Temporal Assessment of Phosphorus Speciation in a Model Ramsar Lake System in Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
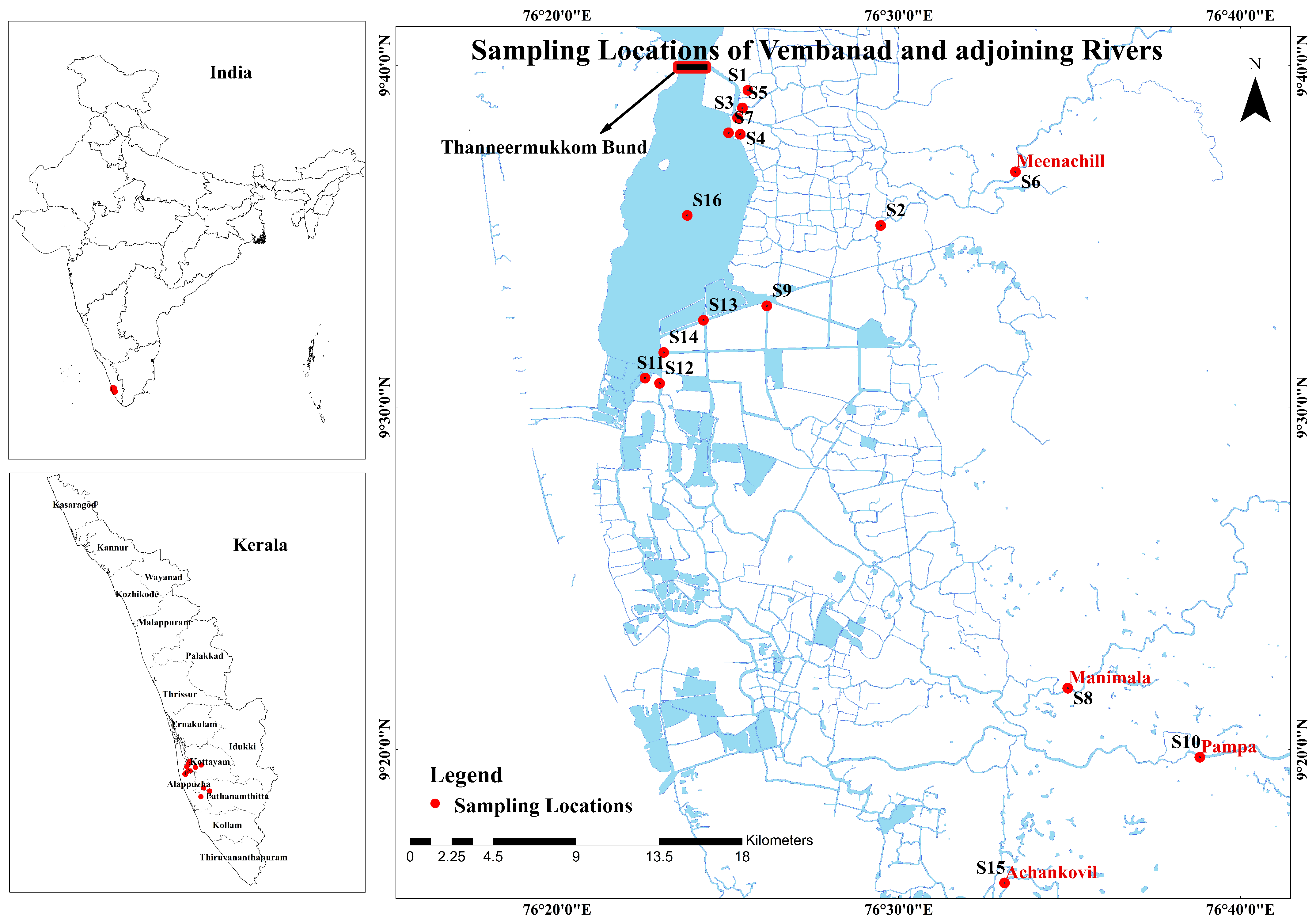
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preservation
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
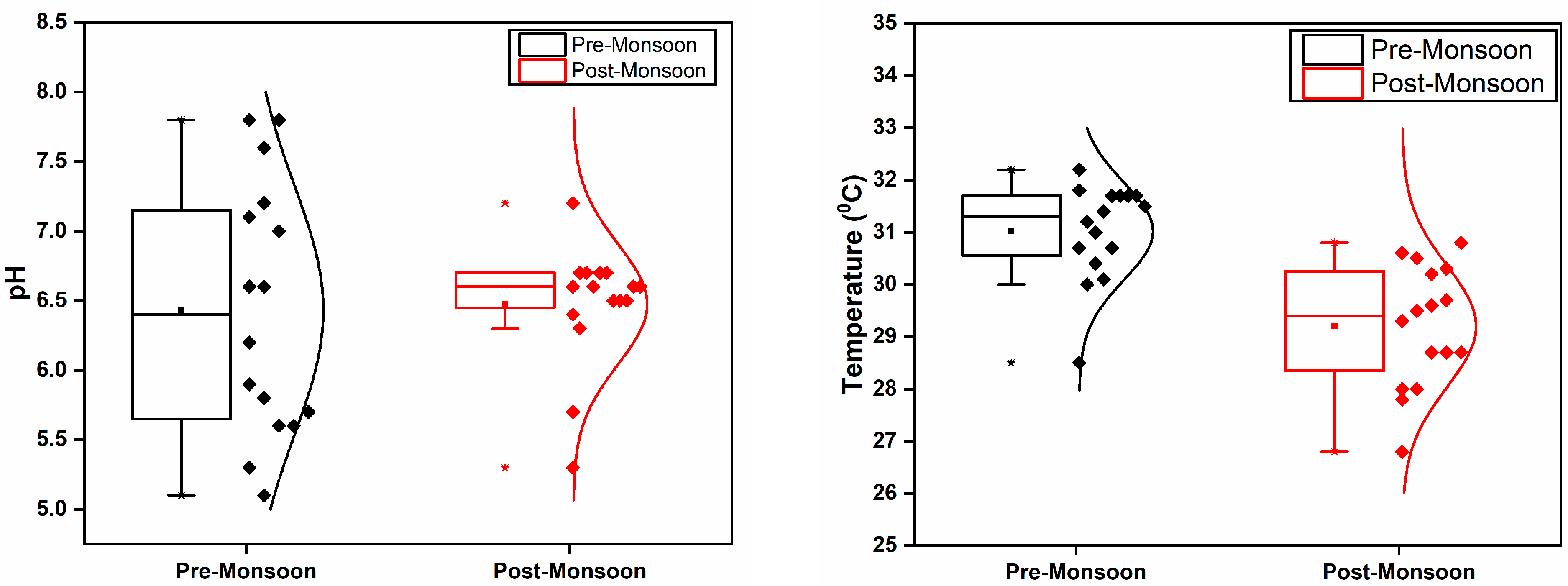
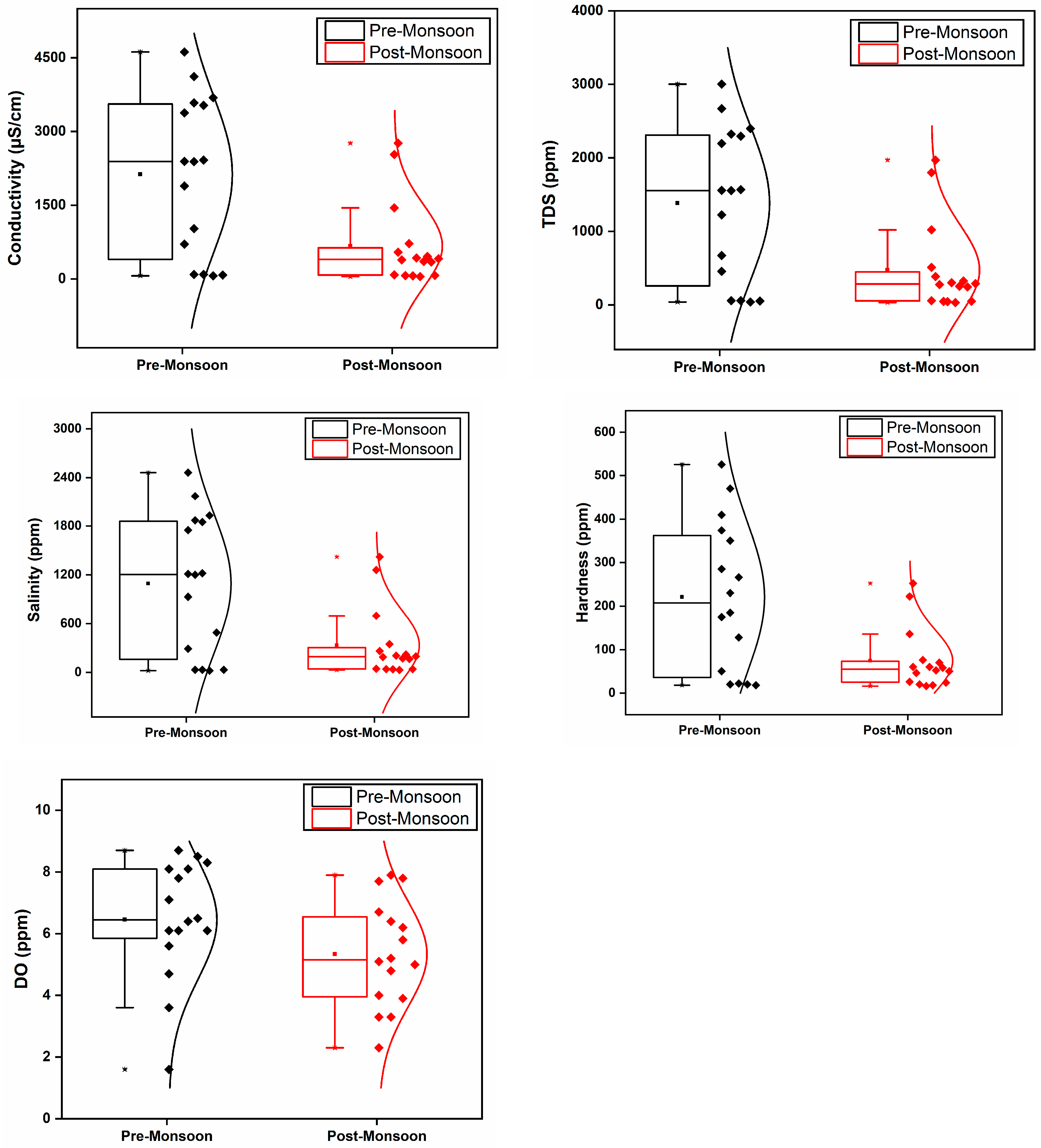
3.1. pH, Water Temperature, Conductivity, TDS, Salinity, and Total Hardness
3.2. Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
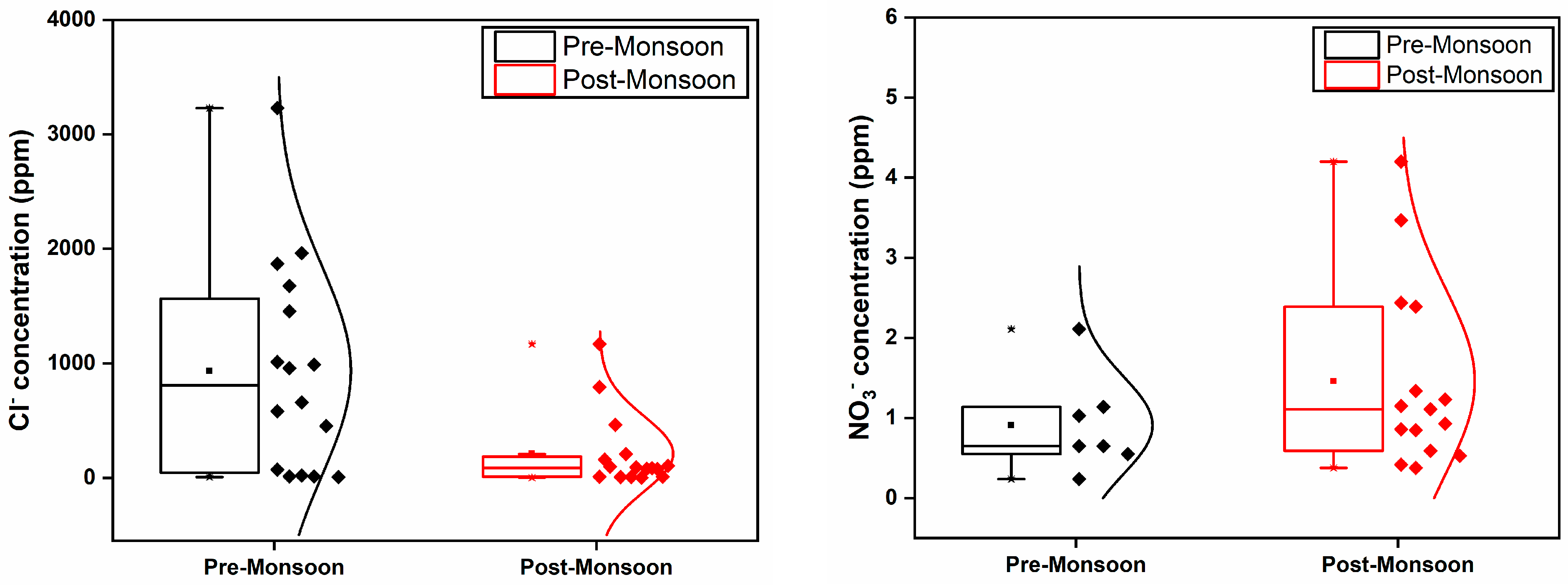
3.3. Ionic Levels
3.4. Phosphorus Speciation in Surface Water
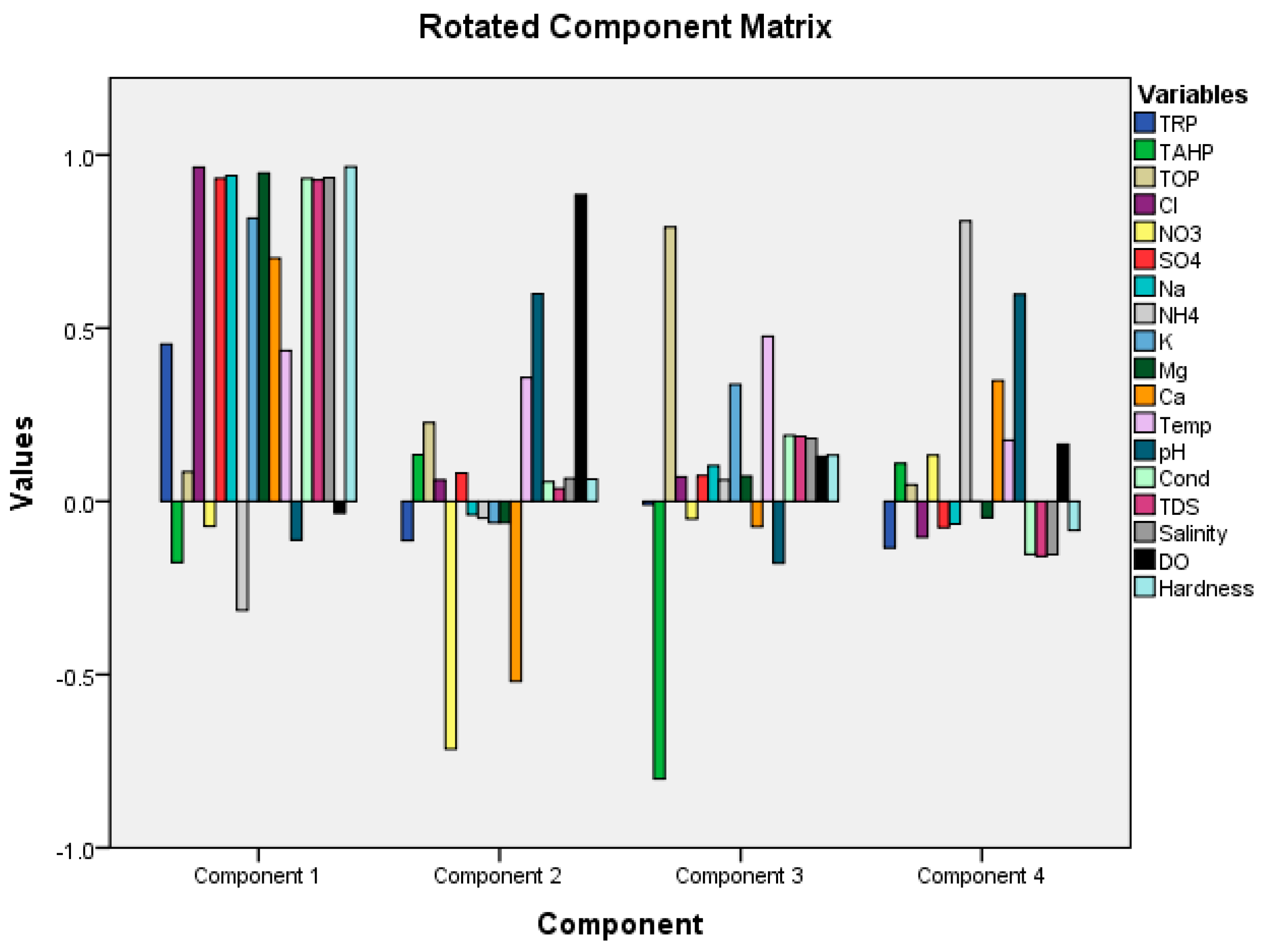
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
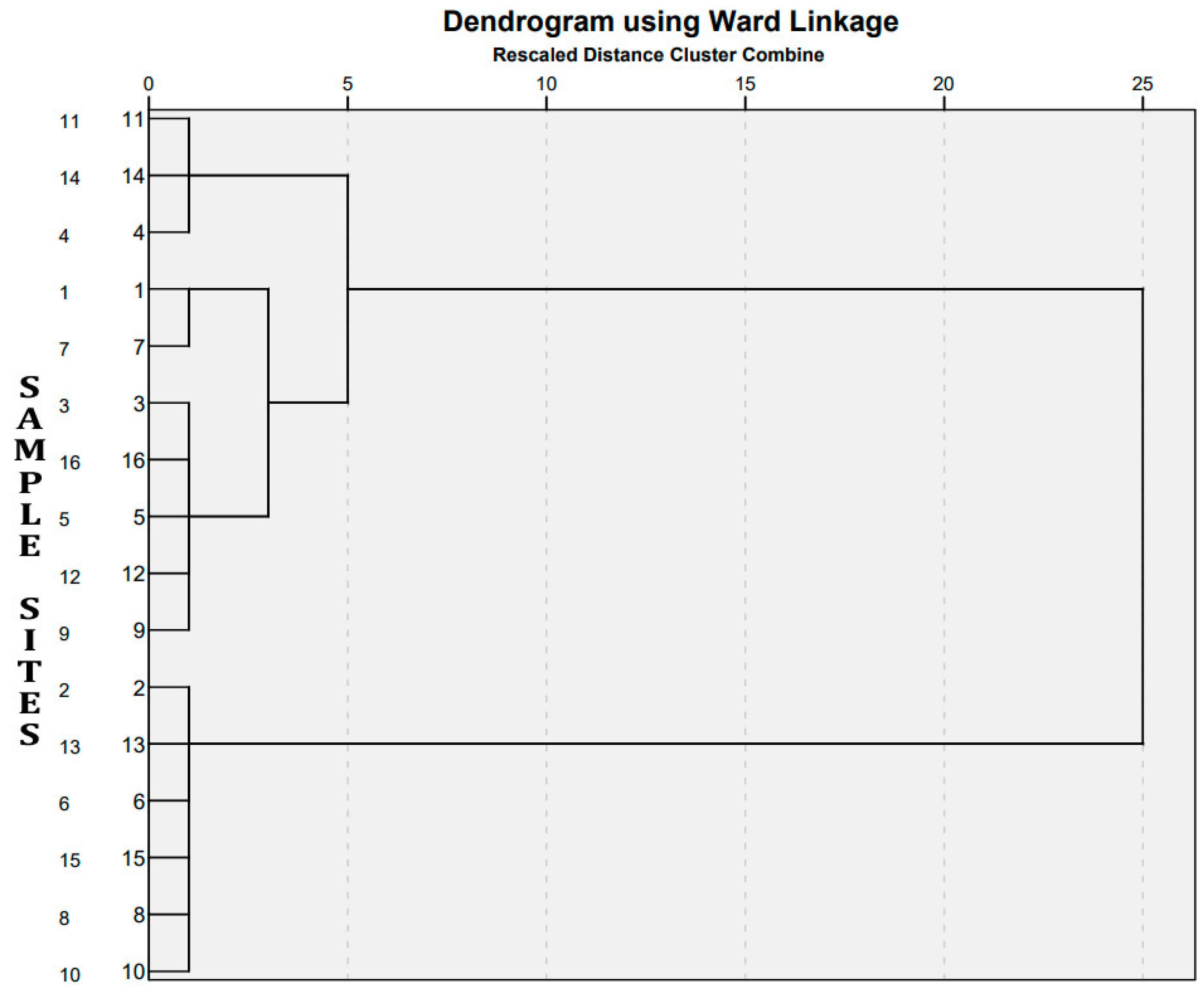
3.6. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crocker, R.; Blake, W.H.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Comber, S. Spatial distribution of sediment phosphorus in a Ramsar wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahilu, B.; Tadesse, M. Review on distribution, importance, threats and consequences of wetland degradation in Ethiopia. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2017, 9, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Acreman, M.; Knowler, D. Economic Valuation of Wetlands. A Guide for Policy Makers and Planners; Ramsar Convention Bureau: Gland, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, E.B. Valuing ecosystem services for coastal wetland protection and restoration: Progress and challenges. Resources 2013, 2, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, C.H.; Benny, N.; Raveendran, R.; Fanimol, C.L.; Samantha, N.K. Nutrient dynamics in the two lakes of Kerala, India. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 38, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainstone, C.P.; Parr, W. Phosphorus in rivers—Ecology and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 282–283, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golterman, H.L.; De Oude, N.T. Eutrophication of Lakes, Rivers and Coastal Seas. Handb. Environ. Chem. 1991, 5, 79–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhateria, R.; Jain, D. Water quality assessment of lake water: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Bai, L.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, J. Spatial–temporal distribution of phosphorus fractions and their relationship in water–sediment phases in the tuojiang river, china. Water 2022, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivakov, B.Y.A.; Maryutina, T.A.; Muntau, H. Phosphorus speciation in water and sediments (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2161–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, P.; Manju, M.N.; Gireeshkumar, T.R.; Ratheesh Kumar, C.S.; Movitha, M.; Shameem, K.; Chandramohanakumar, N. Phosphorous fractionation in mangrove sediments of Kerala, south west coast of India: The relative importance of inorganic and organic phosphorous fractions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, H.S.; Mortensen, P.B.; Andersen, F.O.; Rasmussen, E.; Jensen, A. Phosphorus cycling in a coastal marine sediment, Aarhus Bay, Denmark. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.P.; Amin, A.; Adnan Amin, C. The physico-chemical characteristics of vembanad backwaters at Eramalloor region, Alappuzha district, Kerala, India. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2017, 5, 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- Renjith, K.R.; Chandramohanakumar, N.; Joseph, M.M. Fractionation and bioavailability of phosphorus in a tropical estuary, Southwest India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 174, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renjith, K.R.; Mary, J.M.; Kumar, C.S.R.; Manju, M.N.; Chandramohanakumar, N. Nutrient Distribution and Bioavailability in a Tropical Microtidal Estuary, Southwest India. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 32, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, O.S.; Meenakshi, J.; Resmi, P.; Ragi, A.S.; Rakesh, V.B.; Salas, P.M.; Ratheesh, R.K. Geochemical distribution and dynamics of sedimentary phosphorous fractions in Vembanad wetland ecosystem. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, P.M.; Sujatha, C.H.; Ratheesh Kumar, C.S.; Dayala, V.T. Fate and transport processes of phosphorous fractions in selected surface sediments of Cochin Estuary, Southwest Coast of India. Environ. Forensics 2019, 20, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gireeshkumar, T.R.; Deepulal, P.M.; Chandramohanakumar, N. Phosphorous speciation in surface sediments of the Cochin estuary. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2535–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincy, M.V.; Rajan, B.; Pradeep Kumar, A.P. Water Quality Assessment of a Tropical Wetland Ecosystem with Special Reference to Backwater Tourism, Kerala, South India. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, V.; Muraleedharan Nair, S. Dynamics of Pesticides in the Backwaters of Kuttanad. Ph.D. Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kochi, India, 2001. Available online: http://dyuthi.cusat.ac.in/purl/3442 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Sitharam, B.Y.T.G.; Sreevalsa, K. Thaneermukkom Salt Water Barrier To Prevent Salt Water Intrusion: An Overview of Kuttanad Low Land Development. Hydrolink 2018, 1, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Nandan, B. Final Project Report Hydrochemistry of Vembanad Backwater with Special Reference to Pollution Problems and Its Management Measures; Kerala State Pollution Control Board, Government of Kerala: Thiruvananthapuram, India, 2019.
- Srinivas, K.; Revichandran, C.; Maheswaran, P.A.; Asharaf, T.T.M.; Murukesh, N. Propagation of tides in the Cochin estuarine system, southwest coast of India. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 32, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, K.T. Economic and Social Issues of Biodiversity Loss in Cochin Backwaters; The Kerala Research Programme on Local Level Development, Centre for Development Studies: Thiruvananthapuram, India, 2002; Available online: http://www.cds.ac.in/krpcds/report/thomson.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- Jayaprakash, A.A. Long Term Trends in Rainfall, Sea Level and Solar Periodicity: A Case Study for Forecast of Malabar Sole and Oil Sardine Fishery. 2002. Available online: http://eprints.cmfri.org.in/1992/ (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- Worsfold, P.; McKelvie, I.; Monbet, P. Determination of phosphorus in natural waters: A historical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 918, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; Stand. Methods; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlin, D.A.; María Del Pilar, D.; María Valeria, A.; Fabiana, P.S.; Cecilia, H.A.; María De Los Ángeles, B. Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A Case Study: Suquía River basin (Córdoba-Argentina). Water Res. 2001, 35, 2881–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.R.; Manonmani, K. Assessment of Water Quality of River Kalpathypuzha, Palakkad District, Kerala. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2013, 4, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Ambient Aquatic Life Water Quality Criteria for Dissolved Oxygen (Saltwater): Cape Cod to Cape Hatteras; EPA822-R-00-012; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, Atlantic Ecology Division: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-10/documents/ambient-al-wqc-dissolved-oxygen-cape-code.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- David, S.E.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Impact of human interventions on nutrient biogeochemistry in the Pamba River, Kerala, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P.; Manjusree, T.M.; Arunkumar, K.S. Seasonal variation in major ion chemistry of a tropical mountain river, the southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2333–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucif, K.; Neffar, S.; Menasria, T.; Maazi, M.C.; Houhamdi, M.; Chenchouni, H. Physico-chemical and bacteriological quality assessment of surface water at Lake Tonga in Algeria. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 13, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagnika, M.; Ibikounle, M.; Montcho, J.C.; Wotto, V.D.; Sakiti, N.G. Caractéristiques physico-chimiques de l’eau des puits dans la commune de Pobè (Bénin, Afrique de l’ouest). J. Appl. Biosci. 2014, 79, 6887–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garn, H.S. Effects of Lawn Fertilizer on Nutrient Concentration in Runoff from Lakeshore Lawns, Lauderdale Lakes, Wisconsin; USGS Water-Resources Investigative Report; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2002.
