Evaluation of Rainfall Distribution Based on the Precipitation Concentration Index: A Case Study over the Selected Summer Rainfall Regions of South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
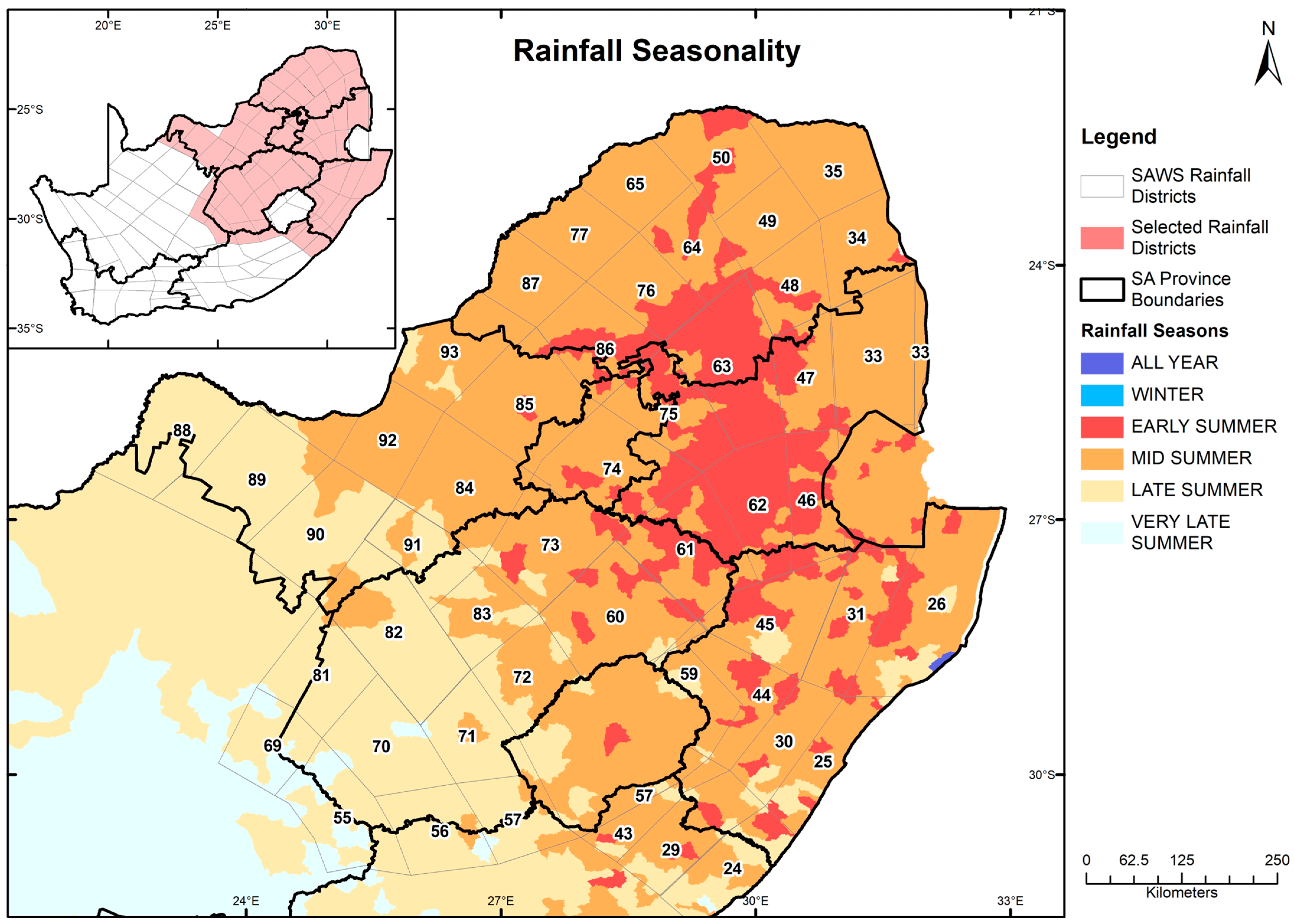
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Precipitation Concentration Index
