1. Introduction
Spinal cord injury (SCI) remains the most worrisome complication of corrective scoliosis surgery [
1,
2] and can even lead to paraplegia in severe cases. Since surgery for scoliosis usually involves multilevel distraction and fusion of the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, distraction is an important mechanism for SCI in corrective scoliosis surgery [
3]. According to the guidelines published by the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society, when SCI occurs, surgeons should look for any mechanical damage, reducing the degree of distraction, adjusting retractors, removing or adjusting grafts or hardware, and prompting the anesthesiologist to quickly raise the blood pressure [
4,
5]. If the source of injury can be removed promptly, spinal cord function can still be restored. Thus, accurate diagnosis of the SCI location during corrective scoliosis surgery will help reduce the time the surgeon needs to investigate.
Techniques for intraoperative imaging, which are an important auxiliary means for spinal surgery, are constantly developing [
6]. However, there are still some shortcomings in the application of intraoperative image-guided technology, such as high cost, radiation exposure, long image acquisition time, and unstable image quality [
6,
7,
8]. In recent years, the use of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM) has increased in order to avoid neurological complications, and somatosensory evoked potential (SEP) is the most commonly used IONM method [
9]. The SEP consists of cortical responses generated by peripheral stimulation electrodes. It can monitor perioperative neurological changes in the sensory pathway [
9,
10]. Detecting the decreasing amplitude or prolonging latency of the SEP provides early warning of possible damage to the sensory pathway. In addition, the SEP has been reported to support the precise localization of an SCI and to diagnose the cervical level of damage in cervical myelopathy [
11,
12]. Unlike traditional measurements using amplitude and latency, SCI location detection is accomplished by identifying changes in the time-frequency component distribution (TFD) of the SEP [
13,
14]. Different components of the SEP have various origins along the somatosensory pathway [
11]; therefore, different locations of SCI result in different distribution patterns of the time-frequency components (TFCs) of the SEP. However, existing studies have only demonstrated the predictive ability of the SEP for the location of SCIs in the cervical spine. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated whether the SEP could be used for the identification of SCI at other locations of the spine.
In order to achieve SCI location identification, it is necessary to utilize the information contained in the TFD of the SEP as much as possible. A change in SCI location causes SEP TFCs to have different distribution boundaries. In addition, the number of TFCs in many subspaces of the time-frequency space is also affected by the change in SCI location. Previous studies have chosen support vector machines (SVMs) to extract the distribution boundaries of SEP TFCs to achieve the goal of identifying SCI locations [
11,
15]. However, this method only uses the distribution boundary information of the SEP TFCs. As reported, the SVM is susceptible to outlier interference [
16]. The quantitative or distribution probability information of TFCs can suppress the influence of random noise. A study applied the random forest to the multiclass classification of SCI locations by repeated random sampling to construct multiple decision trees, each of which can classify SCI locations with the boundary and quantitative information provided by some of the training data [
12]. When revealing the importance of the TFCs of a subspace, statistical analysis of randomly sampled sample points needs to be carried out in combination with the classification results, and the corresponding methods have not been outlined in previous studies. The k-means clustering algorithm has been used to reveal the stable distribution area of the TFCs of a normal SEP [
17]. If SEP data from different locations of SCI are included in training, the clustering models would be more widely applicable, and the correspondence of TFCs with different SCI conditions can thus be established.
In order to detect the location of the SCI intraoperatively to perform remedial action as soon as possible, we explored the correlation between the SEP TFD and the SCI location and developed an SCI location identification method based on SEP TFCs. Firstly, in order to obtain high-resolution TFCs, the SEP was decomposed by matching pursuit (MP), and all the TFCs were described in terms of latency, frequency, and energy. Secondly, to realize the partitioning of the time-frequency space, the distance-based clustering algorithm was used to cluster the TFCs. To emphasize the differences in the number of different SCIs in each TFC cluster, we increased the number of centroids, that is, the time-frequency space was partitioned into smaller subspaces. The combination of multiple different time-frequency subspaces can form an arbitrary SCI TFD pattern. The number of TFCs of different SCIs in each subspace was also counted. The clusters of TFCs, i.e., time-frequency subspaces, were treated as features, and the number of TFCs of different SCIs in that subspace was the feature value. Through feature selection, the distribution boundaries of the TFCs can be extracted and utilized, as well as the quantity information of TFCs in each subspace. Finally, a naive Bayes classifier was constructed, which uses the quantity information of TFCs for SCI location identification.
