Abstract
Storage tanks from rainwater harvesting systems (RWHs) are designed to provide flow equalization between rainfall and water demand. The minimum storage capacity required to take into account the maximum variations of stored water volumes, i.e., the active storage, depends basically on the magnitude and the variability of rainfall profiles and the size of the demand. Given the random nature of the variables involved in the hydrological process, probability theory is a suitable technique for active storage estimation. This research proposes a probabilistic approach to determine an analytical expression for the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the active storage as a function of rainfall moments, water demand and the mean number of consecutive storm events in a deficit sub-period. The equation can be used by developers to decide on the storage capacity required at a desired non-exceedance probability and under a preset water demand. The model is validated through a continuous simulation of the tank behavior using rainfall time series from Milan (Northern Italy).
1. Introduction
Demand for freshwater is rising with population growth and climate variations, resulting in water availability uncertainty in the near future [1]. Climate change leads to rainfall patterns alterations, increasing the frequency of extreme storm events and droughts [2,3,4]. Additionally, urban area sprawling and soil-sealing processes reduceinfiltration and evapotranspiration, increasing runoff peak flow and volume leading to more frequent floods [5,6,7,8]. Sustainable water management strategies encourage the adoption of non-conventional water resources, reducing the use of freshwater and stormwater on-site management as flood mitigation [9].
Harvested rainwater is an alternative water resource that can be used to supply for cases where drinking water is not required, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, cooling tower, fire suppression, washing machines and street washing, increasing the resiliency of urban water resources [10]. With additional treatment and higher costs, rainwater can also be used to meet potable water demands such as drinking, cooking, handwashing and bathing in case of freshwater scarcity [11,12]. Rainwater harvesting systems (RWHs) also serve as detention/retention for roof runoff that would otherwise be discharged directly to the drainage system, contributing to stormwater peak flow and volume control [13,14,15,16]. Stormwater volume control results in increasing receiving water quality, or by reducing untreated stormwater discharge on watercourses in the case of a separated sewer system or reducing the frequency of combined sewer overflows in the case of a combined sewer system, as is normally the case in Italy [17]. By reducing drinking water consumption, environmental impacts and costs related to water abstraction and purification are also reduced [18]. Incorporating RWHs provides multiple benefits for resilient, sustainable urban areas, from better use of water resources to flood and watercourses pollution control.
A rainwater harvesting system collects, concentrates, stores and treats rainwater from rooftops for on-site use, as shown in Figure 1. The storage tank can be either in the form of rain barrels for small-scale applications or cisterns in a large building. Once captured, collected rainwater can undergo treatment on physical and biological parameters through processes, including filtration, disinfection and other treatment strategies. The level of treatment required depends upon the type of use and local policies. Normally, a method for backup supply with municipal drinking water is present for periods of deficit, ensuring the water demand from users.
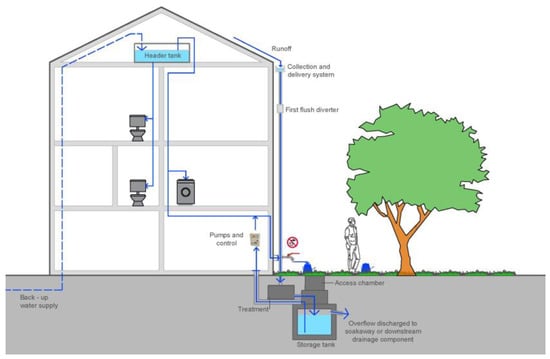
Figure 1.
Scheme of a rainwater harvesting system.
Among the components of RWHs, storage tanks are the most critical components for design, affecting user acceptance and the performance of the system. In the literature, several procedures have been proposed for storage tanks modeling and design [19,20,21,22,23]. They can be classified in the following categories: (i) simplified methods based on user-defined relationships, (ii) continuous mass balance simulations and (iii) statistical methods.
