Abstract
From 18 to 19 June 2013, the Ésera river in the Pyrenees, Northern Spain, caused widespread damage due to flooding as a result of torrential rains and sustained snowmelt. We estimate the contribution of snow melt to total discharge applying a snow energy balance to the catchment. Precipitation is derived from sparse local measurements and the WRF-ARW model over three nested domains, down to a grid cell size of 2 km. Temperature profiles, precipitation and precipitation gradient are well simulated, although with a possible displacement regarding the observations. Snowpack melting was correctly reproduced and verified in three instrumented sites, and according to satellite images. We found that the hydrological simulations agree well with measured discharge. Snowmelt represented 33% of total runoff during the main flood event and 23% at peak flow. The snow energy balance model indicates that most of the energy for snow melt during the day of maximum precipitation came from turbulent fluxes. This approach forecast correctly peak flow and discharge during normal conditions at least 24 h in advance and could give an early warning of the extreme event 2.5 days before.
Keywords:
ROS; snow; rain; flood; WRF; numerical weather forecast; energy balance; discharge estimation; early alert system 1. Introduction
From June 18 to June 19, 2013, the Ésera river in the Pyrenees, Northern Spain, caused widespread damage due to flooding. Damage to public properties, such as roads or bridges, and to private property was estimated in excess of seven million euros. Over 300 people had to be evacuated from their homes, but fortunately there were no fatalities. The increased flow came as a result of torrential rains at a time when the catchment presented an anomalously extensive snow cover above 2000 m [1], and the 0 °C isotherm was above 4000 m a.s.l.
The role of rain on snow events (ROS) is interesting from a scientific and applied point of view, since it is widely recognised that they dominate much of the flood generation in mountainous and boreal regions [2,3]. Most of the largest floods in British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and California have been associated with ROS [4,5,6]. In Germany, ROS have much larger hydrological influence than rain alone in catchments above 400 m a.s.l. ROS have been identified as a primary cause of changes in channel morphology due to erosion [7,8,9,10,11]. For example, at a site in the Oregon Cascades, 85% of all landslides which could be accurately dated were associated with snowmelt during rainfall [7]. Sandersen et al. [12] reported that triggering of debris flows in Norway is caused by the combination of rainfall and snow melt. ROS events are also considered a major cause in the release of some type of avalanches [2].
The importance of ROS events is highlighted above, however there is uncertainty about the physical processes that control the runoff generation during their occurrence and their sensitivity to temperature and other meteorological variables. McCabe et al. [6] made a comprehensive study of several ROS events in the Pacific Northwest of the United States (PNW) concluding that the severity of a ROS events does not only depend on the magnitude of the precipitation but also on the elevation of the freezing level and the extent and characteristics of the existing snowpack. Marks et al. [13] studied a heavy ROS event (winter 1996) in the Pacific North West of the United States, where they found that 60–90% of the energy for snowmelt came from turbulent heat exchange. Condensation during the event was a significant contributor to the flood. Van Heeswijk et al. [14] concluded that wind speed together with vapour pressure and temperature gradients are the most important climate variables that control snow melt. However, in a later study Mazurkiewicz et al. [15] found that radiation was the largest contributor to melt during ROS in the Pacific North West. Other studies show the importance of the low permeability of the snowpack when it is saturated, leading to a quick generation of excess runoff. This indicates that heavy rain water moves several times faster than the natural snowmelt [2,11,16]. During ROS events the potential for flooding is increased if the soil is frozen [17,18].
Quantifying the actual contribution of snow melt and rain to runoff in a particular ROS event is challenging, as well as it is the extrapolation of results to other events or geographical areas. Such complexity makes it difficult to anticipate the hydrological response of a catchment, even when detailed meteorological forecasts are available. In the last decades the spatial resolution and the accuracy of atmospheric mesoscale models have improved rapidly. These models are now able to produce reliable meteorological fields over complex terrain when forced with realistic initial and boundary conditions [19,20,21]. Such fields can be used as inputs for hydrological models enabling the forecasting and analysis of extreme weather events, such as ROS, and their hydrological consequences. However, a small deviation in determining initial conditions, or biases in the input data for snow models may lead to considerable errors in the timing, magnitude and spatial distribution of the simulated flood [22,23].
In this study, we investigate the skill of a high resolution weather model—the weather research and forecasting model, advanced research WRF core, WRF-ARW [24]—to simulate and forecast the occurrence of this extreme precipitation event. The output of the WRF combined with land observations and remote sensing data are used to feed a physically-based snow energy balance model. This approach is useful to improve our understanding of ROS in several aspects:
- To assess the suitability of snow models coupled with atmospheric models to simulate ROS events
- To estimate the spatial distribution of discharge in several sub-catchments
- To estimate the relative forcing of meteorological variables to snow melt
- To estimate the relative contribution of snowmelt and rainfall to the final river discharge
- To estimate how much time in advance a weather model can give an early warning of dangerous floods.
All these questions are key to understanding the nature and predictability of ROS events in the Pyrenees and other similar mountain regions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site of Study
The Ésera river is one of the most important tributaries of the Ebro river in North Eastern Spain. Most of its runoff is generated in the headwater area located in the central Spanish Pyrenees. The flood event described in this study affected mostly the upper portion of the catchment, therefore, we restrict ourselves to the area above the gauging station of Eriste, at 1050 m a.s.l. (Figure 1). It was near this location that the most destructive effects of the flood were experienced. The catchment area is 323 km2 and contains five small sub-catchments: Eriste, Estós, Maladeta, Ramascaró and Vallibierna. They drain one of the highest ranges in the Pyrenees, with many peaks exceeding 3000 m a.s.l., including the highest summit in the whole mountain range: Aneto (3404 m a.s.l.). In this catchment 65.6% of the area is located above 2000 m a.s.l., and 26.4% over 2500 m a.s.l. [25]. The geology exhibits a rather complex structure with granites, slates, schist and limestones heavily fractured and folded [26]. There is a mismatch in the extent of the topographic and the hydrological catchments, since several sinkholes divert part of the flow to the Garona basin (French Pyrenees). These diverted flow could represent 12%–25% of the annual runoff of the catchment [25,27]. The upper portion of the catchment corresponds to a high mountain landscape, with the highest concentration of small glaciers and ice fields of the mountain range [28].
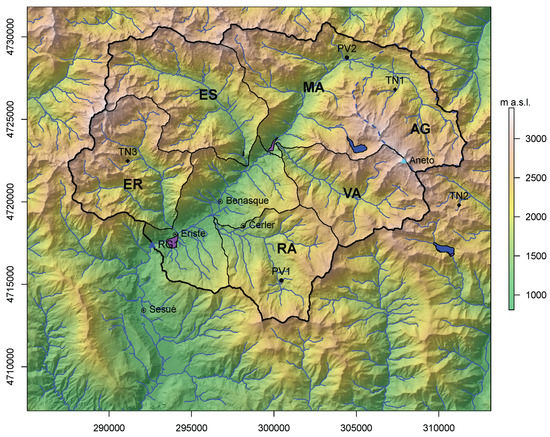
Figure 1.
