Analysis of Runoff Variability and Periodicity in the Qinghai Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
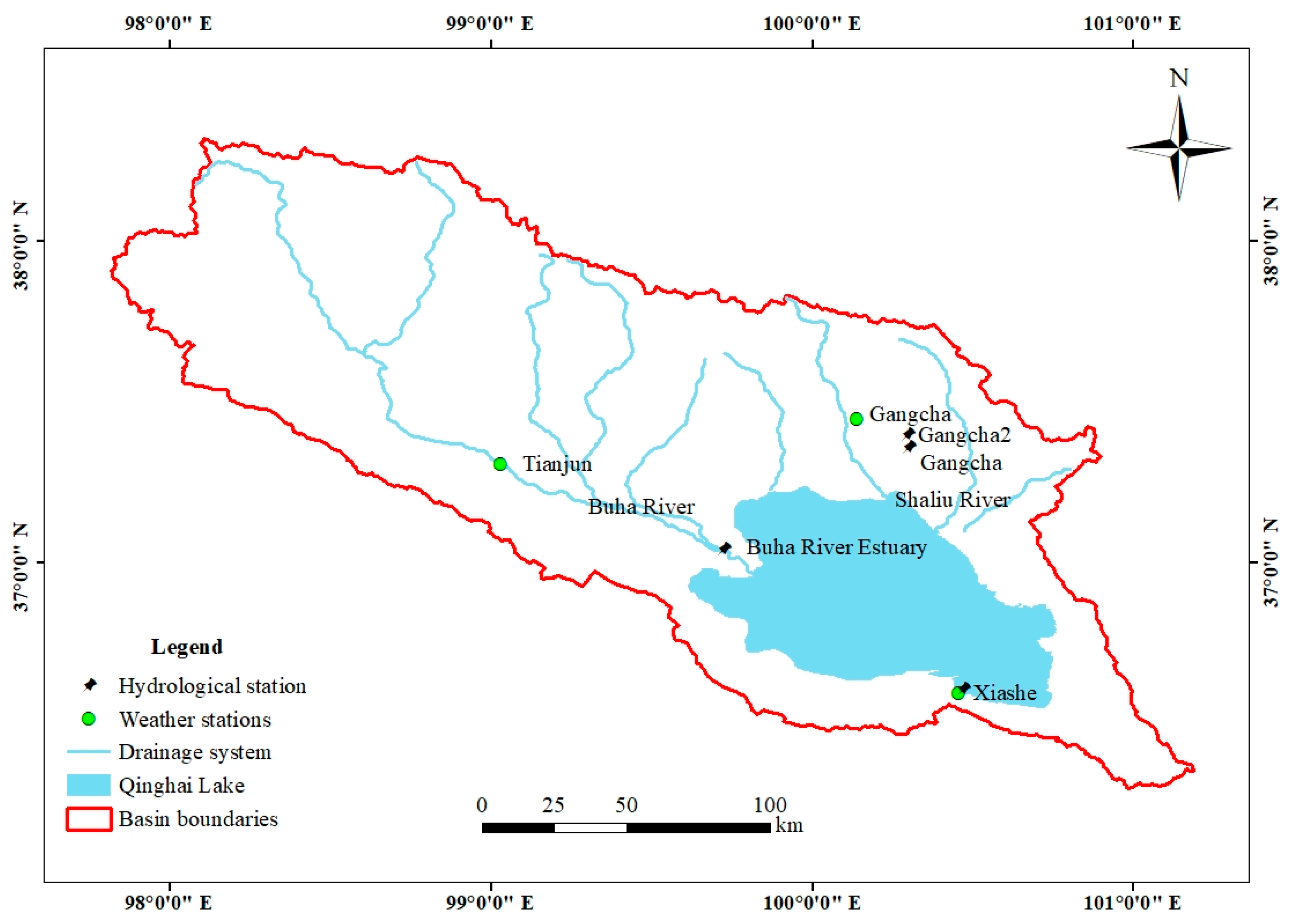
2.1. Regional Background and Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Mann–Kendall Non-Parametric Trend Test
2.4. Mann–Kendall Change Point Test
2.5. Wavelet Analysis
3. Results
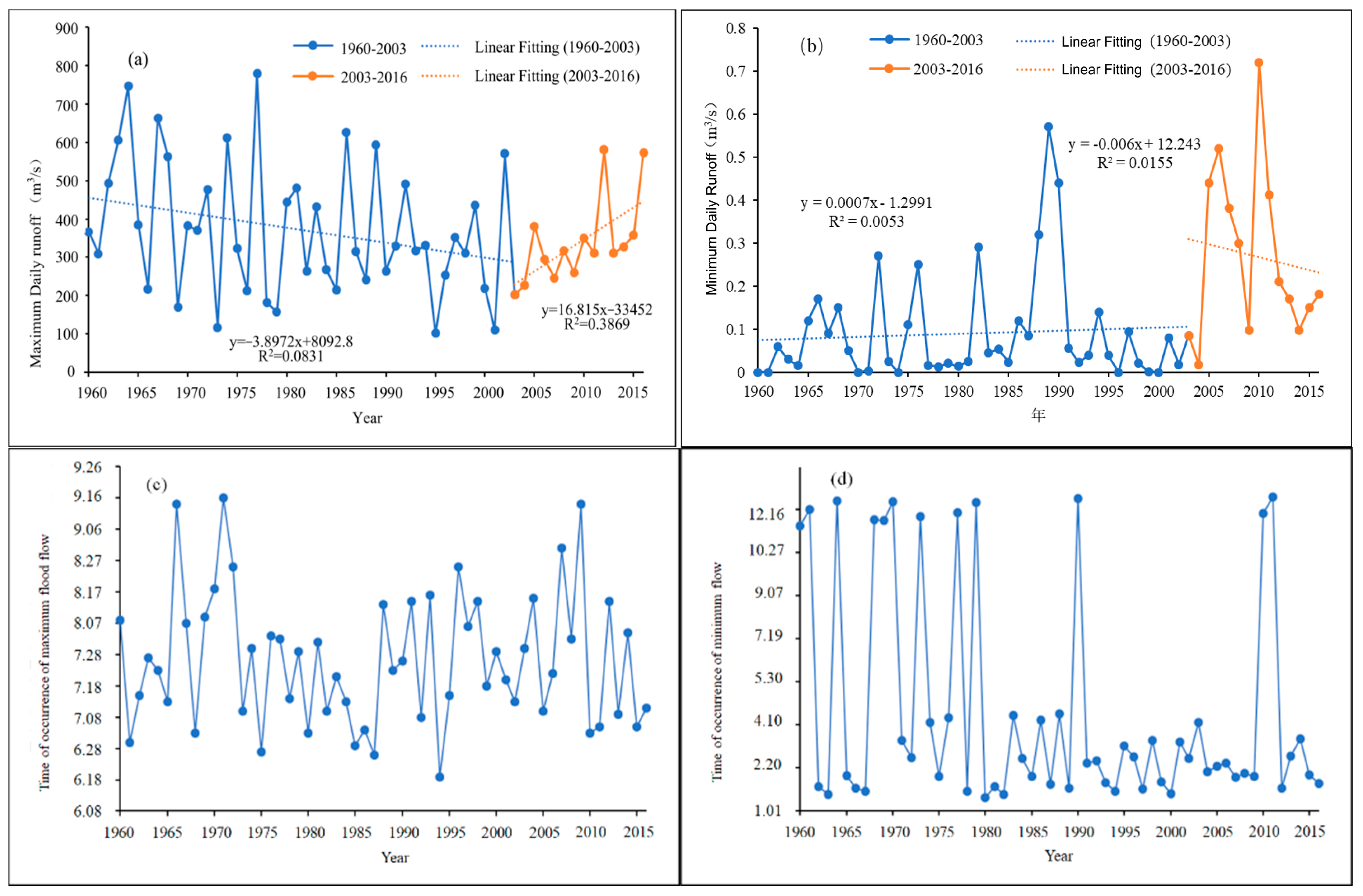
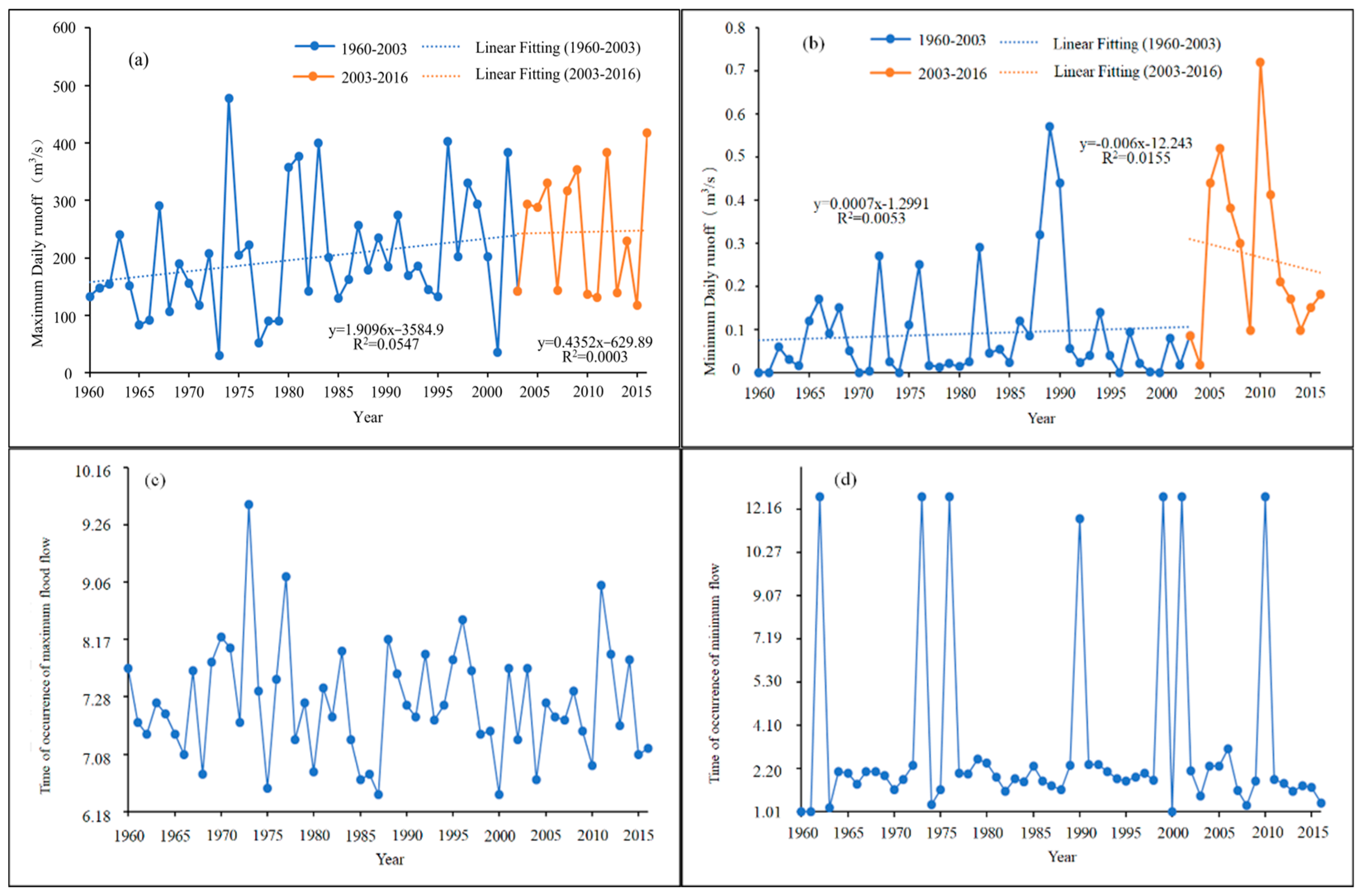
3.1. Daily Runoff Variations
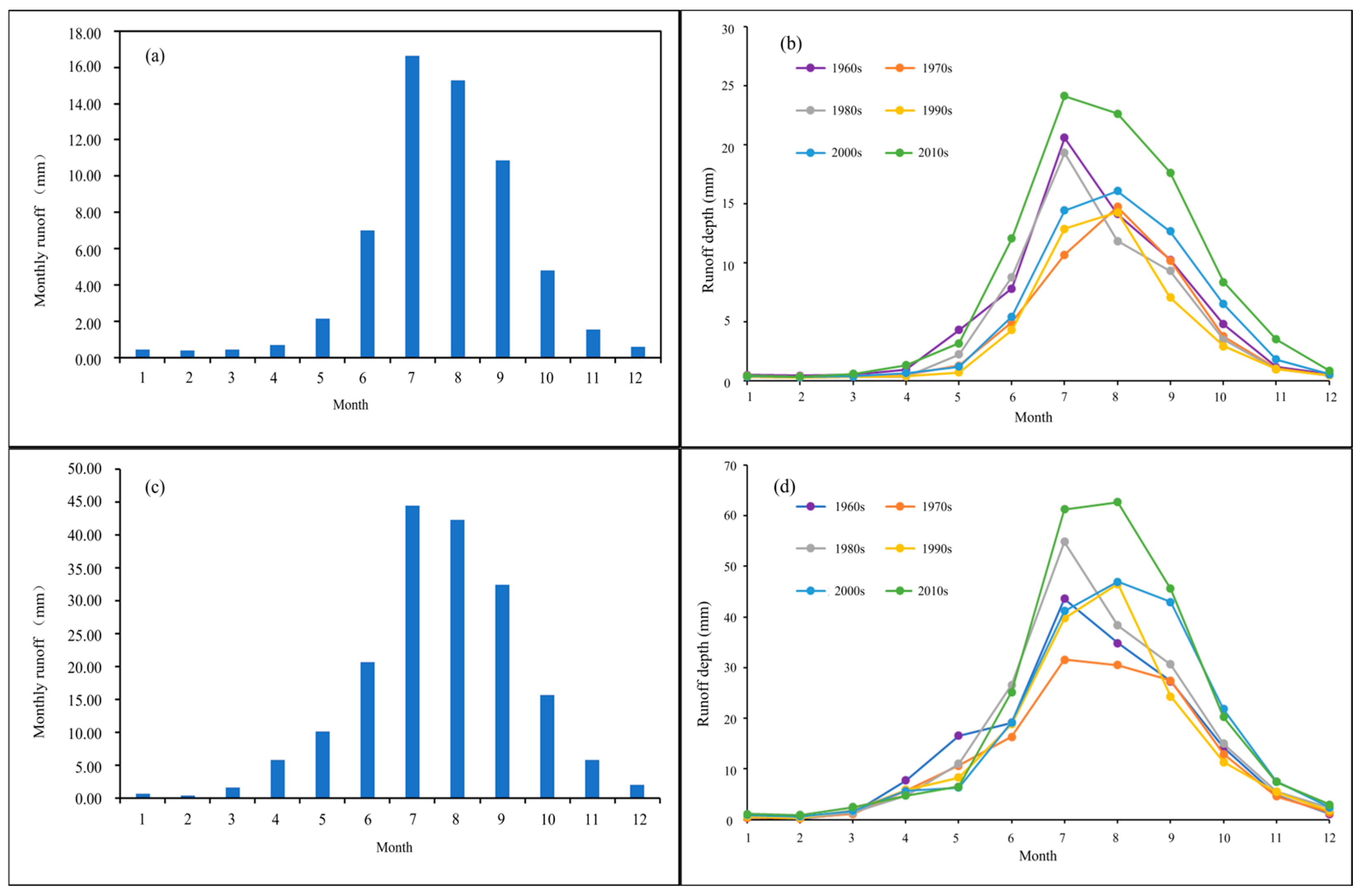
3.2. Seasonal Runoff Variations
3.3. Interannual Runoff Variations
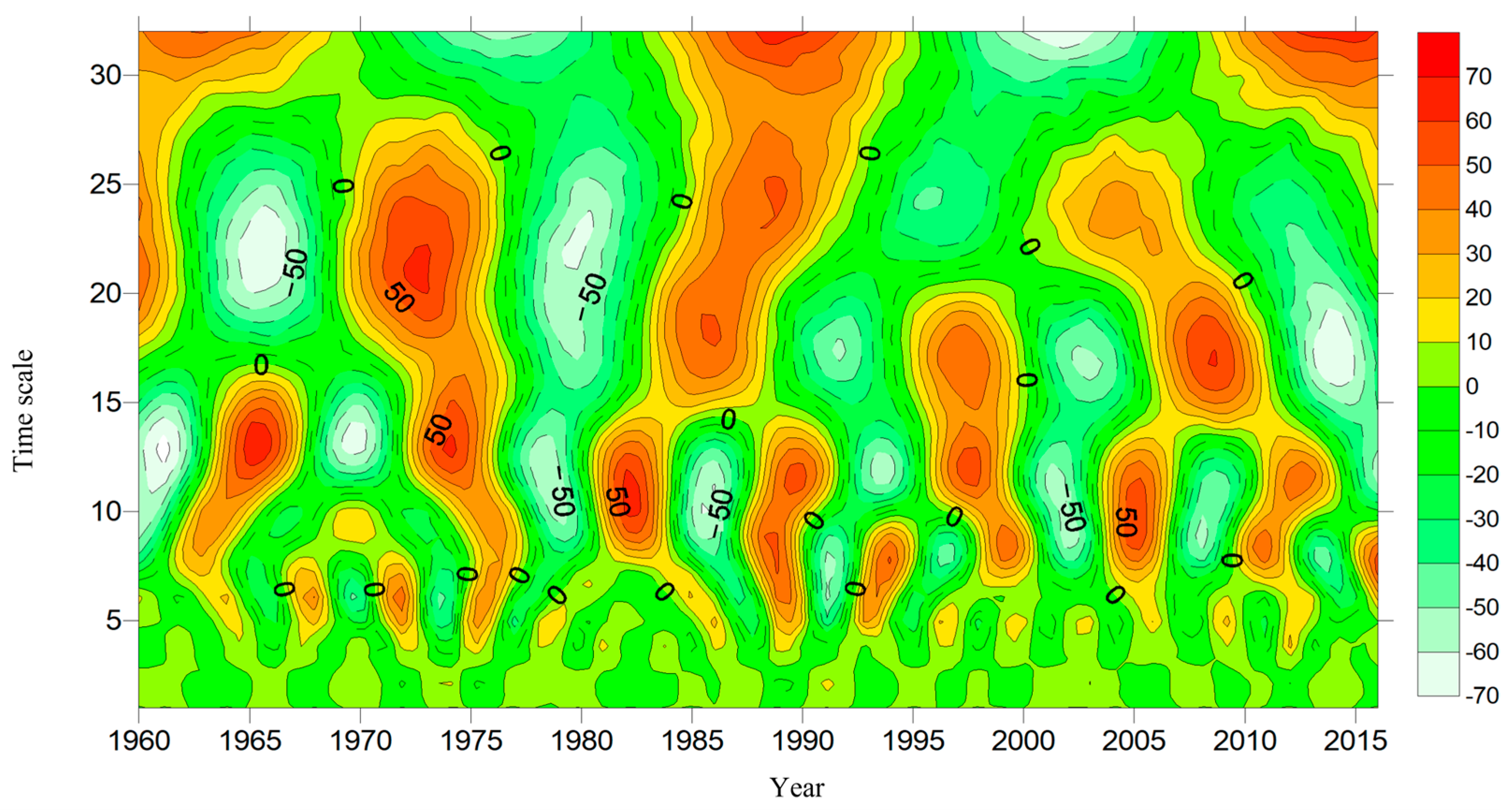
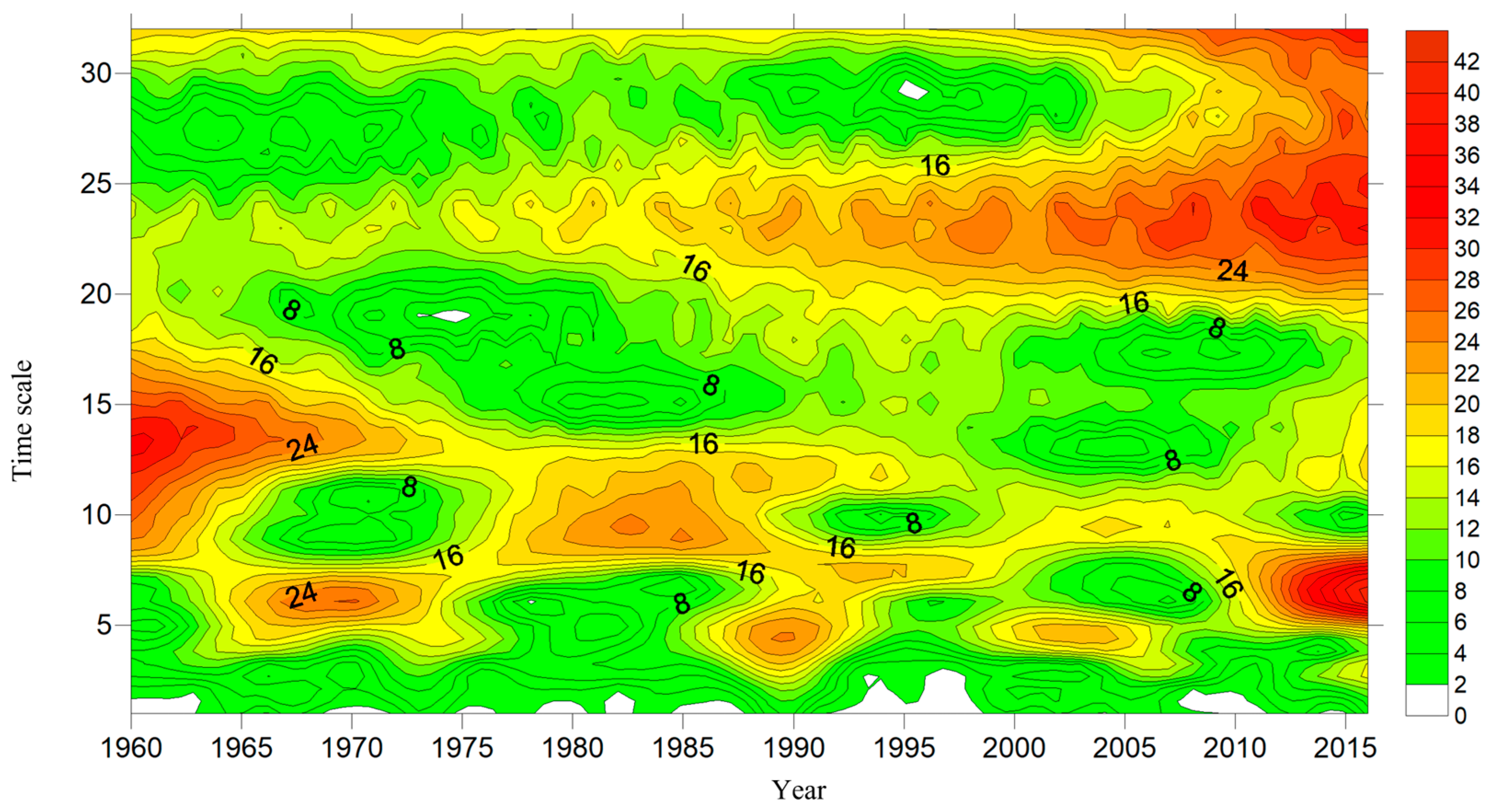
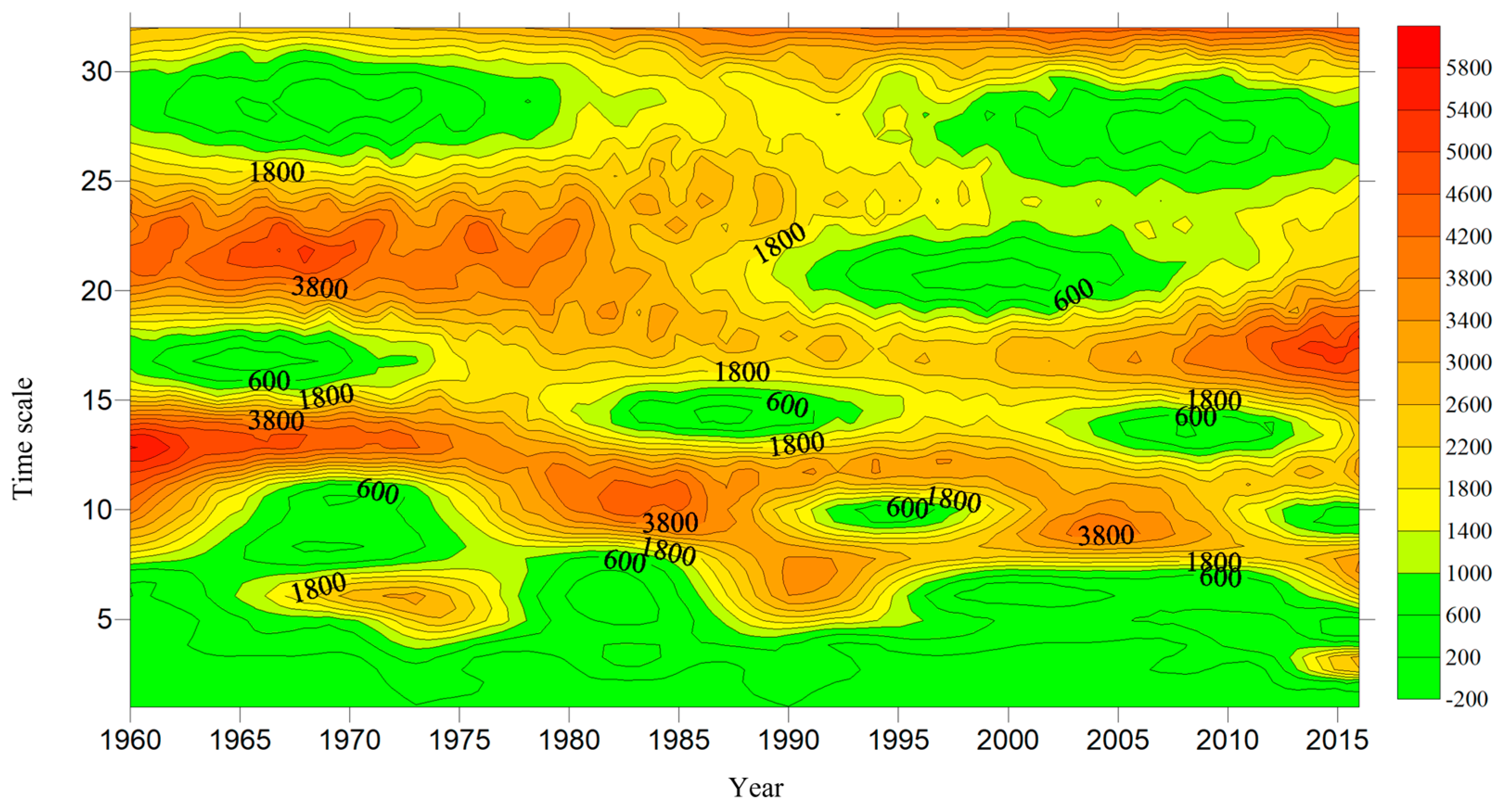
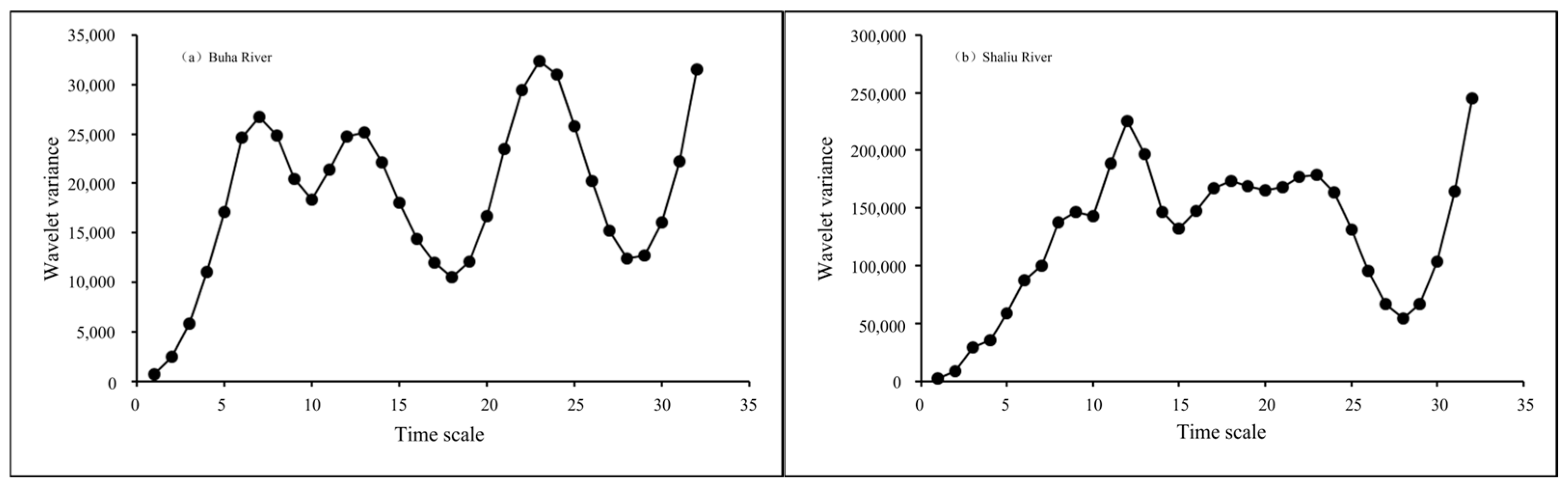
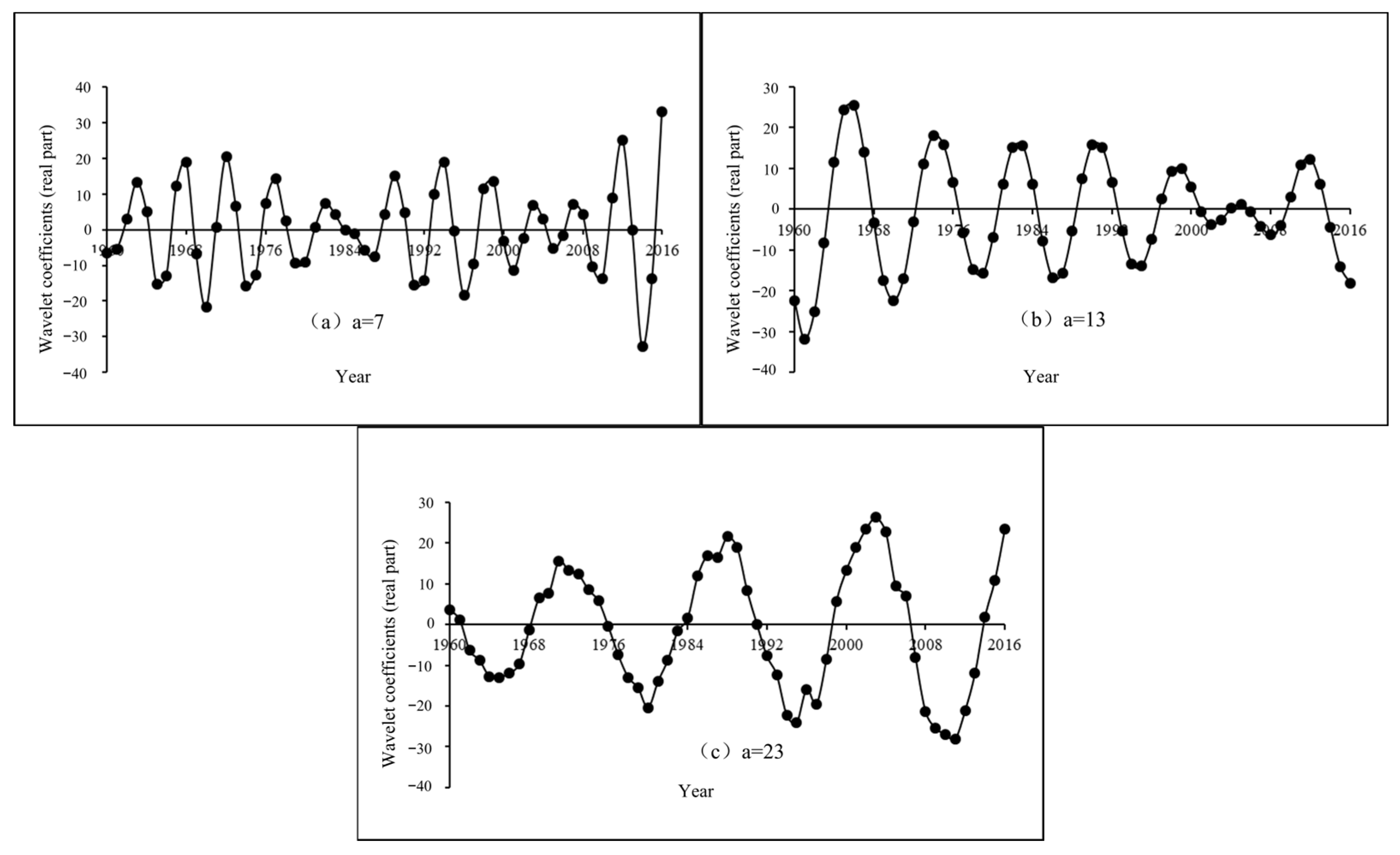
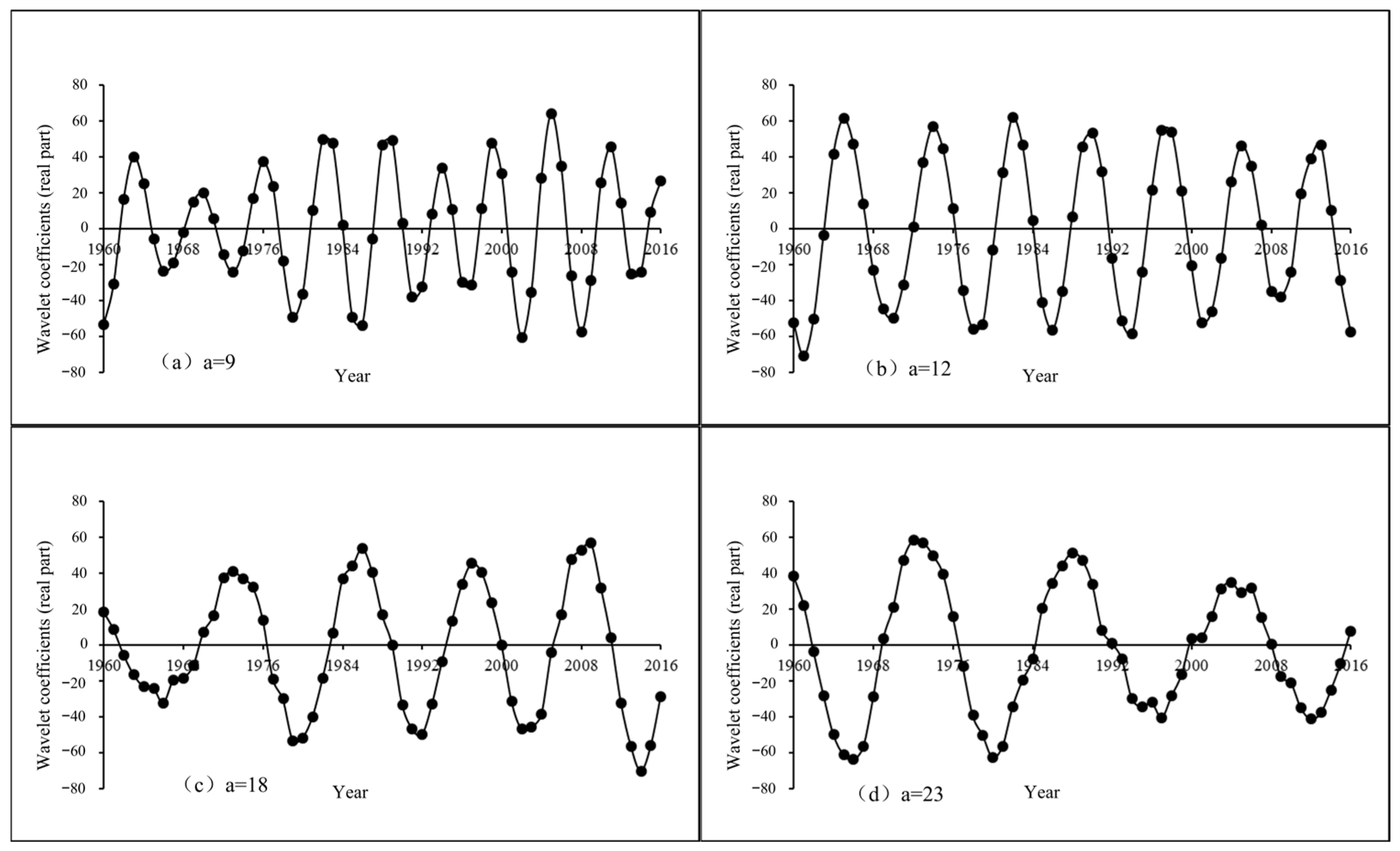
3.4. Periodic Variations of River Runoff
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Climate Change on Runoff Variability
4.2. Impact of Underlying Surface and Land Use Changes on Runoff Variability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wörman, A.; Lindström, G.; Åkesson, A.; Riml, J. Drifting Runoff Periodicity during the 20th Century Due to Changing Surface Water Volume. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3772–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M. Study on Temporal Variability of Hydrological Elements in the Daqing River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2023, 28, 04023032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Y. Impacts of Rainfall Spatial and Temporal Variabilities on Runoff Quality and Quantity at the Watershed Scale. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Song, C.; Li, W.; Liu, K.; Cheng, J.; Fu, C.; Chen, T.; Ke, L.; Wang, J. What Drives the Rapid Water-Level Recovery of the Largest Lake (Qinghai Lake) of China over the Past Half Century? J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Fan, F.; Li, B.; Niu, D.; Shu, P. Rapid Environmental Changes in the Lake Qinghai Basin during the Late Holocene. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1125302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jia, S.; Wang, C.; Lv, Q.; Ji, X. Evolution and Periodicity of Watershed-Scale Runoff: Insight from the Spatiotemporal Variety in Intensive Anthropogenic Activities Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2025, 39, 1855–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, S.K.; Silberstein, R.P.; Fu, G.; Hodgson, G.; Charles, S.P.; McFarlane, D. Understanding Spatio-Temporal Rainfall-Runoff Changes in a Semi-Arid Region. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2510–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xie, T.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Ran, G.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Han, Z.; Hu, C. Improving the Understanding of Rainfall-Runoff Processes: Temporal Dynamic of Event Runoff Response in Loess Plateau, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 123436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Recent Advances in Wavelet Analyses: Part 1. A Review of Concepts. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F. A Review on the Applications of Wavelet Transform in Hydrology Time Series Analysis. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, J.; Prokoph, A. Assessing the Impacts of the Urban Heat Island Effect on Streamflow Patterns in Ottawa, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2013, 496, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F.; Singh, V.P.; Sun, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M. Wavelet-Based Hydrological Time Series Forecasting. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 06016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-M. Wavelet-Based Multi-Scale Entropy Analysis of Complex Rainfall Time Series. Entropy 2011, 13, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.-C.; Zhu, Q.-P.; Wang, L. Wavelet-Based Analysis on the Complexity of Hydrologic Series Data under Multi-Temporal Scales. Entropy 2011, 13, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.L.; Lai, S.H.; El-Shafie, A. Wavelet Transform Based Method for River Stream Flow Time Series Frequency Analysis and Assessment in Tropical Environment. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 2015–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefli, B.; Maraun, D.; Holschneider, M. What Drives High Flow Events in the Swiss Alps? Recent Developments in Wavelet Spectral Analysis and Their Application to Hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 2511–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolgayova, E.; Parajka, J.; Bloeschl, G.; Bucher, C. Long Term Variability of the Danube River Flow and Its Relation to Precipitation and Air Temperature. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-L.; Bao, A.-M.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Pan, X. Response Analysis of Rainfall-Runoff Processes Using Wavelet Transform: A Case Study of the Alpine Meadow Belt. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, R.; Khosa, R. Comparative Study of Different Wavelets for Hydrologic Forecasting. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 46, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinasamy, M.; Adamowski, J.; Khosa, R. Multiscale Streamflow Forecasting Using a New Bayesian Model Average Based Ensemble Multi-Wavelet Volterra Nonlinear Method. J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.-L.; Li, X.-Y. Runoff Processes in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: Insights from Stable Isotope and Hydrochemistry. Quat. Int. 2015, 380, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Guo, Z.; Chen, K.; Fan, L.; Zhan, Y.; Kuang, X.; Cui, B.; Zheng, C. The Effect of Seasonally Frozen Ground on Rainfall Infiltration and Groundwater Discharge in Qinghai Lake Basin, China. Front. Water 2024, 6, 1495763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qi, Y.; Lian, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Zhang, M. Effects of Climate Change and Land Use/Cover Change on the Volume of the Qinghai Lake in China. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, T.; Xie, H.; Huang, X.; Lin, H. Climate-Driven Changes in Grassland Vegetation, Snow Cover, and Lake Water of the Qinghai Lake Basin. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 036017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Yang, R.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Qi, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, H. Impacts of Climate Change and Land Use/Cover Change on the Net Primary Productivity of Vegetation in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Liu, G.; Pang, Q.; Zou, D.; Liu, H. The Impact of Permafrost Degradation on Lake Changes in the Endorheic Basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2020, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M. Hydrological Trend of Qinghai Lake over the Last 60 Years: Driven by Climate Variations or Human Activities? J. Water Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cong, Z.; Gao, B.; Li, G.; Wang, X. The Water Level Change and Its Attribution of the Qinghai Lake from 1960 to 2020. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Song, C.; Xue, B.; Wu, H.; Ji, Z.; Dong, L. Exploring the Potential Factors on the Striking Water Level Variation of the Two Largest Semi-Arid-Region Lakes in Northeastern Asia. Catena 2021, 198, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; He, K.-N.; Li, R.-J.; Sheng, Z.