Empirical Quantification of Optic Nerve Strain Due to Horizontal Duction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
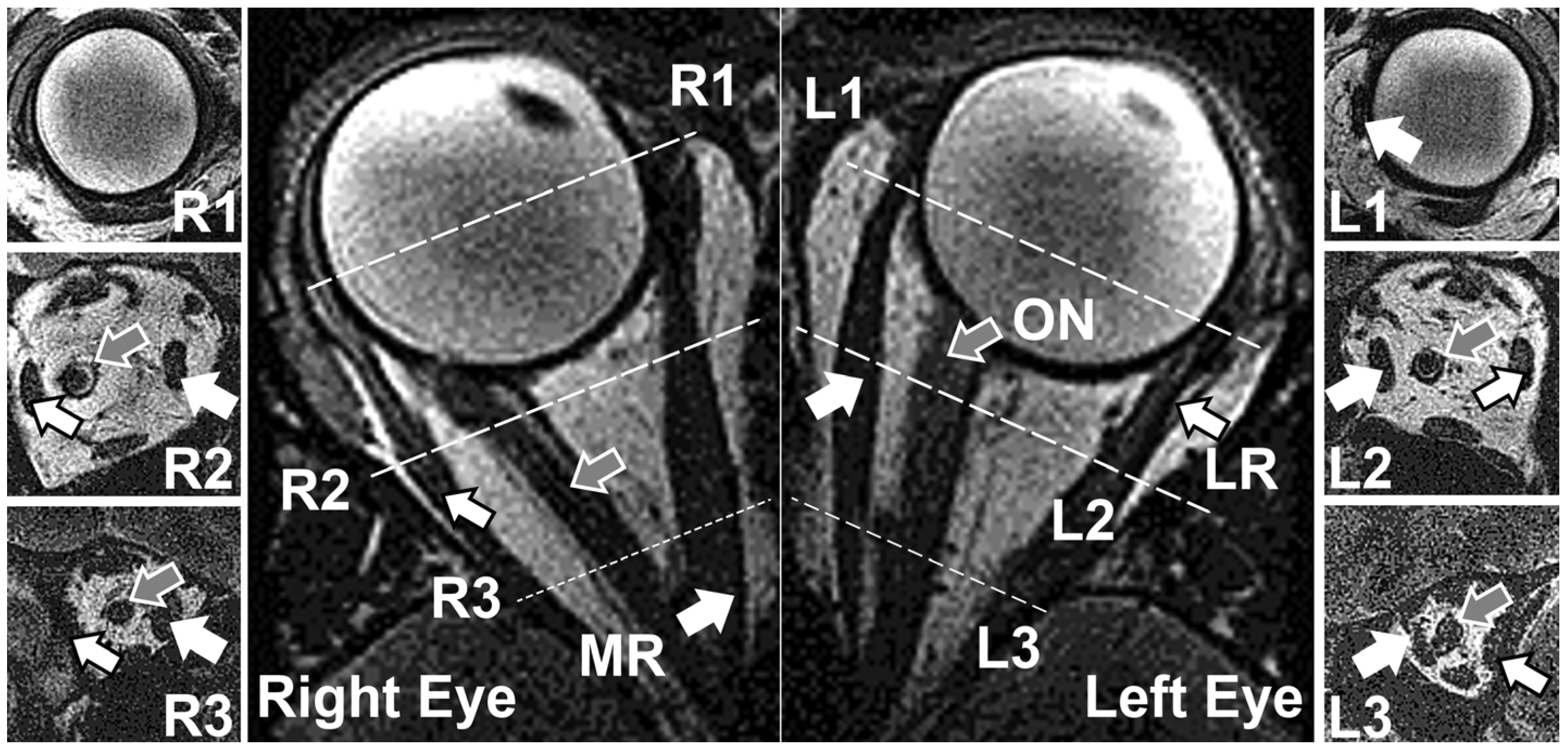
2.1. Human Subjects and MRI Acquisition
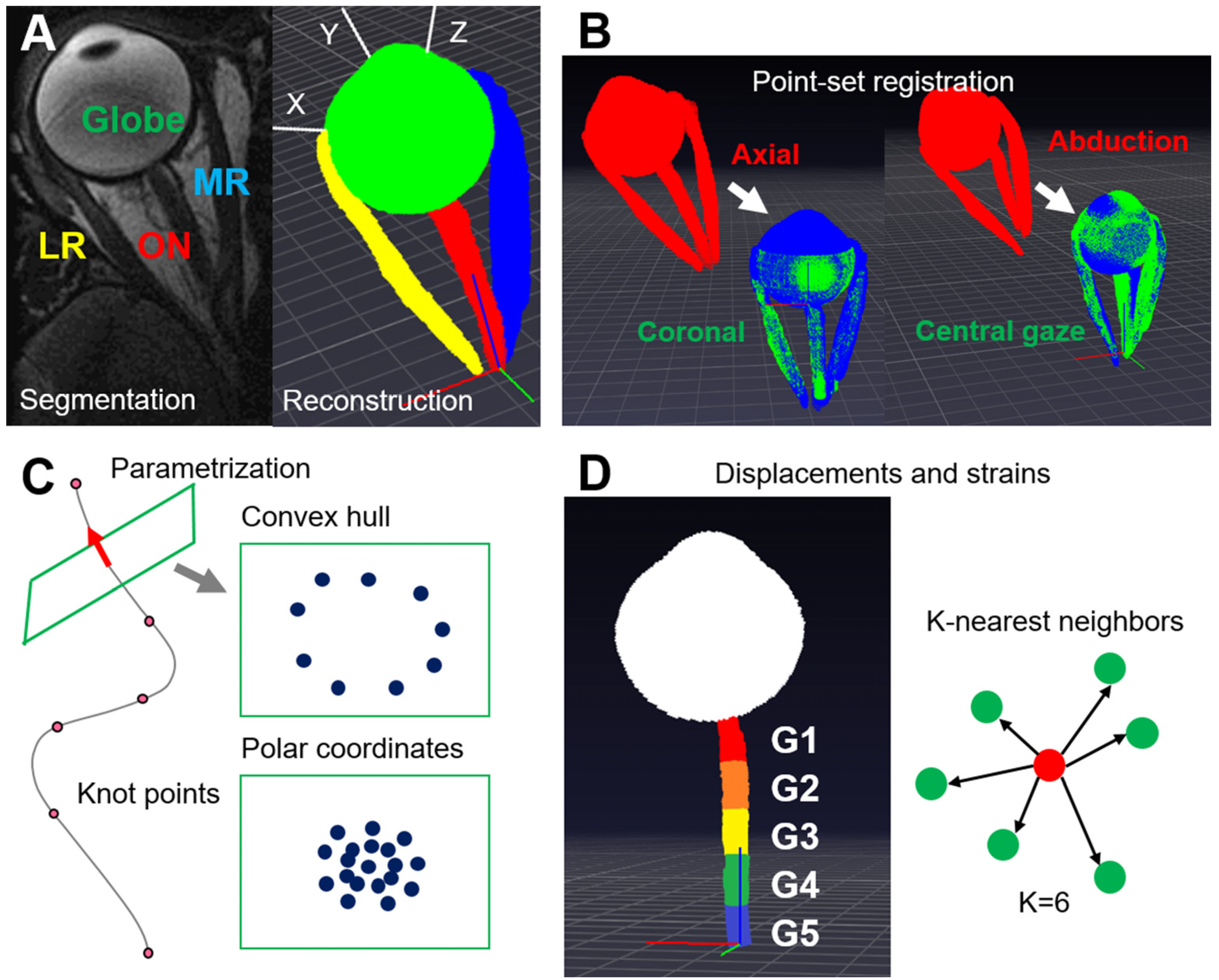
2.2. 3D Reconstruction and Point-Set Registration
2.3. Curve Parametrization
2.4. Local Coordinate System for the Globe and Globe Translation
2.5. Duction Angle Measurements
2.6. Local Coordinate Systems for the ON and the Reconstruction of the ON
2.7. Displacements and Strains
2.8. Measurements of ON and Optic Nerve Sheath (ONS) Diameters
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
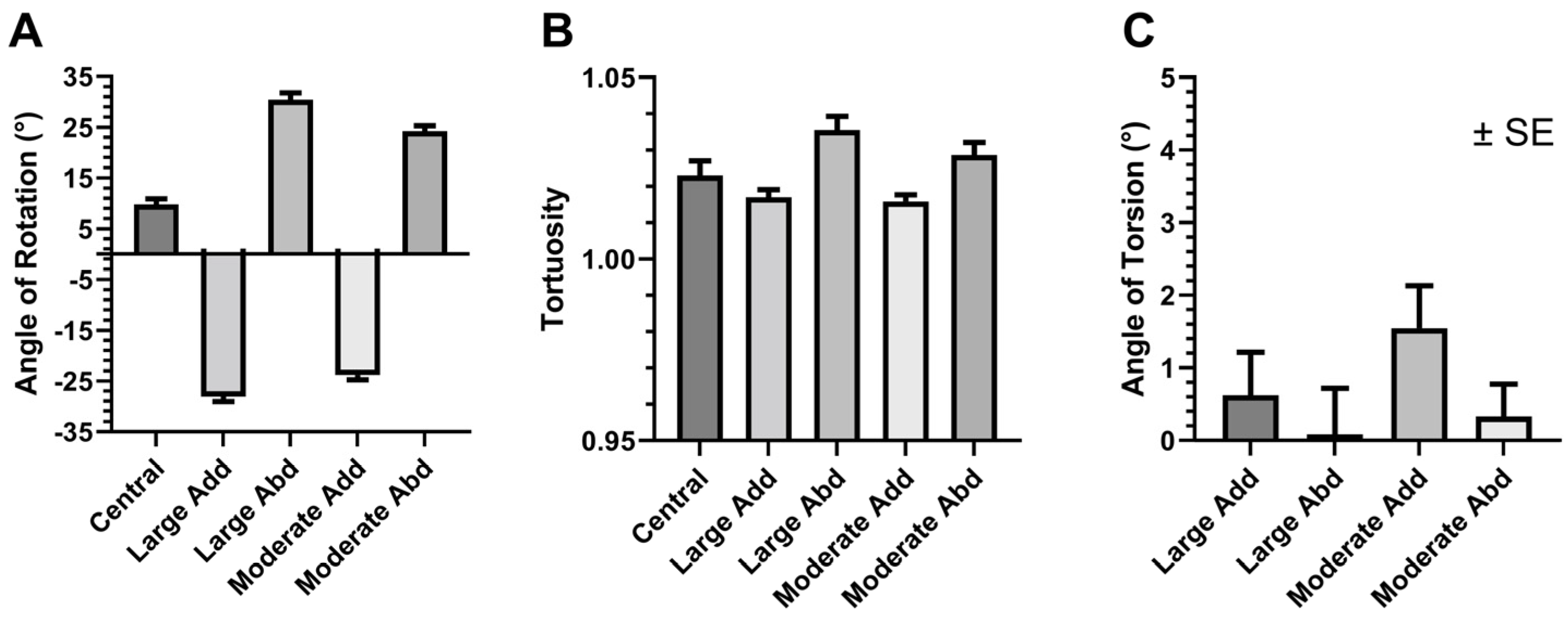
3.1. Changes in Geometry Due to Eye Rotation
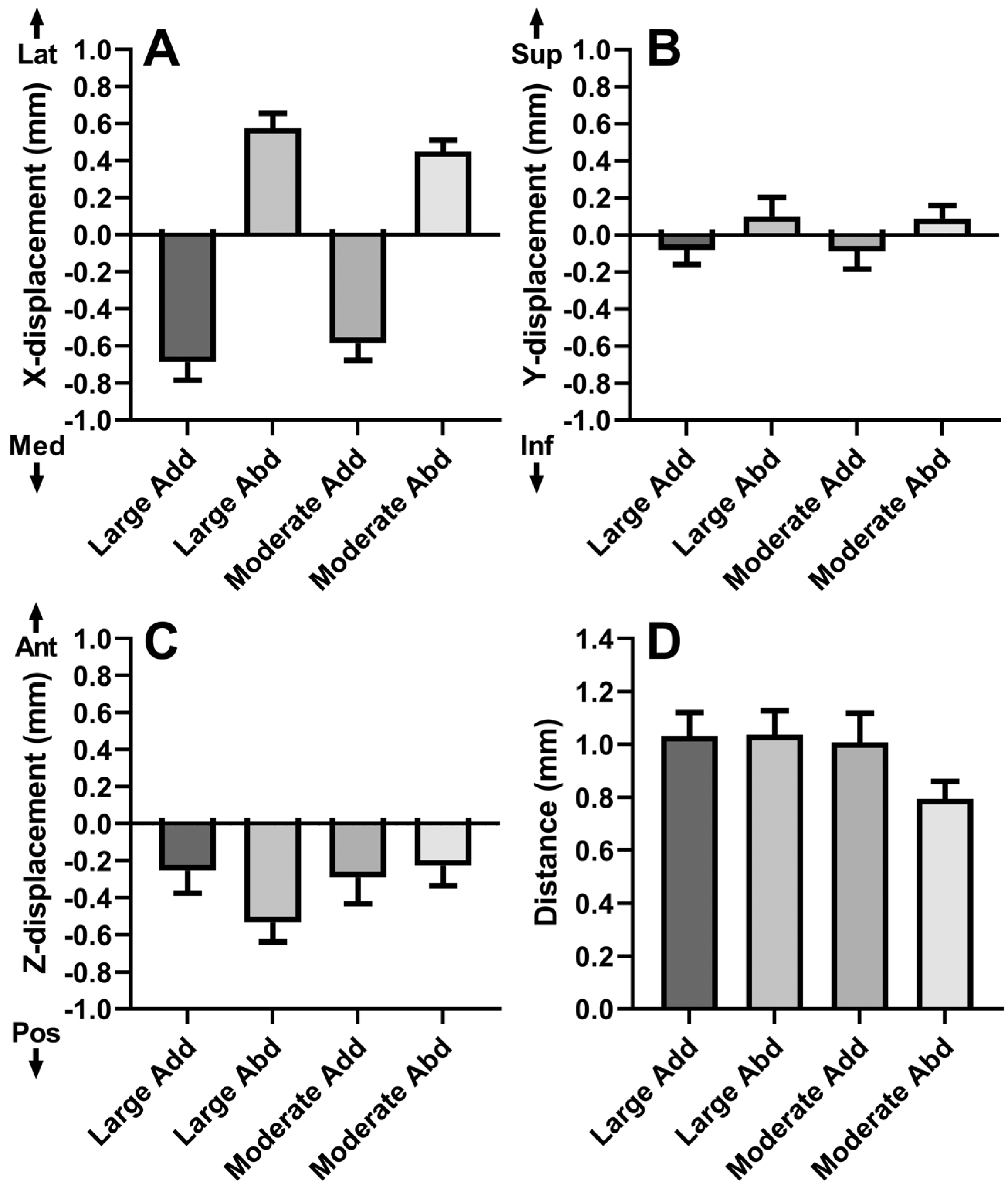
3.2. Globe Translation
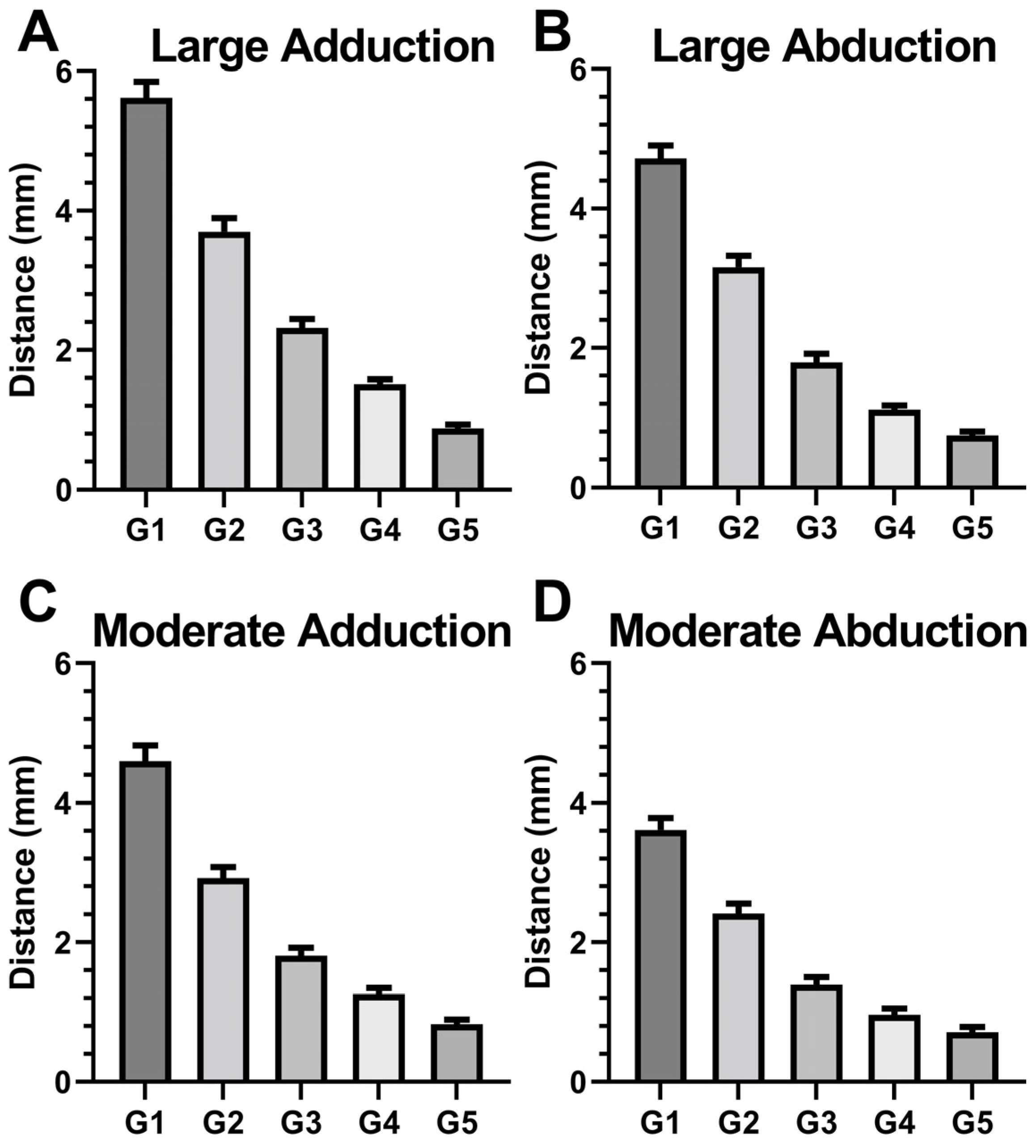
3.3. Local ON Displacements
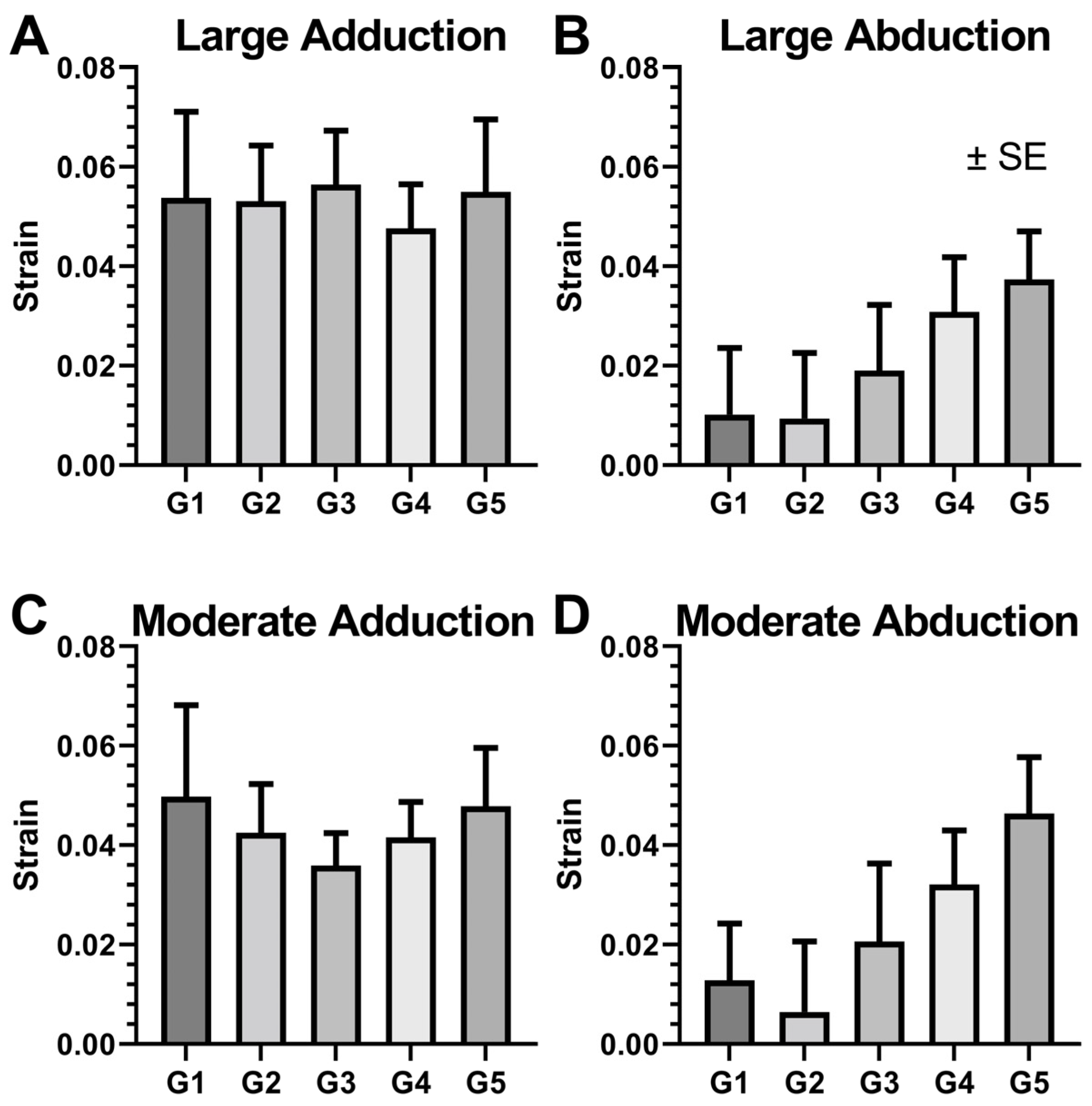
3.4. Local ON Strain Due to Duction
3.5. Optic Nerve and Sheath Diameters during Large Adduction
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morrison, J.C. Elevated intraocular pressure and optic nerve injury models in the rat. J. Glaucoma 2005, 14, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.J.; Downs, J.C.; Burgoyne, C.F.; Suh, J.