Impact of Different Building Roof Types on Hydrological Processes at the Urban Community Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
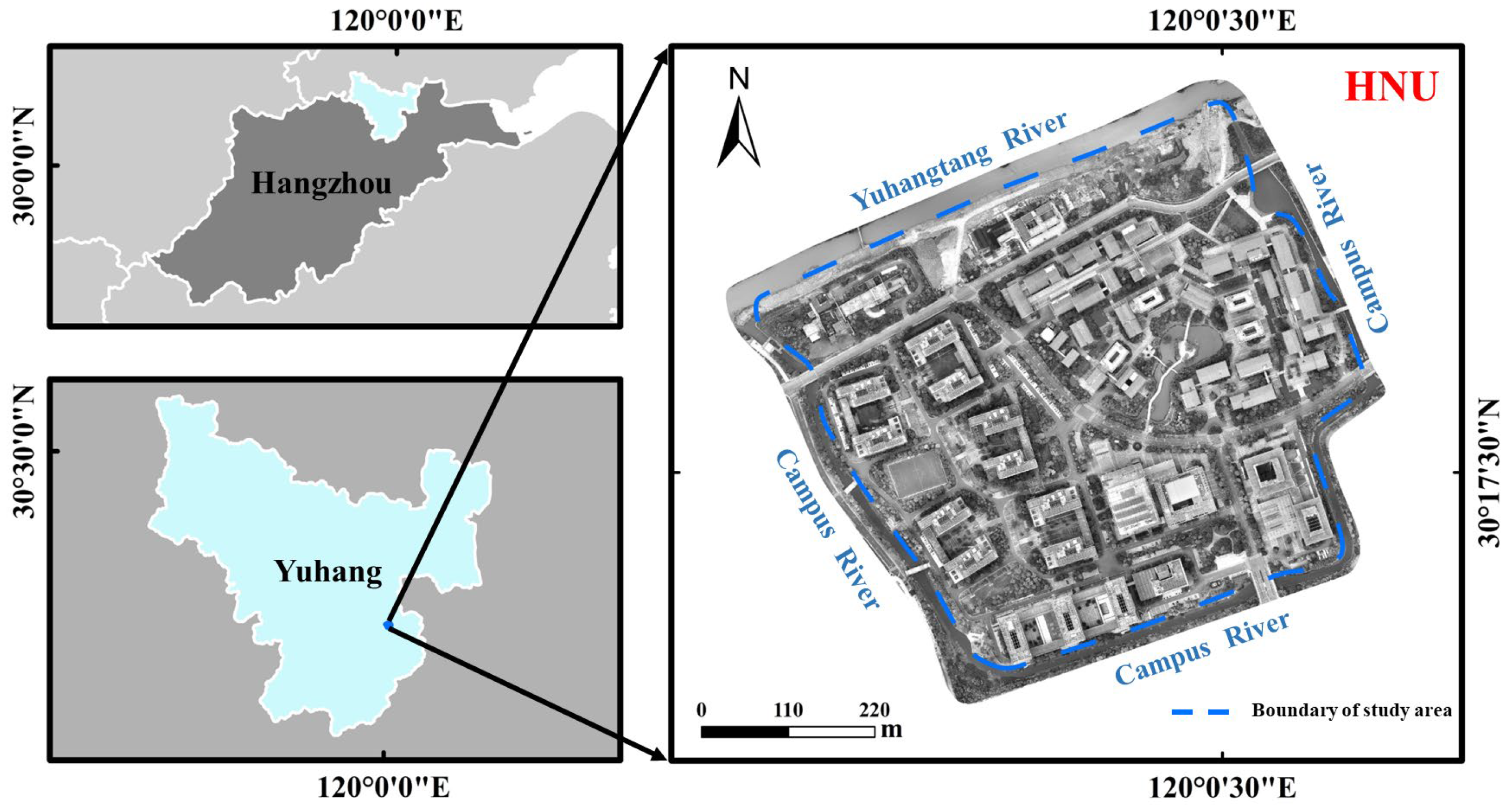
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
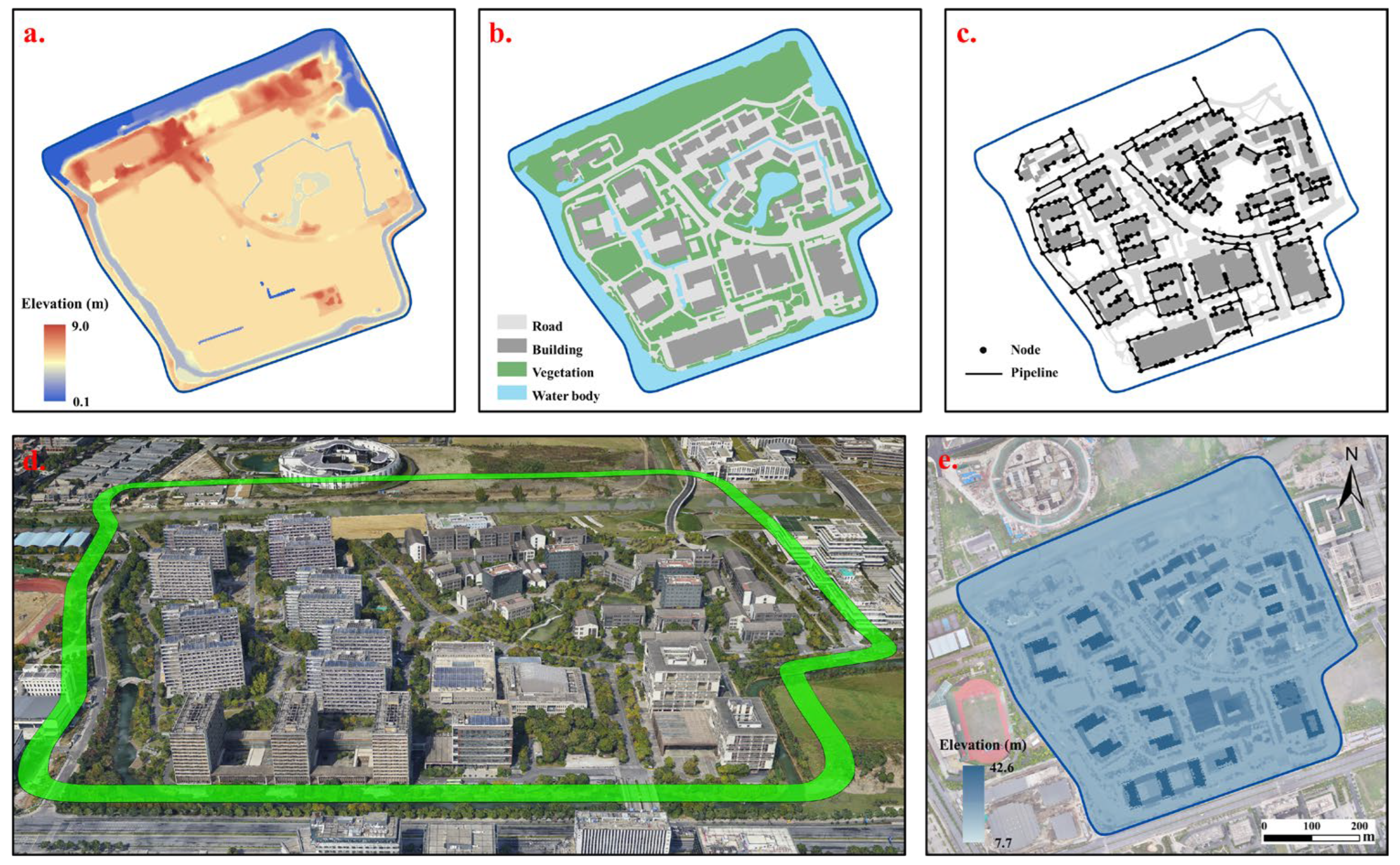
2.2.1. Basic Geographic Data
2.2.2. Digital Surface Modeling
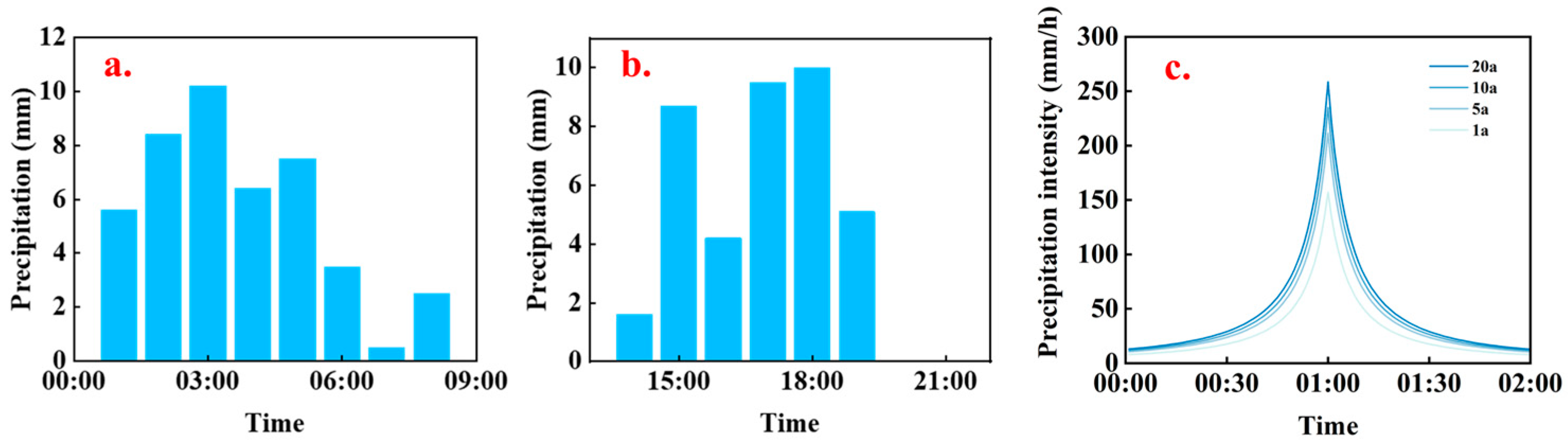
2.2.3. Precipitation Data
2.3. Principles of Hydrological Modeling
Principles of One- and Two-Dimensional Hydrological Modeling
2.4. Roof Structural Identification and Characterization
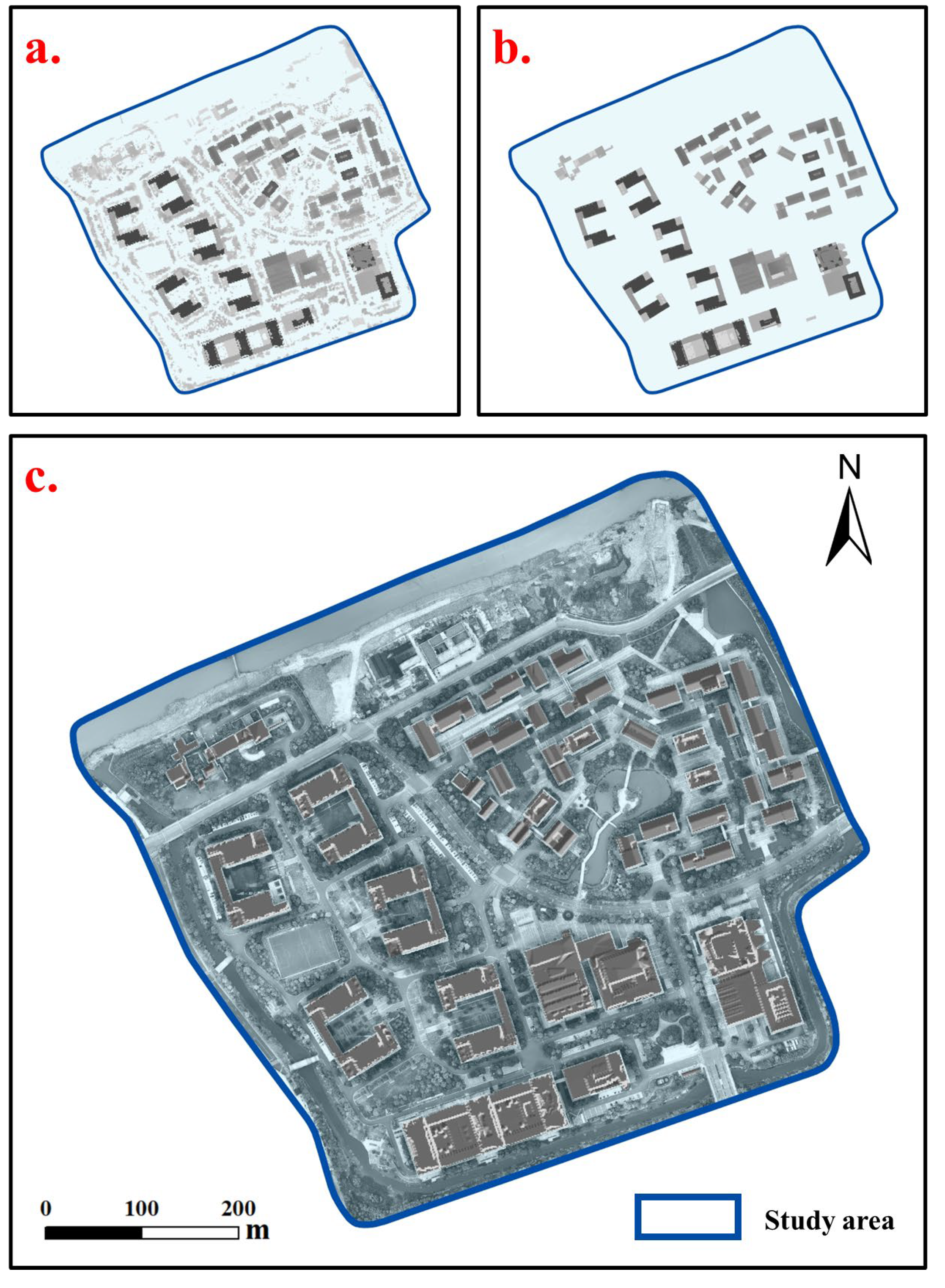
2.4.1. Building Roof Extraction
2.4.2. Roof Type Classification
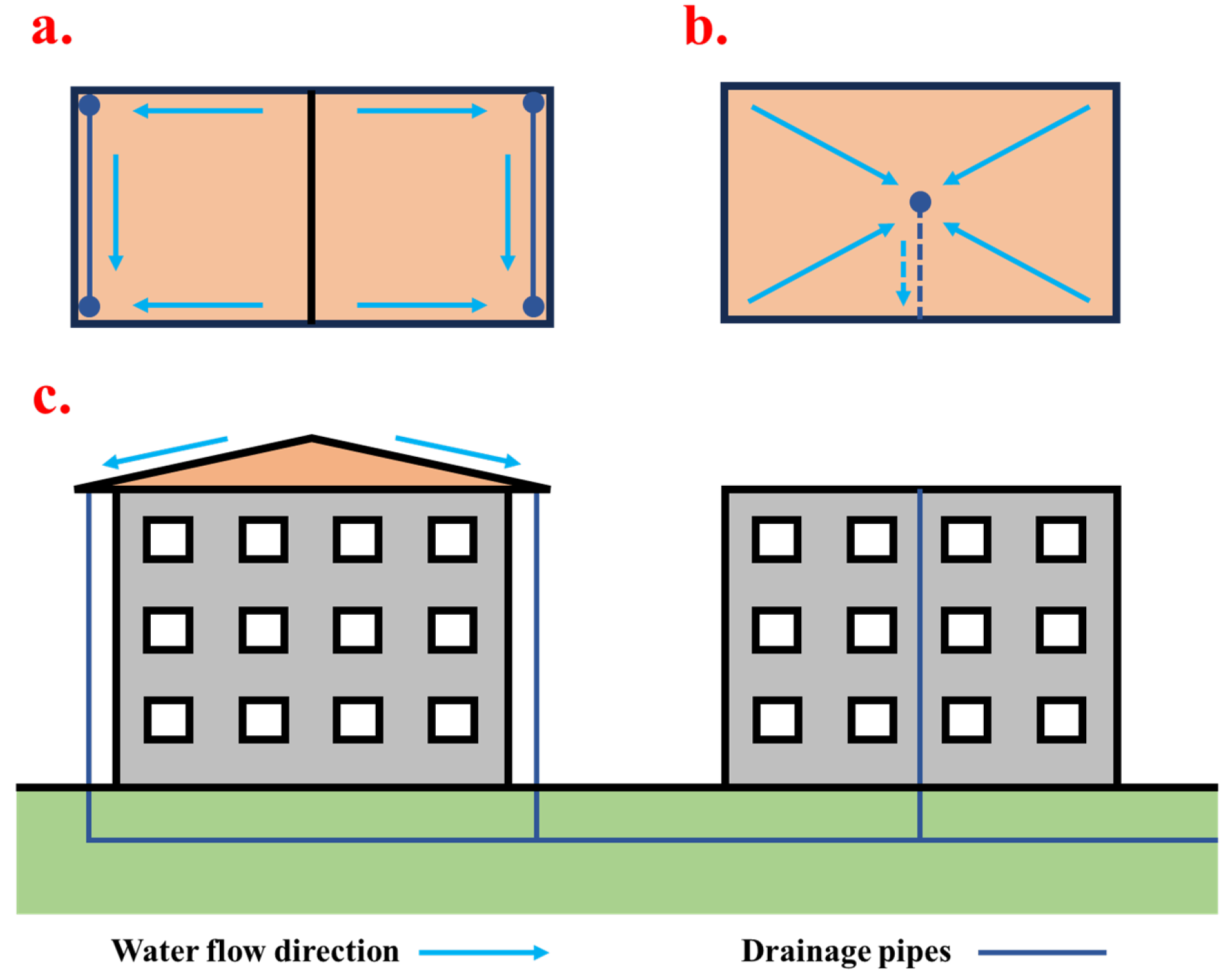
2.5. Establishment of Roof Drainage System Structures
2.6. Catchment Area Delineation
2.7. Modeling and Validation
3. Result
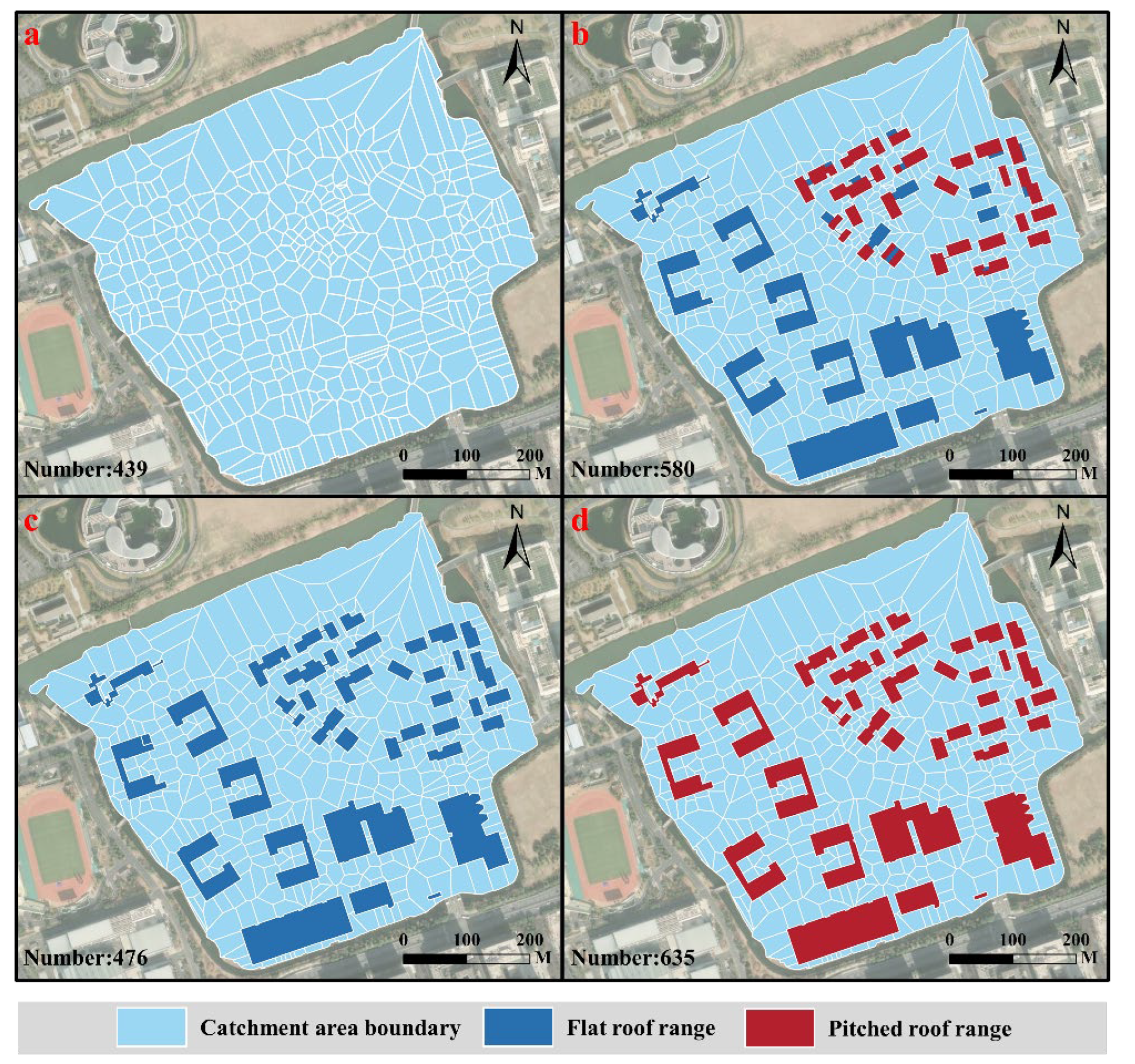
3.1. Results of Catchment Area Delineation
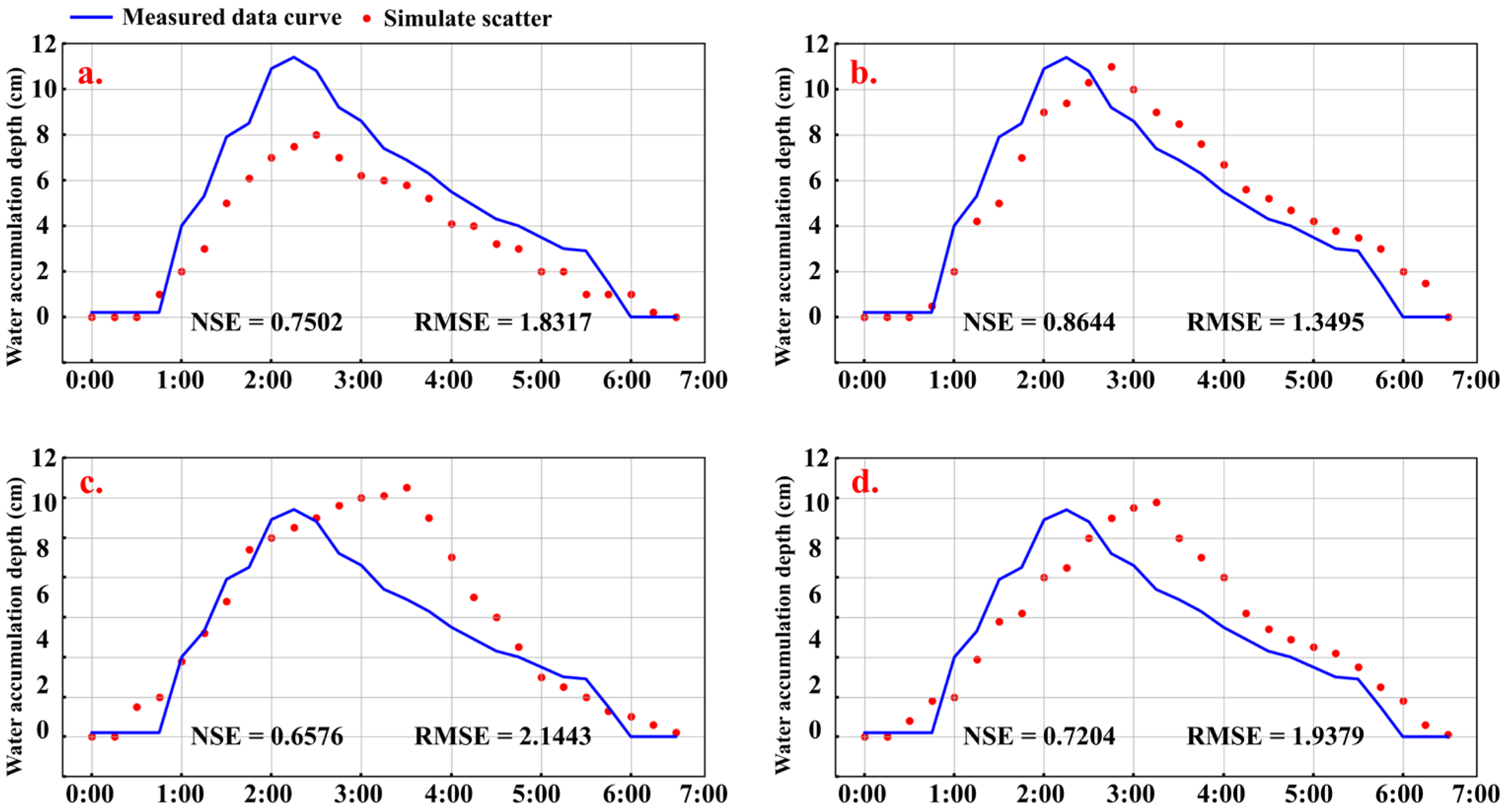
3.2. Evaluation of Simulation Accuracy
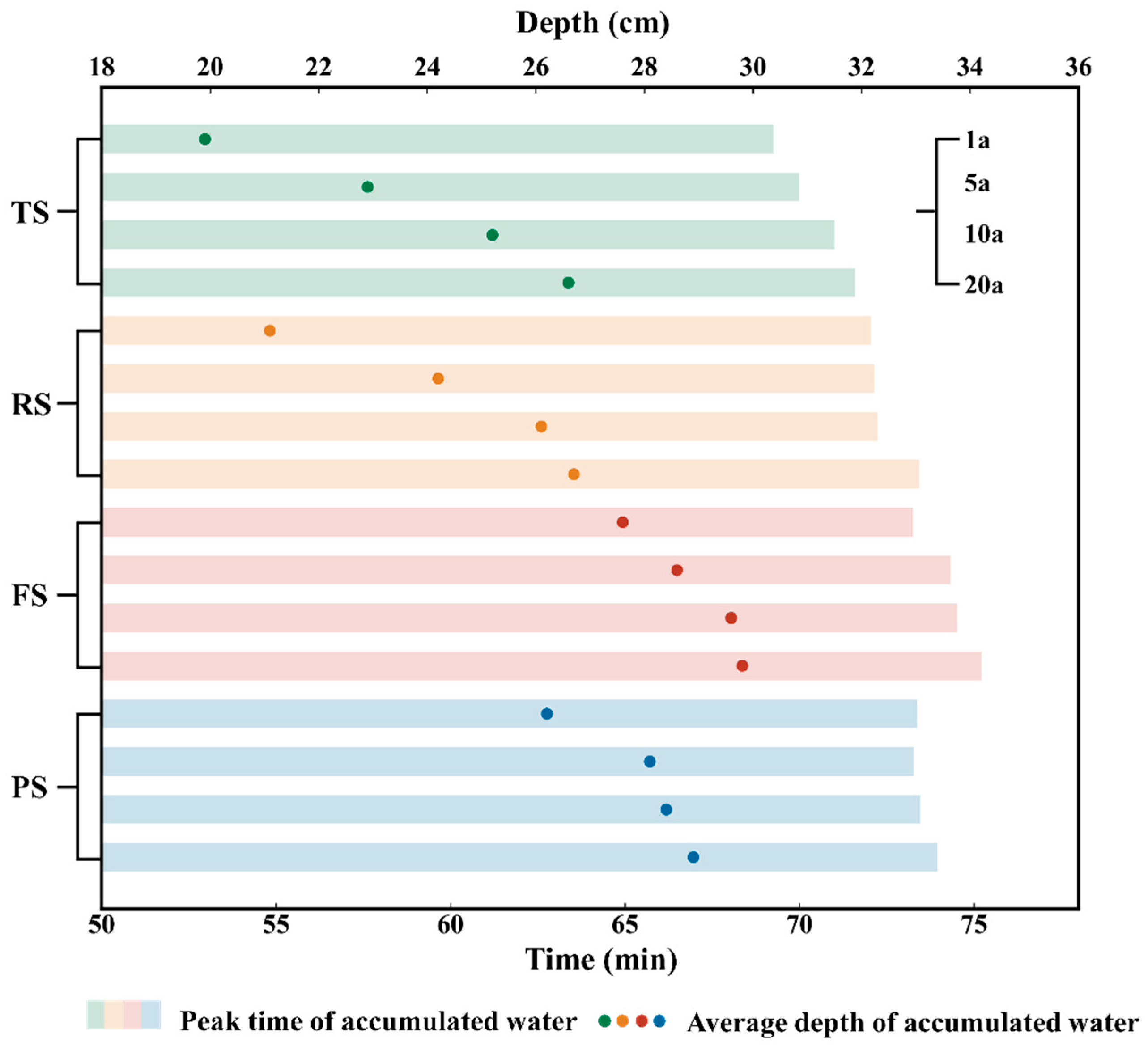
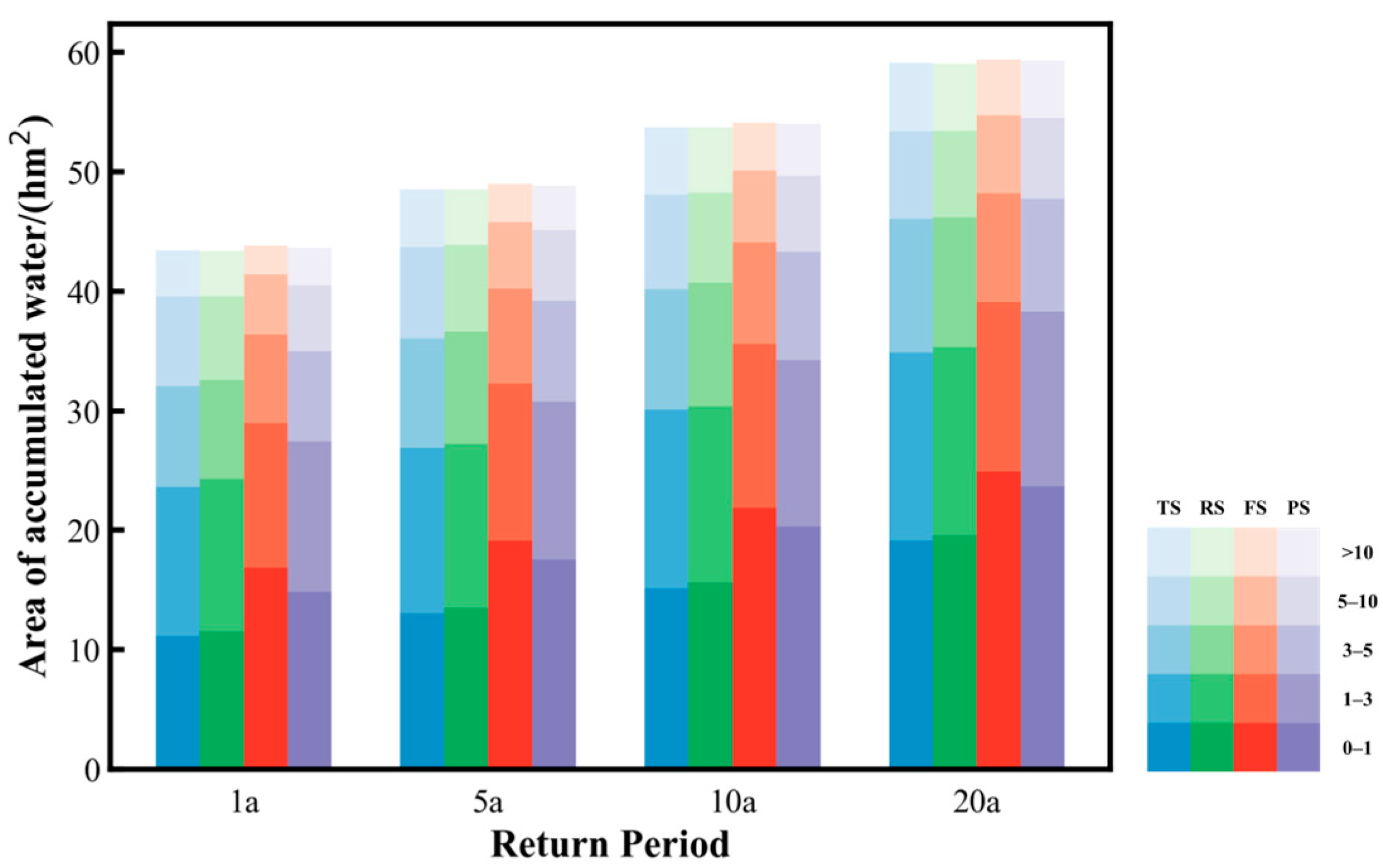
3.3. Peak and Duration of Water Accumulation
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Roofs on Catchment Area Delineation
4.2. Impact of Roof Catchment Area Delineation on Hydrological Processes in Urban Communities
4.3. Shortcomings and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oudin, L.; Salavati, B.; Furusho-Percot, C.; Ribstein, P.; Saadi, M. Hydrological impacts of urbanization at the catchment scale. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Hu, J.; Yang, H.; Guo, W. Effect of urbanization on the river network structure in Zhengzhou City, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhomme, J.; Bouvier, C.; Perrin, J.-L. Applying a GIS-based geomorphological routing model in urban catchments. J. Hydrol. 