Multimodal Stereotactic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D-Znet
Abstract
1. Introduction
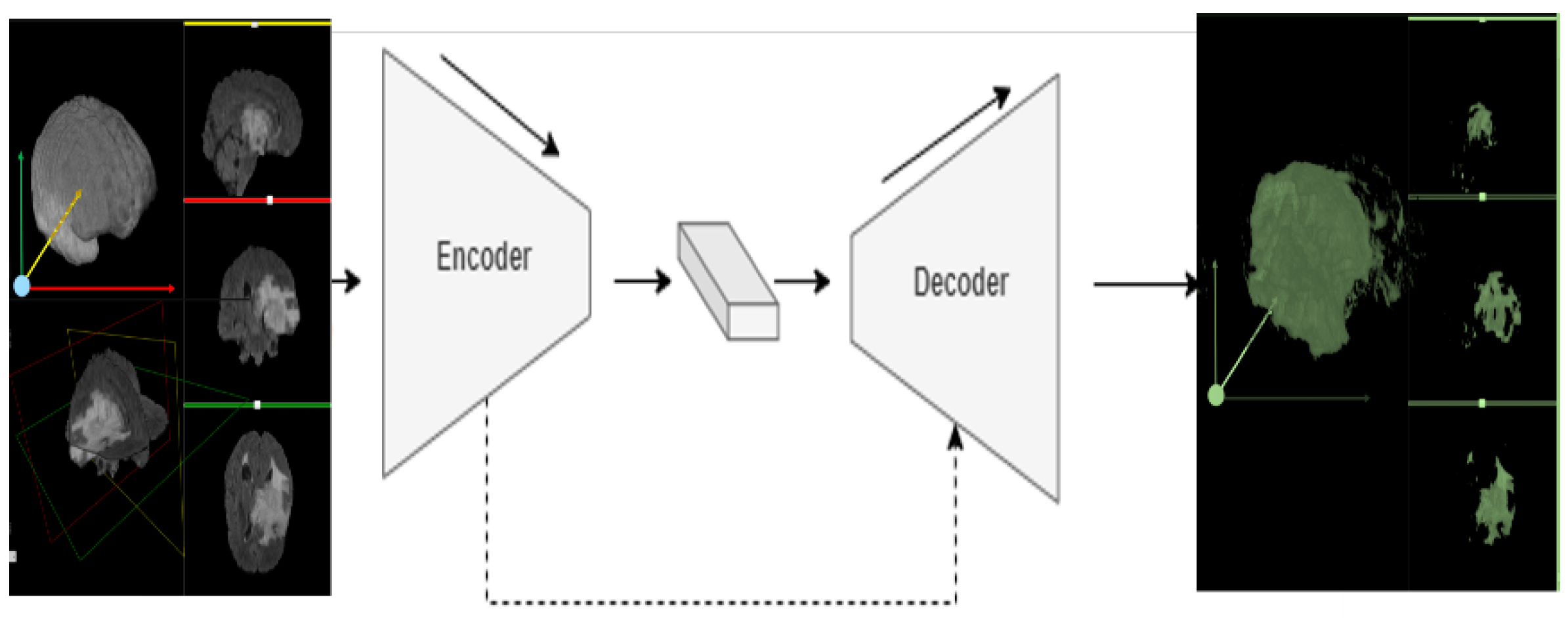
2. Related Work
3. Methods
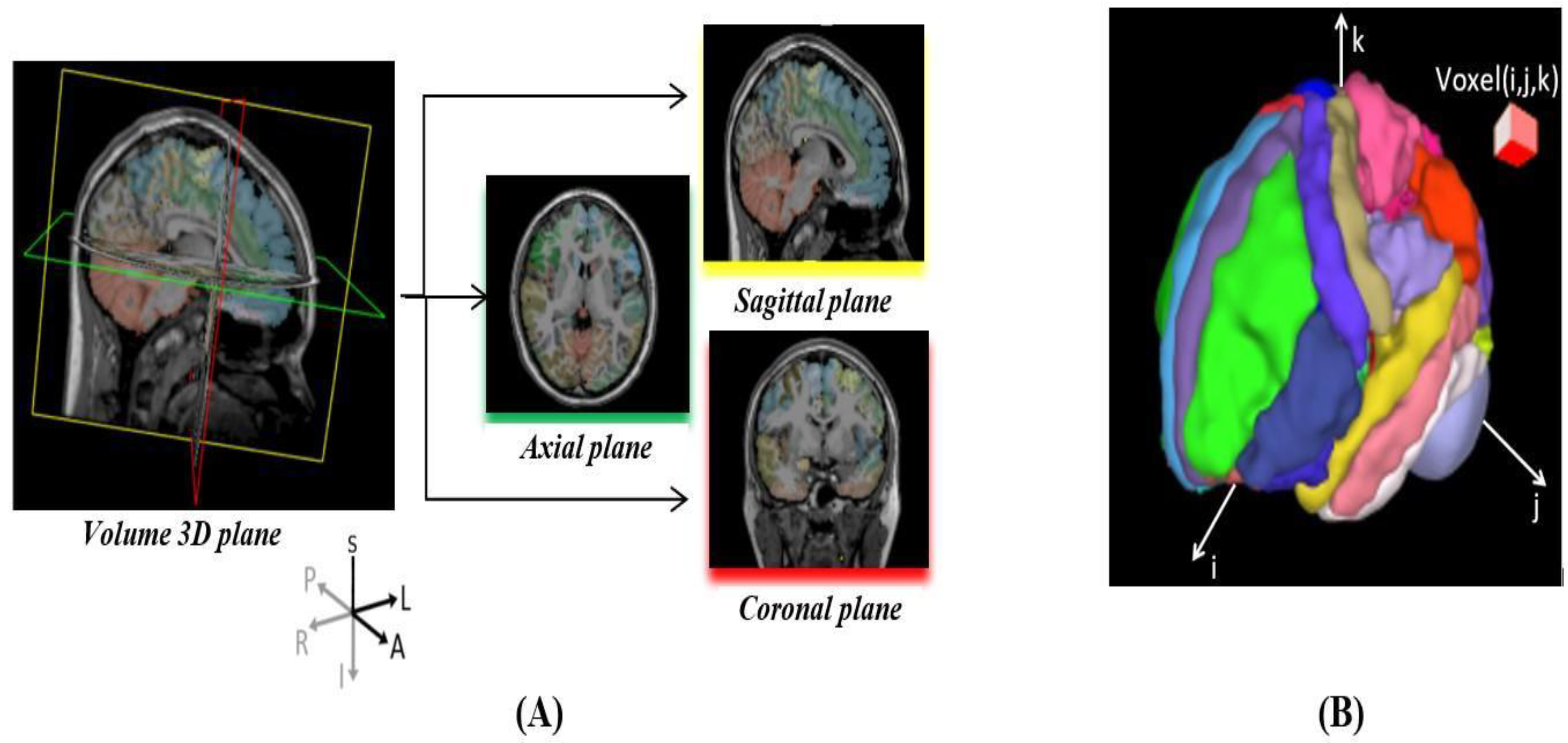
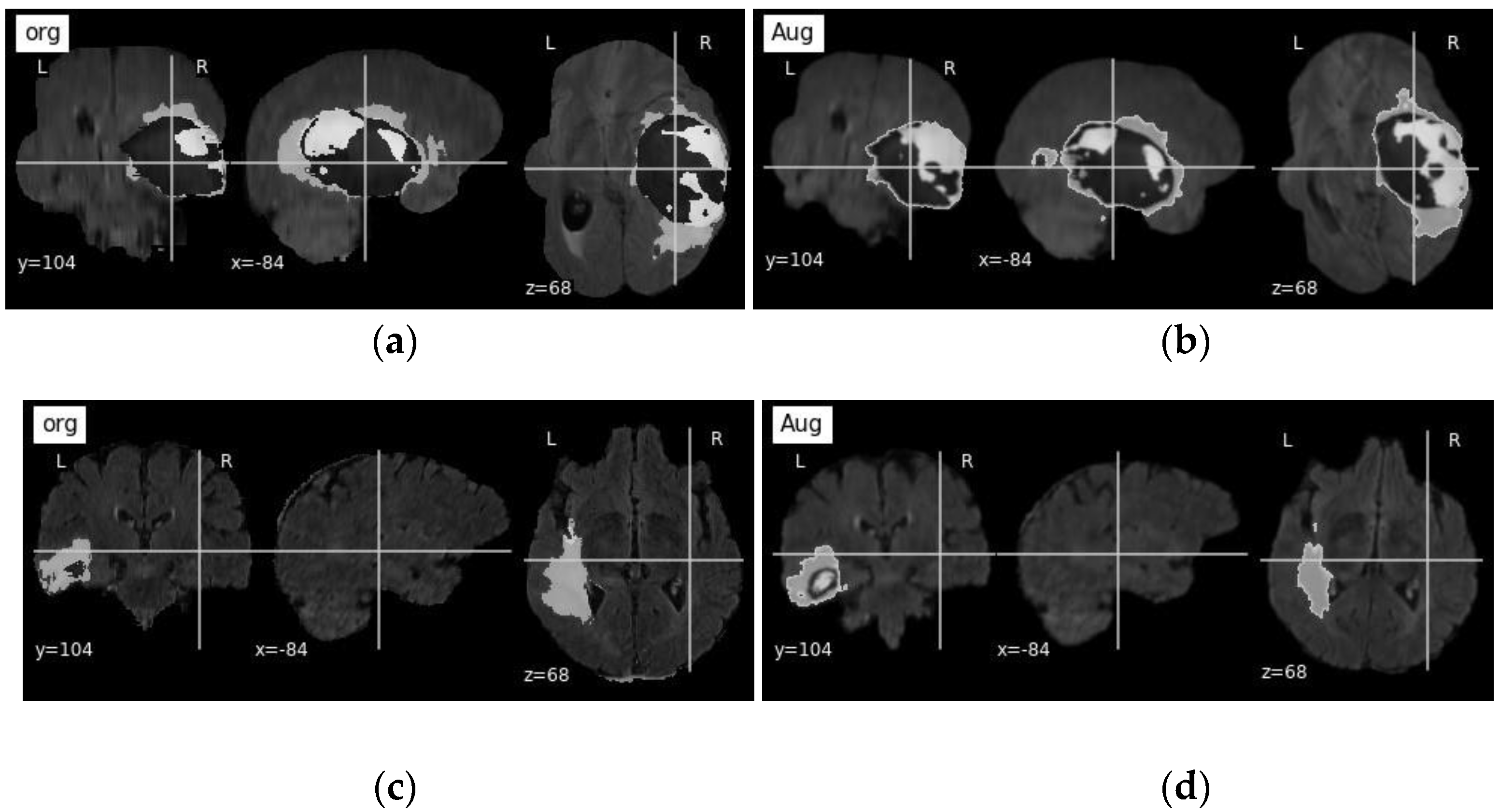
3.1. Dataset and Pre-Processing
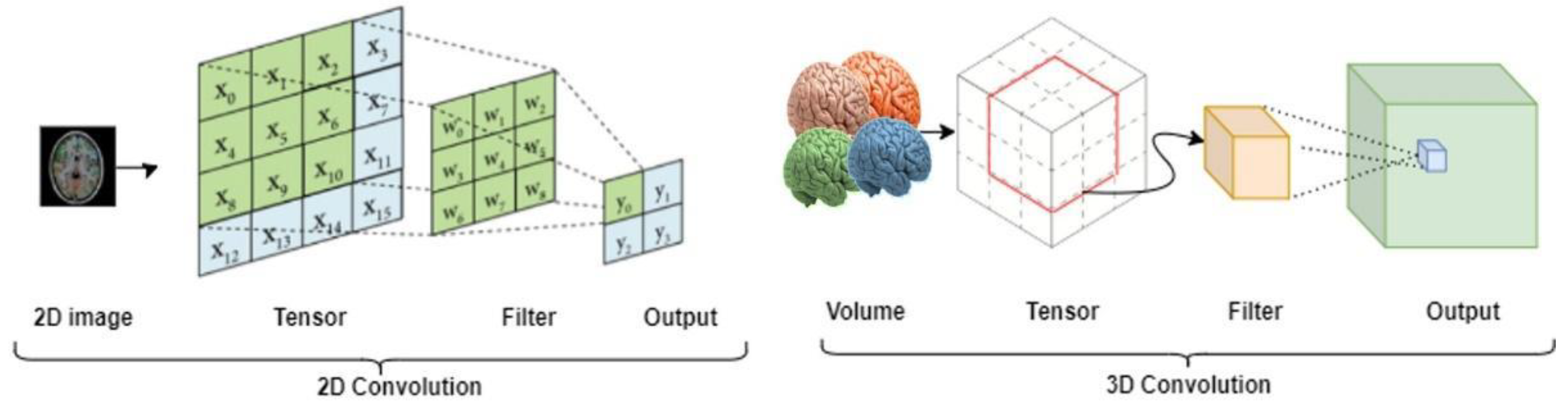
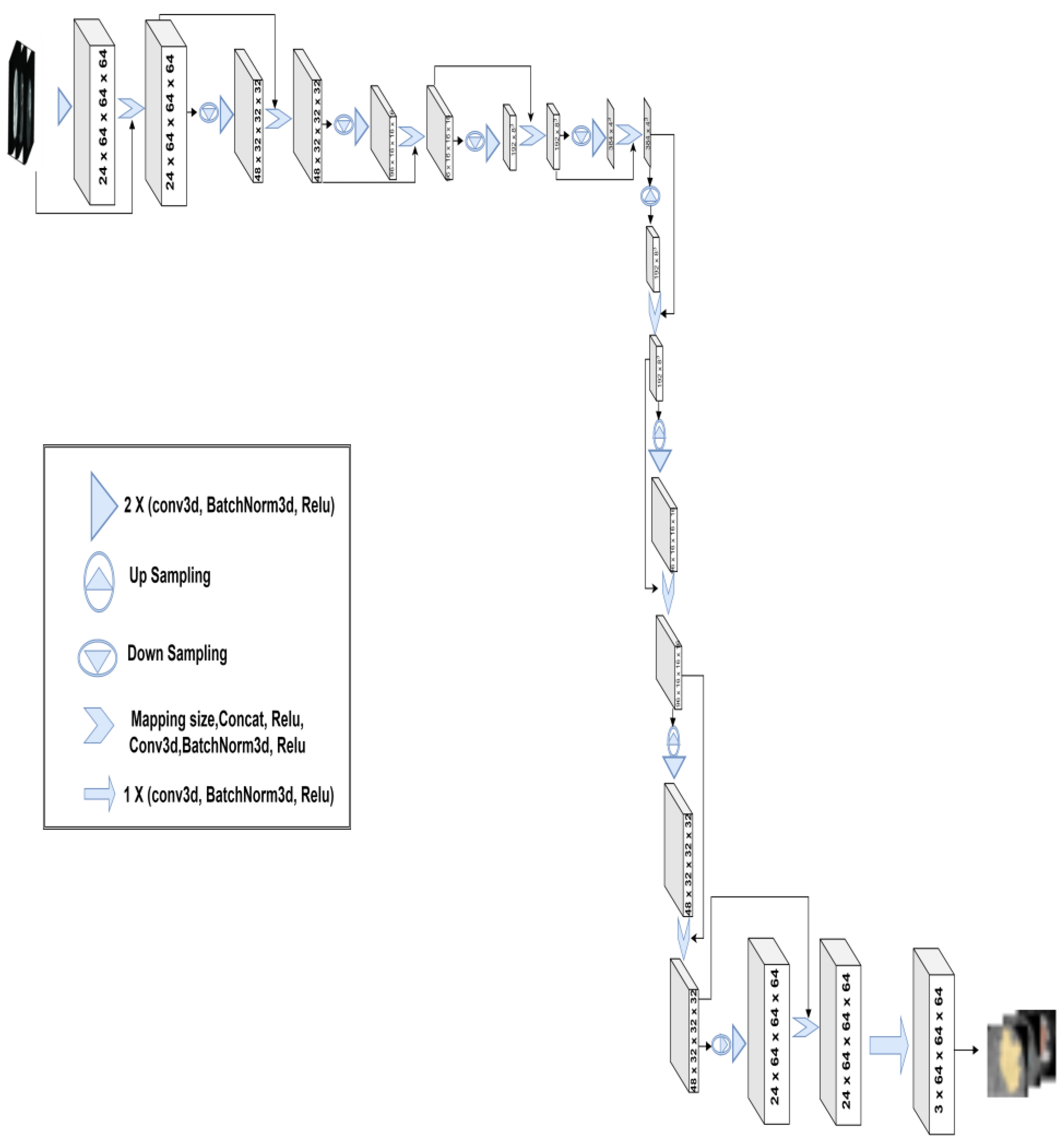
3.2. 3D-Znet Architecture
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Model Training
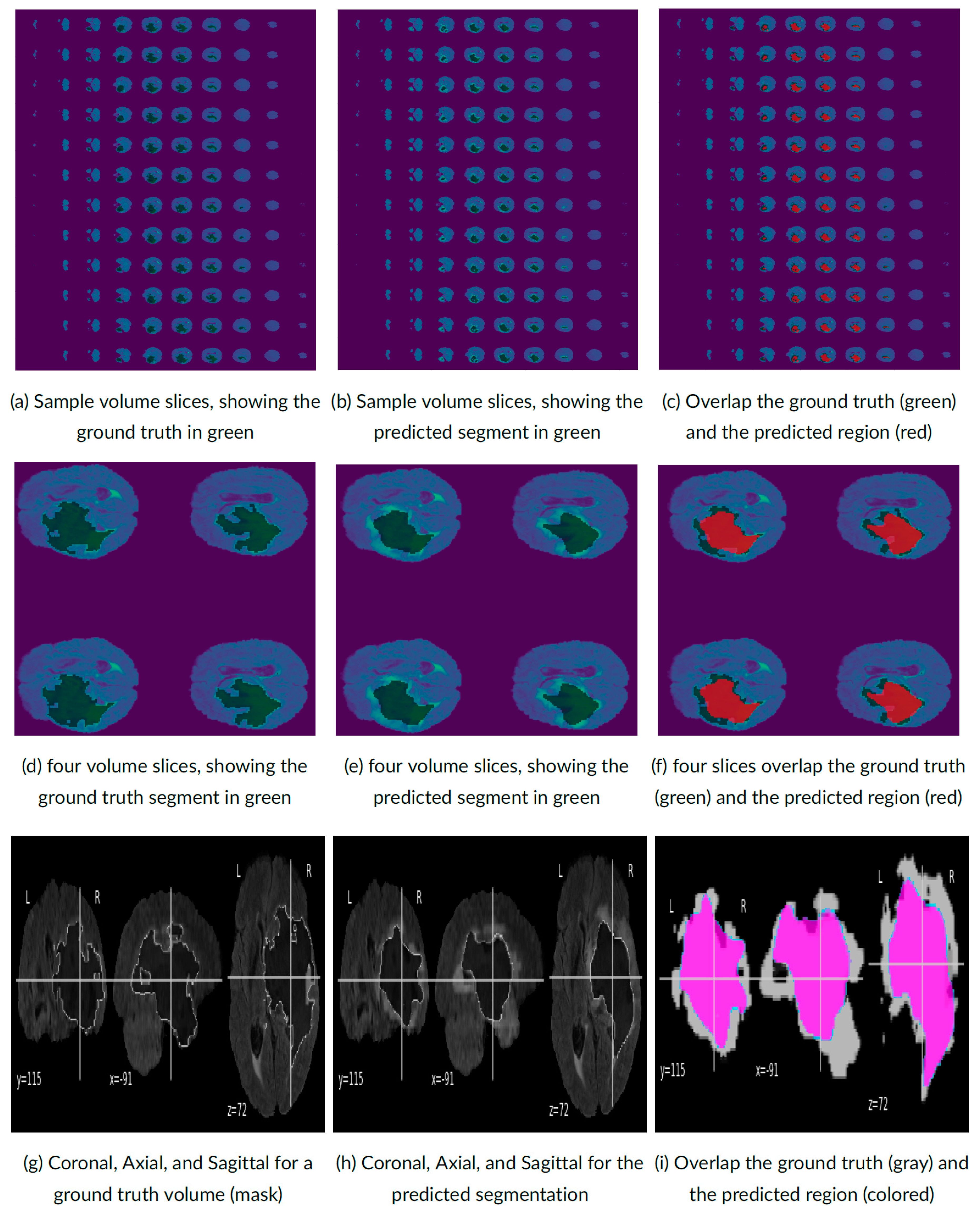
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shinde, P.P.; Shah, S. A review of machine learning and deep learning applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 16–18 August 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dinov, I.D. Data Science and Predictive Analytics: Biomedical and Health Applications Using R; Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhasani, H.; Mohseni, M.; Rahmani, A.M. Deep learning applications for IoT in health care: A systematic review. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 23, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottom, M.A. Convolutional neural network for diagnosing skin cancer. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Liang, K.; Chen, X. A novel extended kalman filter with support vector machine based method for the automatic diagnosis and segmentation of brain tumors. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 200, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preethi, S.; Aishwarya, P. An efficient wavelet-based image fusion for brain tumor detection and segmentation over PET and MRI image. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 14789–14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Razmjooy, N. Brain tumor diagnosis based on metaheuristics and deep learning. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinov, I.D.; Velev, M.V. Data Science: Time Complexity, Inferential Uncertainty, and Spacekime Analytics; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.A.B. Mining Health Data for Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Machine Learning; University of Canberra: Canberra, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Olender, G.; Hurschler, C.; Fleischer, B.; Friese, K.I.; Sukau, A.; Gutberlet, M.; Becher, C. Validation of an anatomical coordinate system for clinical evaluation of the knee joint in upright and closed MRI. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlfing, T.; Zahr, N.M.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. The SRI24 multichannel atlas of normal adult human brain structure. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 31, 798–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, J.M.; Quarrington, R.D.; Magarey, C.C.; Jones, C.F. Center of mass and anatomical coordinate system definition for sheep head kinematics, with application to ovine models of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 100, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, C.; Wang, Y.; Piper, B.; Ishii, H.; Biderman, A. PHOXEL-SPACE: An interface for exploring volumetric data with physical voxels. In Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Designing Interactive Systems: Processes, Practices, Methods, and Techniques, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1–4 August 2004; pp. 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Cassinelli, A.; Ishikawa, M. Volume Slicing Display. In Proceedings of the SA09: SIGGRAPH ASIA 2009, Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 December 2009; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- SOCR University of Michigan, 3D Brain Viewer Using XTK—Boston Children Hospital. Available