Abstract
Microplastics (<5 mm) and nanoplastics (~100 nm), which are invisible to the naked eye, originate primarily from fragmentation and breakdown larger plastic debris are increasingly pervasive in the environment. Once released, they can disperse widely in the environment, pollute them adversely and ultimately be taken up by living organisms, including humans, through multiple exposure pathways. Their distribution in aquatic systems is influenced by their physiochemical properties including density, hydrophobicity, and chemical stability, along with environmental conditions and biological activities. To better understand the dynamics of micro- and nanoplastics in surface water, this study conducted a comprehensive review of 194 published articles and scientific reports covering marine, freshwater, and wastewater systems. We assessed the abundance, spatial distribution and the factors that govern their behavior in aquatic systems and analyzed the sampling techniques, pretreatment process, and detection and removal techniques to understand the ongoing scenario of these pollutants in surface water and to identify the ecological risks and potential toxicological effects on living biota via direct and indirect exposure pathways.
1. Introduction
Plastics have become ubiquitous in modern society, revolutionizing industries and daily life since their commercial development in the 1930s and 1940s. Their production has grown exponentially, surpassing iron after the 1990s and becoming the most extensively used material worldwide due to their convenience and versatility. According to the projections by Geyer et al. (2017), nearly 12,000 metric tons of plastic waste are expected to accumulate in rivers, oceans, and other natural ecosystems by the year 2025 [1] as global production rose from 1.5 million metric tons in 1950 to 442.5 million metric tons in 2023 and is projected to reach 1.2 billion tons by 2060 [2].
The proliferation of plastic has come at a significant environmental cost. Initially, concerns about plastic pollution mainly focused on the persistence of plastic waste and the biodegradability of common products such as bags and disposable diapers, until 2004 has highlighted the pervasive problem of MPs—plastic fragments less than 5 mm in size—due to their growing presence in marine environments [3]. More recently, NPs (1–1000 nm) have emerged as an additional concern worldwide because of their increasing presence in nature and immense toxicological effects on living beings, including humans [4]. These pollutants originate from the degradation of larger plastic debris or are directly released into the environment through various sources, including textiles, cosmetics, and industrial processes. The pervasiveness of these tiny plastic particles is alarming, with their presence documented in all environmental media—surface freshwater, groundwater, air, soil, and sediment [5,6,7]. Current estimates suggest that between 5 and 51 trillion microplastic particles are present in the world’s oceans [8,9].
Although numerous studies have provided valuable insights into the occurrence, toxicity, and removal of MPs and NPs across marine, freshwater, and wastewater systems in diverse geographical regions [10,11], significant challenges persist. A comprehensive understanding of their global distribution, composition, and ecological linkages remains limited, as pinpointing their origins and accurately quantifying their presence are hindered by the absence of standardized monitoring protocols including inconsistencies in sampling approaches, variability in analytical techniques, and heterogenous reporting frameworks. Increasing evidence highlights the potential toxicity of MPs and NPs in terrestrial and aquatic organisms, yet their direct and indirect effects on living biota, including human beings, remain under active investigation.
Considering these challenges, the objective of this review is to delve into the current knowledge regarding MPs and NPs and systematically evaluate the occurrence, characteristics, ecological ramifications and management of MPs and NPs in aquatic systems. Specifically, this review will critically evaluate the concentration, most prevalent types of plastic polymers, and physical and chemical compositions of MPs and NPs and analyze their potential threats to natural water systems. The assessment will also incorporate the current methodologies for quantification and identification of MPs and NPs to identify the strengths and limitations of current techniques along with their toxicity effects across various trophic levels and potential threats to living organisms. Technological advancements in remediation strategies and the progress made in regulatory measures to legal framework aimed at mitigating their environmental impacts will be evaluated. By systematically examining these critical aspects, this review will provide a robust foundation for understanding the current state of MP and NP pollution and to inform future research endeavors to mitigate the threat of MP and NP contamination in aquatic environments specially in surface water.
2. Search Strategy and Literature Evaluation
This article presents a systematic literature review according to the PRISMA diagram (Figure 1). To find relevant studies about the current state MPs and NPs in aquatic environments, we used multiple scientific databases, including ScienceDirect (http://www.sciencedirect.com), PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) Web of Science (https://www.webofscience.com/, Clarivate), Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com/, Google), Scopus (https://www.scopus.com/) and scientific reports. The search strategy applied the string (“microplastic” OR “nanoplastic”) AND (“aquatic” OR “marine” OR “freshwater” OR “wastewater”) and incorporated additional keywords such as “surface water,” “rivers,” “lakes,” “streams,” “sea,” “occurrence,” and “aquatic ecosystems.” focus on publications from 2010 to May 2025. Articles were included if they reported original empirical data on MPs and NPs in aquatic systems particularly surface waters, while duplicates, studies without empirical data, and those lacking methodological detail were excluded. QA/QC assessment emphasized reporting of sample collection and preservation, sample processing, and validated methods for particle quantification and identification. Figure 2 illustrates the number of articles published in ScienceDirect and PubMed on MPs and NPs between 2010 and 2025.
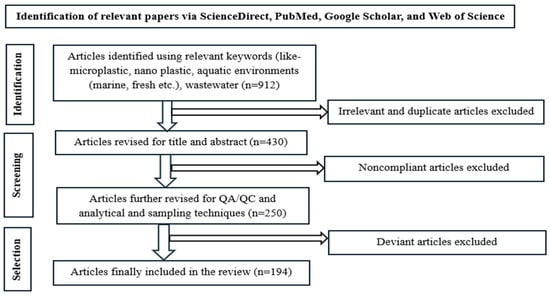
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram illustrates the identification, screening, and selection processes undertaken in the current review.

Figure 2.
MP and NP Publications in ScienceDirect and PubMed (20102025).
3. Categories, Composition and Properties of MPs and NPs
Owing to their small size, microplastics are difficult to discern with the naked eye. Despite their inconspicuous nature, their release into the ocean can have significant detrimental consequences [4,12]. As they move through the ecosystem, MPs accumulate in the food chain, raising concerns about human health due to potential exposure to these contaminants. Their surfaces can adsorb toxins, further magnifying their potential impact [13]. MPs and NPs are generated through two primary processes: manufacturing commercial plastic goods and degrading larger plastic fragments. These tiny contaminants pose a threat to both the environment and animal life [14]. Common sources of microplastics include various industries, such as cosmetics, textiles (shredded microfibers), fishing nets, and clothing production [12,13,14]. The composition of MPs and NPs varies with different combinations of polymers and chemical additives present at varying concentrations. They can be categorized into two main types on the basis of their origin: primary and secondary.
3.1. Categories of MPs and NPs
3.1.1. Primary: Direct Sources of Contamination
Primary MPs and NPs are intentionally manufactured particles <5 mm and <100 nm in size that are found in various commercial products. They originate from sources such as personal care products (e.g., exfoliating scrubs), industrial applications (e.g., sandblasting abrasives), and synthetic textiles (e.g., polyester and nylon). These plastic particles enter the environment directly, contributing to pollution through their presence in exfoliating products and cleaning agents and the release of microfibers during fabric washing. The widespread use and disposal of microplastics significantly adds to the overall microplastic burden in ecosystems [4,12,15,16].
3.1.2. Secondary: The Lingering Legacy of Plastic Waste
Secondary MPs and NPs result from the degradation of larger plastic debris through environmental processes such as sunlight, wind, waves, tidal current, oxidation, reduction, adsorption, hydrolysis and other mechanical and chemical forces. Unlike primary plastics, they are not intentionally produced but rather arise from the breakdown of existing plastics. Common sources include tire wear and the shedding of microfibers from synthetic clothing. Inadequate waste management practices exacerbate this issue by accelerating plastic fragmentation. These secondary MPs and NPs particles pose significant threats to aquatic ecosystems and human health because of their persistent and widespread presence in the environment [14,16,17].
Categories of MPs and NPs based on their sources in the environment are shown in Figure 3.
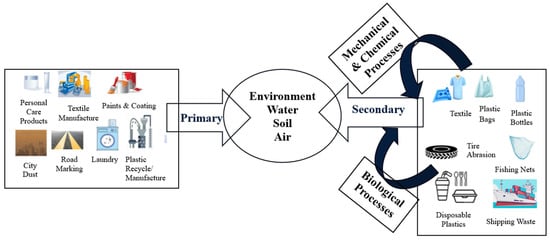
Figure 3.
Categories of MPs and NPs based on their sources in the environment.
3.2. Composition and Properties of MPs and NPs
The composition and properties of MPs and NPs vary depending on their size, shape, inherent properties, source, and the processes they undergo, and these properties can provide crucial information about their sources. Common shapes of MPs include fibers, fragments, films, and foams, each contributing differently to pollution and environmental impacts [16,17].
3.2.1. Shapes
Fibers: These are elongated, thread-like particles commonly derived from synthetic textiles and fishing nets. They are prevalent in aquatic environments and can cause MP/NP pollution. Numerous studies have demonstrated that fibers constitute a significant proportion of microplastic contamination. In both Xiangshan Bay, China, and Tampa Bay, Florida, a substantial portion of the microplastics detected were in the form of fibers [18,19].
Fragments: These irregularly shaped particles resulting from the breakdown and degradation of larger plastic debris can vary widely in size and shape and often exhibit jagged edges and uneven surfaces with different colors. A study revealed that in Malaysian marine waters, most microplastics are fragments, mainly black or gray in color, and have densities greater than 1.02 g/cm3 [20].
Films: Thin, flat plastic pieces that can originate from plastic bags, wrappers, and other packaging materials. Films are often observed floating on the surface of water bodies, accumulating on shorelines and the soil surface [21,22].
Foams: These are small, buoyant plastic particles created from products such as polystyrene foam cups and packaging materials. Foams are less dense than other types of microplastics and tend to float on the water surface, contributing to surface water pollution [18,23].
Pallets and beads: Pellets and beads are typically small, spherical, and persistent and are usually manufactured for use in industrial plastic production and in personal care products. Found in a large quantity of domestic wastewater [4,11,15].
Each shape affects how these particles interact with the environment and with organisms. Similarly, fibers from textiles and fishing gear can affect marine life, whereas a wide range of aquatic species can ingest fragments and films. The variability in size and shape underscores the complexity of microplastic pollution and its pervasive effects across different ecosystems. Shapes and global abundance of MPs and NPs in aquatic systems on the basis of their shape, as shown in Figure 4. This figure was constructed using data extracted from the studies included in this review.

Figure 4.
Abundance of MPs and NPs in aquatic environments (marine, freshwater, and wastewater) on the basis of their shape.
3.2.2. Size
Plastics are generally classified into 4 major classes according to their size: macroplastics (>25 mm), meso plastics (5–25 mm), microplastics (<5 mm), and nanoplastics (<0.1 μm). The size of plastic particles is a key determinant of their environmental behavior, influencing processes such as transport, deposition, and accumulation across different aquatic compartments. Smaller particles, particularly MPs and NPs, have a higher potential for widespread dispersion, can penetrate biological membranes more easily, and are more readily ingested by a wide range of organisms. Particle size affects the surface-area-to-volume ratio, which in turn influences the capacity of plastics to adsorb and transport other pollutants, including heavy metals and persistent organic contaminants [9,10,13,14].
3.2.3. Polymer Type
MPs and NPs are composed of a variety of synthetic polymers with different densities, buoyancy effects, and potential chemical interactions. The most commonly detected polymers in aquatic systems include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (nylon), acrylic, and polyester (PES) [4,22,24]. Polyethylene and polypropylene are lightweight and buoyant, making them dominant in surface waters, whereas polystyrene, PET, and nylon exhibit relatively high densities, leading to sediment accumulation in aquatic environments. Films are often composed of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), whereas foams primarily consist of expanded polystyrene (EPS). The fibers from textiles are predominantly polyester, nylon, or acrylic, reflecting contributions from domestic laundering and industrial effluents. Pellets and beads, which are commonly used in manufacturing and personal care products, are typically made from PE, PP, or PS [15]. The polymer type influences not only the physical fate of microplastics but also their interactions with pollutants and additives, thereby affecting their ecological and toxicological impact [13,14].
3.2.4. Color
MPs and NPs exhibit a wide range of colors, including transparent, white, black, blue, red, green, yellow, orange, purple, violet and pink colors, which generally reflect their parent material, or the degradation processes they have undergone [11,21]. Bright colored particles like blue, red, green, black, white, yellow, violet, pink often originate from textiles, packaging materials, fishing gear and consumer products, whereas white, transparent, yellow often originates from cosmetics, personal care products, industrial abrasives and single use plastics. The polymer type can also influence particle color, as different polymers are manufactured with specific pigments or additives that determine their initial hue [4,11,12,21,22]. Environmental processes, including photodegradation, chemical oxidation, and mechanical abrasion, can cause brightly colored particles to fade or become transparent over time. The small size of MPs and NPs further complicates accurate color identification, and ongoing aging and chemical alterations continue to modify particle coloration, making precise color determination challenging. Table 1 summarizes the composition and physical properties of MPs and NPs, including their size, shape, type, and density, whereas Table 2 presents the corresponding polymer types, chemical formulas, and recyclability.

Table 1.
Properties of MPs and NPs based on their shape, type, color and density.

Table 2.
Polymer types of MPs and NPs with their chemical formulas, degradation rates and recyclability.
