Kidney Segmentation from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Integrating Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Level Set Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Problem Statement
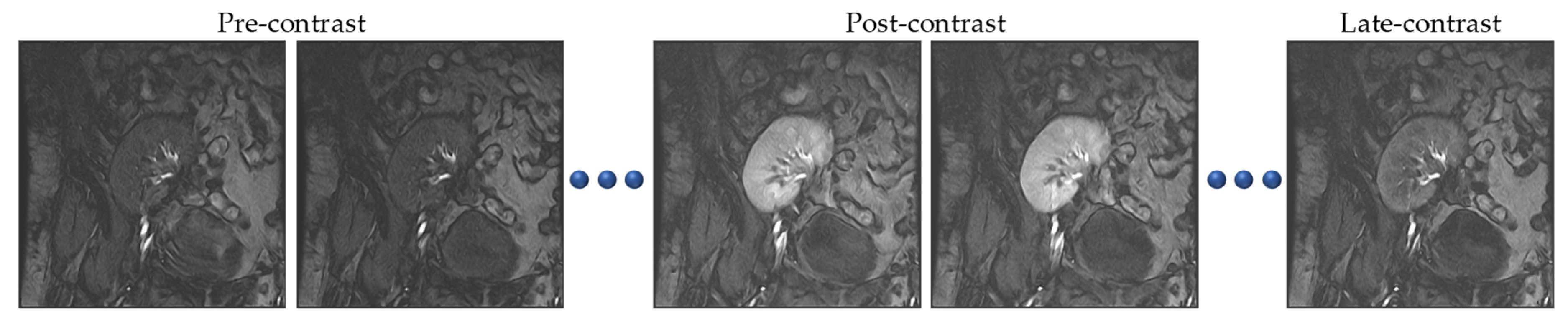
2.1. Data
2.2. Problem Definition and Notations
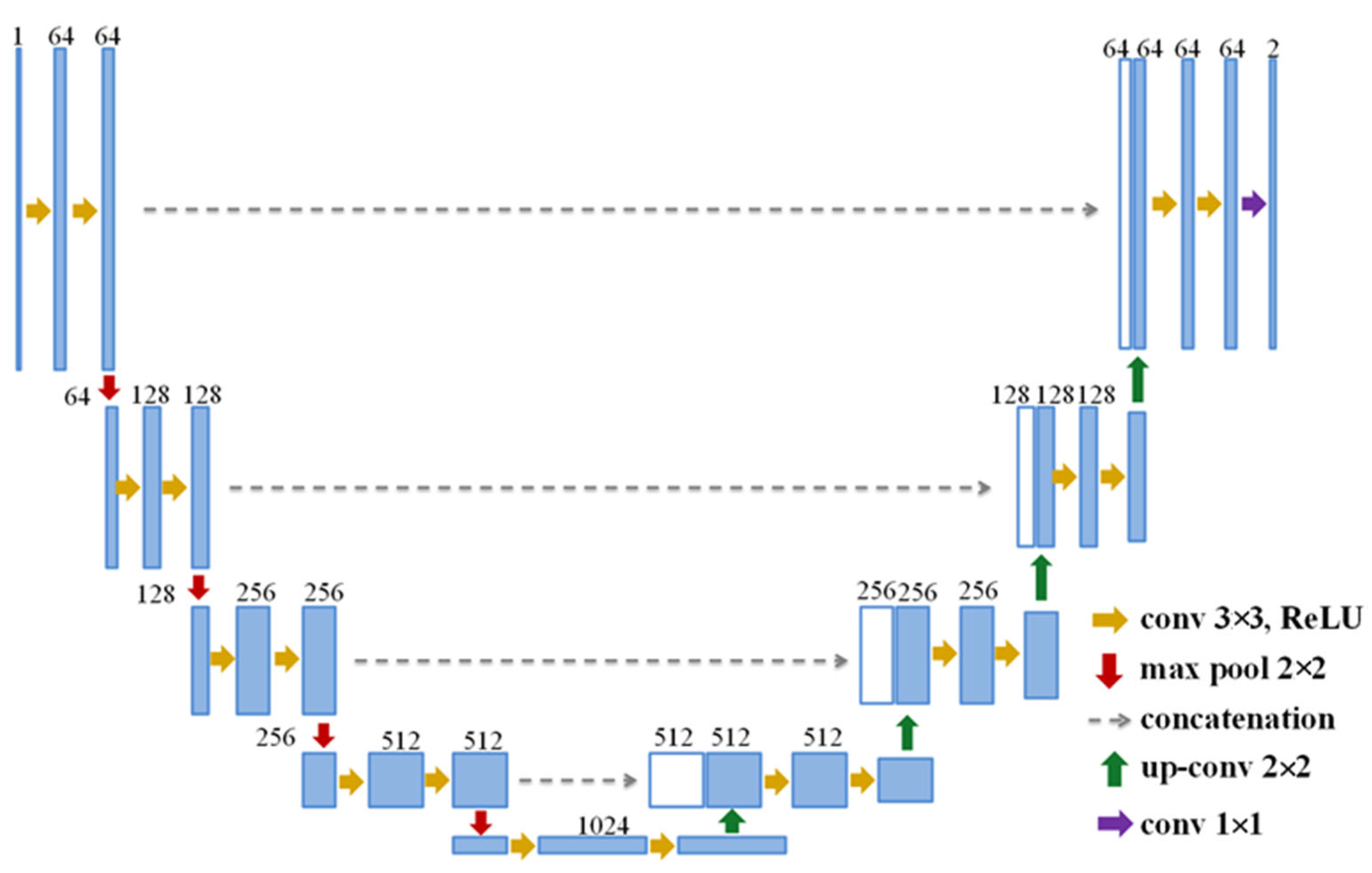
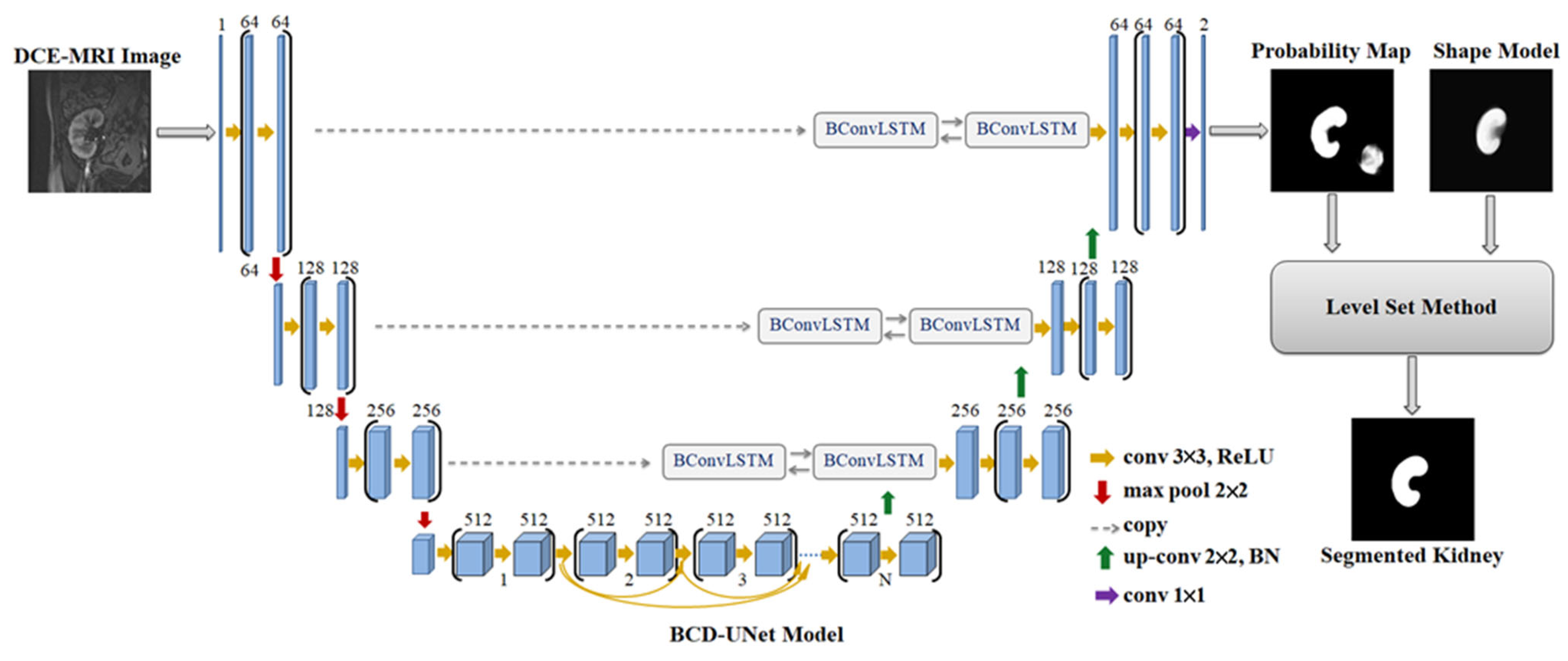
3. Deep UNT-Based Kidney Segmentation Models
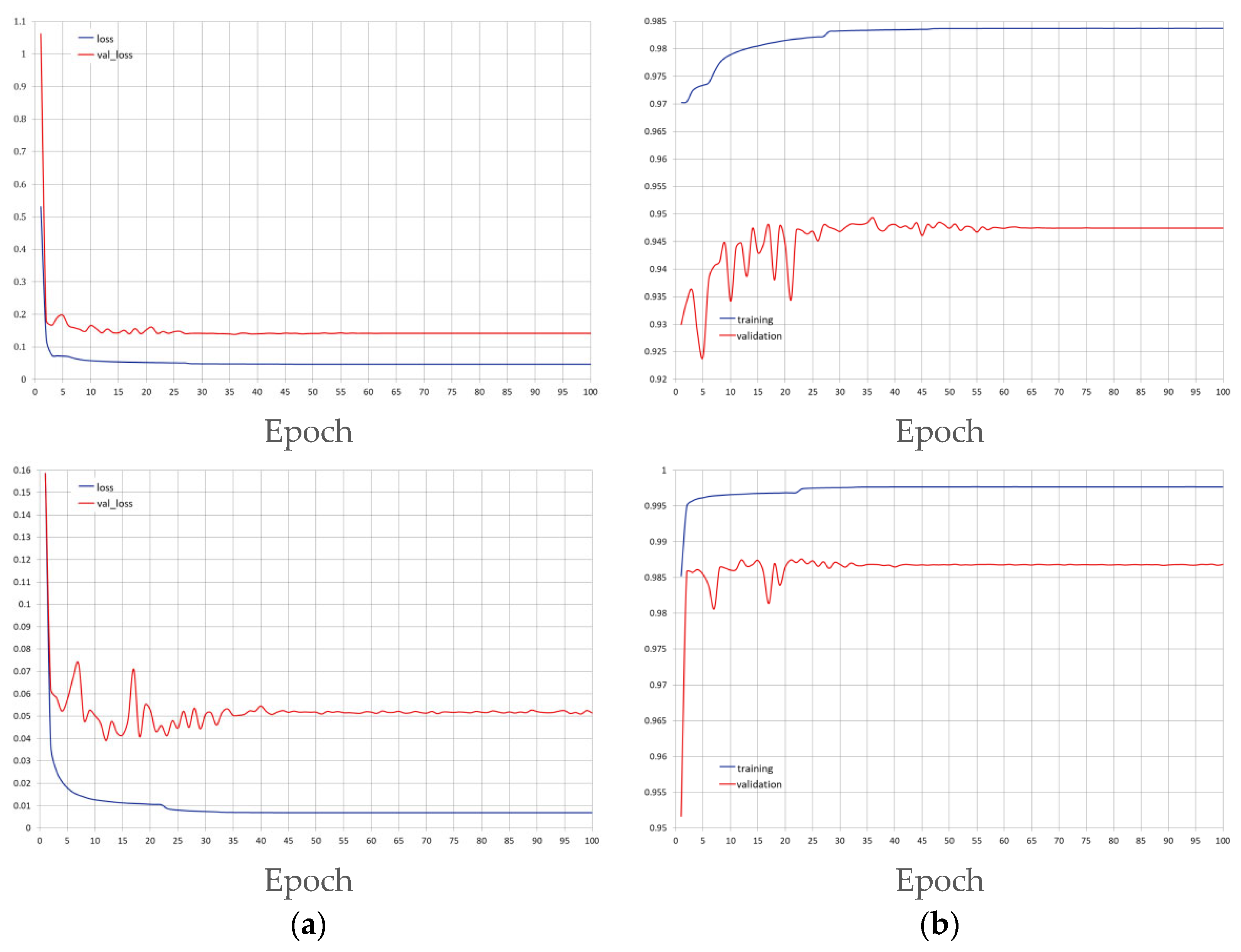
3.1. Implementation Details
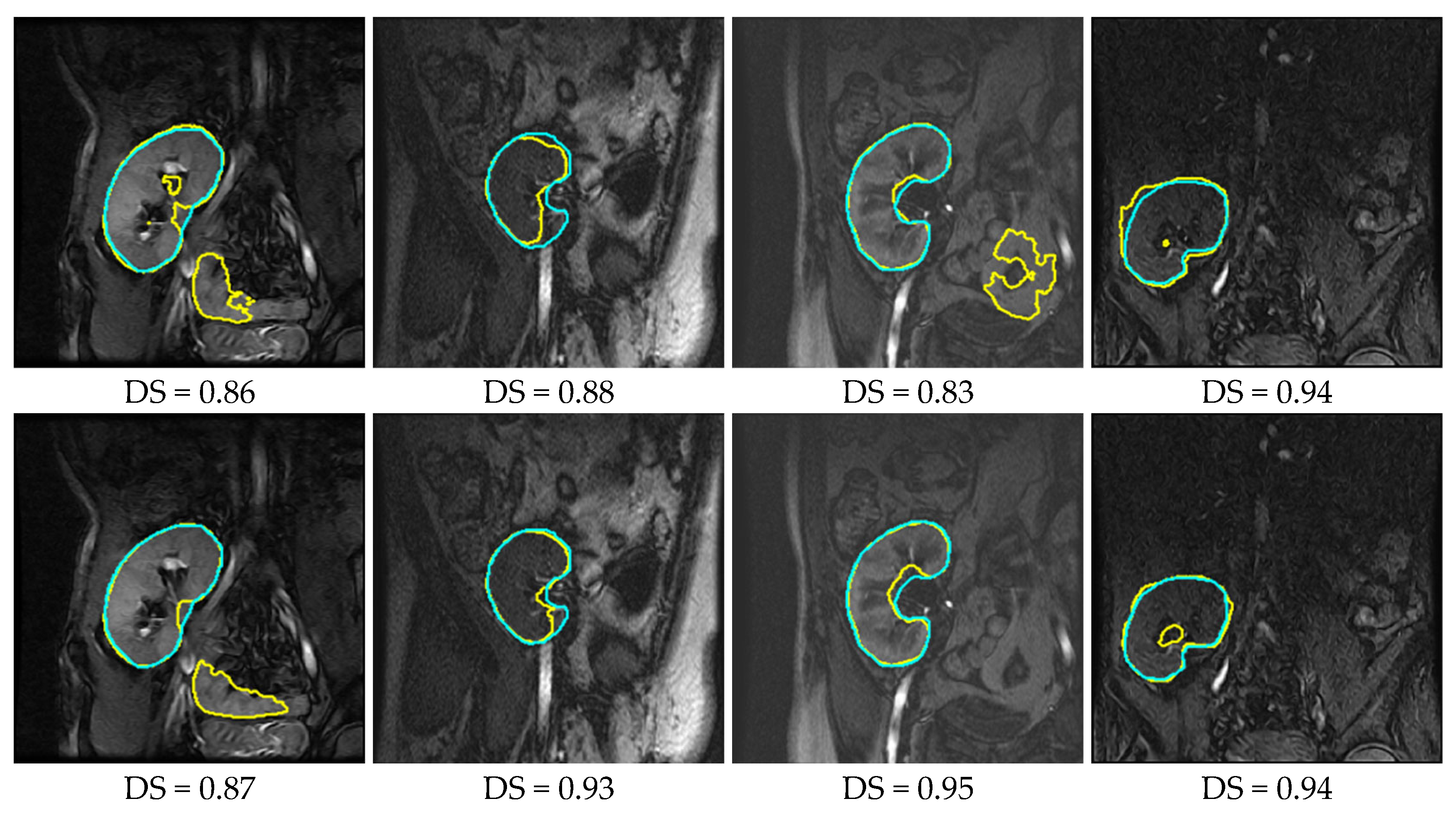
3.2. Performance Evaluation
3.3. Ablation Experiments
4. UNT Level Set-Based Kidney Segmentation Approach
4.1. Probabilistic Shape Model
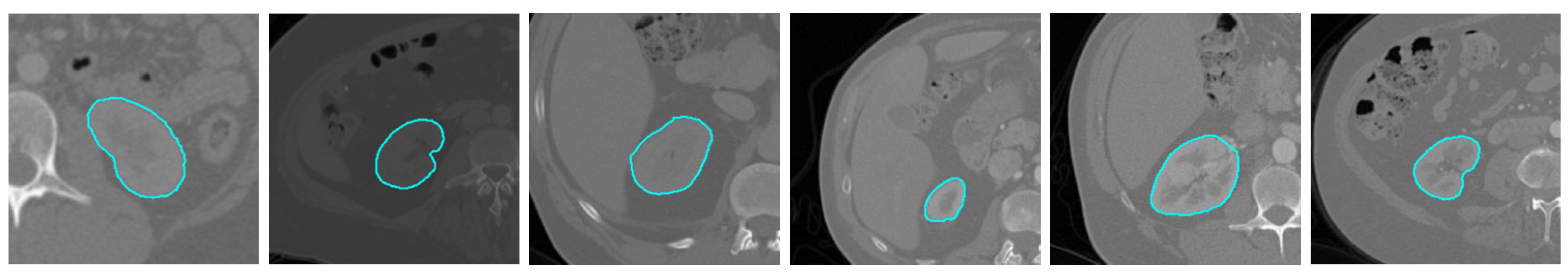
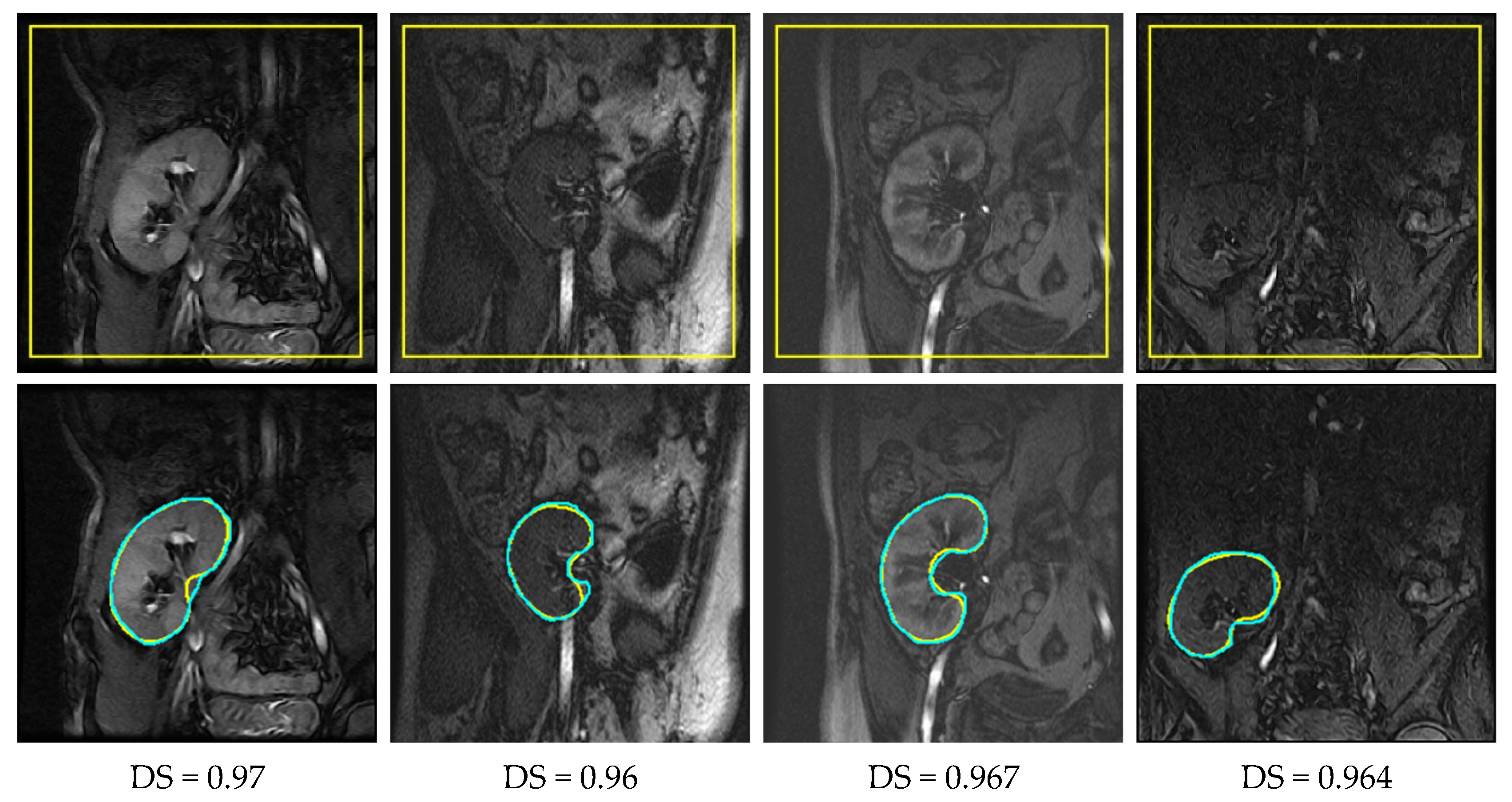
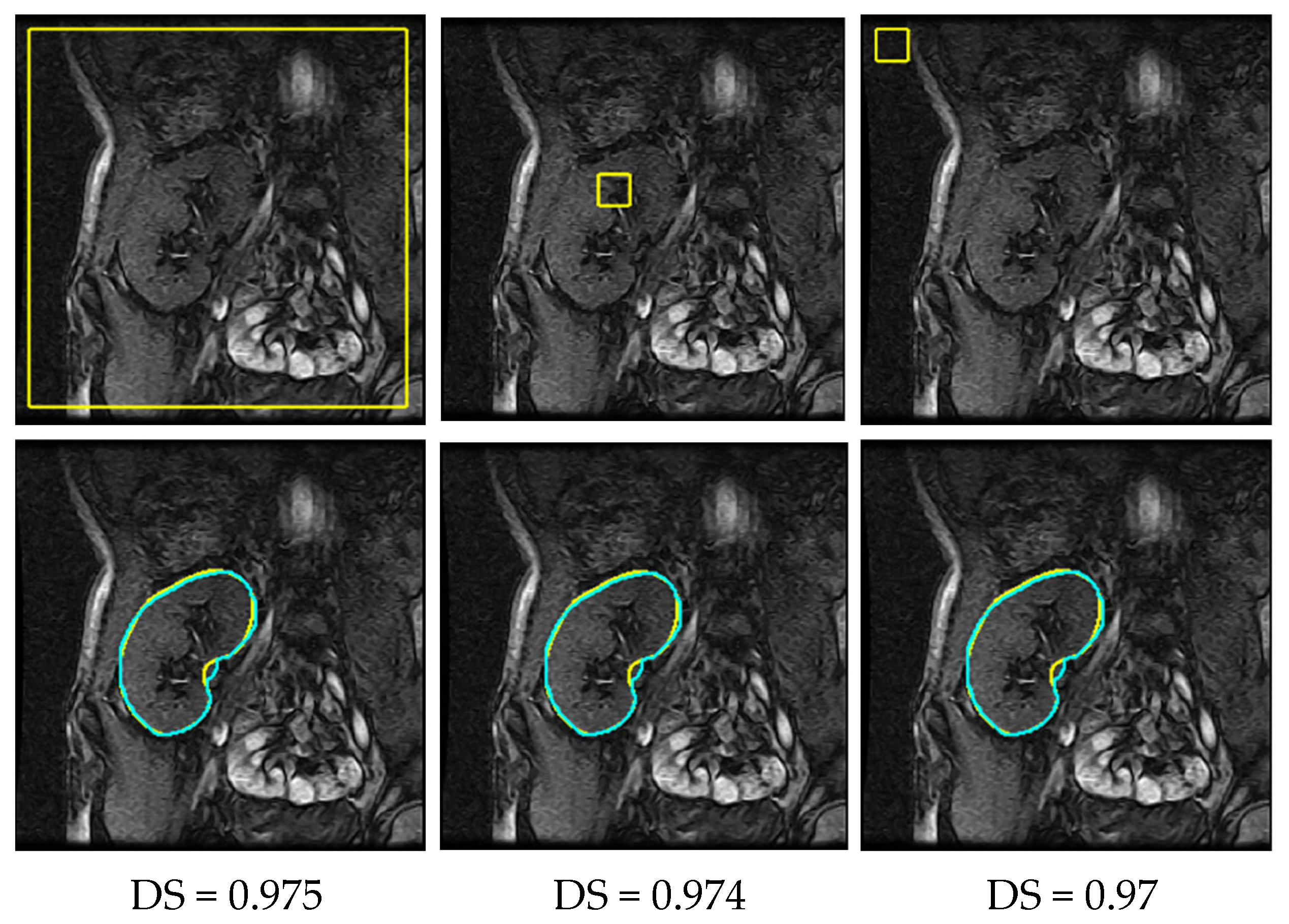
4.2. Results
5. Conclusions
- It integrates the merits of deep neural networks and the LST method, for the first time, to accomplish this task.
- It proposes a new energy functional incorporating a kidney/background probability map generated from a deep neural model and shape prior information to steer the LST contour towards the target kidney.
- It employs an efficient Bayesian parameter estimation method in the computation of SHP information, which can statistically handle the cases of unobserved kidney/background pixels in constructing the shape model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Shehata, M.; Alksas, A.; Abouelkheir, R.T.; Elmahdy, A.; Shaffie, A.; Soliman, A.; Ghazal, M.; Abu Khalifeh, H.; Salim, R.; Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; et al. A comprehensive computer-assisted diagnosis system for early assessment of renal cancer tumors. Sensors 2021, 21, 4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnazer, I.; Bourdon, P.; Urruty, T.; Falou, O.; Khalil, M.; Shahin, A.; Fernandez-Maloigne, C. Recent advances in medical image processing for the evaluation of chronic kidney disease. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostapha, M.; Khalifa, F.; Alansary, A.; Soliman, A.; Suri, J.; El-Baz, A.S. Computer-aided diagnosis systems for acute renal transplant rejection: Challenges and methodologies. In Abdomen and Thoracic Imaging; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourbron, S.P.; Michaely, H.J.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. MRI-measurement of perfusion and glomerular filtration in the human kidney with a separable compartment model. Investig. Radiol. 2008, 43, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, S.; Roy, S.D.; Das, S.; Sen, S.; Velásquez, J.D.; Sarkar, R. Computer based diagnosis of some chronic diseases: A medical journey of the last two decades. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 5525–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Rørvik, J.; Lundervold, A. Fast semi-supervised segmentation of the kidneys in DCE-MRI using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific Symposium, Functional Renal Imaging: Where Physiology, Nephrology, Radiology and Physics Meet, Berlin, Germany, 11–13 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, M.; Warfield, S.K.; Kurugol, S. Automatic renal segmentation in DCE-MRI using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, V.; Brunetti, A.; Cascarano, G.D.; Guerriero, A.; Pesce, F.; Moschetta, M.; Gesualdo, L. A comparison between two semantic deep learning frameworks for the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease segmentation based on magnetic resonance images. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, A.; Cascarano, G.D.; Feudis, I.D.; Moschetta, M.; Gesualdo, L.; Bevilacqua, V. Detection and segmentation of kidneys from magnetic resonance images in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Nanchang, China, 3–6 August 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milecki, L.; Bodard, S.; Correas, J.M.; Timsit, M.O.; Vakalopoulou, M. 3D unsupervised kidney graft segmentation based on deep learning and multi-sequence MRI. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavur, A.E.; Gezer, N.S.; Barış, M.; Aslan, S.; Conze, P.H.; Groza, V.; Pham, D.D.; Chatterjee, S.; Ernst, P.; Özkan, S.; et al. CHAOS challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaturyan, H.; Villarini, B.; Sarao, K.; Chow, J.S.; Afacan, O.; Kurugol, S. Improving automatic renal segmentation in clinically normal and abnormal paediatric DCE-MRI via contrast maximisation and convolutional networks for computing markers of kidney function. Sensors 2021, 21, 7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégou, S.; Drozdzal, M.; Vazquez, D.; Romero, A.; Bengio, Y. The one hundred layers tiramisu: Fully convolutional densenets for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Guo, J.; Hinojosa, L.; Hulsey, K.; Pedrosa, I. Automated kidney segmentation by mask R-CNN in T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Med. Imaging 2022: Comput.-Aided Diagn. 2022, 12033, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-net and its variants for medical image segmentation: A review of theory and applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M.; Fathy, M.; Escalera, S. Bi-directional ConvLSTM U-Net with densley connected convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, Y.H.; Teo, B.W.; Tan, N.L.; O’Doherty, S.; Stephenson, M.C.; Thian, Y.L.; Chiong, E.; Reilhac, A. Comparison of metrics for the evaluation of medical segmentations using prostate MRI dataset. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, A.; Eisenmann, M.; Tizabi, M.D.; Sudre, C.H.; Rädsch, T.; Antonelli, M.; Arbel, T.; Bakas, S.; Cardoso, M.J.; Cheplygina, V.; et al. Common limitations of image processing metrics: A picture story. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.05642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Fedkiw, R. Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, A.; Yezzi, A.; Wells, W.; Tempany, C.; Tucker, D.; Fan, A.; Willsky, A. A shape-based approach to the segmentation of medical imagery using level sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Munim, H.E.A.; Farag, A.A. Curve/surface representation and evolution using vector level sets with application to the shape-based segmentation problem. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, S.E.; El-Baz, A.S.; Farag, A.A.; El-Ghar, M.; Eldiasty, T.; Ghoneim, M.A. A kidney segmentation framework for dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J. Vib. Control. 2007, 13, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; El-Baz, A.S.; Gimel’farb, G.; El-Ghar, M.A. Non-invasive image-based approach for early detection of acute renal rejection. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Beijing, China, 20–24 September 2010; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; Beache, G.M.; El-Ghar, M.A.; El-Diasty, T.; Gimel’farb, G.; Kong, M.; El-Baz, A.S. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI-based early detection of acute renal transplant rejection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1910–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Soliman, A.; Gimel’farb, G.; El-Baz, A. Segmenting kidney DCE-MRI using 1st-order shape and 5th-order appearance priors. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, Switzerland, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltanboly, A.; Ghazal, M.; Hajjdiab, H.; Shalaby, A.; Switala, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Sahoo, P.; El-Azab, M.; El-Baz, A. Level sets-based image segmentation approach using statistical shape priors. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 340, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Melegy, M.T.; Abd El-karim, R.M.; El-Baz, A.S.; El-Ghar, M.A. Fuzzy membership-driven level set for automatic kidney segmentation from DCE-MRI. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Melegy, M.T.; Abd El-Karim, R.M.; El-Baz, A.S.; El-Ghar, M.A. A Combined Fuzzy C-Means and Level Set Method for Automatic DCE-MRI Kidney Segmentation Using Both Population-Based and Patient-Specific Shape Statistics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Melegy, M.; Kamel, R.; El-Ghar, A.; Alghamdi, N.S.; El-Baz, A. Level Set-Based Kidney Segmentation from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Population-Based and Subject-Specific Shape Statistics. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Melegy, M.; Kamel, R.; El-Ghar, M.A.; Shehata, M.; Khalifa, F.; El-Baz, A. Kidney segmentation from DCE-MRI converging level set methods, fuzzy clustering and Markov random field modeling. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Melegy, M.; Kamel, R.; El-Ghar, A.; Alghamdi, N.S.; El-Baz, A. Variational Approach for Joint Kidney Segmentation and Registration from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Shape Priors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.; Viriri, S. Kidney Tumor Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey of State-of-the-Art. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, N.; Sathianathen, N.; Kalapara, A.; Walczak, E.; Moore, K.; Kaluzniak, H.; Rosenberg, J.; Blake, P.; Rengel, Z.; Oestreich, M.; et al. The kits19 challenge data: 300 kidney tumor cases with clinical context, CT semantic segmentations, and surgical outcomes. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.00445. [Google Scholar]