The TFD of the SEP in rats has been reported to be similar to that of humans [
18,
19]. We previously developed an experimental rat model to simulate intraoperative distraction SCI by applying distraction to the spine [
20]. We recorded the SEP signals in the experimental rat model after applying distraction SCI at 19 spinal levels, respectively. Using this model, we constructed a naive Bayes classifier, which maintained similar accuracy to previous studies in the identification of cervical SCI locations and achieved the goal of classifying SCI locations in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. Therefore, the SEP has the potential to identify SCI locations not only at the cervical spine but also across broader spinal ranges. We provide an effective intraoperative SCI localization scheme that can improve diagnostic efficiency. This study also explores the effect of SCI location on the SEP TFD, and it will help to determine the origin of specific SEP TFCs.
2. Materials and Methods
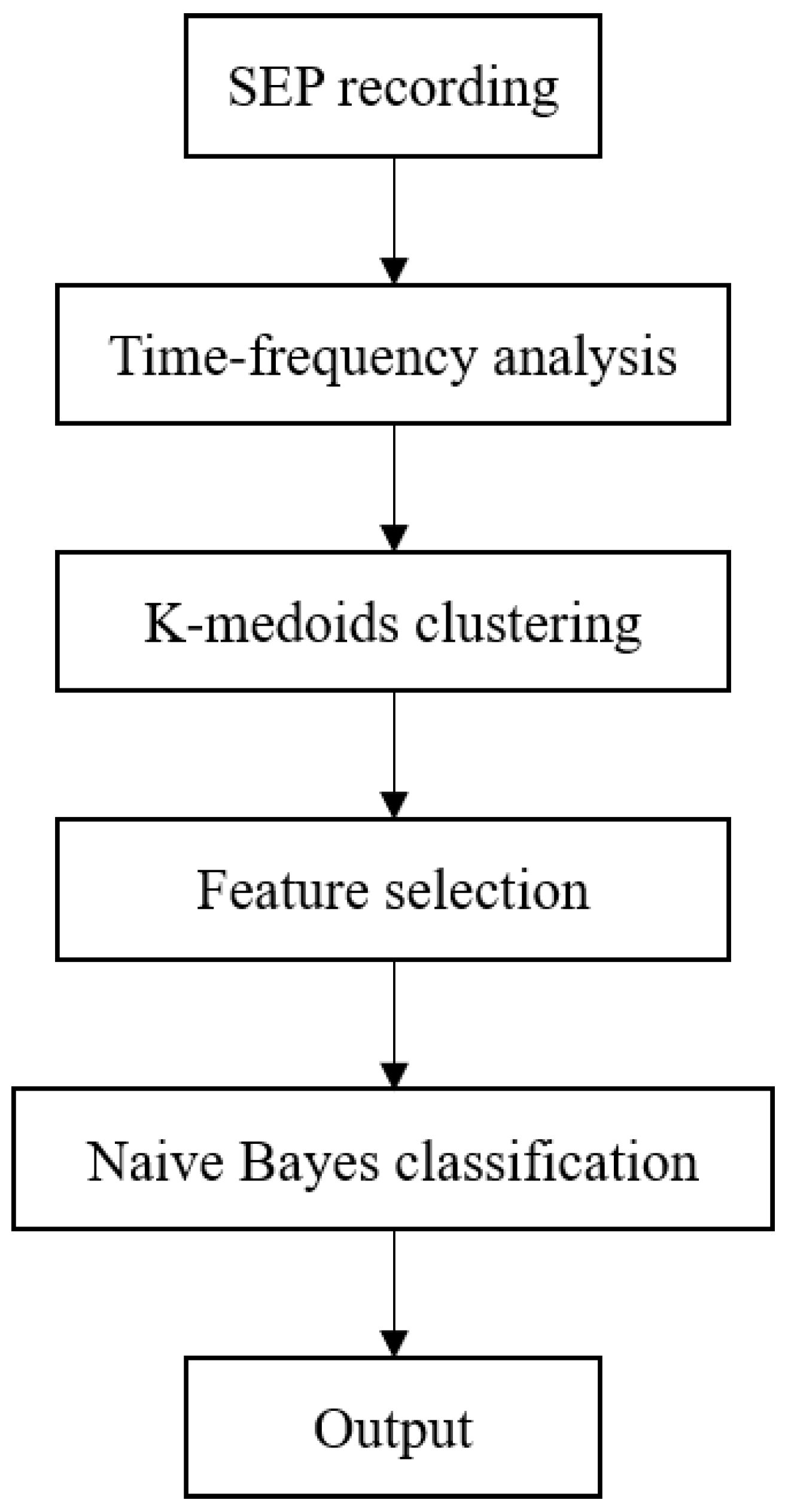
In this section, animal model construction, data collection, feature extraction and selection, and classifier construction are stated. The data processing flow is shown in
Figure 1.