2004, 299, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, K. Effects of block morphology on the surface thermal environment and the corresponding planning strategy using the geographically weighted regression model. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 109037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.K. Impact of urbanization on the hydrology of Ganga Basin (India). Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.; Zommers, Z.; Wreford, A.; Hurlbert, M.; Viner, D.; Scantlan, J.; Halsey, K.; Halsey, K.; Tamang, C. Characteristics of transformational adaptation in climate-land-society interactions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y. Comparison of urbanization and climate change impacts on urban flood volumes: Importance of urban planning and drainage adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, L.; Costabile, P. Flood risk in urban areas: Modelling, management and adaptation to climate change. A review. Hydrology 2022, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.T.; Yassine, M.; Amin, D. Comparison of urbanization, climate change, and drainage design impacts on urban flashfloods in an arid region: Case study, New Cairo, Egypt. Water 2022, 14, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Liu, Z.; Efremochkina, M.; Liu, X.; Lin, C. Study on city digital twin technologies for sustainable smart city design: A review and bibliometric analysis of geographic information system and building information modeling integration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 84, 104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Vivoni, E.R.; Ogden, F.L.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Mirus, B.; Gochis, D.; Downer, C.W.; Camporese, M.; Davison, J.H.; Ebel, B. An overview of current applications, challenges, and future trends in distributed process-based models in hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A.; Dickinson, R.E.; Schade, T.; Chan, C.C.; Burgess, E.; Sullivan, D.; Lai, F.