Simplified methods, designated as preliminary design techniques, can be used for rapid assessment, but their results should adjust with continuous simulation to account for the stochastic nature of rainfall and the equalization process within the storage unit [21,23,24]. They rely on simplifying assumptions, such as assuming releases to be constant and not considering the probability of failure or the variability of rainfall. Preliminary methods are useful tools to obtain a first estimation with few inputs. Examples are “demand-side” and “supply-side” approaches. The classical “demand-side” procedure calculates the rainwater tank volume as the total water demand during the longest water scarcity period, not considering the stochastic nature of the precipitation process at all. The design, in this case, is not related to the probability of failure represented by shorter or longer dry periods [25]. Additionally, the model assumes adequate rainfall and catchment area and neglects the possibility that inflows between dry periods are not enough to meet the water demand, especially when water demands are significant. Due to these assumptions, results can provide a less reliable water supply than expected and the tank may be overestimated. A variation in the “demand-side” has been developed in the United Kingdom [26]. The “supply-side” approach assumes the storage unit volume to contain the whole stormwater volume from the wet season within a year. By neglecting the demand, this method tends to overestimate the storage capacity.
Models based on continuous mass balance simulations are more accurate than simplified methods as they consider the whole rainfall process, incorporating seasonal fluctuations and the variability of water demand [10,25,27,28]. These methods rely on algorithms that describe the operation of the storage unit balancing inflows and outflows. The results accuracy, in this case, is strongly conditioned by the availability of long recorded rainfall time series.
Analytical-probabilistic approaches based on the stochastic nature of storm events relate design variables to a probabilistic level, proving the risk of failure, and can be used as a design tool with an accuracy related to a continuous simulation. These methods require as input the main statistic of rainfall data, i.e., rainfall depth, rainfall duration and interevent time, eliminating the need for long-term rainfall time series that are often unavailable. Probabilistic approaches were first suggested to model stormwater storage units for flood control but then were applied for multiple systems managing stormwater, such as green roofs, permeable pavements, infiltration trenches and RWH systems [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Recently, an equation applicable for different stormwater management systems obtained from the analytical-probabilistic was suggested [40]. Concerning probabilistic approaches developed specifically for RWHS, [41] proposed a model useful to estimate the required rainwater storage as a function of desired water use rate, reliability and local climate. In deriving these formulas, authors represented local climate characteristics by probabilistic models and incorporated them into the stochastic description of storage unit operation. A stochastic model for RWHs was also developed by [42] to quantify the water supply reliability and stormwater capture efficiency of RWH systems representing the input rainfall series as a marked Poisson process. Another contribution was given by [30] that proposed a probabilistic estimation of the active storage of rainwater tanks as function of main moments, expected value and variance, of daily or monthly rainfall depths and the number of rainy days in the reference analysis period. Recently, [32] developed, through stochastic integration, probabilistic equations for RWHs expressing the water balances variations, post-rainfall RWSU full-storage probability and system reliability with random rainfall features and variable water demands.
This research proposes a new probabilistic approach to estimate the CDF of the active storage assuming necessary storage capacity for flow equalization on a RWH under the assumption of constant water demand. The developed equations are functions of the stochastic rainfall process (expected value and standard deviations of rainfall depth, rainfall duration and inter-event time), water demand volume and the mean number of consecutive rainfall events in a deficit sub-period. The probabilistic nature of the method, based on the stochastic process of rainfall events, provides a reliable design tool for RWHs, relating the storage capacity to a probability level.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Probabilistic Modeling of a Rainwater Tank
Although generally tanks in hydraulic systems can perform different functions, for RWHs, the main role is flow equalization. An equalization tank function as a buffer compensating inflow and outflows fluctuations. During the flow balancing period of tank T, surplus sub-periods, where inflows are higher than the outflows, and deficit sub-periods, where outflows are higher than inflows, alternate continuously. Inflows, in case of a rainwater tank, are related to the rainfall pattern over time, while outflows represent water demand profile for non-potable use. The active storage W of a tank, for a certain T, is the minimum storage capacity required to take account of the maximum variations of stored water volumes and is defined by the critical period as the longest period where the tank goes from completely full to empty.