4. Analytical Methodologies for MP and NP Analysis and Characterization
4.1. Sampling Techniques
4.1.1. Sampling Techniques for Seawater (Trawl-Net and Bulk/Pump Methods)
MPs and NPs have been assessed across the global marine system via diverse sampling techniques, each optimized for specific size fractions, with trawl nets and bulk/pump-based methods being the most widely employed methods. In the trawl-net method, manta trawls, plankton and neuston nets (mesh sizes typically 300–500 µm) are widely applied for surface water collection, recovering particles in the 0.3–5 mm range [25,26,27,28]. The trawl-net method, which covers a large surface area, is effective for analyzing this distribution but primarily collects buoyant plastic particles, missing high-density particles and those smaller than the mesh size [26,27,28,29,30]. The bulk sampling method, which is practical for point source collection, allows sampling from various depths and the selective extraction of microplastics by mesh size, but small sample volumes may not reflect true concentrations; thus, a minimum volume of samples needs to be acquired to adjust the local water quality [30]. A variety of pump-based samplers, including Universal Filtering Object pumps, KC Denmark (KCD) pumps, and CTD-based in situ filtration, are used in the bulk sampling method, which allows higher-resolution sampling, capturing smaller fractions down to 20–100 µm, with reported size ranges extending up to several millimeters [31,32,33,34]. The Universal Filtering Object (UFO) pump sampler efficiently collects microplastics as small as 10 µm from both surface and subsurface waters, processing up to 1 m3 per hour [33]. The Jussi sampler, a large-volume Limnos-type water sampler (~30 L), is designed for collecting bulk water samples from defined depths by minimizing contamination to acquire substantial subsurface water samples [35]. Studies comparing trawl nets and bulk sampling methods have revealed that microplastic concentrations in bulk samples are approximately 500 to 1500 times higher, primarily because of the recovery of finer particles [36]. Research has also shown that the use of an 8 μm mesh results in the capture of 8.5 times more microplastics than the use of a 65 μm mesh does, highlighting the importance of the mesh size for detection efficiency [29]. The choice of sampling method and device can greatly influence the measured microplastic concentrations, as variations in sample volume, collection depth, and mesh size affect both the quantity and size range of the particles captured [37]. In addition to sampling techniques, other environmental factors, such as wind speed, wave height, vertical mixing, water turbulence, stratification, prevailing currents, surface accumulation, horizontal transport, hydrodynamics and anthropogenic factors, such as vessel travel speed, can dramatically change the distribution and concentration of these tiny plastic particles. The abundance of microplastics may be overestimated, underestimated, or subject to sampling bias if these factors are not taken into proper consideration [38,39].
4.1.2. Sampling Techniques for Freshwater (Grab Sampling)
In the freshwater system, most samples were collected via the grab sampling method, which involves collecting discrete amounts of water samples directly from the surface or at specific depths. A range of devices have been employed for this purpose across rivers, lakes, creeks, estuaries, wetlands, and catchment areas, including stainless-steel buckets [40], pumps [41], manta nets [42], plankton nets [43], hydro-bio samplers [44], centrifugal pumps [45], automated composite samplers [46], and Niskin water samplers [47], for collecting freshwater samples for subsequent analysis. Grab sampling can provide snapshots of microplastic abundance at specific locations and time points. However, the use of manta and plankton nets is not a preferable option for small and shallow freshwater bodies [48]. Additionally, similar to the marine environment, the mesh size of the sampling net can significantly affect the final count of plastic particles. A study reported that an 80 μm mesh detected up to 100,000 times more microplastics than a 450 μm mesh [49], which can lead to over- or underestimation of these plastic contents in any specific freshwater system.
4.1.3. Sampling Techniques for Wastewater (Electric Pumping)
The sampling of MPs and NPs in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) is somewhat critical compared with that in marine and freshwater systems. Both grab sampling and continuous pumping methods are used, with protocols tailored to flow rates, water turbulence, and plant-specific characteristics. Wastewater samples are generally collected via electric pumps fitted with metal or stainless-steel filtration devices and autosampler containers. The collected water is stored in glass containers to avoid contamination [11]. Sampling can be conducted at various stages of the treatment process, including primary influent, primary settling, secondary treatment, and effluent discharge. The filter size is particularly important, as pore sizes (<20 µm) can capture fine MPs and NPs whereas larger mesh sizes (e.g., 300–500 µm) tend to retain only larger fragments, potentially underestimating overall concentrations [50,51].
4.2. Pretreatment Methods for Isolation: Digestion and Density Separation
The pretreatment method for MPs and NPs analysis involves four key steps: wet sieving, determination of the total solid mass, digestion and density separation [52]. Wet sieving involves passing samples through stacked 5.6 mm to 0.3 mm (MPs) and 0.8 and 0.2 μm (NPs) stainless steel sieves that are rinsed thoroughly to remove dirt and dust. The retained solids are then dried at 90 °C, and their mass is determined by subtracting the pre weighed beaker from the total mass to obtain the total solids. Digestion with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) removes organic matter to improve analysis precision, although other chemicals, such as KOH and Fe (II) solutions, may be used depending on the sample’s organic content. Wet peroxide oxidation (WPO), including Fenton’s reaction, is used to remove organic matter without significantly affecting polymers. However, if the temperature increases above 75 °C, it will boil violently, which can melt or reduce the weight of certain polymers, such as polyamide (PA) and polyethylene (PE) [52,53]. Density separation employs solutions such as NaCl (density: 1.2 g/cm3) and calcium chloride (CaCl2; density: 1.3 g/mL) to extract low-density microplastics such as PE and PP from seawater. However, this method may miss high-density microplastics such as PVC and PET because of their ability to float under certain conditions. Using a zinc chloride (ZnCl2) solution with a relatively high density (1.5–1.6 g/mL) can help recover high-density microplastics [52]. The overall workflow from water collection to MPs and NPs identification and characterization is illustrated in Figure 5.
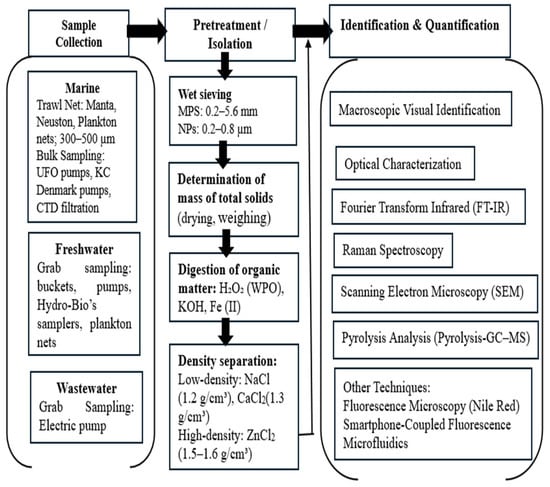
Figure 5.
The workflow of analytical methodologies for MPs and NPs analysis and characterization.
4.3. Methods of Identification and Quantification (Microscopic Examination)
After digestion, micro and nanosized particles are extracted for microscopic examination to determine the size, shape, color and polymer type of these plastic particles [51].
4.3.1. Macroscopic Visual Identification
Macroscopic visual identification uses stereo binocular microscope commonly known as stereo or dissecting for the identification of plastic properties after isolation. A stereo (dissecting) microscope is a low-magnification optical instrument that provides a three-dimensional view of intact specimens using reflected light. It is used for its convenience and low cost [54] and can provide information about physical properties such as size, color, and shape, but due to its low accuracy, it sometimes tends to overestimate, and mis identify errors in micro and nanosized particles [55].
4.3.2. Optical Characterization
Optical sensing uses fluorescence, scattering, or reflection to quantify MPs and NPs and determine their size, morphology, and chemical composition. Fluorescence microscopy uses laser-excited fluorophores to visualize structures in microplastics, often enabling high-resolution, three-dimensional imaging. Confocal systems enhance this by focusing on single points and rejecting out-of-focus light, though limitations include background fluorescence, phototoxicity, and chemical interference [55]. It has been effectively employed in detecting MPs such as PET and LDPE in specific sea locations [56]. This method efficiently detects polyethylene and struggles with polyvinyl chloride, highlighting the need for improved pretreatment steps [57]. A low-cost portable optical system using a collimated laser and CCD sensor can detect MPs at concentrations as low as 0.015% w/v [58], providing a cost-effective solution to this problem.
4.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy is a prominent technique for identifying and quantifying MPs across various environments. FT-IR spectroscopy (including μ-FTIR and ATR-FTIR) uses infrared light to detect molecular vibrations, providing chemical fingerprinting for material identification, including MPs and NPs. Coupled techniques like Atomic Force Microscopy–Infrared Spectroscopy (AFM-IR) enable nanoscale imaging and simultaneous chemical characterization by measuring sample expansion in response to pulsed infrared absorption. FT-IR is a robust technique for analyzing samples containing low to moderate numbers of particles (approximately 150–1000 per sample), but more particles can facilitate clogging [59]. Enhanced methods, such as laser direct infrared (LDIR) FT-IR, automated FT-IR and micro-FTIR, have demonstrated high efficiency in identifying polymers such as PE, PP, PVC, and PTFE with particle sizes of ~10 μm and detection efficiencies of 80–98% [60,61].
4.3.4. Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy uses monochromatic laser-induced inelastic scattering to generate molecular vibrational spectra, enabling chemical identification of materials with minimal sample preparation. Micro-Raman (μ-Raman) integrates an optical microscope for high-resolution analysis of particles down to 1 μm, it is a superior method for detecting and characterizing micro- and nanoparticles in solids, liquids, and complex matrices. Enhanced algorithms such as principal component analysis improve signal recognition and imaging capacity. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) can detect various microplastic particles, such as PS particles with sizes ranging from 350 nm and PE particles with sizes ranging from 1 to 4 μm [62]. A recent study demonstrated that Raman imaging enables visualization and identification of NPs as small as 100 nm [63]. Combining Raman spectroscopy with spatial heterodyne technology (SHS) offers high signal–to–noise ratios, surpassing traditional dispersive Raman spectrometers [64].
4.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
SEM can provide high-resolution imaging of MPs with detailed morphological information, such as particle size, shape, and texture, as well as degradation features, such as cracks, pores, rough surfaces, protrusions, fractures, pits, and flakes about MPs and NPs by using accelerated electrons to probe the sample surface [65] and allows qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis when coupled with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy) [55]. Variants like Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) enable high-magnification imaging with minimal sample preparation, and SEM can also be adapted for nanoparticle characterization using Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) holders. Studies have revealed that SEM analysis can detect microbead sizes ranging from submicron scales (~0.9 μm) to several hundred microns (~750 μm), with particles of approximately 400 μm size [66].
4.3.6. Pyrolysis Method
Pyrolysis analysis, including thermal pyrolysis and pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Py-GC–MS), is used to degrade samples to form a new product that can be identified via GC–MS. Pyrolysis/Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (Pyr-GC/MS) uses a multi-shot micro-furnace pyrolizer coupled with a GC/MS system to thermally decompose polymers and analyze characteristic pyrolysis products. The double-shot mode allows thermal desorption of interferences followed by quantitative measurement of MPs and NPs, with samples injected onto a capillary column and analyzed over m/z (mass-to-charge ratio) 40–600. Calibration with internal and external standards ensures accurate quantification of multiple polymer types while minimizing matrix interferences, making the technique highly sensitive and specific for environmental samples [67]. This method offers high-efficiency MPs and NPs quantification with a wide range of polymers, including PE, PP, PET, PVC, PS, and PMMA, with concentrations ranging from 229–1182 μg/L for MPs (1–100 μm) to 88–305 μg/L for NPs (<1 μm) [67]. Another study measured NPs (<1 µm) in Australian wastewater treatment plants Via pyrolysis GC–MS and detected nylon 66, PE, PP, nylon 6, and PET at concentrations ranging from 0.04 to 7.3 µg/L [68]. This method has recently been applied to detect MPs and NPs particles, including PE, PVC, and PET, in human blood [69].
4.3.7. Other Technologies
Fluorescence microscopy with Nile red (NR) dye is a reliable and cost-effective method for detecting and quantifying hydrophobic MPs such as PE, PP, PS, and nylon, with sizes greater than 5 mm; however, this method involves fewer hydrophobic polymers, such as PC, PU, PET, and PVC [70,71]. The smartphone-coupled fluorescence detection method has gained popularity for the rapid quantification of MPs in recent years; using this technique, MPs greater than 10 μm in size can be quantified within an hour [72]. Microfluidics is considered one of the latest technologies and is considered an efficient and low-cost method for detecting PS, PP, and PMMA within a diameter of 60 μm [73]. A summary of the analytical techniques for MPs and NPs detection in various aquatic systems is given in Table 3.

Table 3.
MP and NP detection techniques in various aquatic systems.
To ensure data reliability in MPs and NPs research, rigorous quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) procedures are required. Common practices include the use of field blanks, laboratory procedural blanks, and airborne contamination controls to minimize false positives. But the absence of standardized QA/QC protocols across studies still remains a major barrier to data comparability. Recovery test experiments with reference particles can provide a critical means to evaluate methodological consistency and extraction efficiency.
Method detection limits (MDLs) represent a critical constraint in the analysis of MPs and NPs, as they determine the minimum particle size that can be reliably detected and quantified. Visual identification has the highest MDL, while optical characterization reduces this threshold to approximately 0.003 mm but remains less effective at nanoscale. Spectroscopic methods, such as FT-IR and µ-FT-IR, typically operate within the ~10–25 µm range, allowing robust identification of microplastics but excluding NPs. Raman spectroscopy achieves higher resolution with detection limits approaching ~100 nm, although fluorescence interference may hinder accuracy. SEM can visualize particles down to ~0.9 µm with detailed surface morphology but lack polymer-specific chemical information. Thermal degradation-based methods (e.g., Py-GC–MS) achieve detection limits as low as ~40 nm and up to 100 µm, enabling quantification of both MPs and NPs but at the cost of particle integrity. Fluorescence microscopy, while rapid and cost-effective, is constrained to the ~5–10 µm range and suffers from false positives, whereas microfluidics detects particles down to ~60 µm but only for select polymers.