-P.; Wang, H. Linkage of Climatic Factors and Human Activities with Water Level Fluctuations in Qinghai Lake in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Water 2017, 9, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.-L.; Li, X.-Y. Stable Isotopes Reveal Sources of Precipitation in the Qinghai Lake Basin of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, B. Frozen Soil Change and Its Impact on Hydrological Processes in the Qinghai Lake Basin, the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2022, 39, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; He, K.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Wen, J. Trends, Abrupt Changes, and Periodicity of Streamflow in Qinghai Province, the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Gu, M.; Chang, J.; Ma, J. Response of Runoff in the Headwater Region of the Yellow River to Climate Change and Its Sensitivity Analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Characterization of Spatial and Temporal Changes of Grasslands and Lakes in Qinghai Lake Basin under the Background of Climate Change. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami, H.; Moradi, Y.; Lotfirad, M.; Gandomi, M.A.; Bazgir, N.; Shokrian Hajibehzad, M. Detection of Abrupt Shift and Non-Parametric Analyses of Trends in Runoff Time Series in the Dez River Basin. Water Supply 2022, 22, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosunoglu, F.; Kisi, O. Trend Analysis of Maximum Hydrologic Drought Variables Using Mann–Kendall and Şen’s Innovative Trend Method. River Res. Appl. 2017, 33, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, R.; Yu, G. Estimation