Abstract
Accurate estimation of actual evapotranspiration (ET) is critical for understanding hydrothermal cycles and ecosystem functioning in arid regions, where water scarcity governs ecological resilience. To address persistent gaps in ET quantification, this study integrates multi-source remote sensing data, energy balance modeling, and ground-based validation that significantly enhances spatiotemporal ET accuracy in the vulnerable desert steppe ecosystems. The study utilized meteorological data from several national stations and Landsat-8 imagery to process monthly remote sensing images in 2019. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) model, chosen for its ability to estimate ET over large areas, was applied to derive modeled daily ET values, which were validated by a large-weighted lysimeter. It was shown that ET varied seasonally, peaking in July at 6.40 mm/day, and reaching a minimum value in winter with 1.83 mm/day in December. ET was significantly higher in southern regions compared to central and northern areas. SEBS-derived ET showed strong agreement with lysimeter measurements, with a mean relative error of 4.30%, which also consistently outperformed MOD16A2 ET products in accuracy. This spatial heterogeneity was driven by greater vegetation coverage and enhanced precipitation in the southeast. The steppe ET showed a strong positive correlation with surface temperatures and vegetation density. Moreover, the precipitation gradients and land use were primary controllers of spatial ET patterns. The process-based SEBS frameworks demonstrate dual functionality as resource-optimized computational platforms while enabling multi-scale quantification of ET spatiotemporal heterogeneity; it was therefore a reliable tool for ecohydrological assessments in an arid steppe, providing critical insights for water resource management and drought monitoring.
1. Introduction
Accurately estimating evapotranspiration (ET) in desert steppes is crucial because these fragile, water-stressed ecosystems are highly sensitive to changes in the hydrological cycle driven by climate change and human activities. A reliable ET value is fundamental for understanding local water budgets, predicting ecological responses to aridity, and informing sustainable water resource management and grazing practices in these vulnerable regions. Accurate measurement of ET is essential across multiple disciplines, including smart agriculture, water resource management, ecosystem service assessments, disaster preparedness, and meteorological and climatic research [1,2]. Traditional methods for monitoring ET rely on instruments such as eddy covariance systems, sap flow sensors, and large-weighted lysimeters, which provide precise data but often come with high costs and operational complexities, particularly in arid and rural regions [3]. In contrast, energy balance ET models, which leverage large-scale, long-term meteorological data from weather stations combined with remote sensing observations spanning extensive areas and periods, offer a viable alternative for estimating water consumption [4,5,6]. Remote sensing technology faces challenges posed by the unique surface characteristics of the desert steppe region, such as sparse vegetation and soils with high albedo, in acquiring remote sensing data and estimating ET. By systematically operationalizing these research priorities, the present study seeks to elucidate ET dynamics through an integrated modeling–observational paradigm, thereby establishing mechanistic frameworks for water flux quantification in water-limited desert steppe ecosystems exposed to increasing aridity gradients.
Advancements in remote sensing technology have revolutionized the study of ET and water resources [7,8]. High-resolution data from satellites such as the Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Landsat provide detailed information on key parameters, including digital elevation models (DEMs), land surface temperature (LST), the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and vegetation coverage, enabling precise ET estimation [9]. Numerous studies have utilized remote sensing for ET assessment through the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS), which demonstrated its potential to validate and extend measured data to daily and regional scales [10]. However, the accuracy of these estimations can be influenced by variations in measurement parameters [11] and advective flux [12,13]. For instance, daily ET retrieved from MODIS using the Penman–Monteith equation has been validated against flux data, with most ecosystems showing lower errors when soil water content and vapor pressure deficit were considered [14,15,16]. Furthermore, in the Sanjiang Plain of Northeast China, MODIS-based remote sensing ET estimates were lower than those derived from the water balance method for rice fields. Nevertheless, the Surface Energy Balance Algorithms for Land (SEBAL) demonstrated strong performance in simulating crop water requirements, aligning well with measured data [17]. The integration of high-resolution remote sensing data, such as Landsat-8 and MODIS, with the SEBS model has significantly improved the accuracy of ET estimation by providing detailed spatial and temporal information on LST, vegetation indices, and surface albedo [18]. This integration underscores the potential of remote sensing in advancing ET research and its applications.
Soil moisture plays a critical role in grass growth under climate change conditions, primarily influenced by the balance between precipitation and ET [19,20]. The grass crop coefficient, a key parameter in ET estimation, is closely linked to the leaf area index (LAI) [21] and the NDVI [22], both of which can be derived from MODIS satellite data. Changes in vegetation cover can significantly impact grassland ET over large spatial scales [23,24], highlighting the need to investigate seasonal variations in grass ET by integrating remote sensing observations with meteorological data [25]. Understanding the relationship between ET and soil moisture is essential for assessing the impacts of droughts, which can drastically alter vegetation cover and ecosystem dynamics [26,27]. The energy balance method provides an effective approach for evaluating ET and explaining the physiological processes of grasslands. Among these methods, the SEBS model stands out for its accuracy and has been extensively validated across diverse regions [5].
