Abstract
This study proposes a framework that (i) uses data assimilation as a post processing technique to increase the accuracy of water depth prediction, (ii) updates streamflow generated by the National Water Model (NWM), and (iii) proposes a scope for updating the initial condition of continental-scale hydrologic models. Predicted flows by the NWM for each stream were converted to the water depth using the Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) method. The water level measurements from the Iowa Flood Inundation System (a test bed sensor network in this study) were converted to water depths and then assimilated into the HAND model using the ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF). The results showed that after assimilating the water depth using the EnKF, for a flood event during 2015, the normalized root mean square error was reduced by 0.50 m (51%) for training tributaries. Comparison of the updated modeled water stage values with observations at testing locations showed that the proposed methodology was also effective on the tributaries with no observations. The overall error reduced from 0.89 m to 0.44 m for testing tributaries. The updated depths were then converted to streamflow using rating curves generated by the HAND model. The error between updated flows and observations at United States Geological Survey (USGS) station at Squaw Creek decreased by 35%. For future work, updated streamflows could also be used to dynamically update initial conditions in the continental-scale National Water Model.
1. Introduction
Flooding is among the most destructive natural disasters globally. In the United States, based on a U.S. National Weather Service (NWS) report, the average annual property/human losses are estimated to be more than $8 billion [1,2,3] (Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), 2013). Flood inundation maps help to detect flood-prone regions and can prevent major catastrophe by providing reliable information to the public about the flood-risk [4,5]. However, these maps are based on predictions of water depth values in the stream and on the landscape for extreme rainfall events [6]. Hydrology and hydraulic models can be useful for predicting these depth values, although, like many other models, these models are only as reliable as the underlying assumptions in the model’s structure and parameters [7,8]. The assimilation of water depth measurements, as a post-processing technique, has the potential to reduce the error between model predictions and observations in order to generate more reliable flood inundation maps [9].
Sequential data assimilation techniques are often used for updating a model’s state variables when new observations become available [10]. A data assimilation process is also able to reduce the uncertainty in prediction by integrating real-time observations from a variety of monitoring technologies [11,12]. The Kalman filter [13] is a commonly used data assimilation technique that was initially developed to update the state variables of linear systems [14]. However, this method has been used for nonlinear problems as well [15]. The ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF) is another data assimilation technique that was introduced by Evensen [16]. In the case of non-linear models for which the assumption of linearity is not satisfied, EnKF can be used as an effective technique. Multiple studies have also used this method in the past to update hydraulic, hydrologic, and hydrodynamic models [17,18,19]
The main objectives of this study include:
- (1)
- Assimilating water depth measurements to dynamically update water level predictions.
- (2)
- Improving streamflow predicted by the National Water Model (NWM) using updated water levels.
- (3)
- Proposing a scope to update continental-scale hydrologic models (e.g., NWM).
2. Study Area and Methodology
2.1. Study Area Characteristics and Data Collection
The study domain is the Squaw Creek watershed (Hydrologic Unit Code (HUC) ID = 0708010503), located in Jasper County, Iowa (Figure 1), which drains 40.3 km2 and discharges into the Skunk River. It is located on Southern Iowa Drift Plain and characterized by steeply rolling hills and well developed drainage [20]. This watershed has experienced several flooding events in the past [21], and it contains a dense network of bridge sensors that measure the water level along the channel. Flow measurements are collected at a USGS station (# 5470500) in this watershed. Water surface elevation were gathered from the Iowa Flood Information System (IFIS). The Iowa Flood Center (IFC) developed and maintains nearly 250 stream stage sensors across the state. Sensors are attached to the sides of bridges and are designed to measure the distance from the sensor to the water surface. Data is transmitted automatically and frequently to the Iowa Flood Information System. Water surface elevation at each time step can be calculated by subtracting the sensor measurements from the elevation of each sensor.
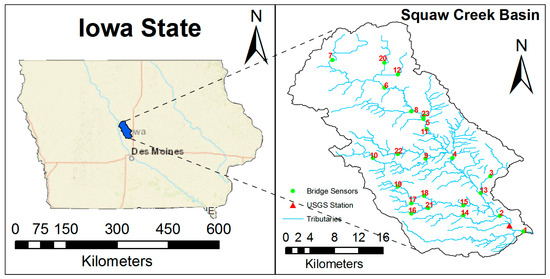
Figure 1.
Squaw Creek watershed (Iowa State).