-H. SWMM 5-the next generation of EPA’s storm water management model. J. Water Manag. Model. 2004, 16, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wei, J.; Yuan, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, F.-F. Constitution analysis of pollution sources in urban rivers of Hangzhou. In Energy, Environment and Green Building Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Arjenaki, M.O.; Sanayei, H.R.Z.; Heidarzadeh, H.; Mahabadi, N.A. Modeling and investigating the effect of the LID methods on collection network of urban runoff using the SWMM model (case study: Shahrekord City). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadore, E.; Bronders, J.; Batelaan, O. Hydrological modelling of urbanized catchments: A review and future directions. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, Z.; Tutulic, D. On the use of 1D and coupled 1D-2D modelling approaches for assessment of flood damage in urban areas. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Dewals, B. Hydraulic modelling of inland urban flooding: Recent advances. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, T.W.; Macdonald, N.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Miller, J.D.; Reynard, N. Current understanding of hydrological processes on common urban surfaces. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.-H.; Chen, F.; Miao, S.; Tewari, M.; Voogt, J.A.; Myint, S. Enhancing hydrologic modelling in the coupled weather research and forecasting–urban modelling system. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 155, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Sánchez, S.; Jato-Espino, D.; Lombillo, I.; Diaz-Sarachaga, J.M. Assessment of the contributions of different flat roof types to achieving sustainable development. Build. Environ. 