Effect of Cilostazol on Delayed Cerebral Infarction in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Explainable Predictive Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
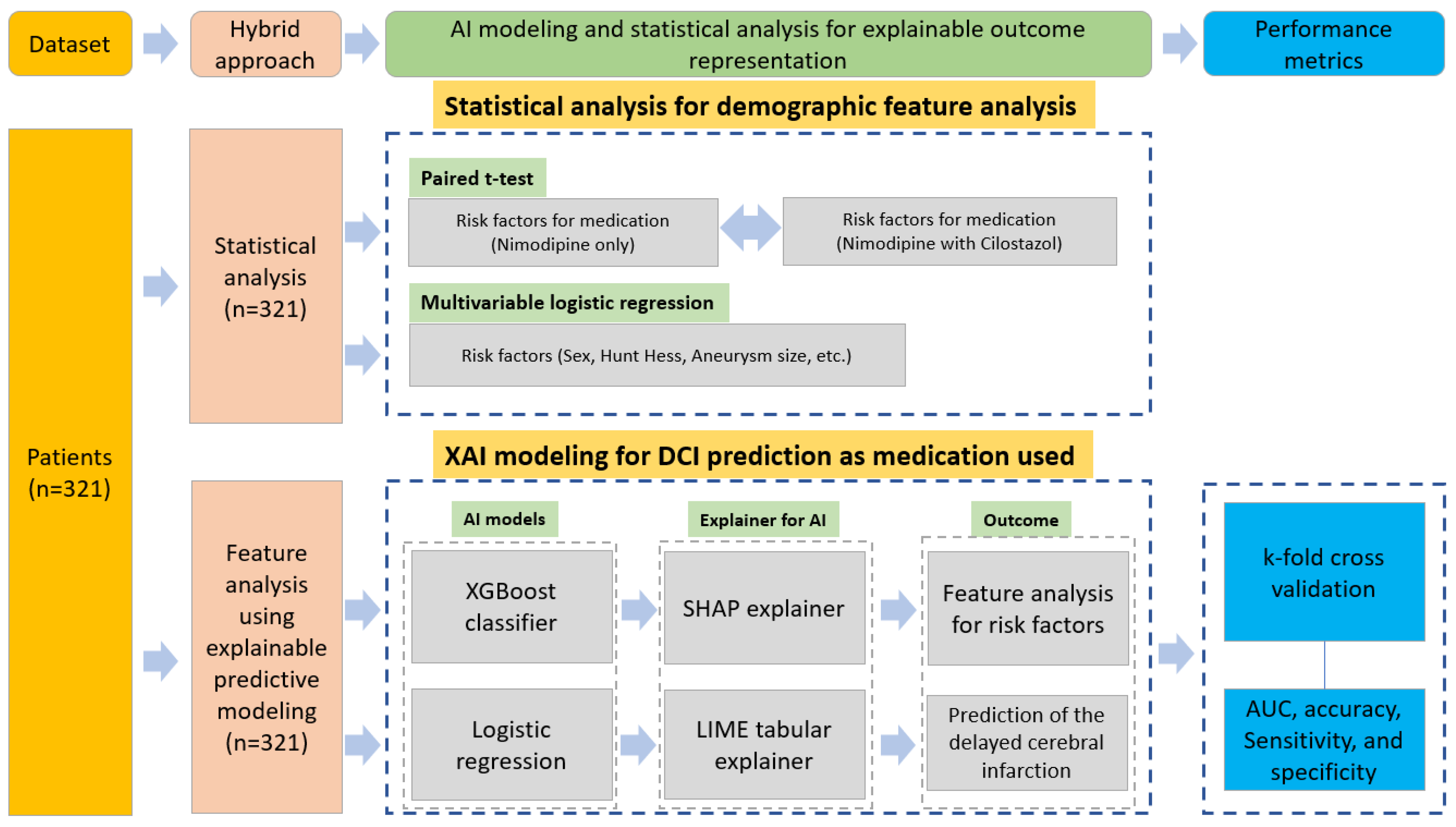
2.3. Hybrid Approach for Feature Analysis and DCI Effect Prediction
2.3.1. XAI
SHAP
LIME
2.3.2. K-Fold Cross-Validation and Programming Environment
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis
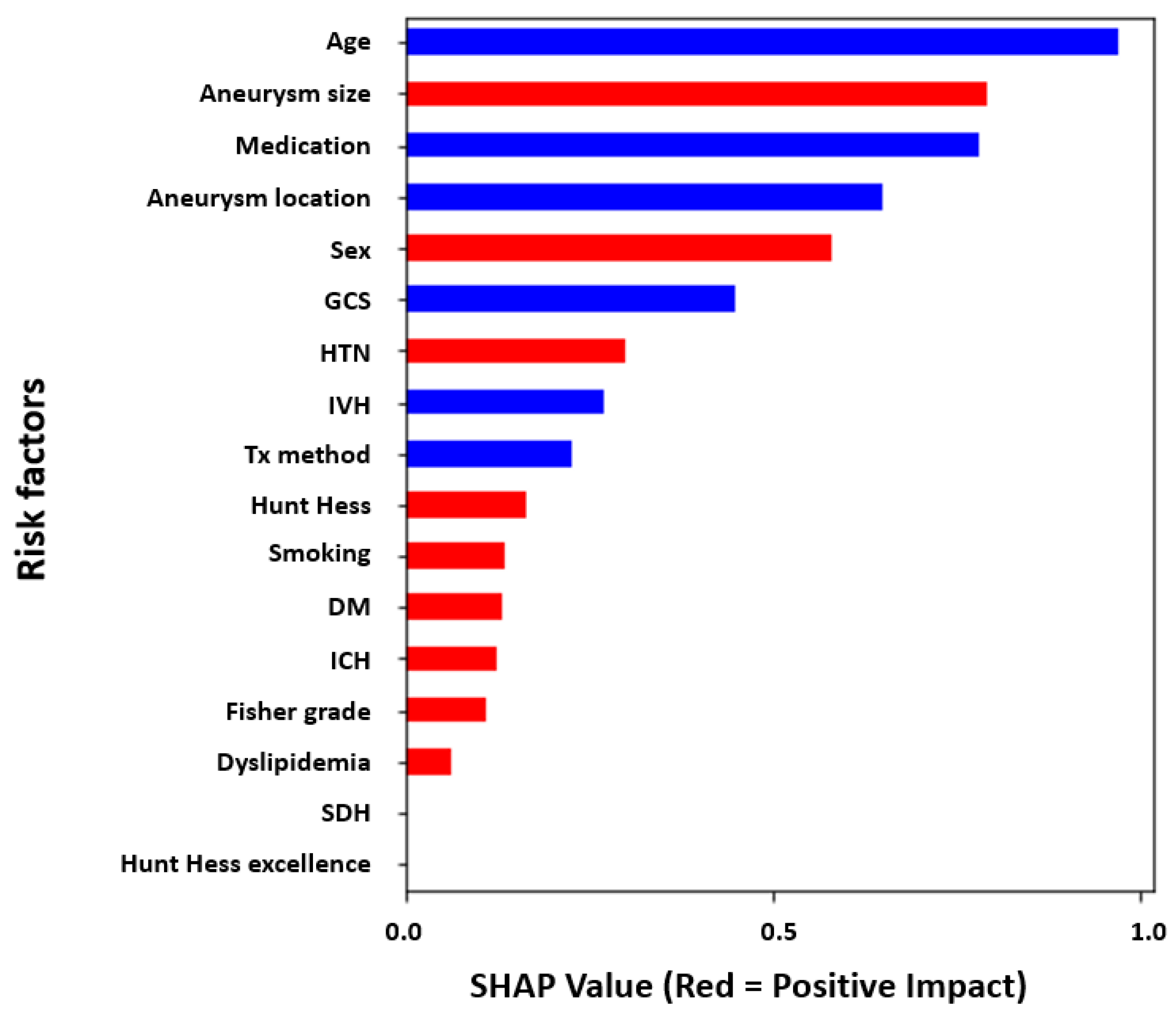
3.2. Global Feature Analysis of the Risk Factors Related to DCI Using XAI
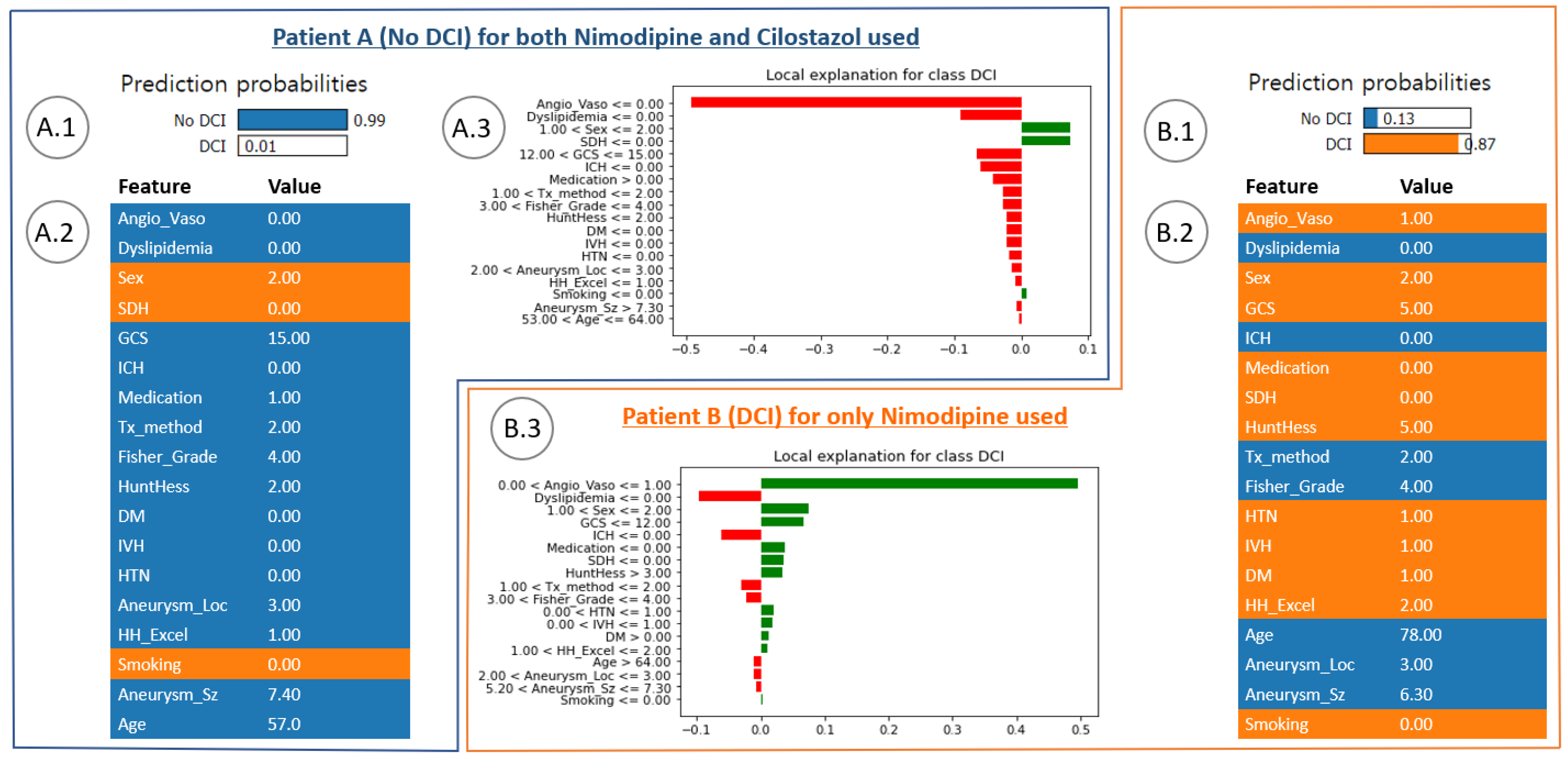
3.3. Local Feature Analysis of the Risk Factors Related to DCI
3.4. Performance Evaluation Using ML Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Conventional Analysis of Cilostazol Effect on DCI in Patients with aSAH
4.2. Explainable Modeling in Patients with aSAH
4.3. In-Depth Understanding of Global and Local Interpretations of Risk Factors
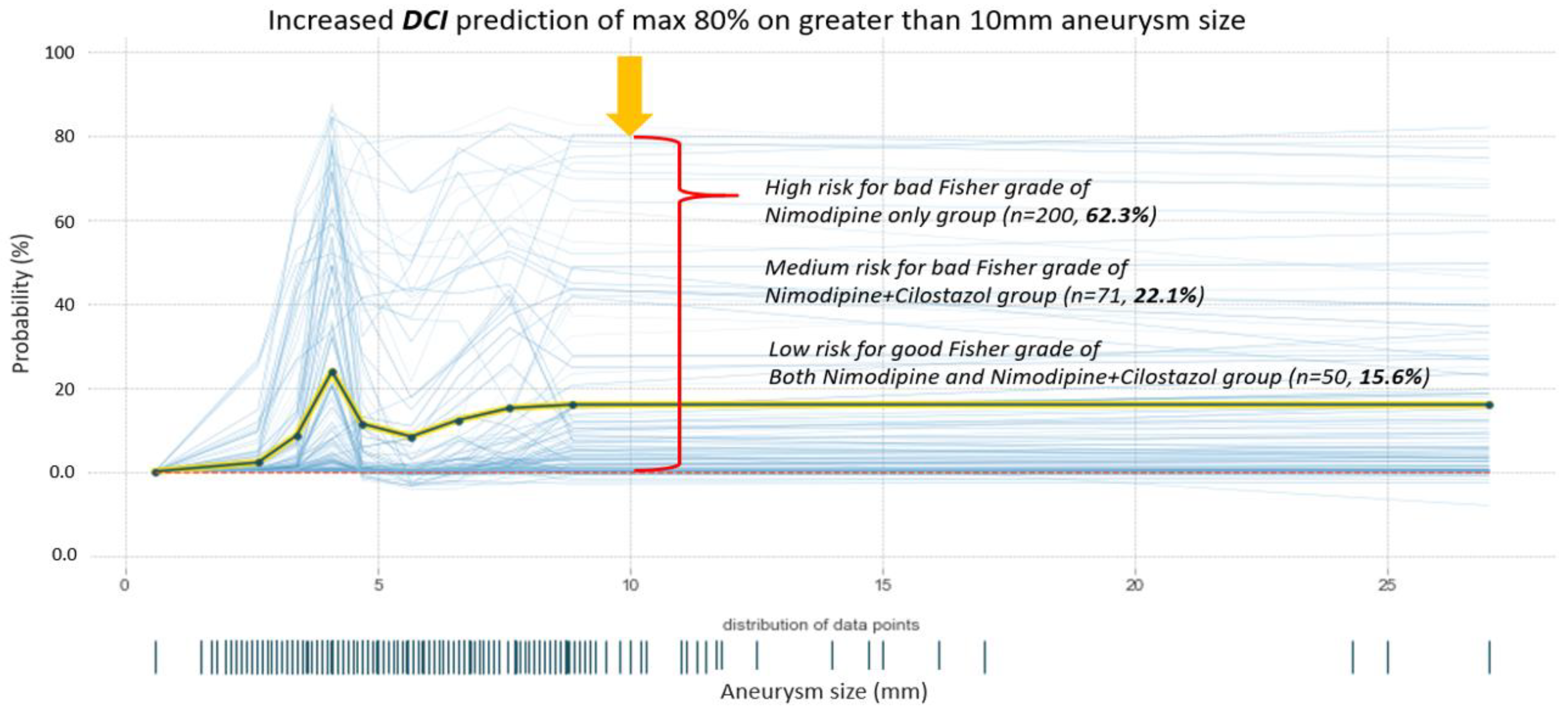
4.4. Prediction Analysis of DCI Probability by Aneurysm Size
4.5. Hyperparameter Tuning within XAI and the Limitation of this Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lovelock, C.E.; Rinkel, G.J.; Rothwell, P.M. Time trends in outcome of subarachnoid hemorrhage: Population-based study and systematic review. Neurology 2010, 74, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassell, N.F.; Helm, G.; Simmons, N.; Phillips, C.D.; Cail, W.S. Treatment of cerebral vasospasm with intra-arterial papaverine. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 77, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hop, J.W.; Rinkel, G.J.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J. Case-fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Stroke 1997, 28, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocco, J.; Zacharia, B.E.; Komotar, R.J.; Connolly, E.S., Jr. A review of current and future medical therapies for cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg. Focus 2006, 21, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotenhuis, J.A.; Bettag, W.; Fiebach, B.J.; Dabir, K. Intracarotid slow bolus injection of nimodipine during angiography for treatment of cerebral vasospasm after SAH. A preliminary report. J. Neurosurg. 1984, 61, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsch, N.W. A review of cerebral vasospasm in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage Part III: Mechanisms of action of calcium antagonists. J. Clin. Neurosci. 