Current techniques can reliably detect and characterize microplastics, but NPs (<100 nm) remain significantly underrepresented due to their small size and colloidal behavior often make them indistinguishable from natural organic and inorganic nanoparticles in environmental samples. This limitation restricts comprehensive environmental monitoring and ecological risk assessments by underestimating exposure to the smallest and potentially most hazardous particles. These limitations highlight the need for standardized QA/QC protocols, more sensitive detection methods, and sampling techniques specifically designed for NPs.
5. Environmental Distribution
5.1. MPs and NPs in Aquatic Environments
The presence of MPs and NPs in aquatic systems has become a critical environmental issue because of their persistence, mobility, and widespread distribution. Research has focused primarily on seawater [3,28,35,36], but recent studies have expanded to include freshwater [46,48,56], wastewater [50,51,68], and groundwater [74]. Asia, particularly China, has led in research on microplastics both in marine and freshwater environments [75,76]. In Asia, MP and NP pollution has emerged as a major environmental issue due to the combined effects of high population density, rapid industrialization, accelerated economic growth, limited regulatory frameworks and public awareness. These factors drive large-scale plastic consumption, particularly of single-use plastics, resulting in substantial waste generation. In many East and Southeast Asian countries, underdeveloped waste management infrastructure leads to uncollected and mismanaged plastic waste, which enters the environment and contributes significantly to the production of MPs and NPs particles in the region. Europe has focused on MPs and NPs in wastewater systems [51,68] due to the critical role these systems play in mitigating the release of such pollutants into the environment. The region benefits from advanced waste management infrastructure, higher recycling rates, and stringent regulations targeting intentionally added microplastics, along with strategies to minimize unintentional microplastic formation. These measures help limit the release of plastic debris into aquatic ecosystems; however, wastewater treatment plants remain important reservoirs and potential pathways for MPs and NP pollution. Despite their high removal efficiency, wastewater treatment plants continue to discharge significant quantities of MPs and NPs in their effluents, underscoring their role as critical control points for mitigating the pollution. Figure 6 illustrates the continental distribution of MPs and NPs, and Figure 7 presents the percentage of MPs and NPs across different aquatic systems. Both figures were generated using data extracted from the studies included in this review.

Figure 6.
The continental distribution of MPs and NPs in aquatic systems.

Figure 7.
Relative Abundance of MPs and NPs in aquatic environments (seawater, freshwater and wastewater across continents.
5.1.1. Marine Environments
Prevalence and Distribution in Oceans and Seas
MP and NP pollution has been reported across all oceanic regions, including the Pacific Ocean [25,27,31], Atlantic Ocean [26,30,32,33,77], Baltic Sea [35,78], Mediterranean Sea [79,80], Indian Ocean [81], Arabian Sea [82], Bay of Bengal [83], Arctic [84,85], and Antarctic Oceans [86,87]. These MP and NP pollution range from the deepest marine trenches to coastal zones, impacting both densely populated coastal areas and remote environments, including the Arctic and Antarctic [25,27,84,87,88,89,90,91]. Microplastic concentrations are found to be higher nearshore (545–9870) MPs/m3 or in estuaries (680–137.3) MPs/m3 adjacent to land than in the open sea (0.007–0.015) MPs/m3 [84,92]. In contrast, remote areas in the Atlantic Ocean have much lower concentrations, approximately 1.15 items/m3, with minimum concentrations of potentially plastic contamination (0–0.4 items/m3) [26]. Recent investigations into Arctic MP pollution have revealed that transport mechanisms differ significantly from those in temperate and tropical regions [85]. While rivers are typically considered major sources of MPs to marine environments in other regions, in the Arctic Ocean, they appear to dilute rather than contribute to MP pollution, as indicated by higher concentrations in central Fjords and lower levels in river plume waters [85]. The presence of MPs and NPs in sea surface water is given in Table 4.

Table 4.
MP and NP pollution in sea surface water.
Sources and Pathways
Sources of MP and NP pollution in marine ecosystems include land-based activities, shipping, fishing, and marine aquaculture. Approximately 60–80% of plastic debris in marine environments originates from land-based sources such as urban runoff, industrial discharges, improper waste disposal, stormwater outflows, and riverine transport. The remaining ~20% is contributed by maritime activities, including vessel operations, offshore industrial processes, coastal tourism, and commercial fishing, often in the form of discarded fishing gear and aquaculture-related plastics [93]. The concentration of plastic waste varies significantly by location, as many countries directly dump plastic waste into the ocean. A study by Jang et al. highlighted that 95% of plastic waste found on the Sarikum Lagoon coast originates from 25 neighboring countries. In 2005, approximately 5 million tons of plastic waste were dumped into the ocean by ships [94]. Even remote regions in the Antarctic and Arctic Oceans, which were previously considered relatively free of plastic pollution, have shown contamination at the micro- and nanoscales in both coastal surface and subsurface waters [84,85,86,87,90,91]. This indicates the pervasive nature of MP pollution, with airborne particles reaching remote areas in the ocean through mechanisms such as dry and wet deposition, sea spray, aerosolization, and atmospheric circulation, while precipitation further transports these particles directly into marine environments or indirectly via rivers and streams [95].
5.1.2. Freshwater Systems
Presence in Rivers, Lakes, and Streams
MPs, along with a notable quantity of NPs, have been widely documented in major lakes and rivers across different continents. In North America, the Laurentian Great Lakes present an average abundance of approximately 43,000 items/km2 of MPs, with Lake Ontario reporting concentrations of 0.8 particles/L [49,96,97]. In Europe, significant contamination has been observed in the German Elbe, Mosel, Neckar, and Rhine rivers [98]. Across Asia, studies have reported the presence of MPs and NPs plastics in various rivers and lakes in China and India [40,99,100,101]. Notable amounts of MP particles have been identified in the Buffalo and Swartkops Rivers in South Africa [102]. The variability in MP concentrations among these aquatic systems is largely associated with anthropogenic pressures, including population density, industrial activities, and urban runoff. Urban rivers consistently exhibit higher levels of contamination than their rural counterparts do, reflecting the strong influence of urban environments as primary sources of microplastic pollution. Lakes located near urbanized areas, such as Lake Ontario, which has high concentrations of microplastics, indicate the direct relationship between human activities and microplastic accumulation in freshwater systems [97]. The presence of MPs and NPs in freshwater systems is given in Table 5.

Table 5.
MP and NP pollution in freshwater systems (surface water).
Sources and Pathways
MPs and NPs migrate from terrestrial sources to aquatic environments through several interconnected pathways, including freshwater stream transport, stormwater runoff, effluent discharge from wastewater treatment plants, leaching from landfills and atmospheric deposition [46]. MPs and NPs enter freshwater systems through various processes and routes, including effluent discharge, agricultural runoff, industrial segregation, littering and flooding [110]. Although WWTPs can remove a substantial portion of MPs and NPs, they are not fully effective at eliminating all these tiny plastic particles as a result wastewater effluent contains residual MPs and NPs, which are released into rivers and lakes subsequently. MPs and NPs that accumulate in sludge can be transferred to soil when the sludge is applied as fertilizer, and effluent used for irrigation can further introduce these particles into agricultural soils and eventually transport into adjacent freshwater systems via runoff and leaching [110,114,115,116]. Runoff and leaching from urban areas, commercial sites and landfills constitute another pathway for MPs and NPs to enter wastewater systems. During rainfall events, these particles from agricultural land, road dust, vehicle tires, road markings, other debris and litter are washed in storm drains and ultimately released into urban rivers and streams [110]. Studies have highlighted the role of stormwater systems in transporting MPs from roads to aquatic environments [117]. Industrial activities and population density also contributed significantly to MP and NP pollution. Factories producing plastics and other related products often release a profound number of MPs and NPs as byproducts with other chemical discharges directly into water bodies. Litter, improper disposal, mismanagement of plastic waste and recycling failure in both urban and rural areas lead to the fragmentation of larger plastic items into MPs and NPs, which are then transported by wind and water into rivers and lakes [115]. Atmospheric deposition is a less well-known but significant pathway for microplastics to enter freshwater systems. MPs and NPs can be transported by wind and deposited onto water surfaces through rainfall. Studies have reported the presence of synthetic fibers in atmospheric dust, indicating that airborne MPs and NPs can contribute to contamination in freshwater environments [114].
5.1.3. Presence in Wastewater System
Wastewater Treatment Plants
MPs and NPs are prevalent in wastewater systems and originate from various anthropogenic sources, and these wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are significant contributors to this pollution. MPs and NPs are often discharged into wastewater through domestic and industrial activities. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) receive substantial amounts of MPs from household sources, such as personal care products containing microbeads and synthetic fibers released during the washing of synthetic textiles [12,15]. Although WWTPs are designed to remove contaminants from wastewater, their efficiency in removing MPs and NPs varies, and sometimes, the treatment processes involved in WWTPs are not enough to remove all types of MPs and NPs from the system because of their extremely tiny particle sizes. Studies have shown that while primary and secondary treatment processes can remove a significant portion of MPs and NPs, a considerable amount still escapes into the treated effluent [117]. Tertiary treatments, although more effective, still fail to eliminate all microplastics, resulting in their release into aquatic environments. The presence of MPs and NPs in wastewater is given in Table 6.

Table 6.
MPs and NPs present in wastewater treatment plants (water samples).
Sources and Pathways
Waste water treatment plants (WWTPs) work as major links to transfer MPs and NPs in nearby water systems, as they carry large amounts of these tiny plastic particles from various domestic, municipal and industrial sources. In terms of the type of WWTP and treatment process, the physical, chemical and morphological characteristics of MPs and NPs significantly change. In domestic WWTPs, large loads of microfibers, plastic fragments, microbeads and pallets come from various synthetic clothing, and personal care products such as exfoliating scrubs, sunscreen, toothpaste and other cosmetics [51,121,123], such as a single wash, can release hundreds of thousands of microfibers, which are small enough to pass through filtration systems at WWTPs, as most WWTPs are not particularly designed for removing MPs and NPs from the effluent [50,125]. Industrial and municipal WWTPs receive substantial amounts of MPs in the form of fibers, granules, foams, films and fragments from nearby industries that manufacture or use plastic products during production processes. Improper handling, plastic pellet spills during transportation and the use of other plastic-containing products, such as abrasive blasting media, can increase the load of this contaminant in the influent [126]. Although conventional WWTPs do not specialize in dealing with this large load of MPs and NPs, they are able to remove a significant portion of these tiny particles on the basis of their efficiency. Secondary- and tertiary-level WWTPs can remove up to 80–99% of MPs before discharge [118,123]. During primary treatment, larger particles are removed through sedimentation and filtration; however, smaller MPs and NPs often bypass these processes. Secondary treatment, which relies on biological mechanisms, further reduces MP and NP concentrations, although fibers and small fragments may still persist in the effluent. Tertiary treatment, including advanced filtration and chemical processes, can remove up to 99% of MPs. Despite high removal efficiencies, the large daily volumes of treated effluent result in a substantial cumulative load of MPs and NPs being discharged into receiving waters, contributing to increasing environmental contamination over time [50,51,125,126]. The percentages of MPs and NPs based on their polymer type in surface water are shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
Percentage of MPs and NPs in aquatic systems based on their polymer type.
6. Dynamics of MP and NP Transport and Fate in Aquatic Environments
6.1. Transport Mechanisms
6.1.1. Transport of Floating Particles via Surface Drift
Floating plastic particles with sufficient buoyancy are passively transported by geostrophic circulation, wind forcing, Stokes drift, currents, and horizontal diffusion [9,95,109,114], allowing them to travel long distances from their source and leading to accumulation in remote oceanic regions, subtropical gyres [26,127] and onshore transport into coastal waters [22].
6.1.2. Transport Through Vertical Mixing
Initially, floating MPs and NPs can become suspended in the water column from the subsurface to deep waters due to vertical mixing. This vertical distribution results from wind-driven mixing and changes in advective velocity along the water column [9,22,127].
6.1.3. Settling of High-Density Plastic Particles
High-density nonbuoyant particles tend to settle naturally and accumulate in deep-sea environments, with sedimentation influenced by their density, shape, and morphology. Biofouling, microbial colonization, and aggregation with organic matter further increase sinking rates and facilitate deposition on the seabed [22,128].
6.1.4. Inland Waters and Water Colum Mixing
Inland water bodies serve as primary conduits for MPs and NPs transport. These particles are transported horizontally from inland waters into the ocean under hydrological factors such as precipitation, infiltration, runoff, subsurface flow, and river geomorphology [110,116,129,130].
6.1.5. Marine Aggregates as Vectors for Other Pollutants
Aging both homogeneous and heterogeneous MPs and NPs through UV photoaging and chemical oxidation significantly alters their physicochemical properties, influencing their aggregation, and interactions with other pollutants in aquatic systems can control their stability and significantly change their toxicity to living biota [76,128,131].
6.1.6. Riverine Surface Current and Outflow
Riverine outflows can deliver large quantities of MPs and NPs into coastal and estuarine zones or other nearby freshwater systems, where flow velocity, seasonal flooding, and sediment interactions critically influence their dispersal and accumulation [105,116,129,130].
