Optimizing Wastewater Treatment Reactor Design Using Computational Fluid Dynamics: Impact of Geometrical Parameters on Residence Time and Pollutant Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Experimental study of the flow field in a reactor under various geometric conditions.
- A CFD model for the velocity field in the system and the mass transport of MB validated using experimental RTD.
- Modeling of the MB ozonation process and investigation of the impact of geometry on the conversion of the reaction.
2. Materials and Methods
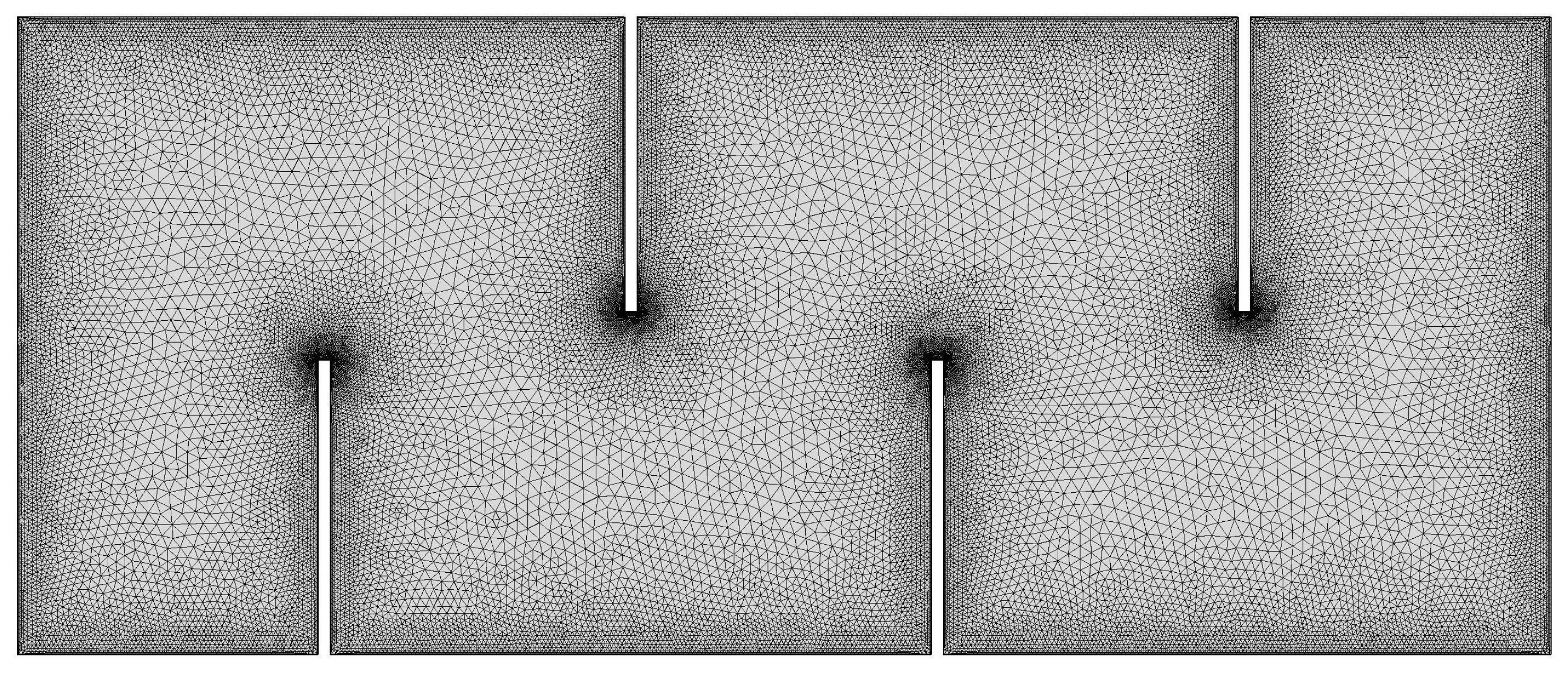
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Modeling Procedure
3. Results
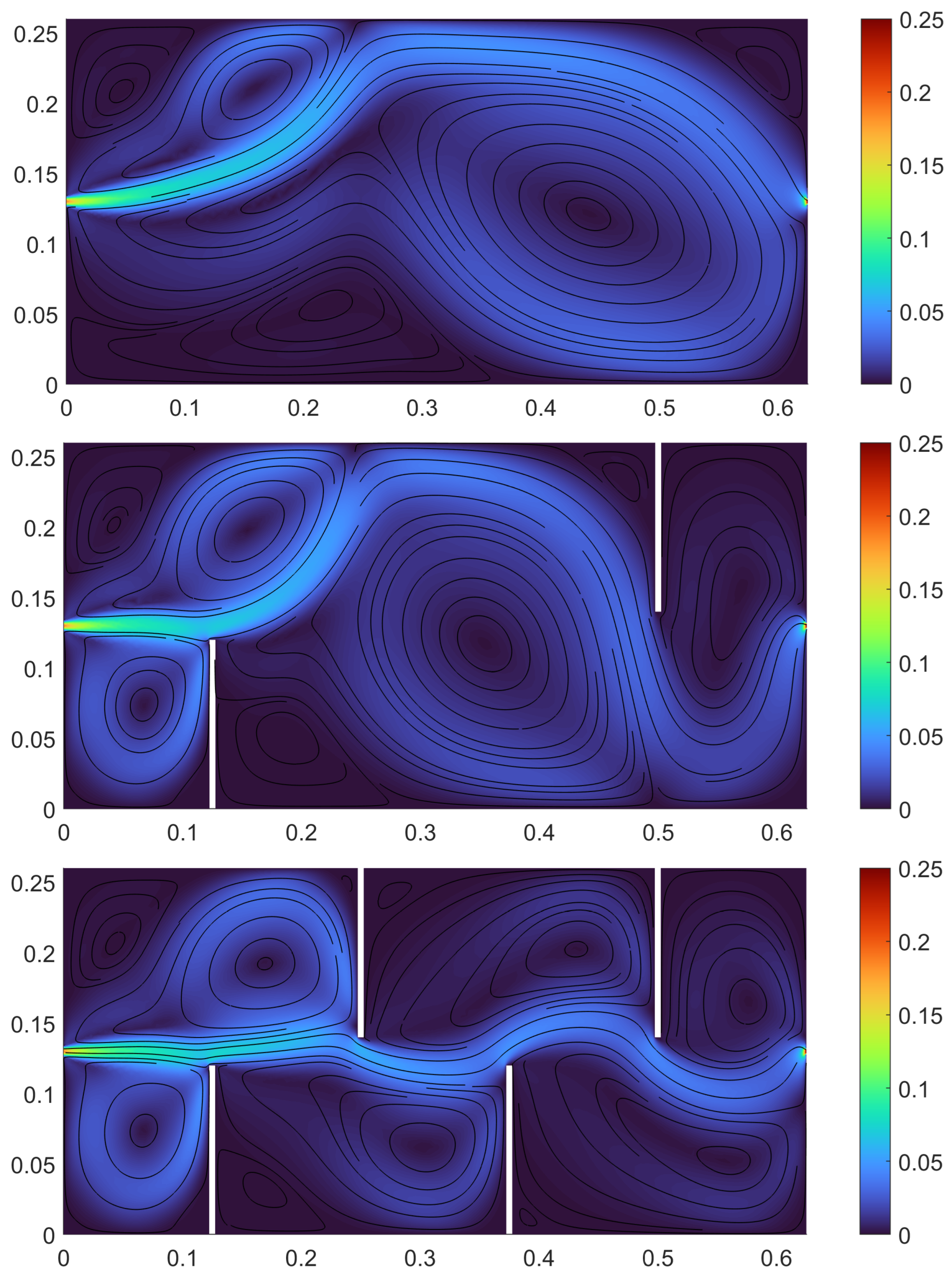
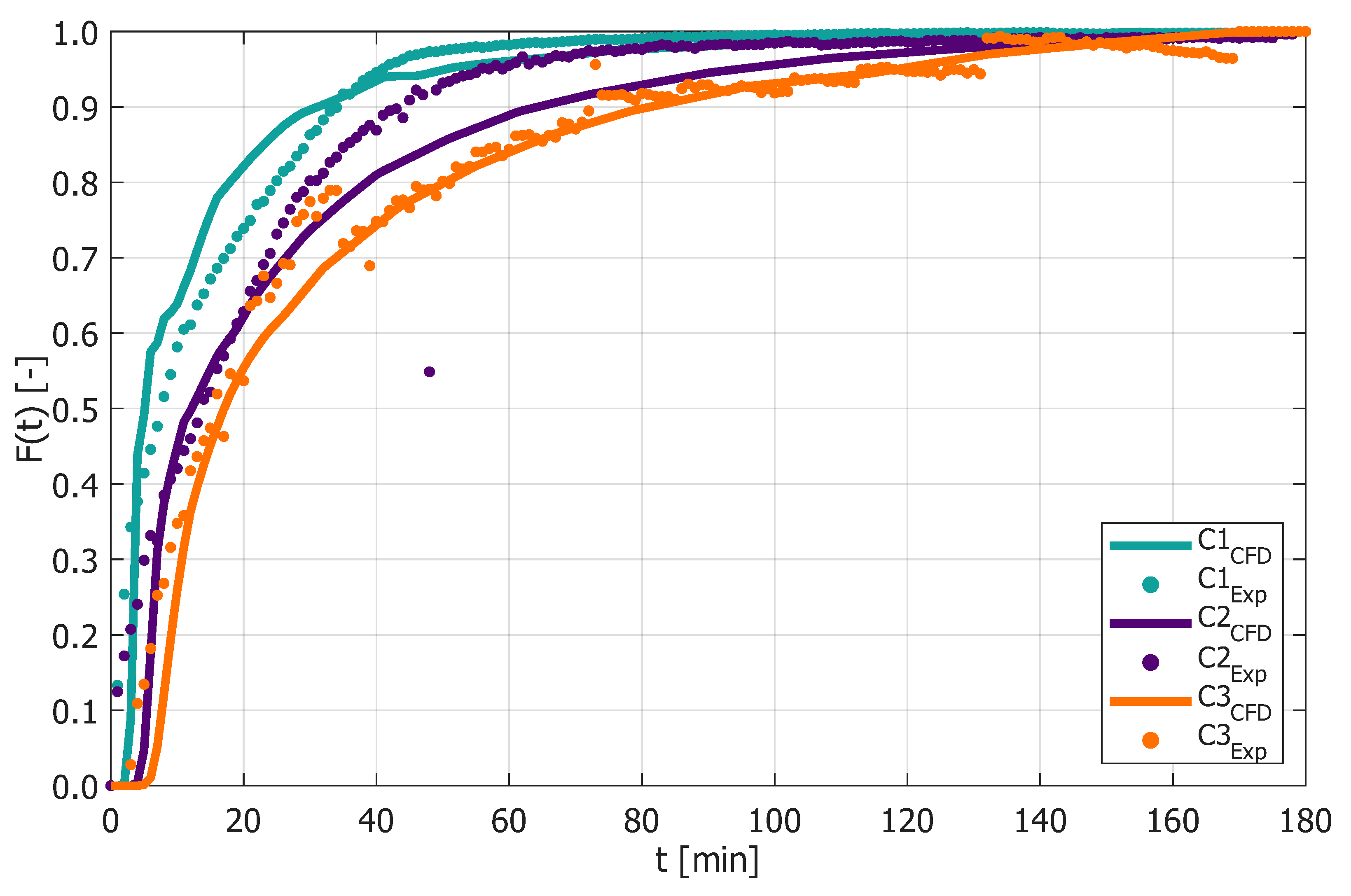
3.1. Flow Field Analysis and Experimental Validation
3.2. Case Study of MB Ozonation, Conversion and Ozone Distribution as a Function of Geometry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, O.A.; Hsu, A.; Johnson, L.A.; de Sherbinin, A. A global indicator of wastewater treatment to inform the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanka-Pedige, H.M.K.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, I.S.A.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Evaluating wastewater treatment infrastructure systems based on UN Sustainable Development Goals and targets. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaideen, K.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Olabi, A. The role of wastewater treatment in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) and sustainability guideline. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.H.; Lei, S.; Ali, M.; Doronin, D.; Hussain, S.T. Prosumption: Bibliometric analysis using HistCite and VOSviewer. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 1020–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moullec, Y.; Potier, O.; Gentric, C.; Leclerc, J.P. Flow field and residence time distribution simulation of a cross-flow gas–liquid wastewater treatment reactor using CFD. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 2436–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moullec, Y.; Gentric, C.; Potier, O.; Leclerc, J. CFD simulation of the hydrodynamics and reactions in an activated sludge channel reactor of wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, E.; Noori, M.; Zahmatkesh, S. Modeling and CFD simulation of volatile organic compounds removal from wastewater by membrane gas stripping using an electro-spun nanofiber membrane. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 30, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jin, M.; Yue, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Qiao, N.; Yu, D. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of Trichosporon fermentans flocculation in refined soybean oil wastewater and flocculation rate prediction method. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapelo, D.; Bridgeman, J. Euler-Lagrange Computational Fluid Dynamics simulation of a full-scale unconfined anaerobic digester for wastewater sludge treatment. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 117, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, M.B.; Hejazi, M.A.; Karimi, A. Enhanced removal of nitrate and phosphate from wastewater by Chlorella vulgaris: Multi-objective optimization and CFD simulation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Tian, H.; Yuan, X.; Liu, S.; Peng, Q.; Shi, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, L.; Jia, J.; Ying, D.; et al. CFD-assisted modeling of the hydrodynamic cavitation reactors for wastewater treatment—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibian, S.; Hazrati, H.; Rostamizadeh, M. Continuous electrooxidation of Methylene Blue in filter press electrochemical flowcell: CFD simulation and RTD validation. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2020, 150, 107880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Jin, S.; Xia, Y. Experimental and CFD investigation of the counter-flow spray concentration tower in solar energy air evaporating separation saline wastewater treatment system. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 144, 118621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.E. Residence time distribution (RTD) revisited. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 230, 116188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto, J.; Domınguez, J.; Griffith, J.; Fick, M.; Leclerc, J. Technetium-99m as a tracer for the liquid RTD measurement in opaque anaerobic digester: Application in a sugar wastewater treatment plant. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2003, 42, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewsky, M.; Gallé, T.; Bayerle, M.; Goel, R.; Fischer, K.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Xenobiotic removal efficiencies in wastewater treatment plants: Residence time distributions as a guiding principle for sampling strategies. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6152–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Manenti, S.; Todeschini, S.; Sperone, E.; Cavallo, G.; Abbà, A. Identification and localization of hydrodynamic anomalies in a real wastewater treatment plant by an integrated approach: RTD-CFD analysis. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.A.; Laurent, J.; Bois, P.; Wanko, A. A coupled RTD and mixed-order kinetic model to predict high rate algal pond wastewater treatment under different operational conditions: Performance assessment and sizing application. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 162, 107709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvy, S.; Debaste, F.; Martinelli, L.; Chauveheid, E.; Haut, B. Development of a tool, using CFD, for the assessment of the disinfection process by ozonation in industrial scale drinking water treatment plants. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.; Farshchi, M.E.; Fathinia, M.; Aghdasinia, H. Photocatalytic ozonation process for degradation of an anthelmintic drug using ceramic coated TiO2 NPs: CFD simulation coupling with kinetic mechanisms. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzer, A.; Harvey, B.H.; Wegener, G.; Petzer, J.P. Azure B, a metabolite of methylene blue, is a high-potency, reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Fan, P. Ozonation and carbon-assisted ozonation of methylene blue as model compound: Effect of solution pH. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al jibouri, A.K.H.; Wu, J.; Upreti, S.R. Continuous ozonation of methylene blue in water. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 8, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A.; Meetanim, M.A.; Khaleel, A.; Ahmed, A. Photocatalytic degradation of Methylene Blue using a mixed catalyst and product analysis by LC/MS. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Matko, T.; Chew, J.; Wenk, J.; Chang, J.; Hofman, J. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of two-phase flow and dissolved oxygen in a wastewater treatment oxidation ditch. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 145, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaist, D.G. The effects of aggregation, counterion binding, and added NaCl on diffusion of aqueous methylene blue. Can. J. Chem. 1988, 66, 2452–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, L.; Sedev, R.