2.1. Animal Model and Data Collection
As shown in
Table 1, 210 female Sprague-Dawley rats (specific-pathogen-free level, aged 7 to 8 weeks, weight 280 to 320 g) were purchased from the Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center (license No. SCXK (Yue) 2018-0002) and randomly assigned to 1 normal group (
n = 20) and 19 SCI groups (
n = 10). The 19 groups of rats were assigned to the cervical injury group, the thoracic injury group, and the lumbar injury group, including 2, 11, and 6 groups of rats, respectively. The normal group only received anesthesia and SEP collection. The cervical group was injured at C5 and C6; the thoracic group was injured at T1–T4 and T7–T13; and the lumbar group was injured at L1–L6.
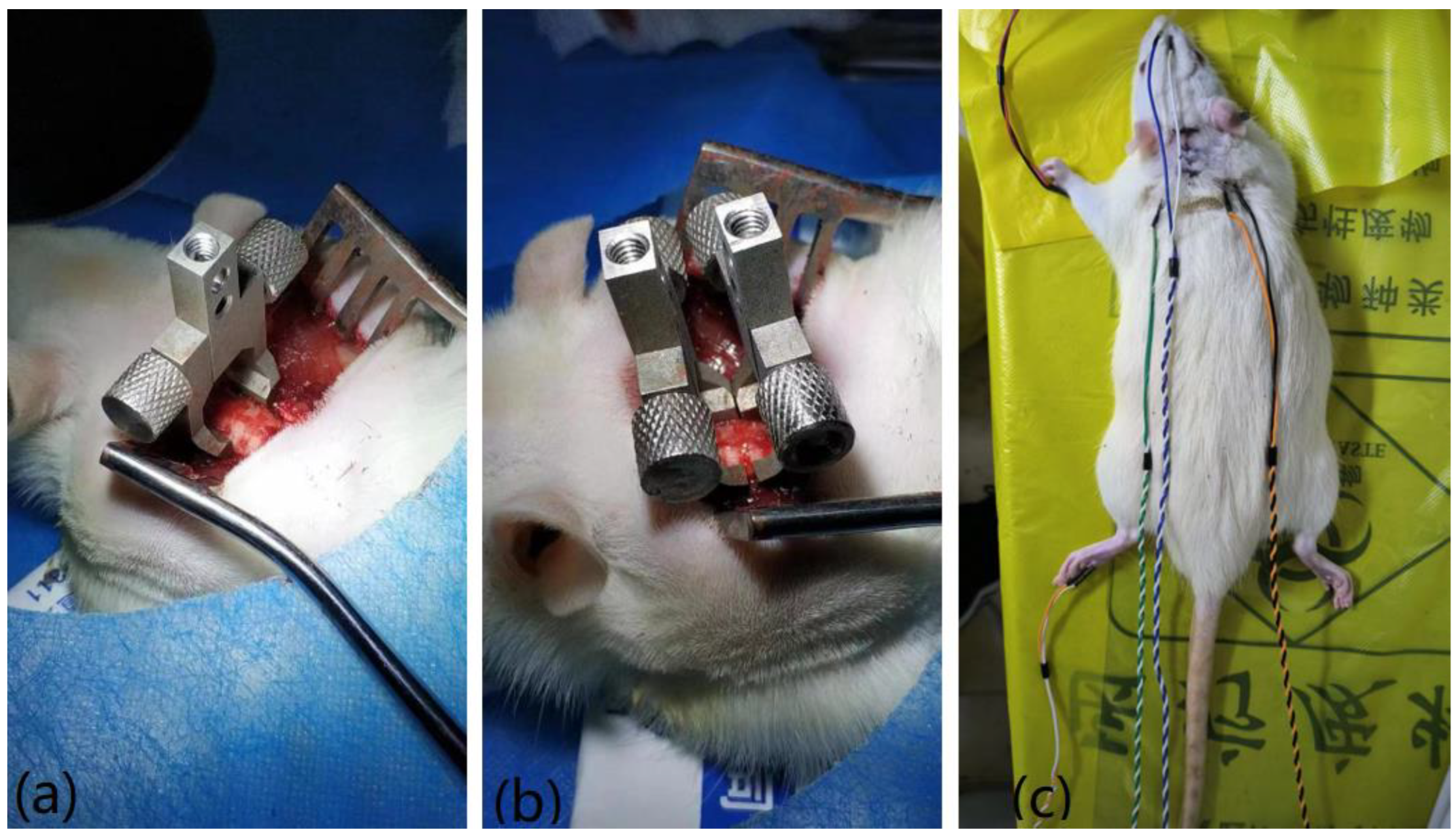
In a previous study, a distraction SCI was produced in rats using customized vertebral clamps [
20]. For example, the distraction injury between cervical vertebra 5 and 6 (C5/C6) was denoted as C5, and the procedure was as follows: Animals were anesthetized for SCI and evoked potential testing and sacrificed using intraperitoneally injected pentobarbital sodium (60 mg/kg; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and xylazine (10 mg/kg; Sigma). The rats were placed on a thermostatic pad at 37 °C to receive a subcutaneous injection of 5 mL physiological saline solution to prevent dehydration. Using standard aseptic principles and techniques, dorsal ligament resection and facet arthrotomy were performed at the C4–C7 interspace. Customized vertebral clamps were used to rigidly hold the transverse processes of C4–C5 and C6–C7. The respective clamps of C6–C7 were distracted rostrally and caudally to produce a displacement of 3 mm and held for 1 s before being returned to their initial position.
