Hydrogeological Characteristics of the Makaresh Carbonate Karst Massif (Central Albania)
Abstract
1. Introduction
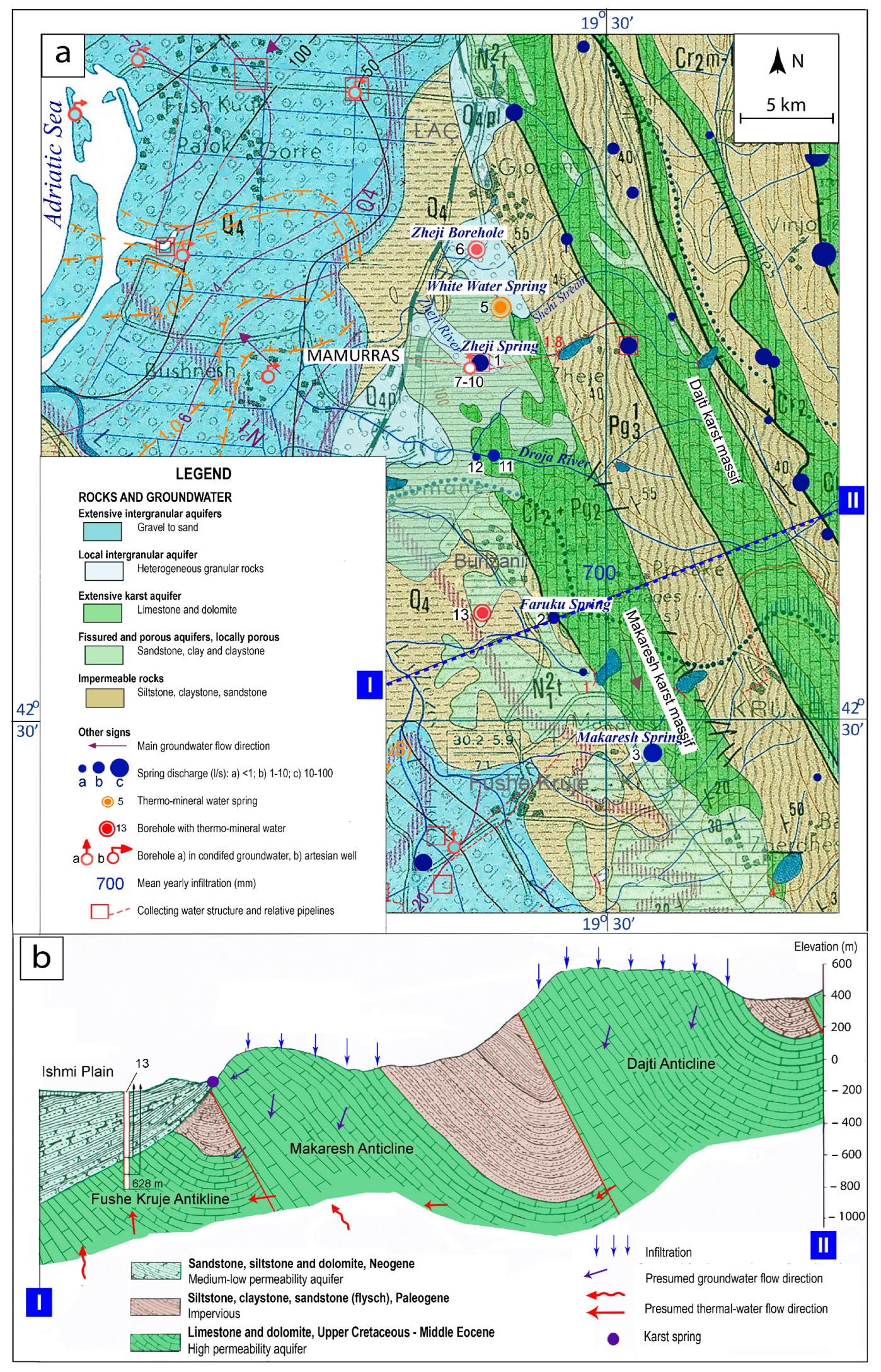
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
4. Geology
5. Hydrogeology
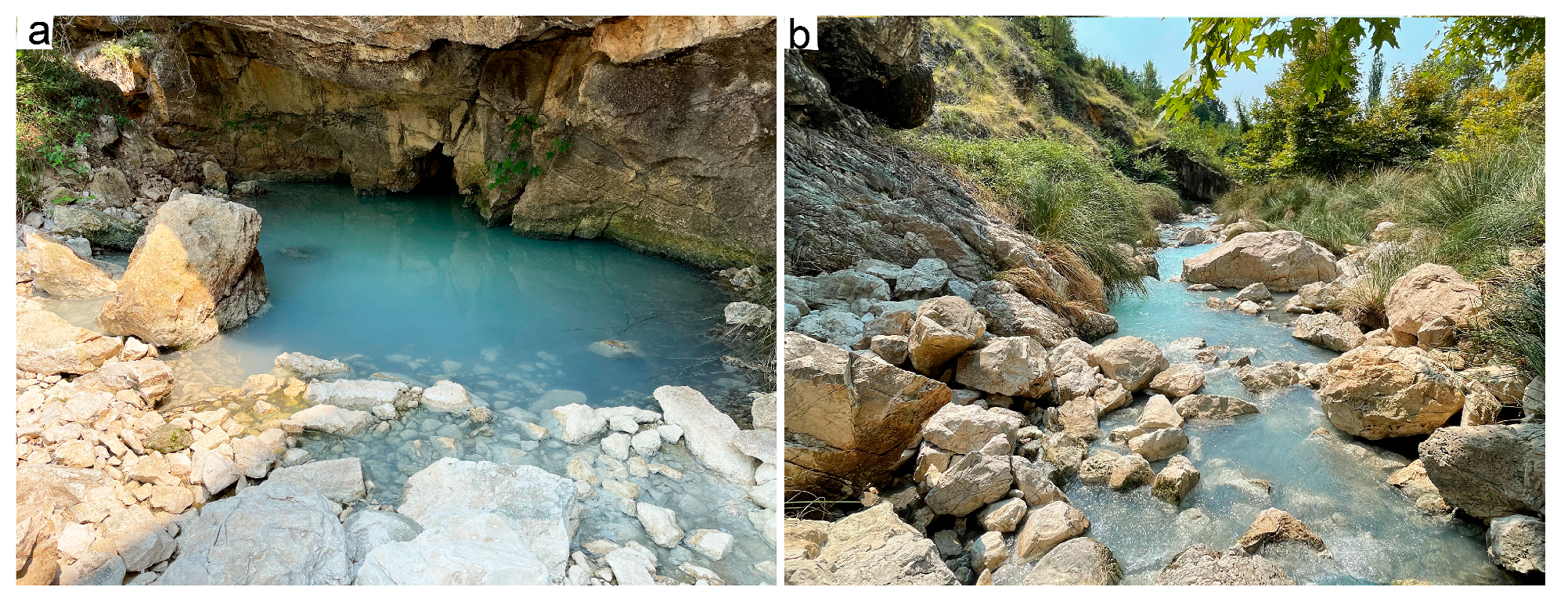
5.1. Cold Springs
5.2. Thermal Springs
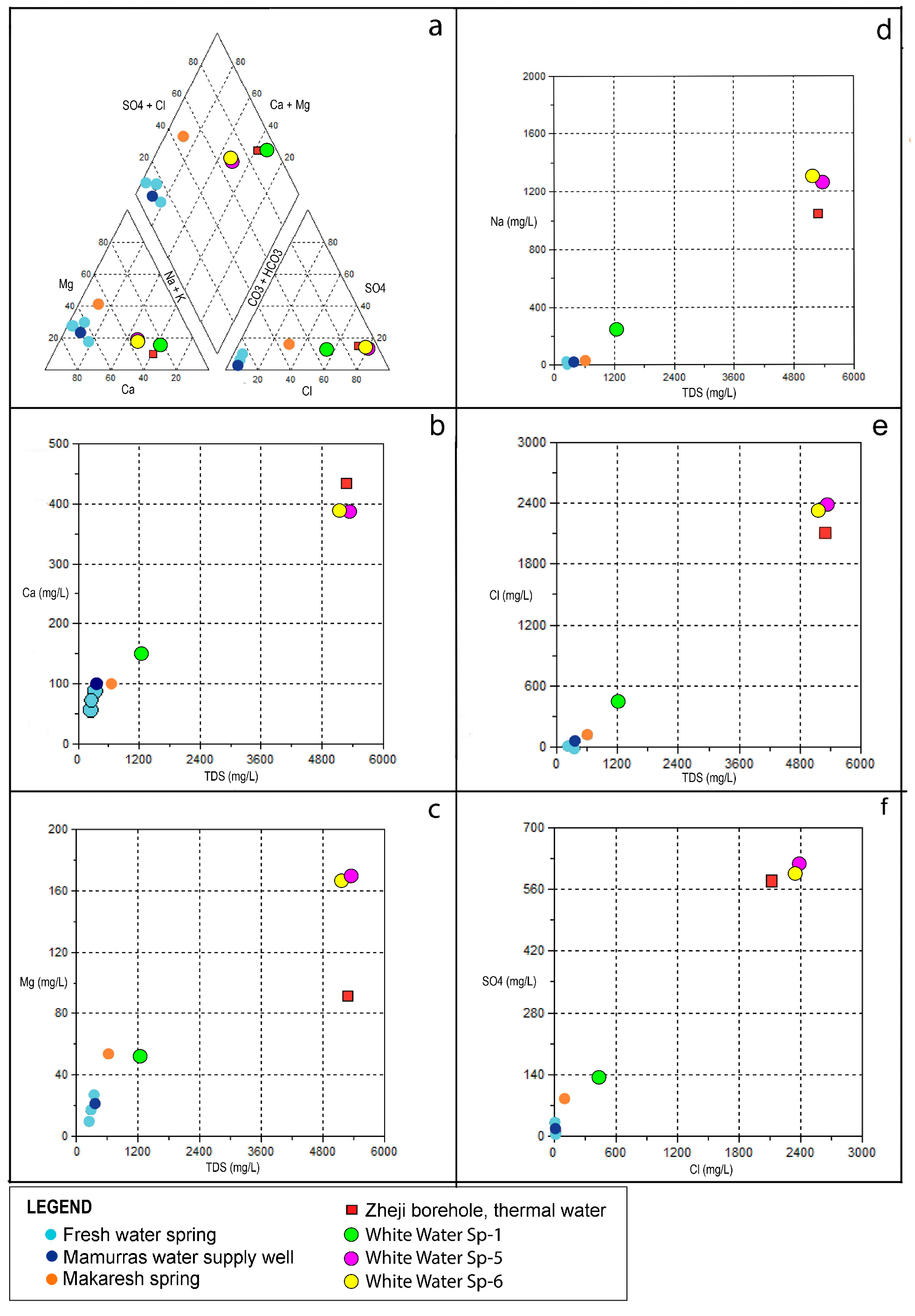
6. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics
7. Groundwater Circulation
8. Groundwater Exploitation
8.1. Cold Waters
8.2. Thermal Waters
8.3. Groundwater Protection
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stringfield, V.T.; Legrand, H.E. Hydrology of carbonate rock terrenes. A review with special reference to the United States. J. Hydrol. 1969, 8, 349–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kresić, N. Hydrogeology. Introduction to Groundwater Science and Engineering; Blue Ridge Press: Asheville, NC, USA, 2023; ISBN 970-8-2-218-06984-1. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović, Z. Global distribution and use of water from karst aquifers. In Advances in Karst Research: Theory, Fieldwork and Applications; Parise, M., Gabrovsek, F., Kaufmann, G., Ravbar, N., Eds.; Geological Society: London, UK, 2018; Volume 466, pp. 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M.; Ravbar, N.; Živanović, V.; Mikszewski, A.; Kresic, N.; Mádl-Szőnyi, J.; Kukurić, N. Hazards in Karst and Managing Water Resources Quality. In Karst Aquifers—Characterization and Engineering; Stevanović, Z., Ed.; Professional Practice in Earth Sciences; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 601–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, E. Coastal aquifers of Europe: An overview. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 10, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Wagner, T.; Lange, J.; Weiler, M. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrogeological modelling approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalowicz, M. Karst and karst groundwater resources in the Mediterranean. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Auler, A.S.; Bakalowicz, M.; Drew, D.; Griger, F.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Richts, A.; Stevanović, Z.; et al. The World Karst Aquifer Mapping project: Concept, mapping procedure and map of Europe. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Goldscheider, N.; Auler, A.S.; Bakalowicz, M.; Broda, S.; Drew, D.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Richts, A.; et al. World Karst Aquifer Map; IAH-UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, Z. (Ed.) Karst aquifers—Characterization and Engineering; Professional practice in earth sciences; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-12849-8. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović, Z. Kast water in potable water supply: A global scale overview. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.; Gabrovsek, F.; Kaufmann, G.; Ravbar, N. Recent advances in karst research: From theory to fieldwork and applications. In Advances in Karst Research: Theory, Fieldwork and Applications; Parise, M., Gabrovsek, F., Kaufmann, G., Ravbar, N., Eds.; Geological Society: London, UK, 2018; Volume 466, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldscheider, N.; Chen, Z.; Auler, A.S.; Bakalowicz, M.; Broda, S.; Drew, D.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Stevanović, Z.; et al. Global distribution of carbonate rocks and karst water resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margat, J. Les eaux souterraines dans le basin méditerranén. Ressources et utilisations. In Documents BRGM; BRGM: Orléans, France, 1998; p. 282. [Google Scholar]
- Bakalowicz, M. Coastal Karst groundwater in the Mediterranean: A resource to be preferably exploited onshore, not from karst submarine springs. Geosciences 2018, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, G.; Güner, N.; Törk, N. Turkish karst aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalioras, A.; Marinos, P. Water resources assessment and management of karst aquifer systems in Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liso, I.S.; Parise, M. Apulian karst springs: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarinoye, T.; Gleeson, T.; Marx, V.; Seeger, S.; Adinehvand, R.; Allocca, V.; Andreo, B.; Apaéstegui, J.; Apolit, C.; Arfib, B.; et al. Global karst springs hydrograph dataset for research and management of the world’s fastes flowing groundwater. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanović, Z.; Eftimi, R. Karstic sources of water supply for large consumers in south-eastern Europe—Sustainability, disputes and advantages. In Proceedings of the International Interdisciplinary Scientific Conference “Sustainability of the karst environment. Dinaric karst and other karst regions”, Plitvice Lakes, Croatia, 23–26 September 2009; Bonacci, O., Ed.; Series on Groundwater; IHP-UNESCO: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Goldscheider, N.; Mádl-Szönyi, J.; Eröss, A.; Schill, E. Review: Thermal water resources in carbonate rock aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mádl-Szönyi, J.; Tóth, A. Basin-scale conceptual groundwater flow model for an unconfined and confined thick carbonate region. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 1359–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, I. Hydrochemical properties of deep carbonate aquifers in the SW German Molasse basin. Geotherm Energy 2014, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papić, P. (Ed.) Mineral and Thermal Waters of Southeastern Europe; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R.; Bisha, G.; Tafilaj, I.; Habilaj, L. Hydrogeological Map of Albania, Scale 1: 200,000; Hamid Shijaku: Tirana, Albania, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Xhomo, A.; Kodra, A.; Xhafa, Z.; Shallo, M. Gjeologjia e Shqipërisë; Shërbimi Gjeologjik Shqiptar: Tirana, Albania, 2002; 410p.
