On the Relationship between Experimental and Numerical Modelling of Gravel-Bed Channel Aggradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Numerical Modelling
2.1. Laboratory Facility and Experimental Tests
2.2. Morphological Numerical Tool and Modelling Strategy
3. Results
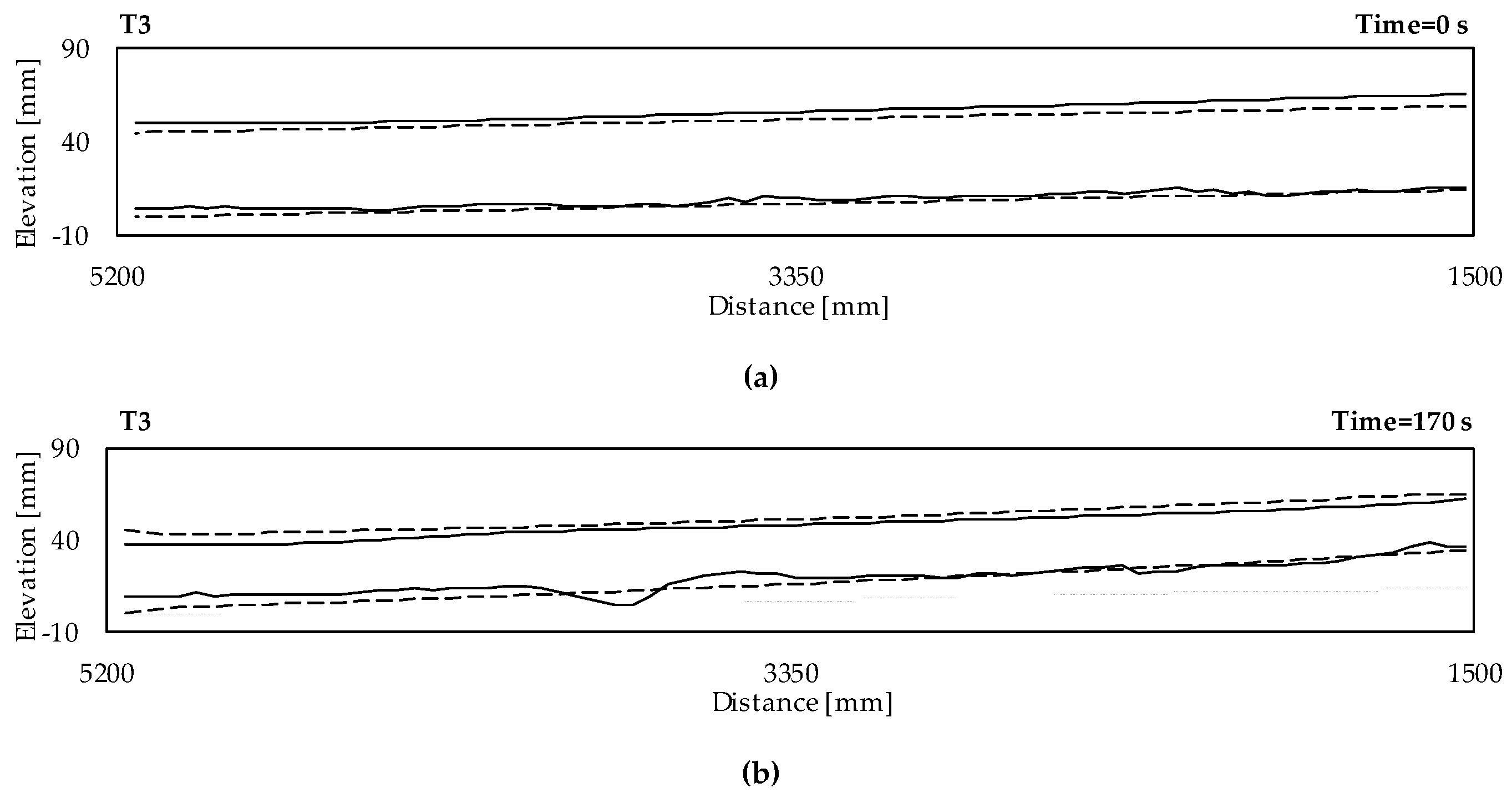
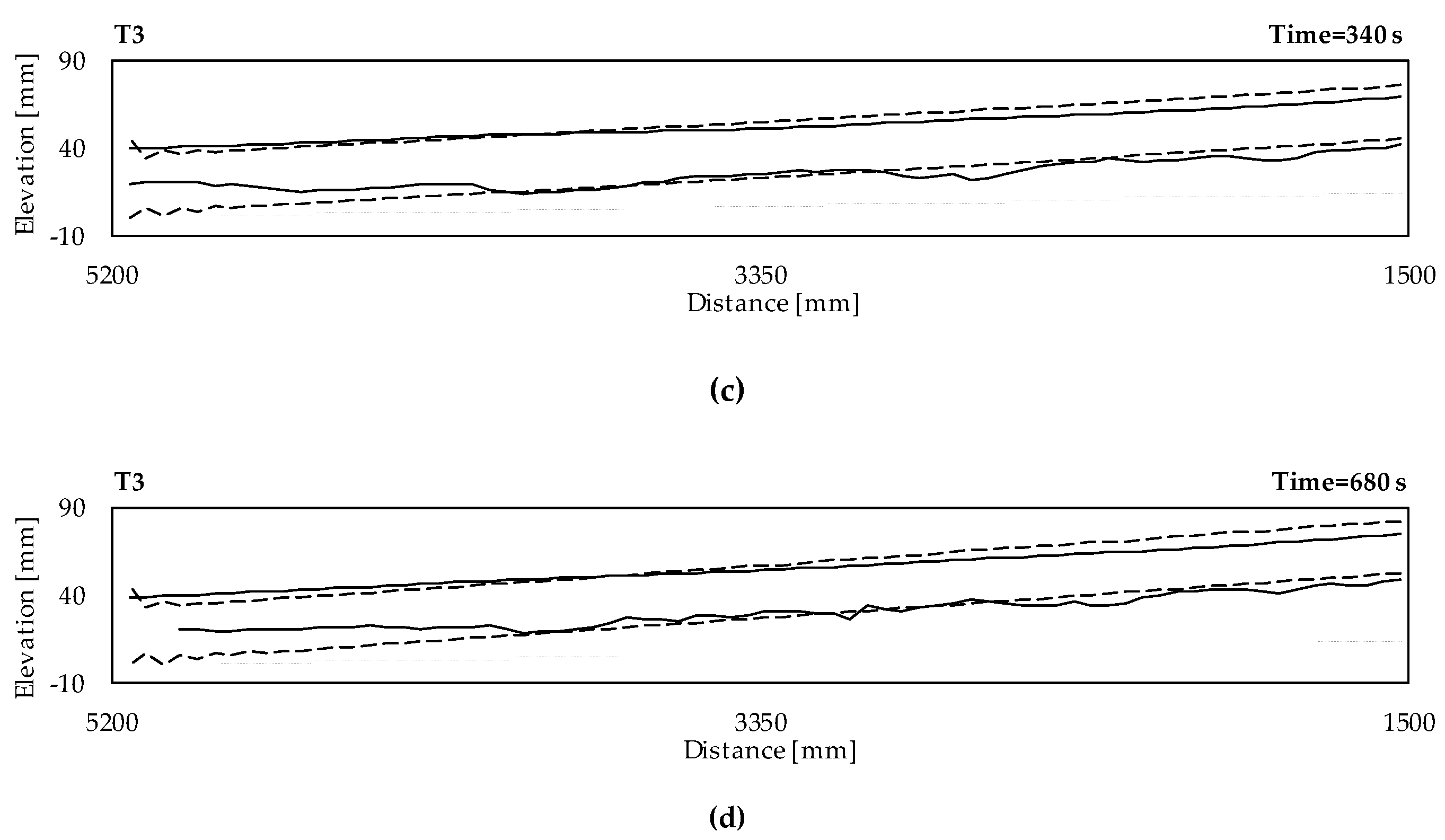
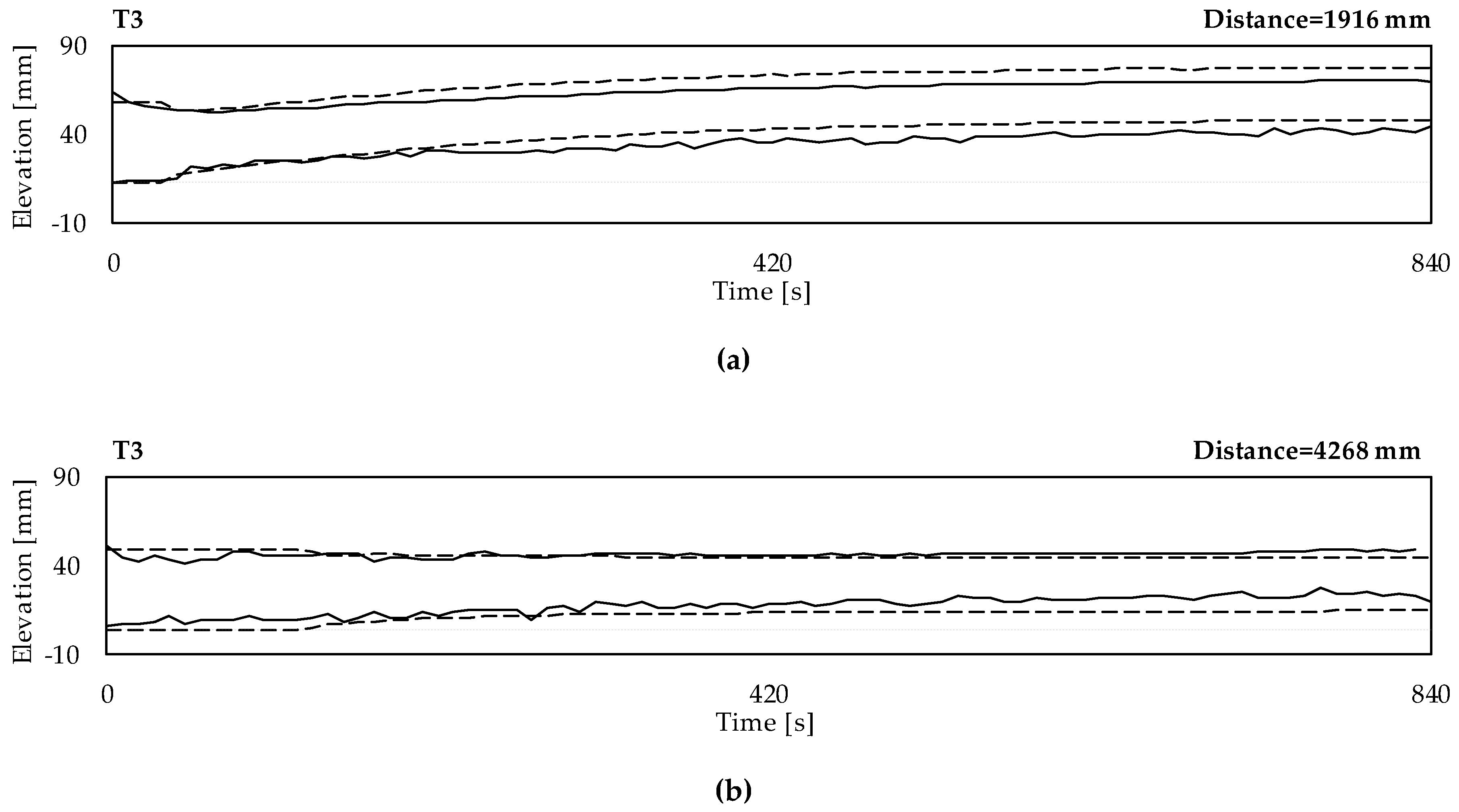
3.1. Phenomenological Description of the Experimental Aggradation Profiles
3.2. Calibration and Validation of the Numerical Model
3.3. Application of the Calibrated Model to a Transcritical Flow
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, S.N.; Tayefi, V.; Reid, S.C.; Yu, D.; Hardy, R.J. Interactions between sediment delivery, channel change, climate change and flood risk in a temperate upland environment. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2007, 32, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotterweich, M. The history of soil erosion and fluvial deposits in small catchments of central Europe: Deciphering the long-term interaction between humans and the environment—A review. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhold, C.; Stanzel, P.; Nachtnebel, H.P. Incorporating river morphological changes to flood risk assessment: Uncertainties, methodology and application. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, P.M.; Biron, P.M.; Ferguson, R.I.; Hoey, T.B. Implications of climate change in the twenty-first century for simulated magnitude and frequency of bed-material transport in tributaries of the Saint-Lawrence River. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, A.; Giorgetti, E.; Brambilla, D.; Longoni, L.; Papini, M. On integrated sediment transport modeling for flash events in mountain environments. Acta Geophys. 2012, 60, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, A.; Rosatti, G.; Ballio, F.; Franzetti, S.; Mauri, M.; Spagnolatti, M.; Garegnani, G. Management of flood hazard via hydro-morphological river modelling. The case of the Mallero in Italian Alps. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2013, 6, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, R.B.; Mauad, F.F. Influence of sedimentation on hydroelectric power generation: Case study of a Brazilian reservoir. J. Energy Eng. 2014, 141, 04014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, D.; Patidar, S.; Hassan, K.; Haynes, H. Method for incorporating morphological sensitivity into flood inundation modeling. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, G.; Mohajeri, S.H.; Righetti, M. The pernicious problem of streambed colmation: A multi-disciplinary reflection on the mechanisms, causes, impacts, and management challenges. WIREs Water 2017, 4, e1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsapour-Moghaddam, P.; Rennie, C.D. Influence of meander confinement on hydro-morphodynamics of a cohesive meandering channel. Water 2018, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysanova, V.; Hattermann, F.; Wechsung, F. Development of the ecohydrological model SWIM for regional impact studies and vulnerability assessment. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 763–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, T.J.; Macklin, M.G.; Kirkby, M.J. A cellular model of Holocene upland river basin and alluvial fan evolution. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2002, 27, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Katopodes, N.D. Modeling erosion and sedimentation coupled with hydrological and overland flow processes at the watershed scale. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5134–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.A.; Topping, D.J.; Rubin, D.R.; Melis, T.S. An approach for modeling sediment budgets in supply-limited rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, A.; Longoni, L.; Papini, M.; Brambilla, D.; Ivanov, V.I. Generation of a design flood-event scenario for a mountain river with intense sediment transport. Water 2016, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, A.N.; Bdour, A.; Wicklein, E. One-dimensional