1994, 1, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.T.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, A.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Chin, S.C.; Hsieh, P.C.; Yeap, M.C.; Hsu, S.Y.; Lin, Y.J. Early strategy of scepter XC balloon angioplasty and simultaneous Nimodipine infusion for vasospasm following ruptured aneurysm. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockel, K.; Diedler, J.; Steiner, J.; Birkenhauer, U.; Ernemann, U.; Schuhmann, M.U. Effect of Intra-Arterial and Intravenous Nimodipine Therapy of Cerebral Vasospasm After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage on Cerebrovascular Reactivity and Oxygenation. World Neurosurg. 2017, 101, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherallah, R.Y.; Khawaja, M.; Olson, M.; Angiolillo, D.; Birnbaum, Y. Cilostazol: A Review of Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Uses. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2021, 36, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohara, S.; Garg, K.; Singh Rajpal, P.M.; Kasliwal, M. Role of Cilostazol in Prevention of Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021, 150, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawley, T.; Claus, C.F.; Tong, D.; Rajamand, S.; Sigler, D.; Bahoura, M.; Garmo, L.; Soo, T.M.; Kelkar, P.; Richards, B. Efficacy and safety of cilostazol-nimodipine combined therapy on delayed cerebral ischaemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: A prospective, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial protocol. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, A.; Umegaki, M.; Fujinaka, T.; Yoshimine, T. Cilostazol attenuates cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol. Res. 2010, 32, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Koo, H.W.; Lee, B.J.; Sohn, M.J. Analysis of risk factors correlated with angiographic vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage using explainable predictive modeling. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 91, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarraj, J.P.J.; Hergenroeder, G.W.; Zhu, L.; Chang, T.; Park, S.; Megjhani, M.; Vahidy, F.S.; Zhao, Z.; Kitagawa, R.S.; Choi, H.A. Machine Learning to Predict Delayed Cerebral Ischemia and Outcomes in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurology 2021, 96, e553–e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, M.; Kawamura, S.; Koh, A. Easily Created Prediction Model Using Automated Artificial Intelligence Framework (Prediction One, Sony Network Communications Inc., Tokyo, Japan) for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Outcomes Treated by Coiling and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia. Cureus 2021, 13, e15695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Perry, J.J.; English, S.W.; Alkherayf, F.; Joseph, J.; Nobile, S.; Zhou, L.L.; Lesiuk, H.; Moulton, R.; Agbi, C. Clinical prediction of delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanioka, S.; Ishida, F.; Nakano, F.; Kawakita, F.; Kanamaru, H.; Nakatsuka, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Suzuki, H. Machine learning analysis of matricellular proteins and clinical variables for early prediction of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 7128–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergouwen, M.D.; Vermeulen, M.; van Gijn, J.; Rinkel, G.J.; Wijdicks, E.F.; Muizelaar, J.P.; Mendelow, A.D.; Juvela, S.; Yonas, H.; Terbrugge, K.G.; et al. Definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as an outcome event in clinical trials and observational studies: Proposal of a multidisciplinary research group. Stroke 2010, 41, 2391–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raatikainen, E.; Vahtera, A.; Kuitunen, A.; Junttila, E.; Huhtala, H.; Ronkainen, A.; Pyysalo, L.; Kiiski, H. Prognostic value of the 2010 consensus definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 420, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning, D.; Stefik, M.; Choi, J.; Miller, T.; Stumpf, S.; Yang, G.-Z. XAI—Explainable artificial intelligence. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaay7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. New machine learning algorithm: Random forest. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Computing and Applications, Chengde, China, 14–16 September 2012; pp. 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, E.; Ma, J.; Collins, G.S.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Verbakel, J.Y.; Van Calster, B. A systematic review shows no performance benefit of machine learning over logistic regression for clinical prediction models. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 110, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.; Ungar, L. Generalized SHAP: Generating multiple types of explanations in machine learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Ramon, Y.; Martens, D.; Provost, F.; Evgeniou, T. A comparison of instance-level counterfactual explanation algorithms for behavioral and textual data: SEDC, LIME-C and SHAP-C. Adv. Data Anal. Classif. 2020, 14, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakharia, V.; Shah, M.; Nair, P.; Borade, H.; Sahlot, P.; Wankhede, V. Estimation of Lithium-ion Battery Discharge Capacity by Integrating Optimized Explainable-AI and Stacked LSTM Model. Batteries 2023, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shao, J.; Asmann, Y.W. Assessment and optimization of explainable machine learning models applied to transcriptomic data. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, M.; Hu, J. Evaluating explorative prediction power of machine learning algorithms for materials discovery using k-fold forward cross-validation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 171, 109203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmann, A.; Wang, W.T.; Dodier, P.; Bavinzski, G.; Engel, A.; Herta, J.; Plochl, W.; Reinprecht, A.; Gruber, A. The Impact of Intra-Arterial Papaverine-Hydrochloride on Cerebral Metabolism and Oxygenation for Treatment of Delayed-Onset Post-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Vasospasm. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, A.; Le Jean, L.; Puybasset, L. Clinical experience of selective intra-arterial nimodipine treatment for cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 474. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, R.L.; Rosengart, A.; Huo, D.; Karrison, T. Factors associated with the development of vasospasm after planned surgical treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilha, L.; Marques, E.L.; Carelli, E.F.; Fernandes, Y.B.; Cardoso, A.C.; Maldaum, M.V.; Borges, G. Risk factors and outcome in 100 patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2001, 59, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.P.; Edgell, R.C.; Alshekhlee, A.; Borhani Haghighi, A.; Sweeny, J.; Felton, J.; Kitchener, J.; Vora, N.; Bieneman, B.K.; Cruz-Flores, S.; et al. Age-associated vasospasm in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, E.S., Jr.