Map of the area of study. Coordinates are Universal Transverse Mercator UTM zone 31. The Ésera catchment and sub-catchments are shown. ER: Eriste, ES: Estós, MA: Maladeta, RA: Ramascaró and VA:Vallibierna, the Aiguallut endorheic sub-catchment is indicated by AG. Aneto, to the northeast is the highest peak in the range. Main towns are indicated by their full name and sensors listed in Table 1 by their acronyms. River network and natural lakes are drawn in blue and artificial dams in purple.
The estimated mean annual precipitation is 1840 mm [25], exceeding 2500 mm per year above 3000 m a.s.l. [29] Spring and autumn are the wettest seasons, while summer exhibits a marked dry period. Mean lapse rates have been estimated between −0.0049 and −0.0056 °C m−1 [30,31], and the 0 °C isotherm at around 1700 m a.s.l. during the cold season (November-April). This leads to a deep and extensive snow cover from late autumn to late spring. Consequently, the Ésera river exhibits a marked nival river regime with high flows in late spring and early summer. The lowest runoff occur in winter as consequence of snow accumulation, followed by late summer (August and September) in response to the lowest precipitation [32]. The annual runoff of the catchment is 309.2 hm3 (9.8 m3s−1 on average).
2.2. Data
There are two pluviometers from the Automatic Hydrologic Information System of the Ebro river basin (SAIH) in the whole catchment. Temperature measurements are recorded at three snow gauges (“telenivometers”), which also record snow height and snow water equivalent (SWE). Two of the snow gauges are inside the catchment and a third one very close to the catchment boundary. The location of measuring stations is indicated in Table 1. Rain gauges are tipping bucket pluviometers, which are not suitable for solid precipitation and need careful calibration (WMO 2008). Snow height is recorded by an ultrasonic sensor and snow water equivalent using a cosmic-ray snow gauge. All data are public but additional information on sensor type and specifications is limited. These measured data were used to evaluate the model output, but the snow model was fed with WRF data directly. Precipitation distribution is difficult to evaluate as there were only two measurement sites, insufficient for a correct spatial extrapolation.

Table 1.
Coordinates of the measuring stations indicated in Figure 1. SWE is snow water equivalent, pcp is precipitation, temp is temperature and P is atmospheric pressure.
Initial snow extent and albedo were derived from a Landsat image acquired from the U.S. Geological Survey and readily available through their online site http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/. For the derivation of catchments and to calculate terrain parameters in the snow model, a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) was used. The original DEM at 5 m resolution was Lidar-generated and provided by the Spanish Geographical Office (IGN, Instituto Geográfico Nacional), this DEM was resampled at 30 m resolution in order to minimise artefacts, to make it compatible with the resolution of the Landsat images and to increase the computation speed of the snow model.
We approached the publicly funded Spanish Met Office (AEMET) for additional data, but were denied. We also tried to get data from the hydropower company operating the river dams, although this was an unsuccessful effort.
2.3. Remote Sensing
Initial albedo and snow cover extent were derived from a Landsat 8 image of 10 June 2013. The snow extent was obtained by estimating the Normalised Difference Snow Index (NDSI), according to Equation (1):
where is TOA (Top Of the Atmosphere) reflectance of Landsat band number n (see for example: [33]).
For the albedo we used the Landsat surface reflectance and the conversion from narrow band to broadband was done according to Wang et al. [34]. Additional corrections were made for the angle of incidence of the sun on the slope surface, which can vary greatly on mountain areas. The solar-terrain geometry was derived from the DEM following Corripio [35] and using the R package insol [36]. The resulting initial albedo is shown in Figure 2 and compared the original false colour Landsat image. The northern fringes of the image are partially covered in clouds, in these areas the snow cover limit was set according to the elevation. The limit was derived from the surrounding cloud-free areas as the mean lower elevation with snow. This limit was dependent on the orientation of the slope, and was calculated in steps of 15° from 0° to 345°.
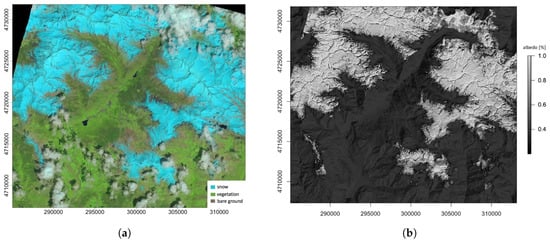
Figure 2.
Initial conditions for snow cover and albedo derived from Landsat. (a) Landsat “natural look” image of 10 June 2013; (b) Derived albedo superimposed on a shaded relief of the DEM.
2.4. Snow Model
We use a multi-layered, distributed snow energy balance developed by Corripio [37], and applied successfully to previous studies in the Andes [38] and the Alps [39]. The energy balance of the snow pack can be described as in Equation (2):
is the net energy balance at the snow pack, is incoming short-wave radiation, is snow albedo, is received long-wave radiation, both from the atmosphere and surrounding slopes, is emitted long-wave radiation, is turbulent sensible heat transfer with the atmosphere, is latent heat transfer, is heat transfer due to precipitation, and is subsurface heat transfer within the snow pack.
If the snow pack reaches the melting point temperature will be the energy available for melting the snow, otherwise the net energy is used to change the snow pack temperature. Sublimation depends on the specific humidity gradient, whether the snow pack reaches melting point or not. Short wave incoming radiation was modified locally to account for shading, sky view factor and reflected radiation. A detailed description of the radiation components and the effect of surrounding topography is explained in Corripio [37]. Long Wave was derived from the WRF model, an additional cloud factor following Iziomon et al. [40] was applied to discriminate between the direct and diffuse radiation fraction depending on cloud cover. The WRF model calculates incoming long wave radiation independent of the local topography, so a further modification was applied to account for terrain influences such as sky view factor. Turbulent fluxes with the atmosphere were calculated according to the bulk aerodynamic flux method [41,42,43,44]. This method seems to be one of the most reliable according to a comparative study by Sexstone et al. [45]. Heat transfer due to precipitation was estimated according to Brun et al. [46]. The subsurface component of the model is a simplified three layer scheme where heat transfer is computed following Oke [47] with a simplified solar radiation snow extinction following Fukami et al. [48] and Warren [49]. Initial Albedo is derived from a Landsat image and local measurements, the temporal evolution of albedo is estimated according to an ageing parameterization considering local air temperature [50,51]. The temperature field was interpolated to the high resolution model according to local elevation and lapse rates from the WRF model. Snow-rain limit was prescribed by a wet bulb temperature of 1.3 °C [52,53]. This gives a satisfactory result but an estimation that includes the precipitation rate could be an improvement. Finding the correct solution is not easy as the identification of the correct snow line is difficult during heavy precipitation and on mountain ranges with sparse instrumentation. The detailed equations of the model and derived variables are given in the Appendix A.