2018, 141, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Han, R.; Shi, T.; Qu, X.; Wu, Y. Evaluating the hydrologic performance of low impact development scenarios in a micro urban catchment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.A. The Water Balance of Urban Impermeable Surfaces: Catchment and Process Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, G.; Jack, L.B.; Swaffield, J. Investigation and numerical modelling of roof drainage systems under extreme events. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, C.O. Modelling and Design of Flat Timber Roof and High Pitch Timber Roof, a Comparative Analysis; Final Year Project & Postgraduate Portal; NAU Department of Civil Engineering: Awka, Nigeria, 2023; Volume 2, pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Engel, B.A.; Feng, Q. Modelling the hydrological responses of green roofs under different substrate designs and rainfall characteristics using a simple water balance model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolani, G.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Gandolfi, C.; Castelli, F.; Masseroni, D. Evaluating performances of green roofs for stormwater runoff mitigation in a high flood risk urban catchment. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyumi, M.; Abenayake, C.; Jayasinghe, A.; Wijegunarathna, E. Urban flood modeling application: Assess the effectiveness of building regulation in coping with urban flooding under precipitation uncertainty. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versini, P.-A.; Ramier, D.; Berthier, E.; De Gouvello, B. Assessment of the hydrological impacts of green roof: From building scale to basin scale. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, F.; Hewage, K. How “green” are the green roofs? Lifecycle analysis of green roof materials. Build. Environ. 2012, 48, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S.; Catania, F.; Gagliano, A.; Sciuto, G. A comprehensive study on green roof performance for retrofitting existing buildings. Build. Environ. 2018, 136, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susca, T. Green roofs to reduce building energy use? A review on key structural factors of green roofs and their effects on urban climate. Build. Environ. 2019, 162, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Ran, Q.J.S. Optimizing the valuation and implementation path of the gross ecosystem product: A case study of Tonglu County, Hangzhou City. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodoque, J.M.; Aroca-Jiménez, E.; Eguibar, M.Á.; García, J.A. Developing reliable urban flood hazard mapping from LiDAR data. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıtaş, B.; Kaplan, G. Enhancing ground point extraction in airborne LiDAR point cloud data using the CSF filter algorithm. Adv. LiDAR 2023, 3, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zeng, Y.; Yin, C. 3D city reconstruction: A novel method for semantic segmentation and building monomer construction using oblique photography. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X. Surveying and mapping of large-scale 3D digital topographic map based on oblique photography technology. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2024, 17, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, M.; Weatherly, H.; Bale, S.; Perkins, A.; MacDonald, B. A multi-faceted debris-flood hazard assessment for Cougar Creek, Alberta, Canada. Hydrology 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiao, W.