FAST (Flexible Acetylcholine Sensing Thread): Real-Time Detection of Acetylcholine with a Flexible Solid-Contact Potentiometric Sensor
Abstract
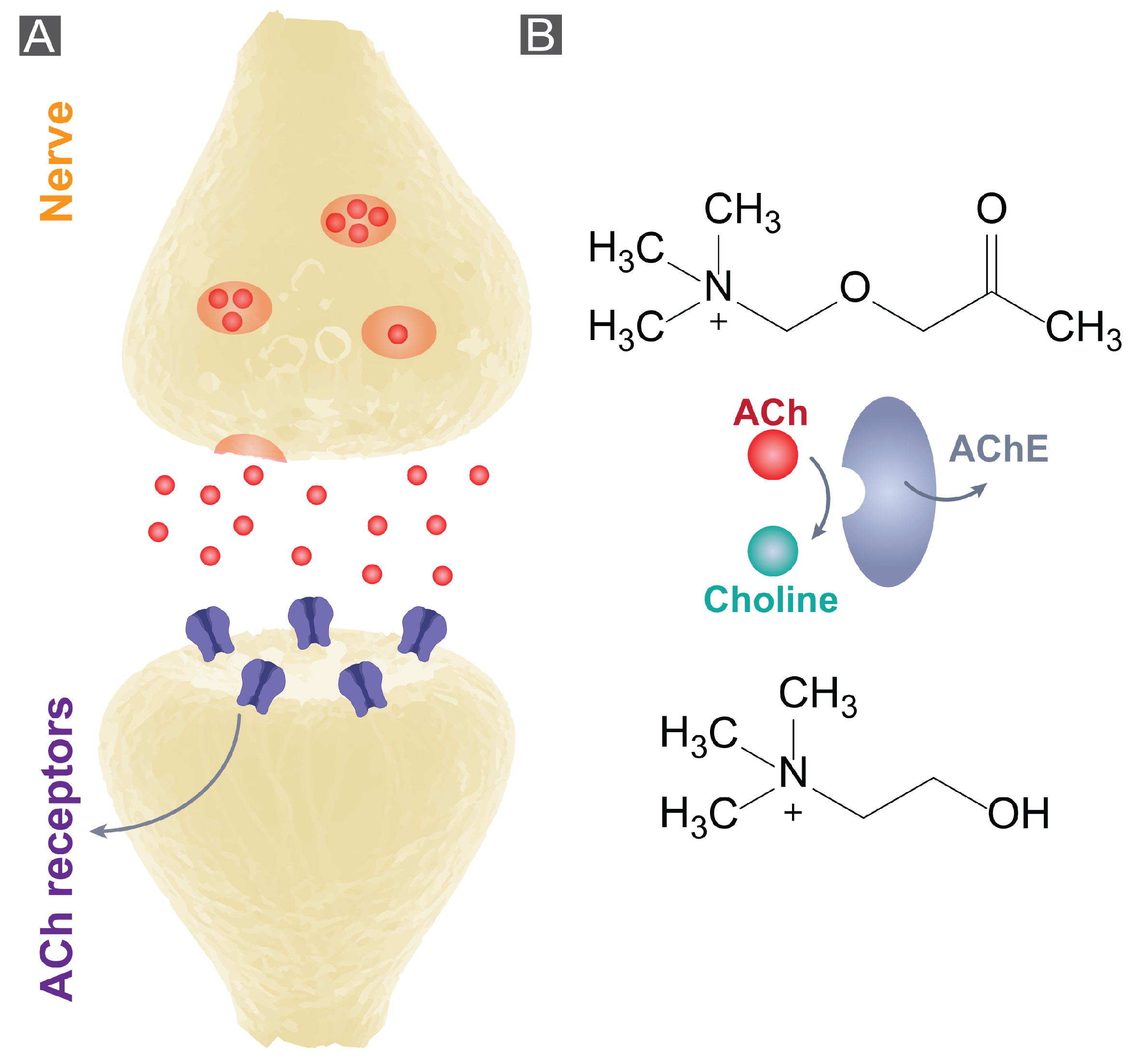
1. Introduction
| Electrode Specifics | Electrode Size | Flexible | Ion-to-Electron Transducer | Ionophore | Limit of Detection (μM) | Sensitivity (Slope, mV/dec) | Linear Range (M) | Biospecimen Used for Sensor Validation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid-Contact Electrodes | |||||||||
| Pulled-glass micropipettes | 50.00 μm tip diameter | No | Ag/AgCl | Acetylcholine dipicrylaminate | 20 | 59.4 | 10−5–10−1 | striatum of rat | [49] |
| Membrane glued to a PVC tube | NR | No | Ag/AgCl | Dioctyloctad- ecylamine | 5 | 52.92 | 10−5–8 × 10−3 | NR | [52] |
| Commercial electrode body | NR | No | Ag/AgCl | (allyloxy)12 cucurbituril[6] | 0.97 | 49.1 | 10−6–10−3 | NA | [50] |
| Membrane glued to a PVC tube | 0.5 cm tip diameter | No | Ag/AgCl | Calix[4]arene | 0.008 | 52.92 | 10−9–10−3 | rat brain homogenate | [45] |
| Commercial electrode body | NR | No | Ag/AgCl | aryl-extended calix[4]pyrrol | 0.3 | 59.5 | 10−6–10−2 | urine | [51] |
| Commercial electrode body | NR | No | Ag/AgCl | Oxatub[4]arenes | 0.1 | 58.6 | 10−6–10−2 | mouse brain homogenate | [48] |
| Solid-Contact Electrodes | |||||||||
| Commercial macrodisk electrode | NR | No | glassy carbon | Dibenzo-18-crown-6 | 10 | NR | NR | NA | [54] |
| Commercial electrode body | NR | No | Carbon paste | -Cyclodextrins | 0.83 | 55.6 | 10−6–10−2 | blood serum | [55] |
| Coated copper wire | NR | No | Graphite | MIP/MAA | 4.5 | 55.2 | 10−5–10−2 | NR | [56] |
| Coated gold wire | 500 μm tip diameter | No | PEDOT:PSS | h--Cyclodextrin | 5.69 | 54.04 | 10−5–10−1 | synthetic serum | [58] |
| Solid graphite support | NR | No | polyaniline and carbon nanotubes | NA (MIP) | 34.5 | 83.86 | 3.40 × 10−5–10−3 | synthetic serum | [57] |
| Ceramic screen-printed | NR | No | PEDOT:PSS | acetyl--cyclodextrin | 0.32 | 55.3 | 3.60 × 10−6–10−3 | human serum | [53] |
| Carbon-coated cotton fiber | 300 μm tip diameter | Yes | Carbon black | Calix[4]arene | 2.6 | 56.11 | 10−6–10−2 | sheep brain | This work |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
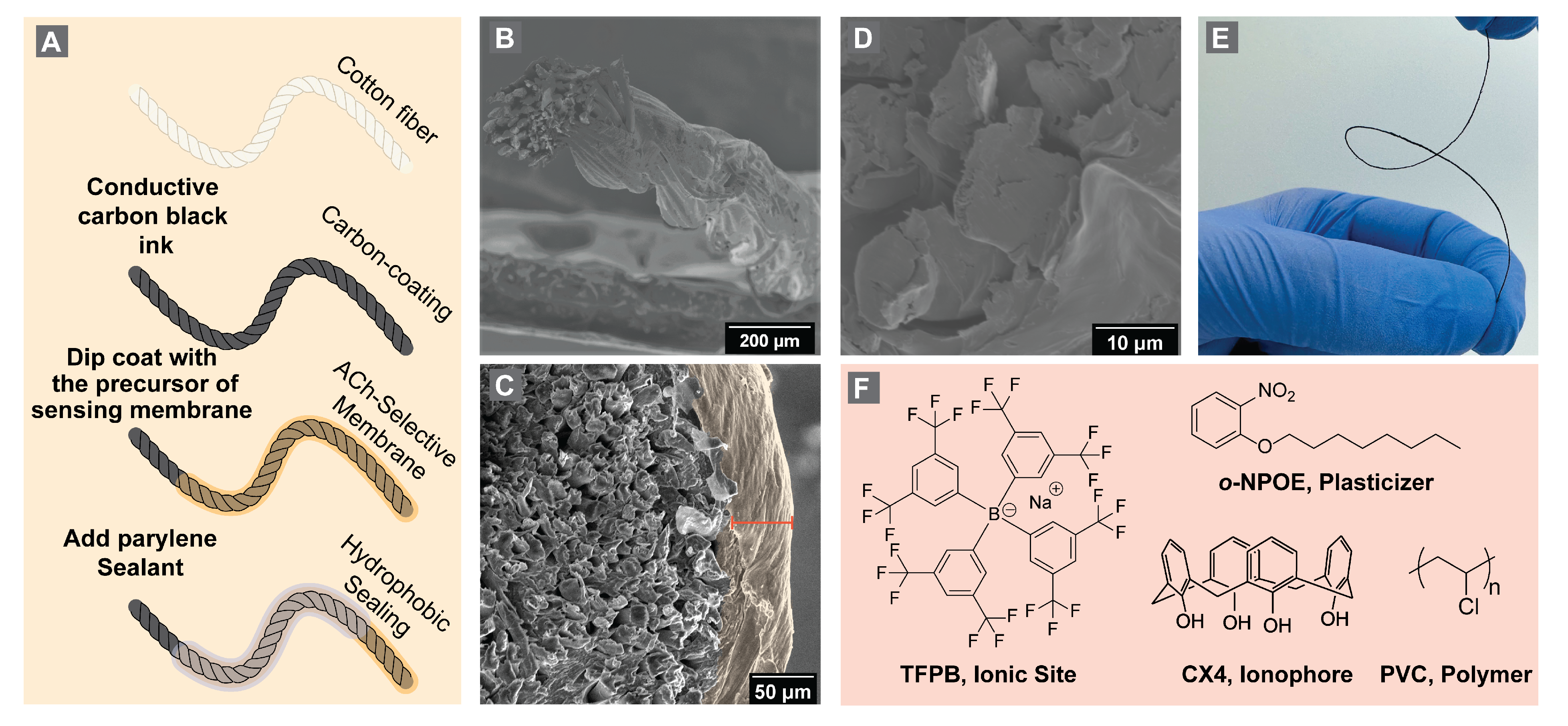
2.2. Electrode Fabrication
2.3. Measurement Protocols
3. Results and Discussions
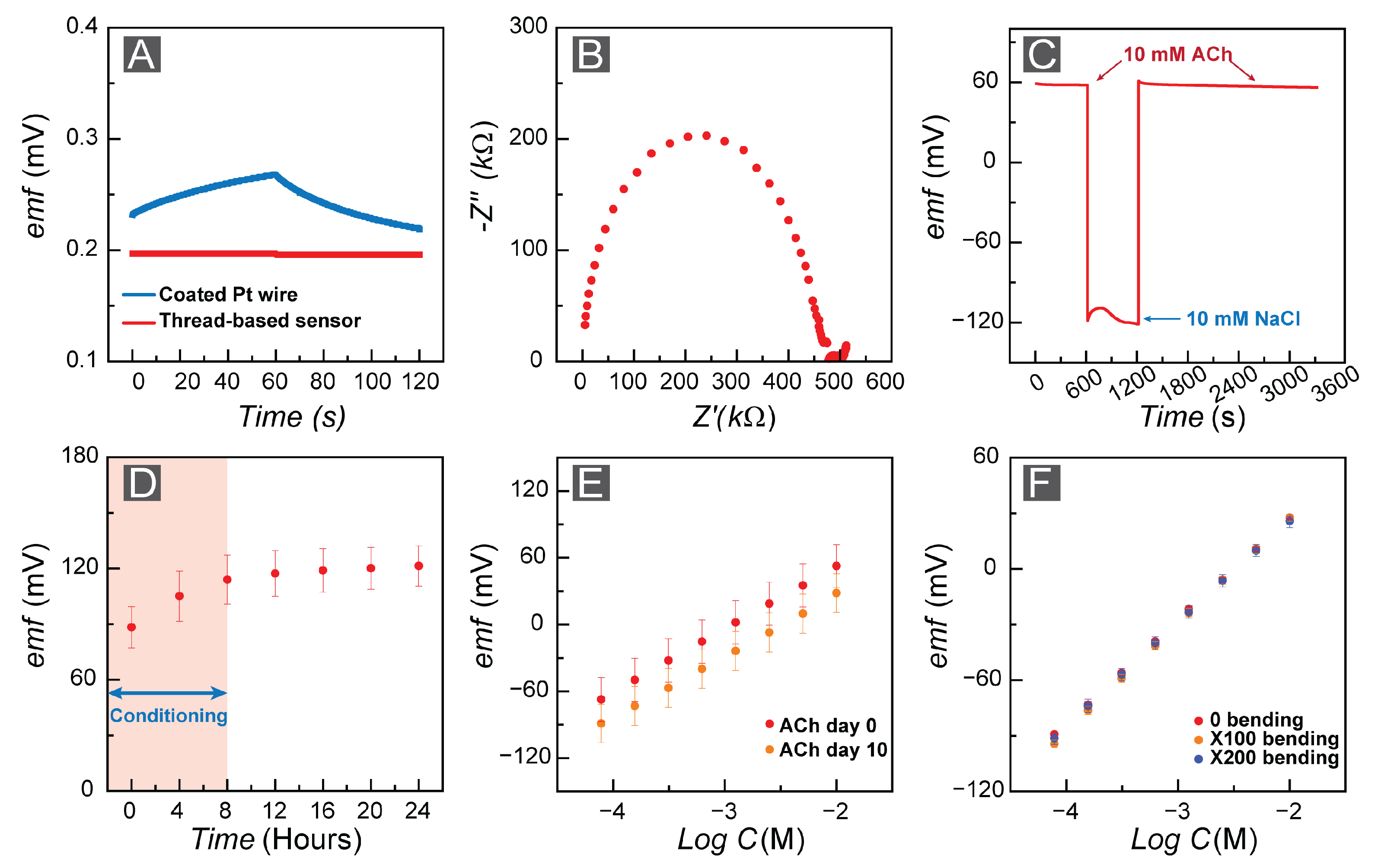
3.1. FAST Response: Sensitivity and Selectivity
3.2. FAST Stability: Drift Analysis for Long-Term Measurements
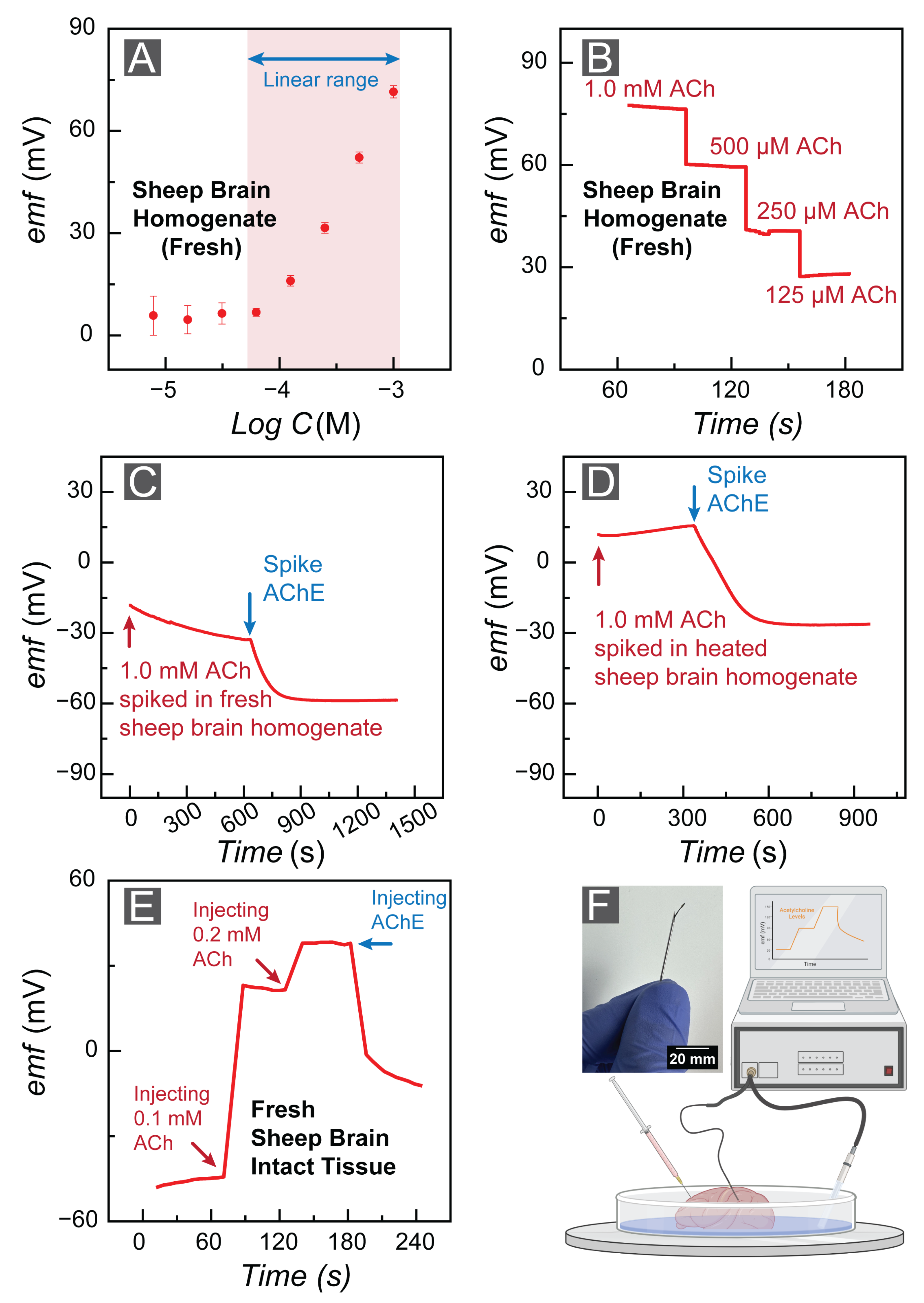
3.3. FAST Feasibility: Application of FAST Sensors in Cerebrospinal Fluid
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| GABA | -Aminobutyric Acid |
| NA | Not applicable |
| NR | Not reported |
| emf | Electromotive force |
| ISE | Ion-selective electrode |
| MWCNT | Multi-wall carbon nanotube |
| f-SWCNT | Functionalized single-wall carbon nanotube |