online: https://socr.umich.edu/HTML5/BrainViewer/ (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Multiple Sclerosis Org, Basic Plane Mathematics of MRI. Available online: https://my-ms.org/mri_planes.htm (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep learning for computer vision: A brief review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 7068349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Yin, S.; Tang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Cardiac-DeepIED: Automatic pixel-level deep segmentation for cardiac bi-ventricle using improved end-to-end encoder-decoder network. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, F. Deep Learning with Python; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.-A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotović, I.; Goossens, B.; Philips, W. MRI segmentation of the human brain: Challenges, methods, and applications. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 450341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayegen, G.; Aksahin, M.F. Brain tumor prediction on MR images with semantic segmentation by using deep learning network and 3D imaging of tumor region. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqazzaz, S.; Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Nokes, L. Automated brain tumor segmentation on multi-modal MR image using SegNet. Comput. Vis. Media 2019, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.U.; Ali, G.; Bin, W.; Almotiri, S.H.; AlGhamdi, M.A.; Nagra, A.A.; Masood, K.; Amin, R.U. RMU-Net: A Novel Residual Mobile U-Net Model for Brain Tumor Segmentation from MR Images. Electronics 2021, 10, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Huo, Q.; Gao, Y.; Sui, H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Y.; Mo, Z.; Shi, F. Segmenting Brain Tumor Using Cascaded V-Nets in Multimodal MR Images. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Tustison, N.J.; Patel, S.H.; Meyer, C.H. Brain Tumor Segmentation Using an Ensemble of 3D U-Nets and Overall Survival Prediction Using Radiomic Features. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Dong, J.; Cheng, T.; Liang, J. SwinBTS: A Method for 3D Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Swin Transformer. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajagbe, S.A.; Amuda, K.A.; Oladipupo, M.A.; Oluwaseyi, F.A.; Okesola, K.I. Multi-classification of Alzheimer disease on magnetic resonance images (MRI) using deep convolutional neural network (CNN) approaches. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Res. 2021, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotunde, J.B.; Ajagbe, S.A.; Oladipupo, M.A.; Awokola, J.A.; Afolabi, O.S.; Mathew, T.O.; Oguns, Y.J. An Improved Machine Learnings Diagnosis Technique for COVID-19 Pandemic Using Chest X-ray Images. In International Conference on Applied Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, N.; Benzaoui, A.; Jacques, S.; Hamiane, M.; El Kourd, K.; Bouakaz, A.; Ouahabi, A. Particle swarm optimization and two-way fixed-effects analysis of variance for efficient brain tumor segmentation. Cancers 2022, 14, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CBICA University of Pennsylvania, Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge 2020: Data. Available online: https://www.med.upenn.edu/cbica/brats2020/data.html (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Whitcher, B.; Schmid, V.J.; Thornton, A. Working with the DICOM and NIfTI Data Standards in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 44, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Reyes, M.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Rempfler, M.; Crimi, A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Berger, C.; Ha, S.M.; Rozycki, M. Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. arXiv 2018, arXiv:181102629. [Google Scholar]