- Eftimi, R. Hydrogeological characteristics of Albania. AQUAmundi 2010, 1012, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Avgustinski, V.L.; Astashkina, A.A.; Shukevich, L.L. Mineral Water Resources of Albania; Health Ministry, Central Archive, Albanian Geological Survey: Tirana, Albania, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R. Karst and karst water resources of Albania and their management. Carbonates and Evaporites 2020, 35, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frashëri, A. (Ed.) Geothermal Atlas of Albania; Academy of Science of Albania, Faculty of Geology and Mining, Polytechnical University of Tirana: Tirana, Albania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R.; Frashëri, A. Thermal and Mineral Waters of Albania; PRINT-AL: Tirana, Albania, 2016; 214p. [Google Scholar]
- Klimchouk, A. Hypogene Speleogenesis: Hydrogeological and Morphogenetic Perspective; Special paper no 1; National Cave and Karst Research Institute: Carlsbad, NM, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Klimchouk, A. Morphogenesis of hypogenic caves. Geomorphology 2009, 106, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchouk, A. Types and settings of hypogene karst. In Hypogene karst Regions and Caves of the World; Klimchouk, A.B., Palmer, A.N., De Waele, J., Audra, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaho, S. (Ed.) Climate of Albania; Institute of Hydrometeorology: Tirana, Albania, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Aliaj, S.; Melo, V.; Hyseni, A.; Skrami, J.; Mëhillka, L.; Muço, B.; Profiti, K.; Prillo, S. The Technical Structure of Albania; Seismological Institute: Tirana, Albania, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tartari, M. Hydrogeological Investigation for the Water Supply of the Town of Mamurras; Archive of AGS: Tirana, Albania, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R. Hydrogeological Investigation: The Result of the Water Supply Wells of the Town of Mamurras; Archive of ITA Consult: Tirana, Albania, 2002. (In Albanian) [Google Scholar]
- Meço, N.; Aliaj, S. Geology of Albania; Gebruder Bornatrager: Berlin, Germany, 2000; 246p. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, B.R.G.; Girbacea, R.; Mesonjesi, A.; Aydin, A. Evolution of fracture and fault-controlled fluid pathways in Carbonates of the Albanides fold-thrust belt. AAPG Bull. 2006, 90, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geet, J.; Swennen, R.; Durmishi, C.; Rour, F.; Muchez, P.H. Paragenesis of Cretaceous to Eocene carbonate reservoirs in the Ionian fold and thrust belt (Albania): Relation between tectonism and fluid flow. Sedimentology 2002, 49, 697–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliaj, S. Seismotectonic of the Albanides collision zone: Geometry of the under-thrusting Adria microplate beneath the Albanides. JNTS 2020, 51, 3–40. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R. Some data about the hydrochemistry of groundwater of Krujë-Dajt mountain chain (in Albanian). Stud. Gjeogr. 