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Carhuapoma, J.R.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Dion, J.; Higashida, R.T.; Hoh, B.L.; Kirkness, C.J.; Naidech, A.M.; Ogilvy, C.S.; et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke 2012, 43, 1711–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Deryke, X.; Rhoney, D.H. Cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: An overview of pharmacologic management. Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.L.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Luo, H.R.; Chen, W.F.; Jiang, Y.X.; Cheng, Y. Effectiveness comparisons of drug therapies for postoperative aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients: Network meta-analysis and systematic review. Bmc. Neurol. 2021, 21, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Suzuki, H.; Miyakoda, G.; Ishikawa, M.; Yabuuchi, Y.; Taki, W. Effect of cilostazol on delayed cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: Evaluation using black blood magnetic resonance imaging. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 32, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi-Okada, M.; Nishizawa, S.; Mizutani, A.; Namba, H. Multifaceted effects of selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase III, cilostazol, for cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in a dog model. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senbokuya, N.; Kinouchi, H.; Kanemaru, K.; Ohashi, Y.; Fukamachi, A.; Yagi, S.; Shimizu, T.; Furuya, K.; Uchida, M.; Takeuchi, N.; et al. Effects of cilostazol on cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A multicenter prospective, randomized, open-label blinded end point trial Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, H.; Desai, A.; Palla, M.; Mohamed, W.; Seraji-Bozorgzad, N.; Ibrahim, M. Efficacy of Cilostazol in Prevention of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 2979–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.A.; van der Steen, W.E.; Barros, R.S.; Majoie, C.B.; van den Berg, R.; Verbaan, D.; Vandertop, W.P.; Zijlstra, I.J.A.J.; Zwinderman, A.; Strijkers, G.J. Machine learning improves prediction of delayed cerebral ischemia in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurointerventional. Surg. 