-K.F. Peripapillary and posterior scleral mechanics—Part I: Development of an anisotropic hyperelastic constitutive model. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 051011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgoyne, C.F.; Downs, J.C.; Bellezza, A.J.; Suh, J.-K.F.; Hart, R.T. The optic nerve head as a biomechanical structure: A new paradigm for understanding the role of IOP-related stress and strain in the pathophysiology of glaucomatous optic nerve head damage. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2005, 24, 39–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demer, J.L. Optic nerve sheath as a novel mechanical load on the globe in ocular duction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1826–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demer, J.L.; Clark, R.A.; Suh, S.Y.; Giaconi, J.A.; Nouri-Mahdavi, K.; Law, S.K.; Bonelli, L.; Coleman, A.L.; Caprioli, J. Magnetic resonance imaging of optic nerve traction during adduction in primary open-angle glaucoma with normal intraocular pressure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 4114–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Beotra, M.R.; Tun, T.A.; Baskaran, M.; Perera, S.; Aung, T.; Strouthidis, N.G.; Milea, D.; Girard, M.J. In vivo 3-dimensional strain mapping confirms large optic nerve head deformations following horizontal eye movements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 5825–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rumpel, H.; Lim, W.E.H.; Baskaran, M.; Perera, S.A.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Aung, T.; Milea, D.; Girard, M.J. Finite element analysis predicts large optic nerve head strains during horizontal eye movements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.; Yoo, L.; Park, J.; Demer, J.L. Finite element biomechanics of optic nerve sheath traction in adduction. J. Biomech. Eng. 2017, 139, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Lu, Y.; Park, J.; Demer, J.L. Finite element model of ocular adduction by active extraocular muscle contraction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, L.K.; Wang, X.; Tun, T.A.; Chung, H.