1998, 11, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, F.; Parise, M.; De Waele, J.; Jourde, H. A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M. Sinkholes. In Encyclopaedia of Caves, 3rd ed.; White, W.B., Culver, D.C., Pipan, T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 934–942. ISBN 978-0-12-814124-3. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M. Sinkholes, Subsidence and Related Mass Movements. In Treatise on Geomorphology, 2nd ed.; Shroder, J.J.F., Ed.; Elsevier; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 5, pp. 200–220. ISBN 9780128182345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, Z.; Gunn, J.; Goldscheider, N.; Ravbar, N. Karst Environment and Management of Aquifers; The Groundwater Project: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, I. La prima volta. Ipogea 2021, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Turc, L. Le bilan d’eau des sols. Relations entre les precipitation, l’évaporation et l’écoulement. Ann. Agron. 1954, 5, 491–595. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R.; Malik, P. Assessment of regional flow type and groundwater sensitivity to pollution using hydrograph analyses and hydrochemical data of the Selita and Blue Eye karst springs, Albania. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2045–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B. Geomorphology and Hydrology of Karst Terrains; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Karoly, G. Investigation of Bauxites in Albania During 1958; Archive of AGS: Tirana, Albania, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, J. A theoretical analyses of groundwater flow in small drainage basins. J. Geophys. Res. 1963, 68, 4795–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J. Groundwater as a geologic agent: An overview of the cause, processes, and manifestations. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J. Springs seen and interpreted in the context of groundwater flow-systems. In Proceedings of the GSA Annual Meeting 2009, Portland, OR, USA, 18–21 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Doucette, R.; Peterson, E.W. Identifying water sources in a karst aquifer using thermal signatures. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 5171–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.V.; Nevrev, A.G. Klasifikacija Podzemnih Mineralni Vod (Classification of Underground Mineral Waters); Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1964. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hem, D.H. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1970; 360p.
- Reiman, C.; Birke, M. Geochemistry of European Bottled Water; Borntraeger Science Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thraikill, J. Relative solubility of limestone and dolomite. Karst Hydrol. AIH Mem. 1977, 12, 491–500. [Google Scholar]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Longmuir, D. The geochemistry of some carbonate waters of Central Pennsylvania. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1971, 35, 1023–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, E.T.; White, W.B. Seasonal fluctuations in the chemistry of limestone springs: A possible mean for characterizing carbonate aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1971, 14, 93–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zötl, J.G. Karst Hydrogeology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1974; p. 291. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R. Hydrochemical characteristics of some lithologically different karst massifs of Albania. In Proceedings of the Water Resources & Environmental Problems in Karst, Proceeding International Conference and Field Seminar, Belgrade, Serbia, 14–19 September 2005; Stevanović, Z., Milanovic, P., Eds.; Geological Faculty of Belgrade University: Belgrade, Serbia, 2005; pp. 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Klimchouk, A.; Eftimi, R.; Andreychouk, V. Hypogene karst in the External Albanides and its pronounced geomorphological effect. In Proceedings of the 18th International Congress of Speleology, Savoie Mont Blanc, France, 24–31 July 2022. Karstologia Mémoires 24. [Google Scholar]
- Velaj, T. The effect of the evaporate tectonic in the structural model of the Berati belt of Albanides. Balk. Geophys. Soc. 1999, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Velaj, T. Evaporites in Albania and their impact on thrusting processes. J. Balk. Geophys. Soc. 2001, 4, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J. Groundwater flow systems: Analyses, characterization and agency in karst genesis. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Hierarchical Flow Systems in Karst Regions, Budapest, Hungary, 4–7 September 2013; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Andreychouk, V.; Eftimi, R.; Nita, J.; Klimchouk, A. Geomorphology and hydrogeology of an exposed evaporite dome: The Dumre karst area, Central Albania. Geol. Q. 2021, 65, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, Y.; Bertrand, C.; Compagnon, F.; Follaci, I.P.; Mudry, I. Acquisition of water chemistry in a mobile fissured basement massif: Its role in the hydrogeology knowledge of the Clipière landslide (Mercauntour massif, southern Alps, France). J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalowicz, M. Karst groundwater: A challenge for new resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.W. The role of the epikarst in karst and cave hydrogeology: A review. Int. J. Speleol. 2008, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotzl, H. Industrial and urban produced impacts: In Karst Hydrogeology and Human Activities; Drew, D., Hotzl, H., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 81–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, J. The geomorphological impacts of limestone quarrying. Catena 1993, 25, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, J. Quarrying of limestones. In Encyclopedia of Cave and Karst Science; Gunn, J., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2004; pp. 