Field Study and Numerical Modeling to Assess the Impact of On-Site Septic Systems on Groundwater Quality of Jeju Island, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
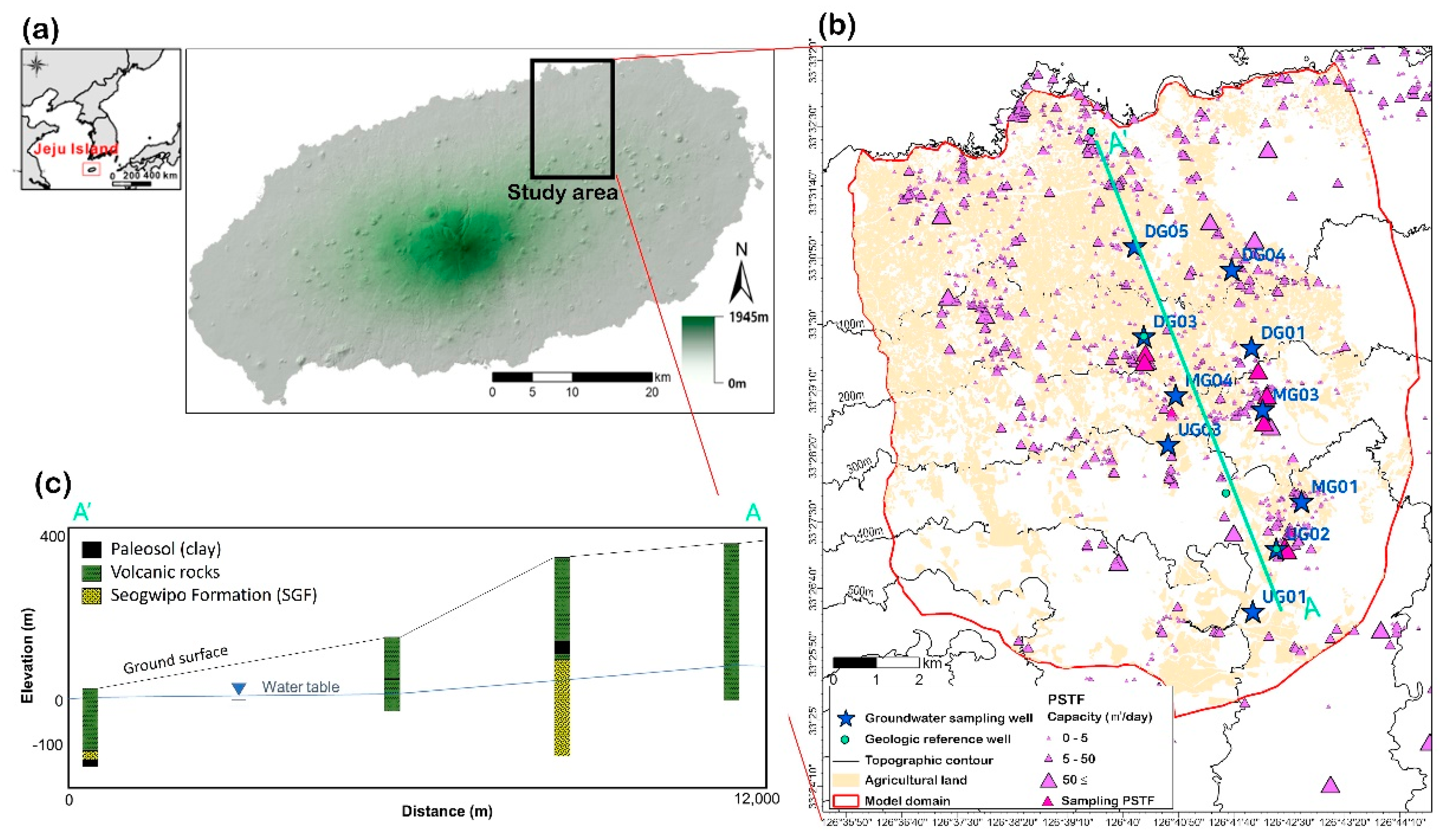
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. PSTFs and Groundwater Sampling
3.2. Estimation of Discharge and N Loading from the PSTFs Effluents
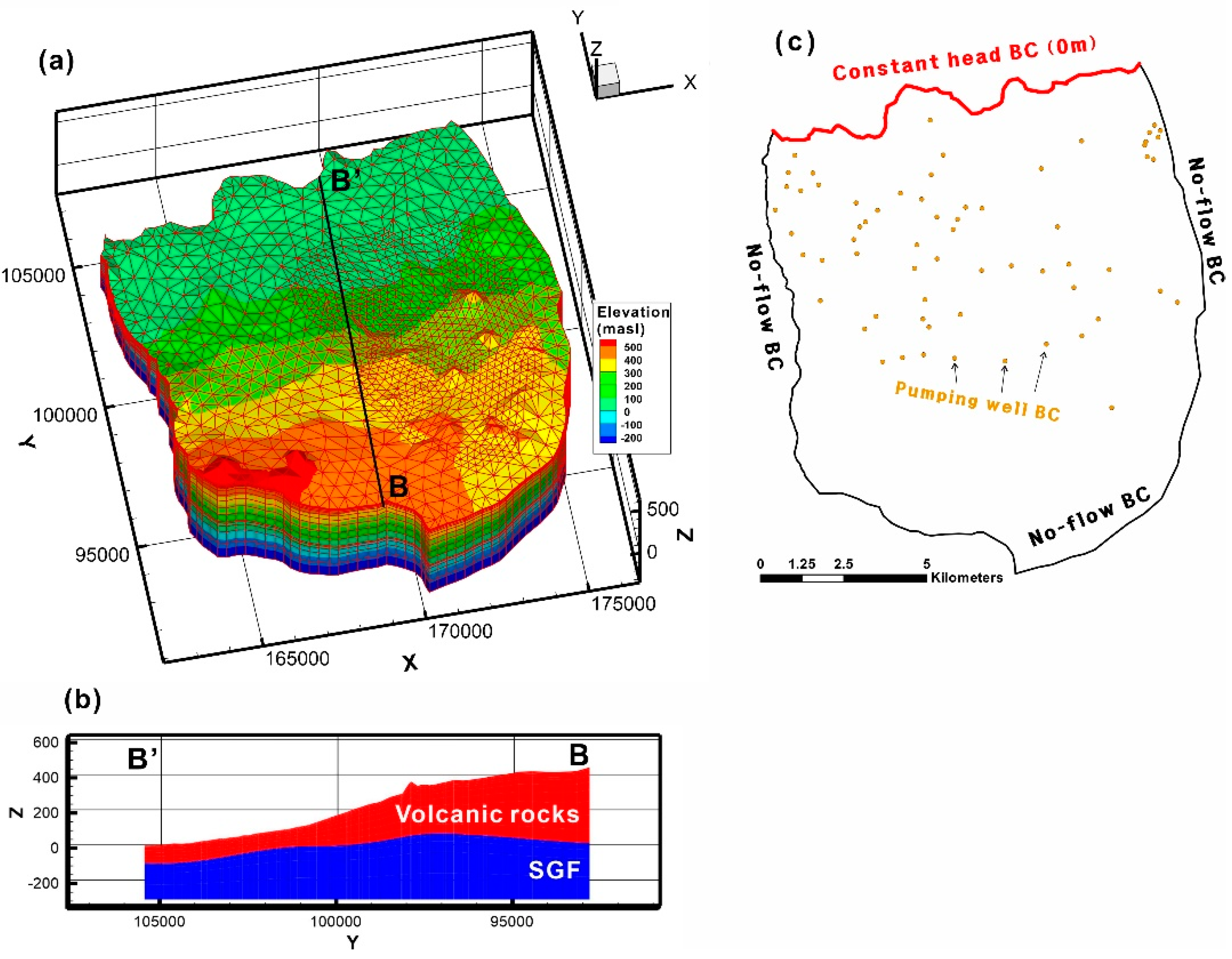
3.3. Model Settings
4. Results and Discussion
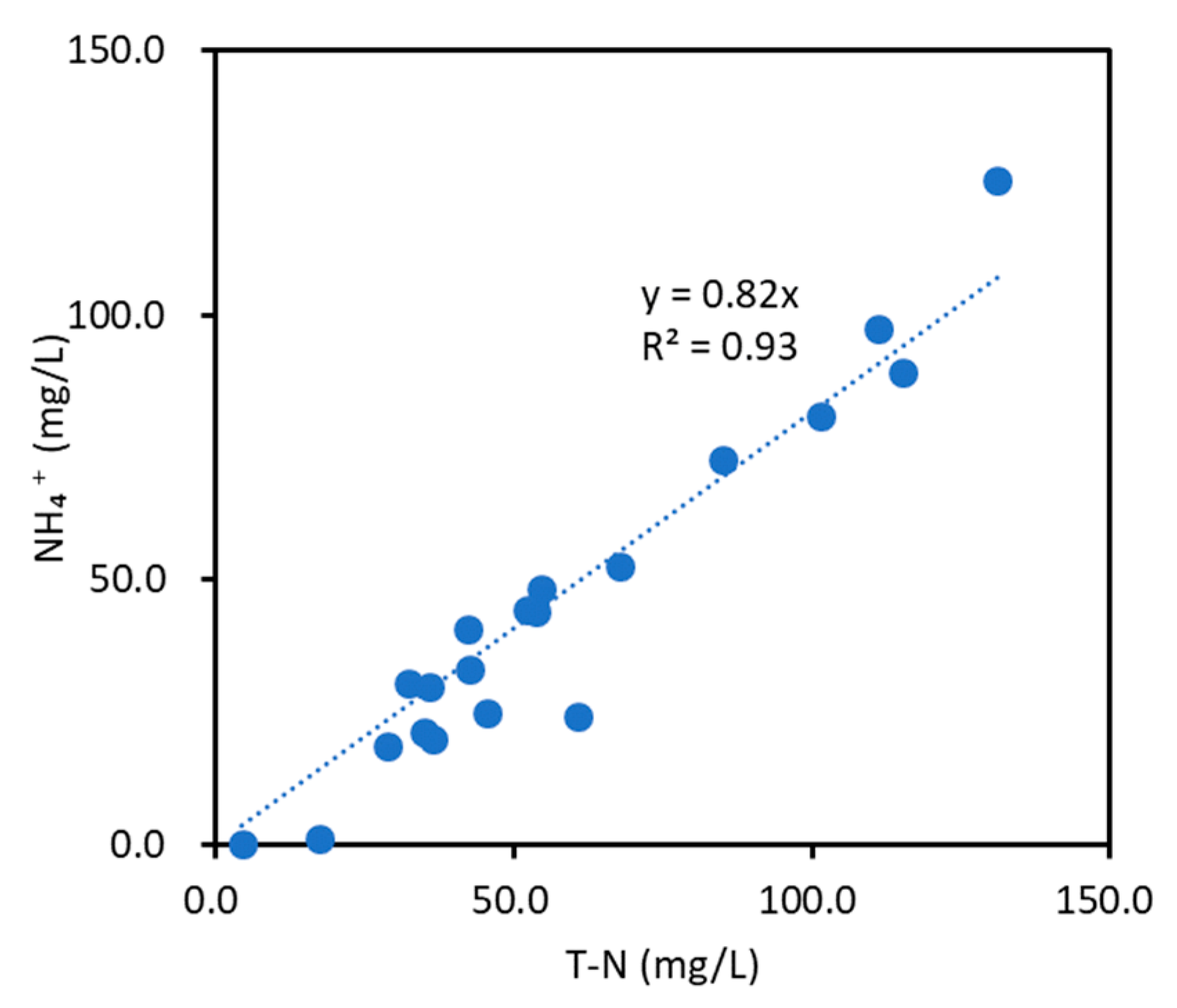
4.1. PSTFs Effluent Quality
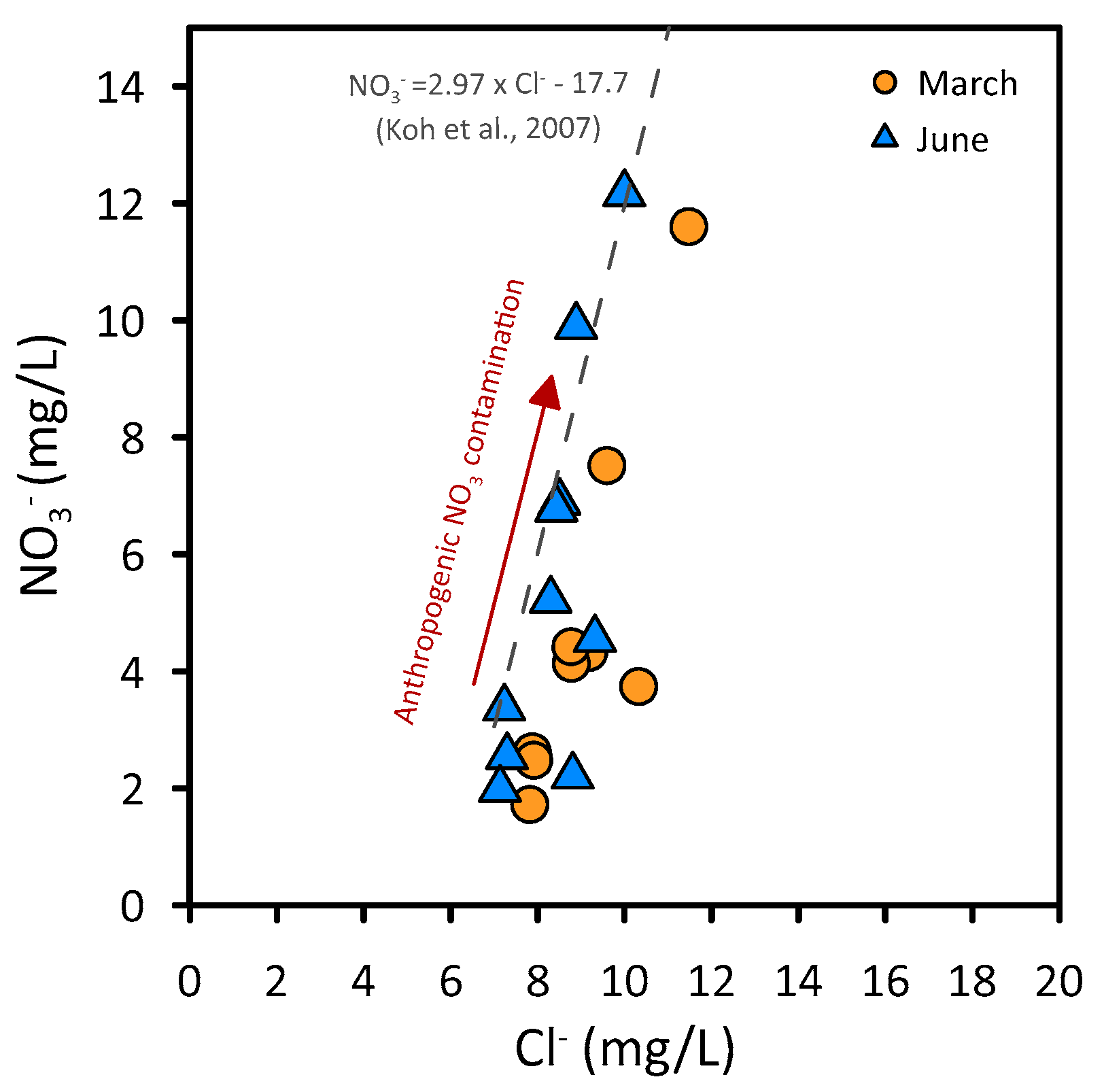
4.2. Groundwater Quality
4.3. Calculation of T-N Loading by PSTFs Effluent
4.4. Numerical Modeling Results
4.4.1. Model Calibration
4.4.2. N Species Transport
4.5. Suggestion of PSTFs Management Strategies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lall, U.; Josset, L.; Russo, T.A. Snapshot of the world’s groundwater challenges. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2020, 45, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Saxena, A. Sources and leaching of nitrate contamination in groundwater. Curr. Sci. 2020, 118, 883–891. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/27226382 (accessed on 7 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Richa, A.; Touil, S.; Fizir, M. Recent advances in the source identification and remediation techniques of nitrate contaminated groundwater: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.H.; Kaown, D.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.K. Nitrate sources, timing, and pathways of a permeable volcanic aquifer system with mixed land use in Jeju Island, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SCF (Scientific Committee on Food). Assessment of dietary intake of nitrates by the population in the European Union, as a consequence of the consumption of vegetables. In Reports on Tasks for Scientific Cooperation: Report of Experts Participating in Task 3.2.3; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- ME (Ministry of Environment). Groundwater Act Enforcement Rules; Ministry of Environment: Sejong City, Republic of Korea, 2024. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/lsInfoP.do?lsiSeq=263417&efYd=20240624&ancYnChk=0#0000 (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Umezawa, Y.; Hosono, T.; Onodera, S.I.; Siringan, F.; Buapeng, S.; Delinom, R.; Yoshimizu, C.; Tayasu, I.; Nagata, T.; Taniguchi, M. Sources of nitrate and ammonium contamination in groundwater under developing Asian megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wu, J.