- Cootes, T.F.; Taylor, C.J.; Cooper, D.H.; Graham, J. Active shape models-their training and application. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1995, 61, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.; Singer, Y. Efficient Bayesian parameter estimation in large discrete domains. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’98), Denver, CO, USA, 1–3 December 1998; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Wells III, W.M. Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 24, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Method | Number of Patients/Modality | DS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lundervold et al. [6] | ConvNets | 20 | DCE-MRIs | 0.87/85 Left/Right |
| Haghighi et al. [7] | Two cascaded 3D UNTs | 30 | Pediatric DCE-MRIs | 0.91 ± 0.03 Normal 0.83 ± 0.03 Abnormal |
| Bevilacqua et al. [9] | ConvNets (VGG-16) | 18 | T2-Weighted MRIs | 0.85 |
| Brunetti et al. [10] | ConvNets With Genetic Algorithm | 18 | T2-Weighted MRIs | 0.91 |
| Milecki et al. [11] | ConvNets With Thresholding | 32 | DCE and T2 MRIs | 0.89 ± 0.0317 |
| Isensee et al. [12] | nnUNT | 40 | T1-DUAL IP/OP and T2-SPIR MRIs | 0.94 ± 0.0159 |
| Asaturyan et al. [14] | 3D Rb-UNT | 60 | 4D DCE-MRIs | 0.88 ± 0.064 |
| Goyal et al. [16] | Mask R-CNN | 100 | MRIs | 0.90 ± 0.041 |
| Method | All DCE-MRIs | Low-Contrast DCE-MRIs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | IU | HD95% | DS | IU | HD95% | |
| UNT | 0.940 ± 0.04 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 10.3 ± 23.8 | 0.88 ± 0.07 | 0.77 ± 0.13 | 19.9 ± 28.8 |
| BCD-UNT | 0.942 ± 0.04 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 4.6 ± 12.4 | 0.90 ± 0.06 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 7.9 ± 12.3 |
| Exp. | Loss Function | ILR | DP | All DCE-MRIs | Low-Contrast DCE-MRIs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | IU | HD95% | DS | IU | HD95% | ||||