6.1.7. Urban Sources as Anthropogenic Inputs
Urban sources, such as combined sewer overflows, untreated wastewater, stormwater runoff, industrial effluents, plastic littering, agricultural runoff, recreational activities, navigation, fishing, shipping and sewer discharges, are also considered major contributors to transportation [12,13,93,110,117].
6.1.8. Atmospheric Deposition
Atmospheric deposition is a key pathway for introducing MPs and NPs into aquatic environments. It encompasses both wet and dry deposition processes and facilitates the global dispersion of these particles, including in remote regions such as the Arctic and Antarctic snowpack [86,95,114].
6.1.9. Sea Ice Melting
Accelerated sea ice melting extensively alters the dynamics of microplastic transport within the Arctic region by releasing MPs and NPs previously entrapped within the ice matrix into the surrounding environment [132]. The ongoing mass loss of the Greenland ice sheet and Arctic glaciers exacerbates the extent of contamination.
6.2. Morphological Properties of Plastic Particles (Size, Shape and Polymer Type)
In both marine and freshwater environments, the distribution and transport of MPs and NPs are significantly influenced by their inherent physical properties, such as density, size, and shape. Low-density polymers, such as PE, with a density of ~0.91–0.94 g/cm3, and PP, with a density of ~0.85–0.92 g/cm3, tend to float on the surface of seawater. In contrast, high-density polymers, such as PVC, with a density of ~1.3–1.45 g/cm3, and PET, with a density of ~1.38–1.41 g/cm3), tend to sink [4,22,24,133]. The size of these particles in water systems varies from large debris to nanoscopic particles. MPs with diameters less than 1 mm and NPs smaller than ~1 μm exhibit extended suspensions within the water column, facilitating long-distance transport and widespread distribution throughout the water body [128,129,134]. The shape of the particles significantly impacts their distribution and transport. The elongated shape and substantial surface area of fibers and fragments, which have a larger surface area-to-volume ratio than do spherical particles, promote entanglement with natural organic matter, algae, other pollutants and suspended particles, increasing their aggregation. Fibers can form surface mats or sinks based on their interactions, whereas irregular surfaces promote biofilm formation and adsorption of metals, altering their density and transport behavior [76,113,133,134].
In both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), particle properties and the efficacy of treatment processes influence the distribution of microplastics within these systems. Low-density polymers such as PE and PP remain in the water phase, potentially bypassing treatment and ending up in the effluent, and high-density polymers such as PVC and PET are more likely to settle and be captured in sludge [117,135]. Smaller microplastics, typically less than 10 µm, are less likely to be captured by physical filtration and may pass through treatment stages, leading to discharge into receiving waters [51,126,135]. Fiber-type textile microplastics can bypass filtration systems and form aggregates with biofilms and organic matter, complicating their removal owing to their elongated shape and small diameter [125].
6.3. Chemical Properties of Plastic Particles
The surface charge, chemical composition, ionic strength, hydrophobicity, and valency critically affect their transport and fate in aquatic systems. Most of these MPs and NPs are negatively charged and are often dominated by hydroxyl groups [128]. Particle charge can sometimes be affected by pH if hydrolysable functional groups are present and reduce the repulsion force, which makes them less stable in the system. A higher ionic strength also lowers stability because of the low repulsion force. Compared with hydrophilic compounds and monovalent ions, hydrophobic particles and multivalent ions are less stable in aquatic systems because they have greater attraction forces for other particles [85,117,133,134].
6.4. Degradation Process
The degradation of MPs and NPs in aquatic systems can be classified into four primary processes: physical degradation, photodegradation, chemical degradation, and microbial degradation. These processes are modulated by various environmental factors, including temperature, salinity, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, particle concentration, the presence of metals and other pollutants, and microbial activity. Physical degradation occurs through mechanical forces such as ocean circulation, surface currents, water volume and velocity, wind-induced turbulence, vertical mixing, and thermal oxidation, which collectively fragments larger plastic debris into micro- and nanoscale particles. Aging is also considered a form of physical degradation, as it alters particle size and morphology. Aged MP and NP fragments exhibit irregular shapes and increased surface roughness relative to their pristine counterparts [128,136]. Photodegradation is essentially induced by sunlight; exposure to UV light triggers photooxidation, and gradual degradation can break the chemical bonds of particles and generate free radicals that react with oxygen to form oxygen-containing functional groups. This process is limited by water depth and the presence of other particles that may shield them from UV exposure [136,137,138]. Chemical degradation involves the cleavage of covalent bonds and the generation of free radicals through oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis and pyrolysis processes. Chemical oxidation in natural aquatic systems depends on the amount of free oxygen radicals generated from the photochemical degradation process and the presence of organic matter, nitrates, and carbonates in the system [128]. Hydrolysis of ester bonds further contributes to degradation by releasing low-molecular-weight fragments from the polymer matrix [139]. In wastewater systems, chemical oxidation occurs during chlorination and ozonation processes, where the introduction of chlorine and ozone facilitates the oxidative transformation of these pollutants. [128]. Biodegradation by microorganisms involves the colonization of specific microbial communities on micro- and nanoparticle surfaces and initiates the breakdown of polymer chains. Biodegradation efficiency widely varies with the polymer type and species and number of microorganisms, along with other environmental conditions, such as pH, salinity, and oxidation and reduction agents. In general, biodegradation is slow, takes years to decades, and it is more effective for certain biodegradable plastics than for conventional plastics [139]. Figure 9 illustrates the influencing factors of physiochemical properties of MPs and NPs along with the environmental and anthropogenic parameters on their transport in various aquatic systems highlighting their potential impact.

Figure 9.
Influence of physiochemical properties and environmental and anthropogenic factors on MPs and NPs transportation in aquatic systems.
MPs and NPs exhibit distinct behaviors in aquatic environments due to differences in size, density, and physicochemical properties. MPs are more influenced by buoyancy, shape, and sedimentation processes, often accumulating in sediment or sub surface waters, while NPs remain suspended, undergo extensive transport, disperse more widely for longer periods due to surface drifting through horizontal diffusion, surface current and wind forcing. The degradation rate for MPs and NPs differ significantly, NPs degrade more rapidly and interact strongly with dissolved organic matter and co-contaminant due to small size, higher surface area and higher surface reactivity.
7. Ecotoxicological Effects of MPs and NPs Exposure
7.1. Ecotoxicological Scenario in a Marine Environment
The sizes of MP and NP particles range from 1 mm to ~1 µm, which resemble the size of zooplankton (e.g., Acartia tonsa, Penilia airstrips, Temora turbinata and Paracalanus spp.) considered to be the primary food sources for fish. Because they are similar in size, shape and color, fish often mistake this plastic for actual food and ingest it [140]. Zooplankton, which serves as a critical link in marine food webs, transfer energy from primary producers to higher trophic organisms and ingest MPs and NPs. Several studies have revealed that MPs and NPs can be ingested by zooplankton either passively or actively, leading to a range of adverse effects [141]. Over 690 species of aquatic animals ingest macro or microplastics [142], and in the marine environment, microplastics have been widely detected in the digestive tracts or tissues of numerous animals, including crustaceans, fish, bivalves, turtles, mammals, and seabirds, with concentrations ranging from 0.04 g per bird to 96.2% of ingested debris in turtles [143]. Adverse physiological and neural effects have been observed in various marine species due to exposure to contaminated environments. Similarly, white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) exposed to nanosized plastic show alterations in the gut microbiota, enzyme activities, and nutrient composition, indicating potential health risks for human consumers [144]. Zebrafish Danio rerio exposed to the microscale polymers PA, PE, PP, PVC, and PS showed intestinal damage, reduced Ca2+ levels, and increased intestinal glutathione S-transferase 4 expression [145]. Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) display reduced phagocytosis and lysosomal destabilization [146], whereas purple sea urchins (Paracentrotus lividus) exhibit high phthalic acid ester concentrations and altered protein profiles from polystyrene microbeads [147]. Compared with MPs, sea cucumbers (Apostichopus japonicus) experience severe growth inhibition and oxidative stress from NPs [148].
7.2. Ecotoxicological Scenario in Freshwater Systems
MP uptake has been documented for various taxa, including ligochaetes (Tubifex tubifex), bivalves (Corbicula fluminea), fish (Gobio gobio) and birds (Ardea cinerea), across the world from multiple freshwater systems [142]. PS MPs, aminomethyl-functionalized PS (PS-NH2, 37–74 μm) and fluorescent nano-PS (15–18 nm) (15–18 nm), induced pronounced adverse effects on the freshwater Hyalella azteca, including impaired growth, reduced reproduction, and altered oxidative stress enzyme activity, whereas regular nano-PS of 25 nm exhibited negligible toxicity to this specific amphipod [149]. Chinese soft-shelled turtles (Pelodiscus sinensis) exposed to 80 nm polystyrene nanoplastics penetrate turtle eggs, impair embryo metabolism (causing bradycardia), and disrupt gut microbiota diversity and balance but do not affect hatchling morphology or behavior; these changes may have long-term impacts on freshwater turtle health and population viability [150]. In the Susurluk River Basin Bursa, Türkiye, zooplankton showed no MP ingestion, whereas mussels (Anodonta anatina) and fish (Carassius gibelio) ingested 617 and 792 particles, respectively, in the form of fibers and films. MPs uptake is correlated with mussel size and water turbidity but does not show any clear pattern in fish [151]. In Germany, the freshwater insect Chironomus riparius exposed to PA and PVC MPs presented alterations in gene expression, oxidative stress and inflammation, premature molting, and reduced life cycle fitness, with daily population growth rates decreasing by 2.3–7.6% [152]. In the Periyar River, Kerala, a high concentration of MPs was detected in clams (Villorita cyprinoides) and fish (Etroplus suratensis, E. maculatus, with fibers dominating PE, PP, and PS). Researchers have estimated that humans may ingest approximately 936 MPs per year from consuming these two fish species and approximately 26 microplastics per 100 g of clam meat [153]. Perca fluviatilis, a freshwater fish in Greece, exhibited DNA damage, nuclear abnormalities, and metabolic disruptions after exposure to both virgin and UV-aged polyethylene MPs. Aged MPs are responsible for stronger stress responses, inflammation, and tissue damage because of their greater toxicity due to their lower crystallinity, irregular shapes, and greater number of oxygen/carbonyl groups [154]. Trophic transfer of NPs from freshwater algae to Scenedesmus subspicatus to the freshwater bivalve (Clam) Corbicula fluminea revealed oxidative stress and downregulated genes related to immunity, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, endocytosis, and apoptosis in a study conducted in the Garonne River, France [155].
7.3. Human Health Risks Associated with MPs and NPs Exposure
7.3.1. Pathways to Humans
MP and NP pollution have emerged as significant environmental pollutants with potential implications for human health. The primary exposure pathways are ingestion, inhalation and dermal contact. All these pathways pose potential health risks due to the toxic properties of these pollutants. Ingestion of MPs occurs when humans consume contaminated food and water. Currently, microplastics are commonly present in the human diet, including drinking water, vegetables, milk, eggs, fish, meat, and everyday condiments such as salt, and can enter human tissues through the food chain [156,157,158]. Plastic pollution in marine and freshwater ecosystems leads to bioaccumulation and biomagnification of MPs and NPs in aquatic food chains, posing dietary exposure risks to humans, especially while consuming seafood and freshwater fishes. MPs and NPs have been widely detected in zooplankton [141], invertebrates (crustaceans) [144,159], vertebrates (fish, lobsters, mussels, oysters) [145,160] and freshwater mussels and fishes [153,154,155].
The inhalation of airborne MPs and NPs represents another significant exposure pathway from the environment to humans. The degradation of plastic particles can produce airborne MPs and NPs ~100 µm to ~100 nm in size through industrial processes, vehicle emissions, sea spray, indoor activities, and abrasion. These airborne particles can be inhaled and enter the respiratory system, potentially causing health issues. Urban areas where sources of airborne plastic pollution are more concentrated may present higher risks of inhalation exposure. These tiny particles can easily inhale through nasopharyngeal airways and subsequently reach the lungs [161]. The ability of microplastics to remain suspended in the air and penetrate deep into the lungs is a growing concern, particularly given the widespread nature of air pollution. The presence of microplastic particles in the lungs was first reported in 1997, with 87% of both cancerous and noncancerous lung samples found to contain them [162]. A study investigated the environmental sources contributing to inhaled MPs in 454 participants undergoing bronchoscopy in Zhuhai, China. MPs were detected in 96.3% of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples, with PE, PU, and PVC being the most common. Geospatial analysis revealed that greater distance from branch roads and coastlines was associated with lower microplastic levels in the lungs [163]. In another study, MPs found in human lungs dominated polymeric particles (≤5.5 µm) and fibers (8–17 µm) in 13 of 20 autopsy samples, with PE and PP being the most common [164]. In indoor environments, MPs and NPs can be released from various sources. A study revealed that building blocks made of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) or PC could be potential sources of these particles and can generate thousands of MPs and hundreds of thousands of NPs per mm2 [165].
Dermal contact is another potential route of exposure to MPs and NPs; because of their tiny size, they can penetrate through the skin. Microbeads, which are commonly found in personal care products such as scrubbers, body washes, exfoliators, sun protection, shampoos and cosmetics [4,12,15,16], are considered the primary source of dermal contact. Recent analyses have shown that personal care products (PCCPs) can contain up to 50,391 microbeads per gram [166]; despite this large quantity, dermal contact is considered to be safest compared with the other two methods, as our outer skin layer protects against penetration up to ~100 nm [166]. MPs and NPs are internalized primarily by cells through endocytosis, with uptake efficiency influenced by particle size, shape, surface properties, and exposure conditions. Smaller particles (<500 nm) penetrate membranes more readily, whereas larger particles require prolonged exposure, and hydrophobic interactions govern their membrane integration [167].