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Pan, X. Does the groundwater nitrate pollution in China pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3640–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Nie, X.; Sun, Y.; Ran, F. The application and potential non-conservatism of stable isotopes in organic matter source tracing. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huno, S.K.; Rene, E.R.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Annachhatre, A.P. Nitrate removal from groundwater: A review of natural and engineered processes. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2018, 67, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, E.; Gómez-Coma, L.; Ortiz, I.; Ortiz, A. Global diagnosis of nitrate pollution in groundwater and review of removal technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.H.; Lee, E.; Kaown, D.; Green, C.T.; Koh, D.C.; Lee, K.K.; Lee, S.H. Comparison of groundwater age models for assessing nitrate loading, transport pathways, and management options in a complex aquifer system. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Sen, R.; Onyekwelu, I.; Wiederstein, T.; Sharda, V. Modeling of Groundwater Nitrate Contamination Due to Agricultural Activities—A Systematic Review. Water 2022, 14, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruzzaman, M.; Pinzon, J.; Oppenheimer, J.; Jacangelo, J.G. Source of nutrients impacting surface waters in Florida: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 109, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducci, L.; Rizzo, P.; Pinardi, R.; Solfrini, A.; Maggiali, A.; Pizzati, M.; Balsamo, F.; Celico, F. What is the impact of leaky sewers on groundwater contamination in urban semi-confined aquifers? A test study related to fecal matter and Personal Care Products (PCPs). Hydrology 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzacapo, M.; Donohue, M.J.; Smith, C.; El-Kadi, A.; Falinski, K.; Lerner, D.T. Review Article: Hawai‘i’s Cesspool Problem: Review and Recommendations for Water Resources and Human Health. J. Contem. Water Res. Ed. 2020, 170, 35–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Sakura, Y. Impact of septic tank systems on local groundwater quality and water supply in the Pearl River Delta, China: Case study. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2008, 22, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, K.D.; Cole, M.L.; York, J.K.; Valiela, I. Nitrogen loads to estuaries from waste water plumes: Modeling and isotopic approaches. Ground Water 2006, 44, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, P.G. Report for Evaluation of Existing Data and Sampling Protocol; Leggette, Brashears&Graham, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mester, T.; Szabó, G.; Sajtos, Z.; Baranyai, E.; Szabó, G.; Balla, D. Environmental Hazards of an Unrecultivated Liquid Waste Disposal Site on Soil and Groundwater. Water 2022, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kookana, R.S.; Drechsel, P.; Jamwal, P.; Vanderzalm, J. Urbanisation and emerging economies: Issues and potential solutions for water and food security. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, J.; Robertson, W.D.; Cherry, J.A.; Zanini, L. Impacts on a sand aquifer from an old septic system: Nitrate and phosphate. Groundwater 1996, 34, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heatwole, K.K.; McCray, J.E. Modeling potential vadose-zone transport of nitrogen from onsite wastewater systems at the development scale. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 91, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori-Sánchez, O.L.; Ramos-Fernández, L.; Lluén-Chero, W.E.; Pino-Vargas, E.; Flores del Pino, L. Application of the Iber two-dimensional model to recover the water quality in the Lurín River. Hydrology 2023, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlović, I.; Posavec, K.; Larva, O.; Marković, T. Numerical groundwater flow and nitrate transport assessment in alluvial aquifer of Varaždin region, NW Croatia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuhata, B.K.; El-Kadi, A.I.; Henrietta, D.; Lee, J.; Wada, C.A.; Bremer, L.L.; Burnett, K.M.; Delevaus, J.M.S.; Shuler, C.K. A density-dependent multi-species model to assess groundwater flow and nutrient transport in the coastal Keauhou aquifer, Hawaii, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Nokes, C.; Šimůnek, J.; Kikkert, H.; Hector, R. Modeling the impact of clustered septic tank systems on groundwater quality. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; Edward, A.S.; William, D.R. Multicomponent simulation of wastewater-derived nitrogen and carbon in shallow unconfined aquifers: II. Model application to a field site. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2001, 47, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.; O’Driscoll, M.A.; Armstrong, M.C. Onsite wastewater system nitrogen loading to groundwater in the Newport River watershed, North Carolina. Environ. Nat. Resour. 2012, 2, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.C.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.G.; Chang, H.W. Effect of agricultural land use on the chemistry of groundwater from basaltic aquifers, Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kaown, D.; Moon, H.S.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.K.; Kang, B.R. Impacts of land use change and groundwater management on long-term nitrate-nitrogen and chloride trends in groundwater of Jeju Island, Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.; Park, J.; Park, W.B.; Kang, B.R.; Woo, N.C. Nitrate contamination of coastal groundwater: Sources and transport mechanisms along a volcanic aquifer. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 145204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KOSIS (Korean Statistical Information Service). Statistics Korea, KOSIS, Daejeon City, Republic of Korea. 2024. Available online: https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1B040A3&conn_path=I2 (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- JSSGP (Jeju Special Self-Governing Province). Statistics of JSSGP; Jeju Special Self-Governing Province: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2024. (In Korean)
- JRI (Jeju Research Institute). A Basic Study on the Improvement of Individual Sewage Treatment Facilities on Jeju Island; JRI: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- JSSGP (Jeju Special Self-Governing Province); Korea University. Jeju Special Self-Governing Province Tap Water Source Characteristics Survey and Efficient Management Strategy Research; Korea University: Seoul City, Republic of Korea, 2021; p. 70. (In Korean)
- Brenna, M.; Cronin, S.J.; Smith, I.E.; Sohn, Y.K.; Maas, R. Spatio-temporal evolution of a dispersed magmatic system and its implications for volcano growth, Jeju Island Volcanic Field, Korea. Lithos 2012, 148, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Koh, G.W. Groundwater occurrence on Jeju island, Korea. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JSSGP (Jeju Special Self-Governing Province). Basic Plan for Integrated Water Management in Jeju Special Self-Governing Province (2023–2032); Jeju Special Self-Governing Province: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2022.