| PEDOT:PSS | Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate |
| ANI | Aniline |
| MIP | Molecular imprinted polymer |
| MAA | Methacrylic acid |
| KTpClPB | Potassium tetrakis(4-chlorophenyl)borate |
| bTPCX4p | Bis/Tetraphosphonatecalix[4]pyrroles |
| h--cyclodextrin | Heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)--cyclodextrin |
| CX6-HEA | Calix[6]arene-hexaethylacetate |
References
- Dani, J.A. Overview of nicotinic receptors and their roles in the central nervous system. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 49, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, R.; Rollema, H.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: From basic science to therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 22–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- File, S.E.; Gonzalez, L.E.; Andrews, N. Endogenous acetylcholine in the dorsal hippocampus reduces anxiety through actions on nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Behav. Neurosci. 1998, 112, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higley, M.J.; Picciotto, M.R. Neuromodulation by acetylcholine: Examples from schizophrenia and depression. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 29, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowsky, D.S.; El-Yousef, K.M.; Davis, J.M. Acetylcholine and depression. Psychosom. Med. 1974, 36, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimlott, S.; Piggott, M.; Owens, J.; Greally, E.; Court, J.; Jaros, E.; Perry, R.; Perry, E.; Wyper, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor distribution in Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease, and vascular dementia: In vitro binding study using 5-[125I]-A-85380. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmo, M.E.; Bower, J.M. Acetylcholine and memory. Trends Neurosci. 1993, 16, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Hershey, N.D.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Slaney, T.R.; Kennedy, R.T. Mass spectrometry “sensor” for in vivo acetylcholine monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4659–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persike, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Klein, J.; Karas, M. Quantitative determination of acetylcholine and choline in microdialysis samples by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Drewes, L.R. Improved analysis of acetylcholine and choline in canine brain and blood samples by capillary gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1985, 339, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Suga, Y.; Saito, N.; Suda, T.; Yao, I. Imaging mass spectrometry to visualise increased acetylcholine in lungs of asthma model mice. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4327–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, E.; Pilyser, L.; Paquet, C.; Bouaziz-Amar, E.; Grassin-Delyle, S. High-sensitivity quantification of acetylcholine and choline in human cerebrospinal fluid with a validated LC-MS/MS method. Talanta 2021, 224, 121881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Kim, E.H.; Flask, C.A.; Clark, H.A. Nanosensors for the chemical imaging of acetylcholine using magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5761–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, X. An overview of recent analysis and detection of acetylcholine. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 632, 114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Li, Y.; Zeng, J.; Huang, P.; Skirzewski, M.; Kljakic, O.; Peng, W.; Qian, T.; Tan, K.; Zou, J.; et al. An optimized acetylcholine sensor for monitoring in vivo cholinergic activity. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Yang, H.; Mu, M.; Micovic, N.; Poskanzer, K.E.; Monaghan, J.R.; Clark, H.A. Imaging in vivo acetylcholine release in the peripheral nervous system with a fluorescent nanosensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023807118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.S.; Uzunova, V.D.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Nau, W.M. Operational calixarene-based fluorescent sensing systems for choline and acetylcholine and their application to enzymatic reactions. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Ren, J.; Liu, J.; Meng, X.; Ren, X.; Chen, Z.; Tang, F. An eco-friendly, simple, and sensitive fluorescence biosensor for the detection of choline and acetylcholine based on C-dots and the Fenton reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, L.; Chen, B. A fluorometric biosensor based on H2O2-sensitive nanoclusters for the detection of acetylcholine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, M.; Cao, H.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, F. A “turn-on” fluorometric assay for kanamycin detection by using silver nanoclusters and surface plasmon enhanced energy transfer. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametshina, A.R.; Fedorenko, S.V.; Petrov, A.M.; Zakyrjanova, G.F.; Petrov, K.A.; Nurullin, L.F.; Nizameev, I.R.; Mustafina, A.R.; Sinyashin, O.G. Targeted nanoparticles for selective marking of neuromuscular junctions and ex vivo monitoring of endogenous acetylcholine hydrolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14948–14955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R.; Gupta, B.D. Fiber-optic SPR based acetylcholine biosensor using enzyme functionalized Ta2O5 nanoflakes for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 4018–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Canales, A.; Anikeeva, P. Neural recording and modulation technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HajjHassan, M.; Chodavarapu, V.; Musallam, S. NeuroMEMS: Neural probe microtechnologies. Sensors 2008, 8, 6704–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, A.; Descamps, E.; Bergaud, C. A review on mechanical considerations for chronically-implanted neural probes. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltman, A.; Yoo, J.; Meng, E. Flexible, penetrating brain probes enabled by advances in polymer microfabrication. Micromachines 2016, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xue, N.; Chen, J. A Review: Research Progress of Neural Probes for Brain Research and Brain–Computer Interface. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Shim, H.J.; Choi, C.; Kim, D.H. Soft high-resolution neural interfacing probes: Materials and design approaches. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielen, B.; Meng, E. A comparison of insertion methods for surgical placement of penetrating neural interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 041003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Srivastava, R. A polyaniline–zeolite nanocomposite material based acetylcholinesterase biosensor for the sensitive detection of acetylcholine and organophosphates. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 6899–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Tiwari, S.; Narayan, T.; Jain, U. Bienzymatic assembly formed@ Pt nano sensing framework detecting acetylcholine in aqueous phase. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 474, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Ou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, B. Amperometric acetylcholine biosensor based on self-assembly of gold nanoparticles and acetylcholinesterase on the sol–gel/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/choline oxidase composite-modified platinum electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, D.Y.; Kucherenko, I.; Soldatkin, O.; Topolnikova, Y.V.; Dzyadevych, S.; Soldatkin, A. A highly selective amperometric biosensor array for the simultaneous determination of glutamate, glucose, choline, acetylcholine, lactate and pyruvate. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 128, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodur, O.C.; Dinç, S.; Özmen, M.; Arslan, F. A sensitive amperometric detection of neurotransmitter acetylcholine using carbon dot-modified carbon paste electrode. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 68, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, H.; Zhu, J. Improved enzyme immobilization for enhanced bioelectrocatalytic activity of choline sensor and acetylcholine sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynacı, E.; Yaşar, A.; Arslan, F. An amperometric biosensor for acetylcholine determination prepared from acetylcholinesterase-choline oxidase immobilized in polypyrrole-polyvinylsulpfonate film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Vágföldi, Z.; Tóth, K.; Nagy, G. Fast response potentiometric acetylcholine biosensor. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 1999, 11, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Cui, T. Carbon nanotube thin film pH electrode for potentiometric enzymatic acetylcholine biosensing. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 93, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarahmady, N.; Heli, H.; Vais, R.D. An electrochemical acetylcholine sensor based on lichen-like nickel oxide nanostructure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Balamurugan, T.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, T.W.; Sathesh, T. Rational design of Cu@Cu2O nanospheres anchored B, N Co-doped mesoporous carbon: A sustainable electrocatalyst to assay eminent neurotransmitters acetylcholine and dopamine. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 5669–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anithaa, A.; Asokan, K.; Sekar, C. Low energy nitrogen ion beam implanted tungsten trioxide thin films modified indium tin oxide electrode based acetylcholine sensor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 84, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, W. Non-enzymatic acetylcholine electrochemical biosensor based on flower-like NiAl layered double hydroxides decorated with carbon dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitollahi, H.; Safaei, M.; Tajik, S. Screen-printed Electrode Modified with ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Detection of Acetylcholine. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Balamurugan, T.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, T.W. Facile synthesis of spinel-type copper cobaltite nanoplates for enhanced electrocatalytic detection of acetylcholine. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7642–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.P.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Bühlmann, P. In situ sensing of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in a dynamic range of 1 nM to 1 mM. ACS Sensors 2018, 3, 2581–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühlmann, P.; Chen, L.D. Ion-selective electrodes with ionophore-doped sensing membranes. Supramol. Chem. Mol. Nanomater. 2012, 5, 2539. [Google Scholar]
- Bühlmann, P.; Pretsch, E.; Bakker, E. Carrier-based ion-selective electrodes and bulk optodes. 2. Ionophores for potentiometric and optical sensors. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1593–1688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, L.P.; Li, D.H.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, W.; Xie, X. Potentiometric determination of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine with ion-selective electrodes containing oxatub [4] arenes as the ionophore. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, A.; Lopez, S.; Justice, J.B., Jr.; Salamone, J.D.; Neil, D.B. Acetycholine and choline ion-selective microelectrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1983, 146, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Oh, J.; Jeon, W.S.; Selvapalam, N.; Hwang, I.