Figure 2 shows the recording of the surgical procedure.
Immediately after the SCI, electrophysiological evaluation (YRKJ-G2008; Yirui Technology Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China) was conducted. Tibial SEPs were evoked from stimulation proximal to the ankle via a pair of needle electrodes (NE-S-1500/13/0.4; Friendship Medical Electronics Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China) using the following parameters: 0.1 ms duration, 5.3 Hz frequency, and 3–5 mA intensity (to elicit mild toe twitching). Recordings were collected using two scalp needle electrodes subcutaneously inserted over the primary somatosensory cortex and a frontal midline reference electrode. The recorded signal was amplified 2000 times at sampling rate of 10 kHz with a bandpass filter between 30 and 3000 Hz. The SEP signals were averaged over 200 responses for each trial [
11,
12]. In this study, all signal processing routines used for the analysis were developed in MATLAB (version R2019a; MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA).
2.2. Time-Frequency Analysis
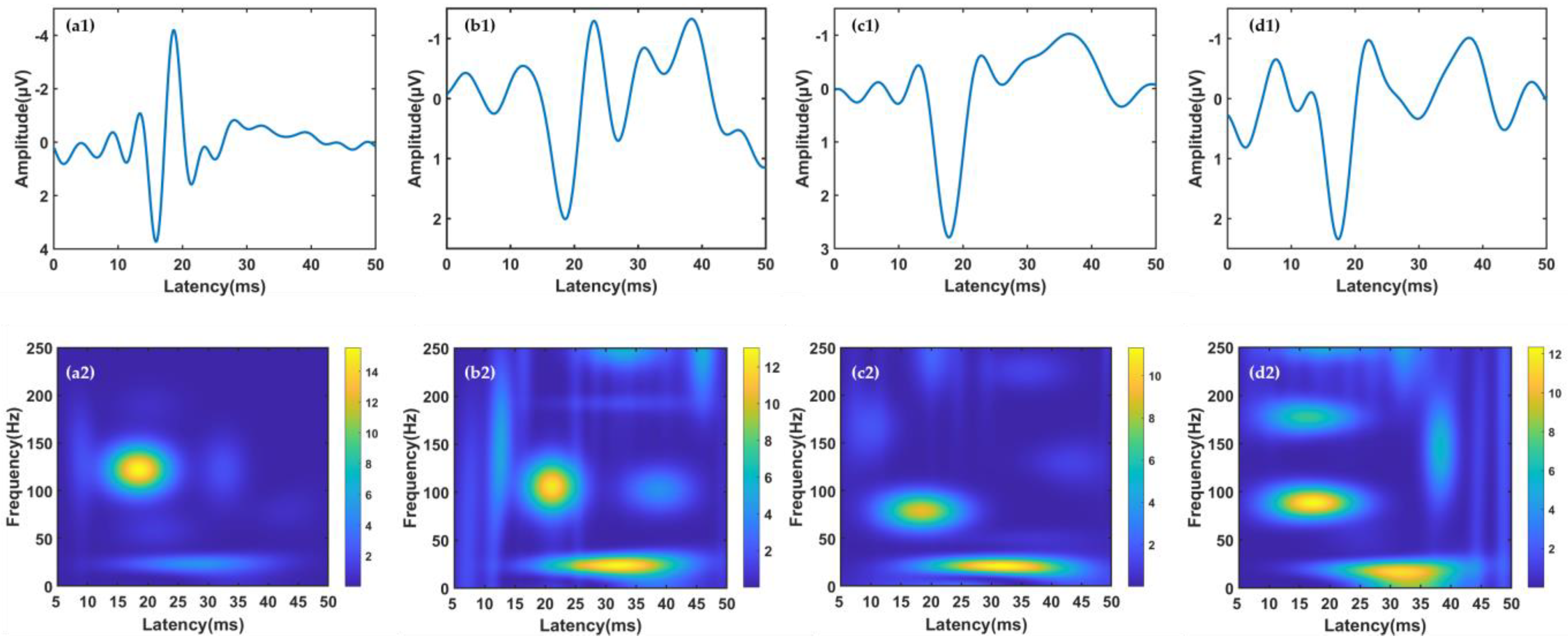
In this study, obtaining reliable TFCs is the basis for subsequent feature extraction and classification. Therefore, the high-resolution MP algorithm was used for time-frequency decomposition. The MP algorithm represents the SEP signal as a linear combination of TFCs:
where
gm(
t) represents TFCs after decomposition, and
e(
t) represents the residual component. In the MP algorithm, TFCs are selected from redundant dictionaries, and the Gabor dictionary has been recommended in previous studies. Therefore, the m-th TFC can be described as follows:
where
T,
f,
a,
σ, and
ϕ define the latency, frequency, amplitude, span, and phase of
gm(
t), respectively. The TFC is generally selected by an iterative algorithm. In the initial step, a TFC is analyzed by identifying the waveform
g1(
t) with the highest inner product with the signal
S(
t). At the same time, we obtain the residual, which is the difference between
S(
t) and
g1(
t). Then,
S(
t) is iterated with residuals and the process is repeated to determine a new
gm(
t), until the total energy of the TFCs reaches 99.5% of
S(
t). During iteration, the values of
T,
F,
a,
σ, and
ϕ are constants. The relative energy
of a TFC
gm(
t) is calculated as follows:
Finally,
T,
f, and
were selected to describe all the TFCs. For the details of the MP algorithm, please refer to [
17,
21,
22,
23].
