, S.S. Serum albumin. Hepatology 1988, 8, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckart, A.; Struja, T.; Kutz, A.; Baumgartner, A.; Baumgartner, T.; Zurfluh, S.; Neeser, O.; Huber, A.; Stanga, Z.; Mueller, B.; et al. Relationship of Nutritional Status, Inflammation, and Serum Albumin Levels During Acute Illness: A Prospective Study. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 713–722.e717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinskaia, D.A.; Voronina, P.A.; Batalova, A.A.; Goncharov, N.V. Serum Albumin. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arques, S. Serum albumin and cardiovascular disease: State-of-the-art review. Ann. Cardiol. Angeiol. 2020, 69, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, N.; Jiang, J.; Ni, L.; Zhang, X.A.; Wang, D.W. Decreased serum albumin level indicates poor prognosis of COVID-19 patients: Hepatic injury analysis from 2,623 hospitalized cases. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Yu, J. Relationship between the Blood Urea Nitrogen to Creatinine Ratio and In-Hospital Mortality in Non-Traumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients: Based on Propensity Score Matching Method. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zheng, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, S. The association of blood urea nitrogen levels upon emergency admission with mortality in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2021, 18, 14799731211060051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogi, K.; Ueda, T.; Nakamura, T.; Nogi, M.; Ishihara, S.; Nakada, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Nishida, T.; Seno, A.; et al. New Classification for the Combined Assessment of the Fractional Excretion of Urea Nitrogen and Estimated Plasma Volume Status in Acute Heart Failure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e025596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Liu, K.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Niu, R.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Blood urea nitrogen, blood urea nitrogen to creatinine ratio and incident stroke: The Dongfeng-Tongji cohort. Atherosclerosis 2021, 333, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, D.; Hammerman, H.; Beyar, R.; Yalonetsky, S.; Kapeliovich, M.; Markiewicz, W.; Goldberg, A. Serum blood urea nitrogen and long-term mortality in acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 127, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.Q.; Zeng, C.L. Blood Urea Nitrogen and In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Cardiogenic Shock: Analysis of the MIMIC-III Database. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5948636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, K. Comparison of IVC diameter ratio, BUN/creatinine ratio and BUN/albumin ratio for risk prediction in emergency department patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 47, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, Z.D.; Kucukceran, K.; Ayranci, M.K. Blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio is a predictor of in-hospital mortality in older emergency department patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 46, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.N.; Chuang, T.I.; Wong, L.T.; Chan, M.C.; Chao, W.C. Association between early blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio and one-year post-hospital mortality in critically ill surgical patients: A propensity score-matched study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Stoner, B.; Wool, T.; Vaidya, G. Frailty in heart transplant recipients: The role of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Altunok, I. Comparison of the Predictive Ability of the Blood Urea Nitrogen/Albumin, C-Reactive Protein/Albumin, and Lactate/Albumin Ratios for Short-Term Mortality in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients. Avicenna J. Med. 2023, 13, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiliç, M.; Tekyol, D. Predictive power of blood urea nitrogen and albumin ratio for mortality in acute ischemic stroke. Ann. Clin. Anal. Med. 2022, 13, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Hong, L.; Hou, T.