hydrodynamic/sediment transport model applicable to steep mountain streams. J. Hydraul. Res. 2004, 42, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, M.; Friedl, K.; Rickenmann, D. A one-dimensional bedload transport model for steep slopes. J. Hydraul. Res. 2010, 48, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosatti, G.; Bonaventura, L.; Deponti, A.; Garegnani, G. An accurate and efficient semi-implicit method for section-averaged free-surface flow modeling. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2011, 65, 448–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viparelli, E.; Haydel, R.; Salvaro, M.; Wilcock, P.R.; Parker, G. River morphodynamics with creation/consumption of grain size stratigraphy 1: Laboratory experiments. J. Hydraul. Res. 2010, 48, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viparelli, E.; Sequeiros, O.E.; Cantelli, A.; Wilcock, P.R.; Parker, G. River morphodynamics with creation/consumption of grain size stratigraphy 2: Numerical model. J. Hydraul. Res. 2010, 48, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, J.P.; Garde, R.J.; Ranga Raju, K.G. Aggradation in streams due to overloading. ASCE J. Hydraul. Div. 1980, 106, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, J.P. Laboratory study of aggradation in alluvial channels. J. Hydrol. 1981, 49, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.L.; Chang, S.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Aggradation-degradation process in alluvial channels. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1992, 118, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.; Cardoso, A. Experimental study on aggradation. Int. J. Sediment Res. 1999, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Miglio, A.; Gaudio, R.; Calomino, F. Mobile-bed aggradation and degradation in a narrow flume: Laboratory experiments and numerical simulations. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2009, 3, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unigarro Villota, S. Laboratory Study of Channel Aggradation due to Overloading. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchi, B. Indagine Sperimentale Sul Fenomeno di Deposito in un Canale a Fondo Mobile Sovralimentato. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, July 2018. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Radice, A.; Unigarro Villota, S. Propagation of aggrading sediment fronts in a laboratory flume. In Proceedings of the River Flow 2018, Lyon, France, 5–8 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchi, M. Experimental and Numerical Study of Channel Aggradation. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Radice, A.; Zanchi, B. Multicamera, multimethod measurements for hydromorphologic laboratory experiments. Geosciences 2018, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, H.W.; Altinakar, M.S. Fluvial Hydraulics. Flow and Transport Processes in Channels of Simple Geometry; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Strickler, A. Beitraege zur Frage der Geschwindigkeitsformel und der Rauhigkeitszahlen Fuer Stroeme, Kanaele und Geschlossene Leitungen; Mitteilungen des Amtes fuer Wasserwirtschaft; Eidgenoessisches Departement des Innern: Bern, Switzerland, 1923; Volume 16. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Peter, E.; Müller, R. Formulas for Bed-Load Transport; Report on the Second IAHR Meeting, Stockholm, Sweden; TU Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 1948; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, A. Anwendung der aehnlichkeitsmechanik und der turbulenz forschung auf die geschiebebewegung. In Mitteilungen der Preussische Versuchanstalt für Wasserbau und Schiffsbau Heft 26; TU Delft: Berlin, Germany, 1936. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Sediment transport, part II: Suspended load transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1613–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetsch, D.; Siviglia, A.; Caponi, F.; Ehrbar, D.; Gerke, E.; Kammerer, S.; Koch, A.; Peter, S.; Vanzo, D.; Vonwiller, L.; et al. System manuals of