- Koh, G.W. Characteristics of the Groundwater and Hydrogeologic Implications of the Seoguipo Formation in Cheju Island. Ph.D. Thesis, Pusan National University, Pusan City, Republic of Korea, 1997; pp. 126–161, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- ME (Ministry of Environment). Land Cover Map, Environmental Spatial Information System; Ministry of Envirionment: Sejong City, Republic of Korea, 2022. Available online: https://egis.me.go.kr/intro/land.do (accessed on 7 February 2024). (In Korean)
- ME (Ministry of Environment). Calculate the Amount of Water and Sewage Generation in a Housing Complex in Unit Intensity and Study the Cost of Sewage; ME: Sejong City, Republic of Korea, 2001. (In Korean)
- Therrien, R.; McLaren, R.; Sudicky, E.; Panday, S.M. A Three-Dimensional Numerical Model Describing Fully-Integrated Subsurface and Surface Flow and Solute Transport; User Guide; University of Waterloo: Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jeju Water Resources Management Office. Data Collection Book of Geological Logs of Jeju Island; Jeju Special Self-Governing Province: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2001. (In Korean)
- Batu, V. Aquifer Hydraulics: A Comprehensive Guide to Hydrogeologic Data Analysis; LNC John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hodnett, M.G.; Tomasella, J. Marked differences between van Genuchten soil water-retention parameters for temperate and tropical soils: A new water-retention pedo-transfer functions developed for tropical soil. Goederma 2002, 108, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelhar, L.W. Stochastic subsurface hydrology from theory to application. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeju-do Report on the Overall Investigation of Hydrogeology and the Groundwater Resource in Jeju Island (III); Jeju Provincial Government: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2003. (In Korean)
- Peña-Haro, S.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Sahuquillo, A. A hydro-economic modelling framework for optimal management of groundwater nitrate pollution from agriculture. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceazan, M.L.; Thurman, E.M.; Smith, R.L. Retardation of ammonium and potassium transport through a contaminated sand and gravel aquifer: The role of cation exchange. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; He, H.; Zhu, J.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ma, L.; Tao, Q. Adsorption of ammonium by different natural clay minerals: Characterization, kinetics and adsorption isotherms. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 159, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Sejna, M. The HYDRUS-1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. Univ. Calif.-Riverside Res. Rep. 2005, 3, 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- JSSGP (Jeju Special Self-Governing Province). Study on Groundwater Water Quality Improvement and Pollution Control; JSSGP and Jeju Research Institute: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2019. (In Korean)
- Koh, E.H.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.K. Impact of leaky wells on nitrate cross-contamination in a layered aquifer system: Methodology for and demonstration of quantitative assessment and prediction. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, P.; Lucas, S. Contamination of estuaries from failing septic tank systems: Difficulties in scaling up from monitored individual systems to cumulative impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 2132–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, G.; Szponar, N.; Edwards, B. Groundwater Microbiology; Groundwater Project: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2021; pp. 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cey, E.E.; Rudolph, D.L.; Aravena, R.; Parkin, G. Role of the riparian zone in controlling the distribution and fate of agricultural nitrogen near a small stream in southern Ontario. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1999, 37, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, K.M.; Lloyd, J.W.; Lerner, D.N. Review of natural and artificial denitrification of groundwater. Water Res. 1991, 25, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.C.; Chae, G.T.; Yoon, Y.Y.; Kang, B.R.; Koh, G.W.; Park, K.H. Baseline geochemical characteristics of groundwater in the mountainous area of Jeju Island, South Korea: Implications for degree of mineralization and nitrate contamination. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeju-do, Report on the Overall Investigation of Hydrogeology and the Groundwater Resources in Jeju Island (I); Jeju Provincial Government: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 2001. (In Korean)
- Hyun, I.H.; Seo, B.W.; Kim, T.H.; Song, B.H.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, S.J.; Yun, S.T.; Oh, S.S. Tracking sources of nitrate in groundwater around livestock manure spill area. Rep. JIHE (Jeju Inst. Health Environ.) 2017, 28, 111–124. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Yu, S.; Kang, H.J.; Hyun, I.H.; Song, Y.C.; Kim, H.; Yun, S.T. Shift of nitrate sources in groundwater due to intensive livestock farming on Jeju Island, South Korea: With emphasis on legacy effects on water management. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.H.; Kaown, D.; Mayer, B.; Kang, B.R.; Moon, H.S.; Lee, K.K. Hydrogeochemistry and isotopic tracing of nitrate contamination of two aquifer systems on Jeju Island, Korea. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, J.E.; Kirkland, S.L.; Siegrist, R.L.; Thyne, G.D. Model parameters for simulating fate and transport of on-site wastewater nutrients. Groundwater 2005, 43, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeju-do, Report on the General Investigation of the Mountainous Area in Jeju Island; Jeju Provincial Government: Jeju City, Republic of Korea, 1997.