| 1 | BCE | 0.0001 | 0.1 | 0.929 ± 0.11 | 0.88 ± 0.13 | 5.77 ± 16.9 | 0.72 ± 0.28 | 0.62 ± 0.29 | 26.9 ± 32.9 |
| 2 | BCE | 0.0001 | 0.5 | 0.942 ± 0.04 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 4.62 ± 12.4 | 0.90 ± 0.057 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 7.89 ± 12.3 |
| 3 | BCE | 0.0001 | 0.8 | 0.946 ± 0.05 | 0.90 ± 0.08 | 8.57 ± 21.2 | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 0.85 ± 0.09 | 13.4 ± 23.6 |
| 4 | DS-BCE | 0.0001 | 0.5 | 0.94 ± 0.053 | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 7.24 ± 17.9 | 0.88 ± 0.13 | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 12.2 ± 20.6 |
| 5 | BCE | 0.001 | 0.5 | 0.92 ± 0.068 | 0.86 ± 0.098 | 16.27 ± 25.5 | 0.81 ± 0.15 | 0.70 ± 0.18 | 26.9 ± 29.4 |
| 6 | BCE | 0.0005 | 0.5 | 0.90 ± 0.25 | 0.83 ± 0.24 | 25.57 ± 31.7 | 0.87 ± 0.26 | 0.79 ± 0.25 | 49.1 ± 31.8 |
| Method | All DCE-MRIs | Low-Contrast DCE-MRIs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | IU | HD95% | DS | IU | HD95% | |
| UNLS | 0.952 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 1.6 | 0.93 ± 0.039 | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 2.6 ± 2.8 |
| Method | All DCE-MRIs | Low-Contrast DCE-MRIs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | IU | HD95% | DS | IU | HD95% | |
| VLST [24] | 0.91 ± 0.074 | 0.84 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 6.71 | 0.93 ± 0.06 | 0.87 ± 0.09 | 2.00 ± 4.44 |
| SLST [23] | 0.92 ± 0.037 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | 2.4 ± 1.4 | 0.93 ± 0.033 | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 2.05 ± 1.4 |
| FCMLS [30] | 0.94 ± 0.035 | 0.89 ± 0.04 | 1.4 ± 2.0 | 0.90 ± 0.06 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 4.7 ± 4.6 |
| PBPSFL [31] | 0.95 ± 0.025 | 0.90 ± 0.036 | 1.09 ± 1.8 | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.87 ± 0.07 | 2.8 ± 3.96 |
