Analysis of the 2014 Wet Extreme in Bulgaria: Anomalies of Temperature, Precipitation and Terrestrial Water Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
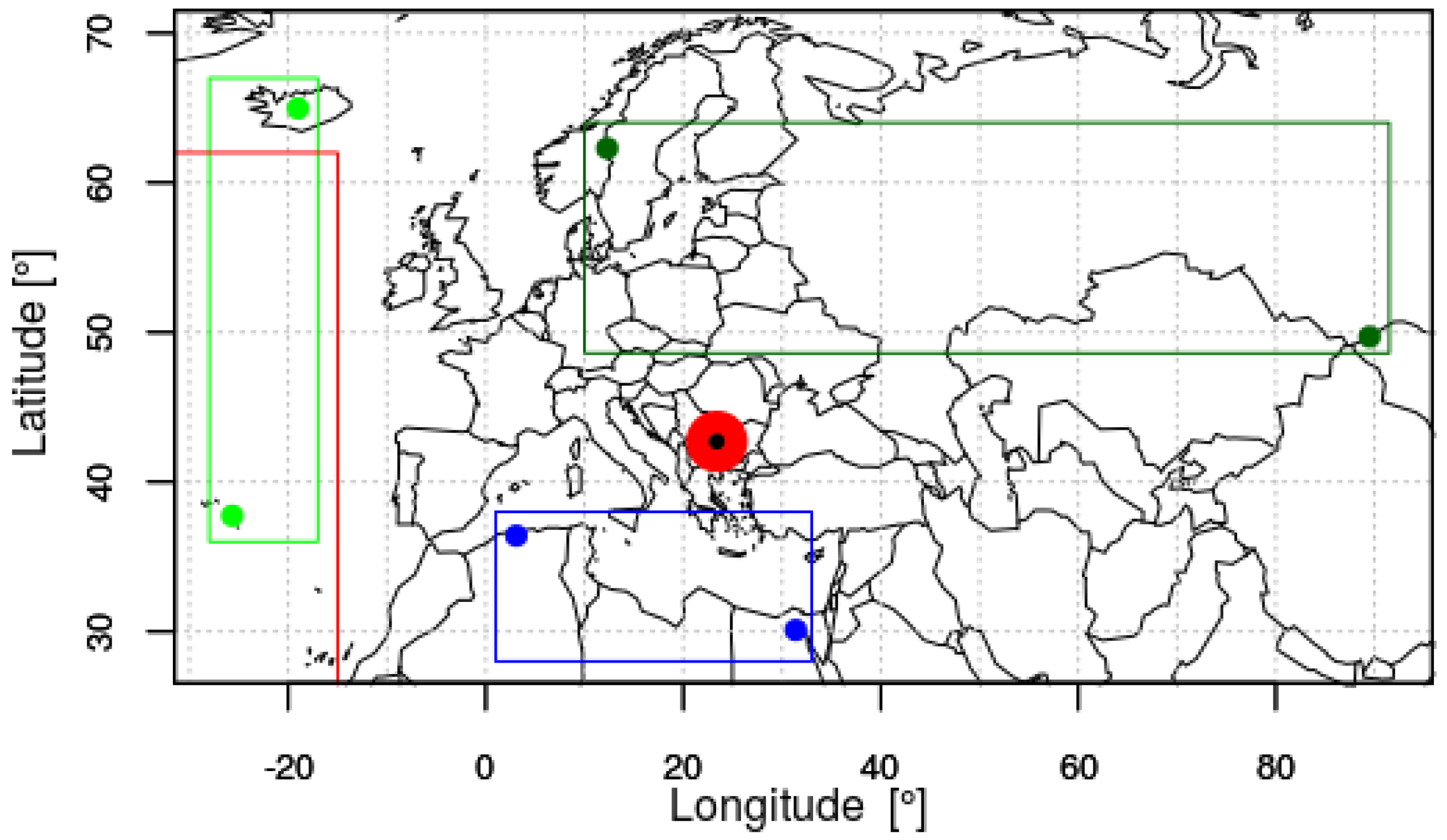
2. Data Sets and Method
2.1. Grace TWS Data
2.2. Surface Synoptic Data
2.3. ERA5
2.4. Oscillation Indices
2.5. Decomposition Method
3. 2014 Wet Extreme in Bulgaria: Time Series Analysis
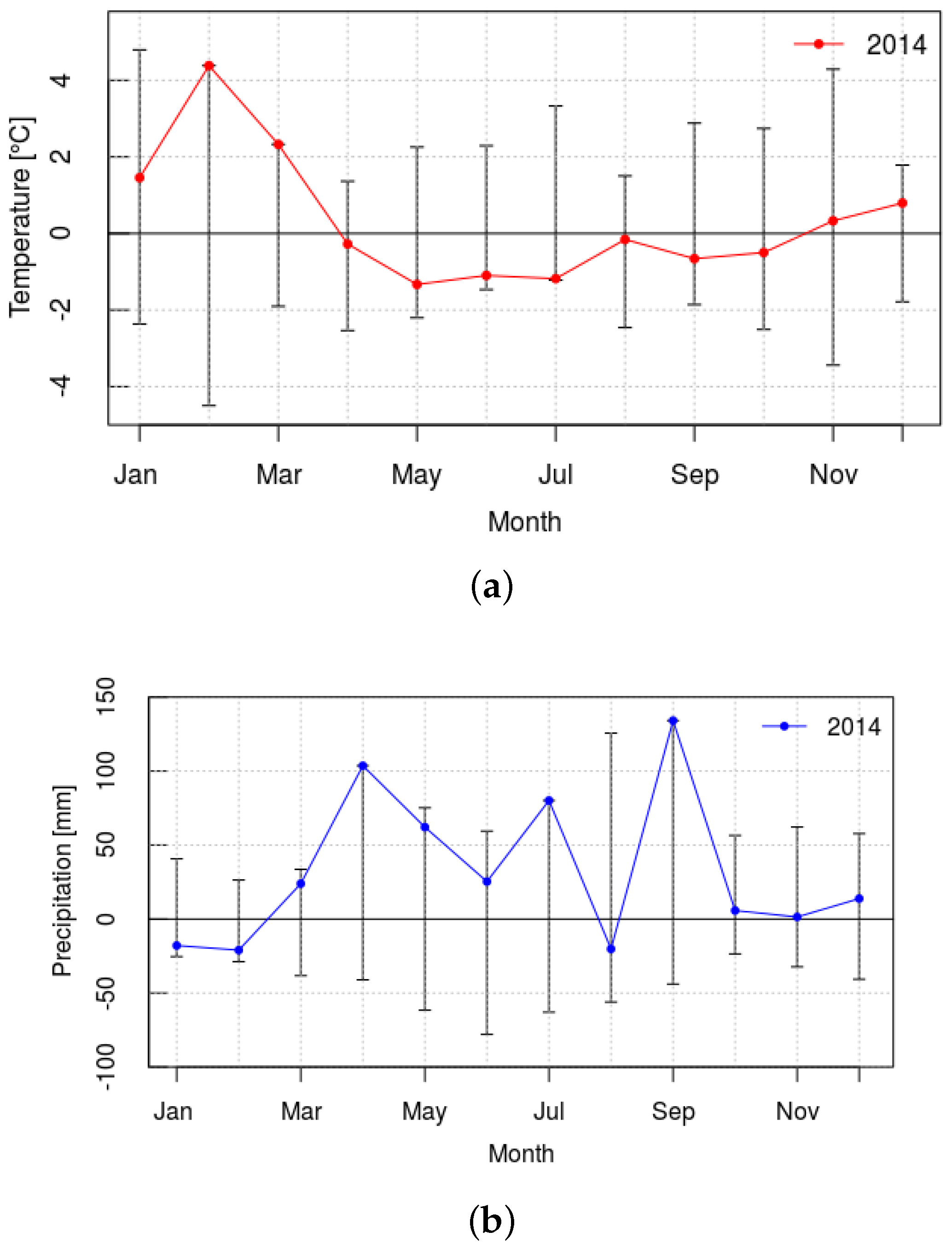
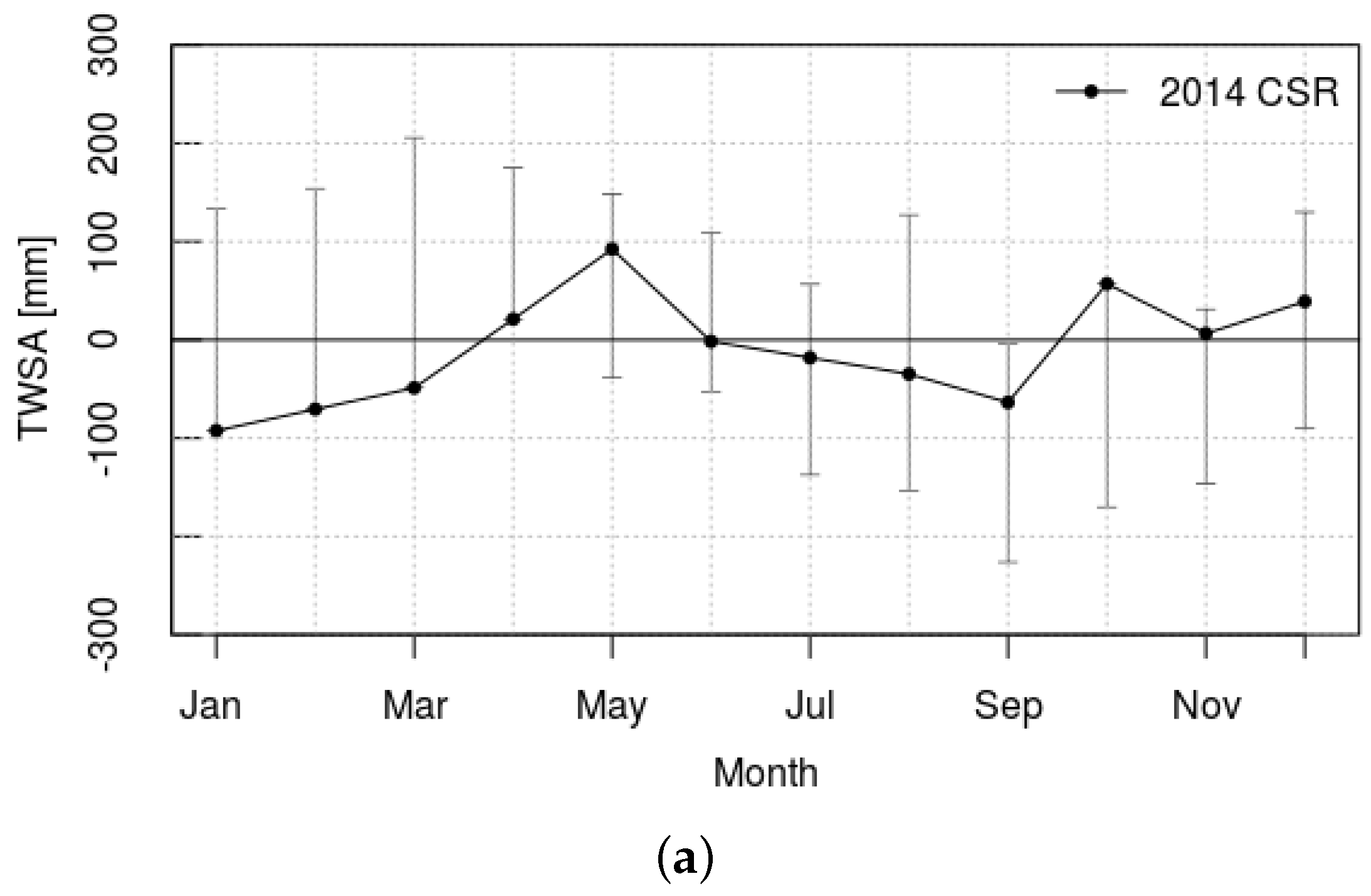
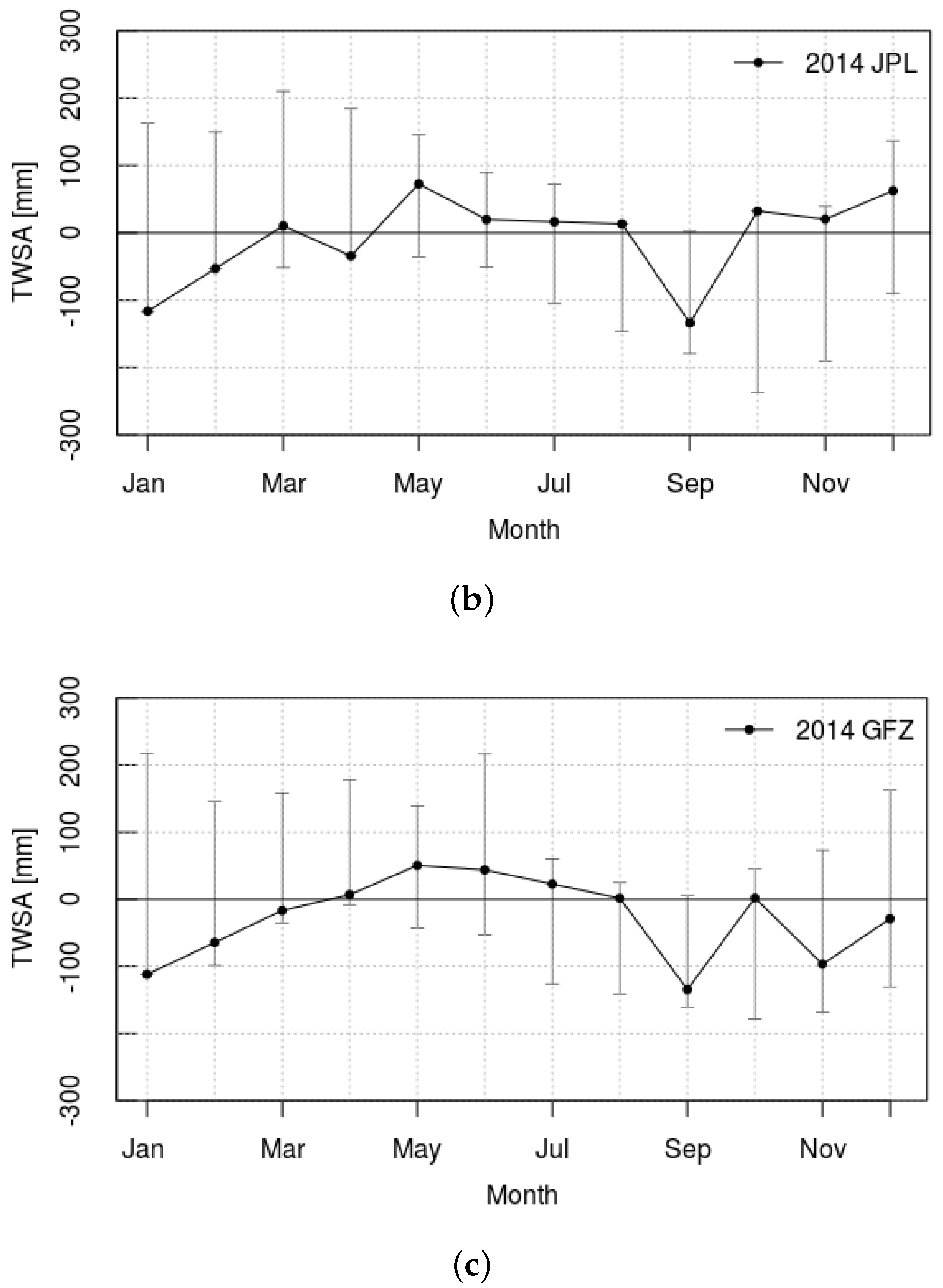
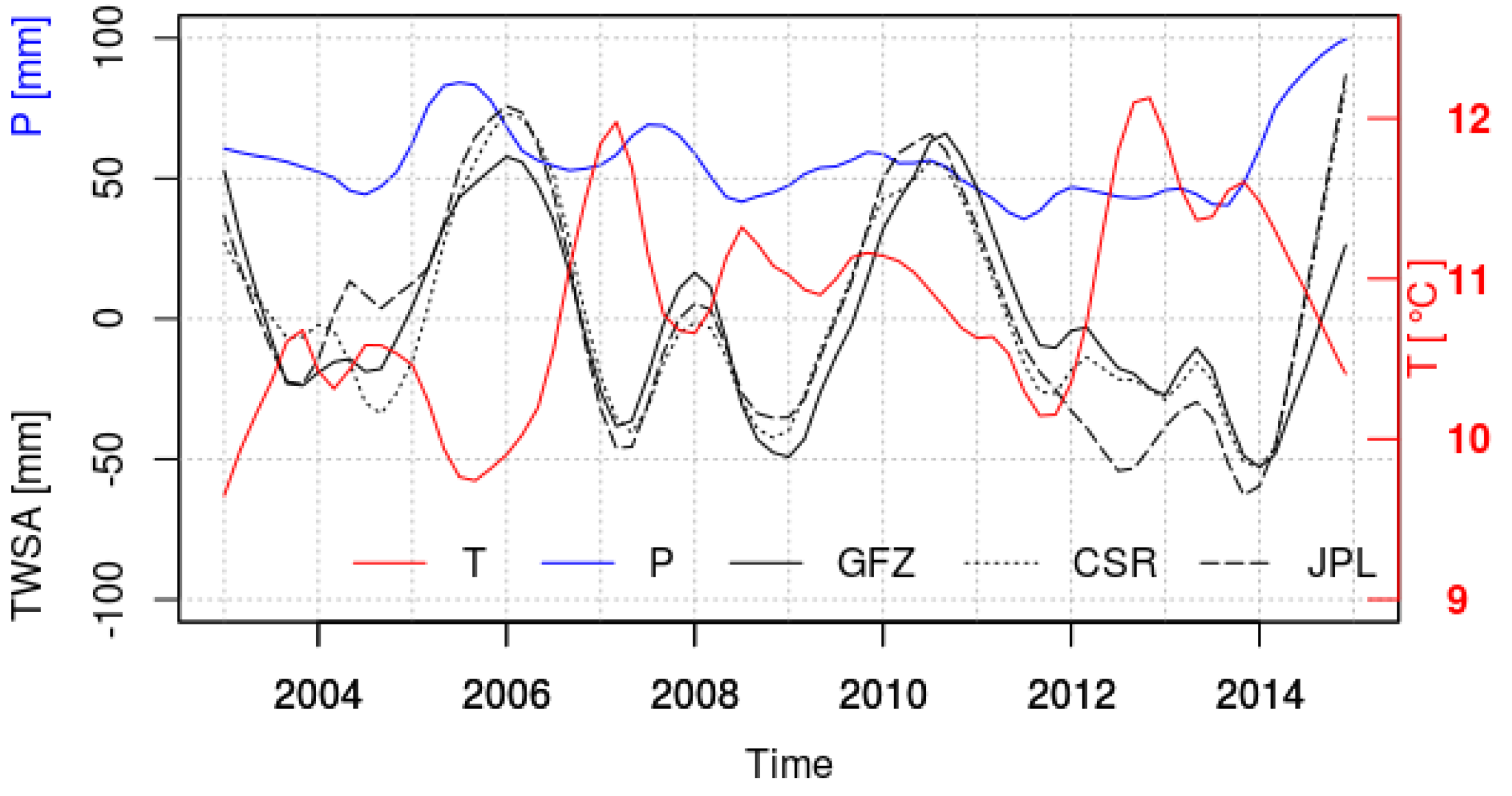
3.1. Anomalies of Temperature, Precipitation and TWS in 2014
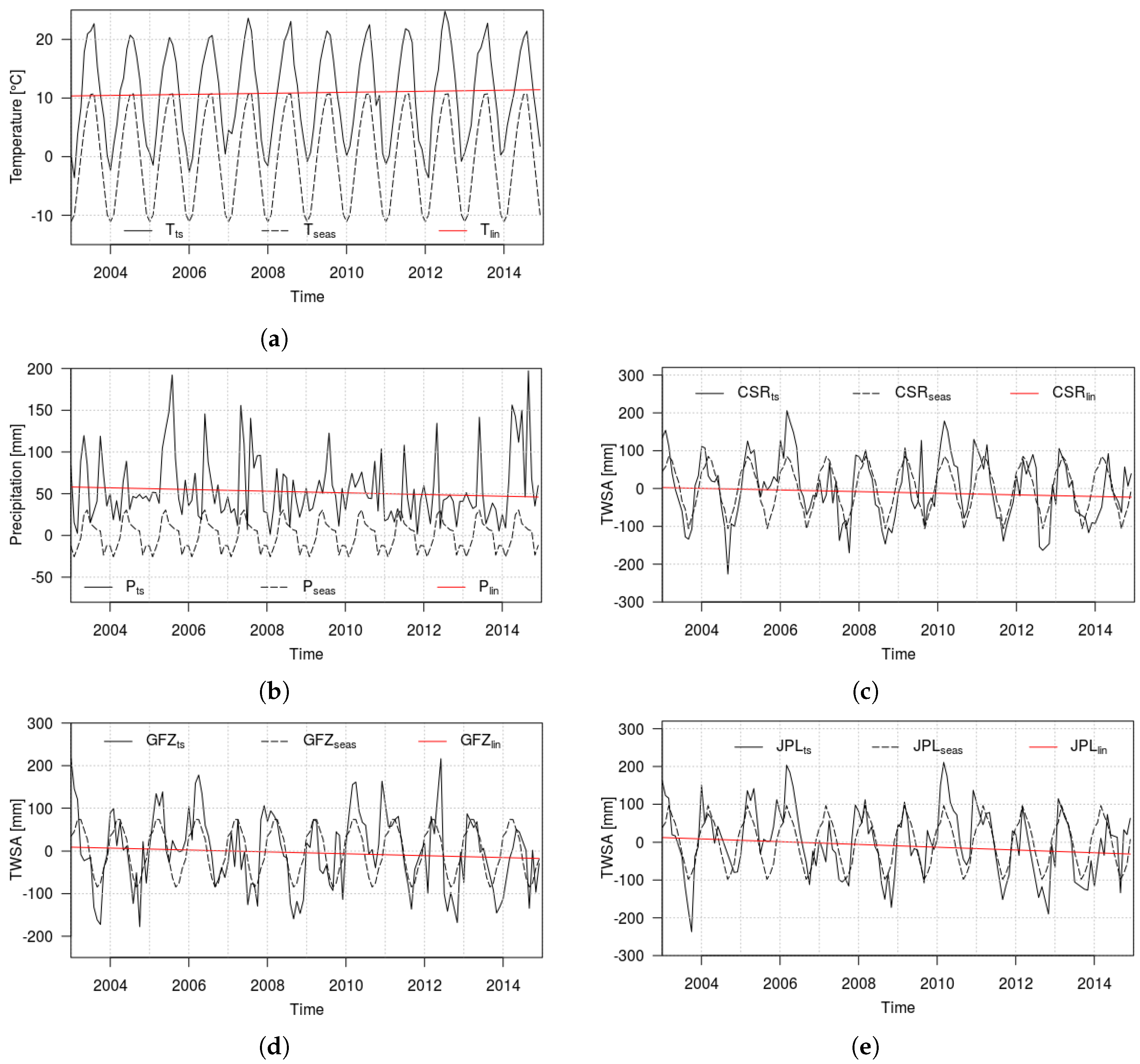
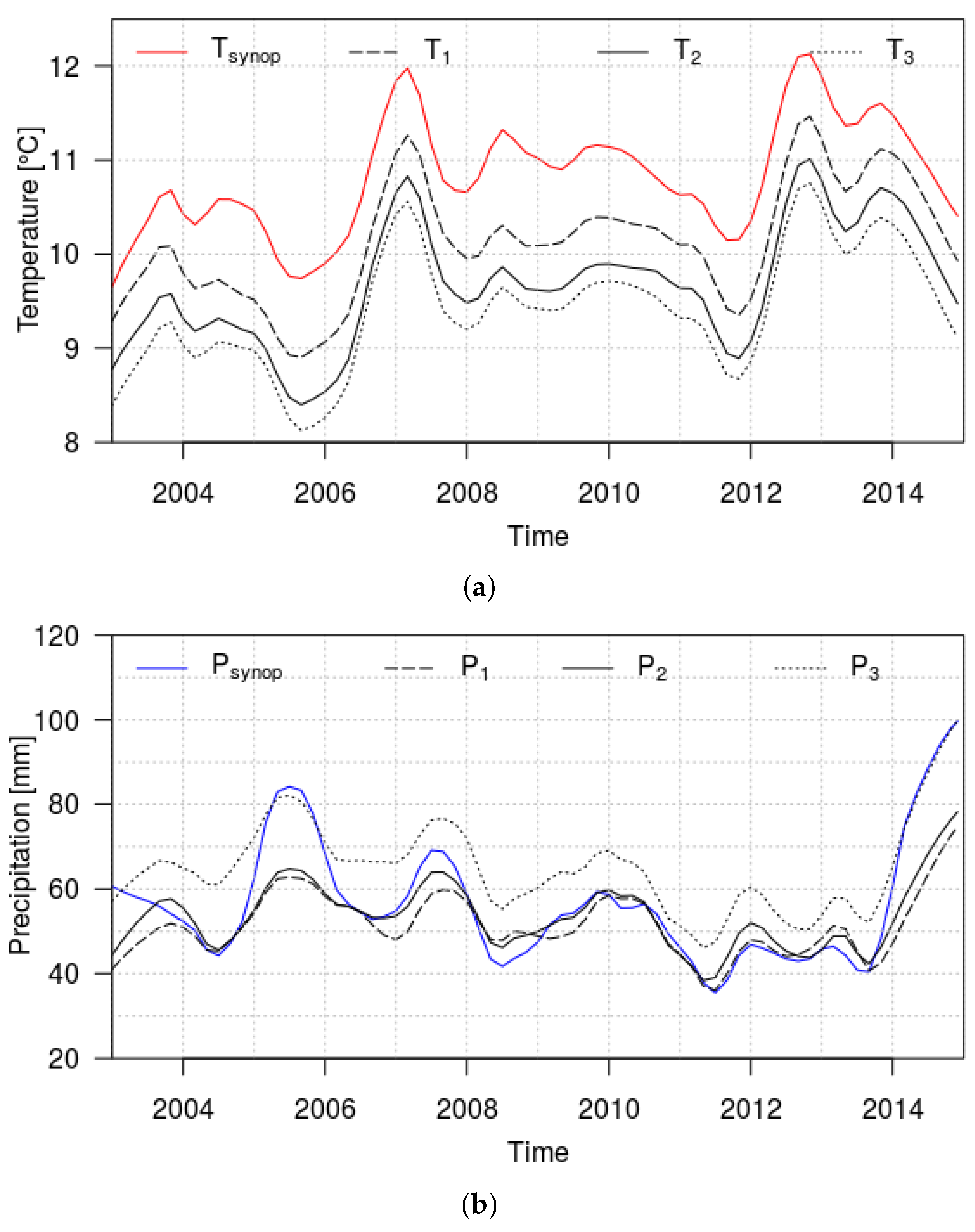
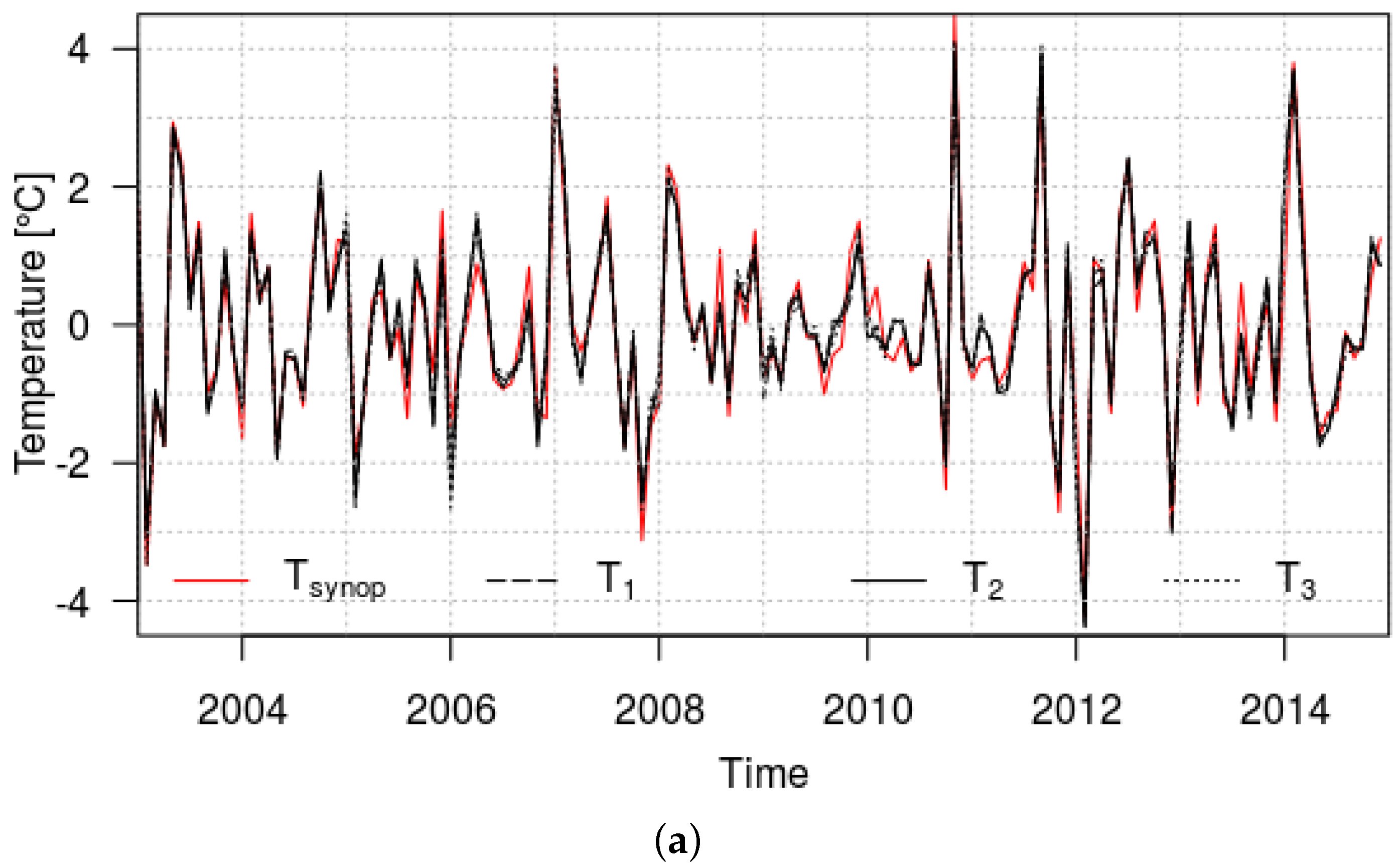
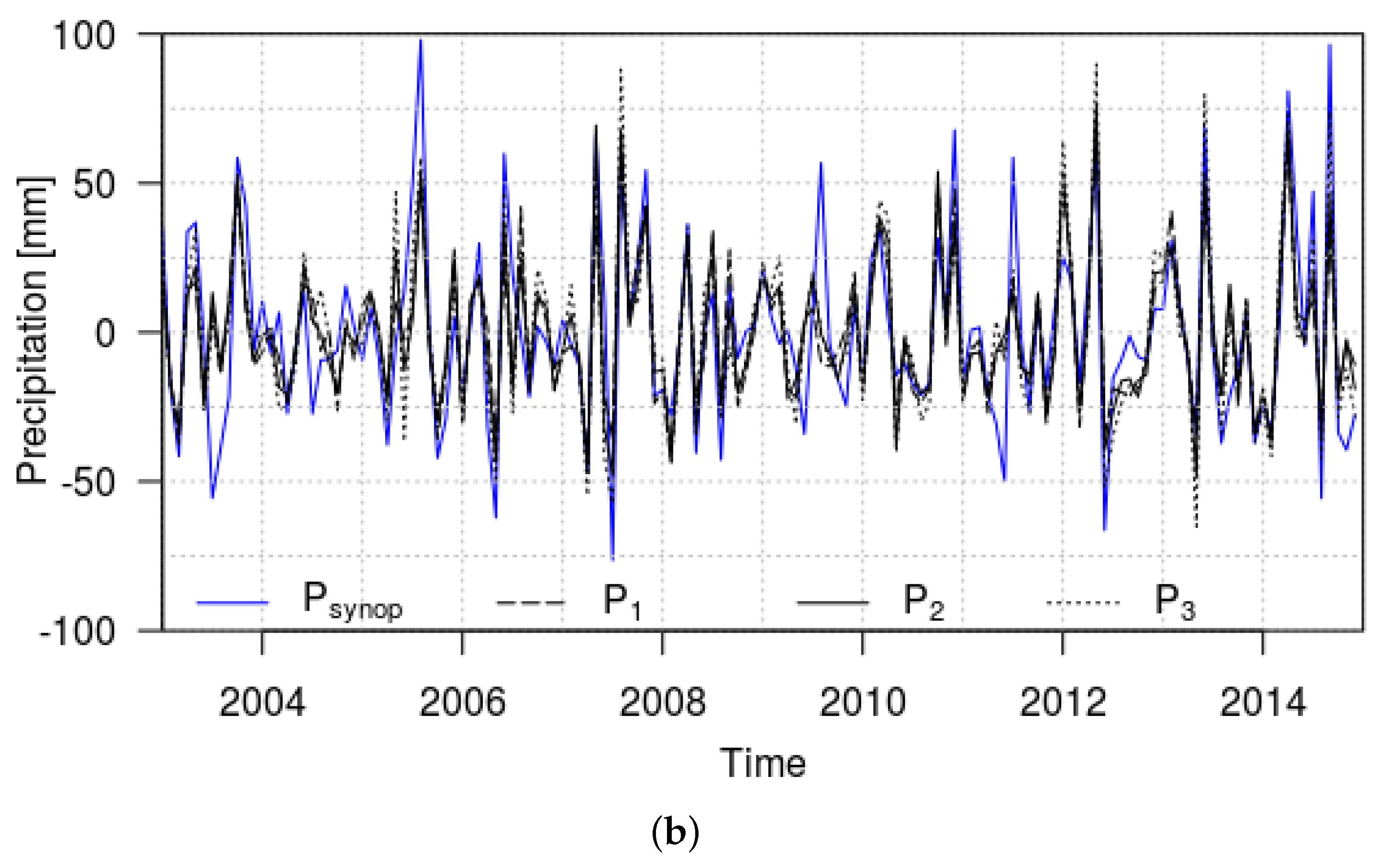
3.2. Time Series Decomposition: Temperature, Precipitation and TWSA
3.2.1. Long-Term Trends and Variability
3.2.2. Seasonal Cycle Component
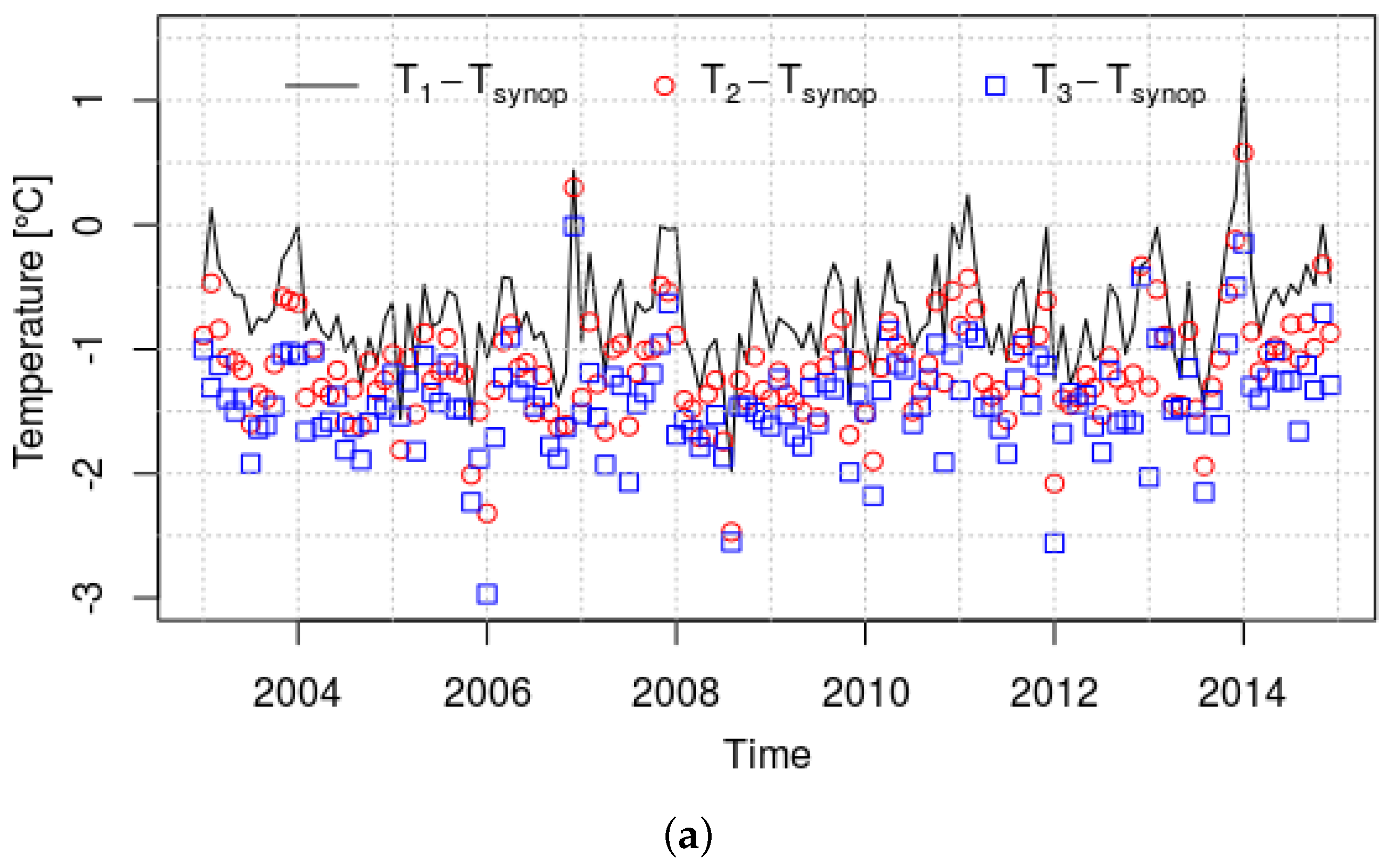
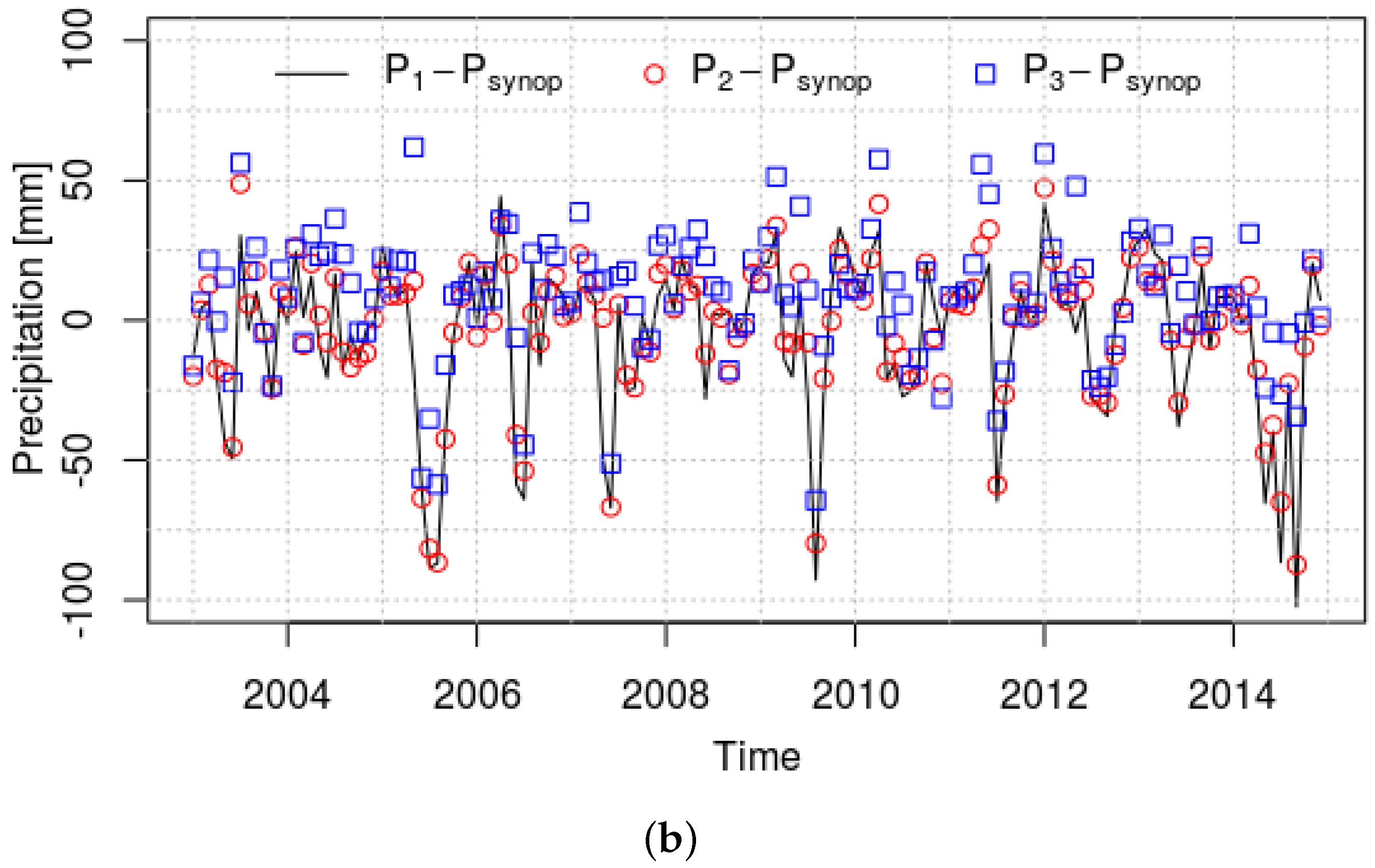
3.3. Comparison between ERA5 and SYNOP Temperature and Precipitation
3.4. Cross-Correlations between Climate Oscillation Indices and P, T and TWS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zscheischler, J.; Westra, S.; Hurk, B.J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Ward, P.J.; Pitman, A.; AghaKouchak, A.; Bresch, D.N.; Leonard, M.; Wahl, T.; et al. Future climate risk from compound events. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014–Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Regional Aspects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Several Flood Highlight Climate Change Challenge for Insurer and EU. Available online: https://www.euractiv.com/section/climate-environment/news/severe-floods-highlight-climate-change-challenge-for-insurers-and-eu/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Serbia Floods 2014. Available online: http://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/-ed_emp/documents/publication/wcms_397685.