2.3. Clustering of Time-Frequency Components
In order to explore the local characteristics of the TFCs, we used the k-medoids clustering method to divide the hindlimb SEP TFCs of all rats into multiple component clusters. Different from k-means, which uses the mean value of objects in the cluster as the center in the iterative process of searching for the optimal centers, the k-medoids algorithm selects the object with the minimum Euclidean distance in each cluster. The k-medoids algorithm can deal with outliers better than the k-means can [
24]. The silhouette coefficient was used to evaluate the effect of the number of clustering centers on the clustering results [
25]. For the i-th object, the silhouette coefficient is calculated as follows:
where
a(
i) is the mean distance between the i-th vector and all the other points in the cluster that it belongs to, and
b(
i) is the mean distance between the i-th vector and all points in the nearest cluster. The silhouette coefficient ranges from −1 to 1. The larger the value, the better the clustering performance. The TFC clusters are referred to herein as features. For each SEP, the features with the presence of TFCs were denoted as 1, and those with no TFCs were denoted as 0.
TFC clusters obtained by k-means clustering were also taken as features to compare the classification effects.
2.4. Feature Selection
To remove random noise components and select the most valuable features for classification, we applied filter feature selection before the classification.
Two types of TFCs were considered as noises to be excluded. One was the noise feature of each group. If a feature contained less than 1% of the TFCs of a group, the feature was labeled as random noise from the corresponding group. Another was the outlier TFCs in the remaining features. TFCs corresponding to outliers in any direction of T, f, or E were also identified as random noise. Each group deleted its own noise feature and TFCs. The features composed of the remaining TFCs after removing random noise were used for feature selection.
In order to measure the value of each feature in the classification, we constructed the index
of the feature. Using the filter feature selection method, all features were evaluated as follows:
where
represents the number of TFCs of class m at feature
fj,
NCm represents the total number of TFCs of class m, and
σ2 represents the variance.
The larger the value of a feature, the greater the difference between classes. Features with the smallest 10% of were excluded. Each class had a feature selection pattern, denoted as FS_pattern_N, FS_pattern_C, FS_pattern_T, and FS_pattern_L for the normal, cervical spine injury, thoracic spine injury, and lumbar spine injury data, respectively. The SEPs whose TFCs were all noise were excluded. The denoised TFCs were used for subsequent analysis.
2.5. Classification of SEP Time-Frequency Components
In this study, naive Bayes was used to distinguish the SEP TFD of SCI at different locations, so as to realize the identification of SCI locations.
Naive Bayes has become one of the most efficient learning algorithms [
26]. A naive Bayes is a probabilistic classifier that is based on Bayesian theory with the assumption of attribute conditional independent [
27]. It is noted that Bayesian theory is a mathematical formula used to determine the conditional probability of events. The most important step of the classification is to obtain the posterior probability according to Bayes’ theorem:
where
is the posterior probability, representing the probability that the given sample
x belongs to class
c.
P(
c) represents the class prior probabilities,
is the class-conditional probability of
x conditioned on class
c,
P(
x) is the prior probability of
x.
Based on the attribute conditional independence assumption, Equation (7) could be rewritten as follows:
where
d is the number of attributes,
xi represent the value of the i-th attribute for the dataset.
P(
x) is same for all classes
c, so the classifier expression can be written as follows:
In this paper, the attributes represent the time-frequency features.
