Fuzzy Analytical Solution of Horizontal Diffusion Equation into the Vadose Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Classical (Crisp) Case
- Initial condition
- Initial condition
- Boundary condition
- The sorptivity S;
- The moisture content front ;
- The water profiles in the form of
2.2. Fuzzy Case
2.2.1. Fuzzy Theory
- (a)
- is increasing, is decreasing as functions of α, and , or
- (b)
- is decreasing, is increasing as functions of α, and .
- is (i)-gH-differentiable at x0 if
- (i)
- is (ii)-gH-differentiable at x0 if
- (ii)
- is [(i)-p]-differentiable w.r.t. x at (x0, t0) if:
- is [(ii)-p]-differentiable w.r.t. x at (x0, t0) if:
- [(i)-p]-differentiable w.r.t. x, if the type of [gH-p]-differentiability of both is the same,
- [(ii)-p]-differentiable w.r.t. x, if the type of [gH-p]-differentiability of both is different,
2.2.2. Possibility Theory
2.2.3. Fuzzy Model
- Initial condition
- Boundary conditions
- (a)
- The soil moisture contents θs (saturated soil moisture content);
- (b)
- θr (the residual soil moisture content);
- (c)
- The parameter λ1 (in the exponent of the diffusivity D).
- Non-dimensional form:
- Dimensional form:
- Non-dimensional form:
- Dimensional form:
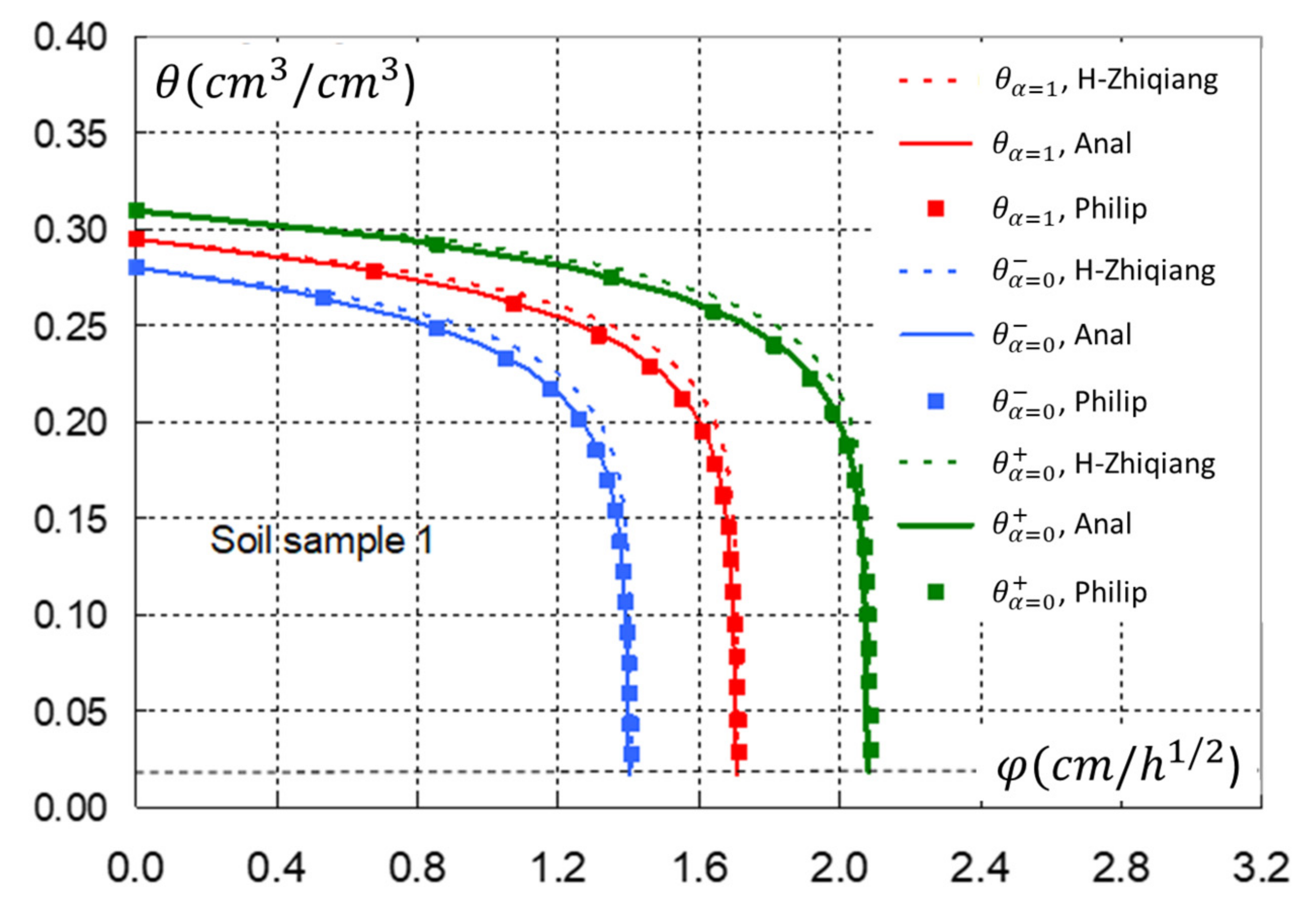
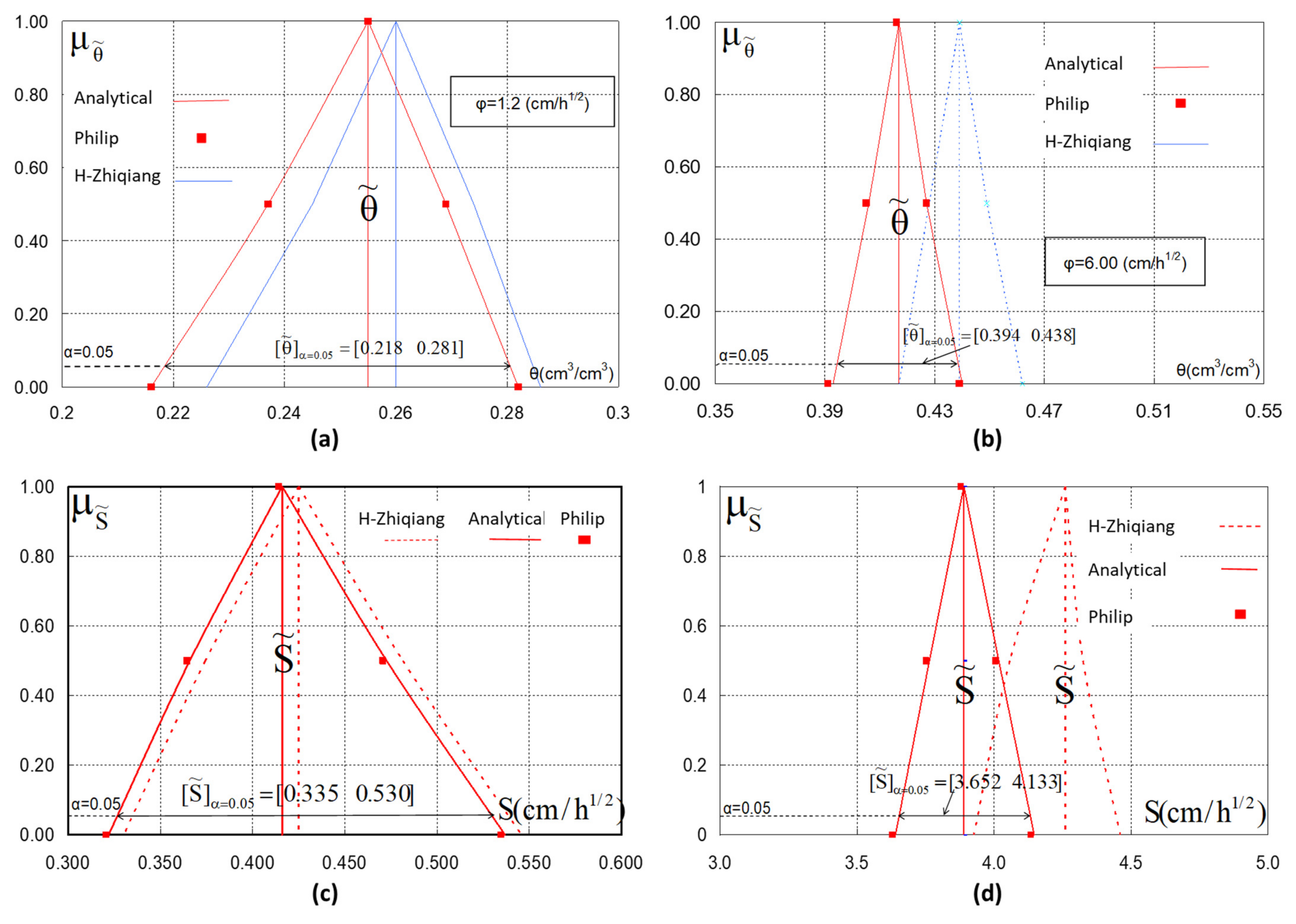
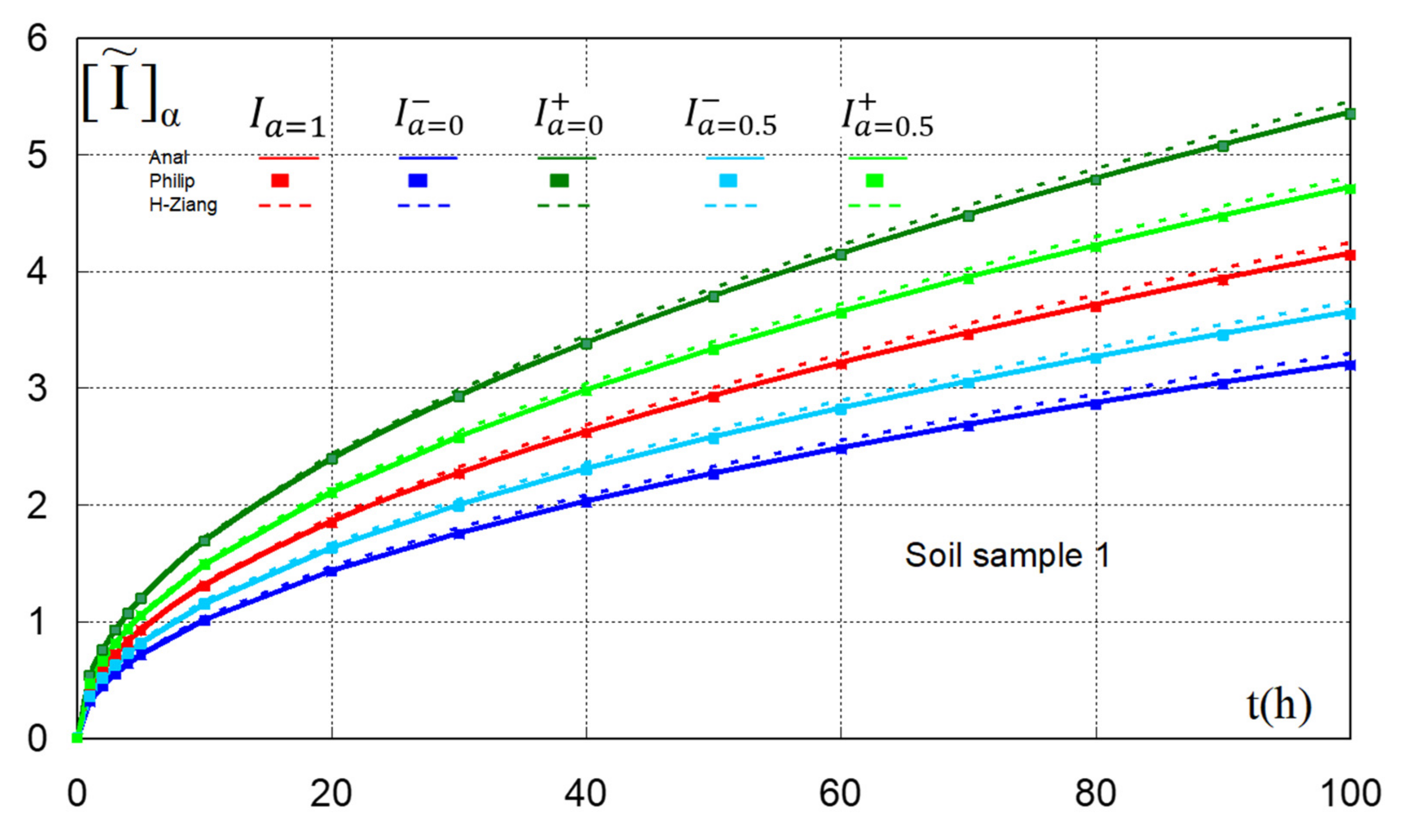
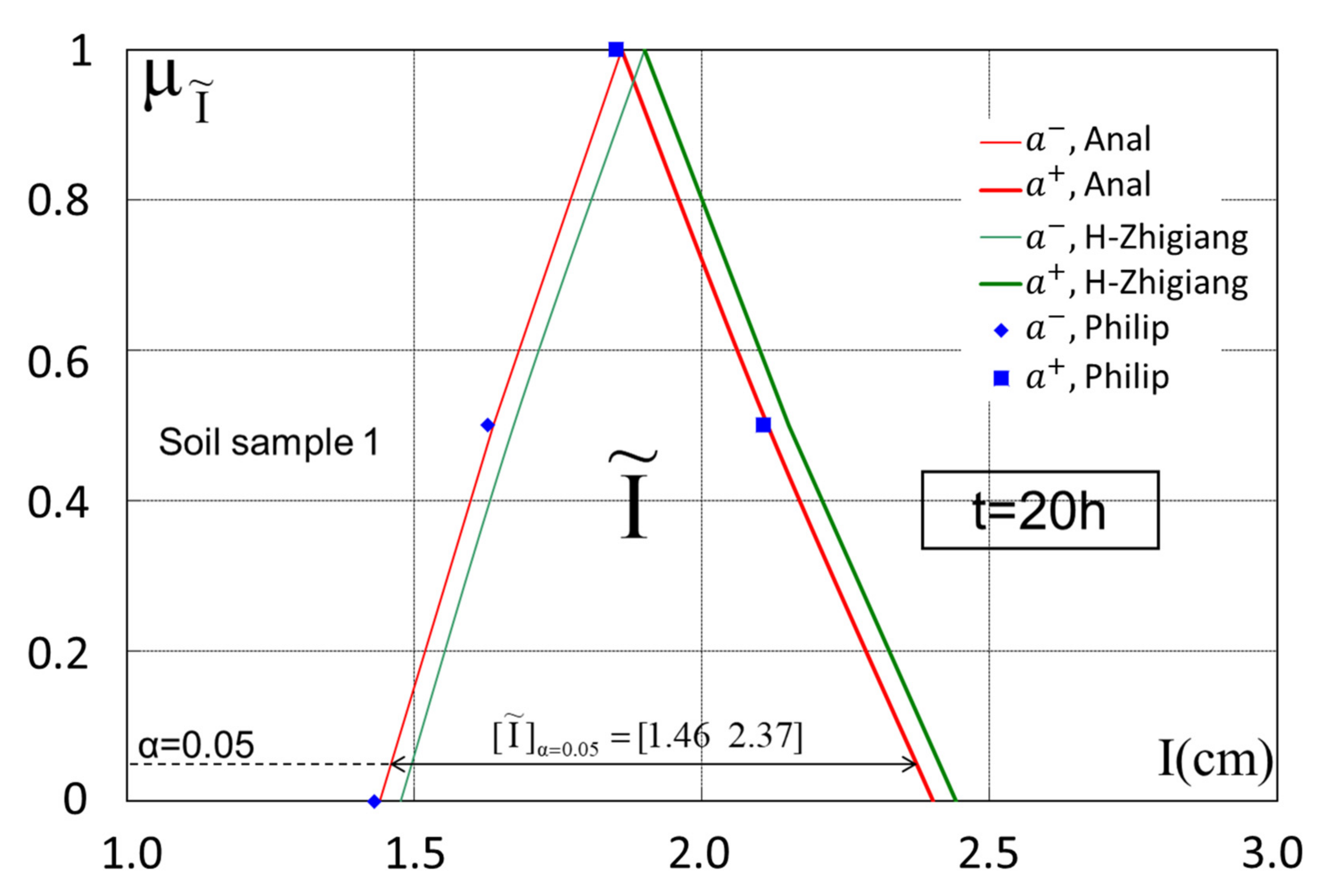
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Construction of the Hang and Zhiqiang Solution
- Diffusivity is an exponential function of Θ;
- The value of the moisture wetting front is a priori known.
3.2. Results
- (a)
- Soil sample 1 εmean = 2.669 × 10−2;
- (b)
- Soil sample 2 εmean = 8.04 × 10−2.

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckingham, E. Studies on the Movement of Soil Moisture; Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.; Widtsoe, J.A. The Movement of Soil Moisture. Soil Sci. 1921, 11, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, E.C. The Transport of Water through Heavy Clay Soils. I. J. Agric. Sci. 1936, 26, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, E.C. The Transport of Water through Heavy Clay Soils. III. J. Agric. Sci. 1936, 26, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A. A numerical method for solving the flow equation for water in unsaturated materials. Soil Sci. 1952, 73, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de La Ville de Dijon; Victor Dalmont: Paris, France, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. Theory of Infiltration. In Advances in Hydroscience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1969; pp. 215–296. [Google Scholar]
- Shahraiyni, H.T.; Ashtiani, B.A. Comparison of Finite Difference Schemes for Water Flow in Unsaturated Soils. Int. J. Mech. Ind. Aerosp. Eng. 2009, 3, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez-Negrete, C.; Domínguez-Mota, F.J.; Santana-Quinteros, D. Numerical Solution of Richards’ Equation of Water Flow by Generalized Finite Differences. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 101, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarinas, N.; Tzimopoulos, C.; Evangelides, C. Fuzzy Numerical Solution to Horizontal Infiltration. Int. J. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Savović, S.; Drljača, B.; Djordjevich, A. A Comparative Study of Two Different Finite Difference Methods for Solving Advection–Diffusion Reaction Equation for Modeling Exponential Traveling Wave in Heat and Mass Transfer Processes. Ric. Mat. 2022, 71, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarinas, N.; Tzimopoulos, C.; Evangelides, C. Fuzzy Numerical Solution to the Unconfined Aquifer Problem under the Boussinesq Equation. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3210–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarinas, N.; Tzimopoulos, C.; Evangelides, C. An Efficient Method to Solve the Fuzzy Crank–Nicolson Scheme with Application to the Groundwater Flow Problem. J. Hydroinformatics 2022, 24, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevoisier, D.; Chanzy, A.; Voltz, M. Evaluation of the Ross Fast Solution of Richards’ Equation in Unfavourable Conditions for Standard Finite Element Methods. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahs, M.; Younes, A.; Lehmann, F. An Easy and Efficient Combination of the Mixed Finite Element Method and the Method of Lines for the Resolution of Richards’ Equation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzis, G.K.; Tzimopoulos, C.D.; Evangelides, C.H. Numerical Solution of Richards’ Equation With Control Volume Method. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 2004, 15, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.; Shoshtari, M.; Adid, A. Numerical Solution of Richards Equation by Using of Finite Volume Method. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 14, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. On Solving the Unsaturated Flow Equation 1: The Flux Concentration Relation. Soil Sci. 1973, 116, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Evangelides, C.; Papadopoulos, B. Fuzzy Solution to the Unconfined Aquifer Problem. Water 2018, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Evangelides, C. Fuzzy Analytical Solution to Horizontal Infiltration. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2019, 19, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Papaevangelou, G.; Papadopoulos, K.; Evangelides, C.; Arampatzis, G. Fuzzy Analytical Solution to Vertical Infiltration. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 2020, 13, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Evangelides, C.; Papadopoulos, B. Analytical Solutions of Advection-Dispersion Equation Using Fuzzy Theory. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 193, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Samarinas, N.; Papadopoulos, K.; Evangelides, C. Fuzzy Unsteady-State Drainage Solution for Land Reclamation. Hydrology 2023, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolikas, P.K.; Sidiropoulos, E.G.; Tzimopoulos, C.D. A Simple Analytical Solution for the Boussinesq One-Dimensional Groundwater Flow Equation. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Some Exact Solutions for Nonlinear Desorptive Diffusion. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 1982, 33, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Lisle, I.G.; Parlange, J.