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Impact and analysis of urban water system connectivity project on regional water environment based on Storm Water Management Model (SWMM). J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB33/T 1191–2020; Standard of Rainfall Intensity Computation. Zhejiang Provincial Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Hangzhou, China, 2020.
- UFIM Model. Available online: https://www.antmap.net/web/ufim/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Bañas, K.; Robles, M.E.; Maniquiz-Redillas, M. Stormwater harvesting from roof catchments: A review of design, efficiency, and sustainability. Water 2023, 15, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Hu, X.; Shu, Z.; Qin, N.; Zhang, J. Deep ground filtering of large-scale ALS point clouds via iterative sequential ground prediction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trhan, O.; Marčiš, M. Building models created from UAV photogrammetry data. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConference SGEM 2016, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z. Boundary shape-preserving model for building mapping from high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Batelaan, O.; Guan, H.; Liu, T.; Duan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Assessing long-term trends in vegetation cover change in the Xilin River Basin: Potential for monitoring grassland degradation and restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienhold, K.J.; Li, D.; Li, W.; Fang, Z.N. Flood inundation and depth mapping using unmanned aerial vehicles combined with high-resolution multispectral imagery. Hydrology 2023, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Men, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Men, C. A cascade domain clustering algorithm for multi-view DSM fusion from urban satellite images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4505321. [Google Scholar]