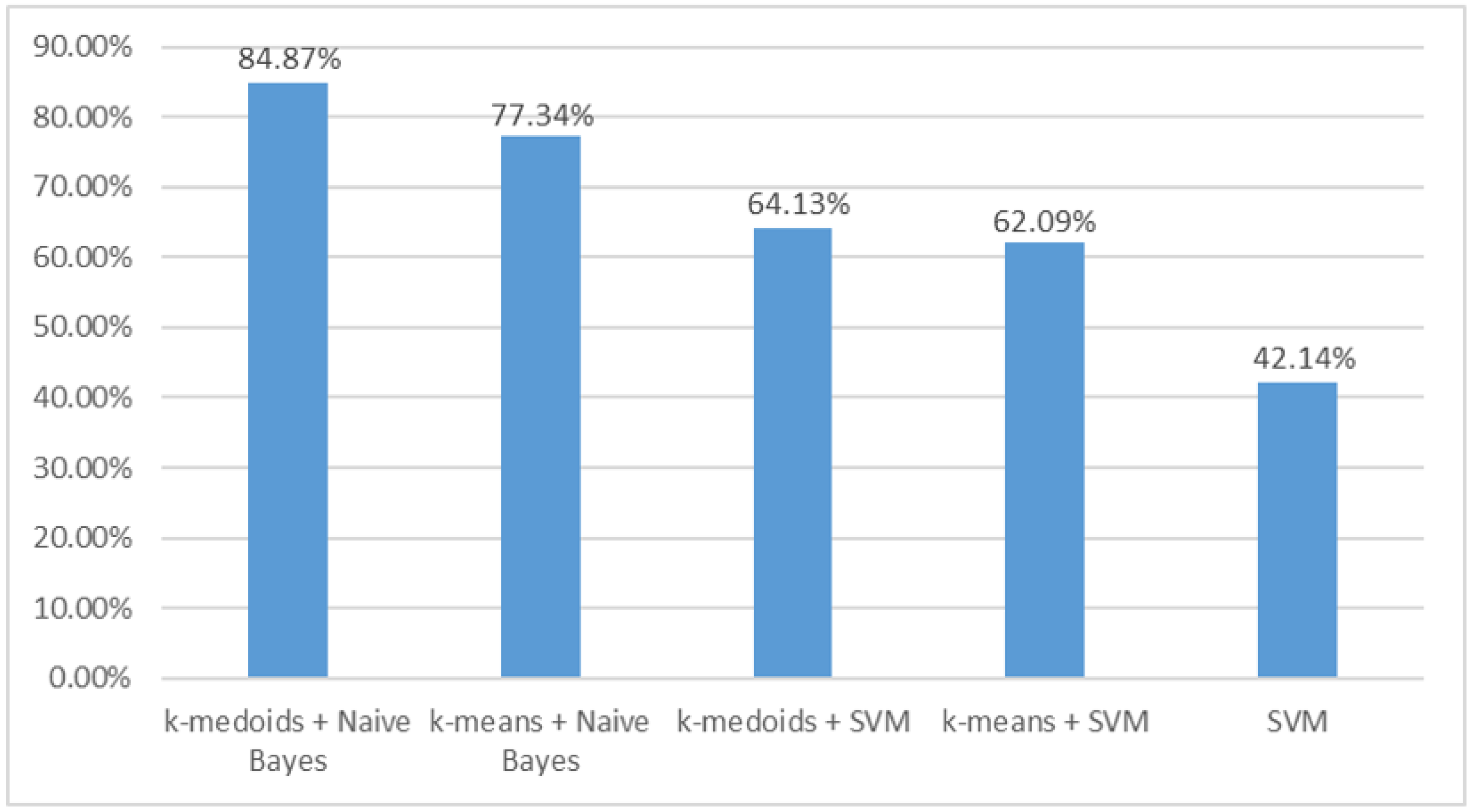
In order to know the accuracy of the method proposed in this paper, we compared the performance of the classifier with that of the support vector machine (SVM) used in a previous study. In the dataset of this study, the classification methods of k-medoids + naive Bayes, k-means + naive Bayes, k-medoids + SVM, k-means + SVM, and SVM were recorded with the highest accuracy. For a specific breakdown of the SVM, please refer to [
11].
4. Discussion
SCI is a serious complication of corrective scoliosis surgery and may even lead to paraplegia [
1,
2]. Direct spinal cord distraction is a common type of SCI injury in scoliosis correction surgery. Timely removal of the SCI source can effectively reduce or even avoid SCI [
4,
5]. In order to accurately detect the source of distraction SCI during surgery, we developed an SCI location identification algorithm based on k-medoids clustering and naive Bayes, utilizing the correlation between the SCI location and the SEP TFD and achieved satisfactory classification results.