-Y. Analytical Reduction for a Concentration Dependent Diffusion Problem. ZAMP Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 1993, 44, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, L.; Zhiqiang, L. Almost Analytic Solutions and Their Tests of the Horizontal Diffusion Equation for the Movement of Water in Unsaturated Soil. Appl. Math. Mech. 1997, 18, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedello, C.L.; Loyola, J.M.T.; Reichardt, K.; Nielsen, D.R. New Analytic Solution of Boltzmann Transform for Horizontal Water Infiltration into Sand. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Evangelides, C.; Arampatzis, G. Explicit Approximate Analytical Solution of the Horizontal Diffusion Equation. Soil Sci. 2015, 180, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauclin, M.; Haverkamp, R. Solutions Quasi Analytiques de l’équation d’absorption de l’eau Par Les Sols Non Saturés. Agronomie 1985, 5, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Analytical Model for Volatile Organic Compound Transport in the Coupled Vadose Zone–Groundwater System. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2021, 26, 04020058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Saleem, M.T. Applications of Orthogonal Polynomials in Simulations of Mass Transfer Diffusion Equation Arising in Food Engineering. Symmetry 2023, 15, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Saleem, M.T. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Reaction–Diffusion System and Its Application to Turing Pattern Formation in a Gray–Scott Model. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy logic. Computer 1988, 21, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M.L.; Ralescu, D.A. Differentials of Fuzzy Functions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1983, 91, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukuhara, M. Integration Des Applications Measurables Dont La Valeur Est Un Compact Convexe. Funkc. Ekvacioj 1967, 10, 205–233. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobiev, D.; Seikkala, S. Towards the Theory of Fuzzy Differential Equations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2002, 125, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, D.; Lakshmikantham, V.; Nieto, J. Initial and Boundary Value Problem for Fuzzy Differential Equations. Nonlinear Anal. 2003, 54, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, J.J.; Rodríguez-López, R. Bounded Solutions for Fuzzy Differential and Integral Equations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2006, 27, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, B.; Gal, S.G. Generalizations of the Differentiability of Fuzzy-Number-Valued Functions with Applications to Fuzzy Differential Equations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2005, 151, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, B. A Note on “Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Associated with Non-Linear Fuzzy Differential Equations”. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2006, 157, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, L. A Generalization of Hukuhara Difference and Division for Interval and Fuzzy Arithmetic. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2010, 161, 1564–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahviranloo, T.; Gouyandeh, Z.; Armand, A.; Hasanoglu, A. On Fuzzy Solutions for Heat Equation Based on Generalized Hukuhara Differentiability. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2015, 265, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazandarani, M.; Xiu, L. A Review on Fuzzy Differential Equations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 62195–62211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.R.; Mayhugh, M.S. Solutions and Tests of the Diffusion Equation for the Movement of Water in Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1958, 22, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, K.; Nielsen, D.R.; Biggar, J.W. Scaling of Horizontal Infiltration into Homogeneous Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.D.; Bresler, E. A Quick Method for Estimating Soil Water Diffusivity Functions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer zur Capellen, W. Integraktafelf—Sammlung Unbestimmter Integrale Elementarer Functionen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Oldham, K.; Myland, J.; Spanier, J. An Atlas of