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Balkan Flood 2014. Available online: http://www.aon.com/czechrepublic/attachments/2014 (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Plavšić, J.; Blagojević, B.; Todorović, A.; Despotović, J. Long-term behaviour of precipitation at three stations in Serbia. Acta Hydrotech. 2016, 29, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stadtherr, L.; Coumou, D.; Petoukhov, V.; Petri, S.; Rahmstorf, S. Record Balkan floods of 2014 linked to planetary wave resonance. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Statistical Institute. Flood Events Statistics for the Period 2010–2017. Available online: http://www.nsi.bg/bg/content/2915/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Stoycheva, A.; Markova, B.; Diakova, A.; Popova, M.; Kirilova, A.; Stoev, K.; Slavchev, M.; Tsekov, G.; Balabanova, S.; Koshnicharov, G.; et al. The 2014 floods and their condisions. Bul. J. Meteo Hydros 2015, 20, 73–105. [Google Scholar]
- Baldini, L.M.; McDermott, F.; Foley, A.M.; Baldini, J.U. Spatial variability in the European winter precipitation δ18O-NAO relationship: Implications for reconstructing NAO-mode climate variability in the Holocene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, M.; García, J.; Vaquero, J. The NAO signal in daily rainfall series over the Iberian Peninsula. Clim. Res. 2005, 29, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiou, P.; Nogaj, M. Extreme climatic events and weather regimes over the North Atlantic: When and where? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, T.J. Variability and changes in the North Atlantic Oscillation index. In Hydrological, Socioeconomic and Ecological Impacts of the North Atlantic Oscillation in the Mediterranean Region; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; El Kenawy, A.