Physical, Chemical and Functional Attributes of Neera Honey Infused Extrudates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Raw Materials for Extrusion
2.3. Extrusion
2.4. Measurement of Physical Properties
2.5. Measurement of Functional Properties
2.6. Measurement of Color Properties
2.7. Measurement of Biochemical Properties
2.8. Estimation of Mineral Contents
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Raw Material Analysis
3.1.1. Functional Properties and Proximate Composition of Raw Materials Used for Preparation of Extrudates
3.1.2. Biochemical Composition of Raw Materials Used for Preparation of Extrudates
3.1.3. Mineral Profile of Raw Materials Used for Preparation of Extrudates
3.2. Neera Honey Incorporated Extrudates
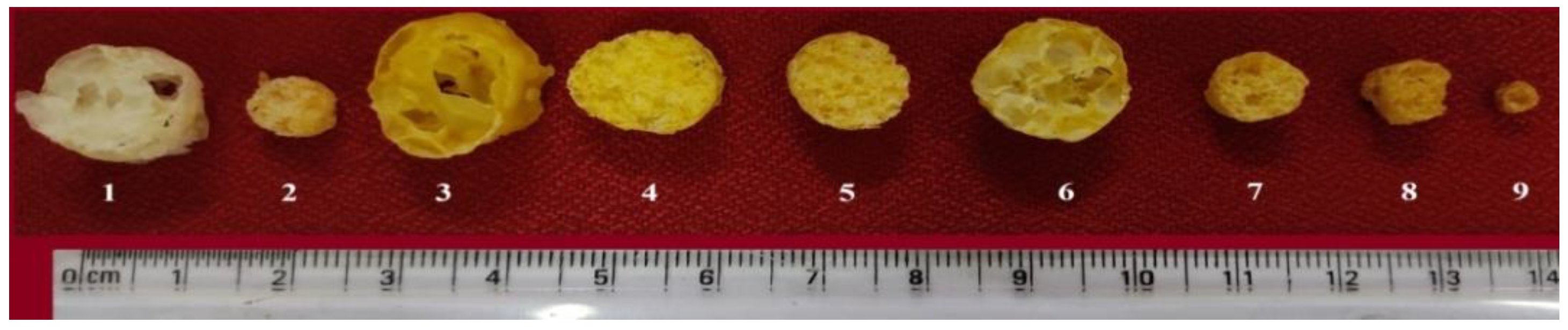
3.2.1. Physical Properties of Neera Honey Infused Extrudates
Expansion Ratio
Bulk Density
Specific Length
3.2.2. Functional Properties of Neera Honey Incorporated Extrudates
Water Absorption Index
Water Solubility Index
Oil Absorption Index
3.2.3. Color Attributes of Neera Honey Incorporated Extrudates
3.2.4. Biochemical Properties of Neera Honey Extrudates
3.2.5. Proximate Composition of Neera Honey Incorporated Extrudates
3.2.6. Phenolics, Flavonoids, Vitamin C and Antioxidant Properties of Neera Honey Based Extrudates
3.2.7. Mineral Composition of Neera Honey Incorporated Extrudates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- İbanogˇlu, Ş.; Ainsworth, P.; Özer, E.A.; Plunkett, A. Physical and sensory evaluation of a nutritionally balanced gluten-free extruded snack. J. Food Eng. 2006, 75, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, R.J.; Medina-Meza, I.G.; Thapa, B.B.; Murphy, K.M.; Ganjyal, G. Extrusion processing characteristics of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) var. Cherry Vanilla. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 70, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köksel, H.; Ryu, G.H.; Basman, A.; Demiralp, H.; Ng, P.K. Effects of extrusion variables on the properties of waxy hulless barley extrudates. Food/Nahrung 2004, 48, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbar, K.; Mathew, A.; Arivalagan, M.; Samsudeen, K.; Thomas, G.V. Value added products from Neera. Indian Coconut J. 2013, 56, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Pandiselvam, R.; Manikantan, M.; Sunoj, S.; Sreejith, S.; Beegum, S. Modeling of coconut milk residue incorporated rice-corn extrudates properties using multiple linear regression and artificial neural network. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikantan, M.; Arivalagan, M.; Mathew, A.; Hebbar, K. Effect of processing parameters on recovery of hot process virgin coconut oil and co-products utilization. J. Plant. Crops 2015, 43, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavendra, S.; Swamy, S.R.; Rastogi, N.; Raghavarao, K.; Kumar, S.; Tharanathan, R. Grinding characteristics and hydration properties of coconut residue: A source of dietary fiber. J. Food Eng. 2006, 72, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinidad, T.P.; Valdez, D.H.; Loyola, A.S.; Mallillin, A.C.; Askali, F.C.; Castillo, J.C.; Masa, D.B. Glycaemic index of different coconut (Cocos nucifera)-flour products in normal and diabetic subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegum, P.S.; Sharma, M.; Manikantan, M.; Pandiselvam, R.; Gupta, R. Incorporation of coconut milk residue in pasta: Influence on cooking quality, sensory and physical properties. Indian Soc. Plant. Crops 2021, 49, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, K.; Arivalagan, M.; Pavithra, K.; Roy, T.; Gopal, M.; Shivashankara, K.; Chowdappa, P. Nutritional profiling of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) inflorescence sap collected using novel coco-sap chiller method and its value added products. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, P.; Mangalassery, S.; Shradha, K.; Pandiselvam, R.; Manikantan, M.; Reddy, S.; Devi, S.R.; Nayak, M. Cashew apple pomace powder enriched the proximate, mineral, functional and structural properties of cereal based extrudates. LWT 2021, 139, 110539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Conway, H.; Peplinski, A. Gelatinization of corn grits by roll cooking, extrusion cooking and steaming. Starch-Stärke 1970, 22, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.t.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somogyi, M. Notes on sugar determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, K.N.; Prasadani, W.C.; Jayawardena, B. Phenolic extracts of coconut oil cake: A potential alternative for synthetic antioxidants. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.; Ray, S. Determination of plasma ascorbic acid by 2, 6-dichlorophenol indophenol titration. Lancet 1935, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Apak, R.; Güçlü, K.; Özyürek, M.; Karademir, S.E. Novel total antioxidant capacity index for dietary polyphenols and vitamins C and E, using their cupric ion reducing capability in the presence of neocuproine: CUPRAC method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7970–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists International, 18th ed.; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Methods of Analysis for Soils, Plants and Waters; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1961; Volume 150-1, pp. 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, H.A. Toward practical definitions of quality for food science. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, S.; Wani, I.A.; Gani, A.; Sharma, P.; Wani, H.M.; Masoodi, F.A.; Khan, A.A.; Hamdani, A.M. Effect of water and ether extraction on functional and antioxidant properties of Indian horse chestnut (Aesculus indica Colebr) flour. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2016, 10, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, R.; Shen, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Studies on Quality of Potato Flour Blends with Rice Flour for Making Extruded Noodles. Cereal Chem. J. 2016, 93, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Singh, Y.; Anil, A. Effects of grinding methods on the characteristics of Pusa 1121 rice flour. J. Trop. Agric. Food Sci. 2015, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Alcázar-Alay, S.C.; Meireles, M.A.A. Physicochemical properties, modifications and applications of starches from different botanical sources. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otegbayo, B.; Oguniyan, D.; Akinwumi, O. Physicochemical and functional characterization of yam starch for potential industrial applications. Starch 2014, 66, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Bains, G. Effect of some extruder variables on physico-chemical properties of extruded rice—Legume blends. Food Chem. 1988, 27, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.S.; Munira, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.; Hasan, M.; Siddique, M.A.H.; Biswas, S.; Khan, M.H.; Rahman, M. Analysis of biochemical composition of honey and its anti-oxidant, Phytochemical and anti-bacterial properties. J. Biomed. Pharm. Res. 2015, 4, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bhati, D.; Singh, B.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S.; Pandiselvam, R. Assessment of physicochemical, rheological, and thermal properties of Indian rice cultivars: Implications on the extrusion characteristics. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 854–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.P.; Dalbhagat, C.G.; Mishra, H.N. Development of instant low glycemic rice using extrusion technology and its characterization. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e16077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajita, T.; Jha, S.L. Extrusion Cooking Technology: Principal Mechanism and Effect on Direct Expanded Snacks—An Overview. Int. J. Food Stud. 2017, 6, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Arivalagan, M.; Manikantan, M.; Yasmeen, A.; Sreejith, S.; Balasubramanian, D.; Hebbar, K.; Kanade, S.R. Physiochemical and nutritional characterization of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) haustorium based extrudates. LWT 2018, 89, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suknark, K.; Phillips, R.; Chinnan, M. Physical properties of directly expanded extrudates formulated from partially defatted peanut flour and different types of starch. Food Res. Int. 1997, 30, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Jindal, N.; Sharma, S.; Nanda, V. Physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of extrudates developed from honey and barley. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobade, H.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, A.; Singh, B. Effect of extrusion conditions and honey on functionality and bioactive composition of whole wheat flour-based expanded snacks. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.; Sanei, A.; Van Hecke, E.; Bouvier, J. Effect of ingredients on physical/structural properties of extrudates. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, S.; Hamann, D.; Schwartz, S. Effect of starch gelatinization on physical properties of extrused wheat-and corn-based products. Cereal Chem. 1992, 69, 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Basediya, A.; Pandey, S.; Shrivastava, S.; Khan, K.A.; Nema, A. Effect of process and machine parameters on physical properties of extrudate during extrusion cooking of sorghum, horse gram and defatted soy flour blends. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.-B.; Ainsworth, P.; Tucker, G.; Marson, H. The effect of extrusion conditions on the physicochemical properties and sensory characteristics of rice-based expanded snacks. J. Food Eng. 2005, 66, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezreb, K.; Goullieux, A.; Ralainirina, R.; Queneudec, M. Application of image analysis to measure screw speed influence on physical properties of corn and wheat extrudates. J. Food Eng. 2003, 57, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, N.L.; Vamadevan, V.; Bruni, G.P.; Ferreira, C.D.; Pinto, V.Z.; Seetharaman, K.; Zavareze, E.d.R.; Elias, M.C.; Berrios, J.D. Extrusion of rice, bean and corn starches: Extrudate structure and molecular changes in amylose and amylopectin. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, E2932–E2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.; Schmiele, M.; Steel, C.J. Development of whole grain wheat flour extruded cereal and process impacts on color, expansion, and dry and bowl-life texture. LWT 2017, 75, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Threinen, D.; Hansen, M.; Driedger, D. Effects of extrusion conditions on system parameters and physical properties of a chickpea flour-based snack. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, H.; Kozlowska, H.; Lewczuk, B. Bioactive compounds in the cereal grains before and after hydrothermal processing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2001, 2, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, M.G.; Hollman, P.C.; Van de Putte, B. Content of potentially anticarcinogenic flavonoids of tea infusions, wines, and fruit juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gamlath, S.; Wakeling, L. Nutritional aspects of food extrusion: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.R.; Fernández, P.C.R.; Rodríguez, E.O.C.