7.3.2. Potential Health Risk Implications of Micro- and NPs in the Human Body
The toxicological effects of MPs and NPs and their associated chemicals are of considerable concern. MPs are known to act as vectors for hazardous substances, such as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), which can leach into human tissues upon ingestion [76,113,128,131]. Compared with pristine PS-MPs, chlorinated polystyrene microplastics (Cl-PS-MPs) exhibit increased surface roughness and cellular uptake, causing greater cytotoxicity in gastric GES-1 cells. They disrupt cell membranes, alter morphology, and trigger inflammation and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis [168]. Compared with 100 nm particles, 44 nm polystyrene nanoparticles (PS-NPs) accumulate more rapidly and efficiently in gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cells and enter via energy-dependent, clathrin-mediated endocytosis [169]. PS-NPs of 20 nm and 50 nm, regardless of surface charge (positive or negative), are responsible for epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), which can contribute to tissue remodeling, fibrosis, or cancer progression [170]. Polystyrene MPs and NPs (PS MNPs) impair human iPSC-derived cardiomyocyte viability and contractility in a time- and dose-dependent manner, with low doses disrupting calcium dynamics. In hypertrophic cells, 0.05 μm PS exacerbated hypertrophy, likely via mitochondrial dysfunction and increased ROS (reactive oxygen species), highlighting the potential cardiac toxicity of MNPs [171]. Polystyrene NPs cause concentration- and time-dependent cytotoxicity in human endothelial (HUVEC) cells, resulting in oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis [172]. In a recent study, PET, PE, and styrene-based polymers (including PS, expanded PS, and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene) ranging from 0.7 to 500 μm were detected in the blood of 22 healthy individuals [173]. The cytotoxicity of various nanomaterials (metal and metal oxide nanoparticles, carbon nanomaterials) and MPs/NPs (PEs and PSs) in human cerebral (T98G) and epithelial (HeLa) cells has been evaluated, and the results revealed that 10 ng/mL–10 µg/mL, 24–48 h, oxidative stress due to increased reactive oxygen species, which is a vital factor for toxicity [174]. Negative effects on human kidney organoid development, reduced size, abnormal tubular structures, increased mitochondrial ROS, and DNA damage have been observed in the context of exposure to environmental microplastics. MPs disrupt metabolism by decreasing glycolysis and increasing TCA (Tricarboxylic Acid cycle) or Krebs cycle activity [175].
Research evidence clearly demonstrates that ingestion of MPs and NPs is widespread across aquatic taxa and ecosystems, with impacts documented from zooplankton to top predators. NPs appear to exert more severe effects than microplastics due to their enhanced potential for cellular uptake and interference with physiological processes. Across species, common biological responses include oxidative stress, immune suppression, metabolic disruption, reproductive impairment, and alterations in gut microbiota, although the magnitude of these effects varies depending on particle size, shape, polymer type, and environmental conditions. Field observations further indicate that habitat characteristics such as turbidity and polymer weathering influence both uptake and toxicity. The frequent detection of microplastics in edible species, including fish, shellfish, and crustaceans, raises concerns not only for ecological integrity but also for human health through trophic transfer and seafood consumption as humans are at greater risk exposure to MPs and NPs through ingestion and inhalation primarily and with dermal contact to a lesser extent. Though growing evidence indicates that MPs and NPs can induce oxidative stress, inflammation, and organelle dysfunction across multiple human tissues, in vitro and short-term studies have primarily highlighted impacts on cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal, and neurological systems but long-term health consequences along with co-exposure to environmental contaminants such as heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants may further exacerbate toxicity but remain poorly understood. The detection of plastics in human blood, lungs, and other tissues underscores an urgent need for risk assessments to better characterize potential health impacts and inform appropriate public health interventions.
Pathways and ecotoxicological effects of MPs and NPs in terrestrial (human) and aquatic species are shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10.
Pathways and ecotoxicological effects of MPs and NPs in terrestrial (human) and aquatic species.
8. Current Mitigation and Management Strategies
8.1. Technological Approaches for MPs and NPs Removal and Recycling
8.1.1. Advancement and Technology Used in the Removal Process
Membrane Filtration
Currently, a variety of commercial membranes, such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) microfiltration/ultrafiltration membranes [176], polyether sulfone (PESP) ultrafiltration membranes, and polypropylene (PP)-hollow fiber (HF) microfiltration membranes [177], have been used to remove MPs and NPs from aqueous solutions. Most of them have demonstrated high MP removal efficiencies, often achieving near-total filtration success, with removal percentages ranging from 85% to 99.3% for a range of MP sizes under optimal conditions. The PVDF microfiltration membranes achieved 100% removal efficiency for PE and PVC MPs under specific conditions, whereas the PESP ultrafiltration membranes achieved 91–96% removal efficiency [177].
Adsorption
Adsorption, including physical and chemical methods, is a versatile and cost-effective approach for removing MPs and NPs with efficiencies ranging from 71.6% to 99.46% with various novel composites, such as zeolite adsorbents, polydopamine-modified sodium alginate hydrogels, and iron oxide nanoparticles [178,179,180,181]. This method is simple, energy-saving, reusable, capable of separating small-sized particles and achieving high purification, but challenges such as low adsorption efficiency, capacity, and selectivity, along with the need for better recyclability and simpler preparation processes, remain unanswered.
Chemical-Induced Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation
Chemical-induced coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation (CFS) effectively removes MPs and NPs through charge neutralization and floc formation, achieving removal efficiencies of >90–99.4% with aluminum [182] and iron-based coagulants [183]. The combination of these coagulants with organic agents such as polyacrylamide significantly enhances efficiency, reaching up to 96%. Factors such as coagulant type, dosage, pH, and water quality influence effectiveness, necessitating further optimization and development of safe, green coagulants for practical applications. A newly developed covalently bonded organic silicon–aluminum/iron composite coagulant (CSA/F) with varying Al/Fe ratios showed >90% removal efficiency for MPs while enhancing arsenate [As(V)] removal. [183]. A magnetic Fe3O4/C nano-adsorbent combined with PACl (polyaluminum chloride), achieved highly efficient (up to 99%) and reusable removal of polystyrene NPs through adsorption bridging and electrostatic interactions [184].
Bioremediation
Bioremediation for the removal of MPs and NPs through bacterial and fungal degradation or absorption by marine organisms presents a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution. Bacteria and fungi degrade MPs into harmless substances, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water, whereas algae and marine creatures can adsorb MPs and NPs through charge interactions. An impedimetric sensor based on Cyanobacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substances can remove MPs (0.1 µm–1 mm) at extremely low concentrations (limit of detection of 10−11 M) [185]. A study evaluating the potential of the green seaweed Chaetomorpha linum to capture MPs in an integrated multitrophic aquaculture (IMTA) system revealed that seaweed can trap MPs, predominantly fibers (97.3%) ranging from 0.025 to 2.00 mm, mostly 0.80 to 1.00 mm, composed mainly of PP, PS, and PE [186]. Despite its potential, bioremediation is a slow process, often requiring months or years, and efficiency improvements are essential to increase its viability for large-scale applications. The current removal efficiency varies significantly, typically ranging from 4.0% to 94.5%, depending on the specific microorganisms and conditions employed.
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) effectively degrade persistent organic pollutants and MPs in water by generating hydroxyl radicals under various conditions. Techniques such as the Fenton reaction, electrochemical oxidation, and photocatalysis have shown removal efficiencies of up to 95.9% for polyethylene and 76% for polyethylene when Ag/TiO2/RGO catalysts are used [187,188,189,190]. However, AOPs face challenges such as high operational costs and the generation of secondary pollutants, limiting their large-scale application.
8.1.2. Innovations in Plastic Waste Management and Recycling
Plastics at end-of-life follow four main fates: recycling into secondary plastics, incineration with/without energy recovery, controlled landfilling, or mismanagement (open burning, dumping, or uncollected litter). Technological advances have significantly contributed to plastic waste management. Innovations such as advanced sorting technologies, chemical recycling, and biodegradable plastics offer promising solutions. Chemical recycling processes can break down plastics into their monomers, enabling the production of new plastics from previously unrecyclable waste. Recent developments include enzymatic recycling, where specific enzymes degrade plastics into reusable components, presenting a potential breakthrough in addressing the challenges of conventional recycling methods. Recycling is expected to rise significantly from 33 Mt in 2019 to 176 Mt in 2060, increasing its share of total plastic waste from 9% to 17%. This growth reflects a key indicator of circularity, highlighting the gradual transition toward a more circular global plastic economy [191].
8.2. Regulatory Approaches for Mitigation
8.2.1. Existing Regulations and Policies
Regulatory approaches to managing plastic waste and microplastics have evolved globally, reflecting increasing concern over their environmental impacts. Regulations include the European Union’s Plastics Strategy, which aims to reduce plastic waste by banning single-use plastic items and increasing recycling efficiency. In the United States, the Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015 explicitly targets microplastics in personal care products, whereas several states have implemented bans or restrictions on single-use plastics [192]. California became the first state to enact the use of single-use plastic bags, followed by Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Maine, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Vermont, and Washington. Similarly, countries such as Canada and Australia have introduced comprehensive policies targeting plastic waste reduction, including plastic bag bans and extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs. Plastic packaging and other plastics will face progressively increasing taxes, reaching USD 1000/ton for packaging and USD 750/ton for other plastics in the EU and OECD by 2030–2040, and in non-OECD countries by 2060 [191].
8.2.2. Effectiveness and Enforcement Challenges
Despite these regulations, challenges in enforcement and effectiveness persist. Many policies need more adequate implementation, a limited scope, or a lack of stringent penalties for noncompliance. Bans on single-use plastics are common, and enforcement often depends on local authorities, who may need more resources or motivation. Regulations frequently face opposition from industries and consumers, hindering their full adoption and compliance. A 2021 review highlighted that enforcement remains a significant hurdle, with gaps in regulatory frameworks leading to inconsistent application and limited impact on actual plastic waste reduction [193].
8.3. Public Awareness and Behavioral Changes
Public awareness and behavioral changes are crucial for effective plastic waste management. Educational campaigns and advocacy are vital in shifting consumer behavior toward more sustainable practices. Programs targeting schools, communities, and businesses aim to increase the understanding of plastic pollution impacts and promote actions such as reducing single-use plastic consumption and adopting recycling practices. The “Plastic Pollution Coalition” and other organizations have raised awareness and driven policy changes through targeted outreach and educational initiatives.
Several case studies have demonstrated the efficacy of comprehensive waste management strategies and targeted interventions in mitigating microplastic pollution. For example, San Francisco’s zero-waste program, characterized by stringent plastic bag bans and robust recycling/composting infrastructure, achieved an impressive 80% waste diversion rate [194]. The “Beat the Microbead” campaign’s success in securing legislative bans on microbeads in personal care products underscores the impact of concerted public and policy efforts.
Technological solutions along with innovations in plastic waste management through chemical and enzymatic recycling have demonstrated high efficiencies with removal rates often exceeding 90% for MPs and NPs and contribute significantly to reducing environmental plastic loads by enhancing circularity. But these technological approaches alone are insufficient to fully mitigate plastic pollution due to practical limitations, operational costs, and variability in environmental conditions. Regulatory measures, including bans on single-use plastics, extended producer responsibility programs, and plastic taxation, establish the framework for controlling plastic production and disposal. While these policies have successfully reduced certain plastic sources, enforcement challenges, limited scope, and industry resistance constrain their overall effectiveness. Complementing regulations, public awareness campaigns, promoting the 5R concept (Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover) together with behavioral interventions—targeting consumers, schools, and communities—are essential to encourage the sustainable practices, minimize plastic use, ensure proper recycling, and support compliance with regulatory measures to reduce the overall plastic waste production. A comprehensive management strategy emerges when technological, regulatory, and behavioral approaches are combined synergistically. Advance treatment technologies can remove residual MPs and NPs from effluents, while regulations minimize new plastic inputs into the environment, and public engagement ensures adoption of sustainable consumption and recycling behaviors. San Francisco’s zero-waste program and the “Beat the Microbead” campaign, exemplify the effectiveness of integrated approaches, demonstrating that coordinated policy, technological implementation, and public participation can achieve substantial reductions in plastic pollution.
9. Future Perspective
MP and NP pollution in aquatic environments has become a major global concern because of its widespread occurrence and persistent nature. Early MP research focused primarily on marine systems, but studies have now expanded to encompass freshwater and other aquatic environments worldwide. NPs, in particular, have recently gained significant attention because of their smaller size (~100 nm) and higher toxicity, posing considerable risks to both aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Despite being recognized as emerging contaminants, many critical scientific questions remain unresolved, as numerous factors complicate the study and management of MPs and NPs. Addressing these knowledge gaps is essential for improving our understanding and developing effective mitigation strategies. Key areas requiring further investigation include environmental interactions, ecotoxicological effects, social and cultural influences, technological advancements, and interdisciplinary approaches for research and policy development.
