Recognizing Pediatric Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Based on Multi-Contrast MRI and Deep Weighted Fusion Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Optimal Combination of T2W and FLAIR
s.t. α + β = 3
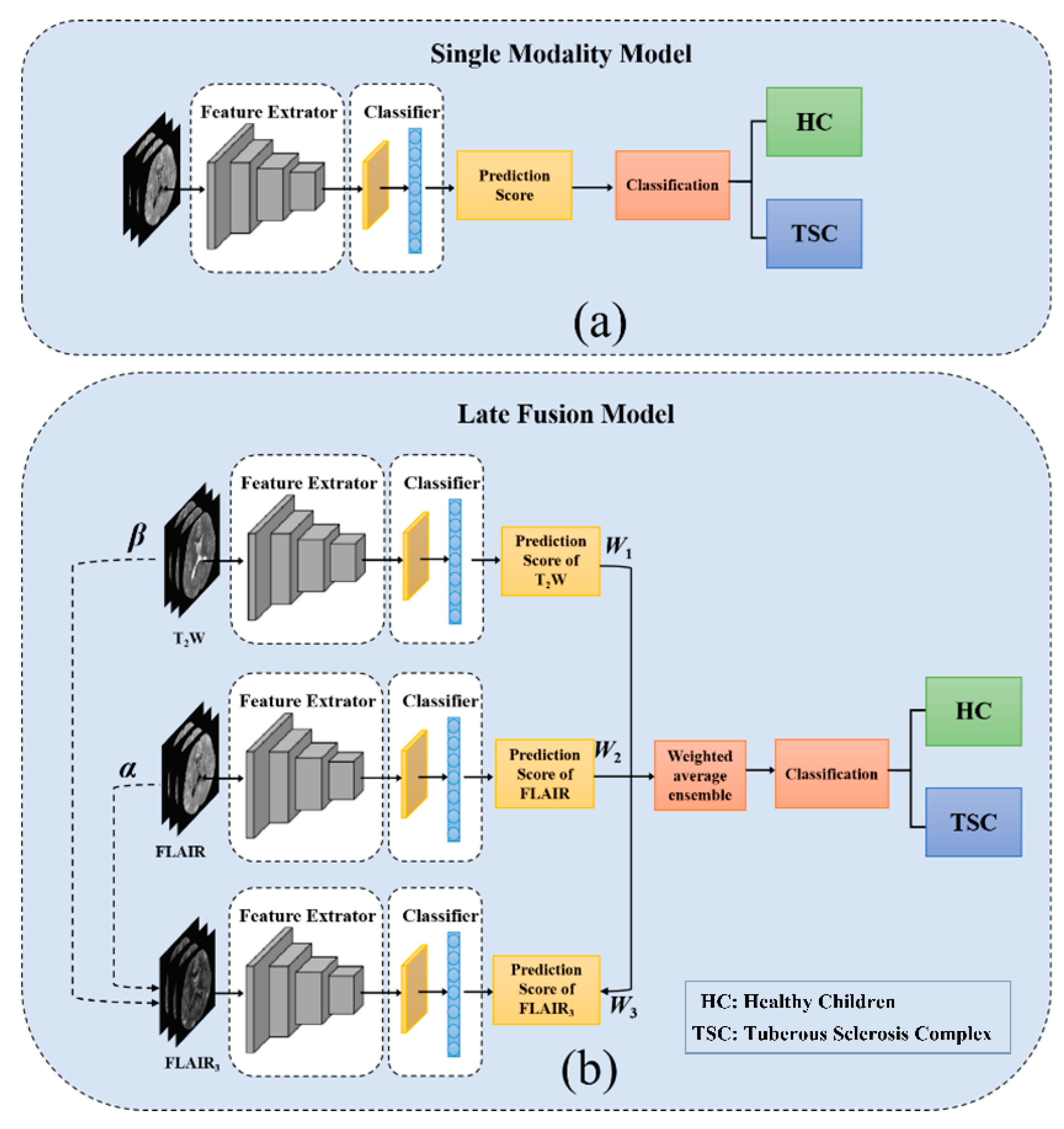
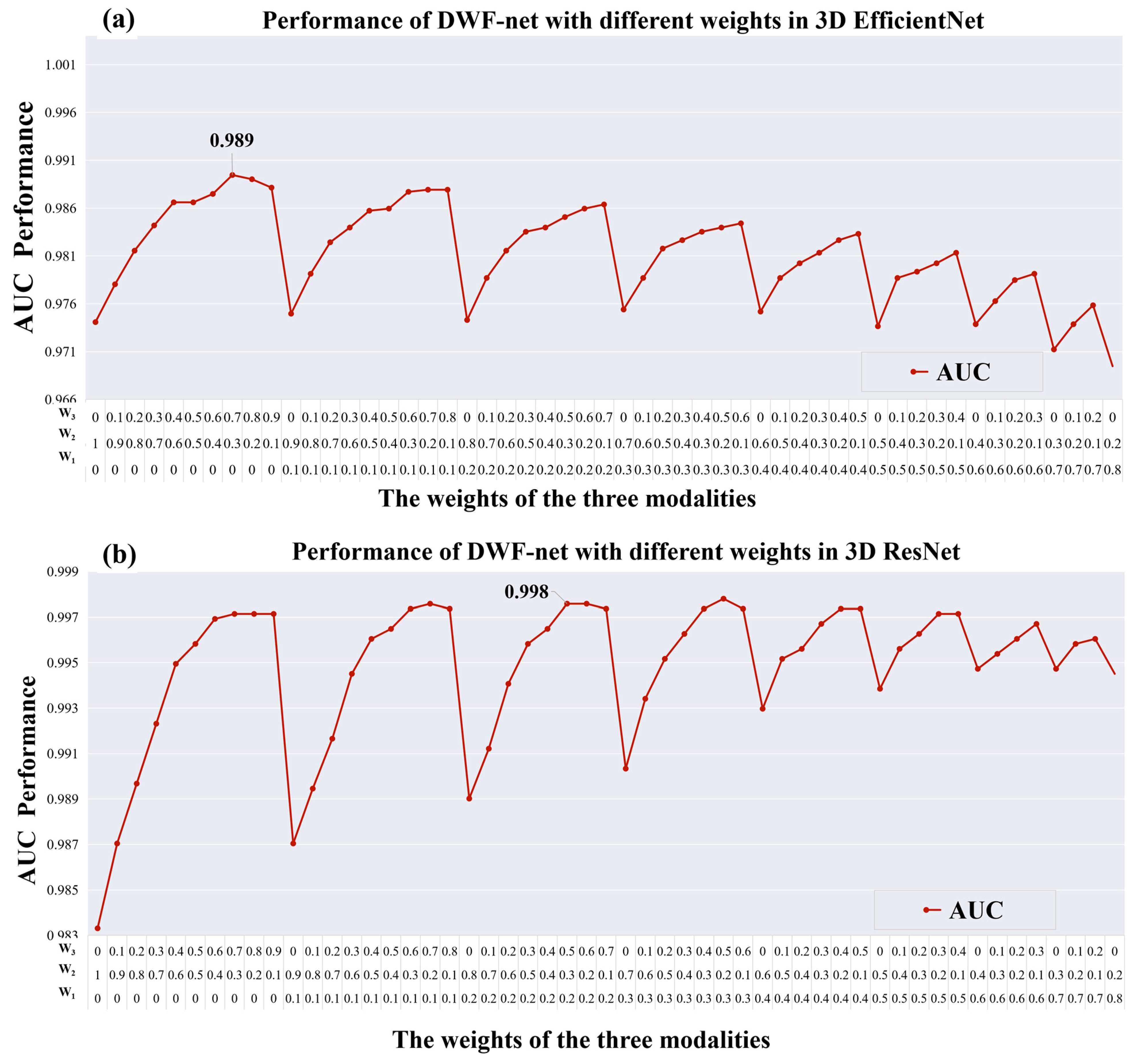
2.2. Late Fusion Strategies
| Algorithm 1 The weight searching algorithm for fusion |
| Input: The prediction scores ST2W, SFLAIR, and SFLAIR3 of three input images and corresponding ground truth y on testing set. |
| Output: The weight (W1, W2, and W3) with best AUC on testing set. |
| 1: Initialize AUC best ← 0. |
| 2: for i: =0 to 10 do 3: for j: =0 to 10–i do |
| 4: k ← 10-i–j |
| 5: S temp = (i×ST2W + j×SFLAIR + k×SFLAIR3) × 0.1 6: AUC temp = Compare (Stemp, y) 7: if AUC temp > AUC best then 8: AUC best ← AUC temp 9: W1 ← i×0.1 10: W2 ← j×0.1 11: W3 ← k×0.1 12: end for 13: end for |
| 14: end for |
| Return W1, W2, and W3 |
2.3. Network Architectures
3. Materials and Experiments
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Data Processing
3.3. Baseline and Effectiveness of Skull Stripping
3.4. Comparison of Normalization Methods
3.5. Model Training and Evaluation
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients
4.2. Visualization Results of FLAIR3
4.3. Performance of the Models
4.4. Results of Skull Stripping
4.5. Comparison of Normalization Methods
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu-Shore, C.J.; Major, P.; Camposano, S.; Muzykewicz, D.; Thiele, E.A. The natural history of epilepsy in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia 2009, 51, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.J.; Lusk, J.B.; Ervin, J.; Burke, J.; O’Brien, R.; Wang, S.H.J. Tuberous sclerosis complex is a novel, amyloid-independent tauopathy associated with elevated phosphorylated 3R/4R tau aggregation. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henske, E.P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Kingswood, J.C.; Sampson, J.R.; Thiele, E.A. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Tominaga, K.; Iwatani, Y.; Kato, Y.; Wataya-Kaneda, M.; Makita, K.; Nemoto, K.; Taniike, M.; Kagitani-Shimono, K. Abnormal White Matter Microstructure in the Limbic System Is Associated with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 782479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, C.; Yan, G. Identification of a novel heterozygous TSC2 splicing variant in a patient with Tuberous sclerosis complex: A case report. Medicine 2022, 101, e28666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miszewska, D.; Sugalska, M.; Jóźwiak, S. Risk Factors Associated with Refractory Epilepsy in Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanishi, T.; Akiyama, T.; Tanaka, S.-I.; Mayo, E.; Mitsutake, A.; Boelman, C.; Go, C.; Snead, O.C.; Drake, J.; Rutka, J.; et al. Interictal high frequency oscillations correlating with seizure outcome in patients with widespread epileptic networks in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hu, W.-H.; Zhang, C.; Meng, F.-G.; Chen, N.; Zhang, J.-G. Predictors of seizure freedom after surgical management of tuberous sclerosis complex: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 105, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, C.; Su, S.; Liang, D.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liao, J. Machine Learning in Epilepsy Drug Treatment Outcome Prediction Using Multi-modality Data in Children with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Big Data and Information Analytics (BigDIA), Shenzhen, China, 4–6 December 2020; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, J.; Verhelle, B.; Vervisch, J.; Lemmens, K.; Kotulska, K.; Moavero, R.; Curatolo, P.; Weschke, B.; Riney, K.; Feucht, M.; et al. Early epileptiform EEG activity in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex predicts epilepsy and neurodevelopmental outcomes. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Nastro, A.; Cicala, D.; De Liso, M.; Covelli, E.M.; Cinalli, G. Neuroimaging in tuberous sclerosis complex. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2497–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggermann, V.; Hernandez-Torres, E.; Traboulsee, A.; Li DK, B.; Rauscher, A. FLAIR2: A Combination of FLAIR and T2 for Improved MS Lesion Detection. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, R.E.; Hasan, K.M.; Haque, M.E.; Nelson, F.M.; Wolinsky, J.S.; Narayana, P.A. Optimal combination of FLAIR and T2-weighted MRI for improved lesion contrast in multiple sclerosis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Q.; Shan, H.; Steber, C.; Helis, C.; Whitlow, C.; Chan, M.; Wang, G. Multi-Contrast Super-Resolution MRI Through a Progressive Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinoglu, Y.K.; Koska, I.O.; Uluc, M.E.; Gelal, M.F. Detection and vascular territorial classification of stroke on diffusion-weighted MRI by deep learning. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 145, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikrishna, M.; Pereira, J.B.; Heckemann, R.A.; Volpe, G.; van Westen, D.; Zettergren, A.; Kern, S.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Westman, E.; Skoog, I.; et al. Deep learning from MRI-derived labels enables automatic brain tissue classification on human brain CT. Neuroimage 2021, 244, 118606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.K.; Kim, W.; Thornburg, O.S.; McBrian, D.K.; McKhann, G.M.; Feldstein, N.A.; Maddocks, A.B.; Gonzalez, E.; Shen, M.Y.; Akman, C.; et al. Convolutional neural network-aided tuber segmentation in tuberous sclerosis complex patients correlates with electroencephalogram. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Fernández, I.; Yang, E.; Calvachi, P.; Amengual-Gual, M.; Wu, J.Y.; Krueger, D.; Northrup, H.; Bebin, M.E.; Sahin, M.; Yu, K.-H.; et al. Deep learning in rare disease. Detection of tubers in tuberous sclerosis complex. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.H.; Poudel, R.P.; Tsagkrasoulis, D.; Caan, M.W.; Steves, C.; Spector, T.D.; Montana, G. Predicting brain age with deep learning from raw imaging data results in a reliable and heritable biomarker. Neuroimage 2017, 163, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffa, A.P.; Grilli, G.; Perfetto, F.; Specchiulli, L.P.; Vinci, R.; Macarini, L.; Zizzo, L. Neuroimaging features of tuberous sclerosis complex and Chiari type I malformation: A rare association. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Xing, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Lin, A.L.; Jacobs, N. Alzheimer’s Disease Classification Using 2D Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; IEEE: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3008–3012. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, B.A.