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rochín, S.M. Changes in nutritional properties and bioactive compounds in cereals during extrusion cooking. In Extrusion of Metals, Polymers and Food Products; Qamar, S.Z., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 104–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghan-Shoar, Z.; Hardacre, A.K.; Brennan, C.S. The physico-chemical characteristics of extruded snacks enriched with tomato lycopene. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
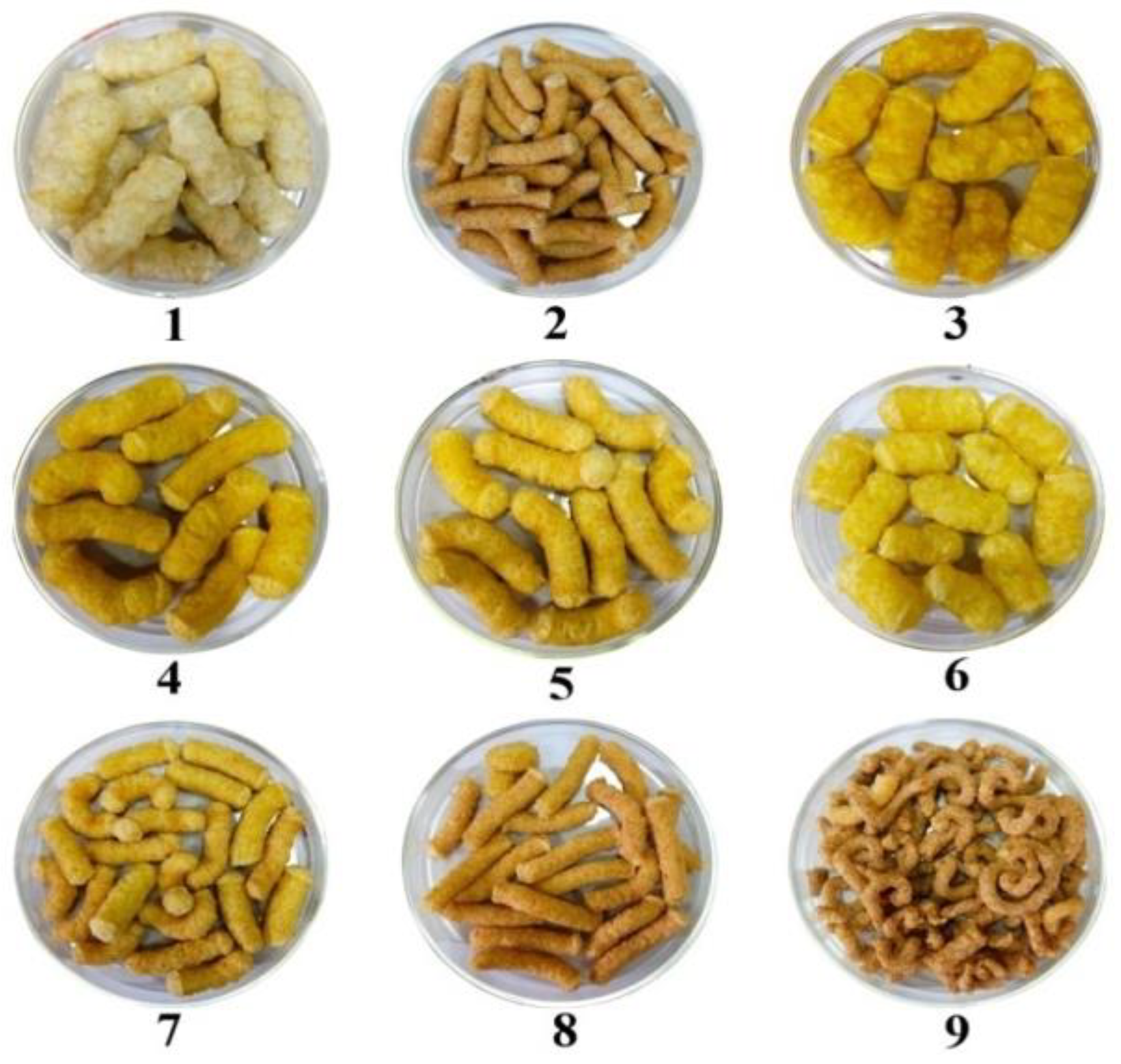

| Materials | Formulation |
|---|---|
| 100% RF + 16% feed moisture with water | F1 |
| 100% RF + 16% feed moisture with NH | F2 |
| 100% CF + 16% feed moisture with water | F3 |
| 100% CF +16% feed moisture with NH | F4 |
| 50% RF + 50% CF + 16% feed moisture with NH | F5 |
| 50% RF + 50% CF + 16% feed moisture with water | F6 |
| 60% RF + 25% CF + 15% CMR + 16% feed moisture with NH | F7 |
| 100% RF + 20% feed moisture with NH | F8 |
| 85% RF + 15% CMR + 20% feed moisture with NH prepared. | F9 |
| Parameters | Raw Materials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Flour | Corn Flour | Coconut Milk Residue | Neera Honey | |
| Functional properties | ||||
| WAI | 2.39B ± 0.05 | 2.18B ± 0.11 | 7.12A ± 0.39 | Fully soluble |
| WSI (%) | 1.19D ± 0.56 | 5.87C ± 2.10 | 12.03B ± 0.12 | 89.22A ± 0.73 |
| OAI (ml/g) | 1.20B ± 0.05 | 1.21B ± 0.01 | 1.31A ±0.03 | 1.30A ±0.05 |
| Proximate composition | ||||
| Moisture content (% wb) | 9.30B ± 0.09 | 8.38C ± 0.48 | 5.72D ± 0.04 | 29.96A ± 0.00 |
| Ash (%) | 0.34B ± 0.35 | 1.37A ± 0.00 | 0.93A ± 0.06 | 0.24B ± 0.07 |
| Fat (%) | 1.12B ± 1.02 | 4.24B ± 0.92 | 44.04A ± 4.96 | 0.044B ± 0.01 |
| Protein (%) | 9.44A ± 1.01 | 7.291B ± 0.49 | 7.297B ± 0.21 | 1.41C ± 0.21 |
| Parameters | Raw Materials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Flour | Corn Flour | Coconut Milk Residue | Neera Honey | |
| Biochemical analysis | ||||
| Total carbohydrate (%) | 92.03A ± 3.11 | 49.29B ± 2.23 | 32.09C ± 4.11 | 30.62C ± 7.26 |
| Total sugar (%) | 0.19B ± 0.10 | 2.73B ± 0.49 | 1.26B ± 0.01 | 68.39A ± 6.09 |
| Reducing sugar (%) | 0.06C ± 0.00 | 0.23B ± 0.01 | 0.10C ± 0.01 | 1.01A ± 0.04 |
| Total Phenols (mg GAE/100 g) | 0.304B ± 0.19 | 0.386B ± 0.03 | 0.237B ± 0.07 | 1.155A ± 0.04 |
| Total Flavonoids (mg QE/100 g) | 0.831C ± 0.01 | 2.400A ± 0.03 | 1.240B ± 0.23 | 0.173D ± 0.09 |
| CUPRAC (mg TE/100 g) | 1.09B ± 0.25 | 3.35A ± 0.39 | 1.22B ± 0.06 | 1.38B ± 0.48 |
| FRAP (mg TE/100 g) | 0.026C ± 0.00 | 0.318A ± 0.02 | 0.047C ± 0.00 | 0.076B ± 0.00 |
| Ascorbic acid (mg/100 g) | 2.34B ± 0.00 | 4.67B ± 0.00 | 3.51B ± 0.00 | 39.21A ± 2.48 |
