Climate Change and Its Impacts on Water Resources in the Bandama Basin, Côte D’ivoire
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. Historical Time Series Data
2.2.2. Projected Future Climate Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Climate Change Simulations
2.3.2. Evaluation of Potential Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources
Climate Change Scenarios
- (1)
- Disturbances “additive” to the temperature:
- (2)
- Disturbances “multiplicative” to the rainfall:where and are disturbed variables, is a baseline variable, and and are the monthly averages of the variable calculated from HadGEM2-ES simulations on the time horizons and baseline period. The disturbance of month m is imputed to the current variable (i.e., observed) Xact, at all-time steps t of the month, for all years.
Hydrological Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment of the Changes in Climate Parameters
3.1.1. Changes in Temperatures
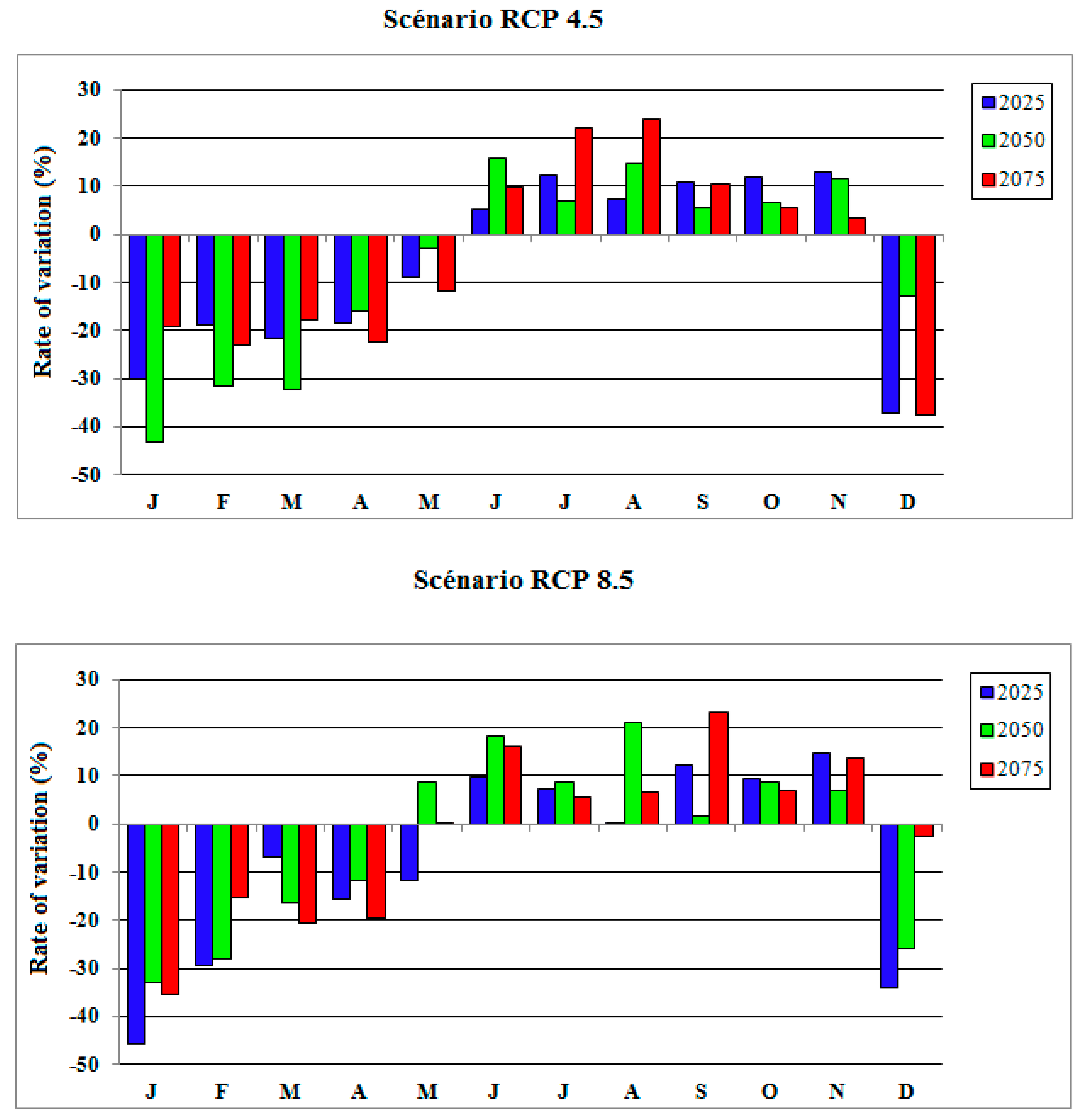
3.1.2. Changes in Rainfall
3.2. Hydrological Model Calibration
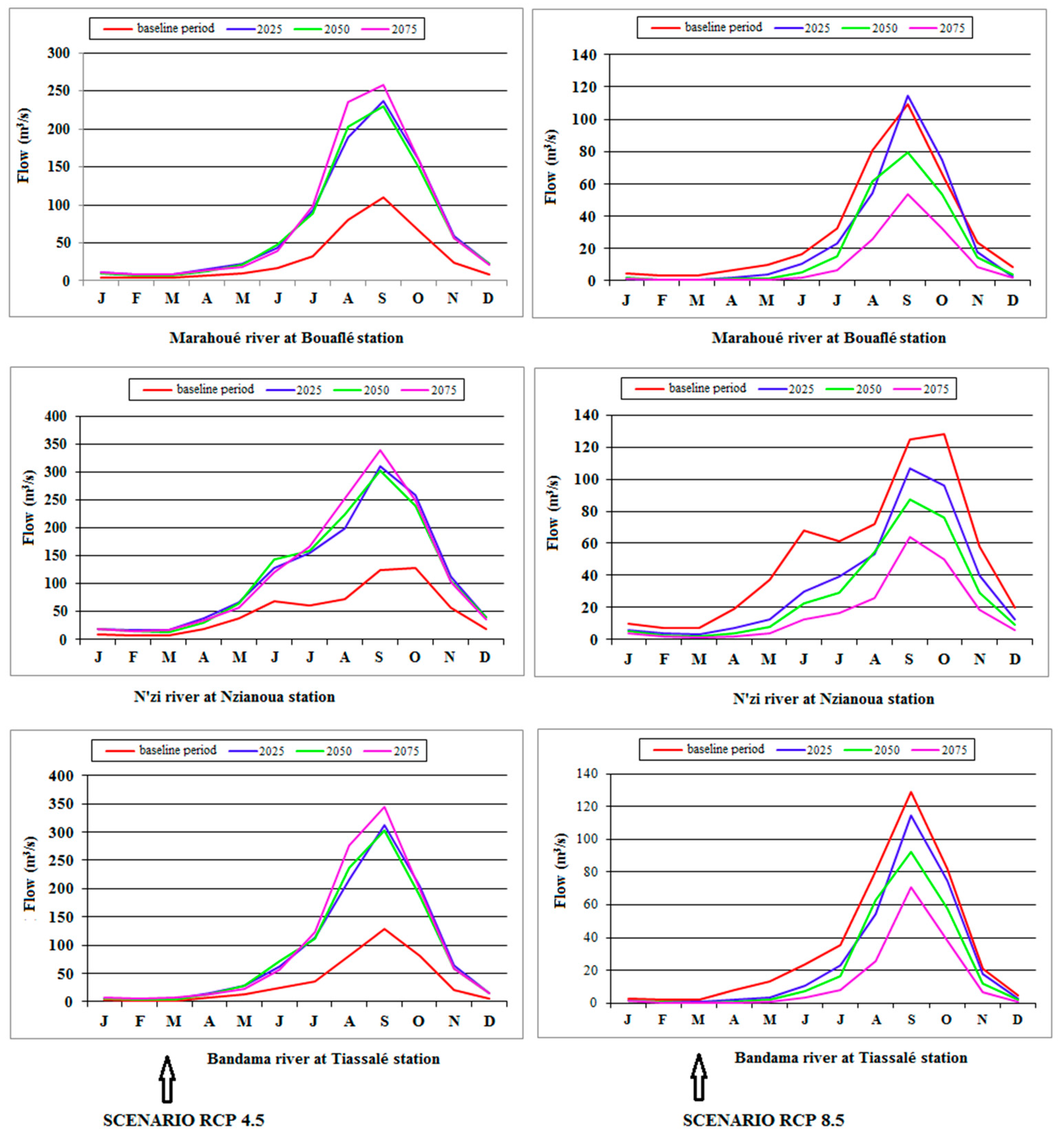
3.3. Impacts of Climate Change on Surface Water
3.4. Impacts of Climate Change on Groundwater
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Special Report: Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; Field, C.B., Barros, V., Stocker, T.F., Dahe, Q., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Valipour, M. Necessity of irrigated and rainfed agriculture in the world. Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2013, S9, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M. Need to update of irrigation and water resources information according to the progresses of agricultural knowledge. Agrotechnology 2013, S10, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurukulasuriya, P.; Mendelsohn, R. Modeling Endogenous Irrigation: The Impact of Climate Change on Farmers in Africa; Center for Environmental Economics and Policy in Africa (CEEPA) Discussion Paper N°8; Special Series on Climate Change and Agriculture in Africa; World Bank Policy Research Working and University of Pretoria: Pretoria, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Burlando, P.; Rosso, R. Effects of transient climate change on basin hydrology. 1. Precipitation scenarios for the Arno River, central Italy. Hydrol. Proc. 2002, 16, 1151–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Xiong, L.; Ying, A.; Li, D. A macro-scale and semi-distributed monthly water balance model to predict climate change impacts in China. J. Hydrol. 2002, 268, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Mirza, M.Q.; Fankhauser, S.; Leemans, R.; Erda, L.; Ogallo, L.; Pittock, B.; Richels, R.; Rosenzweig, C.; et al. Vulnerability to climate change and reasons for concern: A synthesis. In Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; McCarthy, J., Canziana, O., Leary, N., Dokken, D., White, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 913–967. [Google Scholar]