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Ellingsen, L.M.; Walters, G.B.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Stefansson, H.; Ulfarsson, M.O. Brain age prediction using deep learning uncovers associated sequence variants. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweje, F.R.; Bao, B.; Wu, J.; Dalal, D.; Liao, W.H.; He, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, P.; Peng, X.; et al. Deep Learning for Classification of Bone Lesions on Routine MRI. EBioMedicine 2021, 68, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Schell, M.; Pflueger, I.; Brugnara, G.; Bonekamp, D.; Neuberger, U.; Wick, A.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; Heiland, S.; Wick, W.; et al. Automated brain extraction of multisequence MRI using artificial neural networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 4952–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, J.S.; Woo, J.; Jang, S.K.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Deep Learning-Based Method to Differentiate Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder from Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 599042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Gong, W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Smith, S.M. Accurate brain age prediction with lightweight deep neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 68, 101871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luna, A.; Marcia, R.F. Data-Limited Deep Learning Methods for Mild Cognitive Impairment Classification in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 2641–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, J.; Li, Y.A.; Xia, W.; He, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.; Cai, S.; et al. MRI-Based Multiple Instance Convolutional Neural Network for Increased Accuracy in the Differentiation of Borderline and Malignant Epithelial Ovarian Tumors. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2021, 56, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dong, M.; Lee, M.-H.; O’Hara, N.; Juhasz, C.; Asano, E.; Jeong, J.