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Formicola, W.; Gueguen, E.; Martimucci, V.; Parise, M.; Ragone, G. Caves below Quarries and Quarries above Caves: Problems, Hazard and Research. A Case Study from Southern Italy; Abstracts with Program; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M. Hazards in karst. In Proceedings of the International Interdisciplinary Scientific Conference “Sustainability of the Karst Environment. Dinaric Karst and other Karst Regions”, Plitvice Lakes, Croatia, 23–26 September 2009; Bonacci, O., Ed.; Series on Groundwater. IHP-UNESCO: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M. Modern Resource use and Its Impact in Karst Areas—Mining and Quarrying. Z. Geomorphol. 2016, 60, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.; Qiriazi, P.; Sala, S. Natural and anthropogenic hazards in karst areas of Albania. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 4, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.; Qiriazi, P.; Sala, S. Evaporite karst of Albania: Main features and cases of environmental degradation. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiriazi, P.; Parise, M.; Sala, S. Il carsismo nei gessi del territorio albanese. Mem. Ist. Ital. Speleol. 2004, 16, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Eftimi, R.; Zojer, H. Human impacts on karst aquifers of Albania. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beynen, P.E.; Townsend, K.M. A disturbance index for karst environments. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, L.A.; van Beynen, P.E.; Parise, M. Interregional comparison of karst disturbance: West-central Florida and southeast Italy. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1770–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F.; Parise, M. Evaluating the human disturbance to karst environments in southern Italy. Acta Carsologica 2006, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beynen, P.E.; Brinkmann, R.; van Beynen, K. A sustainability index for karst environments. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2012, 74, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.; Parise, M. On the implementation of environmental indices in karst. In Karst Groundwater Contamination and Public Health; White, W.B., Herman, J.S., Herman, E.K., Rutigliano, M., Eds.; Advances in Karst Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 245–247. ISBN 978-3-319-51069-9. [Google Scholar]






| Number Spring-Sp Water Well-WW | Date [d/m/y] | Q L/s | T [°C] | pH | EC µS/cm | TDS mg/L | Th °G | H2S mg/L | C mg/L | Mg mg/L | Na + K mg/L | NH4 mg/L | Cl mg/L | SO4 mg/L | HS mg/L | HCO3 mg/L | Hydrochemical Type | rHCO3/ rCl | rCa/ rMg | rNa/ rCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Zheji Sp | 7 February 1990 (3) | 6.0 | 14.1 | 7.14 | - | 340 | 18 | no | 87.4 | 25.0 | 16.1 | no | 14.2 | 30.4 | - | 370.9 | HCO3-Ca-Mg | 15.2 | 2.13 | 1.75 |
| 2 Faruku Sp | 17 March 1993 | - | 14.5 | 7.05 | - | 243 | 10.2 | no | 56.7 | 9.7 | 17.2 | - | 8.9 | 13.1 | no | 234.8 | HCO3-Ca | 15.4 | 3.53 | 3.0 |