9.1. Interactions with Contaminants and Long-Term Climatic Impact
A key research priority is understanding interactions between MPs and NPs with co-occurring contaminants such as heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants, and emerging chemicals. These interactions can influence particle aging, surface biofilm formation, and environmental persistence due to their heterogeneous nature and complex physicochemical properties. Extreme climatic events (e.g., hurricanes, floods, storm surges) can accelerate transport, redistribute associated contaminants, and modify ecosystem exposure patterns, underscoring the urgent need to evaluate the combined effects of contamination and climate variability on the fate and behavior of MPs and NPs. Future work should incorporate AI-based predictive simulations to anticipate the fate and transport of these plastic particles under varying climate scenarios.
9.2. Ecotoxicological Effects of Direct and Indirect Exposure on Living Biota
High-priority studies should focus on chronic and acute responses to the ecotoxicological impacts of MPs and NPs along with their maximum allowable limit on human health together with other aquatic and terrestrial species and plantss. Particular emphasis is needed to address the effects of both direct and indirect exposure over short and long durations. Developing comprehensive ecotoxicology databases will enable the assessment of thresholds for safe exposure and inform regulatory guidelines. Future research should address the trophic transfer, bioaccumulation, and food web implications, including plant uptake and potential transfer to humans and other biota. Understanding these pathways is vital for assessing the broader ecological risks and ensuring food safety.
9.3. Social and Cultural Factors Influencing Research
Future research should incorporate citizen science platforms enhanced by mobile apps and blockchain-based plastic tracking systems to improve community engagement and accountability to analyze how social and cultural factors influence the rate of contamination in water. Understanding these factors can help in designing more effective public awareness campaigns and community-based interventions aimed at reducing plastic pollution.
9.4. Technological and Methodological Advancements
Technological and methodological innovations are essential to furthering the progress of MP and NP research. A standard protocol for sample collection analysis is required to ensure consistency and reliability in research findings. As current research on MP and NP are heavily lab-intensive and time-consuming, highlighting the need for innovations in rapid, field-deployable detection tools, biosensors, automated analytical techniques and more sensitive removal methods to accelerate monitoring, reduce laboratory dependency, and allow real-time assessment of MP/NP pollution that can streamline laboratory work and provide rapid preliminary assessments of pollution levels. Also, the adoption of alternative sustainable materials, coupled with automated waste management systems, offers transformative potential to minimize plastic dependence while enhancing efficiency and reliability in recycling and disposal practices.
9.5. Interdisciplinary Approaches for Collaborative Research and Policymaking and Regular Monitoring
Effectively addressing the multifaceted challenge of micro- and nanoplastic pollution necessitates a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach that integrates environmental science, public health, and policymaking. Collaborative research is crucial for developing robust strategies for mitigation and management to address complex challenges. Integrating insights from diverse fields, such as public health, with environmental science can enhance risk assessment, inform public health guidelines and support the development of effective and equitable policies. Effective policy development necessitates close cooperation between researchers and policymakers to design regulations that are scientifically sound, equitable, and sustainable.
10. Conclusions
The annual inflow of microplastics into the ocean was estimated at 0.3 Mt in 2019 and is projected to increase to 0.8 Mt per year by 2060, representing a threefold rise in MPs and NPs accumulation within aquatic systems [191]. This review provides a comprehensive overview of MP and NP pollution in aquatic systems, with a focus on surface waters worldwide. We synthesized findings from recent high-impact studies across different regions to assess the current status of these pollutants. This review reveals that much of the research has been conducted in Asia, particularly in China and India, covering both marine and freshwater environments. In Europe, studies have focused primarily on wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), which, despite removing more than 95% of MP and NP still contribute substantial daily loads to the environment. These pollutants have been detected in highly populated urban centers as well as in remote areas, including Arctic snow, underscoring their ubiquity. Research evidence demonstrates the ingestion of MPs and NPs across diverse aquatic taxa, from zooplankton to apex predators, and their detection in human blood, lungs, and other tissues, alongside documented ecological and health effects. NPs are considered to pose comparatively greater risks than MPs in some cases due to their nanoscale dimensions, which facilitate translocation across biological barriers, increased cellular uptake, and subsequent disruption of critical physiological processes. Given their widespread presence, concentration and toxicity, these tiny plastic particles should now be recognized as major environmental contaminants, warranting continuous monitoring rather than one-time sampling and stricter enforcement of a regulatory framework to reduce the production of plastic and enhance plastic waste management. In addition, there are still some unanswered questions related to the health hazards of this pollutant for both aquatic and terrestrial biota to investigate their long-term ecological impacts, potential health effects from short- and long-term exposure, and toxicity as both homogeneous and heterogeneous pollutants. Eventually mitigating the impacts of a combination of technological innovation, robust governance, and sustained public engagement is necessary to safeguard aquatic ecosystems and protect aquatic biota and humans from the pervasive and escalating risks associated with MP and NP pollution, which are invisible and imperceptible but silently pollute our environment like unseen enemies.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data was generated in this study. All data supporting the findings of this review are available within the cited literature.
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted at Florida International University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), AR (Aromatic Resin), CA (Cellulose Acetate), CEL (Cellophane), CMC (Chemically Modified Cellulose), EPR (Ethylene-Propylene Copolymer), EPS (Expanded Polystyrene), EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate), HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), PA (Polyamide or Nylon), PAcr (Polyacrylate), PAc (Polyacrylic), PANMA (Poly(acrylonitrile-co-methyl acrylate)), PC (Polycarbonate), PE (Polyethylene), PE-co-PS (Poly(ethylene-co-styrene)), PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate), PMP (Poly(4-methyl-1-pentene)), PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate), PES (Polyester), PO (Polyolefin), PS (Polystyrene), PSA (Polystyrene Acrylate Ester), PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), RY (Rayon), and UFO (Universal Filtering Object).
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganmohan. Annual Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2022. Statista. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moteallemi, A.; Dehghani, M.H.; Momeniha, F.; Azizi, S. Nanoplastics as Emerging Contaminants: A Systematic Review of Analytical Processes, Removal Strategies from Water Environments, Challenges and Perspective. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, S.; Köper, I.; Mata, J.P.; McGillivray, D.J. Reviewing Nanoplastic Toxicology: It’s an Interface Problem. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental Exposure to Microplastics: An Overview on Possible Human Health Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lett, Z.; Hall, A.; Skidmore, S.; Alves, N.J. Environmental Microplastic and Nanoplastic: Exposure Routes and Effects on Coagulation and the Cardiovascular System. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilapitiya, P.G.C.N.T.; Ratnayake, A.S. The World of Plastic Waste: A Review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sebille, E.; Wilcox, C.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Hardesty, B.D.; van Franeker, J.A.; Eriksen, M.; Siegel, D.; Galgani, F.; Law, K.L. A Global Inventory of Small Floating Plastic Debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.S.; Billah, M.M.; Ali, M.M.; Bhuiyan, M.K.A.; Guo, L.; Mohinuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.B.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Yan, M.; et al. Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Toxicity, Removal, and Remediation Strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Adu, F.A.; Oyebamiji, A.K.; Bamisaye, A.; Adigun, R.A.; Olasoji, S.O.; Ogunjinmi, O.E. Microplastics Toxicity, Detection, and Removal from Water/Wastewater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of Antibiotics on Microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, Z.; Liang, X. Ecotoxicoproteomic Assessment of Microplastics and Plastic Additives in Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 36, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to Marine Pollution by Washing Your Face: Microplastics in Facial Cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, Q.; Li, P.; Liu, J. Sampling of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Environmental Matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Fraterrigo Garofalo, S.; Migliavacca, A.; Tommasi, T. Tackling Marine Microplastics Pollution: An Overview of Existing Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jin, M.; Tao, P.; Wang, Z.; Xie, W.; Yu, X.; Wang, K. Assessment of Microplastics Derived from Mariculture in Xiangshan Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242 Pt B, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEachern, K.; Alegria, H.A.; Kalagher, A.L.; Hansen, C.; Morrison, S.; Hastings, D. Microplastics in Tampa Bay, Florida: Abundance and Variability in Estuarine Waters and Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 148, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Mohd Khalik, W.M.A.; Ibrahim, Y.S.; Tuan Anuar, S.; Govindasamy, S.; Baharuddin, N.F. Microplastics Analysis in Malaysian Marine Waters: A Field Study of Kuala Nerus and Kuantan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Jia, W.; Qin, X. LDPE Microplastic Films Alter Microbial Community Composition and Enzymatic Activities in Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Ubeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, A.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic Debris in the Open Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, V.; Andrade-Garda, J.M.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Impact of Weathering on the Chemical Identification of Microplastics from Usual Packaging Polymers in the Marine Environment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritse, J.; Leslie, H.A.; de Tender, C.A.; Devriese, L.I.; Vethaak, A.D. Fragmentation of Plastic Objects in a Laboratory Seawater Microcosm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Cai, S.; Huang, J. Microplastics in the Northwestern Pacific: Abundance, Distribution, and Characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestrova, K.; Stepanova, N. The Distribution of Microplastics in the Surface Layer of the Atlantic Ocean from the Subtropics to the Equator According to Visual Analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Tian, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Microplastic Abundance, Distribution, and Composition in the Mid-West Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.; Webster, L. Microplastics in Sea Surface Waters around Scotland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covernton, G.A.; Pearce, C.M.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Chastain, S.G.; Ross, P.S.; Dower, J.F.; Dudas, S.E. Size and Shape Matter: A Preliminary Analysis of Microplastic Sampling Technique in Seawater Studies with Implications for Ecological Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, V.; Litti, L.; Lavagnolo, M.C. Microplastic Pollution in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean Surface Water: How the Sampling Approach Influences the Extent of the Issue. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 174561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.; Zhu, L.; Jabeen, K.; Li, C.; Wei, N.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Li, D. Vertical Distribution of Microplastics in the Western Pacific Warm Pool: In Situ Results Comparison of Different Sampling Method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 403, 135722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.; Hildebrandt, L.; Zimmermann, T.; El Gareb, F.; Fischer, E.K.; Pröfrock, D. Quantification and Characterization of Microplastics in Surface Water Samples from the Northeast Atlantic Ocean Using Laser Direct Infrared Imaging. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhhalko, N.; Kuddithamby, G.; Vianello, A.; Rotander, A.; Vidal Liñán, L.; Beiras, R.; Falcou Préfol, M.; Town, R.M.; Hylland, K.; Morin, B.; et al. Microplastics (10 µm–5 mm) in European Atlantic Coastal Waters. Environ. Adv. 2025, 21, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, K.; Vianello, A.; Almeda, R.; Iordachescu, L.; Rotander, A. Comparison of Two Pump-Based Systems for Sampling Small Microplastics (>10 μm) in Coastal Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uurasjärvi, E.; Pääkkönen, M.; Setälä, O.; Koistinen, A.; Lehtiniemi, M. Microplastics Accumulate to Thin Layers in the Stratified Baltic Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönlau, C.; Karlsson, T.M.; Rotander, A.; Nilsson, H.; Engwall, M.; van Bavel, B.; Kärrman, A. Microplastics in Sea-Surface Waters Surrounding Sweden Sampled by Manta Trawl and In Situ Pump. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 111019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, D.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.-K.; Song, Y.K.; Shim, W.J. Abundance and Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Seawaters of the Incheon/Kyeonggi Coastal Region. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulka, T.; Proskurowski, G.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Meyer, D.W.; Law, K.L. The Effect of Wind Mixing on the Vertical Distribution of Buoyant Plastic Debris. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L07601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Deus, B.C.T.; Costa, T.C.; Altomari, L.N.; Brovini, E.M.; Duque de Brito, P.S.; Cardoso, S.J. Coastal Plastic Pollution: A Global Perspective. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 203, 116478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Niu, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, B.-T.; Wang, G.; Yue, W.; Kong, X.; Zhu, J. Distribution of Microplastics in Surface Water of the Lower Yellow River Near Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Kooi, M.; Erich, M.W.; Primpke, S.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Dekker, S.C.; Koelmans, A.A.; van Wezel, A.P. A Systems Approach to Understand Microplastic Occurrence and Variability in Dutch Riverine Surface Waters. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Svipsta, S.; Bikse, J.; Dimante-Deimantovica, I. Microplastics in FLOW: Seasonal Patterns in Major Latvian Rivers. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.I.; Barrick, A.; Hoang, T.C. Discovery of Microplastics in the Alabama River: Distributions, Transport and Loads, Sources, and Relative Comparison with World Rivers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Karakaya, G.; Arısoy, G.; Çelik, B. Comprehensive Analysis of Microplastics in Water, Sediment and Fish from a Large Recreational Lake. Environ. Res. 2025, 279 Pt 1, 121799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebremedhine, M.G.; Tekle, S.G.; Terfie, T.A.; Aragaw, T.A. Occurrence of Microplastics in Water and Sediment of a Highly Urbanized Lake Ecosystem in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leterme, S.C.; Tuuria, E.M.; Drummond, W.J.; Jones, R.; Gascooke, J.R. Microplastics in Urban Freshwater Streams in Adelaide, Australia: A Source of Plastic Pollution in the Gulf St Vincent. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnikrishnan, V.; Anusree, S.; Shaikh, I.; D’Costa, P.M.; Chandran, T.; Valsan, G.; Vandana, T.U.; Tamrakar, A.; Paul, M.M.