-W. Deep Relational Reasoning for the Prediction of Language Impairment and Postoperative Seizure Outcome Using Preoperative DWI Connectome Data of Children with Focal Epilepsy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 40, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.P.; Doshi, J.; Pati, S.; Ha, S.M.; Sako, C.; Talbar, S.; Kulkarni, U.; Davatzikos, C.; Erus, G.; Bakas, S. Skull-Stripping of Glioblastoma MRI Scans Using 3D Deep Learning. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 11992, pp. 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister, F.P.; Höllinger, I.; Klinger, N.; Geissler, A.; Wurnig, M.C.; Matt, E.; Rath, J.; Robinson, S.D.; Trattnig, S.; Beisteiner, R. The benefits of skull stripping in the normalization of clinical fMRI data. NeuroImage Clin. 2013, 3, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleesiek, J.; Urban, G.; Hubert, A.; Schwarz, D.; Maier-Hein, K.; Bendszus, M.; Biller, A. Deep MRI brain extraction: A 3D convolutional neural network for skull stripping. Neuroimage 2016, 129, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, A.; Shahid, A.R.; Raza, B.; Madni, T.M.; Janjua, U.I. State-of-the-Art Traditional to the Machine- and Deep-Learning-Based Skull Stripping Techniques, Models, and Algorithms. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 1443–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, D.; Wang, H. Identification of Children’s Tuberous Sclerosis Complex with Multiple-contrast MRI and 3D Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 2924–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xie, F.; Hu, D.; Sun, S.; Shi, J.; Xue, C. Stain Standardization Capsule for Application-Driven Histopathological Image Normalization. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksson, L.J.; Raimondi, S.; Botta, F.; Pepa, M.; Gugliandolo, S.G.; De Angelis, S.P.; Marvaso, G.; Petralia, G.; DE Cobelli, O.; Gandini, S.; et al. Effects of MRI image normalization techniques in prostate cancer radiomics. Phys. Medica 2020, 71, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curatolo, P. Intractable epilepsy in tuberous sclerosis: Is the tuber removal not enough? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.E.; Filip-Dhima, R.; Sideridis, G.; Peters, J.M.; Au, K.S.; Northrup, H.; Bebin, E.M.; Wu, J.Y.; Krueger, D.; Sahin, M.; et al. Presentation and Diagnosis of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex in Infants. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20164040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Model Name | Input Modality | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Eff_FLAIR | FLAIR only | 3D-EfficientNet |