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Prognostic impact of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio on patients with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirri, S.; Delnevo, G.; Roccetti, M. Is a COVID-19 Second Wave Possible in Emilia-Romagna (Italy)? Forecasting a Future Outbreak with Particulate Pollution and Machine Learning. Computation 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natekin, A.; Knoll, A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobotics 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 3149–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Boulesteix, A.-L.; Schmid, M. Machine learning versus statistical modeling. Biom. J. 2014, 56, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Reinikainen, J.; Adeleke, K.A.; Pieterse, M.E.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C.G.M. Time-varying covariates and coefficients in Cox regression models. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Survival (2260) | Died (342) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.53 [44.05, 78.68] | 72.02 [56.59, 84.66] | <0.001 |
| Male sex (%) | 1497 (66.24) | 206 (60.23) | 0.0344 |
| Average arterial pressure(mmHg) | 62.00 [55.00, 70.00] | 58.00 [49.00, 65.00] | <0.001 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 101.00 [89.00, 115.00] | 104.00 [90.25, 123.75] | 0.0031 |
| Respiratory rate (beats/min) | 25.00 [22.00, 28.00] | 26.00 [23.00, 30.00] | <0.001 |
| Blood oxygen saturation (%) | 94.00 [92.00, 96.00] | 95.00 [92.00, 97.75] | 0.0285 |
| Temperature (°C) | 37.61 [37.17, 38.11] | 37.94 [37.38, 38.61] | <0.001 |
| White blood cell (109/L) | 12.40 [9.10, 16.50] | 14.40 [9.93, 19.45] | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (1012/L) | 11.10 [9.50, 12.40] | 9.75 [8.33, 11.08] | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 32.30 [27.90, 36.40] | 28.85 [24.43, 32.30] | <0.001 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 188.00 [140.00, 235.00] | 159.50 [114.50, 213.00] | <0.001 |
| RDW (%) | 13.80 [13.10, 14.70] | 14.40 [13.50, 15.80] | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 141.00 [139.00, 143.00] | 142.00 [140.00, 146.00] | <0.001 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 3.70 [3.40, 4.00] | 3.60 [3.20, 4.00] | 0.0021 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 106.00 [103.00, 110.00] | 109.00 [104.00, 113.00] | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 8.30 [7.80, 8.80] | 8.20 [7.50, 8.70] | 0.0068 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 3.30 [2.80, 3.80] | 3.40 [2.80, 4.10] | 0.0258 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.90 [1.60, 2.10] | 2.00 [1.70, 2.10] | <0.001 |
| Anion gap (mmol/L) | 16.00 [14.00, 18.00] | 17.00 [15.00, 20.00] | <0.001 |
| BAR | 4.62 [3.24, 6.69] | 6.36 [4.38, 10.68] | <0.001 |
| Urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 16.00 [12.00, 22.00] | 21.00 [14.00, 33.00] | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.50 [3.10, 3.90] | 3.20 [2.80, 3.70] | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.90 [0.70, 1.20] | 1.10 [0.80, 1.60] | <0.001 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 23.00 [20.00, 25.00] | 21.00 [18.00, 24.00] | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 151.00 [124.00, 186.00] | 182.00 [150.00, 233.00] | <0.001 |
| INR | 1.20 [1.10, 1.30] | 1.30 [1.10, 1.70] | <0.001 |
| PT (s) | 13.32 [12.40, 14.80] | 14.30 [13.03, 17.88] | <0.001 |
| APTT (s) | 28.00 [25.50, 31.60] | 30.30 [26.23, 35.98] | <0.001 |