2.5. Atmospheric Model
We run a nested WRF model ARW core [24], with three domains at 18, 6 and 2 km over the Pyrenees. The model initial and boundary conditions were derived from the GFS global model at 00Z every day and run for 30h to overlap the next run. The available resolution of the GFS at the time was 0.5 degrees, while the current resolution is 0.25 degrees. We did not consider using data from the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecast model (ECMWF) for the initial conditions as they are prohibitively expensive and beyond the budget available for this study. The nested model was run daily from the 11th to the 26th of June.
The WRF model allows for different physical and dynamical settings and different radiative schemes, and these have an impact in the model ability to predict intense precipitation [54,55]. It would be desirable to make extensive tests to find which combination of settings perform better during heavy precipitation events in the Pyrenees. To our knowledge this is still to be tested. In the absence of this information, we decided to use the settings shown on Table 2, based on information from previous work in the region and other mountain areas using the WRF model [56,57,58]. For a detailed description of the settings see the WRF User’s Guide [59].

Table 2.
WRF physics settings.
The output of the WRF model is in NetCDF format and the projection is in geographical longitude and latitude. To make it compatible with the DEM in Universal Transverse Mercator UTM projection, the files were reprojected using a Linux implementation of the GDAL - Geospatial Data Abstraction Library [60].
2.6. Discharge
From snowmelt and rainfall inputs river discharge was estimated using a parallel Single Linear Reservoir (SLR) model for every catchment. The SLR model assumes that storage S is linearly related to outflow Q by
where K is the storage coefficient and has units of time [61].
Combining this equation with the hydrologic continuity equation e.g., [61,62] and integrating gives:
where u is inflow at time t.
Hannah and Gurnell [63] suggest deriving the parameter K from the gradient of a semilogarithmic plot of discharge over time when there is no recharge, following Equation (5):
However, deriving the parameter K is problematic without accurate discharge measurements. The problem in this case is that the only river gauge is located after a dam used for hydroelectric generation. Thus, the river flow may change considerably depending on whether turbines are operating or not. If electricity is generated, the stored water in the dam is evacuated directly through a pipeline and bypass the river gauge. To complicate things further, there are two additional dams upriver that channel water to a power station located at the lower dam. The outflow of the lower damn for electricity generation is 30 m3s−1; the capacity of the lower damn (Linsoles) is 3.5 hm3; the two upper dams (Estós and Paso Nuevo) are linked to the lower dam by a pipe with a maximum flow of of 36 m3s−1. This situation makes difficult a proper calibration of the storage coefficient and therefore we have made an approximate calculation by trial and error. We used six different linear reservoirs corresponding to every sub-catchment, with different storage coefficients for snowmelt and rainfall. Travel times for every sub-catchment are taken into account and calculated with the GRASS module r.traveltime [64]. Singh et al. [2] recalls previous work showing that heavy rain may increase the speed of water drainage through snow, as more efficient channels develop in the snow pack. To account for this change we have modified the storage coefficient linearly with time.
The Aiguallut sub-basin on the north east of the main catchment (AG in Figure 1) is an endorheic basin, which drains to the Garona river, north of the area of study and already in French territory. It is a well developed karstic network with several intakes and an outflow at Uelhs deth Joeu to the Garona river [65,66]. Maximum measured outflow is 11–12 m3s−1 [65], at the time of the flood event the main intake at Aigualluts was saturated and discharge overflew to the Ésera river, thus this maximum value was subtracted form the main discharge of the sub-basin.
3. Results
Figure 3 shows a good agreement between measured temperature and temperature simulated by WRF, with an overall mean error of 0.21 °C and a mean absolute error of 1.51 °C at La Renclusa (point TN1 in reference table and map). However, maximum measured temperature is higher (up to 3.5 °C) than simulated temperature during days with high incoming solar radiation. The temperature probes are shielded but not ventilated, which may result in an overestimation of the maximum measured value [67]. The WRF model simulates the amount of precipitation approximately, as seen in Figure 4. It shows the maximum simulated precipitation to the west of maximum measured precipitation, but the sensor network is too sparse to decide whether there is a displacement bias or it is a realistic simulation. The simulated north–south gradient in precipitation is also observed in the measured data, between Llanos del Hospital (PV2) and Ampriu (PV1) The geomorphological evidence also suggest a strong gradient as the Vallibierna sub-catchment (VA) was showing less sediment transport and deposition than in previous floods events in the area (Santiago Somolinos, personal communication).
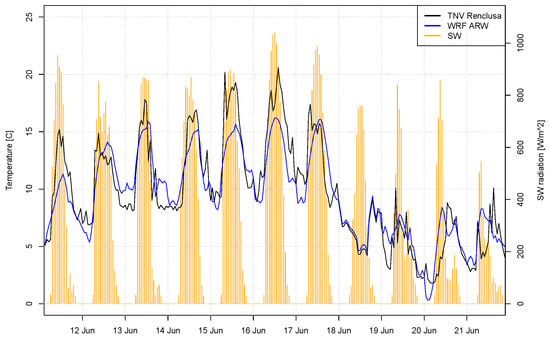
Figure 3.
Comparison temperature simulated by the WRF model and measured at Renclusa “telenivometer” (TN1). Orange bars is shortwave radiation simulated by WRF at the same location.
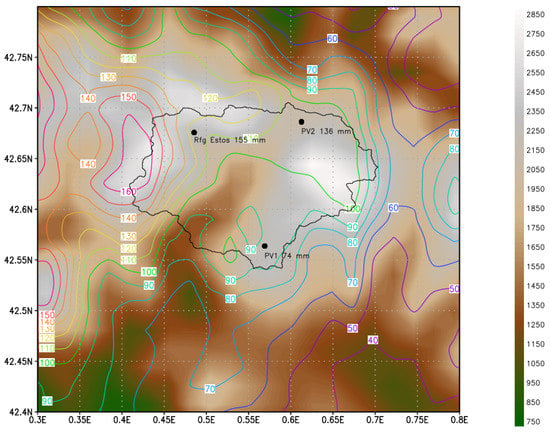
Figure 4.
Simulated precipitation [mm] contour map by the WRF, in black is the Ésera catchment. Background colour is model surface elevation as indicated by the legend on the right side. The points indicate accumulated precipitation measurements at two tipping bucket pluviometers and in a totaliser pluviometer at the Refugio de Estós (Estós mountain Hut). The totaliser data is provided by Serrano Notivoli et al. [68], but they have not been verified.