| Eff_T2W | T2W only | 3D-EfficientNet |
| Eff_FLAIR3 | FLAIR3 only | 3D-EfficientNet |
| Eff_FLAIR_T2W | FLAIR + T2W | DWF_net |
| Eff_DWF_net | FLAIR + T2W + FLAIR3 | DWF_net |
| Res_FLAIR | FLAIR only | 3D-ResNet34 |
| Res_T2 | T2W only | 3D-ResNet34 |
| Res_FLAIR3 | FLAIR3 only | 3D-ResNet34 |
| Res_FLAIR_T2W | FLAIR + T2W | DWF_net |
| Res_DWF_net | FLAIR + T2W + FLAIR3 | DWF_net |
| TSC | HC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 349 | 331 | - |
| Male, number (%) | 188 (53.9%) | 183 (55.3%) | 0.711 |
| Age at imaging, mean ± SD (months) | 45.5 ± 46.6 | 73.3 ± 49.2 | <0.001 |
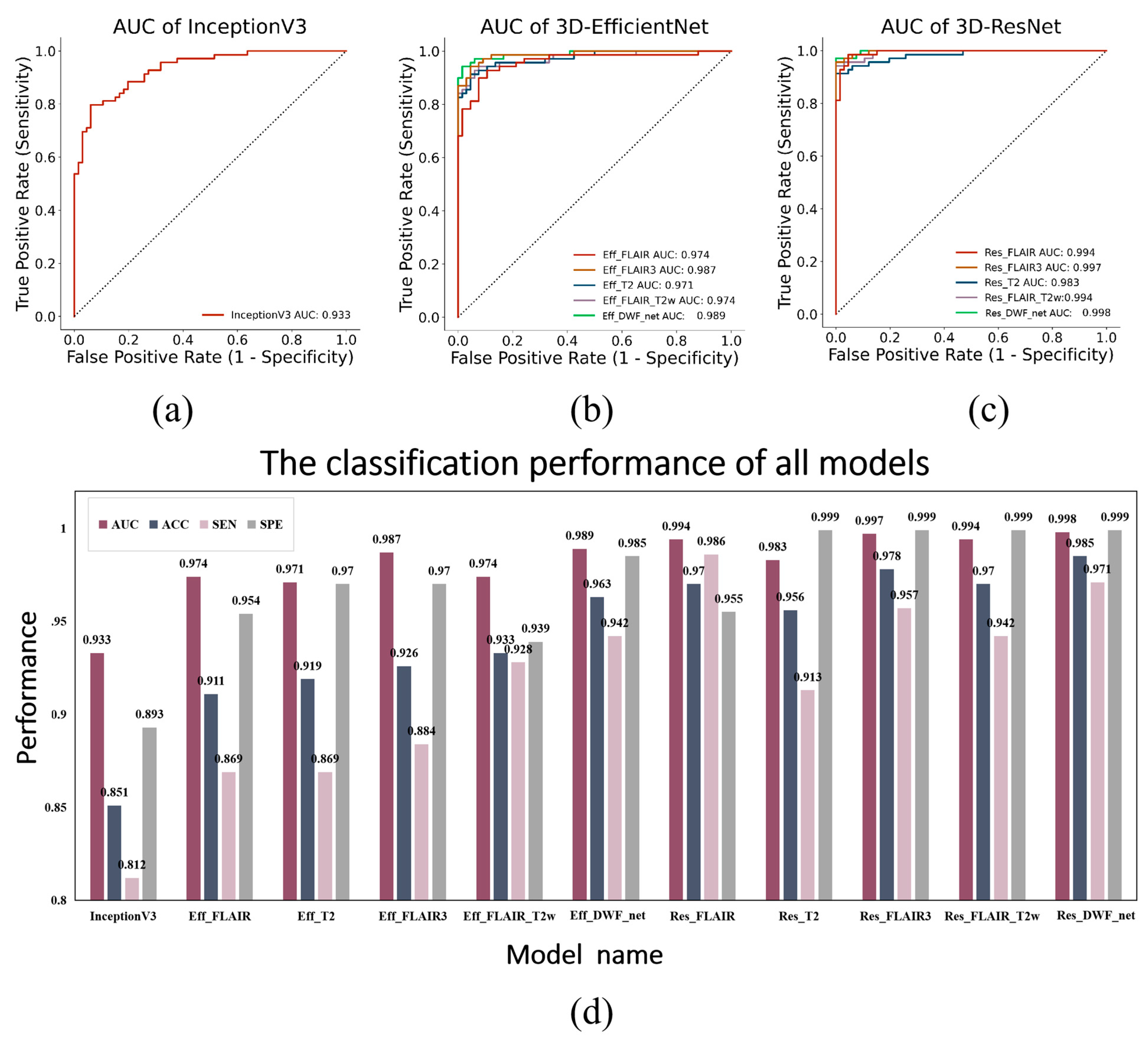
| Input Modality | Model Name | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLAIR + T2W | InceptionV3 [18] | 0.933 | 0.851 | 0.812 | 0.893 |
| FLAIR only | Eff_FLAIR | 0.974 | 0.911 | 0.869 | 0.954 |
| T2W only | Eff_T2W | 0.971 | 0.919 | 0.869 | 0.970 |
| FLAIR3 | Eff_FLAIR3 | 0.987 | 0.926 | 0.884 | 0.970 |
| FLAIR + T2W | Eff_FLAIR_T2W | 0.974 | 0.933 | 0.928 | 0.939 |
| FLAIR + T2W + FLAIR3 (W1 = 0.0, W2 = 0.3, W3 = 0.7) | Eff_DWF_net | 0.989 | 0.963 | 0.942 | 0.985 |
| FLAIR only | Res_FLAIR | 0.994 | 0.970 | 0.986 | 0.955 |
| T2W only | Res_T2W | 0.983 | 0.956 | 0.913 | 0.999 |
| FLAIR3 | Res_FLAIR3 | 0.997 | 0.978 | 0.957 | 0.999 |
| FLAIR + T2W | Res_FLAIR_T2W | 0.994 | 0.970 | 0.942 | 0.999 |
| FLAIR + T2W + FLAIR3 (W1 = 0.2, W2 = 0.3, W3 = 0.5) | Res_DWF_net | 0.998 | 0.985 | 0.971 | 0.999 |
| Modality | Model Name | Preprocessing | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLAIR only | 3D-EfficientNet | Without skull stripping | 0.898 | 0.829 | 0.754 | 0.909 |
| Skull stripping | 0.974 | 0.911 | 0.869 | 0.954 | ||
| 3D-ResNet | Without skull stripping | 0.959 | 0.881 | 0.855 | 0.909 | |
| Skull stripping | 0.994 | 0.970 | 0.986 | 0.955 | ||
| T2W only | 3D-EfficientNet | Without skull stripping | 0.968 | 0.916 | 0.881 | 0.951 |
| Skull stripping | 0.971 | 0.919 | 0.869 | 0.970 | ||
| 3D-ResNet | Without skull stripping | 0.914 | 0.829 | 0.797 | 0.863 | |