- Beyhan, M.; Kaçıkoç, M. Evaluation of water quality from the perspective of eutrophication in Lake Eǧirdir, Turkey. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M.; Ali, M.A. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Water Quality of the Sitalakhya River, Bangladesh. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2012, 2, 953–962. [Google Scholar]
- James, E.J. Forest-Water-Energy Linkages in the Context of Kerala. Proc. Kerala Sci. Congr. 2011, 85–97. Available online: https://cedindia.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/KEC-2011_Proceedings.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Asha, C.V.; Retina, I.C.; Suson, P.S.; Bijoy Nandan, S. Ecosystem analysis of the degrading Vembanad wetland ecosystem, the largest Ramsar site on the South West Coast of India—Measures for its sustainable management. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWAF. South African Water Quality Guidelines. Volume 7: Aquatic Ecosystems; DWAF: Cape Town, South Africa, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pattusamy, V.; Nandini, N.; Bheemappa, K. Detergent and Sewage Phosphates entering into Lake Ecosystem and Its Impact on Aquatic Environment. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 1, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Padmalal, D.; Remya, S.I.; Jyothi, S.J.; Baijulal, B.; Babu, K.N.; Baiju, R.S. Water quality and dissolved inorganic fluxes of N, P, SO4, and K of a small catchment river in the Southwestern Coast of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1541–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, I.V.; Singh, K.; Arumugam, M.; Clarson, D. Monitoring of trace metal pollution in meenachil river at Kottayam, Kerala (India). E-J. Chem. 2011, 8, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.; Joseph, S.; Chidambaram, S. Prominence of seasonal water quality assessment in a tropical river using multivariate analysis: Kerala, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellaiah, G.; Eazon, D.B. Hydrologic flow regimes in humid tropics river basin. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3143–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, R.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kohzu, A. The composition of organic phosphorus in a river during the springtime irrigation period. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaheim, K.E.; Doolette, A.L.; Smernik, R.J.; Mayer, J.; Oberson, A.; Frossard, E.; Bünemann, E.K. Long-term addition of organic fertilizers has little effect on soil organic phosphorus as characterized by 31P NMR spectroscopy and enzyme additions. Geoderma 2015, 257–258, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Leytem, A.B. Phosphorus compounds in sequential extracts of animal manures: Chemical speciation and a novel fractionation procedure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6101–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathy, K.K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Sahu, G.; Sarguru, S.; Sarkar, S.K.; Natesan, U. Spatio-temporal variation in physicochemical properties of coastal waters off Kalpakkam, southeast coast of India, during summer, pre-monsoon and post-monsoon period. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 180, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorioz, J.M.; Cassell, E.A.; Orand, A.; Eisenman, K.G. Phosphorus storage, transport and export dynamics in the Foron River watershed. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.; Kutlu, B.; Demir, T.; Yanik, T. Assessment of metal concentrations and physicochemical parameters in the waters of Lake Tecer. Kastamonu Üniversitesi Orman Fakültesi Derg. 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, V.; Shanmugasundaram, A.; Nithya, B.; Magesh, N.S.; Jayaprakash, M. Water quality of the Uppanar estuary, Southern India: Implications on the level of dissolved nutrients and trace elements. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamagna, A.M.; Murphy, B.R. Ecological and socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A review. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunpandi, N.; Jyothibabu, R.; Dhanya, P.; Jagadeesan, L.; Rashid, C.P.; Sarath, S. Alarming waterweeds proliferation in the Vembanad Lake System might significantly increase water loss through transpiration. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanda, O.I.; Ajayi, T.; Asuwaju, F.P. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms: Uses, Challenges, Threats, and Prospects. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 3452172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottezini, L.; Dick, D.P.; Wisniewski, A.; Knicker, H.; Carregosa, I.S.C. Phosphorus species and chemical composition of water hyacinth biochars produced at different pyrolysis temperature. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 14, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, S.; Prabu, M.; Tamilselvi, N.G. Bioconversion of Water Hyacinth into Enriched Vermicompost and its Effect on Growth and Yield of Peanut. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, S.; Girish, L. Water Hyacinth as a Green Manure for Organic Farming. Int. J. Res. Appl. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2014, 2, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, C.; Huang, S.; Wu, M.; Du, S.; Scholz, M.; Gao, F.; Lin, C.; Guo, Y.; Dong, Y. Comparison of relationships between pH, dissolved oxygen and chlorophyll a for aquaculture and non-aquaculture waters. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2011, 219, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, P.G.C.; Nnaji, C.C.; Tenebe, I.T. Assessment of geospatial and hydrochemical interactions of groundwater quality, southwestern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.C.; Joseph, A.; Padmakumari Gopinathan, V. Hydrochemistry of tropical springs using multivariate statistical analysis in Ithikkara and Kallada river basins, Kerala, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wen, S.; Yao, S.; Zheng, X.; Kang, D.; Zhong, J. Environmental significance of phosphorus existing forms in the sediments of Yuqiao Reservoir in Tianjin. Hupo Kexue/J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Pu, X.; Huang, W.; Yuan, X. Impacts of water temperature on phosphorus release of sediments under flowing overlying water. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 235, 103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, S.P.; Thomas, A.P.; Sreekumar, B. Ornithofauna and its conservation in the Kuttanad wetlands, southern portion of Vembanad-Kole Ramsar site, India. J. Threat. Taxa 2011, 3, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, L.; Alias, N.S.; Economics, M.A.; Com, B.; Gandhi, M. A Study on the Economic Analysis of Duck Farming in Kerala With Special Reference To the Kuttanad Region 1. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2020, 7, 3362–3372. [Google Scholar]
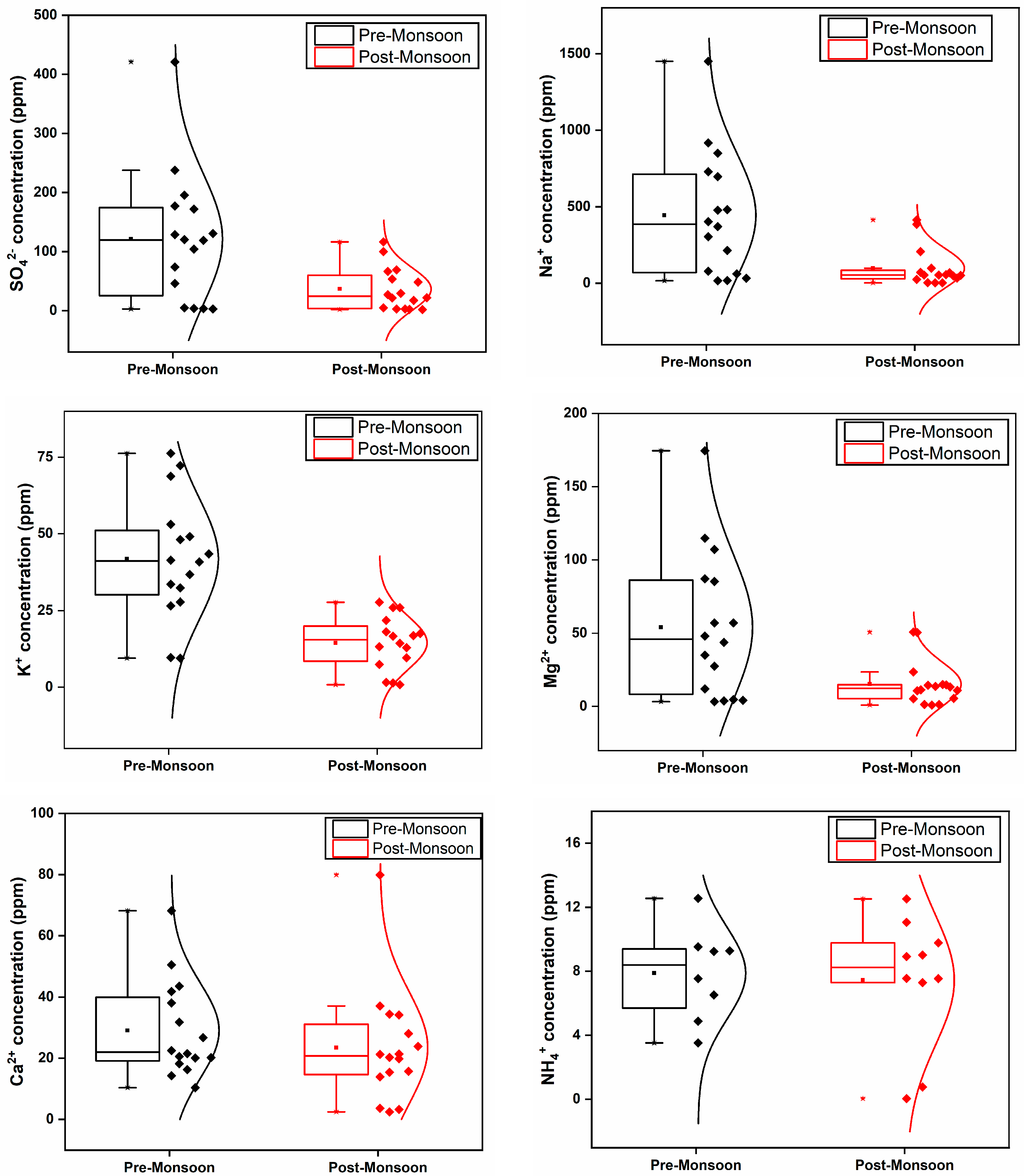

| Parameter | Seasonal Variations | ANOVA-p Value (Seasonal) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Monsoon | Post-Monsoon | ||||
| Range | Mean | Range | Mean | ||
| Temperature (°C) | 28.5–32.2 | 31.01 | 26.8–30.8 | 29.2 | 0.000 |
| pH | 5.1–7.8 | 6.43 | 5.3–7.2 | 6.47 | 0.862 |
| Conductivity (μS/cm) | 64–4618 | 2128.75 | 46.1–2760 | 669.45 | 0.014 |
| TDS (ppm) | 41–3003 | 1382.75 | 32.2–1970 | 475.71 | 0.017 |
| Salinity (ppm) | 20–2460 | 1092.5 | 28.2–1420 | 332.23 | 0.051 |
| DO (ppm) | 1.6–8.7 | 6.45 | 2.3–7.8 | 5.26 | 0.094 |
| Hardness (ppm) | 18–526 | 220.56 | 16–252 | 74.12 | 0.035 |
| Chloride (ppm) | 8.31–3230.57 | 936.06 | 4.01–1168.33 | 210.92 | 0.021 |
| Nitrate (ppm) | ND–2.11 | 0.91 | ND–4.2 | 1.45 | 0.002 |
| Sulphate (ppm) | 2.74–420.93 | 121.25 | 1.89–116.23 | 36.53 | 0.007 |
| Sodium (ppm) | 16.34–1449.55 | 443.85 | 2.72–413.73 | 98.69 | 0.005 |
| Ammonium (ppm) | ND–12.55 | 7.88 | ND–12.52 | 7.44 | 0.564 |
| Potassium (ppm) | 9.49–76.2 | 41.82 | 0.81–27.71 | 14.49 | 0.000 |
| Magnesium (ppm) | 3.26–174.51 | 54.06 | 1.01–50.77 | 15.23 | 0.023 |
| Calcium (ppm) | 10.36–68.17 | 29.01 | 2.45–79.88 | 23.38 | 0.254 |
| TRP | TAHP | TOP | Cl | NO3 | SO4 | Na | NH4 | K | Mg | Ca | Temp | pH | EC | TDS | Salinity | DO | TH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRP | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| TAHP | −0.232 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||
| TOP | −0.067 | −0.400 * | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||
| Cl | 0.399 * | −0.359 * | 0.222 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||
| NO3 | −0.054 | 0.056 | −0.133 | −0.216 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||