The SEP waveform contains a series of TFCs, which have different origins along the somatosensory pathway [
28,
29,
30]. The latency and amplitude of each component peak can be used to explain the changes in neural activity. Therefore, the SEP can effectively evaluate the physiological integrity of the spinal cord, and it has been widely used as intraoperative electrophysiological monitoring tool for the spinal cord [
31]. Animal models of spinal cord compression and contusion have been established, and the SEP has been used to predict the specific location of the SCI. At present, there are relatively few studies on the location prediction of direct spinal cord distraction [
5], so we established an animal model of distraction injury. Clamps coupled to a distraction injury were placed on the corresponding spinal segment. Then, the respective clamps were distracted rostrally and caudally to produce a displacement of 3 mm and held for 1 s before being returned to their initial position [
20]. In the current study, we used this rat distraction model to evaluate how naive Bayes used the SEP to predict the location of the SCI.
Stable SEP components may correspond to unique anatomical structures of the somatosensory pathway [
13,
32]. In traumatic or congenital cases, SEP peaks may be delayed or disappear [
33]. Previous studies had used the energy peak of the maximum power in TFD as an indicator of SCI in intraoperative monitoring, while ignoring other components with relatively low energy [
34,
35]. As reported, there were many stable sub-TFCs outside the main SEP TFC region, and these sub-TFCs were potentially associated with pathological information [
17]. Furthermore, there were also common sub-TFD changes in different injury locations, suggesting that this sub-TFD change was likely to be a product of spinal neuropathy [
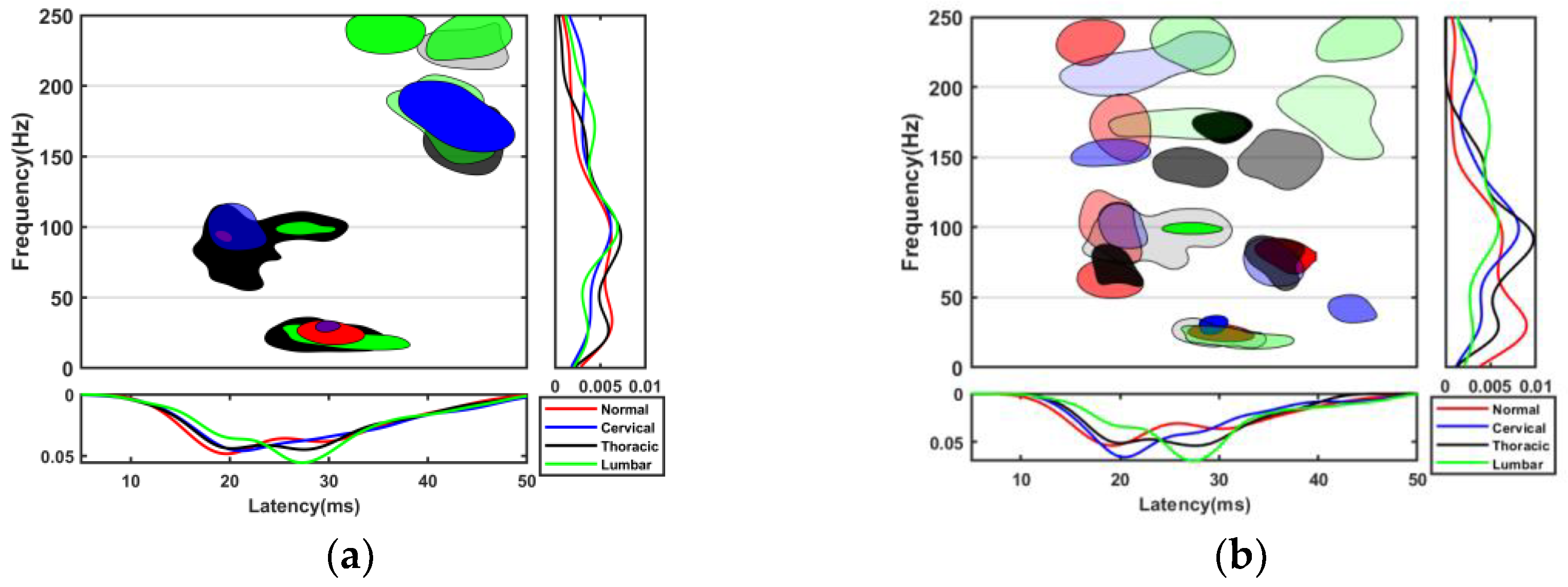
13]. This series of studies showed that smaller TFCs contain useful information about the pathological process, especially the location of the SCI. The results of this study showed that the latency of TFCs distributed in R2 in all SCI groups was significantly longer than that in normal group, and the number of TFCs with latency between 35 and 50 ms was greater than that in the normal group.