The equalization of the fluctuations of supply and demand during an indefinitely long period of time is feasible thanks to the ability of the tank to store the exceeding water during surplus sub-periods and release this water volume during successive deficit sub-periods. The variation of the storage volume is different in each surplus and deficit sub-period. It is positive during sub-surplus periods and negative during deficit ones. The active storage W for a flow balancing time period T can be determined by analyzing the maximum variations of the storage volume over the period of time T. Positive variations can be theoretically illimited, depending mainly on rainfall process. However, in each surplus sub-period, there is no need to store more water than the difference between outflows and inflows in the successive deficit sub-period. Negative differences cannot be greater in modulus than the total demand during the longest deficit sub-period. In this sense, the maximum value of W, , is:
where D represents the average water demand for non-potable use.
For this reason, a widely commonly adopted method for the evaluation of the capacity of a storage tank is to take it equal to the total water demand during the longest deficit period, i.e., taking it equal to . This is called “demand-side” approach. This approach falls on the mentioned simplified methods and may overestimate the active storage volume since it does not take into account the inflows contribution, which in most cases is present even in deficit sub-periods.
A more accurate approach consists of evaluating the active storage volume of a generic rainwater tank in surplus conditions—when cumulative inflows are higher than cumulative outflows over the period T—as the maximum difference between cumulative outflows and inflows during deficit sub-periods, considering the stochastic nature of the variables involved in the process. The development of this new probabilistic approach, useful to evaluate the CDF of the active storage, is based on the simplified assumption that outflows from the storage tank are constant over time and equal to the average water demand for specific water reuse. A more detailed estimate of water demand, considering its variability, would not be easily obtainable due to the number of factors involved in the process. For example, domestic uses vary according to the (random) number of users, to their life habits, to seasonal weather changes, etc. However, regarding the hypothesis of constant water demand, [43] tested that for the toilet water demand considered in the present study, the daily toilet use pattern in residential households is rather constant during the year.
The input variable to the probabilistic approach is rainfall. Independent rainfall events should be identified from a continuous series of rainfall data. Several methods are mentioned in the literature for storm events separation. A common criterion used by hydrologists is the minimum inter-event time (IETD) which consists of the minimum dry period between consecutive storm events that characterizes them as independent [44,45,46,47]. Once an IETD is selected, the independent storm events are separated by analyzing the entire rainfall time series: if interevent time between two consecutive rainfall events is smaller than IETD, the two storms are combined in a single event; otherwise, they are considered independent. The definition of the IETD depends upon catchment response. For small urban catchments with small concentration times, IETD are between 1 to 12 h, whereas, for large anthropized or rural catchment, IETD can be several hours. In this study, an IETD equal to 1 h was selected as RWHs are installed on small catchment with short concentration times.
Let us consider a generic sub-period in , in which n consecutive chained independent rainfall events occur. The variable n is a discrete upper bounded random variable defined in the domain of natural numbers. So, and N . Let us also define the non-monotonic function as:
where D is the average water demand (mm/day), is the ith rainfall event duration (days), is the ith interevent time (days) and is the ith rainfall event depth (mm).
If h, θ and d are independent, first and second moment of the function i.e., expected value and variance, can be determined as follows:
where D is the non-potable water demand (mm/day), , , are sample mean rainfall event duration (days), sample mean interevent time (days) and sample mean rainfall event depth (mm), respectively, are sample variance of the same meteorological random variables and n is the mean number of consecutive rainfall events in the considered sub-period of analysis.
At the end of a deficit sub-period , the cumulative water demand is greater than the cumulative inflow to the tank, so the following condition must hold in :
that is, in .
For this condition, the active storage W can be expressed by the following relationship:
The function defines the difference between the cumulative water demand and the inflow to the tank at the end of the deficit sub-period . Applying the probabilistic approach to the analytical Equations (2) and (8) allows the estimation of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the active storage . The first step is the definition of the probability distribution function for the modeling of the random variable To this scope, a normal distribution function is assumed:
where and represent the cumulative distribution function and the probability density function of the random variable respectively.
With this assumption, expected value and variance of the random variable can be computed as:
where:
Assuming an exponential distribution for the random variable , the cumulative distribution function of the active storage can be finally computed through the following expression:
Equation (16) allows to determine the cumulative distribution function of the active storage for a generic rainwater tank under the assumption of constant water demand through the proposed analytical-probabilistic method. This approach gives the possibility to adjust the design of rainwater system to a predefined level of failure risk considering the whole stochastic process of rainfall events. The flowchart in Figure 2 summarizes the procedure for determination through the analytical-probabilistic method.