By estimating and verifying the grassland ET through the SEBS model, the applicability of the SEBS model in desert grassland water resource management can be clarified. Although the accuracy of SEBS in energy balance-based ET calculations has been verified in many areas, its application in desert grasslands characterized by sparse vegetation remains to be confirmed. By validating the SEBS model with data from large-scale lysimeters, the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of desert grassland ET can be derived, which is beneficial for effective water resource management in fragile ecosystems and helps elucidate its influencing factors. This study was conducted in Damaoqi, a vast and representative desert steppe in western Inner Mongolia. Following the collection of meteorological data from national meteorological stations and remote sensing land surface data from MODIS and Landsat 8, the objectives of this study are threefold: (1) to analyze the spatiotemporal patterns of ET in the desert steppe region; (2) to validate the SEBS model for estimating actual ET using the large-weighted lysimeter method; and (3) to investigate the key factors influencing grassland ET dynamics. By systematically operationalizing these research priorities, the present study seeks to elucidate ET dynamics through an integrated modeling–observational paradigm, thereby establishing mechanistic frameworks for water flux quantification in water-limited terrestrial ecosystems exposed to increasing aridity gradients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
This study focuses on the Darhan Muminggan Joint Banner, a representative desert steppe region in arid and semi-arid areas, as the research area (Figure 1). Located in the North China region, Darhan Muminggan Joint Banner—commonly abbreviated as “Damao Banner”—is administered by Baotou City in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. It lies within the Yinshan Northern Foot-Hunshandake Desert National Key Ecological Function Zone and represents the largest ecosystem in Baotou City. Geographically, the study area spans latitudes 41°20′ N to 42°40′ N and longitudes 109°16′ E to 111°25′ E, covering a total area of 17,410 km2. The terrain slopes from south to north, with an average elevation of 1376 m a.s.l. The region features a gradient of ecosystem types from north to south, including decertified steppe, desert steppe, and meadow steppe, with desert steppe being the predominant type.
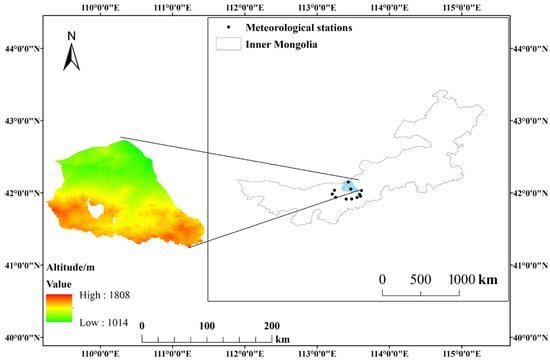
Figure 1.
Geographic altitude of the study area and distribution of meteorological stations. The blank area represents the Bayan Obo Mining District, which is outside the scope of the study area.
Damao Banner experiences a mid-temperate continental climate characterized by hot summers and cold winters, with an average annual temperature of 4.2 °C. The region receives limited precipitation, averaging only 256.2 mm annually, with the majority concentrated in July and August. In contrast, the evaporation rate is exceptionally high, with an average annual evaporation of 2526.4 mm. Strong winds are frequent, with an average annual wind speed ranging from 3.2 to 5.2 m/s, and the area enjoys abundant sunshine, averaging 4439.7 h per year [28]. Despite these climatic conditions, the region suffers from a natural scarcity of water resources, which is further exacerbated by inefficient utilization and wastage. This has led to widespread ecological challenges, including grassland and vegetation degradation, shrinking river and lake areas, and severe land desertification. The progressive environmental degradation exerts significant and multifaceted impacts on the socioeconomic viability of indigenous human populations and the ecological sustainability of native wildlife species within this fragile, semi-arid steppe environment.
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2.1. Landsat Data
Due to its suitable spatial resolution, thermal bands, and frequent revisit capability for accurate and timely monitoring of water and energy fluxes, Landsat-8, a land observation satellite system launched by the United States in 2013, was chosen to estimate regional evapotranspiration (ET). It is equipped with two sensors: the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) [29]. For this study, data from the OLI sensor were primarily utilized for evapotranspiration (ET) calculations. The OLI sensor captures nine spectral bands with a spatial resolution of 30 m, providing detailed and high-quality imagery. Remote sensing data for the study area were acquired from the Geospatial Data Cloud’s Landsat-8 OLI imagery. To ensure comprehensive coverage, one remote sensing image per month from 2019 was selected for analysis. Since a single image could not fully encompass the study area, three images with path/row numbers 127,031, 128,030, and 128,031 were employed. These images were mosaicked and masked to extract the precise study area imagery, ensuring a seamless and accurate dataset for research and analysis (Figure 2).
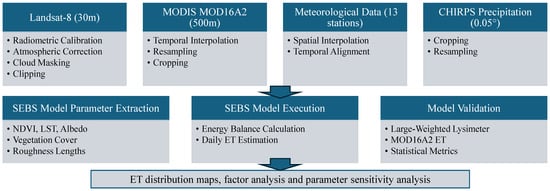
Figure 2.
Workflow diagram for validating the SEBS ET.
2.2.2. MODIS Data
Because of its global coverage, frequent temporal resolution, and consistent long-term datasets for monitoring ET at large scales, MODIS data for this study were obtained from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Specifically, the MODIS Land Surface 4-Level Standard Product MOD16A2 was selected, which features a temporal resolution of 8 days and a spatial resolution of 500 m. This product utilizes a physics-based algorithm that integrates MODIS thermal infrared data, vegetation indices, and meteorological inputs to model the dynamics of land surface energy balance and water flux. Spanning the entire globe from 2000 to the present, MOD16A2 is widely applied in hydrological studies, drought monitoring, agricultural water management, and climate modeling. Distributed in HDF-EOS format, the dataset provides valuable insights into ecosystem water use and terrestrial water cycle processes at regional to global scales.