Figure 5 shows the simulated depletion of snow height in three grid cells containing the cosmic ray snow gauge at La Renclusa, Salenques and Eriste (TN1, TN2 and TN3; at 2180, 2350 and 2600 m a.s.l. respectively). There are no data from radiometers or albedometers in the catchment, and therefore no measurements to check the validity of the model radiation inputs. This could cause large errors in the snow model simulation, nonetheless, the depletion curves of snow height are properly simulated during the previous days to the flood, as shown in Figure 5. During the ROS event, melting is slightly underestimated, except for Salenques, the highest site, where an apparent peak due snow accumulation is missed by the model. The Nash-Stuclife efficiency model coefficient [69] gives values ranging between 0.96 and 0.99, confirming the good agreement between measurements and simulations (Table 3). Figure 5 also shows that except in the highest TN (Salenques at 2600 m a.s.l.) snow cover completely disappeared by the end of the period. Figure 6 shows the snow extent retrieved from a Landsat image in 26th June, 2013; and the simulated snow cover at the same date. It confirms the ability of the model to simulate the spatial distribution of snow cover depletion during the previous days and during the ROS event.
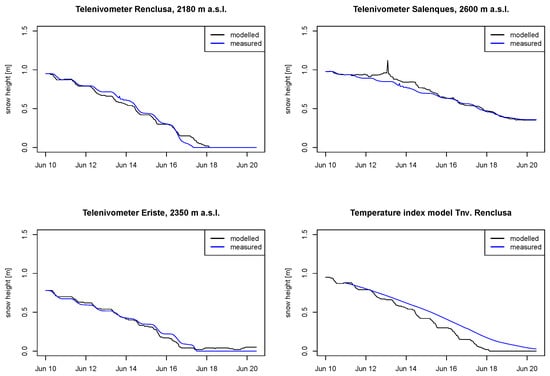
Figure 5.
Snow height modelled and measured in three snow gauges (TN1, TN2 and TN3 in map in Figure 1) at the Ésera catchment. The lower panel is the result of a simpler temperature index model applied to the Renclusa site. The melt factor was computed as the best linear fit to previous 24 h accumulated positive degree days and corresponding melt. The calibration period was the week before the ROS event in this case the Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency value degrades to 0.89.

Table 3.
Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency values for the measured and simulated snow ablation at three snow gauges.
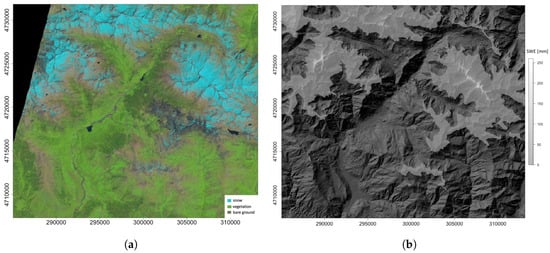
Figure 6.
Observed and simulated snow cover after the event. (a) Landsat image 26 June 2013; (b) Simulated snow water equivalent (SWE) on the same day.
During the day when peak flow occurred, the snow energy balance was dominated by a positive influx of energy from turbulent interchange with the atmosphere. Both sensible heat and latent heat transfer were positive, indicating condensation of atmospheric moisture on the snow (Figure 7). Shortwave radiation was second in importance, followed by advective heat transfer from the rain. Net long wave was positive, contrary to most days when there is an effective radiative cooling of the snow pack. Simulated subsurface fluxes were negligible during the ROS event, except for a short period early on the 19th of June when there was a positive flux toward the surface snow pack. For the calculation of heat transfer due to rain (Equation (A28)) it is necessary to know the temperature of the rain. Byers et al. [70] measured rain temperatures and found that after an intense precipitation event rain temperature was always close to air temperature (about 1 °C difference). For this study we assumed that the rain temperature was 1 °C colder than the air temperature. During the time of peak precipitation, simulated lapse rates above the surface were in the range between −0.003 and −0.0045 °C m−1, thus one degree colder means that the rain had the temperature of a layer between 200 and 300 m above the surface.
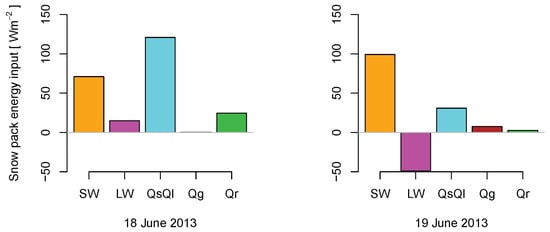
Figure 7.
Snow energy balance flux partition. SW is net shortwave radiation, LW is net long wave radiation, QsQl is turbulent heat interchange with the atmosphere, Qg is heat transfer from the subsurface and Qr is advection of heat due to rain. Following convention, positive indicates flux towards the snow and negative flux is energy leaving the snowpack.
Figure 8 shows the observed and simulated discharge at Eriste gauging station, the grey uncertainty shade is ±30 m3s−1 corresponding to the intake of the hydroelectric plants. The peak discharge is well represented in the simulation (Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient of 0.76), but the river flow seems to decrease very slowly, with a secondary peak in precipitation that is larger than the observed variation. Rainfall is the main contribution to peak flow. Snow melt contribution is very well simulated before the ROS event, which adds confidence to the snow model results. Snowmelt was the main contributor to total water discharge during the previous days. Discharge was larger than the average for the season, probably causing saturation of soils and a very fast hydrological response to the rainfall event. During the flood event of the 18–19th of June estimated snowmelt represented 33% of total runoff, on the day of maximum precipitation (the 18th) snowmelt was calculated as 28% of total discharge and 23% at the time of peak flow.
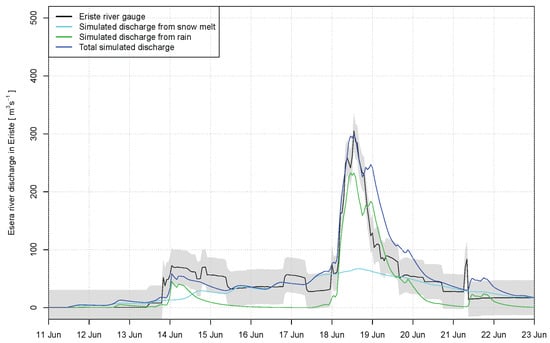
Figure 8.
Observed and simulated discharge (total and originated from snowmelt and rain) at Eriste river gauge, error bands in measured discharge are ±30 m3s−1 which is the pipe discharge of the hydroelectric plant.
4. Discussion
We believe that the combination of high resolution numerical weather prediction models, together with energy balance snow models are excellent tools to predict snowmelt and mountain river discharge, both during extreme events such as intense ROS, or during average conditions. We also think that is useful to stress uncertainty and limitations, so that we can improve this kind of simulation in the future. Simulated precipitation from the WRF model approximates the timing and intensity of the ROS event of 18–19th June, 2013 in the Ésera river. There are large discrepancies with local measurements ranging from 8 to 38% difference in accumulated precipitation. The sensor network in the area is too sparse to detect where the spatial distribution is correct or there is a displacement bias, as has been noted in other WRF simulations in the Pyrenees [58], as well as in other regions and for other variables [71]. Pennelly et al. [57] has shown the impact of cumulus parameterizations on the location and magnitude of precipitation events at lower resolution. It is unclear if this effect is propagated to the higher resolution nested domains, even when they can allow for resolving rather than parameterizing convection. The simulation of the precipitation peak is good enough for regional scale simulations, but it would be a great advantage if location accuracy could be improved. A thorough investigation into the best parameterization and best resolution for accurate numerical precipitation forecast in these mountain ranges is strongly recommended.