2.2. Proposed Approach
Figure 2 illustrates the overall proposed methodology:
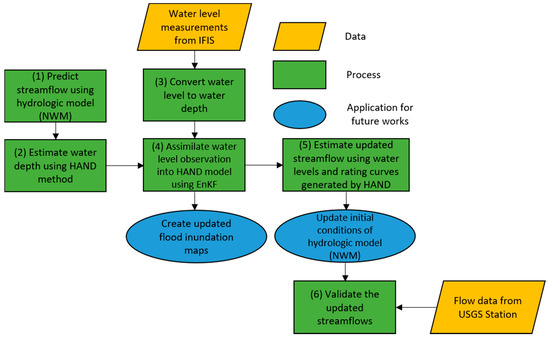
Figure 2.
Schematic methodology.
Hourly predicted flows for each tributary were first obtained from the NWM (Step 1). The Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) [22] method was then used to predict the water depth in river channels (Step 2). Incoming hourly water level observations from the Iowa Flood Information System (IFIS) were converted to water depth (Step 3) to become consistent with HAND water depth predictions, and then assimilated into the HAND model via an ensemble Kalman filter technique (Step 4). Finally, using back calculation, updated water levels were converted to flow using rating curves generated by the HAND (Step 5). For future work, results from Steps 4 and 5 can be used to create flood inundation maps and update the initials conditions of the hydrologic model (NWM), respectively. Finally, updated streamflows were validated using flow measurements at USGS stations (Step 6).
There are 85 tributaries and 20 bridge sensors that measure the water levels. Since the cross-sections were not available for all of these sensor locations, measurements of only 10 sensors were used for data assimilation. Six sensors were randomly selected for training and the other four sensors were selected for testing to make sure that this approach is also suitable for tributaries with no observation. The NWM predicts the flow at the outlet of each sub-basin, however, bridge sensors are located upstream of outlets. Assuming equal soil type and land use for each sub-basin, the flow at the outlet was linearly distributed along the river.
where Qoutlet is the flow at the outlet of each sub-basin, LTotal is the length of river, LPartial is the river length from bridge sensor to the outlet of each sub-basin, and QB is the flow measured at each bridge sensor.
2.3. National Water Model
The National Water Model (MWM) is a continental-scale hydrologic model that generates forecasts for multiple variables [23]. The NWM was released by the National Weather Service (NWS) Office of Water Prediction (OWP) in collaboration with the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and the National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP). The model generates streamflows for 2.7 million reaches of the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) with four forecast products (i.e., analysis and assimilation, short range forecast, medium range forecast, and long range forecast) [24]. Table 1 shows the forecast step, frequency, and forecast duration of each product.

Table 1.
National Water Model details (http://water.noaa.gov/about/nwm).
2.4. The HAND Method
The Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) [22] is a model generated by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Water Center for developing continental-scale inundation mapping [25]. It is based on hydrological terrain analysis to produce flood inundation maps [26,27]. The Digital Elevation Model (DEM) of watershed is used to drive the flow direction and flow accumulation area. A stream grid is then generated to be used as an input to Terrain Analysis Using Digital Elevation Models [28], along with the flow-direction grid, to create the height of each grid cell above the nearest drainage. The NWM predicts flow at the outlet, which can be converted to water depth with a rating curve, and 10 sensors also provide information of water depth. The HAND is a raster-based method and specifies the inundation zone according to the corresponding river segment. It produces an inundation map according to the water depth of tributaries [25].
2.5. Ensemble Kalman Filter
The ensemble Kalman filter algorithm was used in the proposed methodology (Step 4) to assimilate water depth observations into the model. In the ensemble Kalman filter, the prediction model is represented by:
where h denotes the vector of state variables (water depth), Q is the flows from the National Water Model, wk is stationary zero-mean white noises, F represents the prediction model (HAND model), and the subscript “k” denotes the time step. If an ensemble of n predicted state variables is available, can be written as:
where the superscript “” represents the ith forecast ensemble member. Generally, initial condition and inputs are perturbed and ensemble of predicted state variables is generated by running the model for each initial condition. This technique needs to run the model several times for each realization. However, due to computational cost, it is not possible to run the NWM several times to create the ensemble. Instead of perturbing the initial conditions (IC) and inputs, ensemble was created by taking several predicted flows by the NWM up to 4 h (outflow changes by 10% during this period) before the selected events. Outflow was then converted to water depth using rating curves generated by the HAND. For this study, 10 realizations were created to estimate the error matrix in the model.