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; et al. Insights into the Seasonal Distribution of Microplastics and Their Associated Biofilms in the Water Column of Two Tropical Estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordós, G.; Urbányi, B.; Micsinai, A.; Kriszt, B.; Palotai, Z.; Szabó, I.; Hantosi, Z.; Szoboszlay, S. Identification of Micro-Plastics in Fishponds and Natural Freshwater Environments of the Carpathian Basin, Europe. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic Debris in 29 Great Lakes Tributaries: Relations to Watershed Attributes and Hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Wastewater Treatment Plants as a Pathway for Microplastics: Development of a New Approach to Sample Wastewater-Based Microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater Treatment Works (WwTW) as a Source of Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C.; Herring, C. (Eds.) Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-48; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Marine Debris Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Munno, K.; Helm, P.A.; Jackson, D.A.; Rochman, C.; Sims, A. Impacts of Temperature and Selected Chemical Digestion Methods on Microplastic Particles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariano, S.; Tacconi, S.; Fidaleo, M.; Rossi, M.; Dini, L. Micro and Nanoplastics Identification: Classic Methods and Innovative Detection Techniques. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 636640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, B.O.; Kanyathare, B.; Roussey, M.; Peiponen, K.-E. A Prototype of a Portable Optical Sensor for the Detection of Transparent and Translucent Microplastics in Freshwater. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolai, E.; Pizzoferrato, R.; Li, Y.; Frattegiani, S.; Nucara, A.; Costa, G. A New Optical Method for Quantitative Detection of Microplastics in Water Based on Real-Time Fluorescence Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iri, A.H.; Shahrah, M.H.A.; Ali, A.M.; Qadri, S.A.; Erdem, T.; Ozdur, I.T.; Icoz, K. Optical Detection of Microplastics in Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 63860–63866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertsberg, S.; Knepper, T.P. Validation of an FT-IR Microscopy Method for the Determination of Microplastic Particles in Surface Waters. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, D.; Pei, J.; Fei, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Current Status and Future Prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 18, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, G.; Sauerbier, P.; Schmidt, T.C.; Schram, J. Robust Automatic Identification of Microplastics in Environmental Samples Using FTIR Microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9656–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikac, L.; Rigó, I.; Himics, L.; Tolić, A.; Ivanda, M.; Veres, M. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for the Detection of Microplastics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 608, 155239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gibson, C.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M.; Fang, C. Identification and Visualization of Microplastics/Nanoplastics by Raman Imaging (I): Down to 100 nm. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Wang, N.; Yang, H.; Yang, J.; Bai, H. Detection of Microplastics Based on Spatial Heterodyne Raman Spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 283, 121712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gniadek, M.; Dąbrowska, A. The Marine Nano- and Microplastics Characterization by SEM-EDX: The Potential of the Method in Comparison with Various Physical and Chemical Approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 148, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, A.; Mielańczuk, M.; Syczewski, M. The Raman Spectroscopy and SEM/EDS Investigation of the Primary Sources of Microplastics from Cosmetics Available in Poland. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Bai, Q.; Zheng, R.; Li, P.; Liu, R.; Yu, S.; Liu, J. Mass Concentration, Spatial Distribution, and Risk Assessment of Small Microplastics (1–100 μm) and Nanoplastics (<1 μm) in the Surface Water of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Res. 2025, 285, 122214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoffo, E.D.; Thomas, K.V. Mass Quantification of Nanoplastics at Wastewater Treatment Plants by Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, W.; Houthuijs, K.J.; Brits, M.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Lamoree, M.H.; Béen, F.M. Improved Multivariate Quantification of Plastic Particles in Human Blood Using Nontargeted Pyrolysis GC–MS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. Analyzing Microplastics with Nile Red: Emerging Trends, Challenges, and Prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423 Pt B, 127171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengstmann, E.; Fischer, E.K. Nile Red Staining in Microplastic Analysis: Proposal for a Reliable and Fast Identification Approach for Large Microplastics. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Koydemir, H.C.; Koutnik, V.S.; Tseng, D.; Ozcan, A.; Mohanty, S.K. Smartphone-Enabled Rapid Quantification of Microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y. Integrated Sample Processing and Counting Microfluidic Device for Microplastics Analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1261, 341237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.; Kim, H. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Groundwater: Occurrence, Analysis, and Identification. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 44, e00246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, F.; Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. A Review of Microplastic Pollution in Seawater, Sediments and Organisms of the Chinese Coastal and Marginal Seas. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Wei, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, L.; Pan, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Duan, C. Current Status of Microplastic Pollution in China’s Aquatic Environment and Its Interactions with Metal Pollutants on Aquatic Organisms. Water Res. X 2025, 28, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, L.; Fernández Severini, M.D.; Rimondino, G.N.; Colombo, C.V.; Prieto, G.; Forero López, A.D.; Carol, E.S. Assessment of Meso- and Microplastics Distribution in Coastal Sediments and Waters at the Middle Estuary of the Río de la Plata, Argentina (SW Atlantic Ocean). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 170026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskuła, P.; Astel, A.; Pawlik, M. Microplastics in Seawater and Fish Acquired from the Corresponding Fishing Zones of the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 211, 117485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriu, M.; Allinson, G. Microplastics in the Mediterranean Marine Environment: A Combined Bibliometric and Systematic Analysis to Identify Current Trends and Challenges. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2022, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajšt, T.; Bizjak, T.; Palatinus, A.; Liubartseva, S.; Kržan, A. Sea Surface Microplastics in Slovenian Part of the Northern Adriatic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Wei, N.; Zong, C.; Li, D. Pelagic Microplastics in Surface Water of the Eastern Indian Ocean during Monsoon Transition Period: Abundance, Distribution, and Characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.; Mawii, L.; Rao, V.R.; Anitha, G.; Mishra, P.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Kumar, V.A.; Murthy, M.R.; Gvm, G. Characterization of Plastic Debris from Surface Waters of the Eastern Arabian Sea–Indian Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatema, K.; Sumon, K.A.; Moon, S.M.; Alam, J.; Hasan, S.J.; Uddin, H.; Arakawa, H.; Rashid, H. Microplastics and Mesoplastics in Surface Water, Beach Sediment, and Crude Salt from the Northern Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh Coast. J. Sediment. Environ. 2023, 8, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emberson-Marl, H.; Coppock, R.L.; Cole, M.; Godley, B.J.; Mimpriss, N.; Nelms, S.E.; Lindeque, P.K. Microplastics in the Arctic: A Transect through the Barents Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1241829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, S.; Berezina, A.; Zhdanov, I.; Yakushev, E. Microplastic Fate in Arctic Coastal Waters: Accumulation Hotspots and Role of Rivers in Svalbard. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1392680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Williams, K.; Cole, M.; Rowlands, E.; Waluda, C.; Manno, C.; Primpke, S.; Galloway, T. Microplastics in Antarctica—A Plastic Legacy in the Antarctic Snow? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15976–15986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, N.; Metian, M.; Oberhaensli, F.; Sznaider, F.; Ruberto, L.; Vodopivez, C.; Mac Cormack, W.; Alonso Hernandez, C. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in the Antarctic Coastal Waters Using Laser Direct Infrared (LDIR). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 221, 118534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Collard, F.; Fabres, J.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Provencher, J.F.; Rochman, C.M.; van Sebille, E.; Tekman, M.B. Plastic Pollution in the Arctic. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, S.; Berezina, A.; Lusher, A.L.; Zhdanov, I.; Silvestrova, K.; Zavialov, P.; van Bavel, B.; Yakushev, E. Microplastic Variability in Subsurface Water from the Arctic to Antarctica. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, M.; Lory, C.; Le Juge, C.; Blancho, F.; Dia, A.; Grassl, B.; El Hadri, H.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gigault, J. Nanoplastics on the Coast Exposed to the North Atlantic Gyre: Evidence and Traceability. NanoImpact 2020, 20, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, A.J.; Brooks, L.S.R.; Reid, W.D.K.; Piertney, S.B.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Linley, T.D. Microplastics and Synthetic Particles Ingested by Deep-Sea Amphipods in Six of the Deepest Marine Ecosystems on Earth. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 180667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Mei, X.; Mi, B.-B.; Yang, H.; Han, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lü, W.-C. Current Status and Cause Analysis of Microplastic Pollution in Sea Areas in China. China Geol. 2022, 5, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Picking Up Litter: Pointless Exercise or Powerful Tool in the Battle to Beat Plastic Pollution? United Nations Environment Programme. 2023. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/picking-litter-pointless-exercise-or-powerful-tool-battle-beat-plastic (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Jang, M.; Shim, W.J.; Cho, Y.; Han, G.M.; Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H. A Close Relationship between Microplastic Contamination and Coastal Area Use Pattern. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.C.; Allen, D.; Allen, S.; Maselli, V.; LeBlanc, A.; Kelleher, L.; Krause, S.; Walker, T.R.; Cohen, M. Transport and Deposition of Ocean-Sourced Microplastic Particles by a North Atlantic Hurricane. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in Freshwater Eco-Systems: What We Know and What We Need to Know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2017, 29, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbić, J.; Helm, P.; Athey, S.; Rochman, C.M. Microplastics Entering Northwestern Lake Ontario Are Diverse and Linked to Urban Sources. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in Freshwater Systems: A Review of the Emerging Threats, Identification of Knowledge Gaps and Prioritization of Research Needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhao, R.; Meng, X. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Microplastics in Surface Water of Typical Urban Rivers in North China, Risk Assessment and Influencing Factors. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 273, 104626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Liu, S.; Liao, H.; Yue, Q.; Wang, J. Environmental Nanoplastics Quantification by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry in the Pearl River, China: First Insights into Spatiotemporal Distributions, Compositions, Sources and Risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, C.; Phyllei, S.W.E.; Bhatt, S.; Chatterjee, S. Microplastic Surge in the Ariyankuppam River, Puducherry, India: A Study on Abundance, Characterization, and Pollution Load Index. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 274, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owowenu, E.K.; Nnadozie, C.F.; Akamagwuna, F.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Odume, O.N. Occurrence and Distribution of Microplastics in Functionally Delineated Hydraulic Zones in Selected Rivers, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 379, 126544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrows, A.P.W.; Christiansen, K.S.; Bode, E.T.; Hoellein, T.J. A Watershed-Scale, Citizen Science Approach to Quantifying Microplastic Concentration in a Mixed Land-Use River. Water Res. 2018, 147, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, B.; Su, L.; Kellar, C.; Craig, N.J.; Keough, M.J.; Pettigrove, V. Identification of Microplastics in Surface Water and Australian Freshwater Shrimp Paratya australiensis in Victoria, Australia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansoar-Rodríguez, Y.; Rimondino, G.N.; Bertrand, L.; Rivetti, N.; Colombo, C.V.; Bistoni, M.A.; Amé, M.V. Microplastic Distribution and Potential Ecological Risk Index in a South American Sparsely Urbanized River Basin: Focus on Abiotic Matrices and the Native Fish Jenynsia lineata. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierdomenico, M.; Morgana, S.; Latino Chiocci, F. First Report of Microplastics in Water and Sediments of the Alkaline Bagno dell’Acqua Lake (Pantelleria Island, Southern Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Spanjer, A.R.; Rosen, M.R.; Thom, T. Microplastics in Lake Mead National Recreation Area, USA: Occurrence and Biological Uptake. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Su, L.; Craig, N.J.; Du, F.; Wu, C.; Shi, H. Comparison of Microplastic Pollution in Different Water Bodies from Urban Creeks to Coastal Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkola, A.; Runkel, R.L.; Schneidewind, U.; Murphy, S.F.; Kelleher, L.; Sambrook Smith, G.H.; Nel, H.A.; Lynch, I.; Krause, S. Prevailing Impacts of River Management on Microplastic Transport in Contrasting US Streams: Rethinking Global Microplastic Flux Estimations. Water Res. 2023, 240, 120112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyena, A.P.; Tekeme, M.E.; Uwakwe, J.C.; Aderibigbe, D.; Sam, K. Baseline Characterization of Microplastics in Surface Water, Sediment, and Seafood from the Escravos Estuary, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2025, 27, e02591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, D.S.; Hayhurst, B.A.; Grubisich, S.; Schneider, N.; Martin, O.; DeNyse, C.; Chomiak, K.M.; Tyler, A.C.; Eddingsaas, N.C. A Bellwether for Microplastic in Wetland Catchments in the Great Lakes Region. J. Great Lakes Res. 2024, 50, 102411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bydalek, F.; Ifayemi, D.; Reynolds, L.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Wenk, J. Microplastic Dynamics in a Free Water Surface Constructed Wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858 Pt 3, 160113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, J.; Zhao, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Coexposure of Microplastics with Heavy Metals Increases Environmental Pressure in the Endangered and Rare Wildlife Reserve: A Case Study of the Zhalong Wetland Red-Crowned Crane Nature Reserve, Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363 Pt 2, 125287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Dixon, S.J. Microplastics: An Introduction to Environmental Transport Processes. WIREs Water 2018, 5, e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.A.; Geronimo, F.K.; Reyes, N.J.; Kim, L.H. Characterization and Comparison of Microplastic Occurrence in Point and Nonpoint Pollution Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 148939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertel, B.M.; Weinstein, J.E.; Gray, A.D. Rising Seas and Roadway Debris: Microplastic and Low-Density Tire Wear Particles in Street-Associated Tidal Floodwater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.; Carbery, M.; Kuttykattil, A.; Senthirajah, K.; Lundmark, A.; Rogers, Z.; Suresh, S.C.B.; Evans, G.; Palanisami, T. Improved Methodology to Determine the Fate and Transport of Microplastics in a Secondary Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Nguyen, N.-B.-T.; Ngo, T.-P.; Lai, M.-T.; Nguyen, P.-D.; Pham, N.-H.; Le, T.-M.-T. Microplastics in Wastewater and Sludge from Centralized Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 12, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viitala, M.; Tsering, T.; Hyvönen, M.; Reinikainen, S.