| FML [33] | 0.96 ± 0.017 | 0.925 ± 0.03 | 0.68 ± 1.19 | 0.935 ± 0.037 | 0.88 ± 0.06 | 2.23 ± 3.6 |
| PSFL [32] | 0.957 ± 0.016 | 0.93 ± 0.019 | 0.80 ± 1.03 | 0.95 ± 0.014 | 0.90 ± 0.026 | 0.85 ± 0.76 |
| JSRL [34] | 0.954 ± 0.026 | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 0.81 ± 1.3 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 2.6 ± 3.8 |
| UNLS | 0.952 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 1.54 ± 1.6 | 0.93 ± 0.039 | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 2.6 ± 2.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Melegy, M.T.; Kamel, R.M.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Alghamdi, N.S.; El-Baz, A. Kidney Segmentation from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Integrating Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Level Set Methods. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070755
El-Melegy MT, Kamel RM, Abou El-Ghar M, Alghamdi NS, El-Baz A. Kidney Segmentation from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Integrating Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Level Set Methods. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070755
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Melegy, Moumen T., Rasha M. Kamel, Mohamed Abou El-Ghar, Norah Saleh Alghamdi, and Ayman El-Baz. 2023. "Kidney Segmentation from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Integrating Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Level Set Methods" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070755
APA StyleEl-Melegy, M. T., Kamel, R. M., Abou El-Ghar, M., Alghamdi, N. S., & El-Baz, A. (2023). Kidney Segmentation from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Integrating Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Level Set Methods. Bioengineering, 10(7), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070755







