Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
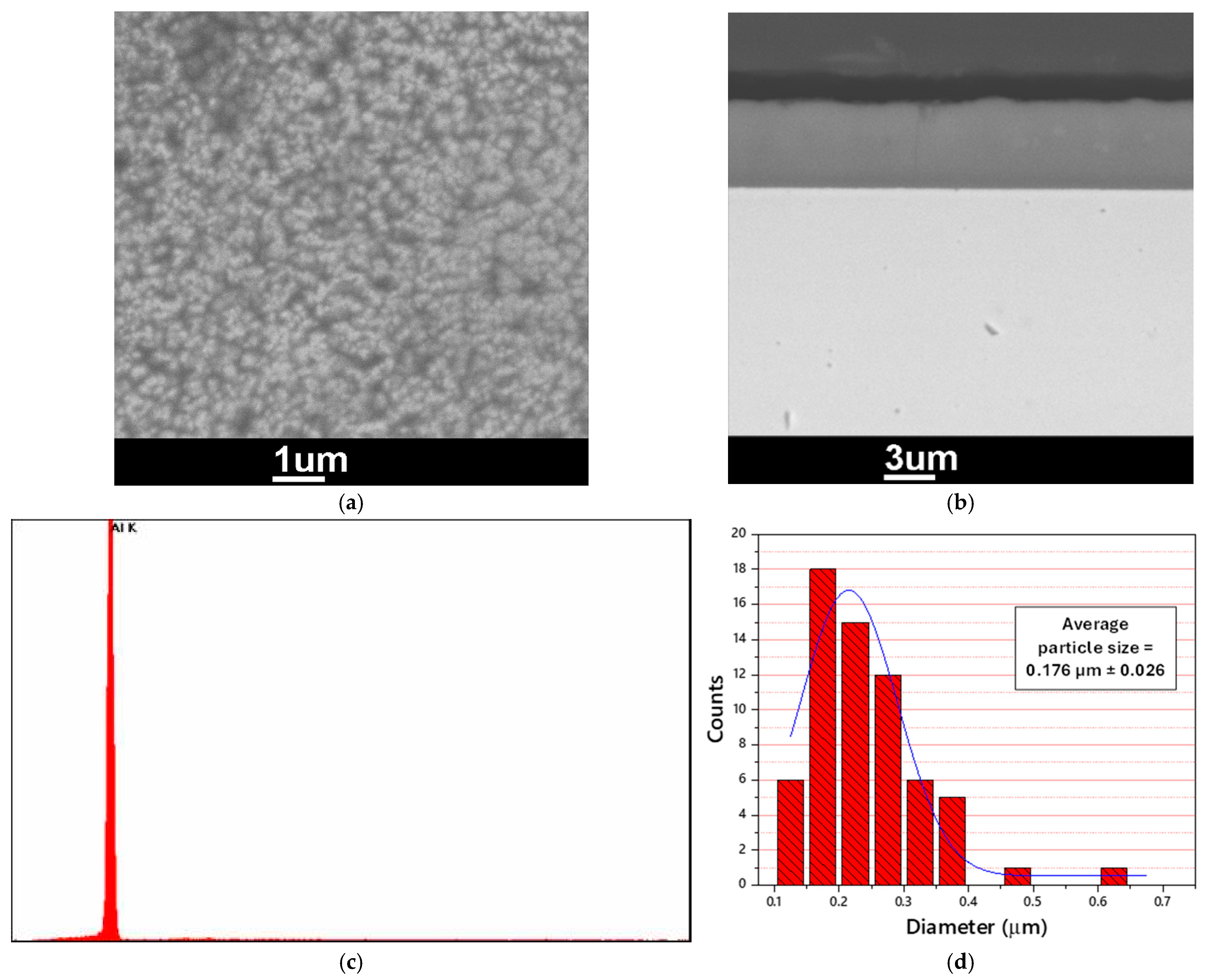
3.1. Electrodeposition of Aluminum