- Huntenburg, J.; Abraham, A.; Loula, J.; Liem, F.; Dadi, K.; Varoquaux, G. Loading and plotting of cortical surface representations in Nilearn. Res. Ideas Outcomes 2017, 3, e12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottom, M.A.; Rahman, H.A.; Dinov, I.D. Znet: Deep Learning Approach for 2D MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2022, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bentley, P.; Mori, K.; Misawa, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Rueckert, D. DRINet for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Feng, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S. Deep Salient Object Detection with Dense Connections and Distraction Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 3239–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeghiazaryan, V.; Voiculescu, I. An Overview of Current Evaluation Methods Used in Medical Image Segmentation; Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14126980. [Google Scholar]
- Torch Contributors, Binary Cross Entropy. Available online: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.BCELoss.html (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Fidon, L.; Ourselin, S.; Vercauteren, T. Generalized Wasserstein dice score, distributionally robust deep learning, and ranger for brain tumor segmentation: BraTS 2020 challenge. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Lima, Peru, 4 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 200–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, F.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z. Modality-pairing learning for brain tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Lima, Peru, 4 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Cai, W.; Huang, H.; Xia, Y. H2 NF-Net for Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Multimodal MR Imaging: 2nd Place Solution to BraTS Challenge 2020 Segmentation Task. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Messaoudi, H.; Belaid, A.; Allaoui, M.L.; Zetout, A.; Allili, M.S.; Tliba, S.; Salem, D.B.; Conze, P.H. Efficient embedding network for 3D brain tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Lima, Peru, 4 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, C.; Liu, S.; Di Ieva, A. Impact of Spherical Coordinates Transformation Pre-processing in Deep Convolution Neural Networks for Brain Tumor Segmentation and Survival Prediction. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Qamar, S.; Shen, L.; Saeed, A. Context aware 3D UNet for brain tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Lima, Peru, 4 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.A.; Pinto, A.; Pereira, S.; Lopes, A. Multi-stage Deep Layer Aggregation for Brain Tumor Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Lima, Peru, 4 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, G.; Huang, H.; Yang, W.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lai, X. ME-Net: Multi-encoder net framework for brain tumor segmentation. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model Information | Dice Coefficient | Dataset | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | Avg. | |||
| Robust Deep Learning and Ranger for brain tumor segmentation 3D Unet | 88.9% | 81.4% | 84.1% | 85.0% | Brats2020 | [46] |
| Modality-Pairing learning method using 3D U-Net | 89.1% | 81.6% | 84.2% | 84.9% | BraTS2020 | [47] |
| Hybrid High-resolution and Non-local Feature Network | 91.3% | 78.8% | 85.5% | 85.2% | BraTS2020 | [48] |