- Koh, D.C.; Chang, H.W.; Lee, K.S.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, W.B. Hydrogeochemistry and environmental isotopes of groundwater in Jeju volcanic island, Korea: Implications for nitrate contamination. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 2225–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ye, M.; Roeder, E.; Hicks, R.W.; Shi, L.; Yang, J. Estimating ammonium and nitrate load from septic systems to surface water bodies within ArcGIS environments. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.G.; Eberts, S.M.; Kauffman, L.J. Using Cl/Br ratios and other indicators to assess potential impacts on groundwater quality from septic systems: A review and examples from principal aquifers in the United States. J. Hydrol. 2011, 397, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Hamm, S.Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.K.; Oh, J.E. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical and personal care products, artificial sweeteners, and pesticides in groundwater from an agricultural area in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitka, A.L.; DeVita, W.M.; McGinley, P.M. Evaluating a chemical source-tracing suite for septic system nitrate in household wells. Water Res. 2019, 148, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widory, D.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Ladouche, B. Tracking the sources of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: A synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Applied Ecology. The Breeze Swept Septic to Sewer Conversion Project Analysis Report for the City of Rockledge; Applied Ecology: Rockledge City, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mester, T.; Balla, D.; Karancsi, G.; Bessenyei, É.; Szabó, G. Effects