Manufacturing and Functional Characterization of Bioengineered Liver Grafts for Extracorporeal Liver Assistance in Acute Liver Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
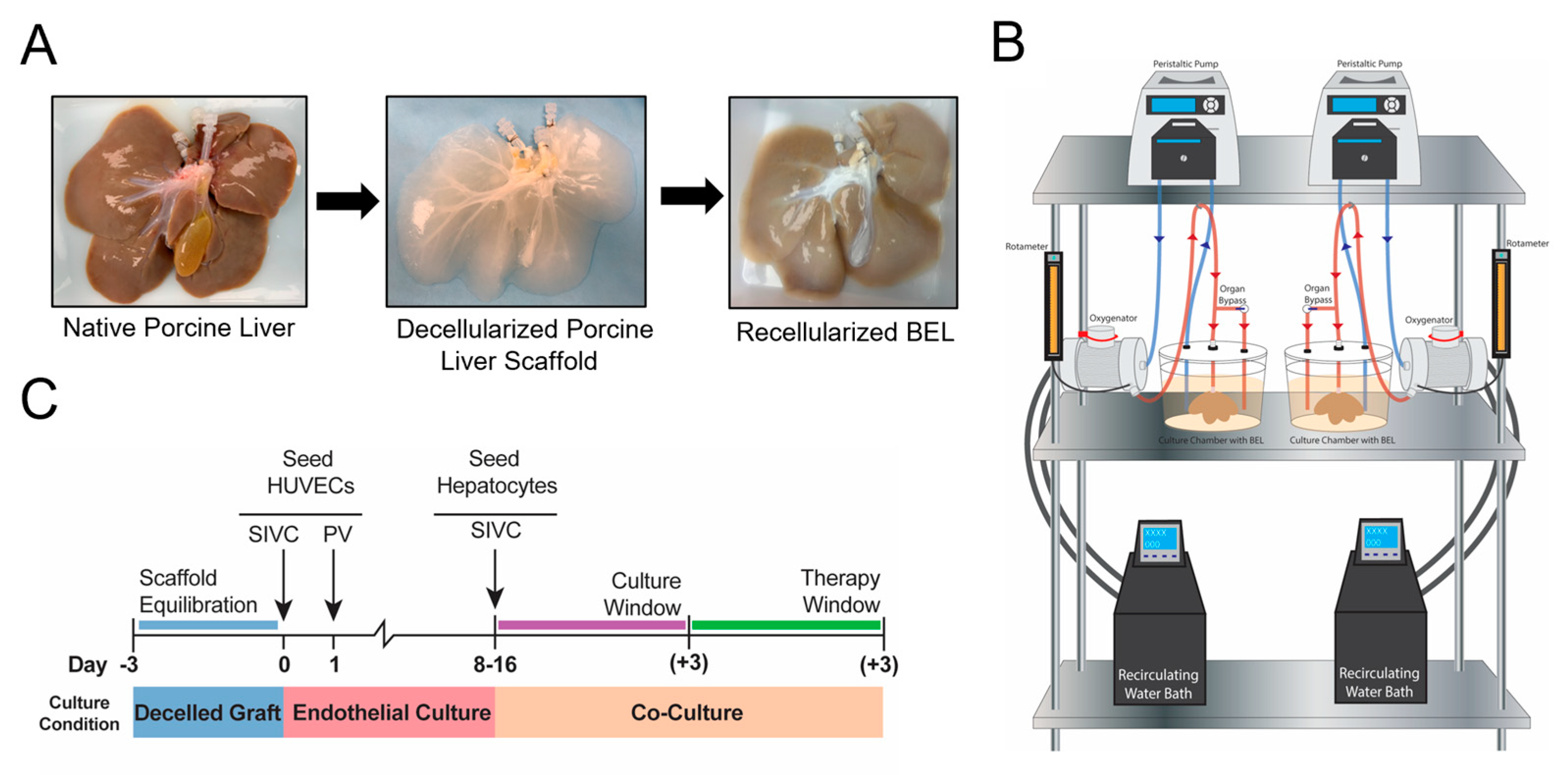
2.1. Porcine Organ Procurement and Whole Liver Decellularization
2.2. Evaluation of Viral Inactivation
2.3. Process Residuals Testing
2.4. BEL Culture and Seeding Overview
2.5. HUVEC Cell Culture and Seeding
2.6. Porcine Hepatocyte Isolation
2.7. Human Hepatocyte Isolation
2.8. HUVEC and Hepatocyte Characterization
2.9. Hepatocyte Seeding
2.10. Analysis of Metabolites
2.11. Quality Testing
2.12. BEL Ammonia Clearance
2.13. Data Analysis
2.14. Cold Storage and Transport Simulation
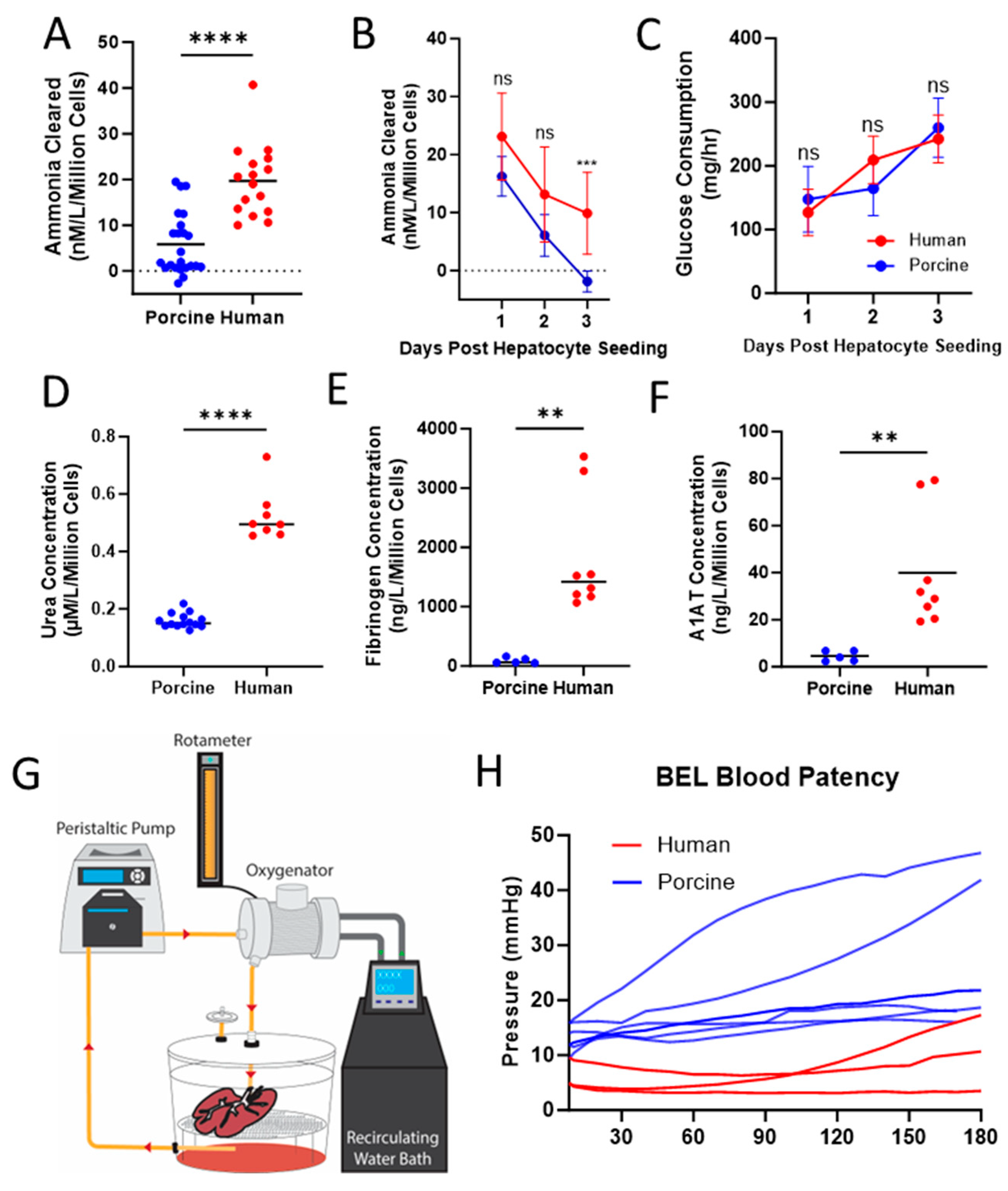
2.15. Blood Perfusion Studies
3. Results
3.1. Decellularization
3.2. HUVEC and Hepatocyte Characterization
3.3. Quality Testing
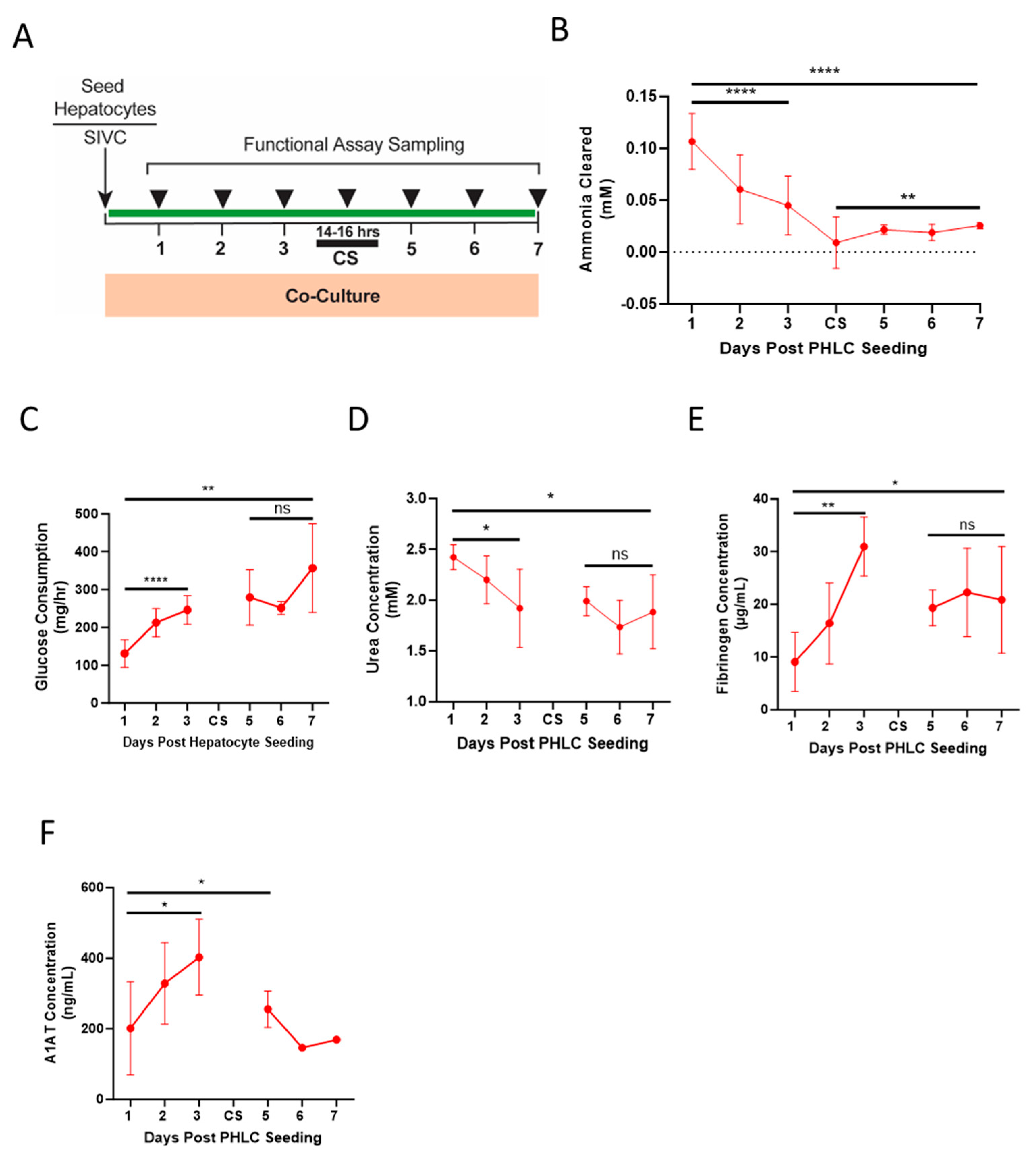
3.4. Functional Comparison between BELs Seeded with PPLCs and PHLCs
3.5. Cold Storage and Transport Simulation
4. Discussion
4.1. Manufacturing Process Creates a Viral, Residual, and Microbial-Free BEL
4.2. Fully Humanized BELs Demonstrate Higher Liver Specific Function When Compared to Porcine Seeded BELs
4.3. Humanized BELs Demonstrate Function through Simulated Transport and Clinically Relevant Therapy Window
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karvellas, C.J.; Leventhal, T.M.; Rakela, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Durkalski, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Fontana, R.J.; Stravitz, R.T.; Lake, J.R.; Lee, W.M.; et al. Outcomes of patients with acute liver failure listed for liver transplantation: A multicenter prospective cohort analysis. Liver Transpl. 2023, 29, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; Ellerbe, C.; Schilsky, M.; Stravitz, R.T.; Fontana, R.J.; Durkalski, V.; Lee, W.M. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Determinants of outcome among patients with acute liver failure listed for liver transplantation in the United States. Liver Transpl. 2016, 22, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pless, G.; Sauer, I.M. Bioartificial liver: Current status. Transpl. Proc. 2005, 37, 3893–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, J.; Lee, K.H. Liver support devices. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2008, 14, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, D.H. Bioartificial liver systems: Current status and future perspective. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetriou, A.A.; Brown, R.S.; Busuttil, R.W.; Fair, J.; McGuire, B.M.; Rosenthal, P.; Am Esch, J.S.; Lerut, J.; Nyberg, S.L.; Salizzoni, M.; et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann. Surg. 2004, 239, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millis, J.M.; Cronin, D.C.; Johnson, R.; Conjeevaram, H.; Conlin, C.; Trevino, S.; Maguire, P. Initial experience with the modified extracorporeal liver-assist device for patients with fulminant hepatic failure: System modifications and clinical impact. Transplant 2002, 74, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Tharwat, M.; Larson, E.L.; Felgendreff, P.; Hosseiniasl, S.M.; Rmilah, A.A.; Safwat, K.; Ross, J.J.; Nyberg, S.L. Re-endothelialization of decellularized liver scaffolds: A step for bioengineered liver transplantation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 833163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badylak, S.F.; Taylor, D.; Uygun, K. Whole-organ tissue engineering: Decellularization and recellularization of three-dimensional matrix scaffolds. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 13, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Zhang, L.; Medberry, C.; Fukumitsu, K.; Faulk, D.; Jiang, H.; Reing, J.; Gramignoli, R.; Komori, J.; Ross, M.; et al. A whole-organ regenerative medicine approach for liver replacement. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2011, 17, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.M.; Siddiqui, M.M.; Lozier, G.; Rodriguez, S.R.; Atala, A.; Soker, S. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology 2011, 53, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Shi, Y.; Sun, H.; Yin, X.; Yang, R.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Bu, H. Construction of a portal implantable functional tissue-engineered liver using perfusion-decellularized matrix and hepatocytes in rats. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Lessa, N.; Estrada, D.C.; Severson, E.B.; Lingala, S.; Zern, M.A.; Nolta, J.A.; Wu, J. Decellularized liver matrix as a carrier for the transplantation of human fetal and primary hepatocytes in mice. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, O.; Abbasi, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Rios, J.; Wood, R.P.; Ozaki, C.; Holley, L.S.; Gauthier, P.K. Use of decellularized porcine liver for engineering humanized liver organ. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 173, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Fukumitsu, K.; Fukuda, K.; Kitago, M.; Shinoda, M.; Obara, H.; Itano, O.; Kawachi, S.; Tanabe, M.; Coudriet, G.M.; et al. Human-scale whole-organ bioengineering for liver transplantation: A regenerative medicine approach. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Glorioso, J.; Elgilani, F.; De Lorenzo, S.; Deeds, M. Sustained In Vivo Perfusion of a Re-Endothelialized Tissue Engineered Porcine Liver. Int. J. Transplant. Res. Med. 2017, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaheen, M.F.; Joo, D.J.; Ross, J.J.; Anderson, B.D.; Chen, H.S.; Huebert, R.C.; Li, Y.; Amiot, B.; Young, A.; Zlochiver, V.; et al. Sustained perfusion of revascularized bioengineered livers heterotopically transplanted into immunosuppressed pigs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 437–445, Erratum in Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 4, 476 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.D.; Nelson, E.D.; Joo, D.; Amiot, B.P.; Katane, A.A.; Mendenhall, A.; Steiner, B.G.; Stumbras, A.R.; Nelson, V.L.; Palumbo, R.N.; et al. Functional characterization of a bioengineered liver after heterotopic implantation in pigs. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Q5A: Viral Safety Evaluation of Biotechnology Products Derived from Cell Lines of Human or Animal Origin. US Fed. Reg. 1998, 63, 51074. [Google Scholar]
- Sohlenius-Sternbeck, A.K. Determination of the hepatocellularity number for human, dog, rabbit, rat and mouse livers from protein concentration measurements. Toxicol. Vitr. 2006, 20, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoke, O.; Oluwole, J.; Parashurama, N. Bioengineering considerations in liver regenerative medicine. J. Biol. Eng. 2017, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.; Berthiaume, F.; Nath, B.D.; Tilles, A.W.; Toner, M.; Yarmush, M.L. Hepatic tissue engineering for adjunct and temporary liver support: Critical technologies. Liver Transpl. 