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Pasho, E.; Zabalza, J.; Beguería, S.; Angulo-Martínez, M. The NAO impact on droughts in the Mediterranean region. In Hydrological, Socioeconomic and Ecological Impacts of the North Atlantic Oscillation in the Mediterranean Region; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 23–40. [Google Scholar]
- Frappart, F.; Ramillien, G. Monitoring groundwater storage changes using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission: A review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicker, A.; Forootan, E.; Springer, A.; Longuevergne, L.; Kusche, J. Does GRACE see the terrestrial water cycle “intensifying”? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dobslaw, H.; Stacke, T.; Güntner, A.; Dill, R.; Thomas, M. Validation of terrestrial water storage variations as simulated by different global numerical models with GRACE satellite observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircheva, B.; Tsekov, M.; Meyer, U.; Guerova, G. Anomalies of hydrological cycle components during the 2007 heat wave in Bulgaria. J. Atmos. -Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2017, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerova, G.; Simeonov, T.; Yordanova, N. The Sofia University Atmospheric Data Archive (SUADA). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.C.; Thompson, P.F.; Watkins, M.M. GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system. Science 2004, 305, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravity Recovery and Experiment. Available online: http://nasa.gov/Grace (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- GRACE Follow-On Mission. Available online: http://gracefo.jpl.nasa.gov (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Flechtner, F.; Morton, P.