2.3.2. Mann–Kendall Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
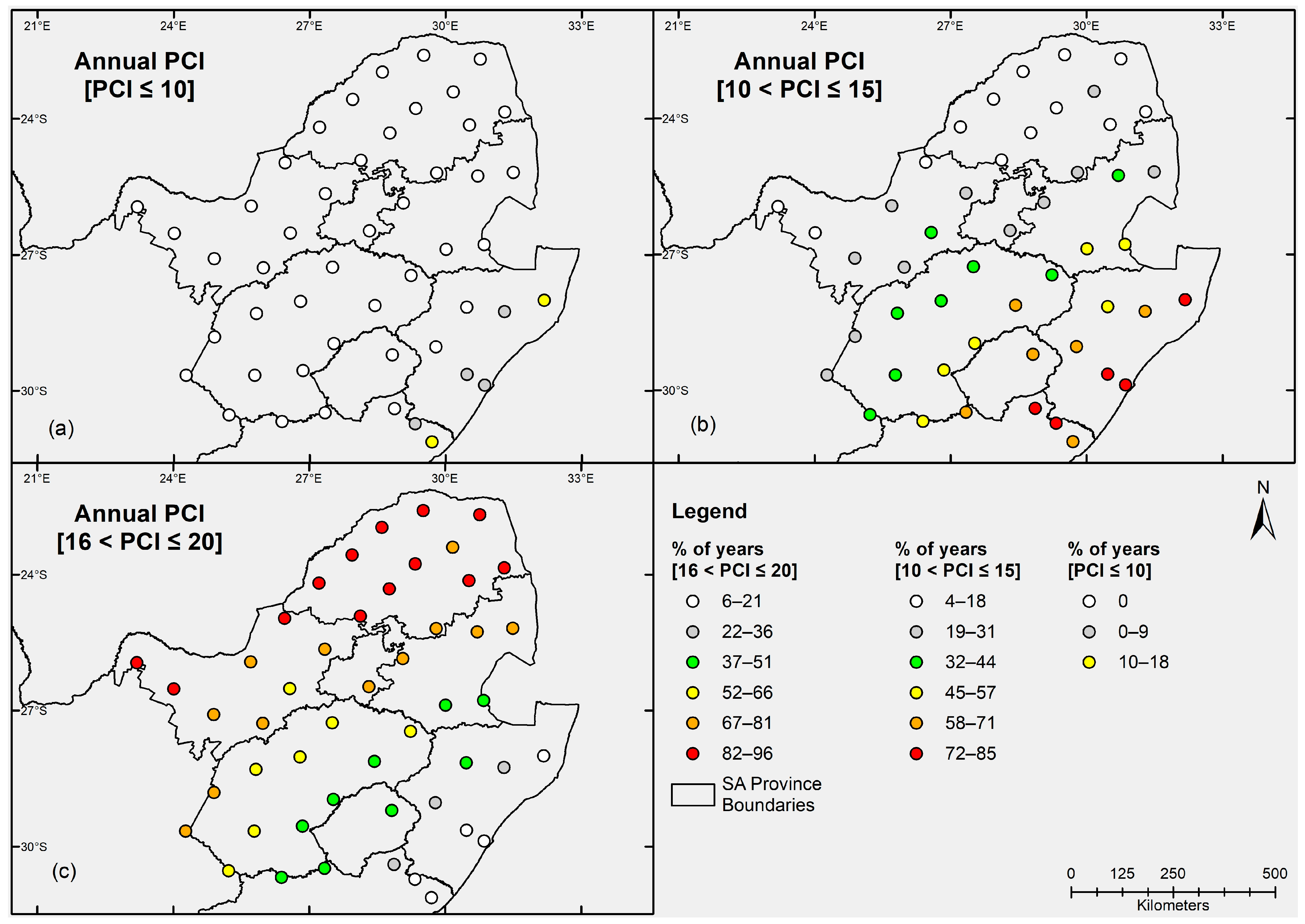
3.1. Characteristics of Annual and Decadal PCI Values
3.2. Seasonal Variations in PCI
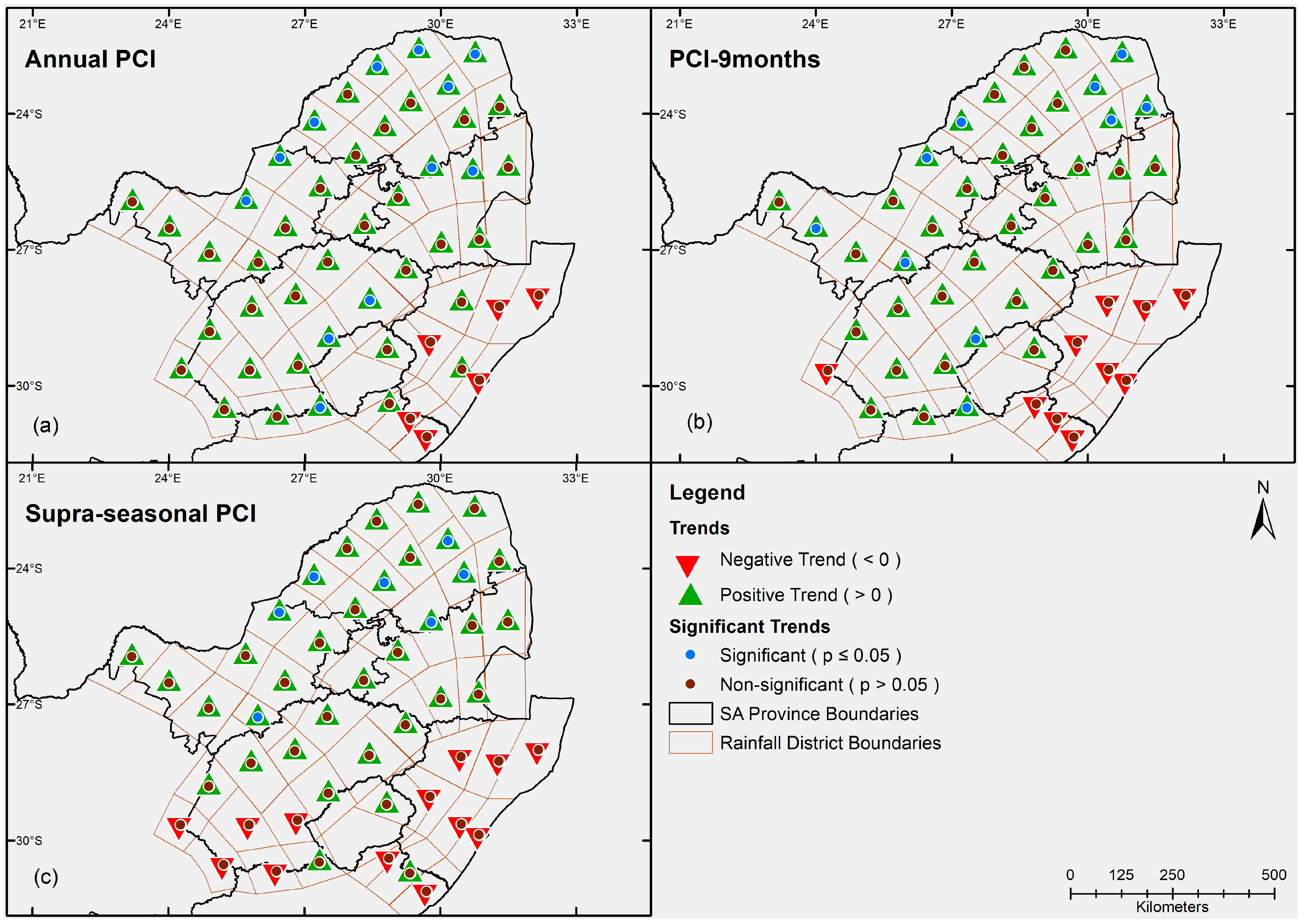
3.3. Trends of PCI Across Timescales
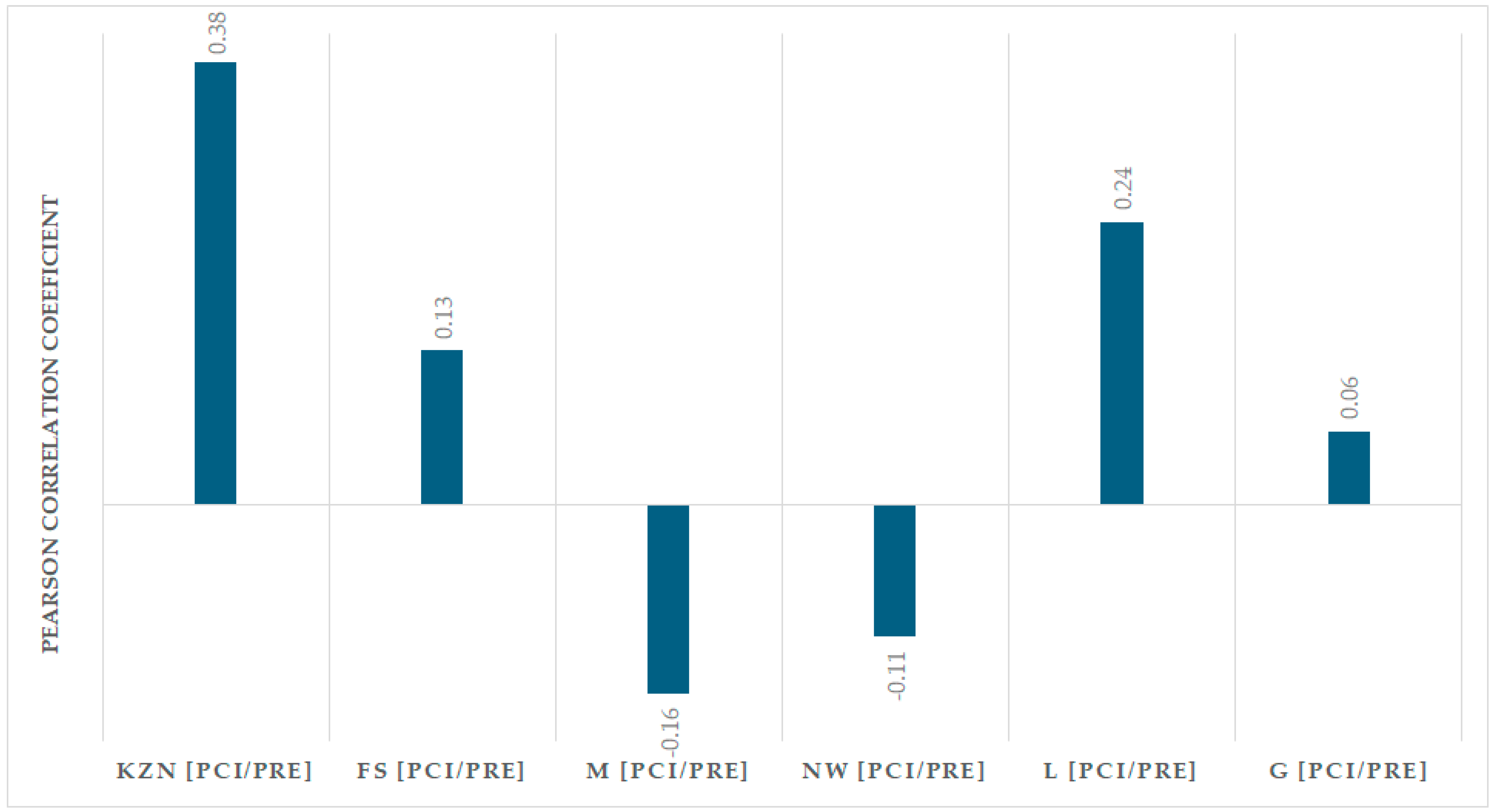
3.4. Correlation Between the PCI and Annual Precipitation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- Vast areas of the study site exhibited annual PCI values within the irregular precipitation concentration category. The KZN and the eastern parts of Free State and Mpumalanga showed annual PCI values within a moderate precipitation concentration category. Only one rainfall district in the FS and NW and Limpopo exhibited strong irregular annual PCI values, suggesting that precipitation was highly concentrated in those pocket areas during the investigated period. The supra-seasonal PCI values indicated a moderate precipitation concentration across the provinces.