| Parameters | Raw Materials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Flour | Corn Flour | Coconut Milk Residue | Neera Honey | |
| Mineral profile (mg/100 g) | ||||
| Major minerals | ||||
| Calcium | 87.34 ± 0.30 | 131.34 ± 0.56 | 196.67 ± 25.69 | 114.51 ± 42.19 |
| Phosphorus | 70.27 ± 5.77 | 282.57 ± 14.41 | 97.34 ± 8.45 | 42.78 ± 1.85 |
| Magnesium | 104.81 ± 0.35 | 26.27 ± 0.11 | 78.60 ± 30.10 | 73.62 ± 26.27 |
| Potassium | 43.6675 ± 10.34 | 231.85 ± 3.79 | 143.75 ± 1.65 | 528.27 ± 55.26 |
| Sodium | 22.83 ± 15.08 | 130.88 ± 15.33 | 68.84 ± 30.35 | 355.21 ± 22.36 |
| Sulphur | 40.42 ± 9.28 | 58.6 ± 3.39 | 36.25 ± 8.13 | 36.75 ± 11.79 |
| Minor minerals | ||||
| Iron | 1.48 ± 1.02 | 5.64 ± 0.18 | 3.12 ± 1.89 | 1.30 ± 0.95 |
| Manganese | 2.02 ± 1.34 | 0.85 ± 0.08 | 3.84 ± 0.16 | 0.45 ± 0.16 |
| Zinc | 2.14 ± 0.33 | 3.50 ± 0.15 | 2.20 ± 0.11 | 3.39 ± 4.21 |
| Copper | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 0.48 ± 0.00 | 1.10 ± 0.09 | 0.61 ± 0.13 |
| Extrudate Formulation | Expansion Ratio (ER) | Bulk Density (BD) (g/mL) | Specific Length (SL) (mm/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 3.60C ± 0.13 | 0.098F ± 0.002 | 38.20BC ± 0.93 |
| F2 | 1.92G ± 0.01 | 0.205D ± 0.001 | 42.21B ± 2.49 |
| F3 | 4.02A ± 0.19 | 0.079H ± 0.001 | 33.99C ± 1.37 |
| F4 | 3.38D ± 0.18 | 0.088G ± 0.00 | 39.59BC ± 1.01 |
| F5 | 2.86E ± 0.02 | 0.126E ± 0.002 | 40.60BC ± 1.12 |
| F6 | 3.78B ± 0.02 | 0.090G ± 0.002 | 35.67BC ± 0.42 |
| F7 | 2.33F ± 0.16 | 0.215C ± 0.004 | 41.8BC ± 0.82 |
| F8 | 1.91G ± 0.01 | 0.252B ± 0.002 | 43.26B ± 3.63 |
| F9 | 1.64H ± 0.09 | 0.281A ± 0.007 | 95.51A ± 15.96 |
| Extrudate Formulation | Water Absorption Index (WAI) | Water Solubility Index (WSI) (%) | Oil Absorption Index (OAI) (mL/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 6.17B ± 0.11 | 13.98DBC ± 1.39 | 1.55 ± 0.06 |
| F2 | 3.49CD ± 0.12 | 14.63BC ± 1.23 | 1.45 ± 0.01 |
| F3 | 7.47A ± 0.25 | 10.17DE ± 0.85 | 1.47 ± 0.04 |
| F4 | 5.95B ± 0.01 | 10.83DEC ± 2.08 | 1.54 ± 0.03 |
| F5 | 5.65B ± 1.07 | 11.72DC ± 0.25 | 1.52 ± 0.03 |
| F6 | 5.80B ± 0.58 | 7.27E ± 3.55 | 1.52 ± 0.05 |
| F7 | 3.73C ± 0.10 | 17.59B ± 1.31 | 1.41 ± 0.12 |
| F8 | 3.27CD ± 0.23 | 14.14DBC ± 0.28 | 1.55 ± 0.17 |
| F9 | 2.61D ± 0.07 | 24.23A ± 2.28 | 1.53 ± 0.01 |
| Extrudates Combination | Color Attributes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| L* | A* | B* | |
| F1 | 57.82AB ± 4.23 | −0.57EF ± 0.21 | 9.99D ± 1.73 |
| F2 | 50.35C ± 2.39 | 5.11A ± 0.38 | 15.92C ± 0.72 |
| F3 | 50.52C ± 3.50 | −0.09E ± 0.46 | 21.41B ± 1.57 |
| F4 | 62.46A ± 0.72 | 2.07D ± 0.45 | 26.73A ± 0.36 |
| F5 | 57.90AB ± 4.82 | 2.88C ± 0.55 | 22.01B ± 2.25 |
| F6 | 56.77B ± 2.59 | −1.05F ± 0.47 | 20.57B ± 2.41 |
| F7 | 54.54CB ± 3.87 | 3.87B ± 0.75 | 20.28B ± 1.53 |
| F8 | 42.91D ± 5.36 | 5.58A ± 0.92 | 14.92C ± 1.86 |
| F9 | 37.68E ± 2.31 | 4.90A ± 0.28 | 11.49D ± 0.80 |