There is a strong north to south precipitation gradient, both in the measurements and the simulations. There is probably a vertical gradient in precipitation, too. This has been observed in many other mountain regions. For example Liston and Elder [72] use a seasonally variable linear gradient, where precipitation increases with altitude, according to work in the western US by Thornton et al. [73]. Closer to the Pyrenees, in the Alps Lehning et al. [74] have noted the problems of deriving a reliable precipitation gradient, either because of lack of measurements at high altitude [75,76], or because the difficulty of measuring solid precipitation at high elevation and with strong winds [77]. In fact, extensive work in the Swiss Alps reveals precipitation gradients ranging from −69 to +15 mm/km in summer or from −27 to +25 mm/km in winter [78]. We do not yet have enough information to derive a reliable elevation gradient of precipitation in the Pyrenees, and therefore it was not applied to the spatial interpolation of precipitation over the model domain.
The simulation of snow melt at a single point is successful, with a mean Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency value of 0.98 (Table 3) and suggests that the energy balance approach to simulate snow melt is a reliable one. This approach works well both for clear days, when solar radiation is the main energy input, and for overcast and rainy days, when the main energy input are turbulent fluxes with the atmosphere and there is an additional influx of long-wave thermal radiation. There is some discrepancy at the highest snow gauge where the model underestimates the amount of fresh snow on the 13th of June. This is probably due to a simplistic estimation of snow-rain limit which does not take into account the precipitation rate. WRF modelled temperature is very similar to measured temperature, but unfortunately we do not have measured data on short-wave radiation, long-wave radiation nor albedo. A full meteorological station measuring these variables would be of great help to test further the reliability of the WRF model. It is interesting to note that the mean slope of ablation rate changes very little after the 17th of June on the highest snow gauge, even when there is a drop of temperature of almost 10 degrees. The reason may be the increase in downwelling long-wave radiation from a cloudier atmosphere, which compensates for the reduced energy input from lower air temperature and reduced solar radiation. This highlights the remarks of Pomeroy et al. [79] on the unsuitability of simplistic temperature index models to simulate snow ablation and rain on snow episodes. These type of models can perform very satisfactorily when there are hardly any data available (e.g., [80,81]), but are more limited for application ROS events, as shown in lower right panel of Figure 5.
The distributed snowmelt model performs very well when comparing the total output of meltwater to discharge on days when there is no precipitation (Figure 7). This is reassuring and indicates that this modelling tools are also useful for standard operational river discharge forecasts in snow-covered regions. This is useful to optimise planning of hydropower production and to minimise conflicts in water usage. On days when there is heavy precipitation, the sum of rainfall and snow melt agrees well with measured discharge (Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency value of 0.76 overall), but rainfall decays too slowly on the WRF model. During heavy precipitation, rain creates more efficient channels and discharge is faster through snow [2]. An additional reason for this behaviour of the model could be an overestimation of the snow line altitude. Minder et al. [82] have reported observations where the snow line on the mountainside is lower than the estimated snow line in the free atmosphere and provide a theoretical explanation supported by model simulations. The main reasons for the depression of the snow line on the mountain slope are (a) latent cooling from melting precipitation; (b) microphysical melting distance (a 10 mm snow flake would melt 100 m lower than a 5 mm snowflake); and (c) adiabatic cooling of orographically forced air masses. This situation has an important impact on runoff, for example in the Sierra Nevada of California a rise in the snow line of 610 m (1000 ft) would triple the runoff from three mountain catchments [83].
Ideally the storage coefficient to estimate discharge should change with time to reflect snow ripening and snow pack reduction, we have set it to vary linearly with time. Further calibration efforts are hindered by the artificial fluctuation of the river discharge in a catchment with hydropower use. This approach uses an empirical calibration, which is not ideal to simulate extreme events. For future work it would be advisable to get enough information on land cover and soil properties to implement different runoff models that are less sensitive to calibration (for example [79]).
At peak flow during the flood event, simulated discharge due to snow melt is 23% of total discharge, and 28% during the day of maximum precipitation, with rainfall being the main contribution to the flood. Problems caused in the catchment due to excess precipitation were exacerbated by a very high freezing level, which caused most of the precipitation to fall as rain, with only some snowfall towards the end of the event on the highest peaks. We did some tests with the GFS and the WRF models (not shown in this paper) to evaluate the lead times for a reliable warning in future cases. Both models identify well the height of the 0 °C isotherm up to 2.5 days before the event. GFS detects unusual precipitation but lacks resolution to identify the valleys most likely to be affected. WRF underestimates precipitation three days ahead and forecasts it approximately correct 24 h before the event.
5. Conclusions
We have shown that mesoscale numerical weather prediction models as the WRF are useful tools to predict the timing and location of rain on snow and flood events in mountain catchments of complex topography. Estimating the exact amount of precipitation is still the weakest point, although it can be improved by a systematic evaluation of current models spatial resolution and parameterization options [54]. An energy balance of the snow pack coupled with precise treatment of terrain parameters is able to simulate the snow depletion in the catchment and therefore the snowmelt input to discharge. Agreement between simulated and measured discharge is excellent in days without precipitation, which highlights the usefulness of these models for operational flow forecasting. The partition of energy fluxes show that the main input during this ROS event was turbulent fluxes of sensible and latent heat. Both fluxes were positive, implying strong condensation of atmospheric moisture. A simplified linear reservoir model to calculate the timing of the discharge gives satisfactory results, but can be improved by applying models that are less prone to calibration. This, however, requires extensive data on land cover, soil types and depth and snow depth. An additional source of uncertainty is the actual transition between snow and rain, we have used a simplified approach based on the local wet bulb temperature. This gives a satisfactory result but an estimation that includes the precipitation rate could be an improvement. Finding the correct solution is not easy as the identification of the correct snow line is difficult during heavy precipitation and on mountain ranges with sparse instrumentation. We have also found that both global and mesoscale models can give lead times of at least 2.5 days on severe ROS and flood events. The WRF model coupled with an energy balance model of the snow can give satisfactory results 24 h in advance, which can be very helpful to to implement early warning systems and to avoid and mitigate potential flood damages.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Automatic Hydrologic Information System of the Ebro river basin (SAIH, http://195.55.247.237/saihebro/index.php for making meteorological and discharge data easily available online). We thank Lorna Raso for help with GIS processing, map production and the English editing of the final version, and Jose Luís Santiago Somolinos, a geologist and local resident, for first hand information on the flood event, geomorphological evidence on debris and sediment distribution and snow cover at the time. We are also grateful to two anonymous reviewers whose suggestions greatly improved the final manuscript. Part of the research of this paper is framed in the objectives of the project IBERNIEVE (CGL201452599-P) from MINECO, I+D+i Spanish National Plan. meteoexploration.com provided computer servers and HPC time.