| MobileNetV2 with residual blocks as encoder and upsampling part of U-Net as decoder | 91.4% | 83.3% | 88.1% | 87.6% | BraTS2020 | [28] |
| Asymmetric U-Net embedding network for 3D brain tumor segmentation | 80.7% | 69.7% | 75.2% | 75.2% | BraTS2020 | [49] |
| Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with spherical space transformed input data | 86.9% | 79.0% | 80.7% | 82.2% | BraTS2020 | [50] |
| Context Aware 3D UNet for Brain Tumor Segmentation | 89.1% | 79.1% | 84.7% | 84.3% | BraTS2020 | [51] |
| Cascade of three Deep Layer Aggregation neural networks | 88.6% | 79.0% | 83.0% | 83.5% | BraTS2020 | [52] |
| Multi-encoder Network for brain tumor segmentation | 70.2% | 73.9% | 88.3% | 77.5% | BraTS2020 | [53] |
| 3D-Znet encoder-decoder Network for 3D brain tumor segmentation | 90.6% | 84.5% | 85.9% | 87.0% | BraTS2020 | Current |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ottom, M.A.; Abdul Rahman, H.; Alazzam, I.M.; Dinov, I.D. Multimodal Stereotactic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D-Znet. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050581
Ottom MA, Abdul Rahman H, Alazzam IM, Dinov ID. Multimodal Stereotactic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D-Znet. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(5):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050581
Chicago/Turabian StyleOttom, Mohammad Ashraf, Hanif Abdul Rahman, Iyad M. Alazzam, and Ivo D. Dinov. 2023. "Multimodal Stereotactic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D-Znet" Bioengineering 10, no. 5: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050581
APA StyleOttom, M. A., Abdul Rahman, H., Alazzam, I. M., & Dinov, I. D. (2023). Multimodal Stereotactic Brain Tumor Segmentation Using 3D-Znet. Bioengineering, 10(5), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050581






