Co-Production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Gluconic Acid from Glucose by Halomonas elongata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism, Composition of Media, and Strain Storage
2.2. Fed-Batch Cultivations
2.3. Analytical Methods
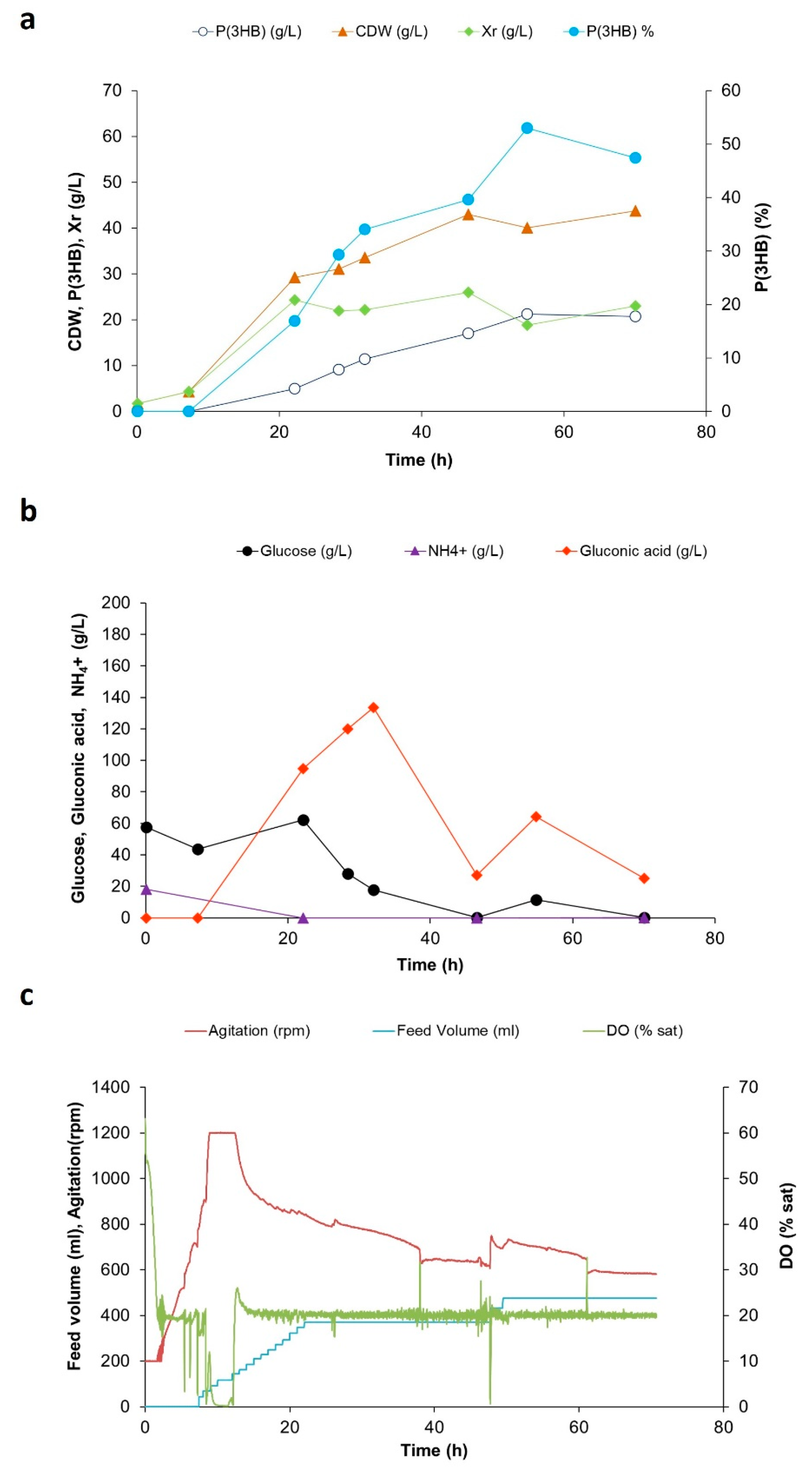
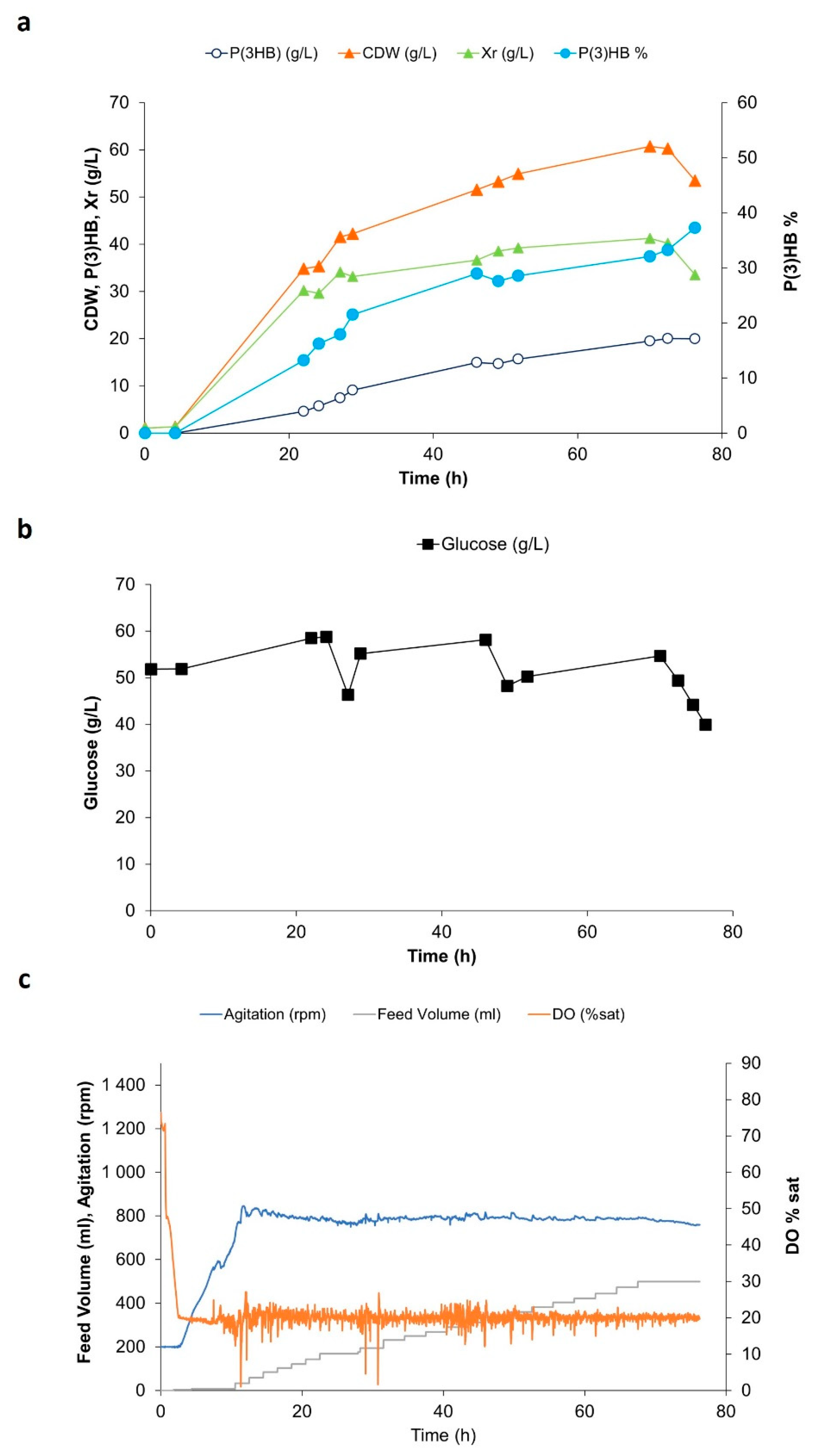
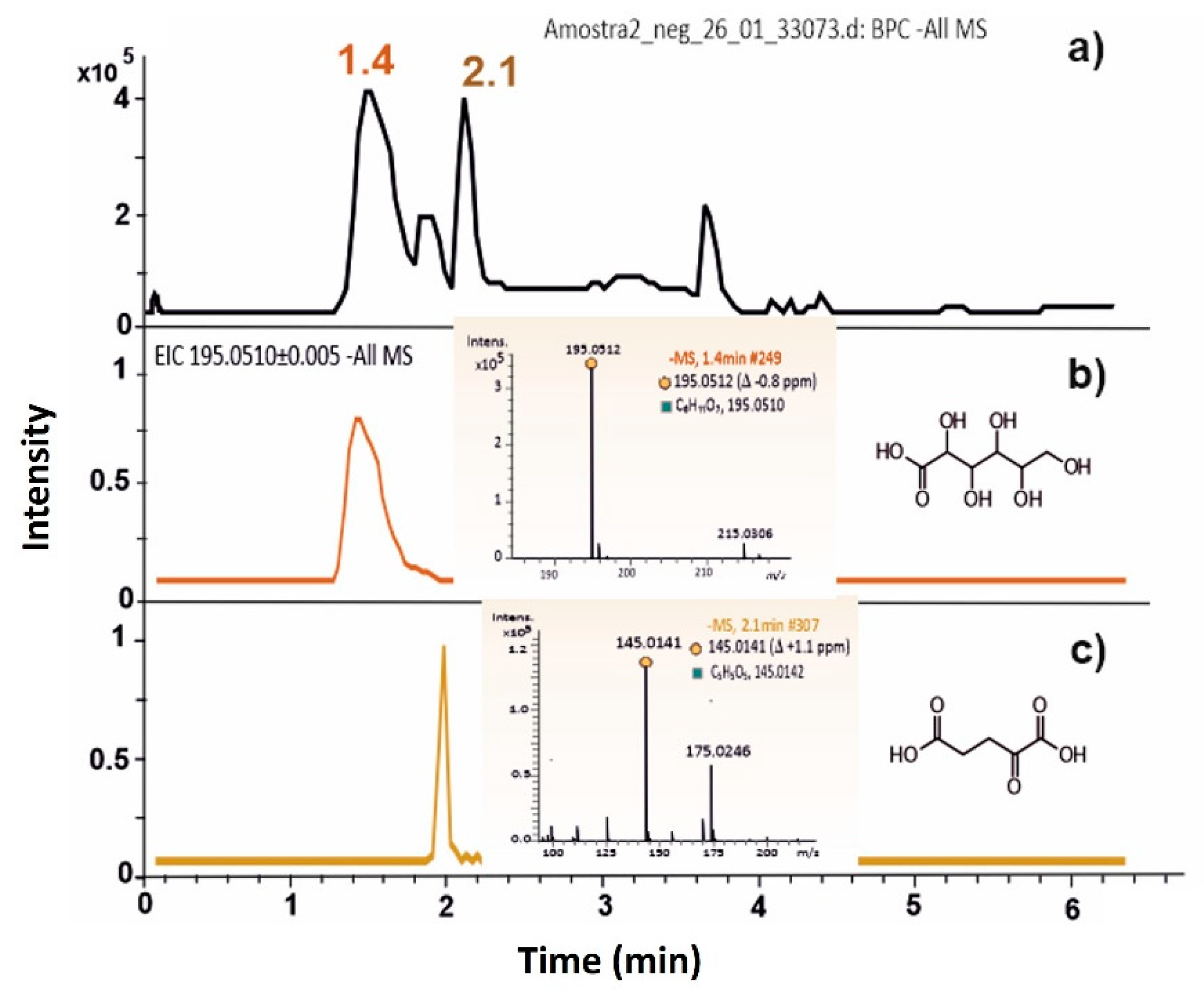
3. Results
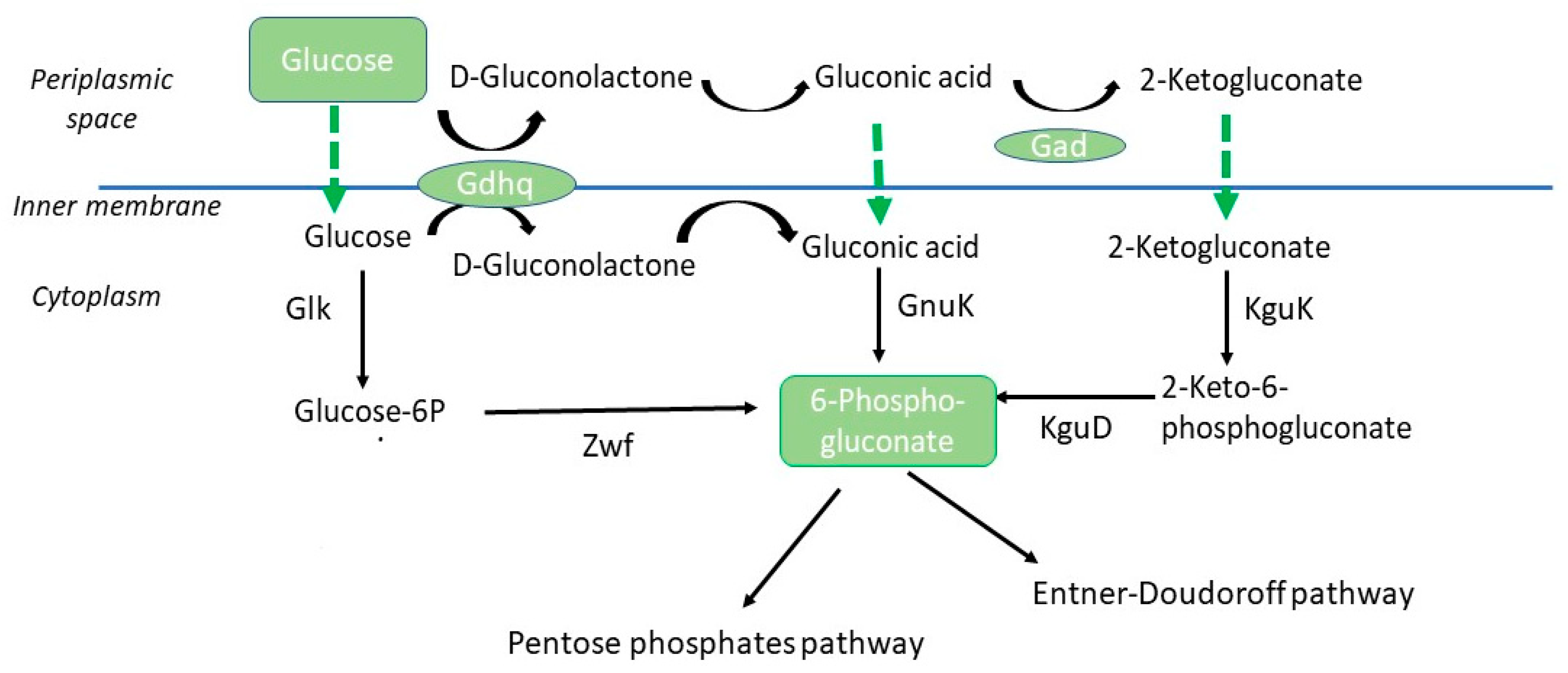
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ventosa, A.; Nieto, J.J.; Oren, A. Biology of Moderately Halophilic Aerobic Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 504–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, Y.S.; Alrumman, S.A.; Otaif, K.A.; Alamri, S.A.; Mostafa, M.S.; Sahlabji, T. Production and Characterization of Bioplastic by Polyhydroxybutyrate Accumulating Erythrobacter aquimaris Isolated from Mangrove Rhizosphere. Molecules 2020, 25, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, R.; Xu, T.; Xiang, H.; Han, J. Current Developments on Polyhydroxyalkanoates Synthesis by Using Halophiles as a Promising Cell Factory. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, A.; Baricz, A.; Leopold, N.; Floare, C.G.; Borodi, G.; Kacso, I.; Tripon, S.; Bulzu, P.A.; Andrei, A.-Ș.; Cadar, O.; et al. Polyhydroxybutyrate Production by an Extremely Halotolerant Halomonas elongata Strain Isolated from the Hypersaline Meromictic Fără Fund Lake (Transylvanian Basin, Romania). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Torreiro, M.; Lu-Chau, T.A.; Lema, J.M. Effect of Nitrogen and/or Oxygen Concentration on Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Accumulation by Halomonas boliviensis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothes, G.; Schubert, T.; Harms, H.; Maskow, T. Biotechnological Coproduction of Compatible Solutes and Polyhydroxyalkanoates Using the Genus Halomonas. Eng. Life