The average of the ensemble is defined by:
Since true states are not known, we estimate them using the average of realizations in the ensemble. Then the error matrix can be estimated by:
The error matrix is then used to calculate the Kalman gain matrix by:
where H is the linear transformation which relates the state variables to observations. The updated state vector (ha) is taken to be a linear combination of the forecast and the observations. The observations should be treated as random variables to obtain consistent error propagation in the ensemble Kalman filter [29]. Hence, the actual measurements were used as reference and random noise with zero mean and covariance R was added to measurements. The updating equation is given by:
where h* is the water level observations after adding random noise.
2.5.1. Undersampling
The accuracy of the ensemble Kalman filter is highly dependent on the size of the ensemble. However, due to the complexity of models and computational cost, it is not always possible to generate a large ensemble. If the number of the ensemble is relatively small, it will not be able to accurately estimate the model covariance matrix and system may be undersampled. Inbreeding, filter divergence, and spurious correlation are the main issues caused by undersampling [30]. Covariance inflation and covariance localization are the most common methods used to solve the undersampling problem [31].
2.5.2. Covariance Inflation
Equation (7) is used to inflate the underestimated covariance [32]:
where ← denotes the replacement of a previous value and r is the inflation factor. The optimal inflation factor is related to the ensemble size and may vary between 1.01 and 1.07 [31]. Several methods have been proposed to estimate the inflated forecast and observational error covariance matrices [33]. The adjusted forms of forecast and observational error covariance matrices are λkPk and μkRk, respectively. Wu et al. (2013) proposed Equations (9) and (10) to estimate λk and μk [34].
where .
2.5.3. Covariance Localization
Covariance localization indicated the cutting of the covariance matrix at a specific length [35]. Correlation function suggested by Gaspari and Cohn (1999) was applied to the covariance matrix by using the Schur product to eliminate the spurious correlation [36,37]. The application of covariance inflation and localization methods transform the updating Equation (7) to the one below (Equation (11).
3. Results
Streamflow obtained from the NWM for all 85 tributaries were converted to water depth using rating curves generated by the HAND model. Figure 3 shows examples of the rating curves derived from the HAND for two tributaries in the watershed.
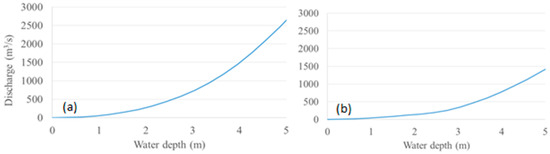
Figure 3.
Rating curves created by the Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) for (a) Squaw Creek River and (b) Prairie Creek River.
Water level measurements were assimilated into the model for seven bridge sensors selected as training points. Figure 4 shows the water depth at the training locations (a) before data assimilation and (b) after data assimilation, compared with observations from the IFIS. Green triangles are model predictions from the HAND before data assimilation, red squares are updated water depths after data assimilation, and blue dots are water depth observations from the IFIS.
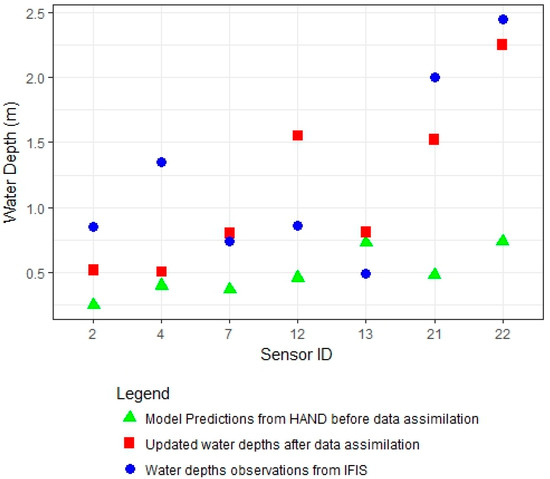
Figure 4.
Water depth at each sensor location.
We found that after the assimilation of water depth, the overall error for training locations reduced from 98 cm to 48 cm. We also calculated the error for the testing locations to make sure that the Kalman filter is able to improve the model accuracy for the sites with no observations. It was found that the overall error decreased for testing locations as well (from 89 to 44 cm). Table 2 compares the water depths before and after data assimilation with observations from IFIS for training and testing tributaries. Results show that overall error for both training and testing locations decreased by 48 cm (51%). However, the error has not been improved or error improvement is not significant in some of the sensor locations. This could be due to a small ensemble size and error in the observations (especially error in cross-sections of bridge sensor). The general Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) formula is indicated in Equation (13).

Table 2.