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F. Status of the GRACE follow-on mission. In Gravity, Geoid and Height Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Jäggi, A.; Meyer, U.; Lasser, M.; Jenny, B.; Lopez, T.; Flechtner, F.; Dahle, C.; Förste, C.; Mayer-Gürr, T.; Kvas, A.; et al. International Combination Service for Time-Variable Gravity Fields (COST-G); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ogimet Weather Information Service. Available online: http://www.ogimet.com (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). Available online: https://climate.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Hurrell, J.W. Decadal trends in the North Atlantic Oscillation: Regional temperatures and precipitation. Science 1995, 269, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donat, M.G.; Leckebusch, G.C.; Pinto, J.G.; Ulbrich, U. Examination of wind storms over Central Europe with respect to circulation weather types and NAO phases. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North Atlantic Oscillation. Available online: https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/nao/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Conte, M.; Giuffrida, A.; Tedesco, S. The Mediterranean oscillation: Impact on precipitation and hydrology in Italy. In Proceedings of the Conference on Climate and Water, Helsinki, Finland, 11–15 September 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Palutikof, J.; Conte, M.; Casimiro Mendes, J.; Goodess, C.; Espirito Santo, F. Climate and climatic change. In Mediterranean Desertification and Land Use; Brandt, C.J., Thomes, J.B., Eds.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 43–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mediterranean Oscillation Index. Available online: https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/moi/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/gcos_wgsp/Timeseries/AMO/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Knight, J.R.; Folland, C.K.; Scaife, A.A. Climate impacts of the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnston, A.G.; Livezey, R.E. Classification, seasonality and persistence of low-frequency atmospheric circulation patterns. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1987, 115, 1083–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Prediction Center-Scandinavia. Available online: http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/data/teledoc/scand.shtml (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; Terpenning, I. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on loess. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L.; Seneviratne, S.I. Assessing global water storage variability from GRACE: Trends, seasonal cycle, subseasonal anomalies and extremes. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 357–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F.; Katti, S.; Wilcox, R.A. Critical values and probability levels for the Wilcoxon rank sum test and the Wilcoxon signed rank test. Sel. Tables Math. Stat. 1970, 1, 171–259. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, M.; Wolfe, D.A.; Chicken, E. Nonparametric Statistical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Frappart, F.; Ramillien, G.; Ronchail, J. Changes in terrestrial water storage versus rainfall and discharges in the Amazon basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 3029–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, R.C.D.; Buarque, D.C.; Collischonn, W.; Bonnet, M.P.; Frappart, F.; Calmant, S.; Mendes, C.A.B. Large-scale hydrologic and hydrodynamic modeling of the Amazon River basin. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, F.; Güntner, A.; Frappart, F.; Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B. Variations of surface water extent and water storage in large river basins: A comparison of different global data sources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Beaudoing, H.K.; L’Ecuyer, T.; Olson, W.S.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Houser, P.R.; Adler, R.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Clayson, C.A.; Chambers, D.; et al. The observed state of the water cycle in the early twenty-first century. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 8289–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.B.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Hinderer, J.; Viterb, P. GRACE-derived terrestrial water storage depletion associated with the 2003 European heat wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L18405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Landerer, F.W.; Wiese, D.N.; Molotch, N.P.; Argus, D.F. GRACE groundwater drought index: Evaluation of California Central Valley groundwater drought. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boergens, E.; Güntner, A.; Dobslaw, H.; Dahle, C. Quantifying the Central European Droughts in 2018 and 2019 with GRACE-Follow-On. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Wet and Dry Conditions. Available online: https://climate.copernicus.eu/european-wet-and-dry-conditions (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- ESOTC. Available online: https://climate.copernicus.eu/ESOTC/2019/european-wet-and-dry-conditions (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Reager, J.; Gardner, A.; Famiglietti, J.; Wiese, D.; Eicker, A.; Lo, M.H. A decade of sea level rise slowed by climate-driven hydrology. Science 2016, 351, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäggi, A.; Weigelt, M.; Flechtner, F.; Güntner, A.; Mayer-Gürr, T.; Martinis, S.; Bruinsma, S.; Flury, J.; Bourgogne, S.; Steffen, H.; et al. European Gravity Service for Improved Emergency Management (EGSIEM)—from concept to implementation. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 1572–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Lags in Month | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −6 | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| T∼P | NS | NS | NS | −0.11 | −0.19 | −0.26 | −0.33 | −0.36 | −0.38 | −0.40 | −0.39 | −0.38 | −0.36 |