| Skull stripping | 0.983 | 0.956 | 0.913 | 0.999 |
| Modality | Model Name | Preprocessing | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLAIR only | 3D-EfficientNet | Without normalization | 0.951 | 0.899 | 0.863 | 0.936 |
| Z-score | 0.965 | 0.867 | 0.754 | 0.984 | ||
| Min–max | 0.974 | 0.911 | 0.869 | 0.954 | ||
| 3D-ResNet | Without normalization | 0.985 | 0.933 | 0.971 | 0.893 | |
| Z-score | 0.914 | 0.867 | 0.797 | 0.933 | ||
| Min–max | 0.994 | 0.970 | 0.986 | 0.955 | ||
| T2W only | 3D-EfficientNet | Without normalization | 0.950 | 0.911 | 0.884 | 0.939 |
| Z-score | 0.967 | 0.933 | 0.898 | 0.969 | ||
| Min–max | 0.971 | 0.919 | 0.869 | 0.970 | ||
| 3D-ResNet | Without normalization | 0.974 | 0.918 | 0.927 | 0.909 | |
| Z-score | 0.982 | 0.918 | 0.884 | 0.954 | ||
| Min–max | 0.983 | 0.956 | 0.913 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, D.; Liao, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, X.; Lin, R.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.-C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, D.; et al. Recognizing Pediatric Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Based on Multi-Contrast MRI and Deep Weighted Fusion Network. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070870
Jiang D, Liao J, Zhao C, Zhao X, Lin R, Yang J, Li Z-C, Zhou Y, Zhu Y, Liang D, et al. Recognizing Pediatric Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Based on Multi-Contrast MRI and Deep Weighted Fusion Network. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070870
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Dian, Jianxiang Liao, Cailei Zhao, Xia Zhao, Rongbo Lin, Jun Yang, Zhi-Cheng Li, Yihang Zhou, Yanjie Zhu, Dong Liang, and et al. 2023. "Recognizing Pediatric Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Based on Multi-Contrast MRI and Deep Weighted Fusion Network" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070870
APA StyleJiang, D., Liao, J., Zhao, C., Zhao, X., Lin, R., Yang, J., Li, Z.-C., Zhou, Y., Zhu, Y., Liang, D., Hu, Z., & Wang, H. (2023). Recognizing Pediatric Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Based on Multi-Contrast MRI and Deep Weighted Fusion Network. Bioengineering, 10(7), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070870