The MOD16A2 product is based on the Penman–Monteith equation and incorporates remote sensing data such as surface albedo, NDVI, and vegetation coverage, along with meteorological data including temperature, pressure, and wind speed, to generate enhanced ET measurements. The dataset includes key variables such as ET, latent heat flux (LE), potential evapotranspiration (PET), and potential latent heat flux (PLE). Temporal resolutions available are 8-day, monthly, and annual ET measurements, making it a versatile tool for long-term and large-scale analyses [15,30,31]. We enhanced its temporal resolution from 8 days to daily through linear interpolation to match the temporal resolution of Landsat data.
2.2.3. Meteorological Data
In order to validate the calculated ET remote sensing, meteorological station data, including temperature, pressure, wind speed, and sunshine duration, were obtained and aligned with the same temporal periods as the Landsat-8 remote sensing data. However, spatial interpolation posed a challenge due to the limited number of meteorological stations within the study area, with only Damao Banner and Mandula stations available. To address this, data from 11 additional meteorological stations across Bayannur, Baotou, Ulanqab, Hohhot, and Ordos City were incorporated. ArcGIS software 10.2 was utilized to perform spatial interpolation and clipping of the meteorological data, ensuring comprehensive coverage and accuracy for the study area.
The annual spatial distribution of precipitation in 2019 was collected from the Climate Hazards Center InfraRed Precipitation with Station data (CHIRPS), which is a 30+ year quasi-global rainfall dataset. CHIRPS incorporates 0.05° resolution satellite imagery with in situ station data to create gridded rainfall time series for trend analysis and seasonal drought monitoring [32].
2.2.4. Actual ET Measured by Large-Weighted Lysimeter and the DEM Data
Additional data utilized in this study include topographic data and lysimeter measurements. The topographic data were obtained from the Geospatial Data Cloud’s Digital Elevation Model (DEM), featuring a spatial resolution of 90 m. The actual ET of the natural steppe was measured using a large-scale auto-weighted lysimeter (BSI-L08W, Xi’an Zhirun Technology Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China), which has dimensions of 2 m in width, length and 2.3 m in depth. The lysimeter boasts a resolution of 0.02 mm and operates with a measurement interval of 1 h, providing high-precision and continuous data on water flux dynamics. Not all the data are valid; we checked the large weighing lysimeter data, and averaged the hourly ET of days with daily valid hours higher than 12 to each day for comparison with model outputs. This advanced instrumentation ensures accurate and reliable quantification of ET in the study area. These data were primarily employed to facilitate the spatial interpolation of meteorological data and to serve as input parameters for the SEBS model in calculating ET. This integration of topographic data ensures enhanced accuracy and reliability in the modeling process.
2.3. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model
The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) was selected as the core modeling framework due to its robust physical mechanism in quantifying land–atmosphere energy exchanges, particularly critical for water-limited ecosystems. Its ability to integrate multi-source satellite data with ground meteorology addresses a fundamental gap in ET estimation across heterogeneous arid landscapes where traditional methods fail. Crucially, SEBS eliminates empirical crop-coefficient dependencies through first-principal energy partitioning—a decisive advantage for natural desert steppes with dynamic phenology. By directly deriving turbulent fluxes from radiative and aerodynamic constraints, the framework ensures scalability from instantaneous satellite overpass to daily ET, making it operationally indispensable for regional water resource diagnostics in data-scarce environments like our Damao Banner study area.
2.3.1. Parameters of SEBS Model
In this study, we employed the SEBS model to calculate ET in arid regions. This model leverages remote sensing data to derive essential surface parameters for the study area, such as the NDVI, surface albedo, and surface emissivity [33]. Additionally, meteorological data obtained from weather stations—including mean atmospheric pressure, mean temperature, and mean wind speed—are integrated to estimate sensible heat flux and soil heat flux. Based on the principle of surface energy balance, latent heat flux is calculated, enabling the derivation of instantaneous ET. By temporally extending these instantaneous ET values, regional daily ET is estimated [10]. These surface parameters and meteorological observations provide a robust foundation for establishing and validating the SEBS model.
Initially, raw data from Landsat-8 are preprocessed using ENVI software 5.3 to eliminate systematic errors in the imagery and correct spectral information affected by atmospheric influences, such as scattering and absorption [34]. The preprocessing steps include radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction, geometric correction, and image cropping, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data for subsequent analysis.
The SEBS model is established based on the principle of surface energy balance and the net radiation flux per unit area over a unit of time can be expressed as:
where α is the surface albedo; Rs↓ represents incoming shortwave radiation from the sun (W/m2); RL↓ represents incoming atmospheric longwave radiation (W/m2); ε denotes surface emissivity and is 0.97 for grassland; RL↑ represents outgoing longwave radiation from the surface (W/m2). Where the surface broadband albedo α is derived through a linear combination of narrowband reflectance after atmospheric correction [6], it is formulated as follows:
Here, α2, α4, α5, α6, and α7 represent the reflectance of the 2nd, 4th, 5th, 6th, and 7th spectral bands after atmospheric correction, respectively.