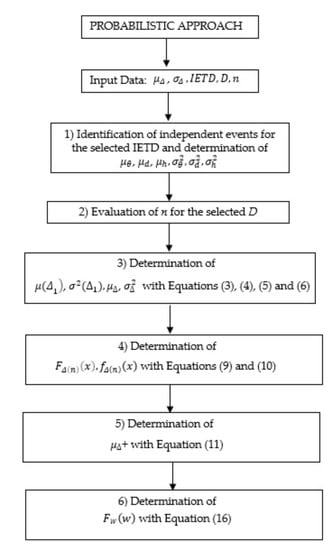
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the proposed probabilistic method.
2.2. Continuous Simulation
To validate the proposed probabilistic method, a continuous simulation based on the Yield Before Spillage (YBS) operating rule was carried out, according to the following equations:
where is the storage volume at time step i, is the storage volume at time step i−1, is the inflow volume at time step i, is the yield at time step i, C is the storage capacity and is the water demand at time step i.
The tank operation was simulated at event scale from 1971–2017 to identify all the deficit sub-periods. For each deficit sub-period, the number of events within and the maximum positive difference between the cumulative outflows and the cumulated inflows were calculated. The parameter n to be used as input of the probabilistic model (Equation (16)) was assumed equal to the mean number of events in a deficit sub-period.
The differences between outflows and inflows represents, for each deficit sub-period, the total water release. These water releases constitute the empirical samples of storage volumes and were used to model their empirical cumulative distribution function through the Kaplan–Meier estimate.
2.3. Model Validation
The continuous simulation and the results obtained with the probabilistic approach were compared using Normalized Root Mean Square Error (NRMSE). To test the potential of the proposed probabilistic method, the results were compared to the “demand-side” simplified approach. According to the latter method, volumes were obtained as the product between the water demand and the longest average dry period. Through the continuous simulation, volumetric reliability indexes Iv were also evaluated considering both design methods. Iv was calculated as the ratio between the total water supplied and the total water demand.
2.4. Application
The proposed approach was tested considering a hypothetical rainwater tank located in Milan, Italy, connected to a practically impermeable roof (φ = runoff coefficient). The modeling considered the rainfall time series recorded at the Milano–Monviso rain gauge station in 47 years (1971–2017), with an average annual precipitation P of 1033 [mm] and a mean of 142 rainfall events per year. Data were recorded with a time resolution of 1 min and a depth resolution of 0.2 mm for a total of 24,720,480 records analyzed. Missing values from the period 2005–2017 were estimated through the inverse distance (reciprocal distance) weighting method (IDWM) considering the nearest neighbor gauging stations of Gattamelata, Sacco, Marino, Sondrio [48]. The rainwater harvesting system is assumed to use rainwater collected from building rooftop for toilet flushing. Three constant rates of water demand (D = 1.2, 1.6, 2 mm/day) were considered. Assuming a rooftop catchment area A = 250 m2 and an average consumption of 20 L/day per person for toilet flushing, those values correspond to a total water demand of 15, 20 and 25 users, respectively. The water demand scenarios analyzed are related to different ratios between mean annual water demand and mean annual water supply from rainfall (Table 1).

Table 1.
Mean annual water demand Ad as a percentage of the mean annual water supply As for the different demand scenarios considered.
3. Results and Discussion
Referring to the flowchart in Figure 2, the first step was to identify the main statistics of the independent storm events that were then used to estimate expected values and variances of the random variables with Equations (5) and (6) and with Equations (11) and (12). A IETD equal to 1 h was assumed to identify independent storm events from the long-term historical rainfall series recorded in Milan (1971–2017), neglecting rainfall depths below 0.2 mm to account for sampling errors. The average and standard deviations for rainfall depth (h), rainfall duration (θ) and interevent time (d) are gathered in Table 2.

Table 2.
Average values and the standard deviations, per event, of the three rainfall variables used in the modeling (rainfall depth h, rainfall duration θ, and interevent time d).