of nitrogen loading from domestic wastewater on groundwater quality. Water SA 2019, 45, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszka, T.T.; Reeves, D.M. Pathways and timescales associated with nitrogen transport from septic systems in coastal aquifers intersected by canals. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State of Hawaii. Report to the Twenty-Ninth Legislature State of Hwaii 2018; Relationg to Cesspools and Prioritization for Replacement; Department of Health and Environmental Management Division: Pearl City, HI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
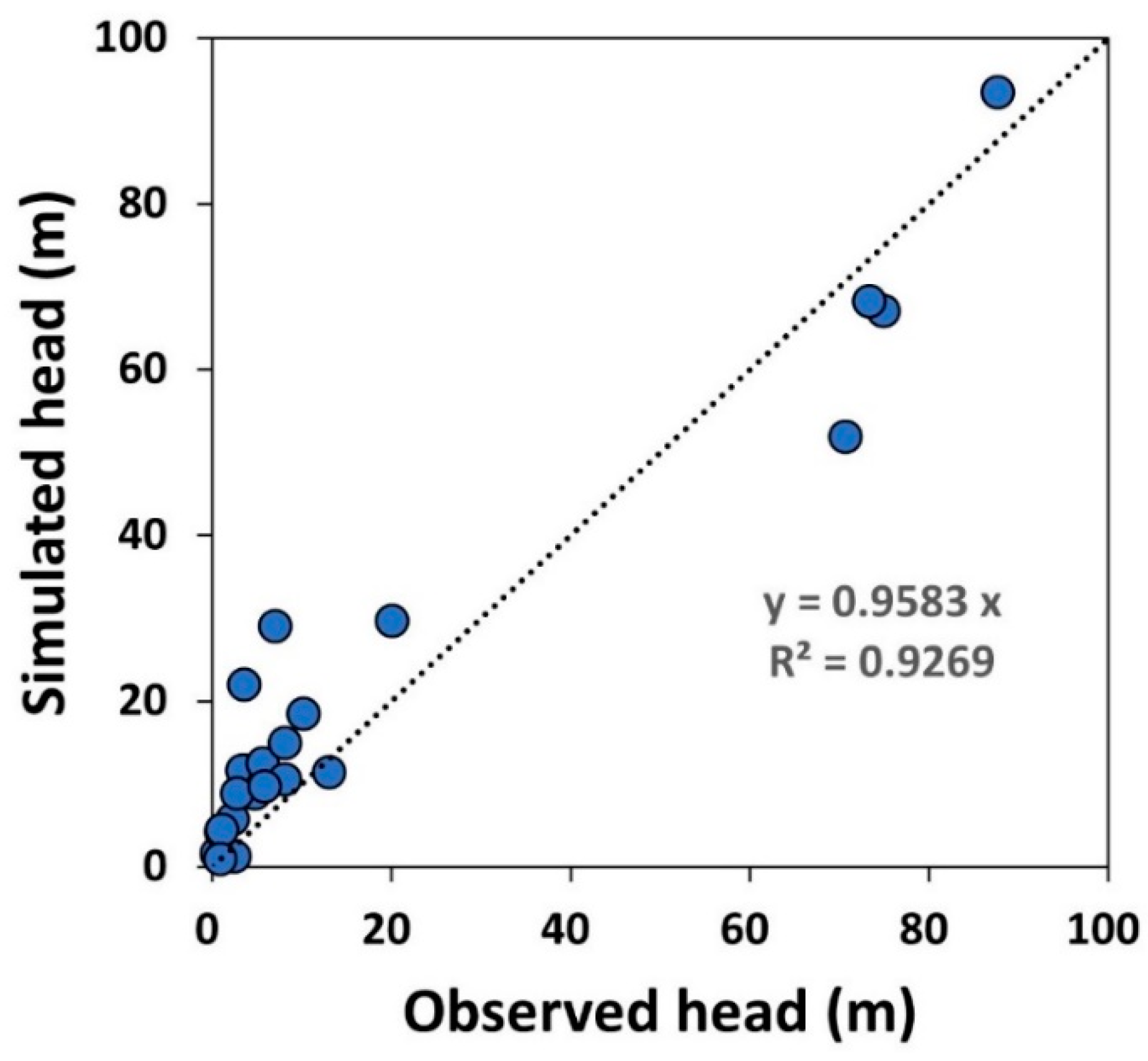
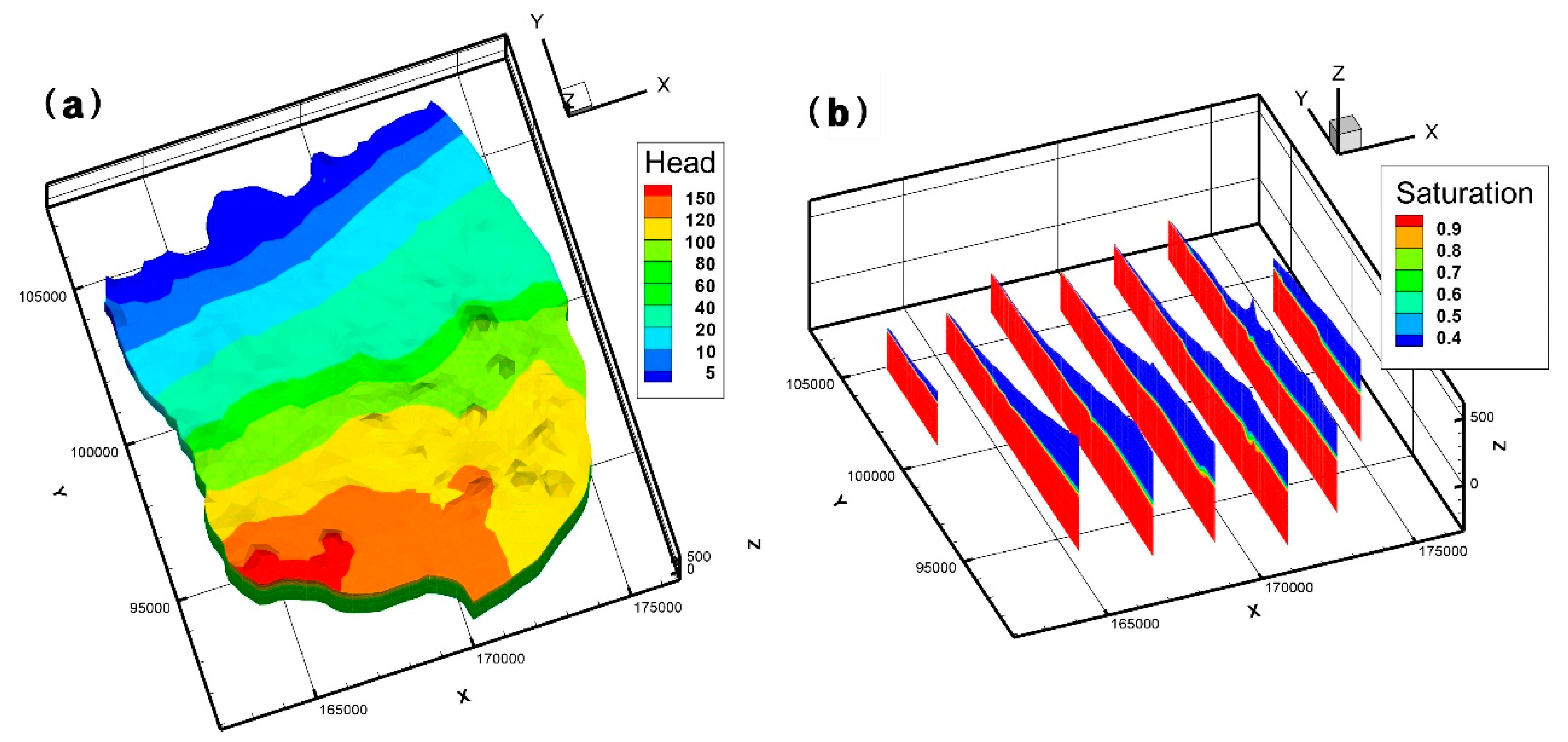
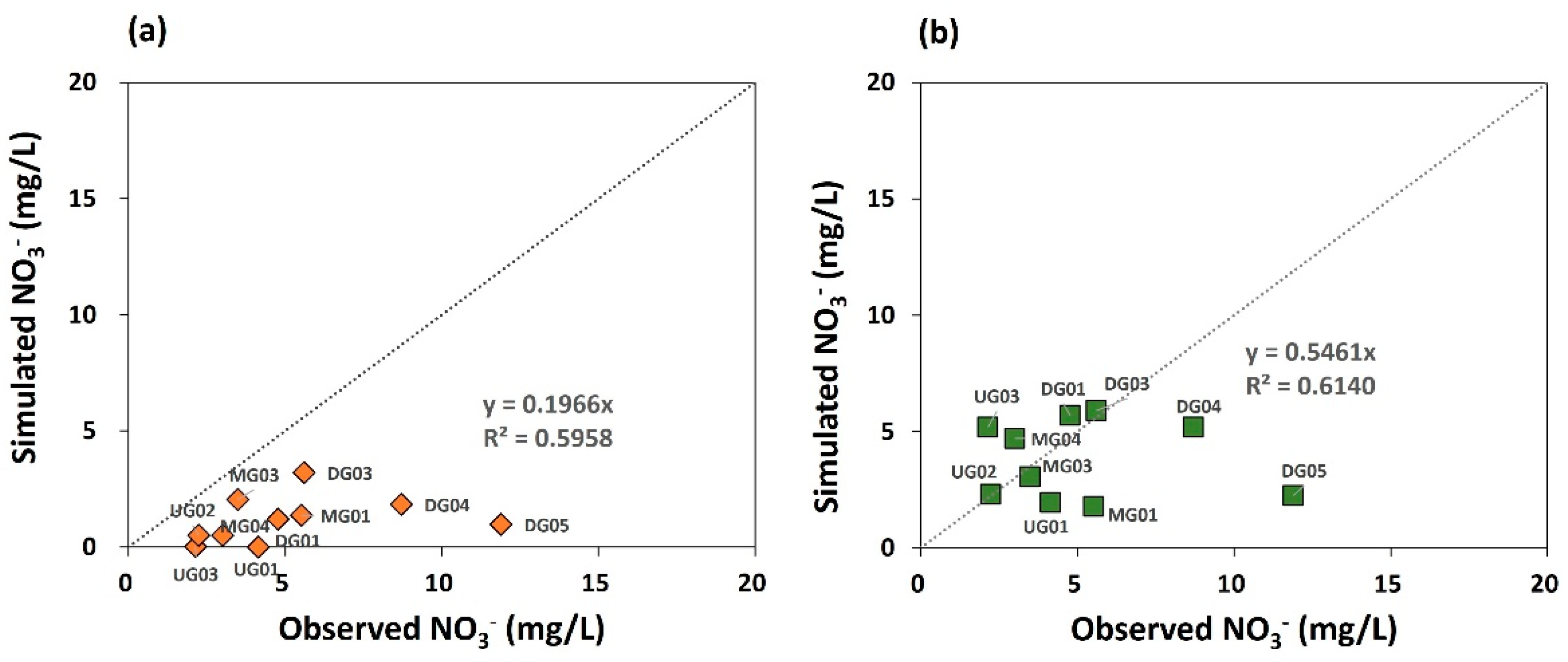

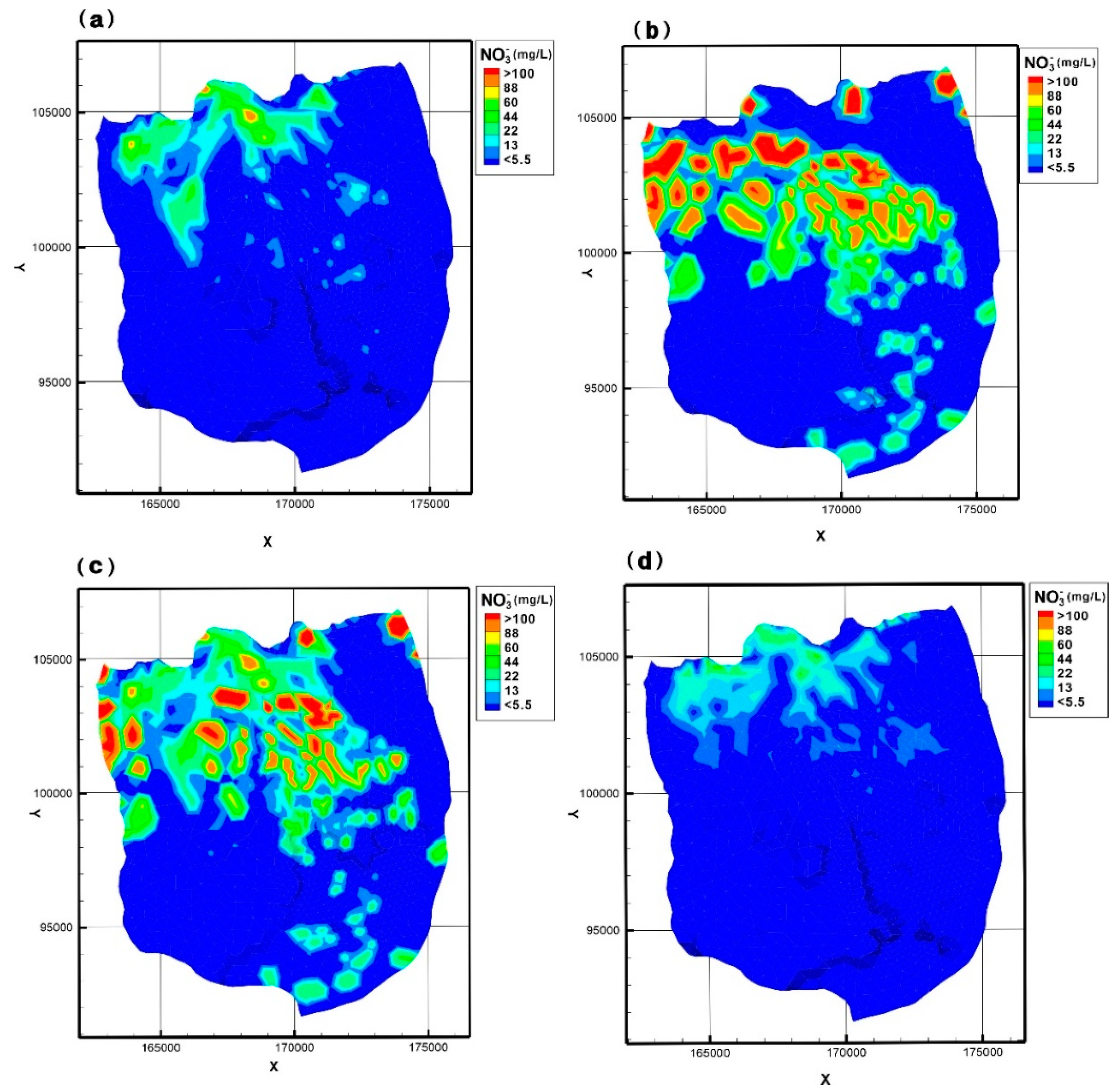
| Geological Layer | Hydraulic Conductivity | Porosity | Specific Storage | Van Genuchten Function Parameter | Dispersivity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kx = Ky (m/s) | Kz (m/s) | n (−) | Ss (m−1) | Swr | α (m−1) | β | aL (m) | aT (m) | |
| Volcanic rocks | 4.0 × 10−4 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 0.35 | 1.0 × 10−5 | 0.38 | 3.50 | 3.18 | 100 | 10 |
| SGF | 5.0 × 10−7 | 5.0 × 10−8 | 0.40 | 1.0 × 10−4 | 0.49 | 0.70 | 1.68 | 30 | 3 |
| Water Quality Parameter | Unit | Mean | Median | STDEV | MIN | MAX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 19.9 | 20.1 | 4.3 | 11.1 | 27.2 |
| EC | μS/cm | 764 | 670 | 344 | 119 | 1711 |
| pH | - | 7.1 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 4.3 | 7.9 |
| DO | mg/L | 2.6 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 8.9 |
| BOD | mg/L | 106.3 | 76.5 | 99.4 | 0.8 | 387.0 |
| T-N | mg/L | 48.9 | 43.9 | 28.5 | 3.2 | 131.1 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | 43.7 | 31.8 | 33.5 | ND 1 | 125.5 |