The soil heat flux is calculated using a formula that integrates vegetation coverage, the vegetation coverage coefficient, the proportion of bare soil, and the net radiation flux at the surface. The calculation formula is as follows:
where G represents soil heat flux (W/m2); Rn represents net radiation flux at the surface (W/m2); Γc is 0.05, the ratio of G/Rn with full covered vegetation; Γs is 0.315, the G/Rn proportion of bare soil; Fv represents vegetation coverage, which is calculated by:
where NDVIs is the NDVI of bare soil, 0 for the desert steppe, and NDVIc is the NDVI with fully covered vegetation, with the value of 0.7 for grassland.
The sensible heat flux is calculated based on the Monin–Obukhov similarity theory and atmospheric boundary layer similarity theory, with modifications applied to enhance accuracy. The calculation formula is as follows:
where u represents wind speed (m/s); u* represents friction velocity (m/s); z represents reference height (m), with a value of 2 m in this equation; d0 represents zero-plane displacement height (m); z0m represents momentum transfer roughness length (m); Ψm and Ψh represent Monin–Obukhov stability correction functions for momentum and heat transfer, respectively; L represents Monin–Obukhov stability length (m); z0h represents the roughness length for heat transfer at the surface (m); θ0 and θa represent potential temperature at observation height and reference height (K), respectively; θv represents potential temperature near the surface (°C); H represents sensible heat flux (W/m2); κ represents the von Kármán constant, typically with a value of 0.4; ρ represents air density (g/m3); Cp represents specific heat capacity of air (J/g°C); g represents gravitational acceleration (m/s2).
2.3.2. Evaporation Ratio
The SEBS model determines the evaporation ratio by establishing dry and wet limits based on the actual conditions of sensible heat flux and latent heat flux under extreme dry and wet conditions. The evaporation ratio is calculated, and daily ET is subsequently estimated. According to the surface energy balance equation, when the surface is extremely dry, the latent heat flux approaches zero, indicating minimal evaporation, while the sensible heat flux reaches its maximum value [10,35]. This relationship is expressed by the following formula:
When the surface is extremely wet, the sensible heat flux reaches its minimum. Combining with the Penman–Monteith equation, this can be expressed as:
where rew represents aerodynamic resistance under wet conditions, which depends on the Monin–Obukhov length L (m); es represents saturation water vapor pressure; e represents actual water vapor pressure; r represents the psychrometric constant; ∆ represents the slope of the saturation vapor pressure–temperature curve.
By combining actual sensible heat and sensible heat at dry and wet limits, the relative evaporation ratio can be obtained:
Substituting into the SEBS model, the evaporation ratio Λ can be expressed as the ratio of actual evapotranspiration to available energy, represented by the following formula:
2.3.3. Evapotranspiration Time Scale Expansion
According to the evaporation ratio calculated and combined with the latent heat of vaporization of water, the daily evapotranspiration is calculated by directly using the evaporation ratio in the SEBS model [36], and the formula is expressed as follows:
where λ represents the latent heat of vaporization of water (J/kg); Ta represents the surface temperature (K); ETd represents daily evapotranspiration (mm/day); Rn represents net radiation flux at the surface (W/m2); ρw represents the density of water (kg/m3).
2.3.4. Accuracy Verification Methods
Accuracy verification methods can be categorized into direct validation methods and indirect validation methods. Direct validation methods include on-site data acquisition using the large-weighted lysimeter. Indirect validation methods, on the other hand, rely on calculations using the Penman–Monteith equation or remote sensing product retrievals. For example, the MODIS16A2 ET product is derived from the Penman–Monteith equation, incorporating surface data such as surface albedo, NDVI, and vegetation coverage, as well as meteorological data including temperature, pressure, and wind speed.
The study area, a desert grassland, utilizes MODIS16A2 product data to verify the ET inversion results based on Landsat-8, which was calculated using the SEBS model. Additionally, the trends in ET changes were analyzed, and the accuracy of the results was further validated using the large-weighted lysimeter measurement data.
2.4. Model Performance Statistics
The actual ET was measured by the large-weighted lysimeter. The determination coefficient (R2), mean absolute error (MAE), and root mean square error (RMSE) were chosen to evaluate the model performances [37].
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of ET Estimation Results to Measured ET
The ET data were derived based on the SEBS model and Landsat-8 inversion, which were validated using both direct and indirect error verification methods. Firstly, direct error verification selects data from the station’s large-weighted instruments in the study area for validation. Secondly, indirect error verification is based on MOD16A2 ET products. MOD16 data has been validated globally through flux tower ET measurements and estimates of ET from 232 basins. The SEBS model ET is shown in Table 1, simultaneously comparing with remote sensing ET based on MOD16A2 and large-weighted lysimeter measured ET. The maximum ET calculated by the SEBS model was 8.21 mm/day, occurring on 21 August, and the minimum was 1.83 mm/day, occurring on 3 December. The extreme ET values monitored by MOD16A2 appeared at the same time as the SEBS model inversion, with a maximum of 8.40 mm/day and a minimum of 1.94 mm/day (Figure 3). By comparing the ET modeled by the SEBS model with the ET measured by the large-weighted lysimeter, the minimum relative error was 1.05% on 6 March, the maximum relative error was 14.94% on 9 May, and the average relative error was 4.30%, which indicates that the SEBS method has better applicability in the research regions with different growing seasons.

Table 1.
Comparison of SEBS model, MOD16A2 ET, and measured ET in 2019.