| GCS score | 14.00 [10.00, 15.00] | 13.50 [7.00, 15.00] | 0.1367 |
| APS-III score | 36.00 [28.00, 47.00] | 54.50 [39.00, 73.00] | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 3.00 [2.00, 5.00] | 5.00 [4.00, 8.00] | <0.001 |
| Charlson | 4.00 [1.00, 5.00] | 5.00 [3.00, 6.00] | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 269 (11.90%) | 85 (24.85%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 259 (11.46%) | 36 (10.53%) | 0.6773 |
| Rheumatic disease | 39 (1.73%) | 8 (2.34%) | 0.5645 |
| Renal disease | 179 (7.92%) | 48 (14.04%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 392 (17.35%) | 88 (25.73%) | <0.001 |
| Liver disease | 175 (7.74%) | 36 (10.53%) | 0.0988 |
| Intraparenchymal hemorrhage | 174 (7.70%) | 43 (12.57%) | 0.0034 |
| Extradural hemorrhage | 40 (1.77%) | 8 (2.34%) | 0.6076 |
| Subdural hemorrhage | 835 (36.95%) | 129 (37.72%) | 0.8293 |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 462 (20.44%) | 91 (26.61%) | 0.0115 |
| Neurosurgery | 617 (27.30%) | 130 (38.01%) | <0.001 |
| First-day RBC infusion | 288 (12.74%) | 83 (24.27%) | <0.001 |
| First-day PLT infusion | 207 (9.16%) | 59 (17.25%) | <0.001 |
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | F Score | Recall Rate | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± SD) | |||||
| Light Gradient Boost Classifier | 0.905 ± 0.016 | 0.888 | 0.560 | 0.459 | 0.717 |
| Extreme Gradient Boost Classifier | 0.903 ± 0.016 | 0.895 | 0.532 | 0.421 | 0.724 |
| Gradient Boost Classifier | 0.898 ± 0.021 | 0.872 | 0.536 | 0.447 | 0.668 |
| Random Forest Classifier | 0.894 ± 0.008 | 0.892 | 0.361 | 0.228 | 0.867 |
| Ada Boost Classifier | 0.877 ± 0.011 | 0.817 | 0.441 | 0.368 | 0.550 |
| Logistic Regression Classifier | 0.873 ± 0.008 | 0.756 | 0.206 | 0.126 | 0.573 |
| Decision Tree Classifier | 0.847 ± 0.016 | 0.656 | 0.405 | 0.398 | 0.413 |
| Naive Bayes Classifier | 0.806 ± 0.018 | 0.755 | 0.372 | 0.439 | 0.323 |
| BAR Level | <4.9 1340 | 4.9~10.5 968 | ≥10.5 294 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 52.61 [37.11, 66.94] | 73.93 [56.33, 84.01] | 77.70 [66.47, 85.63] | <0.001 |
| Male sex (%) | 895 (66.79%) | 613 (63.33%) | 195 (66.33%) | 0.213 |
| Average arterial pressure(mmHg) | 64.00 [57.00, 71.00] | 60.00 [52.00, 67.00] | 57.00 [49.00, 63.00] | <0.001 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 103.00 [92.00, 117.00] | 98.00 [86.00, 114.00] | 101.00 [87.00, 114.00] | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate (beats/min) | 25.00 [22.00, 28.00] | 25.00 [22.00, 29.00] | 27.00 [23.00, 31.00] | <0.001 |
| Blood oxygen saturation (%) | 95.00 [92.00, 97.00] | 94.00 [91.00, 96.00] | 93.00 [90.00, 95.75] | <0.001 |
| Temperature (°C) | 37.72 [37.22, 38.22] | 37.61 [37.17, 38.11] | 37.42 [37.06, 38.00] | <0.001 |
| White blood cell (109/L) | 12.40 [9.10, 16.70] | 12.90 [9.50, 16.80] | 12.80 [8.83, 17.78] | 0.092 |
| Hemoglobin (1012/L) | 11.50 [10.10, 12.90] | 10.40 [8.90, 11.80] | 9.20 [8.10, 10.40] | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 33.50 [29.40, 37.40] | 30.40 [26.10, 34.93] | 27.60 [24.35, 31.50] | <0.001 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 196.00 [149.00, 243.00] | 173.50 [126.00, 222.00] | 151.50 [106.25, 207.75] | <0.001 |
| RDW (%) | 13.60 [13.00, 14.43] | 13.90 [13.20, 15.00] | 15.25 [14.20, 16.70] | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 141.00 [138.00, 143.00] | 141.00 [139.00, 143.00] | 142.00 [139.00, 145.00] | 0.027 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 3.60 [3.30, 3.90] | 3.70 [3.40, 4.10] | 3.90 [3.50, 4.40] | <0.001 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 106.00 [103.00, 109.00] | 107.00 [103.00, 111.00] | 107.50 [102.00, 112.00] | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 8.30 [7.80, 8.80] | 8.30 [7.70, 8.80] | 8.20 [7.40, 8.80] | 0.162 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 3.20 [2.70, 3.70] | 3.30 [2.80, 3.80] | 3.85 [3.20, 5.00] | <0.001 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.80 [1.60, 2.00] | 1.90 [1.70, 2.10] | 2.10 [1.80, 2.28] | <0.001 |