| Water Quality Component | Unit | Mean | Median | STDEV | MIN | MAX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 14.9 | 15.3 | 1.8 | 8.8 | 16.7 |
| EC | μS/cm | 98 | 97 | 22 | 68 | 157 |
| pH | - | 7.9 | 7.9 | 0.4 | 7.0 | 8.6 |
| DO | mg/L | 10.2 | 10.1 | 1.0 | 7.8 | 12.3 |
| BOD | mg/L | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| T-N | mg/L | 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 2.9 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | ND 1 | ND | |||
| NO2− | mg/L | ND | ND | |||
| NO3− | mg/L | 5.2 | 4.3 | 3.2 | 1.7 | 12.2 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 8.7 | 8.8 | 1.1 | 7.1 | 11.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Koh, E.-H.; Kim, J. Field Study and Numerical Modeling to Assess the Impact of On-Site Septic Systems on Groundwater Quality of Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrology 2024, 11, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11090146
Kim M, Koh E-H, Kim J. Field Study and Numerical Modeling to Assess the Impact of On-Site Septic Systems on Groundwater Quality of Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrology. 2024; 11(9):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11090146
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Mijin, Eun-Hee Koh, and Jinkeun Kim. 2024. "Field Study and Numerical Modeling to Assess the Impact of On-Site Septic Systems on Groundwater Quality of Jeju Island, South Korea" Hydrology 11, no. 9: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11090146
APA StyleKim, M., Koh, E.-H., & Kim, J. (2024). Field Study and Numerical Modeling to Assess the Impact of On-Site Septic Systems on Groundwater Quality of Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrology, 11(9), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11090146