2019, 11, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, N.F.; Madai, V.I.; Unteroberdörster, M.; Zihni, E.; Brune, S.C.; Hilbert, A.; Livne, M.; Wolf, S.; Vajkoczy, P.; Frey, D. Outcome prediction in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A comparison of machine learning methods and established clinico-radiological scores. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Alharin, A.; Hu, Z.; Fell, N.; Sartipi, M. Predicting post-stroke hospital discharge disposition using interpretable machine learning approaches. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; 2019; pp. 4817–4822. [Google Scholar]
- Visani, G.; Bagli, E.; Chesani, F.; Poluzzi, A.; Capuzzo, D. Statistical stability indices for LIME: Obtaining reliable explanations for machine learning models. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2020, 73, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lacy, N.; Ramshaw, M.J.; Kutz, J.N. Integrated Evolutionary Learning: An Artificial Intelligence Approach to Joint Learning of Features and Hyperparameters for Optimized, Explainable Machine Learning. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 832530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötsch, J.; Kringel, D.; Ultsch, A. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in biomedicine: Making AI decisions trustworthy for physicians and patients. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, L.-D.; Lei, H.; Deng, S.-H. Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning models based on Bayesian optimization. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 26–40. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristics | Nimodipine Only (n = 232) | Cilostazol and Nimodipine (n = 89) | p-Value | Data Type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y, mean (SD) | 55.47 (12.756) | 55.37 (14.150) | 0.952 | Float | 21–94 |
| Sex, female, n (%) | 147 (63.4) | 51 (57.3) | 0.318 | Binary | 1: male; 2: female |
| GCS on admission, mean (SD) | 12.81 (3.248) | 13.25 (3.185) | 0.279 | Integer | 1–15 |
| Aneurysm size, mm, mean (SD) | 5.63 (3.016) | 6.55 (4.123) | 0.029 | Float | 0.6–27 |
| Hunt–Hess grade | N/A | N/A | 0.142 | Integer | 1–5 |
| 1 | 12 | 1 | |||
| 2 | 115 | 57 | |||
| 3 | 67 | 20 | |||
| 4 | 33 | 9 | |||
| 5 | 5 | 2 | |||
| Fisher grade | N/A | N/A | 0.068 | Integer | 1–4 |