Functions, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanujan, S.; Hardy, G.H.; Seshu Aiyar, P.V.; Wilson, B.M.; Berndt, B.C. Collected Papers of Srinivasa Ramanujan; AMS Chelsea Pub.: Providence, RI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, H.M.; Kirkham, D.; Amemiya, M. A Comparison of Two Methods for Determining Soil Water Diffusivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whisler, F.D.; Klute, A.; Peters, D.B. Soil Water Diffusivity from Horizontal Infiltration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1968, 32, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clothier, B.E.; Scotter, D.R.; Green, A.E. Diffusivity and One-Dimensional Absorption Experiments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D. Porosity and Soil-Water Diffusivity Relations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1963, 27, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.F.; Horton, R. An Empirical Function to Describe Measured Water Distributions From Horizontal Infiltration Experiments. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofziger, D.L. Errors in Gamma-Ray Measurements of Water Content and Bulk Density in Nonuniform Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelides, C.; Arampatzis, G.; Tzimopoulos, C. Estimation of Soil Moisture Profile and Diffusivity Using Simple Laboratory Procedures. Soil Sci. 2010, 175, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoiţă, C.V.; Ralescu, D.A. Representation Theorems for Fuzzy Concepts. Kybernetes 1975, 4, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetshel, R.; Voxman, W. Elementary Fuzzy Calculus. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 18, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, B.; Stefanini, L. Generalized Differentiability of Fuzzy-Valued Functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2013, 230, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khastan, A.; Nieto, J.J. A Boundary Value Problem for Second Order Fuzzy Differential Equations. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 2010, 72, 3583–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. When Upper Probabilities Are Possibility Measures. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1992, 49, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Foulloy, L.; Mauris, G.; Prade, H. Probability-Possibility Transformations, Triangular Fuzzy Sets, and Probabilistic Inequalities. Reliab. Comput. 2004, 10, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Possibility Theory and Possibilistic Logic: Tools for Reasoning under and about Incomplete Information. In Intelligence Science III; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mylonas, N. Applications in Fuzzy Statistic and Approximate Reasoning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Thrace, Komotini, Greece, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.T. A Note on the Extension Principle for Fuzzy Sets. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1978, 64, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimopoulos, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Papadopoulos, B.; Samarinas, N.; Evangelides, C. Fuzzy Solution of Nonlinear Boussinesq Equation. J. Hydroinformatics 2022, 24, 1127–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| a/a | Soil Type | θr (cm3/cm3) | θs (cm3/cm3) | Dr cm2/min | λ1 | φexpfront (cm/min0.5) | φanalfront (cm/min0.5) | Sexp (cm/min0.5) | Sanal (cm/min0.5) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hagenet sand | 0.0540 | 0.370 | 9.443 × 10−2 | 6.756 | 5.857 | 5.870 | 1.490 | 1.490 | [54] |
| 2 | Hayden sandy loam | 0.0146 | 0.510 | 6.824 × 10−3 | 7.256 | 1.906 | 1.908 | 0.780 | 0.780 | [55] |
| 3 | Manawatu fine sand. loam | 0.0800 | 0.360 | 1.168 × 10−3 | 11.337 | 4.490 | 4.490 | 1.138 | 1.138 | [56] |
| 4 | Adelanto loam | 0.0380 | 0.387 | 6.678 × 10−8 | 18.690 | 1.010 | 1.010 | 0.333 | 0.333 | [57] |
| 5 | Edina silt loam | 0.0560 | 0.500 | 4.214 × 10−3 | 7.995 | 2.013 | 2.014 | 0.760 | 0.760 | [54] |
| 6 | Nicollet sandy loam | 0.0380 | 0.364 | 2.151 × 10−5 | 13.094 | 1.346 | 1.348 | 0.404 | 0.404 | [58] |
| 7 | Fayette silty clay loam | 0.0480 | 0.448 | 3.418 × 10−4 | 9.223 | 0.960 | 0.960 | 0.337 | 0.337 | [58] |
| 8 | Panoche clay loam | 0.0480 | 0.443 | 2.554 × 10−3 | 8.731 | 2.129 | 2.129 | 0.730 | 0.730 | [49] |