Author Contributions
Juan Ignacio López-Moreno conceived the original research idea and contributed to data collection and data analysis. Javier G. Corripio did the atmospheric, snow and discharge modelling and also contributed to data collection and data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. There was no funding for this study, therefore the founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ARW | Advanced research WRF core |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| GFS | Global Forecast System |
| HPC | High Performance Computing |
| ROS | Rain On Snow |
| SAIH | Automatic Hydrologic Information System of the Ebro river basin |
| SLR | Single Linear Reservoir |
| SWE | Snow Water Equivalent |
| UTM | Universal Transverse Mercator |
| WRF | Weather Research and Forecasting Model |
Appendix A
Here we describe the detailed components of the energy balance of the snow pack. The incoming global solar radiation on every grid cell of the DEM is calculated as:
where is direct normal radiation is the cosine of the angle of incidence of the sun on the terrain slope, is a shading factor (0 if in shade, 1 if in sun), is the snow albedo, is diffuse solar radiation, is diffuse solar radiation reflected from the surrounding slopes, is the sky view factor or fraction of upper hemisphere visible from the DEM cell, and is an estimation of the ratio of surrounding cells in the shadow.
The ratio of direct to diffuse solar radiation is given by some compilations of the WRF or can be derived from a parametric solar radiation model, we used that of [84,85] and additional work by [86,87,88] for the estimation on cloudy days. The cosine of incidence of sun on the slope is the dot product
where is a unit vector in the direction of the sun:
with as latitude, is declination, is the hour angle and is the unit vector normal to the surface. For a regular DEM of cell size ℓ and elevation values z at row and column respectively, would be:
For a detailed description of the sun terrain geometry and the calculation of sky view factor see Corripio [35].
Long wave downwelling radiation is derived from the WRF model and compared to clear sky long-wave flux to determine the degree of cloud cover.
where is emissivity, T is temperature (K) with subscripts a and s for atmosphere and snow respectively and is the Stefan-Boltzman constant ( Wm−2K−4).
From this, atmospheric emissivity is calculated according to Prata [89] as
where precipitable water () is calculated following an empirical equation given also by Prata [89]:
where is screen level air temperature in K. The actual vapour pressure is , where is saturated vapour pressure computed following [90] polynomials (Equation (A8)), and is relative humidity from 0.0 to 1.0.
For the saturation vapour pressure over ice, the polynomials are:
The Obukhov’s stability length L is defined as:
where g is the acceleration of gravity [41,42].
The profiles for wind speed, water vapour and heat, considering measurements at one level and at the surface, as:
Subscripts refer to momentum, water vapour and heat respectively.
The functions are stability corrections, which depend on the Obukhov’s stability length. There is some disagreement on their values, which have been obtained empirically [91]. The values used here are similar to those used by Marks and Dozier [92], also reported by Brutsaert [91]. Thus, for unstable conditions ():
with .
For stable conditions ():
where
The transfer mechanisms of momentum and of other scalar admixtures are different at the surface, and consequently the roughness lengths have different values for momentum, water vapour and heat, which were calculated following Andreas [43]. He developed a fitting polynomial of the scalar roughness lengths over snow and sea ice (the coefficients for this are given in Table A1):
where refers to water vapour or heat depending on the coefficients used. The Reynolds number is a ratio of inertial to viscous forces [93] defined as:
and is the kinematic viscosity of air, with the coefficient of dynamic viscosity for air.

Table A1.
Values of the coefficients in the polynomials (Equation (A18)) that predict for temperature and water vapour [43] for smooth, transition and rough surfaces.
Table A1.
Values of the coefficients in the polynomials (Equation (A18)) that predict for temperature and water vapour [43] for smooth, transition and rough surfaces.
| Temperature | |||
| 1.250 | 0.149 | 0.317 | |
| – | −0.550 | −0.565 | |
| – | – | −0.183 | |
| Water vapour | |||
| 1.610 | 0.351 | 0.396 | |
| – | −0.628 | −0.512 | |
| – | – | −0.180 |
The air density for a given pressure is computed as the sum of densities of dry air and water vapour [91,94]:
where the partial pressure of water vapour is and is atmospheric pressure, is the gas constant for dry air and is the ratio of the molecular weights of water and dry air. The specific humidity at screen level and on the snow surface is calculated as:
For a one dimensional system atmosphere—snow surface layer—subsurface snow pack the thermodynamic equation describing the conservation of energy, neglecting melting and refreezing, can be described as [95,96]:
This equation is applied in a very simplified form following Oke [47] and implemented using finite differences:
where is the flux density energy used to heat the snow at the surface, and is the heat capacity of the snow , is snow density and is the specific heat of snow (2.09 × 103 Jkg−1K −1). As the main energy input comes from the surface, while the subsurface remains at a relatively stable temperature, we need to consider the thermal conductivity of the snow and the energy losses to subsurface layers:
where is the thermal diffusivity of the snow and its thermal conductivity.
The volume of snow considered is that affected by the daily temperature changes at the surface. This temperature oscillation decreases exponentially with depth, and its amplitude at any given distance from the surface can be estimated according to Oke [47] by
where P is the wave period. Brutsaert [91] has shown that, roughly, 95% of the wave is damped at a depth of , where .
Heat transfer due to precipitation is estimated following Brun et al. [46] as:
where is rain water density, is specific heat of water, is precipitation rate and is temperature of the snow and temperature of the rain.