| 1 | 14 | 6 | |||
| 2 | 18 | 12 | |||
| 3 | 103 | 26 | |||
| 4 | 97 | 45 | |||
| Location | N/A | N/A | 0.007 | Integer | 1: ACA; 2: MCA; 3: ICA; 4: VA or BA |
| ACA | 86 | 40 | |||
| MCA | 60 | 10 | |||
| ICA | 74 | 28 | |||
| VA or BA | 12 | 11 | |||
| HTN, n (%) | 95 (40.9) | 35 (39.3) | 0.791 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| DM, n (%) | 25 (10.8) | 13 (14.6) | 0.342 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 17 (7.3) | 12 (13.5) | 0.085 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 76 (32.8) | 37 (41.6) | 0.139 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| Clip/coil, n (%) | 169 (72.8)/63 (27.2) | 16 (18.0)/73 (82.0) | 0 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| ACV | 68 (29.3) | 12 (13.5) | 0.003 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| DCI | 48 (20.7) | 7 (7.9) | 0.006 | Binary | 0 or 1 |
| Variables | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cilostazol with nimodipine | 0.556 | 0.351–0.879 | 0.012 |
| Female sex | 3.713 | 1.683–8.191 | 0.001 |
| Age | 0.972 | 0.946–0.999 | 0.042 |
| Aneurysm size | 1.106 | 1.008–1.214 | 0.034 |
| Treatment method | 1.1 | 0.483–2.502 | 0.821 |
| Models | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | 0.91 | 0.70 | 0.95 |
| Logistic regression | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.H.; Lee, B.-J.; Koo, H.-W. Effect of Cilostazol on Delayed Cerebral Infarction in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Explainable Predictive Modeling. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070797
Kim KH, Lee B-J, Koo H-W. Effect of Cilostazol on Delayed Cerebral Infarction in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Explainable Predictive Modeling. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070797
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kwang Hyeon, Byung-Jou Lee, and Hae-Won Koo. 2023. "Effect of Cilostazol on Delayed Cerebral Infarction in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Explainable Predictive Modeling" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070797
APA StyleKim, K. H., Lee, B.-J., & Koo, H.-W. (2023). Effect of Cilostazol on Delayed Cerebral Infarction in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Using Explainable Predictive Modeling. Bioengineering, 10(7), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070797