2004, 10, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozga, J.; Williams, F.; Ro, M.S.; Neuzil, D.F.; Giorgio, T.D.; Backfisch, G.; Moscioni, A.D.; Hakim, R.; Demetriou, A.A. Development of a bioartificial liver: Properties and function of a hollow-fiber module inoculated with liver cells. Hepatology 1993, 17, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, I.K.; Okamoto, T.; Kim, B.H.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Chowdhury, J.R.; Fox, I.J. Transplantation of conditionally immortalized hepatocytes to treat hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1996, 24, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.D.; Shackleton, C.R.; Cohen, S.M.; Goldman, D.E.; Arnaout, W.S.; Hewitt, W.; Colquhoun, S.D.; Fong, T.L.; Vierling, J.M.; Busuttil, R.W.; et al. Treatment of acetaminophen-induced fulminant hepatic failure with a bioartificial liver. Transplant. Proc. 1997, 29, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 22442-3:2007; Medical Devices Utilizing Animal Tissues and Their Derivatives—Part 3: Validation of the Elimination and/or Inactivation of Viruses And Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy (TSE) Agents. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Guan, L.Y.; Fu, P.Y.; Li, P.D.; Li, Z.N.; Liu, H.Y.; Xin, M.G.; Li, W. Mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective effects of nitric oxide. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 27, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naorungroj, T.; Yanase, F.; Eastwood, G.M.; Baldwin, I.; Bellomo, R. Extracorporeal Ammonia Clearance for Hyperammonemia in Critically Ill Patients: A Scoping Review. Blood Purif. 2021, 50, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocskay, K.; Kanjo, A.; Gede, N.; Szakács, Z.; Pár, G.; Erőss, B.; Stange, J.; Mitzner, S.; Hegyi, P.; Molnár, Z. Uncertainty in the impact of liver support systems in acute-on-chronic liver failure: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Virus | Genome | Envelope | Size (nm) | Shape | Resistance | Log Reduction Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parvovirus (PPV) | DNA | - | 18–24 | Icosahedral | V. high | >6.00 |