To test the hypothesis of independence between rainfall variables, the correlation indexes were obtained and gathered in Table 3. While the correlation between rainfall depth and interevent time and between interevent time and rainfall duration are negligible, the correlation between rainfall depth and duration is significant. Although copula functions are used to model the statistical dependence of rainfall event variables, they are not used in this research since their complexity in this case does not lead to significant improvement in results [49].

Table 3.
Correlation index among rainfall depth and rainfall duration (ρh,θ), rainfall duration and interevent time (ρθ,d) and rainfall depth and interevent time (ρh,d) in Milan.
The following input necessary to the method application was the parameter n. It was assumed, for the required water demand, equal to the mean number of events in a deficit sub-period. The parameter n tends to increase with demand since as demand increases, so does the possibility of having more consecutive events in deficit conditions. The identification of the number of events on each deficit sub-period was held by using the continuous simulation with the operating rule in Equations (17) and (18) with sufficiently large storage to avoid spills and then obtaining the average value. The results obtained were 1.42, 1.51 and 1.56 for D = 1.2 mm/day, D = 1.6 mm/day and D = 2.0 mm/day, respectively. The values used as input for the model were adjusted during model validation and are reported in Table 4.

Table 4.
Values of the parameter n as function of water demands.
As all required inputs for the model were defined, as in step 3 of the flowchart (Figure 2), Equations (3)–(6) were used to obtain µ(Δ1), σ2(Δ1), µΔ, σΔ2 and afterwards (step 4) using Equations (9) and (10) to obtain FΔ(n) (x), fΔ(n)(x), and µΔ+ with Equation (11). At this point, the CDF of the active storage FW (w) was estimated with Equation (16). The obtained FW (w) for the defined water demands and rainfall data from Milan are shown in Figure 3.
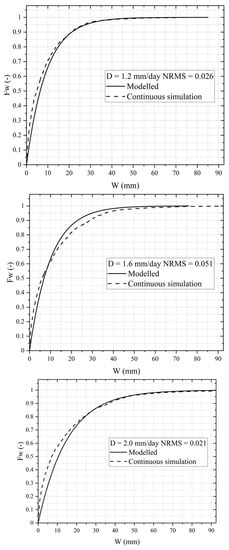
Figure 3.
Empirical CDF from continuous simulation and modeled CDF of the active storage W of the tank for different water demand (D = 1.2 mm/day; D = 1.6 mm/day; D = 2.0 mm/day).
An empirical distribution function obtained from the continuous simulation was then used to validate the model FW (w). The continuous simulation was held with the operation rule in Equations (17) and (18) on a storm-event-based step with a storage capacity sufficiently large to avoid spills, obtaining the active storage after each event. The empirical distribution function from the continuous simulation of active storage is plotted on Figure 3.
The proposed model provides a good estimation of the active storage CDF when compared with the empirical data from continuous simulation, with Normalized Root Mean Square Error (NRMSE) of 0.026, 0.051 and 0.021 for D = 1.2 mm/day, D = 1.6 mm/day and D = 2 mm/day, respectively. The theoretical model for the CDF of active storage, computed with Equation (16), seems particularly satisfactory for a cumulative non-exceedance probability greater than 0.8. For lower probabilities, an overestimation is observed. This overestimation could be explained by the high number of single events with deficit conditions, especially for the lower values of water demand D. In this case, the approximations used in the model are more relevant with respect to the averaging effects in longer sub-periods (sub-periods of more than one event). The proposed model, by giving the CDF of the active storage during a sub-deficit period, can be used as a design tool where the selected volume is related to a non-exceedance probability, commonly represented as a return period on stormwater management designs. Table 5 shows the volumes obtained with the model for return periods from 2 to 50 years, considering a contribution area of 250 m2 and volume in m3. A volumetric reliability index (Iv) was obtained as the ratio of total volume supplied and requested. The volume supplied was estimated using the operating rule in Equations (17) and (18) for the selected volumes from the entire historical long-term rainfall series. The Iv obtained for the rainfall series from 1971–2017 in Milan, considering the three demands refer on this study, showed agreement with the probability obtained from the model, as can also be observed in Figure 4, assessing that the model provides accuracy comparable with continuous simulation using an analytical equation. Decisionmakers can use this methodology coupled with a cost–benefit analysis to establish the optimal level of probability of failure for each project, for example, by considering local water tariff and tank costs per m3.