Sci. 2008, 8, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Mattiasson, B.; Alvarez, M.T.; Delgado, O. Halomonas boliviensis Sp. Nov., an Alkalitolerant, Moderate Halophile Isolated from Soil around a Bolivian Hypersaline Lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Yin, J.; Ye, J.-W.; Xiang, R.-J.; Ning, Z.-Y.; Huang, W.-Z.; Chen, G.-Q. Promoter Engineering for Enhanced P(3HB-Co-4HB) Production by Halomonas bluephagenesis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Xue, Y.-S.; Aibaidula, G.; Chen, G.-Q. Unsterile and Continuous Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate by Halomonas TD01. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8130–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, D.; Pernicová, I.; Kovalcik, A.; Koller, M.; Mullerova, L.; Sedlacek, P.; Mravec, F.; Nebesarova, J.; Kalina, M.; Marova, I.; et al. Characterization of the Promising Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Producing Halophilic Bacterium Halomonas halophila. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Ling, C.; Yang, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.-Q. A Seawater-Based Open and Continuous Process for Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production by Recombinant Halomonas campaniensis LS21 Grown in Mixed Substrates. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, A.; Punil Kumar, H.N.; Mutturi, S.; Vijayendra, S.V.N. Fed-Batch Strategies for Production of PHA Using a Native Isolate of Halomonas venusta KT832796 Strain. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 184, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondar, M.; Pedro, F.; Oliveira, M.C.; da Fonseca, M.M.R.; Cesário, M.T. Red Algae Industrial Residues as a Sustainable Carbon Platform for the Co-Production of Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate and Gluconic Acid by Halomonas