| 3 Upper-Zheji Sp | 17 March 1993 | - | 13.9 | 7.10 | - | 256 | 14.0 | no | 71.9 | 16.8 | 3.0 | no | 10.6 | 7.4 | no | 271.4 | HCO3-Ca-Mg | 17.8 | 2.6 | 0.43 |
| 4 Makaresh Sp | 27 December 1955 (1) | 500 | 16.2 | 6.95 | - | 616.3 | 33.0 | 14.8 | 102.4 | 53.7 | 29.4 | - | 115.6 | 83.1 | - | 341.0 | HCO3-Cl-Ca-Mg | 1.71 | 1.51 | 0.39 |
| 5 White water Sp-1 | 1 December 1955 (1) | 20.0 | 18.5 | 6.9 | - | 1254 | 33.0 | 69.7 | 150.3 | 51.1 | 242.4 | 2.4 | 432.6 | 131.7 | 21.5 | 413.6 | Cl-HCO3-Na | 0.56 | 1.79 | 0.86 |
| October 1970 (2) | 7.0 | 19.7 | 6.6 | - | 1005 | 37.3 | 70.0 | 144.1 | 74.3 | 145.1 | 10.0 | 294.3 | 97.1 | 420.9 | Cl-HCO3-Na | 0.83 | 2.35 | 0.76 | ||
| 5 White water Sp-5 | 1 December 1955 (1) | 20.0 | 22.5 | 6.75 | - | 5332 | 93.0 | 357.8 | 388.8 | 167.8 | 1264.5 | 16.6 | 2382.0 | 615.6 | 114.2 | 531.9 | Cl-Na-Ca | 0.13 | 1.41 | 0.82 |
| October 1970 (3) | 6.0 | 22.3 | 6.65 | - | 6130 | 120.0 | - | 583.0 | 168.0 | 1011.6 | - | 2220 | 788.0 | 480.6 | Cl-Na-Ca | 0.13 | 2.11 | 0.70 | ||
| 5 White water Sp-6 | 1 December 1955 (1) | 7.0 | 21.5 | 6.85 | - | 5190 | 93.0 | 326.5 | 388.8 | 166.4 | 1300.9 | 6.1 | 2340.5 | 599.0 | 94.7 | 526.4 | Cl-Na-Ca | 0.13 | 1.42 | 0.86 |
| 6 Water well no 10 | 10 October 1970 (2) | 3.8 | 22.0 | 6.90 | - | 5282 | 82 | - | 434.4 | 91.66 | 1044.3 | 125.0 | 2109.9 | 579.4 | - | 579.3 | Cl-Na-Ca | 0.16 | 2.77 | 0.82 |
| 7 Water supply well | 25 November 2002 | 40 | 16.4 | 7.4 | 645 | 350 | 19 | no | 98.2 | 22.5 | 16.1 | no | 16.0 | 12.8 | no | 409.9 | HCO3-Ca-Mg | 15.0 | 2.65 | 1.56 |
| 8 Water supply well | 7 February 1990 | - | 16.4 | 7.5 | 613 | 369 | 19 | no | 100.2 | 21.45 | 17.25 | trace | 14.2 | 15.2 | no | 414.8 | HCO3-Ca-Mg | 21.2 | 2.8 | 1.5 |
| 9 Water well | 7 February 1990 | - | 16.4 | 7.45 | 612 | 365 | 336 | no | 99.2 | 21.45 | 18.4 | - | 16.0 | 14.4 | no | 413.6 | HCO3-Ca-Mg | 15.0 | 2.8 | 1.8 |
| 10 Water well | 7 February 1990 | - | 16.4 | 7.05 | 577 | 327 | 194 | no | 93.3 | 21.45 | 16.1 | trace | 12.4 | 11.1 | no | 398.9 | HCO3-Ca-Mg | 18.7 | 2.6 | 2.0 |
| 11 Droja Sp-1 | 29 March 1999 | 6.5 | 13.8 | 7.5 | 459 | 275 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | HCO3-Ca-Mg | - | - | - |
| 12 Droja Sp-2 | 29 March 1999 | 0.5 | 14.1 | 7.7 | 565 | 339 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | HCO3-Ca-Mg | - | - | - |
| Location | Date d/m/v | Q l/s | T °C | pH | EC µS/cm | Water Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Water, no. 1 | 17 November 1999 | 3.0 | 21.1 | - | 5530 | Thermal |
| 10 February 2002 | - | 20.9 | - | 5720 | ||
| 13 April 2000 | - | 21.2 | - | 5730 | ||
| 2 August 2000 | - | 21.2 | - | 5340 | ||
| 15 December 2000 | - | 21.0 | - | 6350 | ||
| 15 August 2010 | 3.5 | 21.2 | 6.8 | 6080 | ||
| 23 August 2023 | 2.8 | 21.5 | 6.47 | 4980 | ||
| White Water, no. 2 | 17 November 1999 | 0.7 | 21.3 | - | 6970 | Thermal |
| 15 August 2010 | 3.0 | 22.3 | 6.6 | 6890 | ||
| White Water, no. 3 | 17 November 1999 | 0.8 | 20.9 | - | 7430 | Thermal |
| 15 August 2010 | 1.0 | 22.6 | 6.6 | 5990 | ||
| White Water, no. 4 | 17 November 1999 | 3.0 | 21.2 | - | 7210 | Thermal |