| T∼ CSR | −0.37 | −0.42 | −0.46 | −0.50 | −0.52 | −0.53 | −0.53 | −0.48 | −0.42 | −0.36 | −0.30 | NS | NS |
| T∼ GFZ | −0.34 | −0.40 | −0.46 | −0.51 | −0.55 | −0.57 | −0.58 | −0.54 | −0.50 | −0.43 | −0.37 | −0.30 | −025 |
| T∼ JPL | −0.33 | −0.40 | −0.46 | −0.52 | −0.57 | −0.61 | −0.63 | −0.61 | −0.57 | −0.53 | −0.48 | −0.43 | −0.37 |
| P∼ CSR | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.19 | NS | NS | −0.15 | −0.22 |
| P∼ GFZ | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.27 | NS | NS | NS | −0.23 | −0.29 |
| P∼ JPL | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.13 | NS | NS | NS |
| Data | Lags in Month | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −6 | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| T∼P | 0.11 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | −0.34 | −0.37 | −0.37 | −0.37 | −0.34 | −0.31 | −0.27 |
| T∼ CSR | −0.33 | −0.39 | −0.44 | −0.49 | −0.52 | −0.53 | −0.52 | −0.45 | −0.37 | −0.28 | NS | NS | NS |
| T∼ GFZ | −0.28 | −0.36 | −0.43 | −0.49 | −0.53 | −0.55 | −0.56 | −0.51 | −0.44 | −0.37 | −0.30 | NS | NS |
| T∼ JPL | −0.21 | −0.29 | −0.38 | −0.45 | −0.52 | −0.56 | −0.59 | −0.55 | −0.50 | −0.43 | −0.37 | −0.30 | NS |
| P∼ CSR | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.17 | NS | NS | −0.23 | −0.25 |
| P∼ GFZ | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.26 | NS | NS | NS | NS | −0.25 | −0.31 |
| P∼ JPL | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.35 | 0.23 | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Data | Lags in Month | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −6 | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| MOI∼T | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | −0.19 | −0.19 | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| MOI∼P | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | 0.25 | NS | NS | 0.13 | NS | NS | NS |