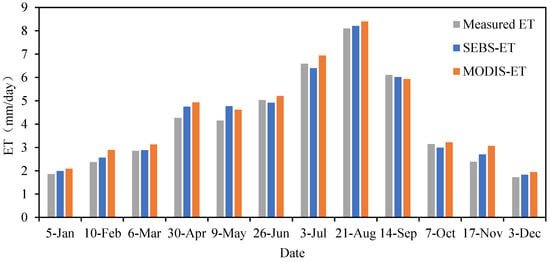
Figure 3.
Seasonal variation of SEBS modeled ET, MOD16A2 ET, and measured ET by the large-weighted lysimeter method (mm/day).
3.2. Comparison of ET Modeled by SEBS and Measured by Large-Weighted Lysimeter
A correlation analysis was performed between actual ET and SEBS-modeled ET, with results illustrated in Figure 4. Accuracy validation metrics, summarized in Figure 4, reveal a strong alignment between modeled and observed ET. The coefficient of determination (R2 = 0.91) demonstrates a robust positive correlation, indicating that the model accounts for 91% of the variability in observed ET. The root means square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) are 0.27 mm/day and 0.21 mm/day, respectively, which further confirms the model’s reliability. For the 2019 desert steppe study area, the growing season was observed to span from 6 March to 30 April, as evidenced by a distinct upward trend in ET values between these dates.
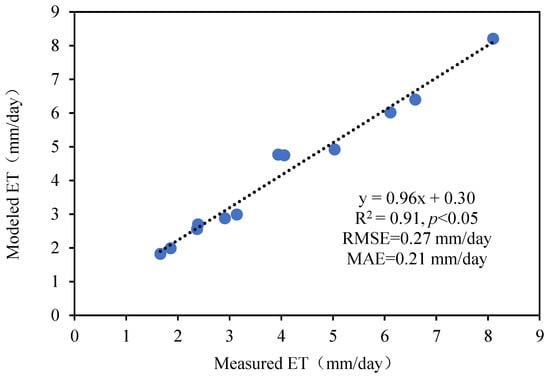
Figure 4.
Comparison of modeled ET by SEBS and measured ET by the large-weighted lysimeter.
3.3. The Influence Factors for Calculating Spatial ET
Land use classification within the study area is presented in Figure 5, revealing distinct spatial patterns: dryland systems dominate the southern region, while grasslands are distributed across central and northern zones. Grassland ecosystems accounted for approximately 70% of the total study area. Vegetation distribution in this desert steppe environment is principally governed by water availability, a critical limiting factor for ecosystem productivity. Notably, vegetation in high-coverage grassland exhibited elevated leaf area index (LAI) values. Surface energy partitioning in these areas demonstrated reduced sensible heat flux relative to latent heat flux, a pattern strongly modulated by LAI variations characteristic of steppe ecosystems. The regional ET is largely controlled by grassland vegetation, which also responds strongly to precipitation and soil moisture.
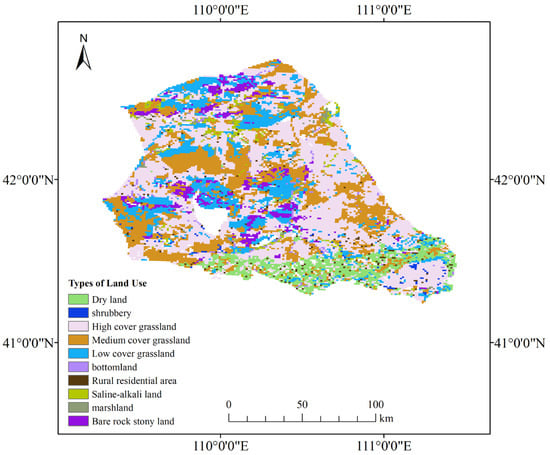
Figure 5.
The spatial distribution of land use.
3.4. The Spatial Distribution of Modeled ET
Figure 6 illustrates the spatiotemporal distribution of ET derived from SEBS model simulations across seasons. The temporal trend reveals a progressive increase in daily ET from January to July, followed by a decline from August to December. Seasonally, peak ET values occurred during the summer months (June to August), with a maximum daily value of 14.1 mm/day observed on 21 August. In contrast, winter months (December to February) displayed minimal ET activity, reaching a daily minimum of 4.9 mm/day on 3 December. Spatially, the eastern and southern sectors exhibited significantly enhanced ET rates compared to the western and northern regions, a pattern attributable to synergistic vegetation–climate interactions. As demonstrated in Figure 5, the southern zone is characterized by high-coverage grasslands and rain-fed croplands, which drive elevated ET through elevated LAI values and higher transpiration rates relative to the low-density desert steppe vegetation in northern areas. The annual precipitation was 161–424 mm during 2019, and the value is decreased from a southeast to a northwest direction. Moreover, precipitation may dominate ET spatial variability through threshold-dependent soil moisture recharge, creating patchy ET patterns where infrequent high-intensity events sustain localized hotspots while low-rainfall zones remain ET-limited especially in the southern area during July to September (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
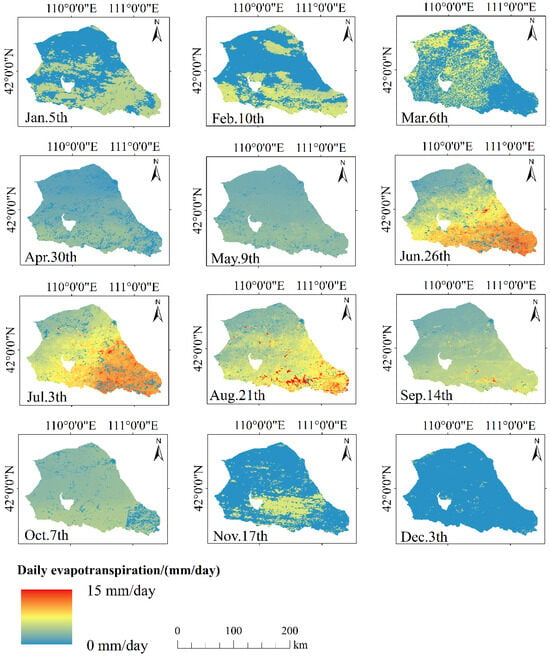
Figure 6.