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, K. A new cucurbit [6] uril-based ion-selective electrode for acetylcholine with high selectivity over choline and related quaternary ammonium ions. Supramol. Chem. 2012, 24, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Du, P.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Q. Polymeric membrane electrodes using calix [4] pyrrole bis/tetra-phosphonate cavitands as ionophores for potentiometric acetylcholine sensing with high selectivity. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14740–14746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, Y.H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, G.L.; Yu, R.Q. A potentiometric acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on plasma-polymerized film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 104, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmawy, N.H.; Almehizia, A.A.; Youssef, T.A.; Amr, A.E.G.E.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Kamel, A.H. Novel Carbon/PEDOT/PSS-Based screen-printed biosensors for acetylcholine neurotransmitter and acetylcholinesterase detection in human serum. Molecules 2019, 24, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poels, I.; Nagels, L. Potentiometric detection of amines in ion chromatography using macrocycle-based liquid membrane electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 440, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, E.; Hassan, H.; Mohamed, G.G.; Ragab, F.A.; Seleim, A.E.A. β-Cyclodextrin-based potentiometric sensors for flow-injection determination of acetylcholines. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 5, 448–458. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, A.H.; Al Hamid, F.A.; Soror, T.Y.; Galal, H.R.; El Gendy, F.A. Solid Contact Biosensor Based On Man-Tailored Polymers For Acetylcholine Detection: Application To Acetylcholinesterase Assay. Eur. Chem. Bull 2015, 5, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Sacramento, A.S.; Moreira, F.T.; Guerreiro, J.L.; Tavares, A.P.; Sales, M.G.F. Novel biomimetic composite material for potentiometric screening of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter in Alzheimer’s disease. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, G. Nonenzymatic all-solid-state coated wire electrode for acetylcholine determination in vitro. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, K.A.; Lee, J.M.; Boughner, D.R. Mechanical suitability of glycerol-preserved human dura mater for construction of prosthetic cardiac valves. Biomaterials 1984, 5, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y. Numerical human head model for traumatic injury assessment. KSME Int. J. 2001, 15, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Massia, S.; He, J. Biocompatible benzocyclobutene-based intracortical neural implant with surface modification. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2005, 15, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A.; Tarrés, Q.; Chamorro, M.À.; Soler, J.; Mutjé, P.; Espinach, F.X.; Vilaseca, F. Modeling the stiffness of coupled and uncoupled recycled cotton fibers reinforced polypropylene composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.P.; Ainla, A.; Tan, E.K.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Yoshida, Y.; Yuan, L.; Sigurslid, H.H.; Arkan, N.; Yip, M.C.; Abrahamsson, C.K.; et al. Ion sensing with thread-based potentiometric electrodes. Lab A Chip 2018, 18, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, M.; Amirghasemi, F.; Mitchell, E.; Mousavi, M.P. Home-Based Electrochemical Rapid Sensor (HERS): A Diagnostic Tool for Bacterial Vaginosis. Sensors 2023, 23, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, V.; Cortez, N.R.; Xu, Z.; Amirghasemi, F.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Mousavi, M.P. An Accessible Yarn-Based Sensor for In-Field Detection of Succinylcholine Poisoning. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Umezawa, Y. Performance evaluation criteria for preparation and measurement of macro-and microfabricated ion-selective electrodes (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P. Selectivity of potentiometric ion sensors. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, Y.; Bühlmann, P.; Umezawa, K.; Tohda, K.; Amemiya, S. Potentiometric selectivity coefficients of ion-selective electrodes. Part I. Inorganic cations (technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1851–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, D.B.; Rogers, T.D.; Blaha, C.D. Acetylcholine–dopamine interactions in the pathophysiology and treatment of CNS disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 16, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurrish, S.; Ségalat, L.; Kaplan, J.M. Serotonin inhibition of synaptic transmission: Gαo decreases the abundance of UNC-13 at release sites. Neuron 1999, 24, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Current advancement in electrochemical analysis of neurotransmitters in biological fluids. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 86, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J. Potential stability of all-solid-state ion-selective electrodes using conducting polymers as ion-to-electron transducers. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4932–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veder, J.P.; De Marco, R.; Clarke, G.; Chester, R.; Nelson, A.; Prince, K.; Pretsch, E.; Bakker, E. Elimination of undesirable water layers in solid-contact polymeric ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6731–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, V.; Soleimani, A.; Amirghasemi, F.; Khazaee Nejad, S.; Abdelmonem, M.; Razaviyayn, M.