| SO4 | 0.359 * | −0.300 | 0.216 | 0.952 ** | −0.176 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| Na | 0.424 * | −0.348 | 0.229 | 0.960 ** | −0.177 | 0.934 ** | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| NH4 | −0.352 * | 0.288 | 0.020 | −0.395 * | 0.059 | −0.361 * | −0.337 | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| K | 0.375 * | −0.402 * | 0.289 | 0.713 ** | −0.263 | 0.708 ** | 0.833 ** | −0.223 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Mg | 0.469 ** | −0.322 | 190 | 0.953 ** | −0.069 | 0.950 ** | 0.964 ** | −0.370 * | 0.775 ** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Ca | 0.326 | −0.035 | −0.118 | 0.682 ** | 0.111 | 0.669 ** | 0.705 ** | −0.132 | 0.616 ** | 0.786 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Temp | 0.052 | −0.313 | 0.321 | 0.487 ** | −0.399 * | 0.519 ** | 0.469 ** | −0.105 | 0.534 ** | 0.431 * | 0.261 | 1.000 | ||||||
| pH | −0.043 | 0.133 | −0.033 | −0.117 | −0.237 | −0.146 | −0.169 | 0.280 | −0.212 | −0.180 | −0.156 | 0.007 | 1.000 | |||||
| EC | 0.317 | −0.364 * | 0.217 | 0.960 ** | −0.187 | 0.940 ** | 0.940 ** | −0.415 * | 0.689 ** | 0.937 ** | 0.665 ** | 0.444 * | −0.201 | 1.000 | ||||
| TDS | 0.321 | −0.372 * | 0.230 | 0.956 ** | −0.171 | 0.941 ** | 0.935 ** | −0.418 * | 0.679 ** | 0.935 ** | 0.652 ** | 0.421 * | −0.199 | 0.999 ** | 1.000 | |||
| Salinity | 0.322 | −0.313 | 0.222 | 0.941 ** | −0.107 | 0.927 ** | 0.929 ** | −0.425 * | 0.662 ** | 0.933 ** | 0.644 ** | 0.378 * | −0.214 | 0.984 ** | 0.988 ** | 1.000 | ||
| DO | −0.084 | −0.020 | 0.354 * | −0.047 | −0.257 | −0.010 | −0.046 | 0.100 | 0.056 | −0.081 | −0.257 | 0.396 * | 0.615 ** | −0.084 | −0.085 | −0.087 | 1.000 | |
| TH | 0.404 * | −0.278 | 0.202 | 0.975 ** | −0.143 | 0.968 ** | 0.957 ** | −0.386 * | 0.707 ** | 0.974 ** | 0.727 ** | 0.442 * | −0.155 | 0.959 ** | 0.957 ** | 0.957 ** | −0.082 | 1.000 |
| Period of Sampling | Phosphate Species | Lowest | Highest | Average | Phosphate Species | ANOVA (Seasonal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRM | TRP (ppb) | 76.66 | 676.66 | 332.91 | TRP | 0.567 |
| TAHP (ppb) | 100.0 | 1033.33 | 475.0 | |||
| TOP (ppb) | 33.33 | 1243.34 | 676.04 | TAHP | 0.064 | |
| TP (ppb) | 1020.0 | 2286.66 | 1483.95 | |||
| POM | TRP (ppb) | 110.0 | 476.66 | 303.74 | TOP | 0.024 |
| TAHP (ppb) | 243.33 | 1276.67 | 683.12 | |||
| TOP (ppb) | 23.33 | 890.0 | 402.29 | TP | 0.459 | |
| TP (ppb) | 743.33 | 1876.66 | 1389.16 |
| TRP | TAHP | TOP | TP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRP | 1 | |||
| TAHP | −0.232 | 1 | ||
| TOP | −0.067 | −0.400 | 1 | |
| TP | 0.11 | 0.41 | 0.60 | 1 |
| Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | |
| TRP | 0.454 | −0.113 | −0.010 | −0.134 |
| TAHP | −0.177 | 0.135 | −0.801 | 0.110 |
| TOP | 0.085 | 0.227 | 0.791 | 0.048 |
| Cl | 0.965 | 0.062 | 0.071 | −0.104 |
| NO3 | −0.072 | −0.715 | −0.051 | 0.133 |
| SO4 | 0.932 | 0.081 | 0.074 | −0.076 |
| Na | 0.940 | −0.039 | 0.103 | −0.066 |
| NH4 | −0.314 | −0.049 | 0.062 | 0.809 |
| K | 0.817 | −0.062 | 0.337 | 0.000 |
| Mg | 0.948 | −0.062 | 0.073 | −0.047 |
| Ca | 0.702 | −0.520 | −0.074 | 0.348 |
| Temperature | 0.435 | 0.357 | 0.476 | 0.176 |
| pH | −0.112 | 0.599 | −0.178 | 0.598 |
| Conductivity | 0.932 | 0.057 | 0.190 | −0.153 |
| TDS | 0.928 | 0.037 | 0.188 | −0.159 |
| Salinity | 0.934 | 0.066 | 0.182 | −0.154 |
| DO | −0.034 | 0.885 | 0.130 | 0.165 |
| Hardness | 0.966 | 0.064 | 0.133 | −0.084 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venukumar, A.; Azimov, A.M.; Iztleuov, G.M.; Moorchilot, V.S.; Aravind, U.K.; Sataev, M.I.; Koshy, V.J.; Aravindakumar, C.T. Temporal Assessment of Phosphorus Speciation in a Model Ramsar Lake System in Asia. Hydrology 2024, 11, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11050070
Venukumar A, Azimov AM, Iztleuov GM, Moorchilot VS, Aravind UK, Sataev MI, Koshy VJ, Aravindakumar CT. Temporal Assessment of Phosphorus Speciation in a Model Ramsar Lake System in Asia. Hydrology. 2024; 11(5):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11050070
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenukumar, Anjali, Abdugani M. Azimov, Gani M. Iztleuov, Vishnu S. Moorchilot, Usha K. Aravind, Marat I. Sataev, Valsamma J. Koshy, and Charuvila T. Aravindakumar. 2024. "Temporal Assessment of Phosphorus Speciation in a Model Ramsar Lake System in Asia" Hydrology 11, no. 5: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11050070
APA StyleVenukumar, A., Azimov, A. M., Iztleuov, G. M., Moorchilot, V. S., Aravind, U. K., Sataev, M. I., Koshy, V. J., & Aravindakumar, C. T. (2024). Temporal Assessment of Phosphorus Speciation in a Model Ramsar Lake System in Asia. Hydrology, 11(5), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11050070