BASEMENT, version 2.8; Laboratory of Hydraulics, Glaciology and Hydrology (VAW), ETH Zurich: Zurich, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, P.L. Approximate Riemann solvers, parameter vectors and difference schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 43, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanini, A. Principi di Idraulica Fluviale; Editoriale Bios: Cosenza, Italy, 2002. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Lyn, D.A.; Altinakar, M. St. Venant–Exner equations for near-critical and transcritical flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutière, L.; Soares-Frazão, S.; Savary, C.; Laraichi, T.; Zech, Y. One-dimensional model for transient flows involving bed-load sediment transport and changes in flow regimes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellal, M.; Spinewine, B.; Savary, C.; Zech, Y. Morphological evolution of steep-sloped river beds in the presence of a hydraulic jump: Experimental study. In Proceedings of the 30th IAHR Congress, Thessaloniki, Greece, 25–31 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
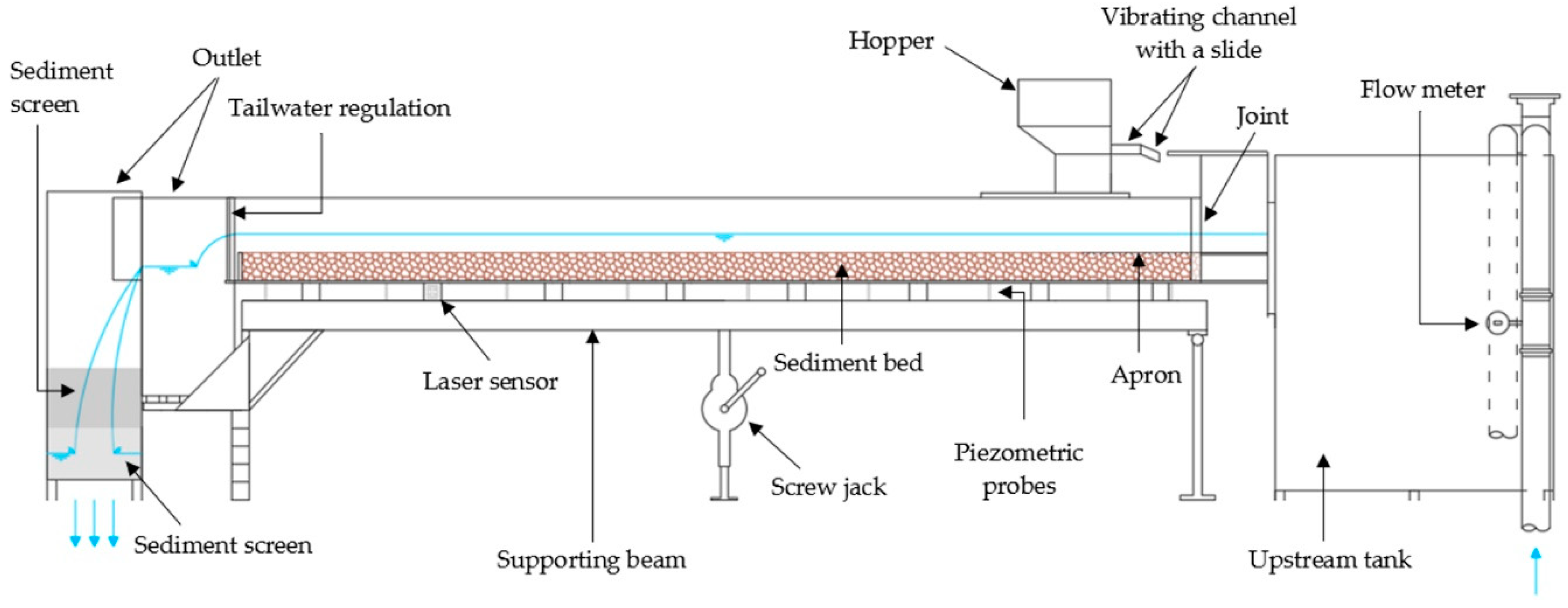
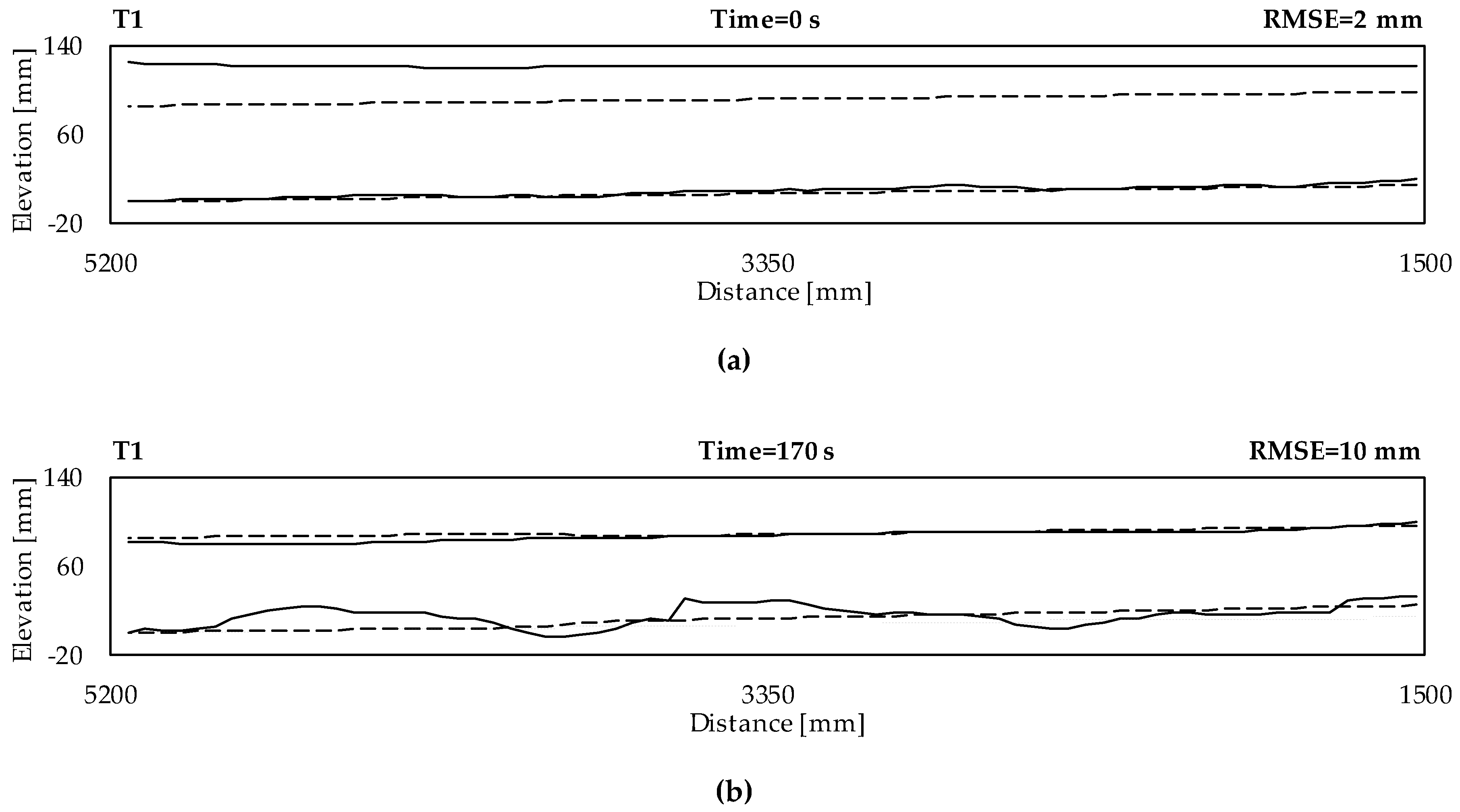
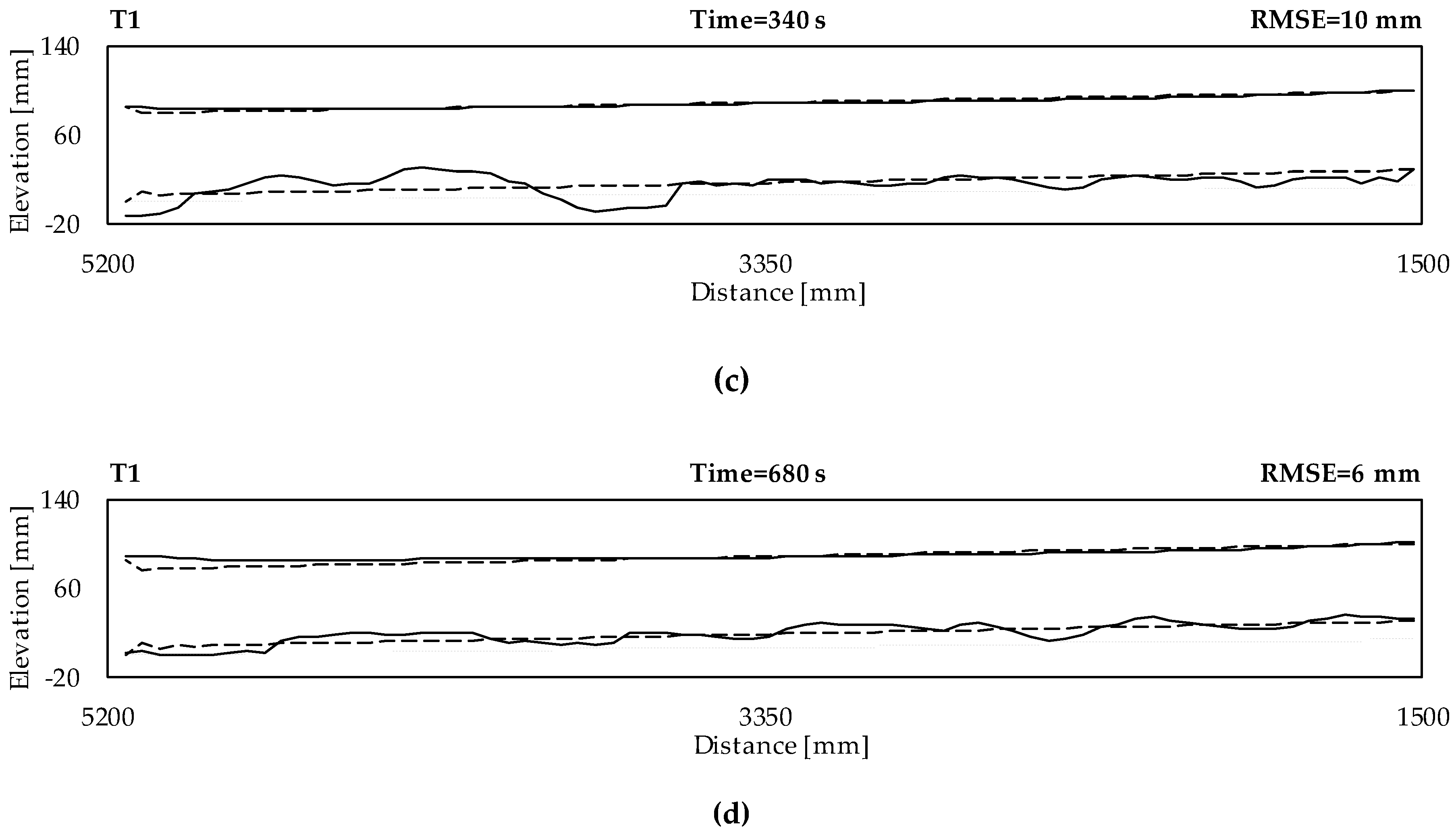
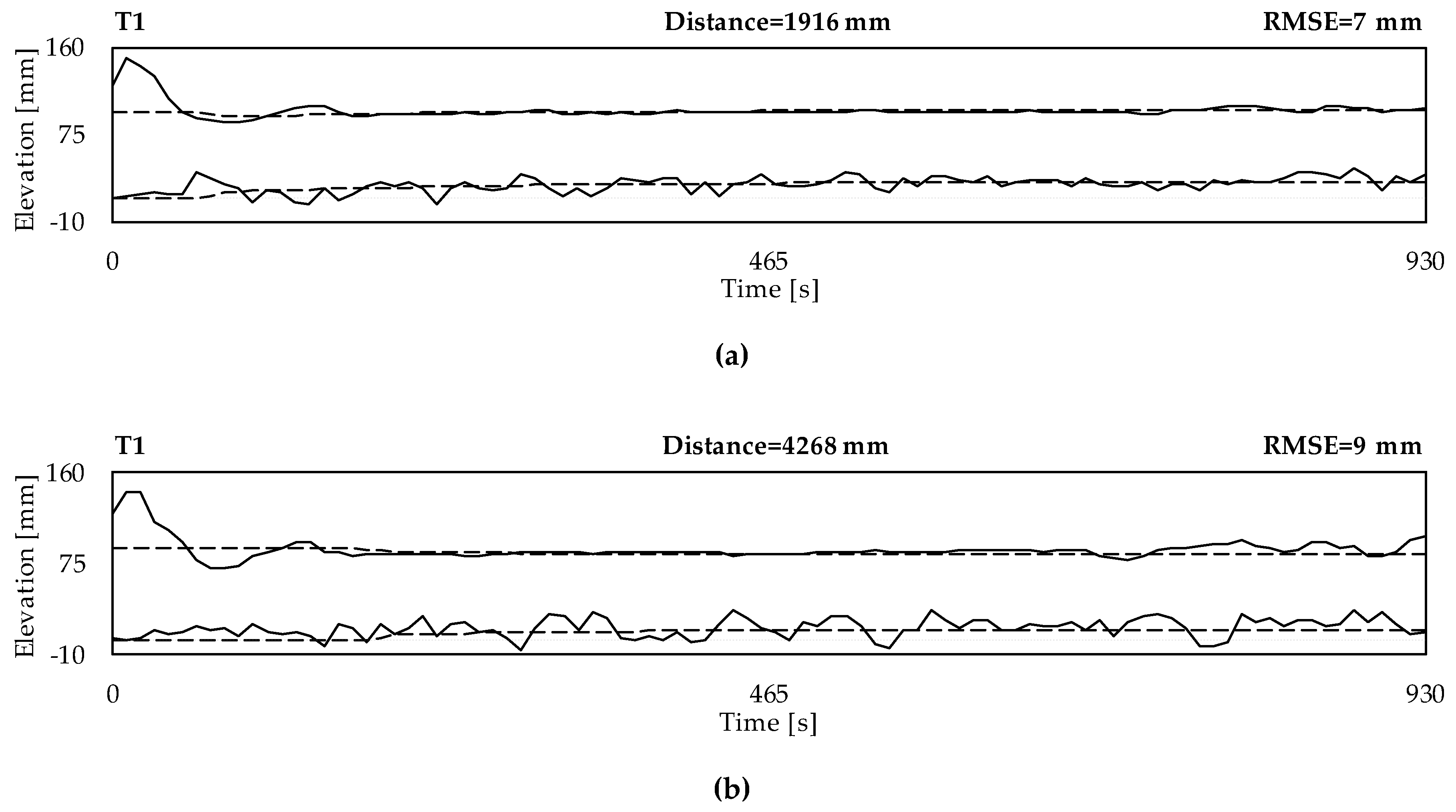
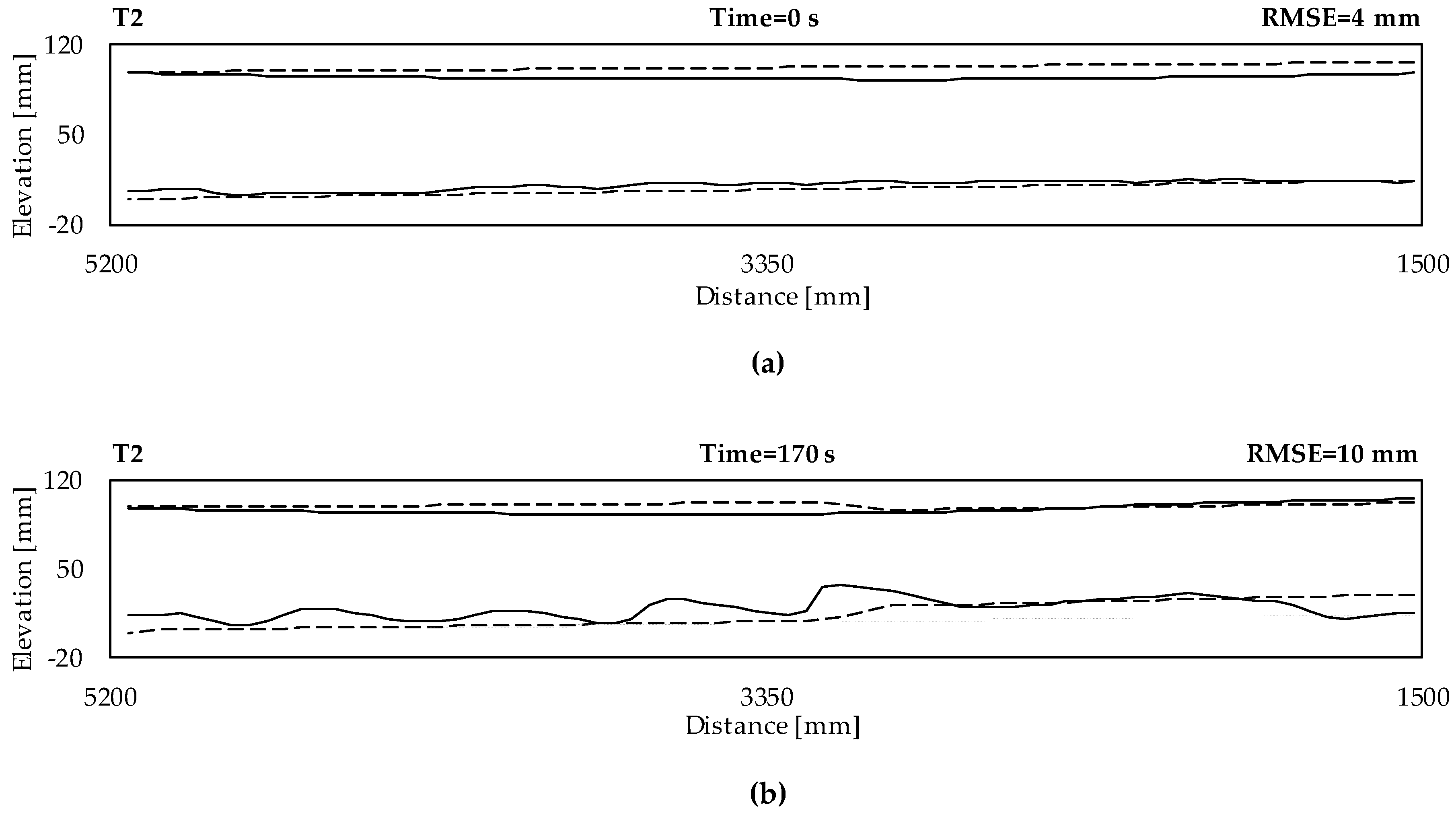
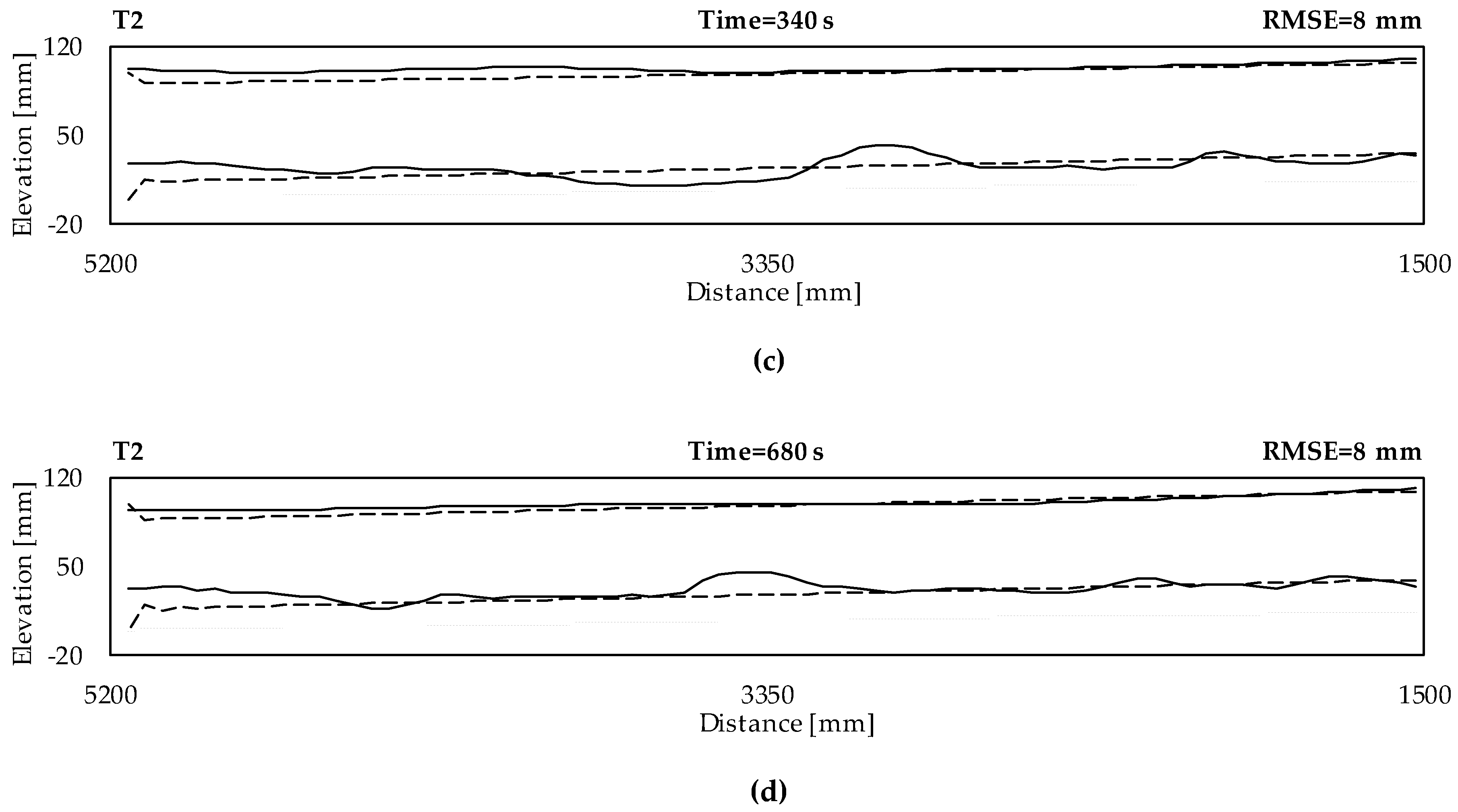
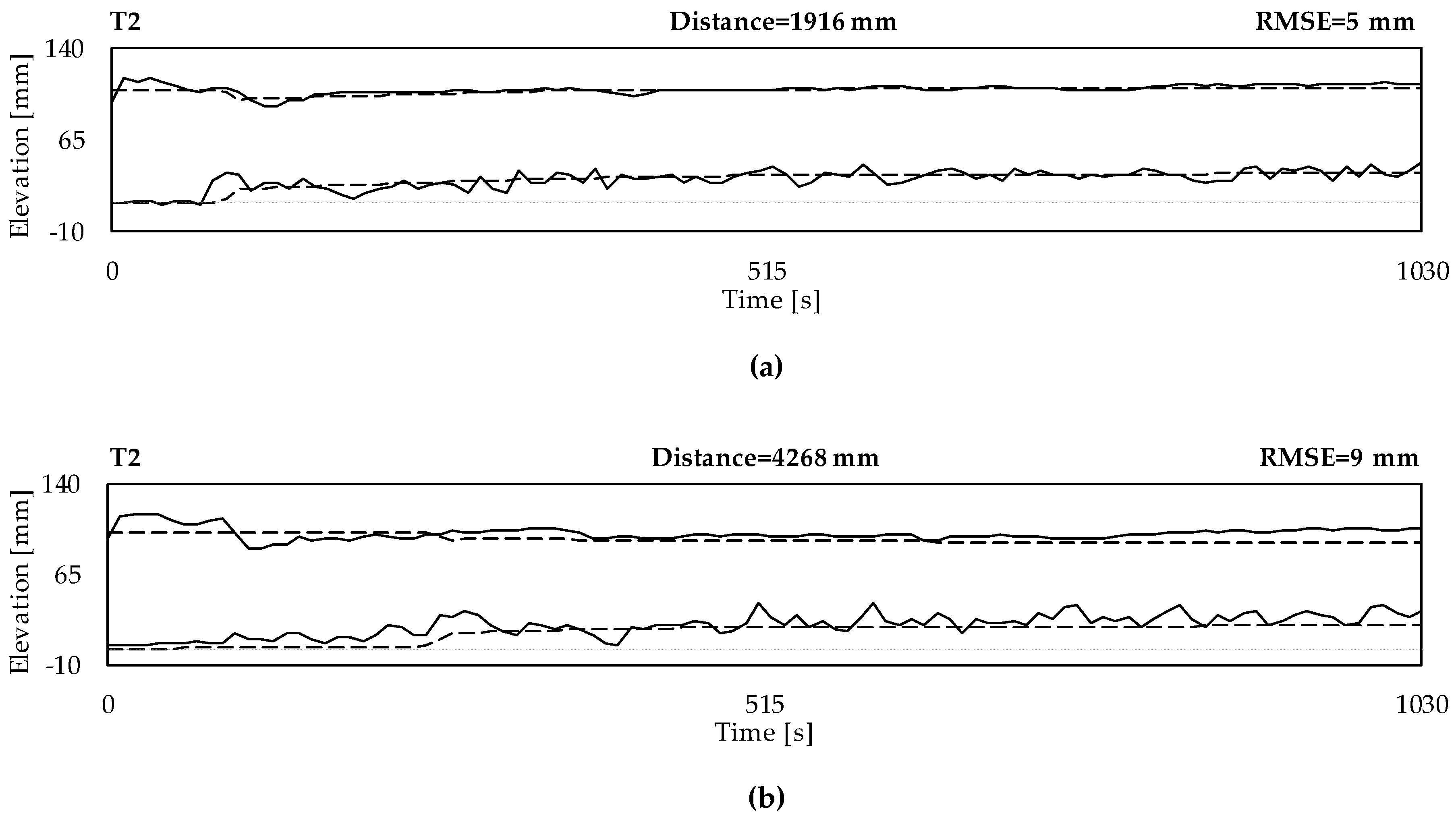