A recent study recorded both the SEP and the motor evoked potential (MEP) [
20], which monitor sensory tracts and the corticospinal tract, respectively. It was found that both SEP and MEP were influenced by the type of SCI. The study only extracted the latency and amplitude of SEP and MEP and did not establish classifiers. However, this has suggested the significance of the MEP in SCI identification. In the follow-up study, it is justifiable to perform more complex feature extraction for SEP and MEP and to establish SCI location classifiers.
In previous studies, TFCs were classified into three categories according to their energy. The TFCs with the highest energy were called the main component, and the others were called sub-TFCs. The subcomponents with energy more than 20% of the main component were called the middle-energy components, and the subcomponents with energy less than 20% were called the low-energy component. These categories are similar to the definition of features in this study.
Nevertheless, there are some shortcomings to this feature extraction method. On the one hand, the intergroup correspondence of features was unstable. The main component can be used to detect the occurrence of SCI based on the reduction in the energy of the main component. When the energy of the original main component is greatly reduced or there is strong noise, other TFCs may become the highest-energy component. Therefore, the feature correspondence determined by this method is unstable. The correlation coefficients of latency and frequency help to explore this correspondence. However, it works only in a few regions [
36]. Sub-TFCs, which have a wider distribution region, were also helpful to identify the location of the SCI [
11,
12]. In this paper, the TFCs were clustered, and the clustering model was applicable to all groups. Thus, the intergroup differences of TFCs could be directly compared.
On the other hand, in the face of a complex SCI, the optimal energy threshold for feature extraction of the original method may require frequent and complex adjustments. The time-frequency space region involved in the middle- and low-energy TFCs is obviously wider than that of a single feature in this paper. This will affect the selection of the classification method. When the TFD boundary is used for classification, a relatively complex TFD of features is good to improve the accuracy, as when using the SVM [
37]. However, the change in the energy threshold will greatly affect the boundary. When the quantity information of TFCs is used, it is better when the features are concentrated in local areas. This study not only used the quantity but also extracted the TFD information through feature selection. Therefore, the division of the time-frequency space was more detailed.
The comparison of accuracy between different classification methods may validate the above hypothesis.
Figure 6 shows that the SVM had lower accuracy than the naive Bayes, especially after feature selection. The use of feature selection distinguished a large number of TFC overlaps in each group. An appropriate energy threshold may also reduce the overlap, but it is difficult when many SCI locations are involved.
The SEP signals collected during the operation may contain power line interference, as well as artifacts of eye movement, EMG, and ECG [
38]. These artifacts are outliers in the TFCs. We designed the SCI location identification method with the consideration of suppressing the artifact interference. For the feature extraction method, the k-medoids algorithm can deal with outliers better than the k-means algorithm can [
24]. For the classification method, naive Bayes uses probability as the classification basis and needs to use all features during each prediction, and hence, it is relatively insensitive to noise and missing values in the training and test data [
39].
Figure 6 shows that the k-medoids + naive Bayes method achieved the highest accuracy.
In the current study, we achieved a consistent time-frequency space division pattern for each group by clustering TFCs. The feature selection method was used to extract the SEP TFD information sensitive to the SCI location. Then, the quantity of TFCs in each feature was used to identify the SCI location (normal, cervical, thoracic, and lumbar; normal, C5, and C6). The results show that our classification method achieved good results. The classification accuracy of the cervical SCI level by this method was similar to that in previous studies [
11,
12]. At the same time, the average accuracy for normal, cervical, thoracic, and lumbar reached 84.8%. This suggests that the SEP has the potential to localize SCI in other locations outside the cervical spine. In addition, the joint method of k-medoids clustering algorithm and naive Bayes classifier proposed in this study provides a new method for intraoperative SCI localization based on the SEP.
In order to avoid the problem of combination explosion and sparsity problems when solving a Bayesian theorem, naive Bayes introduced the conditional independence hypothesis. This assumption is often difficult to hold in real applications, but naive Bayes can achieve quite good performance in many cases. It is assumed that the naive Bayes classifier can produce correct classification results as long as the conditional probability ranking of each category is correct. It is also assumed that the dependencies between features may offset each other, so even if the dependency is ignored, the naive Bayes classifier can still obtain good classification results. However, the impact of the dependencies between features on current research is still unclear [
40,
41]. Therefore, some naive Bayes methods that analyze the dependency between features may achieve better results, such as semi-naive Bayes or Bayesian net. Despite the limitations, this study extracts the probability information of TFCs from the TFD and applies a new detection method to the identification of the SCI location. Some vertebral segments are not covered in the current study, and the amount of data for each segment is still limited. A large-scale study is expected to be conducted. With an increase in the amount of data, the SCI location recognition method proposed in this paper should improve. Moreover, the association between SCI locations and TFD patterns can be further verified.