of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Runoff and Its Contribution to Large Asian Rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nan, Z.; Wang, W.; Ren, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X. Separating Climate Change and Human Contributions to Variations in Streamflow and Its Components Using Eight Time-Trend Methods. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Miao, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Gou, J. Is the Runoff Coefficient Increasing or Decreasing after Ecological Restoration on China’s Loess Plateau? Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F. The Quantitative Attribution of Climate Change to Runoff Increase over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Huang, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, G. Land use and climate changes and their impacts on runoff in the Yarlung Zangbo river basin, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
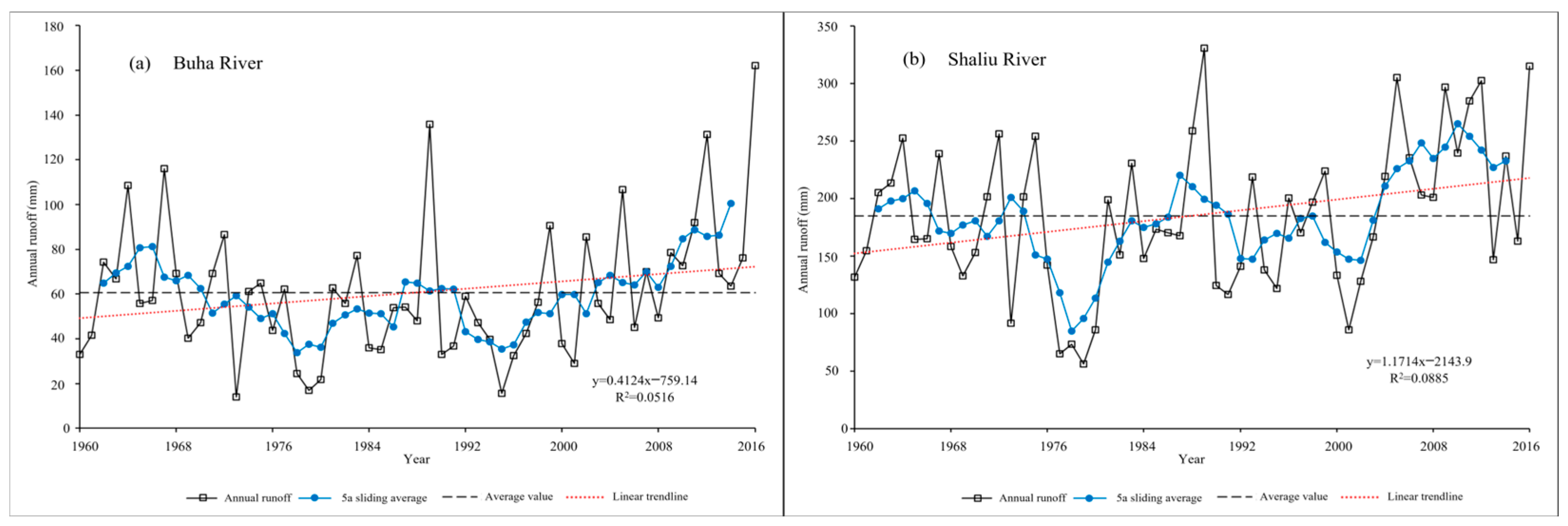
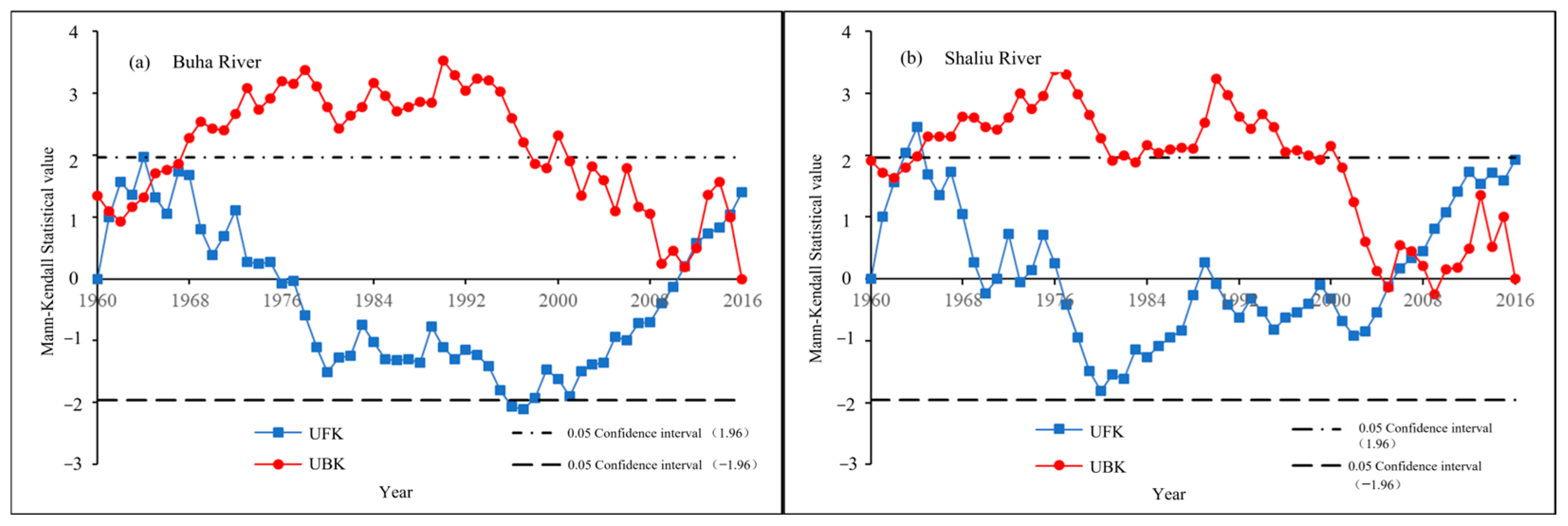
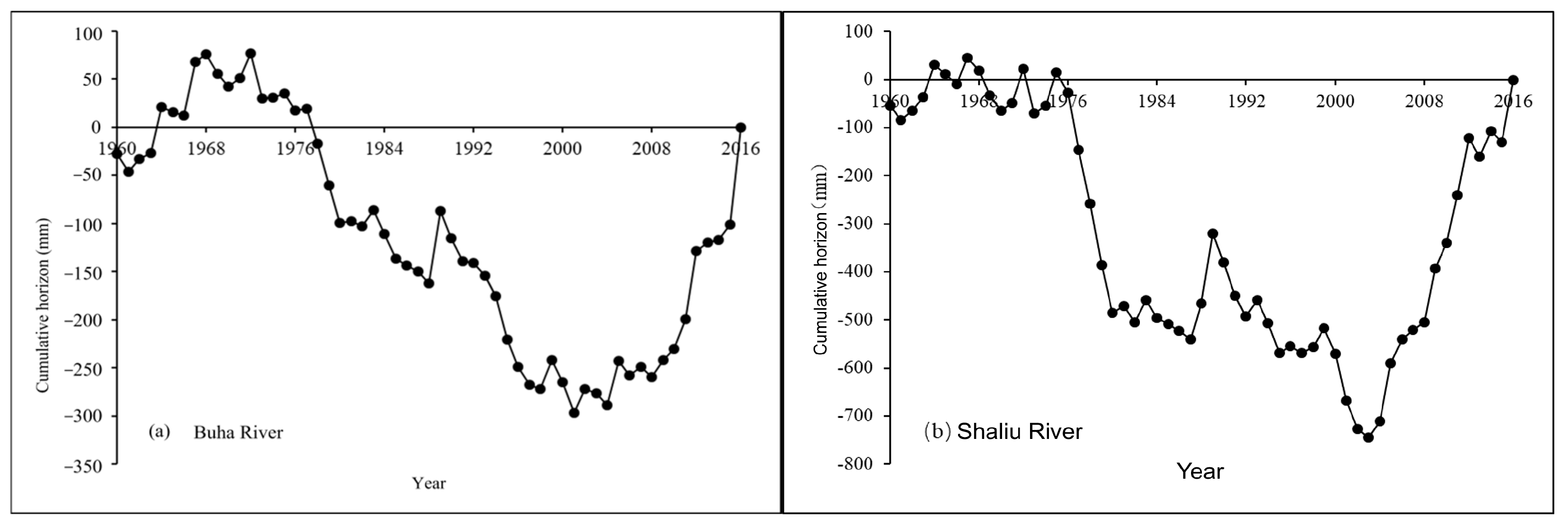
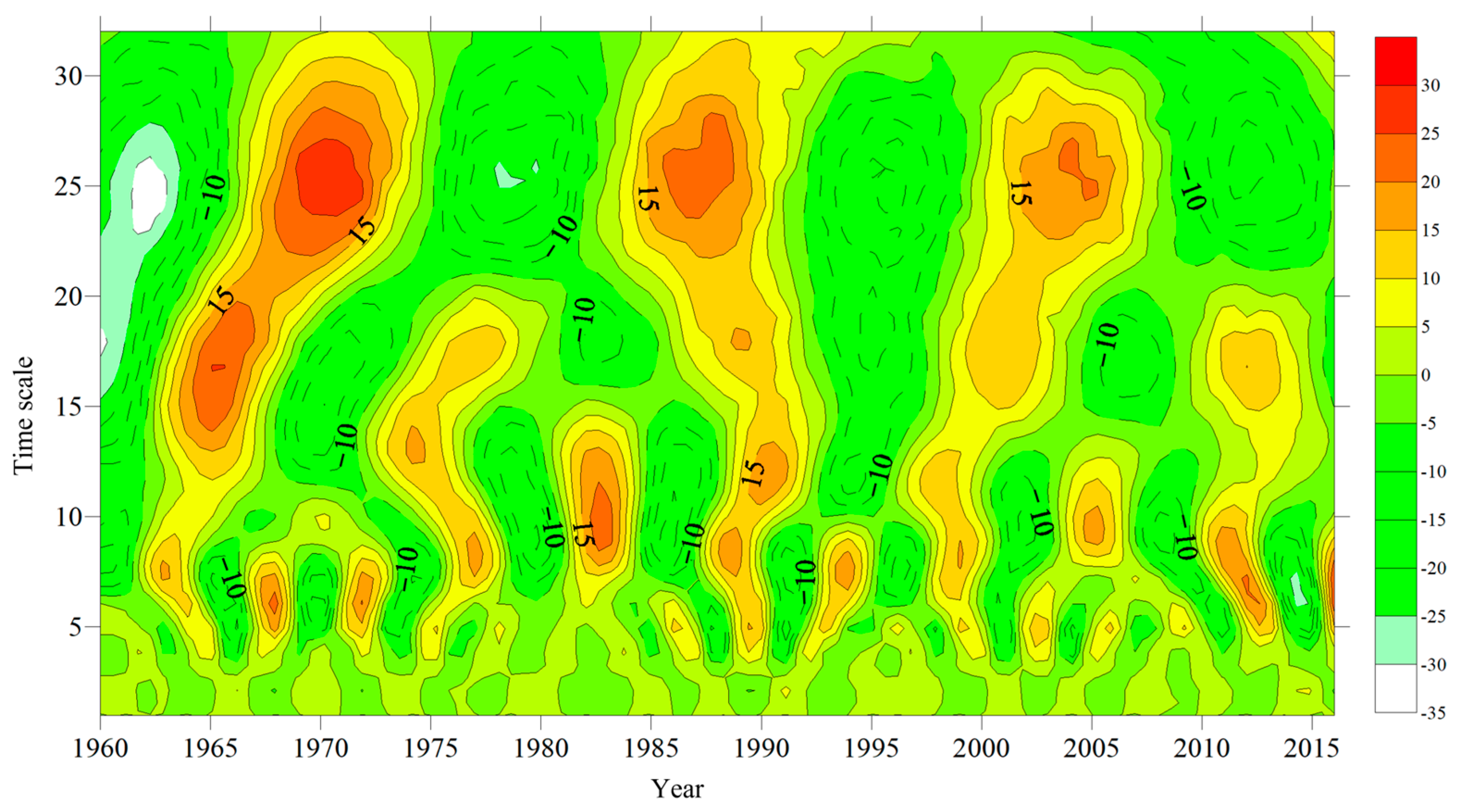


| Hydrological Station | River Name | Drainage Area (km2) | Flow (m3/s) | Annual Runoff (108 m3) | Runoff Depth (mm) | Runoff Modulus [10⁻3 m3/(s·km2)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buha River Estuary | Buha River | 14,337 | 25.6 | 7.83 | 56.3 | 1.79 |
| Gangcha | Shaliu River | 1,442 | 7.2 | 2.51 | 157.5 | 4.99 |