| 9 | Pine silty clay | 0.0500 | 0.463 | 8.349 × 10−9 | 20.262 | 0.750 | 0.750 | 0.294 | 0.294 | [57] |
| 10 | Yolo clay | 0.0400 | 0.490 | 3.265 × 10−4 | 6.869 | 0.360 | 0.360 | 0.131 | 0.131 | [59] |
| 11 | sample 1 | 0.0175 | 0.295 | 1.13 × 10−3 | 9.170 | 1.710 | 1.709 | 0.416 | 0.416 | [60] |
| 12 | sample 2 | 0.0080 | 0.500 | 2.992 × 10−1 | 6.618 | 9.930 | 9.910 | 3.890 | 3.890 | [60] |
| Method | Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | α-Cut | Hang and Zhiqiang (1) | Analytical (2) | Philip (3) | (2) vs. (3) | (1) vs. (3) |
| Soil sample 1 | ||||||
| S | 1 | 0.425 | 0.416 | 0.416 | 0 | 0.0254 |
| S− | 0.5 | 0.374 | 0.366 | 0.364 | 0.005 | 0.0268 |
| S+ | 0.5 | 0.481 | 0.473 | 0.471 | 0.0044 | 0.0225 |
| S− | 0 | 0.33 | 0.322 | 0.32 | 0.0046 | 0.0293 |
| S+ | 0 | 0.546 | 0.537 | 0.535 | 0.0043 | 0.0206 |
| mean = | 0.0037 | 0.0249 | ||||
| Soil sample 2 | ||||||
| S | 1 | 4.26 | 3.89 | 3.878 | 0.003 | 0.09 |
| S− | 0.5 | 4.057 | 3.764 | 3.753 | 0.003 | 0.075 |
| S+ | 0.5 | 4.325 | 4.017 | 4.005 | 0.003 | 0.074 |
| S− | 0 | 3.926 | 3.64 | 3.629 | 0.003 | 0.076 |
| S+ | 0 | 4.461 | 4.146 | 4.134 | 0.003 | 0.073 |
| mean = | 0.003 | 0.078 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tzimopoulos, C.; Samarinas, N.; Papadopoulos, B.; Evangelides, C. Fuzzy Analytical Solution of Horizontal Diffusion Equation into the Vadose Zone. Hydrology 2023, 10, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10050107
Tzimopoulos C, Samarinas N, Papadopoulos B, Evangelides C. Fuzzy Analytical Solution of Horizontal Diffusion Equation into the Vadose Zone. Hydrology. 2023; 10(5):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10050107
Chicago/Turabian StyleTzimopoulos, Christos, Nikiforos Samarinas, Basil Papadopoulos, and Christos Evangelides. 2023. "Fuzzy Analytical Solution of Horizontal Diffusion Equation into the Vadose Zone" Hydrology 10, no. 5: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10050107
APA StyleTzimopoulos, C., Samarinas, N., Papadopoulos, B., & Evangelides, C. (2023). Fuzzy Analytical Solution of Horizontal Diffusion Equation into the Vadose Zone. Hydrology, 10(5), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10050107