- Kurukulasuriya, P.; Rosenthal, R. A Ricardian Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change on African Cropland; Policy Research Working Paper, No. 4305. World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. Avaliable online https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/7508 License: CC BY 3.0 Unported (accessed on 20 December 2016).
- Hassan, R.; Nhemachena, C. Determinants of African farmers’ strategies for adapting to climate change: Multinomial choice analysis. Afr. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2008, 2, 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Roudier, P.; Ducharne, A.; Feyen, L. Climate change impacts on runoff in West Africa: A review. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2789–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; McCusker, B. Climate Change and Agriculture in Africa: Impact Assessment and Adaptation Strategies. Eos Trans. AGU 2008, 89, 474–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Development Programme. Programme d’Appui à la Réduction de la Pauvreté PNUD 2009–2013, Sous Programme Protection de l’Environnement et Gestion Durable des Ressources Naturelles (PGDRN); UNDP: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2009; p. 19. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Soro, N.; Lasm, T.; Kouadio, B.H.; Soro, G.; Ahoussi, K.E. Variabilité du régime pluviométrique du sud de la Côte d’Ivoire et son impact sur l’alimentation de la nappe d’Abidjan. Sud-Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Goula, B.T.A.; Savane, I.; Konan, B.; Fadika, V.; Kouadio, G.B. Impact de la variabilité climatique sur les ressources hydriques des bassins de N’Zo et N’Zi en Côte d’Ivoire (Afrique tropicale humide). Vertigo 2006, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, A.M.; Kouamé, K.F.; Koffi, Y.B.; Djé, K.B.; Paturel, J.E.; Oularé, S. Analyse de la variabilité climatique et de ses influences sur les régimes pluviométriques saisonniers en Afrique de l’Ouest: Cas du bassin versant du N’Zi (Bandama) en Côte d’Ivoire. Cybergéo 2010, 513, 29–In. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.B. Evaluation des Potentialités en eau du Bassin Versant de la Lobo en vue D’une Gestion Rationnelle (Centre-Ouest de la Côte D’ivoire). Ph.D. Thèse, Université Nangui Abrogoua, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Otchoumou, K.F.; Saley, M.B.; Aké, G.E.; Savane, I.; Djê, K.B. Variabilité climatique et production de café et cacao dans la zone tropicale humide: Cas de la région de Daoukro (Centre-Est de la Côte d’Ivoire). Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2012, 1, 194–215. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokoby, V.M.; Saley, M.B.; Kouamé, K.F.; Djagoua, E.M.V.; Affian, K.; Biemi, J. Variabilité spatio-temporelle des paramètres climatiques et son incidence sur le tarissement dans les basins versants de Bô et Debo (département de Soubré au Sud-Ouest de la Côte d’Ivoire). Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2013, 2, 287–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kouamelan, A.N. Géochronologie et Géochimie de Formations Archéennes et Protérozoïques de la Dorsales de Man en Côte D’ivoire: Implication Pour la Transition Archéen-Protérozoïque. Ph.D. Thèse, Université de Renne, Rennes, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine, S. Evolution Géologique de la Région de Dabakala (NE de la Côte D’Ivoire) au Protérozoïque Inférieur. Possibilité D’extension au Reste de la Côte D’ivoire et au Burkina Faso: Similitudes et Différences; les Linéaments Greenville-Ferkessédougou et Grand Cess-Niankaramadougou. Ph.D. Thèse, Université Blaise Pascal (Clermont Ferrand II), Aubière, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Biémi, J. Contribution à L’étude Géologique, Hydrogéologique et par Télédétection des Bassins Versants Subsaheliens du Socle Précambrien d’Afrique de L’ouest: Hydrostructurale, Hydrodynamique, Hydrochimie et Isotopie des Aquifères Discontinus de Sillons et Aires Granitiques de la Haute Marahoué (Côte D’Ivoire) D’Abidjan. Ph.D. Thèse, Naturelles Université Nationale, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kouakou, E.; Koné, B.; N’Go, A.; Cissé, G.; Ifejika Speranza, C.; Savané, I. Ground water sensitivity to climate variability in the white Bandama basin, Ivory Coast. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, K.M. Caractérisation D’une Modification Éventuelle de la relation pluie-débit et Ses Impacts Sur les Ressources en eau en Afrique de L’Ouest: Cas du Bassin Versant du N’zi (Bandama) en Côte D’Ivoire. Ph.D. Thèse, Université de Cocody, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.M.; Bellouin, N.; Collins, W.J.; Culverwell, I.D.; Halloran, P.R.; Hardiman, S.C.; Hinton, T.J.; Jones, C.D.; McDonald, R.E.; McLaren, A.J.; et al. The hadGEM2 family of met office unified model climate configurations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 723–757. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.; Stouffer, R.; Meeh, G. An overview of cmip5 and the experiment design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, R.A.; Golding, N.; Gonzalez, P.; Gornall, J.; Kahana, R.; Kay, G.; Mitchell, L.; Wiltshire, A. Climate and land use change impacts on global terrestrial ecosystems and river flows in the HadGEM2-ES Earth system model using the representative concentration pathways. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1317–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.F.; et al. The representative concentration pathways: An overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, K.; Rao, S.; Krey, V.; Cho, C.; Chirkov, V.; Guenther, F.; Georg, K.; Nakicenovic, N.; Rafaj, P. RCP 8.5-A scenario of comparatively high greenhouse gas emissions. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardoin, B.S. Variabilité Hydroclimatique et Impacts sur les Ressources en eau de Grands Bassins Hydrographiques en Zone Soudano-Sahélienne. Ph.D. Thèse, Université de Montpellier II, Montpellier, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sighomnou, D. Analyse et Redéfinition des Régimes Climatiques et Hydrologiques du Cameroun: Perspectives D’évolution des Ressources en eau. Ph.D. Thèse, Université de Yaoundé I, Yaounde, Cameroun, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Dezetter, A.; Servat, E.; Paturel, J.E.; Mahé, G.; Niel, H.; Dieulin, C. Using general circulation model outputs to assess impacts of climate change on runoff for large hydrological catchments in West Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouakou, K.E. Impacts de la Variabilité Climatique et du Changement Climatique sur les Ressources en eau en Afrique de L’ouest: Cas du Bassin Versant de la Comoé. Ph.D. Thèse, Université Abobo-Adjamé, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kouakou, K.E.; Goula, B.T. A.; Kouassi, A.M. Analyze of climate variability and change impacts on hydro-climate parameters: Case study of Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ducharne, A.; Théry, S.; Viennot, P.; Ledoux, E.; Gomez, E.; Déqué, M. Influence du changement climatique sur l’hydrologie du bassin de la Seine. VertigO 2003, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Karambiri, H.; Polcher, J. Hydrological Impacts of the Changes in Simulated Rainfall Fields on Nakanbe Basin in Burkina Faso. Climate 2015, 3, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institut National de Recherche en Sciences et Technologies Pour L’environnement et L’agriculture. Available online: http://www.irstea.fr/ (accessed on 20 March 2016).