- -
- The decadal PCI values decreased by −1.5 and −1.2 magnitudes of change during the 1979–1989 and 2001–2011 periods and increased by 2.1 and 2.8 magnitudes between 1990–2000 and 2012–2023, respectively.
- -
- Uniform precipitation concentration was mostly recorded during the DJF season. The entire study area recorded moderate precipitation concentration during the MAM and SON seasons (with the exceptions of KZN). In addition, irregular precipitation concentration dominated during the JJA rainy season.
- -
- Positive trends in annual PCI were recorded across the provinces, with exceptions in KZN province. Similarly, during the wet season, positive trends in supra-seasonal PCI were detected across the provinces, with exceptions in KZN and in parts of the Free State. Furthermore, negative trends in seasonal PCI values mostly dominated during DJF and MAM, whereas positive trends were mostly observed during the SON and JJA seasons.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Contractor, S.; Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V. Changes in observed daily precipitation over global land areas since 1950. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Hayhoe, K.; Arblaster, J.M.; Meehl, G.A. Going to the Extremes: An intercomparison of model-simulated historical and future changes in extreme events. Clim. Change 2006, 79, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwecker, S.; Gascón, E.; Park, S.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Schwarb, M.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Stoffel, M.; Vitolo, C.; Rohrer, M. Anticipating cascading effects of extreme precipitation with pathway schemes-Three case studies from Europe. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabari, H.; Paz, S.M.; Buekenhout, D.; Willems, P. Comparison of statistical downscaling methods for climate change impact analysis on precipitation-driven drought. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3493–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; p. 2391. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Platner, G.-K. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, D.; Tang, B. Effects of climate factors and human activities on the ecosystem water use efficiency throughout Northern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, E. Rainfall-to-Reach, Modelling of Braided Morphodynamics. Master’s Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Badenhorst, P.; Cooper, J.A.G.; Crowther, J.; Gonsalves, J.; Laubscher, W.I.; Grobler, N.A.; Mason, T.R.; Illenberger, W.K.; Perry, J.E.; Reddering, J.S.V.; et al. Survey of September 1987 Natal Floods; South African National Scientific Programmes Report 164; CSIR: Pretoria, South Africa, 1989; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.S.; Rouault, M. Spatial patterns of seasonal scale trends in extreme hourly precipitation in South Africa. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 39, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kruger, A.C.; Nxumalo, M.P. Historical rainfall trends in South Africa: 1921–2015. Water SA 2017, 43, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, C.; Kruger, A.C.; Dyson, L. Changes in extreme daily rainfall characteristics in South Africa: 1921–2020. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2022, 38, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. Changes in extreme precipitation in Texas. J. Geophys. Res. Atm. 2010, 115, D14106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, K.; Nhamo, G.; Chikodzi, D. Climate change-induced droughts and tourism: Impacts and responses of Western Cape province, South Africa. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2022, 39, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botai, C.M.; Botai, J.O.; Dlamini, L.; Zwane, N.; Phaduli, E. Characteristics of Droughts in South Africa: A Case Study of Free State and North West Provinces. Water 2016, 8, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, B.G.; Mungatana, E.D.; Baleta, H. Impacts of Drought Induced Water Shortages in South Africa: Economic Analysis; Water Research Commission Report; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adeola, O.M.; Masinde, M.; Botai, J.O.; Adeola, A.M.; Botai, C.M. An analysis of precipitation extreme events based on the SPI and EDI values in the Free State Province, South Africa. Water 2021, 13, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.; Karbalaee, A.R.; Kamangar, M. Projections patterns of precipitation concentration under climate change scenarios. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 4775–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegun, O.; Balogun, I.; Adeaga, O. Precipitation Concentration Changes in Owerri and Enugu. In Special Publication of the Nigerian Association of Hydrological Sciences; Nigerian Association of Hydrological Sciences: Abuja, Nigeria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.E. Monthly precipitation distribution: A comparative index. Prof. Geogr. 1980, 32, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Marco, G.; Chen, Y.P.; Liu, C.L. Changing properties of precipitation concentration in the Pearl River Basin, China. Stoc. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2009, 23, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Pa, R.K.; Singh, S.K. Rainfall variability analysis using Precipitation Concentration Index: A case study of the western agro-climatic zone of Punjab, India. Indones. J. Geogr. 2021, 53, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, M.; Sree, K.S.; Krishna, I.V. Analysis of precipitation concentration index and rainfall prediction in various agro-climatic zones of Andhra Pradesh, India. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Vide, J. Spatial distribution of a daily precipitation concentration index in Peninsular Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, F.; Li, L.; Wang, G. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation concentration index, concentration degree and concentration period in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskander, S.; Rajib, M.A.; Rahman, M. Trending regional precipitation distribution and intensity: Use of climatic indices. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2014, 4, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.A.H.; Mamun, A.; Jang, D. Seasonality Analysis on High- and Low-Rainfall Regions in Bangladesh using Precipitation Concentration Index. J. Clim. Res. 2017, 12, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botai, C.M.; Botai, J.O.; Adeola, A.M. Spatial distribution of temporal precipitation contrasts in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2018, 114, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapangaziwiri, E.; Kahinda, J.M.; Dzikiti, S.; Ramoelo, A.; Cho, M.; Mathieu, R.; Cho, M.; Mathieu, R.; Naidoo, M.; Seetal, A.; et al. Validation and verification of lawful water use in South Africa: An overview of the process in the KwaZulu-Natal Province. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 105, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maponya, P.; Mpandeli, S.; Oduniyi, S. Climate change awareness in Mpumalanga province, South Africa. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusere, F.; Hunter, L.; Collinson, M.; Twine, W. Nexus between summer climate variability and household food security in rural Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. Environ. Dev. 2023, 47, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatji, D.P.; Tsotetsi, A.M.; Muchadeyi, F.C.; Van Marle-Koster, E. A description of village chicken production systems and prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites: Case studies in Limpopo and KwaZulu-Natal provinces of South Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2016, 83, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, W. Trend analysis of rainfall time series in Shanxi Province, Northern China (1957–2019). Water 2020, 12, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Yu, H.; Kan, G.; He, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, M.; Wang, G. Re-evaluation of the power of the Mann-Kendall test for detecting monotonic trends in hydrometeorological time series. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Yao, T.D.; Kattel, D.B.; Devkota, L.P. Precipitation Characteristics of Two Complex Mountain River Basins on the Southern Slopes of the Central Himalayas. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 138, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Tian, F.Q.; Hu, H.P. Changes in Seasonal Maximum Daily Precipitation in China over the Period 1961–2006. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, D.; Reason, C.J. Variability of rainfall characteristics over the South Coast region of South Africa. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, W.; Sumner, P.D. Trends in rainfall total and variability (1970–2000) along the KwaZulu-Natal Drakensberg foothills. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2006, 88, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, M.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Brunetti, M.; Longares, L.A. Precipitation concentration changes in Spain 1946–2005. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsiso, B.K.; Tsidu, G.M.; Stoffberg, G.H.; Tadesse, T. Climate change and population growth impacts on surface water supply and demand of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 18, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, S.; Chen, C.; Clark, D.B.; Folwell, S.; Gosling, S.N.; Haddeland, I.; Hanasaki, N.; Heinke, J.; Ludwig, F.; Voss, F.; et al. Climate change impact on available water resources obtained using multiple global climate and hydrology models. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2013, 4, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, C.; Gaiser, T.; Ahrends, H.E.; Ceglar, A.; Singh, M.; Ewert, F.; Srivastava, A.K. Impact of climate extreme events and their causality on maize yield in South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, A.A. Using the precipitation concentration index for characterizing the rainfall distribution in the Levant. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetó, P.; Khodayar, S. On the need for improved knowledge on the regional-to-local precipitation variability in eastern Spain under climate change. Atmos. Res. 2023, 290, 106795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ya, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, J. Various characteristics of precipitation concentration index and its cause analysis in China between 1960 and 2016. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 4648–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Sreekesh, S.; King, A. Characteristics of extreme rainfall in different gridded datasets over India during 1983–2015. Atmos. Res. 2022, 267, 105930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, M.V.; Kan, J.-C.; Destouni, G.; Barquet, K.; Kalantari, Z. Identifying Hotspots of Heat Waves, Droughts, Floods, and their Co-Occurrences. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhawana, M.B.; Kanyerere, T.; Kahler, D.; Masilela, N.S.; Lalumbe, L.; Umunezero, A.A. Hydrological drought assessment using the Standardized Groundwater Index and the Standardized Precipitation Index in the Berg River Catchment, South Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| IDS | Province | Latitude | Longitude | Annual Rainfall [mm] | Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dis24 | KZN | −31.133 | 29.699 | 1110 | 0.040 |
| dis25 | KZN | −29.879 | 30.861 | 935 | −0.007 |
| dis26 | KZN | −28.002 | 32.174 | 916 | −0.010 |
| dis29 | KNZ | −30.727 | 29.331 | 908 | 0.037 |
| dis30 | KZN | −29.642 | 30.469 | 845 | −0.009 |
| dis31 | KZN | −28.255 | 31.297 | 844 | −0.024 |
| dis33 | M | −25.182 | 31.493 | 685 | −0.018 |
| dis34 | L | −23.851 | 31.307 | 454 | −0.021 |
| dis35 | L | −22.684 | 30.761 | 521 | −0.020 |
| dis43 | KZN | −30.397 | 28.869 | 867 | 0.009 |
| dis44 | KZN | −29.035 | 29.782 | 932 | −0.008 |
| dis45 | KZN | −28.156 | 30.465 | 733 | −0.032 |
| dis46 | M | −26.778 | 30.851 | 865 | 0.001 |
| dis47 | M | −25.261 | 30.706 | 1009 | −0.023 |
| dis48 | L | −24.135 | 30.524 | 684 | −0.017 |