| 15 August 2010 | 1.5 | 22.8 | 6.6 | 7840 | ||
| White Water, no. 5 | 17 November 1999 | 8.0 | 21.7 | - | 6880 | Thermal |
| 15 August 2010 | 4.7 | 22.5 | 6.63 | 7260 | ||
| 23 August 2023 | 7.8 | 22.5 | 6.54 | 5960 | ||
| White Water, no. 7 | 15 August 2010 | 1.5 | 21.7 | 6.65 | 7390 | |
| White Water, no. 8 | 17 November 1999 | 20.0 | 20.1 | - | 4430 | Thermal |
| 10 February 2000 | - | 19.9 | - | 4190 | ||
| 13 April 2000 | - | 20.0 | - | 4120 | ||
| 2 August 2000 | - | 20.2 | - | 4700 | ||
| 15 December 2000 | - | 20.2 | - | 4900 | ||
| 15 August 2010 | 11.0 | 19.8 | 6.7 | 4300 | ||
| Zhjeji borehole, no. 6 | 16 November 1999 | 2.2 | 22.0 | - | 6380 | Thermal |
| 10 February 2000 | - | 22.0 | - | 6417 | ||
| 13 April 2000 | - | 22.1 | - | 6880 | ||
| 2 August 2000 | - | 22.8 | - | 7400 | ||
| 15 December 2000 | - | 22.0 | - | 7470 | ||
| 15 August 2010 | 1.8 | 22.0 | 6.75 | 8200 | ||
| Makareshi spring | 27 June 2007 | 85 | 16.2 | - | 970 | Fresh |
| Zheji fresh-water spring | 7 February 1990 | 6.0 | 14.1 | 7.14 | 577 | Fresh |
| Water supply well, no. 48 | 25 November 2002 | 40 | 16.6 | 7.4 | 645 | Fresh |
| Components | Unit | Spring 5.5 | Spring 5.1 | Spring 5.6 | Makaresh Spring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brom, Br | mg/L | 1.2 | |||
| Jodi, J | mg/L | 0.4 | |||
| Hydrosulfite, HS | mg/L | 114.2 | 21.5 | 94.7 | 6.9 |
| Thiosulfate, S2O3 | mg/L | 1.1 | 1.1 | ||
| Sulfite, SO3 | mg/L | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||
| Acid salicylic, H2SiO3 | mg/L | 28.0 | 13.0 | 27.6 | 32.4 |
| Acid boric, HBO2 | mg/L | 17.8 | |||
| Total sulfidic gas, H2S | mg/L | 357.8 | 69.7 | 326.5 | 14.8 |
| Free sulfidic gas, H2S | mg/L | 239.0 | 47.3 | 228.7 | 7.2 |
| Free carbonic gas, CO2 | mg/L | 141.7 | 74.4 | 138.6 | |
| Free nitrogen gas, N2 | % volume | 71.5 | |||
| Free carbonic gas, CO2 | % volume | 15.41 | |||
| Free methane gas, CH4 | % volume | 8.66 | |||
| Free sulfidic gas, H2S | % volume | 4.43 | |||
| Dissolved sulfidic gas, H2S | ml | 155.1 | |||
| Dissolved carbonic gas, CO2 | ml | 71.7 | |||
| Dissolved nitrogen gas, N2 | ml | 14.7 | |||
| Dissolved methane gas, CH4 | ml | 8.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eftimi, R.; Liso, I.S.; Parise, M. Hydrogeological Characteristics of the Makaresh Carbonate Karst Massif (Central Albania). Hydrology 2024, 11, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11020029
Eftimi R, Liso IS, Parise M. Hydrogeological Characteristics of the Makaresh Carbonate Karst Massif (Central Albania). Hydrology. 2024; 11(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleEftimi, Romeo, Isabella Serena Liso, and Mario Parise. 2024. "Hydrogeological Characteristics of the Makaresh Carbonate Karst Massif (Central Albania)" Hydrology 11, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11020029
APA StyleEftimi, R., Liso, I. S., & Parise, M. (2024). Hydrogeological Characteristics of the Makaresh Carbonate Karst Massif (Central Albania). Hydrology, 11(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11020029