References
- Añel, J.A.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Otto, F.E.L.; Vicente-Serrano, S.; Schaller, N.; Massey, N.; Buisán, S.T.; Allen, M.R. The extreme snow accumulation in the Western Spanish pyrennes during winter and spring 2013. In Explaining Extreme Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective; Herring, S.C., Hoerling, M.P., Peterson, T.C., Stott, P.A., Eds.; Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2014; Volume 95, Chapter 21; pp. S73–S76. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Spitzbart, G.; Hübl, H.; Weinmeister, H. Hydrological response of snowpack under rain-on-snow events: A field study. J. Hydrol. 1997, 202, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Tejeda, E.; López-Moreno, J.; Stoffel, M.; Beniston, M. Rain-on-snow events in Switzerland: Recent observations and projections for the 21st century. Clim. Res. 2016, 71, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattelmann, R. Flooding from Rain-on-Snow Events in the Sierra Nevada. In Proceedings of the North American Water and Environment Congress & Destructive Water (ASCE), Anaheim, CA, USA, 22–28 June 1996; Bathala, C., Ed.; pp. 1145–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Brunengo, M.J. A method of modeling the frequency characteristics of daily snow amount, for stochastic simulation of rain-on-snowmelt events. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Western Snow Conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 17–19 April 1990; Volume 58, pp. 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, G.J.; Hay, L.E.; Clark, M.P.; McCabe, G.J.; Hay, L.E.; Clark, M.P. Rain-on-Snow Events in the Western United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harr, R. Some characteristics and consequences of snowmelt during rainfall in western Oregon. J. Hydrol. 1981, 53, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harr, R.D. Effects of Clearcutting on Rain-on-Snow Runoff in Western Oregon: A New Look at Old Studies. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, J.; Harr, R.D. Peak streamflows from the transient snow zone, western Cascades, Oregon. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Western Snow Conference, Reno, NC, USA, 19–23 April 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, J.A. Rain-on-snow and soil mass failure in the Sierra Nevada of California. In Landslide Activity in the Sierra Nevada during 1982 and 1983; DeGraff, J.V., Ed.; USDA Forest Service: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1987; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.A.; Perkins, R.M. Extreme flood sensitivity to snow and forest harvest, western Cascades, Oregon, United States. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandersen, F.; Bakkehøi, S.; Hestnes, E.; Lied, K. The influence of meteorological factors on the initiation of debris flows, rockfalls, rockslides and rockmass stability. Publ. Nor. Geotek. Inst. 1997, 201, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, D.; Kimball, J.; Tingey, D.; Link, T. The sensitivity of snowmelt processes to climate conditions and forest cover during rain-on-snow: A case study of the 1996 Pacific Northwest flood. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 1569–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heeswijk, M.; Kimball, J.; Marks, D. Simulation of Water Available for Runoff in Clearcut Forest Openings During Rain-on-Snow Events in the Western Cascade Range of Oregon and Washington; Technical Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Tacoma, WA, USA, 1996.
- Mazurkiewicz, A.B.; Callery, D.G.; McDonnell, J.J. Assessing the controls of the snow energy balance and water available for runoff in a rain-on-snow environment. J. Hydrol. 2008, 354, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhanang, S.M.; Frei, A.; Zion, M.; Schneiderman, E.M.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Pierson, D. Rain-on-snow runoff events in New York. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3035–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, J.; Chalmers, A. The effect of frozen soil on snowmelt runoff at Sleepers River, Vermont. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1843–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L. Effects of vegetation canopy processes on snow surface energy and mass balances. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrick, K.J.; Mass, C.F.; Westrick, K.J.; Mass, C.F. An Evaluation of a High-Resolution Hydrometeorological Modeling System for Prediction of a Cool-Season Flood Event in a Coastal Mountainous Watershed. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, E.; Comellas, A.; Molini, L.; Rebora, N.; Siccardi, F.; Gochis, D.; Tanelli, S.; Parodi, A. Analysis and hindcast simulations of an extreme rainfall event in the Mediterranean area: The Genoa 2011 case. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würzer, S.; Jonas, T.; Wever, N.; Lehning, M. Influence of Initial Snowpack Properties on Runoff Formation during Rain-on-Snow Events. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, N.; Jonas, T.; Fierz, C.; Lehning, M. Model simulations of the modulating effect of the snow cover in a rain-on-snow event. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4657–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, K.; Meon, G.; Marke, T.; Strasser, U. Effect of meteorological forcing and snow model complexity on hydrological simulations in the Sieber catchment (Harz Mountains, Germany). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4703–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3. NCAR/TN-475+STR; Technical Report; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Puigdefábregas, J.; Creus, J. Los Recursos Hídricos Superficiales del Alto Aragón (Surface Water Resources of the High Aragón); Technical Report; Instituto de Estudios Altoaragoneses: Huesca, Spain, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez de Pisón, E. Morfoestructuras del Valle de Benasque (Pirineo Aragonés); Anales de Geografía de la Universidad Complutense: Madrid, Spain, 1990; pp. 121–148. [Google Scholar]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Beguería, S.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Influence of the Yesa reservoir on floods of the Aragón River, central Spanish Pyrenees. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueca Cía, J.; Andrés, A.J.; Saz Sánchez, M.; Novau, J.C.; López Moreno, J. Responses to climatic changes since the Little Ice Age on Maladeta Glacier (Central Pyrenees). Geomorphology 2005, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Rijckborst, H. Hydrology of the Upper-Garonne basin (Valle de Arán, Spain). Leidse Geol. Meded. 1967, 40, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lampre, F. Estudio Geomorfológico de Ballibierna, Macizo de la Maladeta, Pirineo Aragonés. Modelado Glaciar y Periglaciar (Geomorphologic Study of Ballibierna, Maladeta Sector, Aragonés Pyrenees. Glacial and Periglacial Forms); Technical Report; Consejo de Protección de la Naturaleza de Aragón: Zaragoza, Spain, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Del Barrio, G.; Creus, J.; Puigdefabregas, J. Thermal Seasonality of the High Mountain Belts of the Pyrenees. Mt. Res. Dev. 1990, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Nogués-Bravo, D. Interpolating local snow depth data: An evaluation of methods. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2217–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.; Riggs, G. Normalized-Difference Snow Index (NDSI). In Encyclopedia of Snow, Ice and Glaciers SE-376; Singh, V., Singh, P., Haritashya, U., Eds.; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 779–780. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Erb, A.M.; Schaaf, C.B.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shuai, Y.; Casey, K.A.; Román, M.O. Early spring post-fire snow albedo dynamics in high latitude boreal forests using Landsat-8 OLI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corripio, J.G. Vectorial algebra algorithms for calculating terrain parameters from DEMs and the position of the sun for solar radiation modelling in mountainous terrain. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2003, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corripio, J.G. Insol: Solar Radiation. R Package. 2013. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=insol (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- Corripio, J.G. Modelling the Energy Balance of High Altitude Glacierised Basins in the Central Andes. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Corripio, J.G.; Purves, R.S. Surface Energy Balance of High Altitude Glaciers in the Central Andes: The Effect of Snow Penitentes. In Climate and Hydrology in Mountain Areas; de Jong, C., Collins, D., Ranzi, R., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dadic, R.; Corripio, J.G.; Burlando, P. Mass-balance estimates for Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland, from 2000 to 2006 using DEMs and distributed mass-balance modeling. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iziomon, M.G.; Mayer, H.; Matzarakis, A. Downward atmospheric longwave irradiance under clear and cloudy skies: Measurement and parameterization. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2003, 65, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businger, J.A.; Yaglom, A.M. Introduction to Obukhov’s paper on ‘Turbulence in an atmosphere with non-uniform temperature’. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1971, 2, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhov, A.M. Turbulence in an Atmosphere with Non-Uniform Temperature. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1971, 2, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. A theory for the scalar roughness and the scalar transfer coefficients over snow and sea ice. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1987, 38, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Parameterizing Scalar Transfer over Snow and Ice: A Review. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexstone, G.A.; Clow, D.W.; Stannard, D.I.; Fassnacht, S.R. Comparison of methods for quantifying surface sublimation over seasonally snow-covered terrain. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3373–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, E.; Martin, E.; Simon, V.; Gendre, C.; Coleou, C. An energy and mass model of snow cover suitable for operational avalanche forecasting. J. Glaciol. 1989, 35, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.J. Boundary Layer Climates; Methuen: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Fukami, H.; Kojima, K.; Aburakawa, H. The extinction and absorption of solar radiation within a snow cover. Ann. Glaciol. 1985, 6, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.G. Optical properties of snow. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1982, 20, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, B.W.; Willis, I.C.; Sharp, M.J. Measurement and parameterisation of albedo variations at Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland. J. Glaciol. 2000, 46, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, J.; Knapp, W.H. A 1 year record of global radiation and albedo in the ablation zone of Morteratschgletscher, Switzerland. J. Glaciol. 1998, 44, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, C. The Numerical Modeling of Wet Snowfall Events. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, C.; Rinaldo, A.; Schaefli, B. Snowfall Limit Forecasts and Hydrological Modeling. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovsky, M.S.; Karoly, D.J. Precipitation simulations using WRF as a nested regional climate model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassola, F.; Ferrari, F.; Mazzino, A. Numerical simulations of Mediterranean heavy precipitation events with the WRF model: A verification exercise using different approaches. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, S.; Valero, F.; Sánchez, J.L.; Gascón, E.; López, L.; García-Ortega, E.; Merino, A. Numerical simulations of snowfall events: Sensitivity analysis of physical parameterizations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10,130–10,148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennelly, C.; Reuter, G.; Flesch, T. Verification of the WRF model for simulating heavy precipitation in Alberta. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapero, L.; Bech, J.; Lorente, J. Numerical modelling of heavy precipitation events over Eastern Pyrenees: Analysis of orographic effects. Atmos. Res. 2013, 123, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bruyere, C.; Duda, M.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.; Kavulich, M.; Keene, K.; Lin, H.C.; Michalakes, J.; Rizvi, S.; et al. User’s Guides for the Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Modeling System, version 3; Technical Report; National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR, 2014. Available online: http://www2.mmm.ucar.edu/wrf/users/docs/user_guide_V3/contents.html (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- GDAL Development Team. GDAL—Geospatial Data Abstraction Library, version 2.1.1; 2016. Available online: http://www.gdal.org/ (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- Pedersen, J.T.; Peters, J.C.; Helweg, O.J. Hydrographs by Single Linear Reservoir Model; Technical Report No. HY5; US Army Corps of Engineers, Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, V. Open-Channel Hydraulics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Hannah, D.M.; Gurnell, A.M. A conceptual, linear reservoir runoff model to investigate melt season changes in cirque glacier hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2001, 246, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M.; Bowman, M.H.; Landa, M.; Metz, M. GRASS GIS: A multi-purpose Open Source GIS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freixes, A.; Monterde, M.; Ramoneda, J. Tracer tests in the Joèu karstic system (Aran Valley, Central Pyrennes, NE Spain). In Tracer Hydrology 97; Kranjc, K., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Monterde García, M. El sistema kárstico de Uelhs Deth Joèu. Treb. Soc. Catalana Geogr. 2001, 52, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Georges, C.; Kaser, G. Ventilated and unventilated air temperature measurements for glacier-climate studies on a tropical high mountain site. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ACL 15-1–ACL 15-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respuesta Hidrológica al Evento de Precipitación de Junio de 2013 en el Pirineo Central. Investigaciones Geográficas 2014, 62, 5–21.
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, H.R.; Moses, H.; Harney, P.J. Measurement of Rain Temperature. J. Meteorol. 1949, 6, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, C.F.; Ovens, D.; Westrick, K.; Colle, B.A. Does increasing horizontal resolution produce more skillful forecasts? The results of two years of real-time numerical weather prediction over the Pacific Northwest. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 407–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, G.E.; Elder, K. A micrometeorological distribution system for high-resolution terrestrial modeling applications (MicroMet). J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.E.; Running, S.W.; White, M.A. Generating surfaces of daily meteorological variables over large regions of complex terrain. J. Hydrol. 1997, 190, 214–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehning, M.; Grünewald, T.; Schirmer, M. Mountain Snow Distribution Governed by an Altitudinal Gradient and Terrain Roughness. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, J.; Marty, C.; Lehning, M. Extreme value statistics of snowfall in the Swiss Alpine region. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevruk, B. Regional Dependency of Precipitation-Altitude Relationship in the Swiss Alps. Clim. Chang. 1997, 36, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevruk, B.; Mieglitz, K. The effect of topography, season and weather situation on daily precipitation gradients in 60 Swiss valleys. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pomeroy, J.W.; Fang, X.; Marks, D.G. The cold rain-on-snow event of June 2013 in the Canadian Rockies—Characteristics and diagnosis. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2899–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscarello, L.; Ravazzani, G.; Rabuffetti, D.; Mancini, M. Integrating glaciers raster-based modelling in large catchments hydrological balance: The Rhone case study. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceppi, A.; Ravazzani, G.; Salandin, A.; Rabuffetti, D.; Montani, A.; Borgonovo, E.; Mancini, M. Effects of temperature on flood forecasting: Analysis of an operative case study in Alpine basins. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.R.; Durran, D.R.; Roe, G.H. Mesoscale Controls on the Mountainside Snow Line. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 2107–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Persson, P.O.G. Coastal Orographic Rainfall Processes Observed by Radar during the California Land-Falling Jets Experiment. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 4, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.E.; Hulstrom, R.L. A Simplified Clear Sky Model for Direct and Diffuse Insolation on Horizontal Surfaces; Technical Report SERI/TR-642-761; Solar Energy Research Institute: Golden, CO, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, R.E.; Hulstrom, R.L. Review, evaluation and improvements of Direct irradiance models. Trans. ASME J. Sol. Energy Eng. 1981, 103, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.H.; Jordan, R.C. The interrelationship and characteristics distribution of direct, diffuse and total solar radiation. Sol. Energy 1960, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, D.G.; Klein, S.A.; Duffie, J.A. Estimation of the diffuse radiation fraction for hourly, daily, and monthly average global radiation. Sol. Energy 1982, 28, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, G.; Kummert, M.; Klein, A.S.; Beckman, W.A. Analysis of short-term solar radiation data. Sol. Energy 2005, 79, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.J. A new long-wave formula for estimating downward clear-sky radiation at the surface. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 122, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, P.R. An approximating polynomial for the computation of saturation vapor pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1977, 16, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Evaporation into the Atmosphere: Theory, History, and Applications; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1982; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, D.; Dozier, J. Climate and energy exchange at the snow surface in the alpine region of the Sierra Nevada. 2. Snow cover energy balance. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; p. 670. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, G.; Jordan, R. Sub-surface melting in a seasonal snow cover. J. Glaciol. 1995, 41, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuell, W.; Konzelmann, T. Numerical modelling of the energy balance and the Englacial temperature of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Calculations for the ETH-Camp location (West Greenland, 111 1 a.s.l.). Glob. Planet. Chang. 1994, 9, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).