| Anion gap (mmol/L) | 16.00 [14.00, 18.00] | 15.00 [13.00, 18.00] | 18.00 [16.00, 21.00] | <0.001 |
| Urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 12.00 [10.00, 15.00] | 22.00 [18.75, 25.00] | 46.00 [37.00, 58.00] | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.70 [3.40, 4.10] | 3.30 [2.88, 3.70] | 3.10 [2.70, 3.48] | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.80 [0.70, 1.00] | 1.00 [0.90, 1.30] | 2.00 [1.50, 2.88] | <0.001 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 23.00 [21.00, 25.00] | 23.00 [20.00, 25.00] | 21.00 [18.00, 24.00] | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 144.00 [121.00, 173.25] | 166.00 [137.00, 203.25] | 182.00 [143.25, 235.00] | <0.001 |
| INR | 1.20 [1.10, 1.30] | 1.20 [1.10, 1.50] | 1.30 [1.10, 1.80] | <0.001 |
| PT (s) | 13.15 [12.30, 14.30] | 13.70 [12.70, 15.88] | 14.50 [12.90, 18.78] | <0.001 |
| APTT (s) | 27.60 [25.40, 30.80] | 28.60 [25.88, 32.90] | 30.85 [26.80, 35.75] | <0.001 |
| GCS score | 14.00 [10.00, 15.00] | 14.00 [9.00, 15.00] | 14.00 [9.00, 15.00] | 0.533 |
| APS-III score | 32.00 [24.00, 42.00] | 41.50 [33.00, 55.00] | 56.00 [45.00, 69.00] | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 3.00 [2.00, 4.00] | 4.00 [2.00, 6.00] | 6.00 [4.00, 8.00] | <0.001 |
| Charlson score | 2.00 [1.00, 4.00] | 4.00 [3.00, 6.00] | 6.00 [5.00, 8.00] | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 63 (4.70%) | 167 (17.25%) | 124 (42.18%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 111 (8.28%) | 137 (14.15%) | 47 (15.99%) | <0.001 |
| Rheumatic disease | 19 (1.42%) | 18 (1.86%) | 10 (3.40%) | 0.068 |
| Renal disease | 19 (1.42%) | 75 (7.75%) | 133 (45.24%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 155 (11.57%) | 208 (21.49%) | 117 (39.80%) | <0.001 |
| Liver disease | 95 (7.09%) | 70 (7.23%) | 46 (15.65%) | <0.001 |
| Intraparenchymal hemorrhage | 98 (7.31%) | 91 (9.40%) | 28 (9.52%) | 0.149 |
| Extradural hemorrhage | 31 (2.31%) | 13 (1.34%) | 4 (1.36%) | 0.187 |
| Subdural hemorrhage | 440 (32.84%) | 394 (40.70%) | 130 (44.22%) | <0.001 |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 245 (18.28%) | 228 (23.55%) | 80 (27.21%) | <0.001 |
| Neurosurgery | 401 (29.93%) | 292 (30.17%) | 54 (18.37%) | <0.001 |
| First-day RBC infusion | 107 (7.99%) | 195 (20.14%) | 69 (23.47%) | <0.001 |
| First-day PLT infusion | 94 (7.01%) | 125 (12.91%) | 47 (15.99%) | <0.001 |
| Mortality | 102 (7.61%) | 147 (15.19%) | 93 (31.63%) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay in ICU | 2.56 [1.40, 5.81] | 3.69 [1.77, 8.74] | 3.56 [1.77, 7.84] | <0.001 |
| Length of stay in hospital | 7.43 [4.05, 14.71] | 9.52 [5.27, 18.14] | 9.49 [5.55, 16.75] | <0.001 |
| 1-month mortality | 114 (8.51%) | 169 (17.46%) | 107 (36.39%) | <0.001 |
| 3-month mortality | 128 (9.55%) | 195 (20.14%) | 123 (41.84%) | <0.001 |
| 1-year mortality | 155 (11.57%) | 230 (23.76%) | 137 (46.60%) | <0.001 |
| Characteristic | Univariate Model | Multivariate Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR 95%CI | p | HR 95%CI | p | |
| Age (years) | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | <0.001 | ||
| Male sex (%) | 0.82 (0.67–1.00) | 0.050 | 0.82 (0.66–1.03) | 0.088 |
| Average arterial pressure(mmHg) | 0.98 (0.97–0.98) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 1.01 (1.00–1.01) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| Respiratory rate (beats/min) | 1.04 (1.02–1.06) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| Blood oxygen saturation (%) | 1.00 (0.98–1.01) | 0.733 | - | |
| Temperature (°C) | 1.45 (1.27–1.66) | <0.001 | 1.42 (1.24–1.64) | <0.001 |