| MOI∼CSR | 0.26 | NS | NS | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.26 | NS | 0.16 | NS | NS | 0.10 | NS | NS |
| MOI∼GFZ | NS | NS | NS | 0.19 | NS | 0.24 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| MOI∼JPL | 0.23 | NS | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.19 | NS | NS |
| Data | Lags in Month | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −6 | −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| NAO∼T | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| NAO∼P | NS | 0.24 | NS | NS | NS | NS | −0.21 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| NAO∼CSR | NS | NS | NS | −0.17 | −0.21 | −0.27 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| NAO∼GFZ | NS | NS | −0.20 | NS | NS | −0.20 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| NAO∼JPL | NS | −0.15 | −0.18 | −0.18 | −0.19 | −0.25 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mircheva, B.; Tsekov, M.; Meyer, U.; Guerova, G. Analysis of the 2014 Wet Extreme in Bulgaria: Anomalies of Temperature, Precipitation and Terrestrial Water Storage. Hydrology 2020, 7, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7030066
Mircheva B, Tsekov M, Meyer U, Guerova G. Analysis of the 2014 Wet Extreme in Bulgaria: Anomalies of Temperature, Precipitation and Terrestrial Water Storage. Hydrology. 2020; 7(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleMircheva, Biliana, Milen Tsekov, Ulrich Meyer, and Guergana Guerova. 2020. "Analysis of the 2014 Wet Extreme in Bulgaria: Anomalies of Temperature, Precipitation and Terrestrial Water Storage" Hydrology 7, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7030066
APA StyleMircheva, B., Tsekov, M., Meyer, U., & Guerova, G. (2020). Analysis of the 2014 Wet Extreme in Bulgaria: Anomalies of Temperature, Precipitation and Terrestrial Water Storage. Hydrology, 7(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7030066