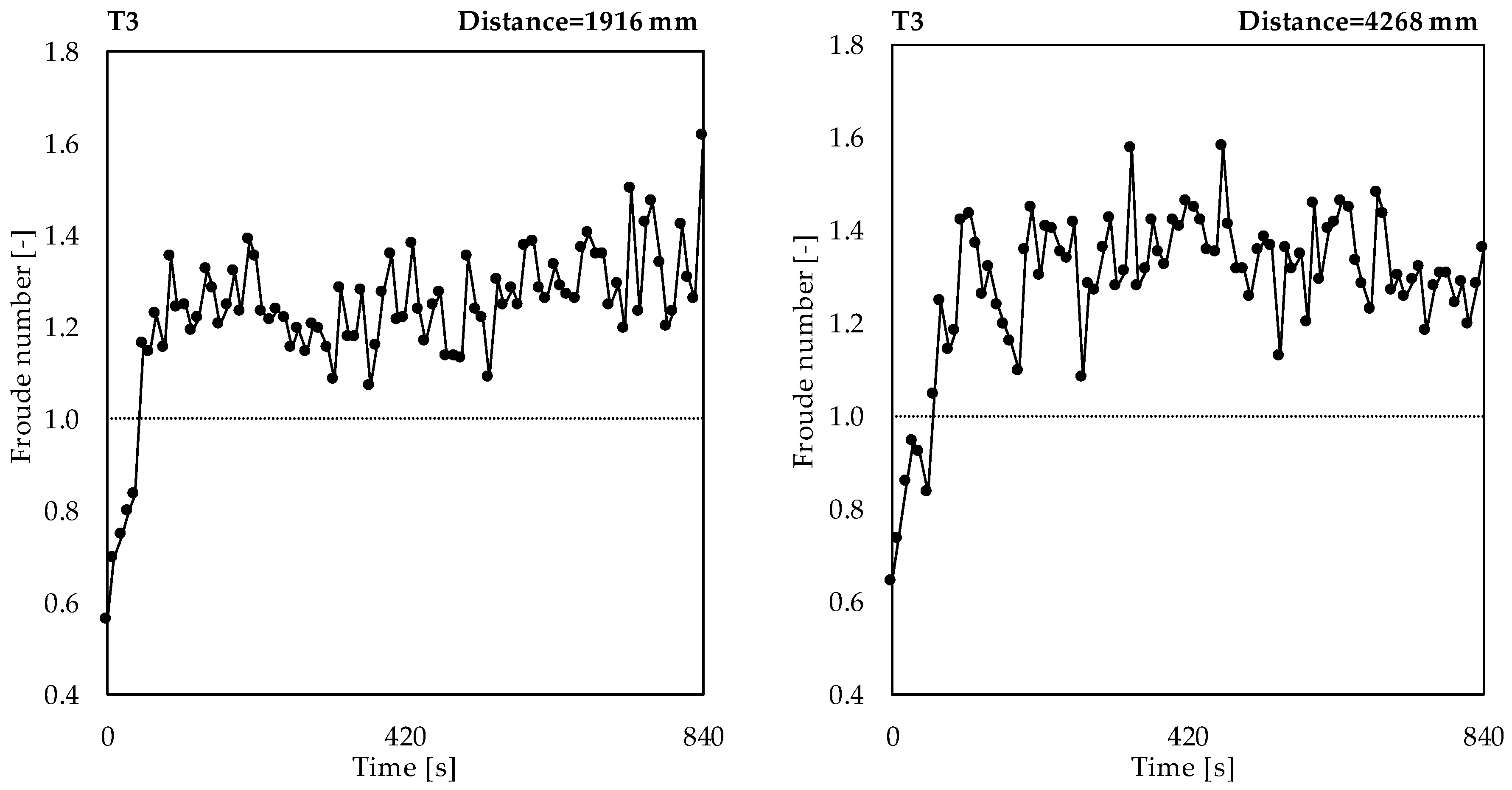
| T [s] | Q [l/s] | hd [cm] | h0 [cm] | Ud [m/s] | Frd [–] | QBin [10−5 m3/s] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 936 | 14.7 | 8.6 | 8.3 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 5.51 |
| T2 | 1113 | 14.7 | 9.9 | 8.3 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 5.55 |
| T3 | 845 | 6.0 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 0.44 | 0.66 | 7.43 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanchi, B.; Zucchi, M.; Radice, A. On the Relationship between Experimental and Numerical Modelling of Gravel-Bed Channel Aggradation. Hydrology 2019, 6, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010009
Zanchi B, Zucchi M, Radice A. On the Relationship between Experimental and Numerical Modelling of Gravel-Bed Channel Aggradation. Hydrology. 2019; 6(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanchi, Barbara, Matteo Zucchi, and Alessio Radice. 2019. "On the Relationship between Experimental and Numerical Modelling of Gravel-Bed Channel Aggradation" Hydrology 6, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010009
APA StyleZanchi, B., Zucchi, M., & Radice, A. (2019). On the Relationship between Experimental and Numerical Modelling of Gravel-Bed Channel Aggradation. Hydrology, 6(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010009