- Kalu, I.; Ndehedehe, C.E.; Okwuashi, O.; Eyoh, A.E.; Ferreira, V.G. Reconstructing terrestrial water storage anomalies using convolution-based support vector machine. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 46, 101326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Xue, S.; Chen, G.; Guan, B. Impact of modeling methods on urban flood processes at community scale. Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, C.; Xie, T.; Jian, S.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Hu, C. BK-SWMM flood simulation framework is being proposed for urban storm flood modeling based on uncertainty parameter crowdsourcing data from a single functional region. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, T.R. Decision Guide for Roof Slope Selection; Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1988.
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Chen, G.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C. High efficiency integrated urban flood inundation simulation based on the urban hydrologic unit. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Zang, D.; Xie, X. A Feature Line Extraction Method for Building Roof Point Clouds Considering the Grid Center of Gravity Distribution. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ma, C.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, J. A calibration method for SWMM to mitigate the impact of the structure defect without considering runoff on building walls. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1212501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.G.; Saniei, K.; Nematollahi, B.; Zahmatkesh, Z.; Poor, M.M.; Nikoo, M.R. Developing sustainable strategies by LID optimization in response to annual climate change impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 416, 137931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanim, A.H.; Smith-Lewis, C.; Downey, A.R.; Imran, J.; Goharian, E. Bayes_Opt-SWMM: A Gaussian process-based Bayesian optimization tool for real-time flood modeling with SWMM. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 179, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Ishidaira, H.; Commey, N.A.; Yang, D. Integrated urban and riverine flood risk management in the Fujiang River Basin-Mianyang city. J. Hydrol. 2024, 645, 132150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TS | RS | FS | PS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 August 2024 | 69.23% | 84.6% | 69.23% | 76.9% |
| 27 August 2024 | 66.7% | 83.3% | 75% | 66.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Hou, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T. Impact of Different Building Roof Types on Hydrological Processes at the Urban Community Scale. Hydrology 2025, 12, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060154
Chen C, Hou H, Shi Y, Zhao P, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Hu T. Impact of Different Building Roof Types on Hydrological Processes at the Urban Community Scale. Hydrology. 2025; 12(6):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060154
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chaohui, Hao Hou, Yongguo Shi, Ping Zhao, Yao Li, Yong Wang, Yindong Zhang, and Tangao Hu. 2025. "Impact of Different Building Roof Types on Hydrological Processes at the Urban Community Scale" Hydrology 12, no. 6: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060154
APA StyleChen, C., Hou, H., Shi, Y., Zhao, P., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Hu, T. (2025). Impact of Different Building Roof Types on Hydrological Processes at the Urban Community Scale. Hydrology, 12(6), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060154