boliviensis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 934432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Hashim, S.; Bento, F.; Mattiasson, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Poly(Beta-Hydroxybutyrate) Production by a Moderate Halophile, Halomonas boliviensis LC1 Using Starch Hydrolysate as Substrate. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwibbert, K.; Marin-Sanguino, A.; Bagyan, I.; Heidrich, G.; Lentzen, G.; Seitz, H.; Rampp, M.; Schuster, S.C.; Klenk, H.-P.; Pfeiffer, F.; et al. A Blueprint of Ectoine Metabolism from the Genome of the Industrial Producer Halomonas elongata DSM 2581 T. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1973–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannya, A.; Nishimura, T.; Matsushita, I.; Tsubota, J.; Kawata, Y. Efficient Production and Secretion of Oxaloacetate from Halomonas Sp. KM-1 under Aerobic Conditions. AMB Express 2017, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Matsushita, I.; Tsubota, J. Efficient Production and Secretion of Pyruvate from Halomonas Sp. KM-1 under Aerobic Conditions. AMB Express 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.M.; Bernal, V.; Salvador, M.; Argandoña, M.; Vargas, C.; Csonka, L.; Sevilla, Á.; Iborra, J.L.; Nieto, J.J.; Cánovas, M. Role of Central Metabolism in the Osmoadaptation of the Halophilic Bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17769–17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Elhadi, D.; Chen, G.-Q. Co-Production of Microbial Polyhydroxyalkanoates with Other Chemicals. Metab. Eng. 2017, 43, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kim, B.S. Valorization of Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production Process by Co-Synthesis of Value-Added Products. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Talan, A.; Tyagi, R.D.; Drogui, P. Concomitant Production of Value-Added Products with Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Synthesis: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, R.; Srienc, F. Effects of Recombinant Precursor Pathway Variations on Poly [(R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate] Synthesis in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 124, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.-J.; Jeon, J.-M.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kim, D.-H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Jung, S.; Yoon, J.-J. Two-Stage Bio-Hydrogen and Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production: Upcycling of Spent Coffee Grounds. Polymers 2023, 15, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdel, F.; Kohring, G.-W.; Mayer, F. Studies on Dissimilatory Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria That Decompose Fatty Acids. Arch. Microbiol 1983, 134, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.E.; Clesceri, S.; Eaton, A. Automated Phenate Method (4500-NH3-H). In Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalheiro, J.M.B.T.; Raposo, R.S.; de Almeida, M.C.M.D.; Teresa Cesário, M.; Sevrin, C.; Grandfils, C.; da Fonseca, M.M.R. Effect of Cultivation Parameters on the Production of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4-Hydroxybutyrate) and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-4-Hydroxybutyrate-3-Hydroxyvalerate) by Cupriavidus necator Using Waste Glycerol. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Filho, E.R.; Silva, J.G.P.; de Macedo, M.A.; Taciro, M.K.; Gomez, J.G.C.; Silva, L.F. Investigating Nutrient Limitation Role on Improvement of Growth and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Accumulation by Burkholderia sacchari LMG 19450 From Xylose as the Sole Carbon Source. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, P.H. ‘Candidatus Halomonas phosphatis’, a Novel Polyphosphate-Accumulating Organism in Full-Scale Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Plants. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2826–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Luo, C.; Liu, F. Characteristics of Intracellular Polyphosphate Granules and Phosphorus-Absorption of a Marine Polyphosphate-Accumulating Bacterium, Halomonas Sp. YSR-3. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, W. Production of Gluconic Acid and Its Derivatives by Microbial Fermentation: Process Improvement Based on Integrated Routes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 864787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Kumar, R.; Banerjee, S. Manufacture of Gluconic Acid: A Review towards Process Intensification for Green Production. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 104, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Lian, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Kuznetsov, B.N.; Jiang, K. Low PH Stress Enhances Gluconic Acid Accumulation with Enzymatic Hydrolysate as Feedstock Using Gluconobacter Oxydans. Fermentation 2023, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, H.; Van-Thuoc, D.; Martín, J.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Quillaguamán, J. A Process for the Production of Ectoine and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) by Halomonas boliviensis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindzierski, V.; Raschke, S.; Knabe, N.; Siedler, F.; Scheffer, B.; Pflüger-Grau, K.; Pfeiffer, F.; Oesterhelt, D.; Marin-Sanguino, A.; Kunte, H.-J. Osmoregulation in the Halophilic Bacterium Halomonas elongata: A Case Study for Integrative Systems Biology. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkins, M.E.; Wilson, S.; Cocuron, J.