-W.; Milea, D.; Girard, M.J. Gaze-evoked deformations of the optic nerve head in thyroid eye disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fisher, L.K.; Milea, D.; Jonas, J.B.; Girard, M.J. Predictions of optic nerve traction forces and peripapillary tissue stresses following horizontal eye movements. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.Y.; Le, A.; Shin, A.; Park, J.; Demer, J.L. Progressive deformation of the optic nerve head and peripapillary structures by graded horizontal duction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 5015–5021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chang, S.; Grinband, J.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Freund, K.B.; Hoang, Q.V.; Girard, M.J. Optic nerve tortuosity and displacements during horizontal eye movements in healthy and highly myopic subjects. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 106, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demer, J.L.; Clark, R.A.; Suh, S.Y.; Giaconi, J.A.; Nouri-Mahdavi, K.; Law, S.K.; Bonelli, L.; Coleman, A.L.; Caprioli, J. Optic nerve traction during adduction in open angle glaucoma with normal versus elevated intraocular pressure. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldstein, S.; Faatz, H.; Szimacsek, M.; Glodan, A.; Podkowinski, D.; Montuoro, A.; Simader, C.; Gerendas, B.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Comparison of penetration depth in choroidal imaging using swept source vs spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Eye 2015, 29, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Suh, S.Y.; Caprioli, J.; Giaconi, J.A.; Nouri-Mahdavi, K.; Law, S.K.; Bonelli, L.; Coleman, A.L.; Demer, J.L. Adduction-induced strain on the optic nerve in primary open angle glaucoma at normal intraocular pressure. Curr. Eye Res. 2021, 46, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demer, J.L.; Dushyanth, A. T2-weighted fast spin-echo magnetic resonance imaging of extraocular muscles. J. AAPOS 2011, 15, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grossman, M. Parametric curve fitting. Comput. J. 1971, 14, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demer, J.L.; Clark, R.A. Translation and eccentric rotation in ocular motor modeling. Prog. Brain Res. 2019, 248, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, H.; Oh, J.; Kim, M. Xvfi: Extreme video frame interpolation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 14489–14498. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Tedrake, R. Filterreg: Robust and efficient probabilistic point-set registration using gaussian filter and twist parameterization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11095–11104. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Bai, J.; Yu, Q. Oriented and directional chamfer distance losses for 3D object reconstruction from a single image. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 61631–61638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Demer, J.L. Effect of aging on human rectus extraocular muscle paths demonstrated by magnetic resonance imaging. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmak, H.; Sahin, A.; Yildirim, N.; Saricicek, T.; Yurdakul, S. The angle kappa in strabismic individuals. Strabismus 2007, 15, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaee, H.; Shafiee, M.; Hoseini, R.; Abrishami, M.; Abrishami, Y.; Abrishami, M. Angle kappa measurements: Normal values in healthy Iranian population obtained with the Orbscan II. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e17873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, I.-S. Continuum Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ying, G.-S. Evaluation of approaches to analyzing continuous correlated eye data when sample size is small. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2018, 25, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.A.; Demer, J.L. The effect of axial length on extraocular muscle leverage. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 216, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.; Demer, J.L. Empirical Quantification of Optic Nerve Strain Due to Horizontal Duction. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080931
Lim S, Demer JL. Empirical Quantification of Optic Nerve Strain Due to Horizontal Duction. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(8):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080931
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Seongjin, and Joseph L. Demer. 2023. "Empirical Quantification of Optic Nerve Strain Due to Horizontal Duction" Bioengineering 10, no. 8: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080931
APA StyleLim, S., & Demer, J. L. (2023). Empirical Quantification of Optic Nerve Strain Due to Horizontal Duction. Bioengineering, 10(8), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080931