| dis49 | L | −23.403 | 30.168 | 976 | −0.009 |
| dis50 | L | −22.594 | 29.516 | 454 | −0.021 |
| dis55 | FS | −30.535 | 25.223 | 384 | −0.015 |
| dis56 | FS | −30.682 | 26.392 | 502 | −0.017 |
| dis57 | KZN/FS | −30.485 | 27.339 | 635 | −0.085 |
| dis59 | KZN | −29.207 | 28.822 | 1131 | −0.001 |
| dis60 | FS | −28.123 | 28.438 | 673 | −0.016 |
| dis61 | FS/M | −27.457 | 29.237 | 656 | −0.009 |
| dis62 | M | −26.879 | 30.009 | 735 | −0.002 |
| dis63 | L/M | −25.192 | 29.802 | 635 | −0.014 |
| dis64 | L | −23.768 | 29.338 | 444 | −0.021 |
| dis65 | L | −22.967 | 28.602 | 363 | −0.044 |
| dis69 | FS | −29.66 | 24.275 | 336 | 0.007 |
| dis70 | FS | −29.659 | 25.786 | 480 | 0.000 |
| dis71 | FS | −29.553 | 26.855 | 598 | 0.003 |
| dis72 | FS | −28.961 | 27.535 | 655 | −0.020 |
| dis73 | FS | −27.274 | 27.506 | 614 | −0.029 |
| dis74 | G | −26.472 | 28.317 | 694 | −0.001 |
| dis75 | G/M | −25.857 | 29.064 | 684 | −0.018 |
| dis76 | L | −24.314 | 28.768 | 566 | −0.016 |
| dis77 | L | −23.571 | 27.948 | 426 | −0.027 |
| dis81 | FS | −28.811 | 24.898 | 401 | −0.004 |
| dis82 | FS | −28.298 | 25.827 | 510 | −0.006 |
| dis83 | FS | −28.026 | 26.797 | 538 | −0.038 |
| dis84 | NW | −26.519 | 26.573 | 589 | −0.018 |
| dis85 | G/NW | −25.65 | 27.344 | 625 | −0.007 |
| dis86 | L/NW | −24.915 | 28.128 | 591 | −0.025 |
| dis87 | L | −24.186 | 27.217 | 484 | −0.032 |
| dis88 | NW | −25.945 | 23.195 | 290 | −0.057 |
| dis89 | NW | −26.526 | 24.013 | 419 | 0.001 |
| dis90 | NW | −27.086 | 24.893 | 474 | −0.019 |
| dis91 | NW | −27.284 | 25.978 | 528 | −0.003 |
| dis92 | NW | −25.925 | 25.708 | 531 | 0.001 |
| dis93 | NW | −24.968 | 26.454 | 521 | −0.005 |
| PCI Value | Significance |
|---|---|
| PCI ≤ 10 | Uniform monthly precipitation distribution (low precipitation concentration) |
| 10 < PCI ≤ 15 | Moderate Precipitation Distribution |
| 16 < PCI ≤ 20 | Irregular Precipitation Distribution |
| PCI > 20 | Strongly irregular precipitation distribution (high precipitation concentration) |
| Correlation Coefficient Range | Strength of Correlation | Correlation Type or Direction |
|---|---|---|
| −0.7 to −1.0 | Very strong | Negative |
| −0.5 to −0.7 | Strong | Negative |
| −0.3 to −0.5 | Moderate | Negative |
| 0 to −0.3 | Weak | Negative |
| 0 | None | Zero |
| 0 to 0.3 | Weak | Positive |
| 0.3 to 0.5 | Moderate | Positive |
| 0.5 to 0.7 | Strong | Positive |
| 0.7 to 1.0 | Very strong | Positive |
| Decade | Total Rainfall in Rainfall Districts with Increased PCI | Total Rainfall in Rainfall Districts with Decreased PCI |
|---|---|---|
| 1979–1989 | 3 | 41 |
| 1990–2000 | 38 | 11 |
| 2001–2011 | 10 | 39 |
| 2012–2023 | 39 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botai, C.M.; Botai, J.O.; Mukhawana, M.B.; de Wit, J.; Masilela, N.S.; Zwane, N.; Tazvinga, H. Evaluation of Rainfall Distribution Based on the Precipitation Concentration Index: A Case Study over the Selected Summer Rainfall Regions of South Africa. Hydrology 2025, 12, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060136
Botai CM, Botai JO, Mukhawana MB, de Wit J, Masilela NS, Zwane N, Tazvinga H. Evaluation of Rainfall Distribution Based on the Precipitation Concentration Index: A Case Study over the Selected Summer Rainfall Regions of South Africa. Hydrology. 2025; 12(6):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060136
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotai, Christina M., Joel O. Botai, Mxolisi B. Mukhawana, Jaco de Wit, Ndumiso S. Masilela, Nosipho Zwane, and Henerica Tazvinga. 2025. "Evaluation of Rainfall Distribution Based on the Precipitation Concentration Index: A Case Study over the Selected Summer Rainfall Regions of South Africa" Hydrology 12, no. 6: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060136
APA StyleBotai, C. M., Botai, J. O., Mukhawana, M. B., de Wit, J., Masilela, N. S., Zwane, N., & Tazvinga, H. (2025). Evaluation of Rainfall Distribution Based on the Precipitation Concentration Index: A Case Study over the Selected Summer Rainfall Regions of South Africa. Hydrology, 12(6), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060136