| Period | T | P | U | SSD | RHU | ET0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960–2016 | 0.17 | 0.72 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.19 | 0.47 ** | −0.50 ** |
| 1960–2003 | −0.19 | 0.72 ** | −0.39 ** | −0.03 | 0.71 ** | −0.73 ** |
| 2004–2016 | 0.39 | −0.10 | −0.08 | 0.55 | −0.44 | 0.37 |
| 1960–1993 | −0.34 * | 0.74 ** | −0.53 ** | −0.09 | 0.76 ** | −0.78 ** |
| 1994–2016 | 0.49 * | 0.70 ** | −0.15 | −0.32 | 0.00 | −0.13 |
| 1960–2016 | 0.17 | 0.72 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.19 | 0.47 ** | −0.50 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, P.; Gao, H.; Yu, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Analysis of Runoff Variability and Periodicity in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Hydrology 2025, 12, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040083
Yao P, Gao H, Yu X, Feng Y, Wang Y. Analysis of Runoff Variability and Periodicity in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Hydrology. 2025; 12(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Panpan, Hongyan Gao, Xinxiao Yu, Yankai Feng, and Yukun Wang. 2025. "Analysis of Runoff Variability and Periodicity in the Qinghai Lake Basin" Hydrology 12, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040083
APA StyleYao, P., Gao, H., Yu, X., Feng, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Analysis of Runoff Variability and Periodicity in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Hydrology, 12(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040083