-P.; Mänttäri, M. Microplastic Budgets and Discharges to Lake Saimaa from Three Finnish Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.; Kerpen, J.; Prediger, J.; Barkmann, L.; Müller, L. Determination of the Microplastics Emission in the Effluent of a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant Using Raman Microspectroscopy. Water Res. X 2019, 2, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel Jessieleena, A.; Premkumar, R.; Iniyan, K.E.; Nambi, I.M. Distribution of Microplastics in Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant: Exploring Ferrofluid Assisted Magnetic Separation for Microplastics Removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 76, 108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I.R.W.; Raj, A.S.; Viaroli, S. Microplastic Removal, Identification and Characterization in Chennai Sewage Treatment Plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Huo, M.; Coulon, F.; Ali, M.; Tang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ying, Z.; Wang, B.; Song, X. Understanding Microplastic Presence in Different Wastewater Treatment Processes: Removal Efficiency and Source Identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridall, A.; Farrar, E.; Dansby, M.; Ingels, J. Influence of Wastewater Treatment Plants and Water Input Sources on Size, Shape, and Polymer Distributions of Microplastics in St. Andrew Bay, Florida, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.-J.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, S.-C.; Sun, X.-D.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Wang, S.-G. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in the acute inhibition of activated sludge by polystyrene nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.; Nair, A.T. The Fate of Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants: An Overview of Source and Remediation Technologies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Maximenko, N.A.; Proskurowski, G.; Peacock, E.E.; Hafner, J.; Reddy, C.M. Plastic Accumulation in the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. Science 2010, 329, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Valsami-Jones, E. Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: The Hidden Impact of Aging on Fate and Toxicity. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1,000 Rivers Account for 80% of Global Riverine Plastic Emissions into the Ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garello, N.A.; Blettler, M.C.M.; Espínola, L.A.; Rodrigues, S.; Rimondino, G.N.; Wantzen, K.M.; Rabuffetti, A.P.; Girard, P.; Malanca, F.E. Microplastics Distribution in River Side Bars: The Combined Effects of Water Level and Wind Intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 16540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Wan Mohd Khalik, W.M.A.; Ong, M.C.; Shao, Y.T.; Pan, H.-J.; Bhubalan, K. Marine Microplastics as Vectors of Major Ocean Pollutants and Its Hazards to the Marine Ecosystem and Humans. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obbard, R.W.; Sadri, S.; Wong, Y.Q.; Khitun, A.A.; Baker, I.; Thompson, R.C. Global Warming Releases Microplastic Legacy Frozen in Arctic Sea Ice. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Worldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradel, A.; Catrouillet, C.; Gigault, J. The Environmental Fate of Nanoplastics: What We Know and What We Need to Know about Aggregation. NanoImpact 2023, 29, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and Fate of Microplastic Particles in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic Implications of Plastic Degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Ruan, J.; Luo, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; et al. Differential Photoaging Effects on Colored Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Physicochemical Properties and Aggregation Kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15656–15666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilinc, Z.; Yesilay, G.; Cetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Rashdan, S.; Hazeem, L.; Bououdina, M.; Kyzas, G.Z. Photodegradation of Polystyrene Microplastics Exposed to Natural Sunlight. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2025, 468, 116462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpa; Basak, N.; Meena, S.S. Microbial Biodegradation of Plastics: Challenges, Opportunities, and a Critical Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Galloway, T.S. Ingestion of Nanoplastics and Microplastics by Pacific Oyster Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14625–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, F.; Yao, Q.; Lin, M.; Zhou, K.; Mi, S.; Pan, H.; Zhao, X. Toxicity Effects and Mechanism of Micro/Nanoplastics and Loaded Conventional Pollutants on Zooplankton: An Overview. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provencher, J.F.; Bond, A.L.; Hedd, A.; Montevecchi, W.A.; Martin, P.; Courchesne, S.J.; Lavers, J.L.; Mallory, M.L. Quantifying Ingested Debris in Marine Megafauna: A Review and Recommendations for Standardization. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1454–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, H.; Jin, S.; Li, R.; Na, G. The Ecotoxicological Effects of Microplastics on Aquatic Food Web, from Primary Producer to Human: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; Choi, M.-J.; Cho, Y.; An, Y.-J. Impact of Nanosized Plastic on the Nutritional Value and Gut Microbiota of Whiteleg Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei via Dietary Exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic Particles Cause Intestinal Damage and Other Adverse Effects in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Nematode (Caenorhabditis elegans). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Giuliani, M.E.; d’Errico, G.; Keiter, S.H.; Cormier, B.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Microplastics as Vehicles of Environmental PAHs to Marine Organisms: Combined Chemical and Physical Hazards to the Mediterranean Mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguso, C.; Grech, D.; Becchi, A.; Ubaldi, P.G.; Lasagni, M.; Guala, I.; Saliu, F. Detection of Microplastics and Phthalic Acid Esters in Sea Urchins from Sardinia (Western Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldeniya, M.U.S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, B.; Yin, J.; Wen, S.; Yuan, L.; Luo, P. Microplastic and Nanoplastic Exposure Induced Transcriptional and Physiological Alterations and Triggered Immune Responses in the Sea Cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 375, 126291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, A.; Strode, E.; Kurach, Ł.; Stachowicz, M. Ecotoxicological Effects of Nanoplastic and Microplastic Polystyrene Particles on Hyalella azteca: A Comprehensive Study on the Impact of Physical and Chemical Surface Properties. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 272, 104574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; He, X.; Xue, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Lin, L.; Qu, Y.; Ward-Fear, G.; et al. Nanoplastic Pollution Changes the Intestinal Microbiome but Not the Morphology or Behavior of a Freshwater Turtle. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başaran Kankılıç, G.; Koraltan, İ.; Erkmen, B.; Çağan, A.S.; Çırak, T.; Özen, M.; Seyfe, M.; Altındağ, A.; Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N. Size-Selective Microplastic Uptake by Freshwater Organisms: Fish, Mussel, and Zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, H.B.; Sohal, N.; Feldmeyer, B.; Pfenninger, M. Size over Substance: Microplastic Particle Size Drives Gene Expression and Fitness Loss in a Freshwater Insect. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 284, 107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Valsalan, S.A. Microplastics in Fish and a Bivalve Species Sampled from Freshwater Environment and Retail Outlets, and the Assessment of Human Exposure. Food Control 2024, 166, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampsonidis, I.; Michailidou, K.; Spritinoudi, K.; Dimitriadi, A.; Ainali, N.M.; Bobori, D.C.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kalogiannis, S. Genotoxicity and Metabolic Changes Induced via Ingestion of Virgin and UV-Aged Polyethylene Microplastics by the Freshwater Fish Perca fluviatilis. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchere, O.; Métais, I.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Lemoing, M.; Feurtet-Mazel, A.; Gonzalez, P.; Daffe, G.; Gigault, J.; Catrouillet, C.; Châtel, A.; et al. Trophic Transfer Effects of PS Nanoplastics and Field-Derived Nanoplastics in the Freshwater Clam Corbicula fluminea. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 277, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, X.; Chen, M.; Yi, H. Removal of Microplastics by Drinking Water Treatment: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tympa, L.-E.; Katsara, K.; Moschou, P.N.; Kenanakis, G.; Papadakis, V.M. Do Microplastics Enter Our Food Chain via Root Vegetables? A Raman Based Spectroscopic Study on Raphanus sativus. Materials 2021, 14, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Song, C.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.S.; Kang, J.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, C. Selective Detection and Tracking of Polyamide Microplastic by Aggregation-Promoted Fluorescent Dye in Environmental Samples, Milk and Live Organisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welden, N.A.; Abylkhani, B.; Howarth, L.M. The Effects of Trophic Transfer and Environmental Factors on Microplastic Uptake by Plaice, Pleuronectes plastessa, and Spider Crab, Maja squinado. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arini, A.; Gigault, J.; Venel, Z.; Bertucci, A.; Baudrimont, M. The Underestimated Toxic Effects of Nanoplastics Coming from Marine Sources: A Demonstration on Oysters (Isognomon alatus). Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozari Asl, R.; Jaafarzadeh Haghighi Fard, N.; Jahedi, F.; Khaksar, M.A.; Shenavar, B. Systematic Review of Pulmonary Toxicity Induced by Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Insights from In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2025, 37, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, J.L.; Stegmeier, S.J.; Allaart, H.A.; Cheney, R.T.; Zhang, P.J.; Mayer, A.G.; Streck, R.J. Inhaled Cellulosic and Plastic Fibers Found in Human Lung Tissue. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1998, 7, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Lan, M.; Chen, C.; Fan, L.; Shen, H.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; Lu, W.; Xu, X.; et al. Geospatial Environmental Sources of Inhaled Microplastics: A Case in Zhuhai, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 496, 139537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Ribeiro Júnior, G.; Galvão, L.D.S.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of Airborne Microplastics in Human Lung Tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Naidu, R.; Fang, C. Toy Building Bricks as a Potential Source of Microplastics and Nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerranti, C.; Martellini, T.; Perra, G.; Scopetani, C.; Cincinelli, A. Microplastics in Cosmetics: Environmental Issues and Needs for Global Bans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W. Cellular Internalization and Release of Polystyrene Microplastics and Nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Xia, P.-F.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Wang, S.-G. Chlorine Disinfection Elevates the Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics to Human Cells by Inducing Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, M.; Iachetta, G.; Tussellino, M.; Carotenuto, R.; Prisco, M.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Valiante, S. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Internalization in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Toxic Effects of Nanoplastics with Different Sizes and Surface Charges on Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells and the Potential Toxicological Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ladd, D.M.; Kaval, N.; Wang, H.-S. Toxicity of Long Term Exposure to Low Dose Polystyrene Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 202, 115489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, M.; Akhtar, M. Cytotoxic Effect of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) and Normal Rat Kidney Cells (NRK52E). J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and Quantification of Plastic Particle Pollution in Human Blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Pérez-Pomeda, I.; Sanchís, J.; Rossini, C.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Cytotoxic Effects of Commonly Used Nanomaterials and Microplastics on Cerebral and Epithelial Human Cells. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, A.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Xue, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Jing, Z.; Xie, J. Microplastics Induce Human Kidney Development Retardation through ATP-Mediated Glucose Metabolism Rewiring. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 137002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Pramanik, S.K.; Monira, S. Understanding the Fragmentation of Microplastics into Nanoplastics and Removal of Nano/Microplastics from Wastewater Using Membrane, Air Flotation and Nanoferrofluid Processes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaranal, N.A.; Subbiah, S.; Mohanty, K. Identification, Extraction of Microplastics from Edible Salts and Its Removal from Contaminated Seawater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczak-Grzesik, M.; Tarach, K.A.; Olszewska, A.; Sobańska, K.; Kowalczyk, A.; Góra-Marek, K. UV–Vis Methodology for Evaluation of Adsorption of Polystyrene Nanoplastics by Zeolite Adsorbents: A Case of Carboxylate-Modified Polystyrene. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Hou, M.; Gao, Z. Polydopamine-Modified Sodium Alginate Hydrogel for Microplastics Removal: Adsorption Performance, Characteristics, and Kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 297, 139947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Shon, H.K.; Jeong, S. Effective Removal of Micro- and Nanoplastics from Water Using Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Mechanisms and Optimization. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 519, 165739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, N.; Peng, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. An Ultralight Sustainable Sponge for Elimination of Microplastics and Nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Lucchini, G.; Torboli, A.; Bruni, L. Flow Cytometry as a Tool for the Rapid Enumeration of 1-μm Microplastics Spiked in Wastewater and Activated Sludge after Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Nie, Y.; Ma, J. Coagulation Performance and Mechanism of Different Novel Covalently Bonded Organic Silicon-Aluminum/Iron Composite Coagulant for As(V) Removal from Water: The Role of Hydrolysate Species and the Effect of Coexisting Microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchakipour, S.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Zarghami Qaretapeh, M.; Dashtian, K. Sustainable Large-Scale Fe3O4/Carbon for Enhanced Polystyrene Nanoplastics Removal through Magnetic Adsorption Coagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongi, W.; Touzi, H.; Sadly, I.; Ben Ouada, H.; Tamarin, O.; Ben Ouada, H. A Novel Impedimetric Sensor Based on Cyanobacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substances for Microplastics Detection. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4738–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Quarta, E.; Giotta, L. The Seaweed Chaetomorpha linum Cultivated in an Integrated Multitrophic Aquaculture System: A New Tool for Microplastic Bioremediation? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangkham, S.; Pitakpong, A.; Kumar, R. Advanced Approaches to Microplastic Removal in Landfill Leachate: Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs), Biodegradation, and Membrane Filtration. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Xu, H.; Hunter, T.N.; Harbottle, D.; Kale, G.M.; Tillotson, M.R. Advanced Polystyrene Nanoplastic Remediation through Electro-Fenton Process: Degradation Mechanisms and Pathways. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, A.; Domínguez, C.M.; Santos, A.; Cotillas, S. Removal of Polystyrene Nanoplastics from Urban Treated Wastewater by Electrochemical Oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363 Pt 2, 132139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, T.; Maksymiuk, K.; Charlton, L.; Koutsos, V.; Chatzisymeon, E. Transformation of Polyester Fiber Microplastics by Sulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Global Plastics Outlook: Policy Scenarios to 2060; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015, H.R. 1321, 114th Congress (2015–2016). Public Law 114-114. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/house-bill/1321/text (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City of San Francisco. Zero Waste Program Annual Report 2021. Available online: https://www.sfenvironment.org/files/events/2021_commission_on_the_environment_annual_report.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).