Water depth before and after data assimilation compared with water depth measurement from the Iowa Flood Information System (IFIS) for training and testing tributaries.
Figure 5 illustrates the time series of flow predicted by the NWM versus flow observation at the USGS station at Squaw Creek at Ames. Water depth observations were assimilated at 6:00, 11:00, and 17:00 on 24 June 2015. After updating the water depth at selected times, the rating curve from the HAND was used to estimate the corresponding flow (green dots in Figure 5). It was found that the overall error between USGS measurements and updated flows from the NWM was reduced by 35% for selected times. Since continental-scale hydrologic models such as the National Water Model are computationally expensive and it is not possible to run them several times to create a larger ensemble, the proposed methodology can be used as an effective method for future studies to update the initial condition of such models.
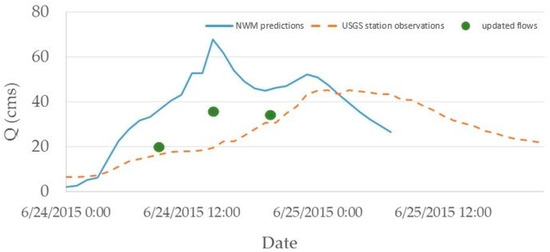
Figure 5.
River flow at a USGS station at Squaw Creek at Ames. Solid blue line shows the NWM predictions, dashed-red line shows the observations at the USGS station, and green dots show the updated flows.
4. Conclusions
The National Water Model provides flow rates for 85 tributaries in the study area. A data assimilation framework was proposed to (i) reduce the error of water depth prediction in tributaries, (ii) update the streamflow prediction, and (iii) introduce a scope for updating the initial conditions of continental-scale hydrologic models. Streamflows from the NWM were first converted to water depth using the HAND model and then assimilated to the model. After data assimilation, the root mean square errors of the estimated depth were reduced by 50 cm (51%). However, the error was not reduced at all sensor locations. The main reason for this is the error in bridge cross-sections. For future works, it is highly recommended to collect accurate cross-sections of rivers at each bridge equipped with a sensor. In this study, cross-sections were estimated based on measurements taken downstream and upstream of each bridge. Another reason could be the small ensemble size. It was also found that the proposed methodology is effective for the tributaries without observation. The model predictions improved by 45 cm for tributaries for which observations were not assimilated to the model. Finally, updated water depth at the outlet of the watershed was converted to streamflow using rating curves generated by the HAND. The proposed methodology could also be used to dynamically update initial conditions in the continental-scale National Water Model.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc. (CUAHSI) and the Office of Water Prediction (OWP) for coordination of Summer Institute. The authors would also like to thank Ibrahim Demir for providing water level observation for state of Iowa.
Author Contributions
Amir Javaheri and Mohammad Nabatian conceived and designed the methodology; Amir Javaheri and Mohammad Nabatian analyzed the data; Amir Javaheri and Ehsan Omranian prepared the graphs; Amir Javaheri and Ehsan Omranian wrote the paper with the multiple inputs and reviews by Meghna Babbar-Sebens and Seong Jin Noh.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saksena, S.; Merwade, V. Incorporating the effect of DEM resolution and accuracy for improved flood inundation mapping. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarekarizi, M.; Rana, A.; Moradkhani, H. Precipitation extremes and their relation to climatic indices in the Pacific Northwest USA. Clim. Dyn. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omranian, E.; Sharif, H.O. Evaluation of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Satellite Rainfall Products Over the Lower Colorado River Basin, Texas. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follum, M.L.; Tavakoly, A.A.; Niemann, J.D.; Snow, A.D. AutoRAPID: A Model for Prompt Streamflow Estimation and Flood Inundation Mapping over Regional to Continental Extents. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, S.; Omranian, E.; Feng, D. Relative Sensitivity of Flood Inundation Extent by Different Physical and Semi-Empirical Models; CUAHSI Technical Report No. 13; Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarzadegan, K.; Merwade, V. A DEM-based approach for large-scale floodplain mapping in ungauged watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, P.A.; Saunders, W.C.; Bouwes, N.; Wall, C.E.; Bangen, S.; Wheaton, J.M.; Nahorniak, M.; Ruzycki, J.R.; Tattam, I.A.; Jordan, C.E. Linking models across scales to assess the viability and restoration potential of a threatened population of steelhead (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the Middle Fork John Day River, Oregon, USA. Ecol. Model. 2017, 355, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, S.A.; Hosseiny, H.; Ekhtari, N.; Khazaei, B. Using MODIS remote sensing data for mapping the spatio-temporal variability of water quality and river turbid plume. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 21, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Andreadis, K.M.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Moller, D.; Wilson, M. Estimation of bathymetric depth and slope from data assimilation of swath altimetry into a hydrodynamic model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, G. Data Assimilation: The Ensemble Kalman Filter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moradkhani, H. Hydrologic Remote Sensing and Land Surface Data Assimilation. Sensors 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Moradkhani, H.; Zarekarizi, M. A probabilistic drought forecasting framework: A combined dynamical and statistical approach. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maybeck, P.S. Stochastic Models, Estimation and Control; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Krener, A.; Duarte, A. A Hybrid Computational Approach to Nonlinear Estimation. In Proceedings of the Decision and Control, Kobe, Japan, 13 December 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Evensen, G. Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 10143–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.; Wood, E. The assimilation of remotely sensed soil brightness temperature imagery into a land surface model using Ensemble Kalman filtering: A case study based on ESTAR measurements during SGP97. Adv. Water Resour. 2003, 26, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh Seong, J.; Tachikawa, Y.; Shiiba, M.; Kim, S. Ensemble Kalman Filtering and Particle Filtering in a Lag-Time Window for Short-Term Streamflow Forecasting with a Distributed Hydrologic Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1684–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.N.; Cane, M.A. A Kalman Filter Analysis of Sea Level Height in the Tropical Pacific. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1989, 19, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Thompson, C.A. Walnut creek watershed monitoring project, iowa monitoring water quality in response to Prairie restoration. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2000, 36, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogg, J. The Top Five Iowa Floods; National Weather Service WFO: Des Monies, IA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Maidment, D.; Tarboton, D.; Zheng, X.; Yıldırım, A.; Sazib, N.; Wang, S. A CyberGIS Approach to Generating High-Resolution Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) Raster for National Flood Mapping. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on CyberGIS and Geospatial Data Science, Urbana, IL, USA, 26–28 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA Launches America’s First National Water Forecast Model; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016.
- Souffront Alcantara, M.A.; Crawley, S.; Stealey, M.J.; Nelson, E.J.; Ames, D.P.; Jones, N.L. Open Water Data Solutions for Accessing the National Water Model. Open Water J. 2017, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Afshari, S.; Tavakoly, A.A.; Rajib, M.A.; Zheng, X.; Follum, M.L.; Omranian, E.; Fekete, B.M. Comparison of new generation low-complexity flood inundation mapping tools with a hydrodynamic model. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, A.D.; Cuartas, L.A.; Hodnett, M.; Rennó, C.D.; Rodrigues, G.; Silveira, A.; Waterloo, M.; Saleska, S. Height Above the Nearest Drainage—A hydrologically relevant new terrain model. J. Hydrol. 2011, 404, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennó, C.D.; Nobre, A.D.; Cuartas, L.A.; Soares, J.V.; Hodnett, M.G.; Tomasella, J.; Waterloo, M.J. HAND, a new terrain descriptor using SRTM-DEM: Mapping terra-firme rainforest environments in Amazonia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3469–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Tarboton, D.; Yildirim, A.; Wilkins-Diehr, N. Accelerating TauDEM as a Scalable Hydrological Terrain Analysis Service on XSEDE. In Proceedings of the 2014 Annual Conference on Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment, Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Burgers, G.; Jan van Leeuwen, P.; Evensen, G. Analysis Scheme in the Ensemble Kalman Filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, R.E. Localization in the Ensemble Kalman Filter; University of Reading: Reading, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hamill, T.M.; Whitaker, J.S.; Snyder, C. Distance-Dependent Filtering of Background Error Covariance Estimates in an Ensemble Kalman Filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2776–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Anderson, S.L. A Monte Carlo Implementation of the Nonlinear Filtering Problem to Produce Ensemble Assimilations and Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2741–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bishop, C.H. A Comparison of Breeding and Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter Ensemble Forecast Schemes. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 1140–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Li, Y. A new structure for error covariance matrices and their adaptive estimation in EnKF assimilation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtekamer, P.L.; Mitchell, H.L. Data Assimilation Using an Ensemble Kalman Filter Technique. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, G.; Cohn, S.E. Construction of correlation functions in two and three dimensions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 723–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, A.; Babbar-Sebens, M.; Miller, R.N. From skin to bulk: An adjustment technique for assimilation of satellite-derived temperature observations in numerical models of small inland water bodies. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 92, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).