| Extrudates Combination | Total Carbohydrate (%) | Total Sugar (%) | Reducing Sugar (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 56.49C ± 1.35 | 4.56E ± 0.92 | 0.29C ± 0.08 |
| F2 | 65.19DCB ± 2.34 | 19.82DBC ± 4.55 | 0.35C ± 0.34 |
| F3 | 80.54AB ± 5.15 | 1.78E ± 0.55 | 0.10C ± 0.04 |
| F4 | 78.64AB ± 22.06 | 17.47DC ± 0.49 | 0.80C ± 0.38 |
| F5 | 65.32DCB ± 8.15 | 26.91B ± 4.12 | 1.11CB ± 0.40 |
| F6 | 63.42DCB ± 7.61 | 2.30E ± 0.68 | 0.03C ± 0.01 |
| F7 | 64.10DCB ± 4.11 | 12.60D ± 0.12 | 0.21C ± 0.06 |
| F8 | 69.02CB ± 0.15 | 25.43BC ± 5.96 | 2.81A ± 1.31 |
| F9 | 63.58DCB ± 0.77 | 36.82A ± 5.72 | 2.11AB ± 0.16 |
| Extrudates Combination | Moisture Content (%w.b) | Ash (%) | Fat (%) | Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 6.38 ± 1.15 | 0.29 ± 0.13 | 1.42 ± 0.81 | 7.99 ± 0.14 |
| F2 | 5.56 ± 0.07 | 0.68 ± 0.41 | 1.14 ± 0.35 | 7.97 ± 0.01 |
| F3 | 8.56 ± 1.37 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 2.14 ± 1.13 | 8.77 ± 0.45 |
| F4 | 6.47 ± 0.91 | 0.59 ± 0.00 | 1.52 ± 0.81 | 8.33 ± 0.24 |
| F5 | 6.44 ± 1.37 | 0.74 ± 0.35 | 1.74 ± 0.99 | 8.20 ± 0.09 |
| F6 | 10.61 ± 3.17 | 0.39 ± 0.00 | 1.94 ± 1.34 | 8.24 ± 0.02 |
| F7 | 3.76 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 4.90 ± 0.75 | 9.23 ± 1.64 |
| F8 | 6.63 ± 0.88 | 0.89 ± 0.13 | 4.96 ± 2.72 | 7.69 ± 0.12 |
| F9 | 6.25 ± 2.12 | 0.68 ± 0.13 | 3.20 ± 0.61 | 7.51 ± 0.14 |
| Extrudates Combination | Phenolic Content (mg GAE/100 g) | Flavonoid Content (mg QE/100 g) | Vitamin C (mg/100 g) | Antioxidant Potential | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUPRAC (mg TE/100 g) | FRAP (mg TE/100 g) | ||||
| F1 | 0.178DB ± 0.01 | 0.361B ± 0.11 | 4.70DE ± 0.01 | 1.11EF ± 0.47 | 0.048D ± 0.007 |
| F2 | 0.197CDB ± 0.01 | 0.177 D ± 0.02 | 8.78C ± 0.83 | 0.80F ± 0.13 | 0.068CAB ± 0.005 |
| F3 | 0.161D ± 0.03 | 0.528A ± 0.00 | 2.34F ± 0.01 | 2.97A ± 0.27 | 0.072AB ± 0.006 |
| F4 | 0.171CD ± 0.04 | 0.303BC ± 0.00 | 5.85D ± 0.01 | 2.30B ± 0.04 | 0.076A ± 0.002 |
| F5 | 0.212CDB ± 0.04 | 0.211DC ± 0.04 | 7.61C ± 0.80 | 2.09BC ± 0.29 | 0.067CB ± 0.001 |
| F6 | 0.188CDB ± 0.02 | 0.245DC ± 0.03 | 3.51FE ± 0.00 | 1.89DBC ± 0.12 | 0.061C ± 0.001 |
| F7 | 0.359A ± 0.10 | 0.180D ± 0.04 | 14.02B ± 0.03 | 1.24DEF ± 0.49 | 0.069CAB ± 0.001 |
| F8 | 0.277CAB ± 0.05 | 0.208DC ± 0.00 | 17.58A ± 1.62 | 1.49DEC ± 0.03 | 0.070AB ± 0.00 |
| F9 | 0.286AB ± 0.03 | 0.201DC ± 0.03 | 17.59A ± 0.07 | 1.26DEF ± 0.16 | 0.076A ± 0.00 |
| Extrudates Combination | Ca (mg/100 g) | P (mg/100 g) | Mg (mg/100 g) | K (mg/100 g) | Na (mg/100 g) | S (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 97.74B ± 22.15 | 75.94BC ± 20.05 | 97.65A ± 12.76 | 46.84E ± 3.83 | 31.21B ± 20.22 | 62.72 ± 25.03 |
| F2 | 151.58A ± 23.85 | 69.47C ± 11.34 | 84.40AB ± 24.34 | 102.86CDB ± 15.78 | 49.67B ± 27.82 | 45.77 ± 18.69 |