| White blood cell (109/L) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| Hemoglobin (1012/L) | 0.81 (0.77–0.84) | <0.001 | 0.92 (0.86–0.97) | 0.005 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| RDW (%) | 1.17 (1.12–1.22) | <0.001 | 1.04 (0.98–1.11) | 0.176 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 1.10 (1.08–1.12) | <0.001 | 1.11 (1.07–1.15) | <0.001 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 0.90 (0.74–1.10) | 0.302 | - | |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 1.06 (1.05–1.08) | <0.001 | 0.95 (0.92–0.98) | 0.001 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 0.93 (0.83–1.04) | 0.199 | - | |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 1.21 (1.11–1.32) | <0.001 | 0.97 (0.88–1.08) | 0.597 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.76 (1.33–2.33) | <0.001 | 1.71 (1.28–2.27) | <0.001 |
| Anion gap (mmol/L) | 1.07 (1.05–1.09) | <0.001 | 0.98 (0.95–1.01) | 0.145 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.14 (1.07–1.22) | <0.001 | 0.83 (0.72–0.95) | 0.008 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 0.91 (0.89–0.93) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.87–0.95) | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| PT (s) | 1.01 (1.01–1.02) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| APTT (s) | 1.01 (1.01–1.02) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| GCS score | 0.89 (0.87–0.92) | <0.001 | 0.94 (0.91–0.97) | <0.001 |
| APS-III score | 1.03 (1.03–1.03) | <0.001 | Not selected | |
| SOFA score | 1.18 (1.15–1.21) | <0.001 | 1.03 (0.98–1.08) | 0.207 |
| Charlson | 1.13 (1.1–1.17) | <0.001 | 1.07 (1.02–1.13) | 0.009 |
| Congestive heart failure | 2.16 (1.72–2.72) | <0.001 | 1.28 (0.95–1.71) | 0.103 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 0.99 (0.73–1.35) | 0.951 | - | |
| Rheumatic disease | 1.31 (0.68–2.53) | 0.428 | - | |
| Renal disease | 2.03 (1.55–2.66) | <0.001 | 0.82 (0.55–1.22) | 0.332 |
| Diabetes | 1.57 (1.25–1.97) | <0.001 | 1.00 (0.76–1.31) | 0.998 |
| Liver disease | 1.19 (0.85–1.67) | 0.310 | - | |
| Intraparenchymal hemorrhage | 1.52 (1.12–2.07) | 0.008 | 1.54 (1.13–2.11) | 0.007 |
| Extradural hemorrhage | 1.31 (0.67–2.53) | 0.429 | - | |
| Subdural hemorrhage | 1.00 (0.81–1.23) | 0.989 | - | |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 1.35 (1.08–1.69) | 0.009 | 1.26 (0.99–1.60) | 0.057 |
| Neurosurgery | 1.40 (1.13–1.72) | 0.002 | 1.41 (1.13–1.78) | 0.003 |
| First-day RBC infusion | 2.04 (1.61–2.57) | <0.001 | 1.03 (0.76–1.40) | 0.853 |
| First-day PLT infusion | 1.76 (1.34–2.30) | <0.001 | 0.96 (0.70–1.31) | 0.795 |
| BAR group1 | Reference | - | Reference | - |
| BAR group2 | 2.13 (1.68–2.70) | <0.001 | 1.77 (1.37–2.30) | <0.001 |
| BAR group3 | 4.90 (3.77–6.38) | <0.001 | 3.17 (2.17–4.62) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Leng, Y.; Gao, C. Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio May Predict Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury from the MIMIC Database: A Retrospective Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010049
Guo Y, Leng Y, Gao C. Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio May Predict Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury from the MIMIC Database: A Retrospective Study. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yiran, Yuxin Leng, and Chengjin Gao. 2024. "Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio May Predict Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury from the MIMIC Database: A Retrospective Study" Bioengineering 11, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010049
APA StyleGuo, Y., Leng, Y., & Gao, C. (2024). Blood Urea Nitrogen-to-Albumin Ratio May Predict Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury from the MIMIC Database: A Retrospective Study. Bioengineering, 11(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010049