The spatial distribution of ET evaluated by the SEBS method during different months in 2019.
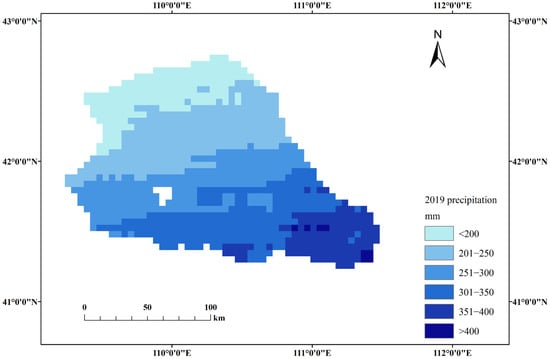
Figure 7.
The annual precipitation in 2019.
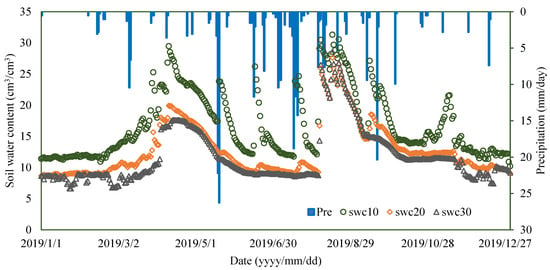
Figure 8.
The annual volume soil water content and precipitation in 2019 at the experiment site.
4. Discussion
The maximum ET measured by the large-weighted lysimeter also occurred on 21 August, with a value of 8.10 mm/day, which was similar to the maximum ET of 6.0 mm/day in July at the desert steppe of the Heihe River Basin [38]. As depicted in Figure 3, the measured ET values are consistently the lowest across the majority of dates. The ET values derived from the SEBS model fall between those obtained from MODIS products and the measured values. This pattern aligns with the comparative results reported in Arou County, Qinghai [39]. Furthermore, when compared with MODIS ET products, the ET data generated by the SEBS model, based on Landsat-8 satellite imagery inversion, demonstrate greater proximity to the measured ET values obtained from large-weighted lysimeter instruments. This finding suggests that the SEBS model-inverted ET data accurately reflect the regional ET conditions and meet the required precision standards. The SEBS model can naturally consider the dry–wet differences at different locations in the study area without the need to specifically set dry and wet points. In contrast, although the MOD16A2 product also considers factors such as vegetation, it may not be as detailed as the SEBS model in comprehensively considering complex surface characteristics. The resolution difference, with SEBS often at a 30–100 m scale compared to MOD16A2’s 500 m, can lead to disparities as SEBS captures more local details while MOD16A2 provides an averaged view [40]. Algorithm biases also play a role. SEBS, a single-source model based on the surface energy balance, has different assumptions about surface processes compared to MOD16A2, which uses the Penman–Monteith equation [41]. Consequently, these data are deemed suitable for conducting correlation analyses between ET and both meteorological factors and surface parameters.
The statistical significance (p < 0.05) of the correlation between SEBS calculated ET and large-weighted lysimeter ET underscores the validity of the inversion results. Notably, drought conditions may extend the growing season relative to typical years, potentially altering daily ET patterns in March and April [42]. The accuracy assessment highlights that model performance is partially influenced by the spatial resolution of remote sensing data. Nevertheless, discrepancies between simulated and measured ET remain within acceptable limits. These findings confirm that the SEBS model, when applied to Landsat-8 data, achieves sufficient accuracy for ET estimation in desert grassland ecosystems. When using the SEBS to calculate ET, assumptions such as high surface homogeneity and steady-state energy flux need to be considered [43].
Complementary meteorological analyses indicate 10–15% greater growing-season precipitation in southern subregions, enhancing soil moisture availability and sustaining vegetation-mediated ET processes. This microclimatic dichotomy, where a denser vegetation canopy and preferential moisture supply collectively enhance latent heat flux, aligns with established arid land ecohydrological principles linking ET variability to vegetation density and soil water status [37,44]. The variability in evapotranspiration and its ecological effects are core issues in hydrological research in arid and semi-arid areas. Simplified models based on the Budyko framework indicate that in semi-arid areas such as the northwestern agro-pastoral transition zone, ET changes are mainly driven by both vegetation sensitivity and precipitation variability, with the sensitivity coefficient of vegetation to ET changes reaching 0.96, while the actual contribution of precipitation dominates due to its greater variability [45,46]. The variability in ET and its ecological responses are the results of vegetation–water feedback. Vegetation influences ET primarily through transpiration and interception evaporation, especially in a dry area. Higher vegetation cover means more leaf surfaces actively transpiring water absorbed by roots. More leaves also intercept more rainfall, increasing evaporation from wet canopies, which means the precipitation is less effective. The plants varied between different grass species, while the different responses to soil moisture stress or high vapor pressure deficit can cause stomatal closure, directly reducing transpiration. Moreover, the grass species determine the land surface’s albedo and roughness, in which a greener, rougher surface absorbs more solar radiation and enhances turbulent transfer of water vapor away from the surface.