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Comai, L.; Mousavi, M.P. Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic. Biosensors 2023, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambly, B.; Guzinski, M.; Pendley, B.; Lindner, E. Evaluation, Pitfalls and Recommendations for the “Water Layer Test” for Solid Contact Ion-selective Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banstola, A.; Reynolds, J.N. Mapping sheep to human brain: The need for a sheep brain atlas. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 961413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, P.G.; Bühlmann, P. Fluorous Bulk Membranes for Potentiometric Sensors with Wide Selectivity Ranges: Observation of Exceptionally Strong Ion Pair Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8958–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.V.; Mousavi, M.P.; Bühlmann, P. Fluorous-Phase Ion-Selective pH Electrodes: Electrode Body and Ionophore Optimization for Measurements in the Physiological pH Range. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13621–13629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, P.G.; Szíjjártó, C.; Jurisch, M.; Gladysz, J.A.; Rábai, J.; Bühlmann, P. Fluorophilic Ionophores for Potentiometric pH Determinations with Fluorous Membranes of Exceptional Selectivity. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Interfering Ions (j) | |
|---|---|
| Sodium | −2.81 |
| Potassium | −2.63 |
| Ammonium | −2.69 |
| Choline | −1.02 |
| Calcium | −3.73 |
| Magnesium | −4.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amirghasemi, F.; Soleimani, A.; Bawarith, S.; Tabassum, A.; Morrel, A.; Mousavi, M.P.S. FAST (Flexible Acetylcholine Sensing Thread): Real-Time Detection of Acetylcholine with a Flexible Solid-Contact Potentiometric Sensor. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060655
Amirghasemi F, Soleimani A, Bawarith S, Tabassum A, Morrel A, Mousavi MPS. FAST (Flexible Acetylcholine Sensing Thread): Real-Time Detection of Acetylcholine with a Flexible Solid-Contact Potentiometric Sensor. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(6):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060655
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmirghasemi, Farbod, Ali Soleimani, Shahd Bawarith, Asna Tabassum, Alayne Morrel, and Maral P. S. Mousavi. 2023. "FAST (Flexible Acetylcholine Sensing Thread): Real-Time Detection of Acetylcholine with a Flexible Solid-Contact Potentiometric Sensor" Bioengineering 10, no. 6: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060655
APA StyleAmirghasemi, F., Soleimani, A., Bawarith, S., Tabassum, A., Morrel, A., & Mousavi, M. P. S. (2023). FAST (Flexible Acetylcholine Sensing Thread): Real-Time Detection of Acetylcholine with a Flexible Solid-Contact Potentiometric Sensor. Bioengineering, 10(6), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060655