Table 5.
Volumetric reliability indexes (Iv) as function of water demand and return period T obtained with probabilistic model and the “demand-side” approach (Ds).
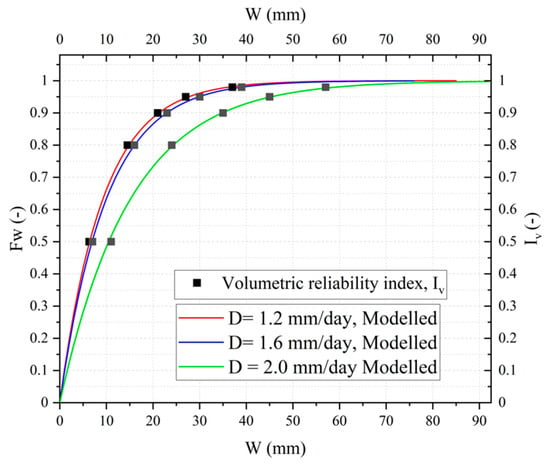
Figure 4.
Active storage CDF obtained with the probabilistic model for different demands and volumetric reliability index (Iv).
A typical design method for RWH systems, the “demand-side” approach (Ds) was then applied for the water demands considered, with W and Iv obtained, as shown in Table 5. Considering the volume for T = 50 years from Table 5, volumes from Ds were, respectively, larger of +87.39%, +137.04% and 102.73%. The overestimation observed with the Ds approach can be explained by the fact that the methodology completely neglects the rainfall stochastic process and defines the volume basely solely on the longest dry period, while the probabilistic approach presented considers the alternation of inflows and outflows and the consequent deficit sub-periods or surplus sub-periods. The total storage capacity designed with the Ds approach may be frequently unused, as the available inflow is insufficient to fill the tank completely. For large-scale projects, this unused volume is translated as a considerable cost factor that does not reflect proportionally on the Iv. For this reason, normal Ds is used as a preliminary design tool that is then adjusted with long-term continuous simulations. However, long-term rainfall data is not often available, neither RWH projects are held by hydrology specialists. The probabilistic approach presented in this research gives a relatively simple analytical equation that can be used as a design tool but provides robustness comparable to continuous simulation.
The proposed method has some limitations. Equation (16) is a function of the parameter n and of the statistics of rainfall events. However, both n and the rainfall statistics of the meteorological variables associated with rainfall events were calculated from the continuous simulation of 47-year rainfall sires that are not always available. Future research could further investigate the n-parameter for different rainfall regimes and demands to evaluate the possibility to establish a priori this parameter. As for the availability of the rainfall main statistical characteristics, future research could test the method with shorter rainfall series or different time resolutions scales. Moreover, considering the dissemination of probabilistic approaches as the current stormwater policies and regulations tend to encourage the use of stormwater control with storage and infiltration, these parameters could become eventually available from local authorities as is currently happening with the Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Equation. In alternative, these parameters could be estimated from IDF equations. Furthermore, the complexity of the equations used for the probabilistic approach leads to the possibility of developing specific software to facilitate the use of those methods from local developers.
Additionally, for the development of Equation (16), the base assumption was that exponential distribution of the data proved to be reasonable with the application and validation of the model using the Milan rainfall series. Applications using additional rainfall series should be provided to assess the validity of this assumption in different scenarios.
This research used constant demand during the entire period, as the demand is highly variable in reality, and future developments could integrate different water demands to the model.