-C.; Alonso, A.P.; Bird, A.J. The Gluconate Shunt Is an Alternative Route for Directing Glucose into the Pentose Phosphate Pathway in Fission Yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13823–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengart, A.; Cesário, M.T.; de Almeida, M.C.M.D.; Raposo, R.S.; Espert, A.; de Apodaca, E.D.; da Fonseca, M.M.R. Efficient P(3HB) Extraction from Burkholderia sacchari Cells Using Non-Chlorinated Solvents. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 103, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, D.; Madkour, M.H.; Al-Ghamdi, M.A.; Shabbaj, I.I.; Steinbüchel, A. Large Scale Extraction of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) from Ralstonia eutropha H16 Using Sodium Hypochlorite. AMB Express 2012, 2, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leandro, T.; Oliveira, M.C.; da Fonseca, M.M.R.; Cesário, M.T. Co-Production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Gluconic Acid from Glucose by Halomonas elongata. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060643
Leandro T, Oliveira MC, da Fonseca MMR, Cesário MT. Co-Production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Gluconic Acid from Glucose by Halomonas elongata. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(6):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060643
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeandro, Tânia, M. Conceição Oliveira, M. Manuela R. da Fonseca, and M. Teresa Cesário. 2023. "Co-Production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Gluconic Acid from Glucose by Halomonas elongata" Bioengineering 10, no. 6: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060643
APA StyleLeandro, T., Oliveira, M. C., da Fonseca, M. M. R., & Cesário, M. T. (2023). Co-Production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Gluconic Acid from Glucose by Halomonas elongata. Bioengineering, 10(6), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060643