5. Conclusions
This study quantified daily evapotranspiration (ET) in a northern Chinese desert steppe using direct large-weighted lysimeter measurements and spatially distributed modeling via the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS). Our primary objective was to evaluate SEBS-driven ET estimates against high-precision ground truth while assessing the framework’s efficacy in this water-limited ecosystem. The study revealed pronounced spatial heterogeneity in ET patterns across the research domain during August 2019, with daily fluxes averaging 8.10 mm. Model validation statistics confirmed SEBS’s suitability for landscape-scale ET estimation in arid grassland ecosystems and supports its application in ecological water management and drought monitoring, demonstrating strong agreement between remote sensing-derived values and ground-based measurements.
The integration of remote sensing with lysimeter-based measurements offers an available scalable framework for monitoring water use amounts in water-limited pastoral systems. These insights can empower land managers to (1) prioritize irrigation or conservation efforts in high-ET zones, (2) adjust grazing intensity with spatiotemporal water availability, and (3) optimize management strategies under climate variability. Future work could extend this approach to multi-seasonal assessments, incorporating machine learning to refine ET predictions under extreme aridification scenarios.
Author Contributions
C.L. and B.Z. conceived and designed the experiments; Y.F. and L.W. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; J.W. contributed analysis tools; Y.F., C.L. and L.W. wrote the paper; B.Z., P.Z. and R.W. revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received the grants from the Yinshanbeilu Grassland Eco-Hydrology National Observation and Research Station, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing 100038, China, Grant NO. YSS2022008, the State Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52130906), the open fund of the Key Laboratory of Ecosystem Carbon Source and Sink, China Meteorological Administration (ECSS-CMA), Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Agricultural and Ecological Meteorology, School of Ecology and Applied Meteorology, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China; Landscape, forest, cropland, lake, grass and desert system management project, Grant/Award Number: AKSSSXM2022620.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to legal reasons.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for all grants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Liu, C.; Qiu, R.; Cui, N.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W. Comparison of Surface Resistance-Based Models for Estimating Maize Evapotranspiration in a Humid Region of China. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2024, 60, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z. Evapotranspiration Estimation Using a Modified Crop Coefficient Model in a Rotated Rice-Winter Wheat System. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.; Agam, N.; Lazarovitch, N.; Heitman, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Ben-Gal, A. A Review of Approaches for Evapotranspiration Partitioning. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Diak, G.T.; Hain, C.R.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Knipper, K.R.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. A Brief History of the Thermal IR-Based Two-Source Energy Balance (TSEB) Model—Diagnosing Evapotranspiration from Plant to Global Scales. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 350, 109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for Estimation of Turbulent Heat Fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.G.; Song, Y.Y. Higher Temporal Evapotranspiration Estimation with Improved SEBS Model from Geostationary Meteorological Satellite Data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y. Evaluation of ICESat-2 Laser Altimetry for Inland Water Level Monitoring: A Case Study of Canadian Lakes. Water 2025, 17, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sun, R.; Wang, H.; Wu, X. Trends and Innovations in Surface Water Monitoring via Satellite Altimetry: A 34-Year Bibliometric Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, Y.A.; Kar, S.K. Evapotranspiration Estimation with Remote Sensing and Various Surface Energy Balance Algorithms-A Review. Energies 2014, 7, 2821–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derardja, B.; Khadra, R.; Abdelmoneim, A.A.A.; El-Shirbeny, M.A.; Valsamidis, T.; De Pasquale, V.; Deflorio, A.M.; Volden, E. Advancements in Remote Sensing for Evapotranspiration Estimation: A Comprehensive Review of Temperature-Based Models. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Shi, L.S.; Lian, X.; Bian, J. Parameter Variability across Different Timescales in the Energy Balance-Based Model and Its Effect on Evapotranspiration Estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungel, R.; Aiken, R.; Evett, S.R.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Marek, G.; Moorhead, J.E.; Baumhardt, R.L.; Brauer, D.; Kutikoff, S.; Lin, X.M. Energy Imbalance and Evapotranspiration Hysteresis Under an Advective Environment: Evidence From Lysimeter, Eddy Covariance, and Energy Balance Modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Su, H.B.; Zhang, R.H.; Tian, J.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, W.Z. Regional Estimation of Remotely Sensed Evapotranspiration Using the Surface Energy Balance-Advection (SEB-A) Method. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a Global Evapotranspiration Algorithm Based on MODIS and Global Meteorology Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Masri, B.; Rahman, A.F.; Dragoni, D. Evaluating a New Algorithm for Satellite-Based Evapotranspiration for North American Ecosystems: Model Development and Validation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, R.; Beighley, E. Estimating Daily Global Evapotranspiration Using Penman-Monteith Equation and Remotely Sensed Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, P.; Yuan, D.; Song, C.; Cui, Y.; Xie, H. Spatiotemporal Variation in Rice Evapotranspiration under the Influence of Rice Expansion: A Case Study in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2024, 22, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, M. Inconsistencies of SEBS Model Output Based on the Model Inputs: Global Sensitivity Contemplations. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fu, Y.H.; Shi, X.; Lock, T.R.; Kallenbach, R.L.; Yuan, Z. Soil Moisture Determines the Effects of Climate Warming on Spring Phenology in Grasslands. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinglan, A.; Wang, G.Q.; Liu, T.X.; Xue, B.L.; Kuczera, G. Spatial Variation of Correlations between Vertical Soil Water and Evapotranspiration and Their Controlling Factors in a Semi-Arid Region. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G.; Noormets, A.; Fang, Y. Environmental Controls on Seasonal Ecosystem Evapotranspiration/Potential Evapotranspiration Ratio as Determined by the Global Eddy Flux Measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Lamb, D.W.; Rahman, M.M. In-Situ Partitioning of Evaporation and Transpiration Components Using a Portable Evapotranspiration Dome-A Case Study in Tall Fescue (Festuca Arundinacea). Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.M.; Zou, C.B.; Wilcox, B.P.; Stebler, E. Effect of Vegetation on the Energy Balance and Evapotranspiration in Tallgrass Prairie: A Paired Study Using the Eddy-Covariance Method. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2019, 170, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwate, O.; Mantel, S.K.; Gibson, L.A.; Munch, Z.; Palmer, A.R. Exploring Dynamics of Evapotranspiration in Selected Land Cover Classes in a Sub-Humid Grassland: A Case Study in Quaternary Catchment S50E, South Africa. J. Arid. Environ. 2018, 157, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, P.; Gowda, P.H.; Northup, B.K. Dynamics of Evapotranspiration over a Non-Irrigated Alfalfa Field in the Southern Great Plains of the United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufkens, K.; Keenan, T.F.; Flanagan, L.B.; Scott, R.L.; Bernacchi, C.J.; Joo, E.; Brunsell, N.A.; Verfaillie, J.; Richardson, A.D. Productivity of North American Grasslands Is Increased under Future Climate Scenarios despite Rising Aridity. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 29, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Katul, G.G.; Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Jiang, X. The Effects of Changing Environments, Abiotic Stresses, and Management Practices on Cropland Evapotranspiration: A Review. Rev. Geophys. 2025, 63, e2024RG000858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; An, C.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Gao, T.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z. Impacts of grazing intensity on soil properties and carbon content in Xilamuren Grassland. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 386, 125773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.L.; Barsi, J.A. The next Landsat Satellite: The Landsat Data Continuity Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Liang, C.; Wang, Z. Estimating the Actual Evapotranspiration Using Remote Sensing and SEBAL Model in an Arid Environment of Northwest China. Water 2023, 15, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Pete, P.; Martin, L.; Diego, P.; James, V.; Shraddhanand, S.; Gregory, H.; James, R.; Laura, H.; Andrew, H.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations-a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadnia, E.; Mobasheri, M.R.; Kamali, G.A. MODIS NDVI Quality Enhancement Using ASTER Images. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2009, 11, 549–558. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Doski, J.; Hassan, F.M.; Mossa, H.A.; Najim, A.A. Incorporation of Digital Elevation Model, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, and Landsat-8 Data for Land Use Land Cover Mapping. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2022, 88, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Baik, J.; Choi, M. A Physical-Based Two-Source Evapotranspiration Model with Monin–Obukhov Similarity Theory. GIScience Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 88–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Lu, L.; Li, X. Improving Estimation of Evapotranspiration under Water-Limited Conditions Based on SEBS and MODIS Data in Arid Regions. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16795–16814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, N.; Gong, D.; Hu, X.; Feng, Y. Evaluation of Seasonal Evapotranspiration of Winter Wheat in Humid Region of East China Using Large-Weighted Lysimeter and Three Models. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, W.; Che, T.; Xu, F. Performance of the Improved Two-Source Energy Balance Model for Estimating Evapotranspiration over the Heterogeneous Surface. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, S. Validation of the SEBS-Derived Sensible Heat for FY3A/VIRR and TERRA/MODIS over an Alpine Grass Region Using LAS Measurements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihan, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X. Preseason Drought Controls on Patterns of Spring Phenology in Grasslands of the Mongolian Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Arfania, R.; Sahour, H. Evaluation of SEBS Algorithm for Estimation of Daily Evapotranspiration Using Landsat-8 Dataset in a Semi-Arid Region of Central Iran. Open J. Geol. 2017, 7, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, M.; Arast, M. Remote sensing products for predicting actual evapotranspiration and water stress footprints under different land cover. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jing, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F. Improvement of Two Evapotranspiration Estimation Models Using a Linear Spectral Mixture Model over a Small Agricultural Watershed. Water 2018, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; You, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Niu, Y.; Shao, C.; Wang, X.; Xin, X.; Yu, G.; Han, X.; et al. Seasonal Variations and Drivers of Energy Fluxes and Partitioning along an Aridity Gradient in Temperate Grasslands of Northern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 342, 109736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; He, C.; Tian, W.; Tian, J. Development of a simple Budyko-based framework for the simulation and attribution of ET variability in dry regions. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Gao, G.; Fu, B. The relationship between grassland ecosystem and soil water in arid and semiarid areas: A review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 3127–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).