| F3 | 184.80A ± 22.02 | 86.90B ± 6.23 | 65.10AB ± 44.96 | 100.01CD ± 16.60 | 48.70B ± 15.10 | 42.24 ± 29.47 |
| F4 | 152.42A ± 24.07 | 87.38B ± 7.17 | 52.30B ± 0.53 | 117.60CAB ± 4.10 | 60.24B ± 15.71 | 37.76 ± 9.58 |
| F5 | 108.61B ± 25.79 | 79.86BC ± 8.17 | 91.05A ± 14.42 | 100.86CDB ± 4.96 | 48.19B ± 24.42 | 46.80 ± 17.42 |
| F6 | 152.07A ± 24.19 | 80.08BC ± 10.63 | 65.30AB ± 15.52 | 91.29D ± 19.06 | 42.29B ± 12.67 | 56.30 ± 17.12 |
| F7 | 173.33A ± 2.43 | 79.42BC ± 5.38 | 52.00B ± 0.73 | 110.59CAB ± 6.03 | 53.63B ± 20.34 | 48 ± 20.70 |
| F8 | 173.83A ± 0.85 | 103.16A ± 2.24 | 91.23A ± 14.80 | 119.02AB ± 9.78 | 114.07A ± 4.33 | 52.78 ± 16.86 |
| F9 | 152.06A ± 24.84 | 87.58B ± 4.08 | 91.24A ± 14.90 | 126.93A ± 10.56 | 107.64A ± 11.32 | 44.61 ± 8.65 |
| Extrudates Combination | Fe (mg/100 g) | Mn (mg/100 g) | Zn (mg/100 g) | Cu (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 9.42BC ±1.71 | 1.31BC ± 0.16 | 2.15A ± 0.31 | 0.540B ± 0.06 |
| F2 | 5.65D ± 3.77 | 1.17DC ± 0.04 | 1.85AB ± 0.34 | 0.820A ± 0.06 |
| F3 | 16.20A ± 0.22 | 0.73E ± 0.14 | 1.29CB ± 0.12 | 0.545B ± 0.10 |
| F4 | 16.05A ± 2.22 | 0.66E ± 0.16 | 0.94C ± 0.56 | 0.552B ± 0.22 |
| F5 | 11.09B ± 0.33 | 0.96 D ± 0.18 | 1.36CB ± 0.51 | 0.560B ± 0.15 |
| F6 | 14.31A ± 1.40 | 1.17 DC ± 0.14 | 1.47CB ± 0.21 | 0.757AB ± 0.19 |
| F7 | 7.21DC ± 1.09 | 1.47B ± 0.22 | 1.38CB ± 0.40 | 0.560B ± 0.14 |
| F8 | 2.86E ± 0.85 | 1.26BC ± 0.13 | 1.43CB ± 0.33 | 0.542B ± 0.11 |
| F9 | 7.68DC ± 1.10 | 1.71A ± 0.17 | 1.53CB ± 0.26 | 0.677AB ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandiselvam, R.; Joseph, L.T.; Manikantan, M.R.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Beegum, P.P.S.; Ramesh, S.V.; Balasubramanian, D.; Neenu, S.; Gopal, M.; Mathew, A.C.; et al. Physical, Chemical and Functional Attributes of Neera Honey Infused Extrudates. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010114
Pandiselvam R, Joseph LT, Manikantan MR, Khanashyam AC, Beegum PPS, Ramesh SV, Balasubramanian D, Neenu S, Gopal M, Mathew AC, et al. Physical, Chemical and Functional Attributes of Neera Honey Infused Extrudates. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010114
Chicago/Turabian StylePandiselvam, Ravi, Liya T. Joseph, M. R. Manikantan, Anandu Chandra Khanashyam, P. P. Shameena Beegum, S. V. Ramesh, D. Balasubramanian, S. Neenu, Murali Gopal, A. C. Mathew, and et al. 2023. "Physical, Chemical and Functional Attributes of Neera Honey Infused Extrudates" Bioengineering 10, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010114
APA StylePandiselvam, R., Joseph, L. T., Manikantan, M. R., Khanashyam, A. C., Beegum, P. P. S., Ramesh, S. V., Balasubramanian, D., Neenu, S., Gopal, M., Mathew, A. C., & Hebbar, K. B. (2023). Physical, Chemical and Functional Attributes of Neera Honey Infused Extrudates. Bioengineering, 10(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010114