4. Conclusions
An analytical equation derived from a probabilistic approach was proposed to estimate the cumulative density function active storage for a storage tank to be used in RWHs. The approach aimed to reproduce the whole stochastic process of storm events in a synthetic mathematical formula. The proposed equation for the tank active storage is derived as a function from moments of the rainfall process, the water demand and the mean number of chained events in a sub-periods with deficit conditions. Relating the volume of equalization to these parameters and to a probabilistic level makes the formulas interesting as design tools. Additionally, the method can be an alternative when sufficient long rainfall time series are not available for continuous simulation. Using the proposed equations, however, the probabilistic estimation of the active storage of the tank under the assumption of constant water demand is possible only if the main moments, expected value and variance, of rainfall events as well as the mean number of events in a deficit sub-period is available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.D.C. and G.B.; methodology, M.G.D.C. and G.B.; investigation, M.G.D.C.; data curation, M.G.D.C.; writing—original draft preparation M.G.D.C.; writing—review and editing, M.M., A.R. and U.S.; supervision, A.R. and G.B.; project administration, G.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
In The authors acknowledge the contribution from MM S.p.A on supplying the rainfall data series used on this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Whitmee, S.; Haines, A.; Beyrer, C.; Boltz, F.; Capon, A.G.; De Souza Dias, B.F.; Ezeh, A.; Frumkin, H.; Gong, P.; Head, P.; et al. Safeguarding human health in the Anthropocene epoch: Report of the Rockefeller Foundation-Lancet Commission on planetary health. Lancet 2015, 386, 1973–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, B.I.; Mankin, J.S.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Climate Change and Drought: From Past to Future. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, E.; Gao, X. Climate change impacts on extreme events in the United States: An uncertainty analysis. Clim. Chang. 2015, 131, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Climate Change and Drought: A Perspective on Drought Indices. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, A.; Urich, C.; Berteni, F.; Pezzagno, M.; Piro, P.; Grossi, G. Suya Duyarlı Şehirler: Parma’da (Kuzey İtalya) Kentsel Sel Direncini Artırmak İçin Bütünleşik Bir Yaklaşım-Water sensitive cities: An integrated approach to enhance urban flood resilience in Parma (Northern Italy). Climate 2021, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, C.R. Identification and quantification of the hydrological impacts of imperviousness in urban catchments: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Kim, H.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Packman, J.; Grebby, S.; Dearden, R. Assessing the impact of urbanization on storm runoff in a peri-urban catchment using historical change in impervious cover. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalenghe, R.; Ajmone-Marsan, F. The anthropogenic sealing of soils in urban areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Sharma, B.R.; Bruggeman, A.; Choukr-Allah, R.; Karajeh, F. Non-conventional water resources and opportunities for water augmentation to achieve food security in water scarce countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisano, A.; Butler, D.; Ward, S.; Burns, M.J.; Friedler, E.; Debusk, K.; Fisher-jeffes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Rahman, A.; Furumai, H. Urban rainwater harvesting systems: Research, implementation and future perspectives. Water Res. 2017, 115, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Tao, Z.; Samali, B.; Khan, M.M.; Shirin, S. Suitability of roof harvested rainwater for potential potable water production: A scoping review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judeh, T.; Shahrour, I.; Comair, F. Smart Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Potable Water Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Hatt, B.E.; Anthony, R.; Walsh, C.J. Can allotment-scale rainwater harvesting manage urban flood risk and protect stream health? In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies for Urban Water Management 2010, Lyon, France, 27 June–1 July 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Freni, G.; Liuzzo, L. Effectiveness of rainwater harvesting systems for flood reduction in residential urban areas. Water 2019, 11, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Study on combining flood control with rainwater utilization of airports in China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 191, 012133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetze, T.; Chelleri, L. Integrating decentralized rainwater management in urban planning and design: Flood resilient and sustainable water management using the example of coastal cities in The Netherlands and Taiwan. Water 2013, 5, 593–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Fletcher, T.D. The impact of stormwater source-control strategies on the (low) flow regime of urban catchments. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teston, A.; Piccinini Scolaro, T.; Kuntz Maykot, J.; Ghisi, E. Comprehensive Environmental Assessment of Rainwater Harvesting Systems: A Literature Review. Water 2022, 14, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisano, A.; Modica, C. Optimal sizing of storage tanks for domestic rainwater harvesting in Sicily. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 63, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londra, P.A.; Kotsatos, I.E.; Theotokatos, N.; Theocharis, A.T.; Dercas, N. Reliability analysis of rainwater harvesting tanks for irrigation use in greenhouse agriculture. Hydrology 2021, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I.; Lanza, L.G. Non-dimensional design parameters and performance assessment of rainwater harvesting systems. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I. On the Effectiveness of Domestic Rainwater Harvesting Systems to Support Urban Flood Resilience. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 5897–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.; Memon, F.A.; Butler, D. Rainwater harvesting: Model-based design evaluation. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisi, E. Parameters Influencing the Sizing of Rainwater Tanks. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2381–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewkes, A.; Butler, D. Simulating the performance of rainwater collection and reuse systems using behavioural models. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2000, 21, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewkes, A.; Warm, P. Method of modelling the performance of rainwater collection systems in the United Kingdom. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2000, 21, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes VA, R.; Marques, G.F.; Dornelles, F.; Medellin-azuara, J. Performance of Rainwater Harvesting Systems under Scenarios of Non-Potable Water Demand and Roof area Typologies using a Stochastic Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, V.G.; Mccarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D. Urban stormwater harvesting e sensitivity of a storage behaviour model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, B.; Balistrocchi, M.; Grossi, G. Proposal of a semi-probabilistic approach for storage facility design. Urban Water J. 2008, 5, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becciu, G.; Raimondi, A.; Dresti, C. Semi-probabilistic design of rainwater tanks: A case study in Northern Italy. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becciu, G.; Raimondi, A. An analytical probabilistic approach for sizing rainwater tanks. In Acqua e Città 2011: Pianificazione, Protezione e Gestione; La Loggia, G., Paoletti, P., Beccin , G., Eds.; Centro Studi Idraulica Urbana: Brescia, Italy, 2011; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Huang, G.; Guo, Y.; Baetz, B.W.; Dong, C. Stochastic Rainwater Harvesting System Modeling Under Random Rainfall Features and Variable Water Demands. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR029731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Becciu, G. On pre-filling probability of flood control detention facilities. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Becciu, G. Performance of Green Roofs for Rainwater Control. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Marchioni, M.; Sanfilippo, U.; Becciu, G. Infiltration-exfiltration systems design under hydrological uncertainty. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2020, 194, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Marchioni, M.; Sanfilippo, U.; Becciu, G. Vegetation survival in green roofs without irrigation. Water 2021, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Marchioni, M.; Sanfilippo, U.; Stroppa, F.F.; Becciu, G. Probabilistic Estimation of Runoff From Green Roofs. Int. J. Comput. Methods Exp. Meas. 2022, 10, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y. Proper Sizing of Infiltration Trenches Using Closed-Form Analytical Equations. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, Y. Analytical Equation for Estimating the Stormwater Capture Efficiency of Permeable Pavement Systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2015, 141, 06014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Di Chiano, M.G.; Marchioni, M.; Sanfilippo, U.; Becciu, G. Probabilistic Modelling of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems. Urban Ecosyst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Baetz, B.W. Sizing of Rainwater Storage Units for Green Building Applications. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Guo, Y. Stochastic modelling of the hydrologic operation of rainwater harvesting systems. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, V.J.; García-Bartual, R.; Cabrera, E.; Arregui, F.; Garca-Serra, J. Stochastic Model to Evaluate Residential Water Demands. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.R.; Almeida, C.D.N.; Coelho, V.H.R.; Freitas, E.D.S.; Galvão, C.D.O.; Araújo, J.C.D. Sub-hourly rainfall patterns by hyetograph type under distinct climate conditions in Northeast of Brazil: A comparative inference of their key properties. Rbrh 2018, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, J.B.; Guerreiro, M.S.; de Andrade, E.M.; de Queiroz Palácio, H.A.; Medeiros, P.H.A.; Ribeiro Filho, J.C. Minimum Rainfall Inter-Event Time to Separate Rainfall Events in a Low Latitude Semi-Arid Environment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Identifying individual rain events from pluviograph records: A review with analysis of data from an Australian dryland site. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2008, 22, 5024–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.D.S.; Coelho, V.H.R.; Xuan, Y.; de CD Melo, D.; Gadelha, A.N.; Santos, E.A.; Galvão, C.D.O.; Ramos Filho, G.M.; Barbosa, L.R.; Huffman, G.J.; et al. The performance of the IMERG satellite-based product in identifying sub-daily rainfall events and their properties. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, M.T.; Rezazadeh-Joudi, A.; Kusiak, A. Assessment of different methods for estimation of missing data in precipitation studies. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistrocchi, M.; Bacchi, B. Modelling the statistical dependence of rainfall event variables through copula functions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1959–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).