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. The terminal rise velocity of 10–100 μm diameter bubbles in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, F.J.; Beltran-Heredia, J.; Gonzalez, T.; Pascual, A. Ozone treatment of methylene blue in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1993, 119, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




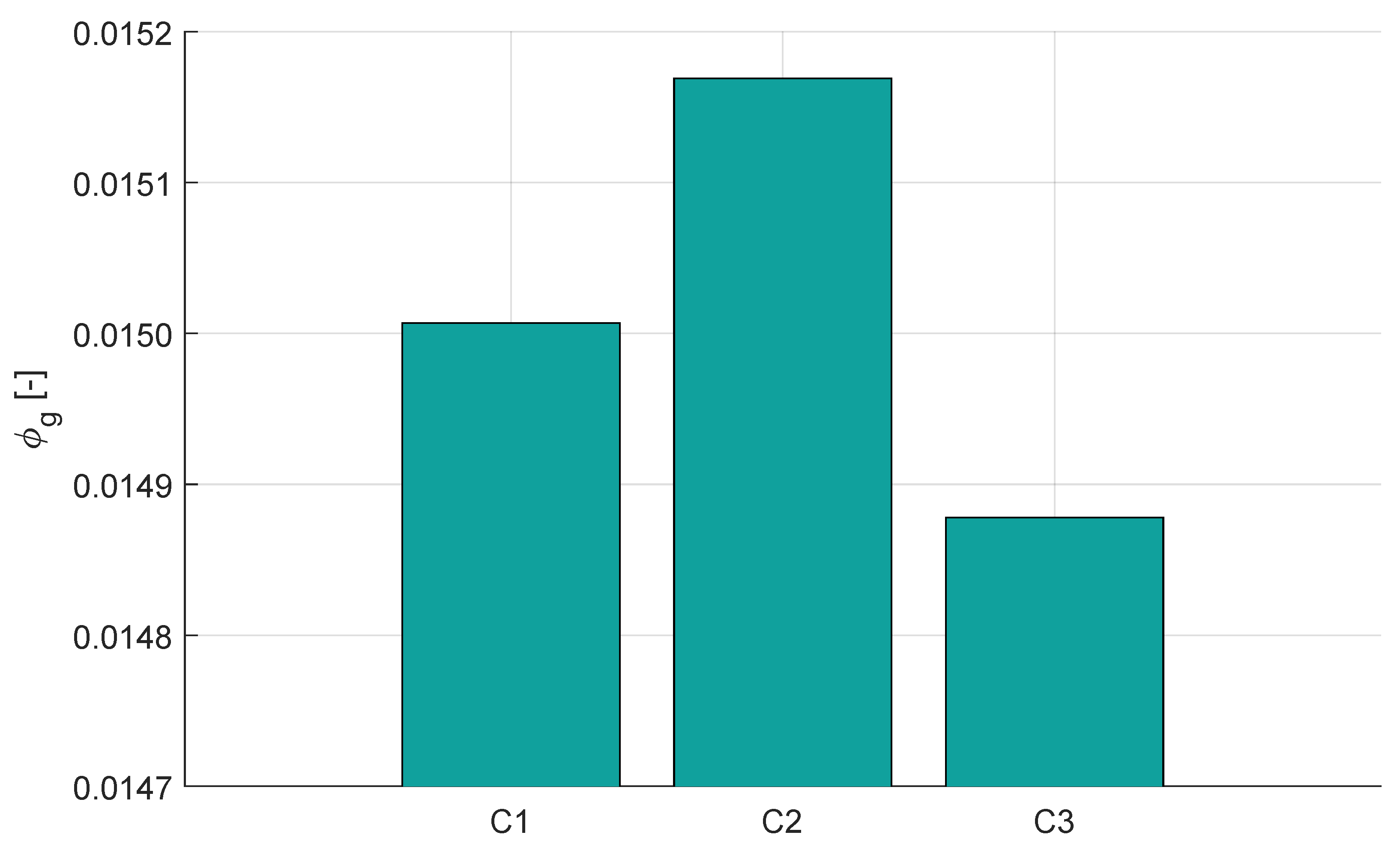

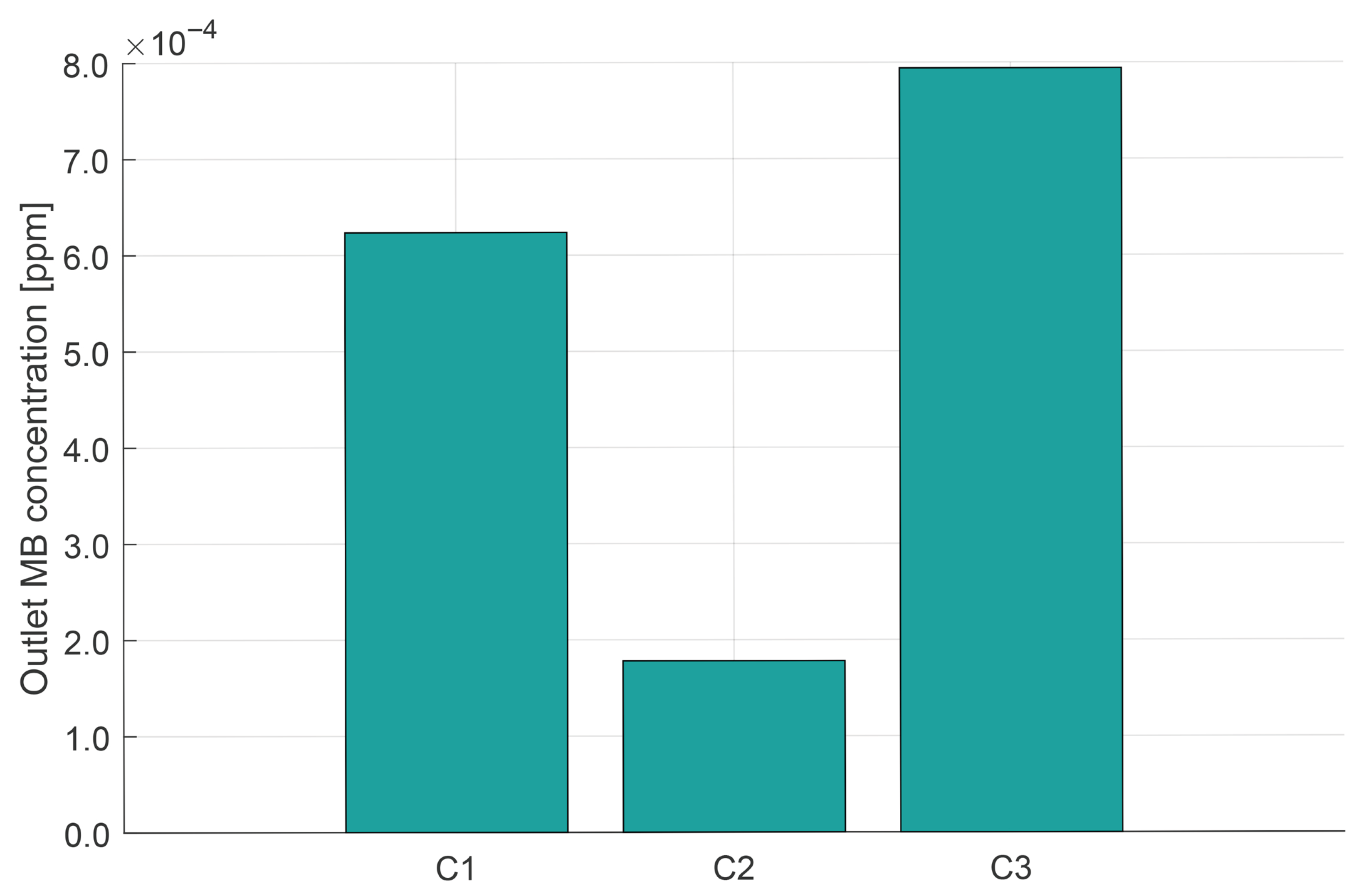
| Construction | Number of Baffles | Longitudinal Baffle Position [mm] | Lateral Baffle Position [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0 | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| C1 | 2 | 125 | 0 |
| 500 | 140 | ||
| C3 | 4 | 125 | 0 |
| 250 | 140 | ||
| 375 | 0 | ||
| 500 | 140 |
| Process Condition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tank volume | 12.5 | L |
| Inlet volumetric flow | 12.5 | |
| Average residence time | 1 | h |
| Inlet velocity | 0.17 | |
| Inlet concentration | 0.1 |
| Study Case | Phenomenon | State | Initial Conditions | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental validation | Laminar flow | Steady | Inlet velocity of | |
| Outlet pressure of 0 Pa | ||||
| MB mass balance | Dynamic | Inlet concentration of | ||
| Investigation of MB degradation during ozonation | Steady | Inlet density of | ||
| Laminar bubbly flow | Outlet pressure of 0 Pa | |||
| MB, mass balance | Outlet density of | |||
| Steady | Inlet MB concentration of | |||
| Inlet concentration of |
| Mesh Identifier | Number of Cells | Min. Element Size [mm] | Max. Element Size [mm] | Computation Time [h] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 17,322 | 17 | 0.17 | ||