- Nash, J.; Sutclie, J. River flow forecasting through conceptual models. Part I: A discussion of principle. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Giorgi, F. Climate change hotspots in the CMIP5 global climate model ensemble. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehl, G.A.; Stocker, T.F.; Collins, W.D.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gaye, A.T.; Gregory, J.M.; Kitoh, A.; Knutti, R.; Murphy, J.M.; Noda, A.; et al. Global Climate Projections. In Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, I.; Sylla, M.B.; Giorgi, F.; Gaye, A.T.; Camara, M. Multimodel GCM-RCM ensemble-based projections of temperature and precipitation over West Africa for the early 21st century. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. Int. J. Geophys. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monerie, P.A.; Fontaine, B.; Roucou, P. Expected future changes in the African monsoon between 2030 and 2070 using some CMIP3 and CMIP5 models under a medium-low RCP scenario. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, I.; Ruppel, O.C.; Abdrabo, M.A.; Essel, A.; Lennard, C.; Padgham, J.; Urquhart, P. Africa. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Part B: Regional Aspects; Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, H.S.; Li, M.-H.; Tung, C.-P.; Liu, T.-M. Impact of Climate Change on Runoff in the Gilgel Abbay Watershed, the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2016, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.H.; Hewitson, B.; Busuioc, A.; Chen, A.; Gao, X.; Held, I.; Jones, R.; Koli, R.K.; Kwon, W.-T.; Laprise, R.; et al. Regional climate projections. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 847–940. [Google Scholar]
- Serdeczny, O.; Adams, S.; Baarsch, F.; Coumou, D.; Robinson, A.; Hare, W.; Schaeffer, M.; Perrette, M.; Reinhardt, J. Climate change impacts in Sub-Saharan Africa: From physical changes to their social repercussions. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Code | Station | Data | Longitude (Decimal Degree) | Latitude (Decimal Degree) | Data Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1090012000 | Korhogo | Meteorological | −5.61 | 9.41 | 1971–2005 |
| 1090006400 | Boundiali | −6.46 | 9.51 | 1922–2005 | |
| 1090005600 | Bouaké | −5.06 | 7.73 | 1966−2005 | |
| 1090018700 | Tafiré | −5.15 | 9.06 | 1950−2005 | |
| 1090007300 | Dabakala | −4.43 | 8.38 | 1945−2005 | |
| 1090015100 | M’Bahiakro | −4.33 | 7.45 | 1944−2005 | |
| 1090022200 | Zuénoula | −6.05 | 7.41 | 1953−2005 | |
| 1090009100 | Dimbokro | −4.70 | 6.65 | 1921−2005 | |
| 1090016900 | Oumé | −5.41 | 6.36 | 1944−2005 | |
| 1090005200 | Bouaflé | −5.75 | 6.98 | 1924−2005 | |
| 1090010300 | Gagnoa | −5.95 | 6.13 | 1922−2005 | |
| 1090019600 | Tiassalé | −4.83 | 5.88 | 1959−2005 | |
| 1090000100 | Abidjan | −3.93 | 5.25 | 1961−2005 | |
| 1090010000 | Ferkessédougou | −5.20 | 9.60 | 1961−2005 | |
| 1090101006 | Marahoué | Hydrological | −5.75 | 6.97 | 1954−2005 |
| 1090102515 | N’Zi | −4.81 | 6.00 | 1953−2005 | |
| 1090100154 | Tiassalé | −4.82 | 5.89 | 1954−2005 |
| River (Station) | Calibration | Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Nash Criteria Value (%) | Period | Nash Criteria Value (%) | |
| Marahoué (Bouaflé) | 1980–1987 | 72.3 | 1967–1977 | 74.5 |
| N’Zi (Zianouan) | 1980–1989 | 77.3 | 1990–1998 | 72.5 |
| Bandama (Tiassalé) | 1969–1975 | 76.7 | 1981–1989 | 78.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soro, G.E.; Yao, A.B.; Kouame, Y.M.; Bi, T.A.G. Climate Change and Its Impacts on Water Resources in the Bandama Basin, Côte D’ivoire. Hydrology 2017, 4, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010018
Soro GE, Yao AB, Kouame YM, Bi TAG. Climate Change and Its Impacts on Water Resources in the Bandama Basin, Côte D’ivoire. Hydrology. 2017; 4(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoro, Gneneyougo Emile, Affoué Berthe Yao, Yao Morton Kouame, and Tié Albert Goula Bi. 2017. "Climate Change and Its Impacts on Water Resources in the Bandama Basin, Côte D’ivoire" Hydrology 4, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010018
APA StyleSoro, G. E., Yao, A. B., Kouame, Y. M., & Bi, T. A. G. (2017). Climate Change and Its Impacts on Water Resources in the Bandama Basin, Côte D’ivoire. Hydrology, 4(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010018