| Pseudorabies (PRV) | DNA | + | 120–200 | Spherical | Medium | >6.00 |
| Reovirus 3 (Reo3) | RNA | - | 60–80 | Spherical | Medium | >6.00 |
| Murine Leukemia virus (MuLV) | RNA | + | 80–110 | Spherical | Low | >6.00 |
| Batch | Scaffolds Tested | Mass of Sample Tested (mg) | Residual DNA (ng/mg) | Total Triton (ppm) | Residual Triton (mg/20 g) | Total SDS (ppm) | Residual SDS (mg/20 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 76.8 | 116 | <1 | <LOD | <1 | <LOD |
| 2 | 73.6 | 102 | <1 | <LOD | <1 | <LOD | |
| B | 3 | 82.0 | 49 | <1 | <LOD | <1 | <LOD |
| 4 | 73.2 | 23 | <1 | <LOD | <1 | <LOD | |
| C | 5 | 81.4 | 102 | <1 | <LOD | <1 | <LOD |
| 6 | 83.9 | 82 | <1 | <LOD | <1 | <LOD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nelson, V.L.; Stumbras, A.R.; Palumbo, R.N.; Riesgraf, S.A.; Balboa, M.S.; Hannah, Z.A.; Bergstrom, I.J.; Fecteau, C.J.; Lake, J.R.; Barry, J.J.; et al. Manufacturing and Functional Characterization of Bioengineered Liver Grafts for Extracorporeal Liver Assistance in Acute Liver Failure. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101201
Nelson VL, Stumbras AR, Palumbo RN, Riesgraf SA, Balboa MS, Hannah ZA, Bergstrom IJ, Fecteau CJ, Lake JR, Barry JJ, et al. Manufacturing and Functional Characterization of Bioengineered Liver Grafts for Extracorporeal Liver Assistance in Acute Liver Failure. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(10):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101201
Chicago/Turabian StyleNelson, Victoria L., Aron R. Stumbras, R. Noelle Palumbo, Shawn A. Riesgraf, Marie S. Balboa, Zachary A. Hannah, Isaac J. Bergstrom, Christopher J. Fecteau, John R. Lake, John J. Barry, and et al. 2023. "Manufacturing and Functional Characterization of Bioengineered Liver Grafts for Extracorporeal Liver Assistance in Acute Liver Failure" Bioengineering 10, no. 10: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101201
APA StyleNelson, V. L., Stumbras, A. R., Palumbo, R. N., Riesgraf, S. A., Balboa, M. S., Hannah, Z. A., Bergstrom, I. J., Fecteau, C. J., Lake, J. R., Barry, J. J., & Ross, J. J. (2023). Manufacturing and Functional Characterization of Bioengineered Liver Grafts for Extracorporeal Liver Assistance in Acute Liver Failure. Bioengineering, 10(10), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101201