| M2 | 54,724 | 13 | 0.3 | ||
| M3 | 82,413 | 7 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarcsay, B.L.; Kincses, J.; Balogh, L.; Kámán, A.; Nagy, L.; Egedy, A. Optimizing Wastewater Treatment Reactor Design Using Computational Fluid Dynamics: Impact of Geometrical Parameters on Residence Time and Pollutant Degradation. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060124
Tarcsay BL, Kincses J, Balogh L, Kámán A, Nagy L, Egedy A. Optimizing Wastewater Treatment Reactor Design Using Computational Fluid Dynamics: Impact of Geometrical Parameters on Residence Time and Pollutant Degradation. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(6):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060124
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarcsay, Bálint Levente, Janka Kincses, László Balogh, András Kámán, Lajos Nagy, and Attila Egedy. 2025. "Optimizing Wastewater Treatment Reactor Design Using Computational Fluid Dynamics: Impact of Geometrical Parameters on Residence Time and Pollutant Degradation" ChemEngineering 9, no. 6: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060124
APA StyleTarcsay, B. L., Kincses, J., Balogh, L., Kámán, A., Nagy, L., & Egedy, A. (2025). Optimizing Wastewater Treatment Reactor Design Using Computational Fluid Dynamics: Impact of Geometrical Parameters on Residence Time and Pollutant Degradation. ChemEngineering, 9(6), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060124