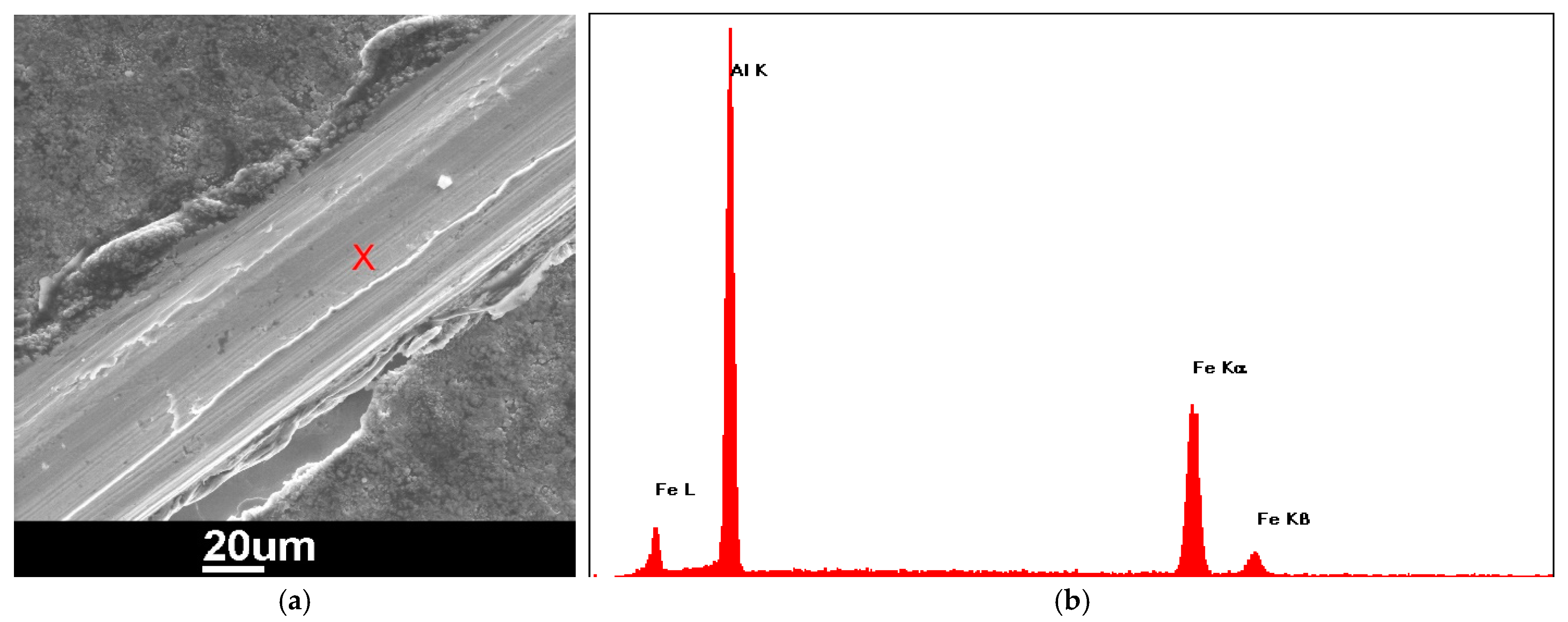
3.2. Electrodeposition of Chromium
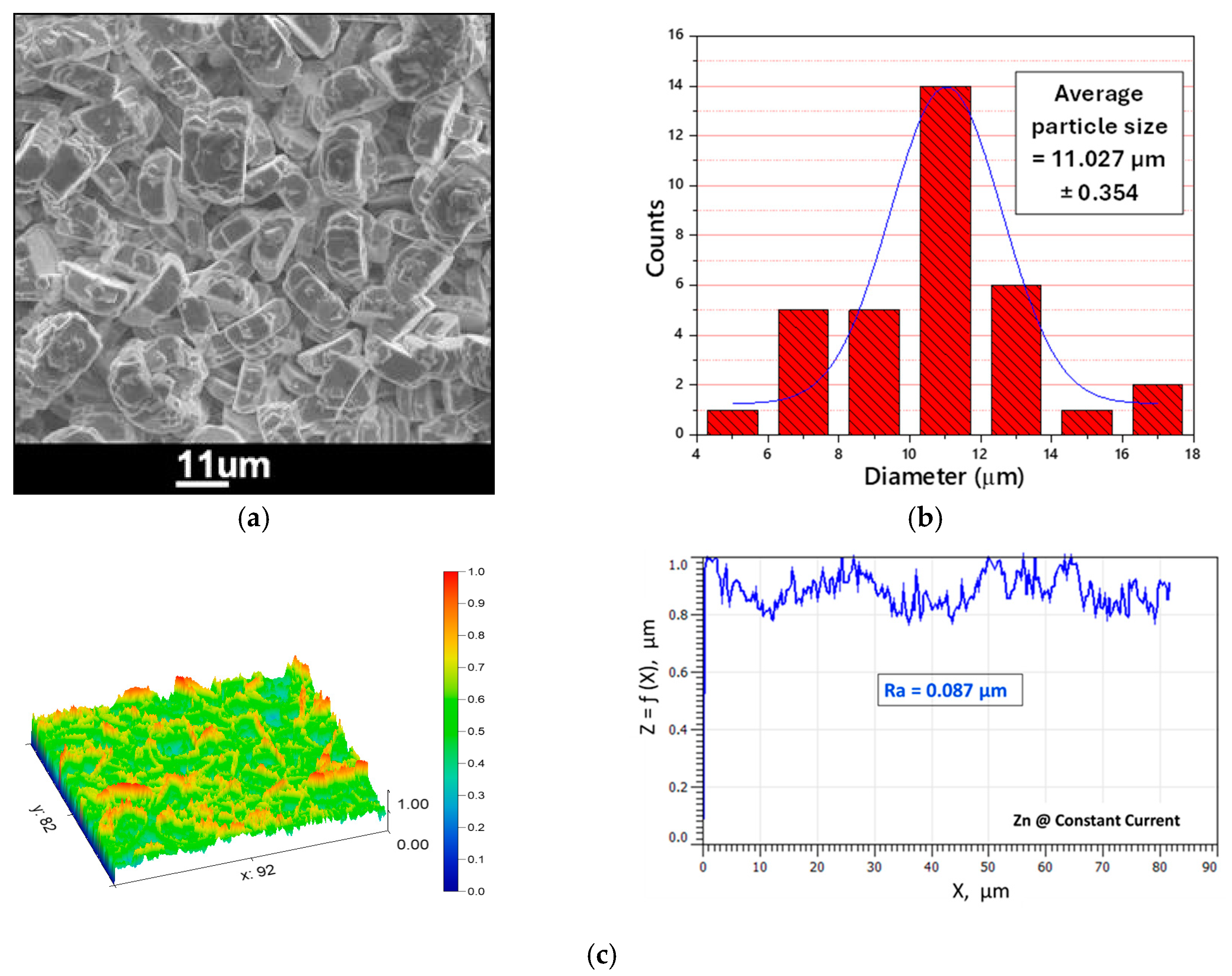
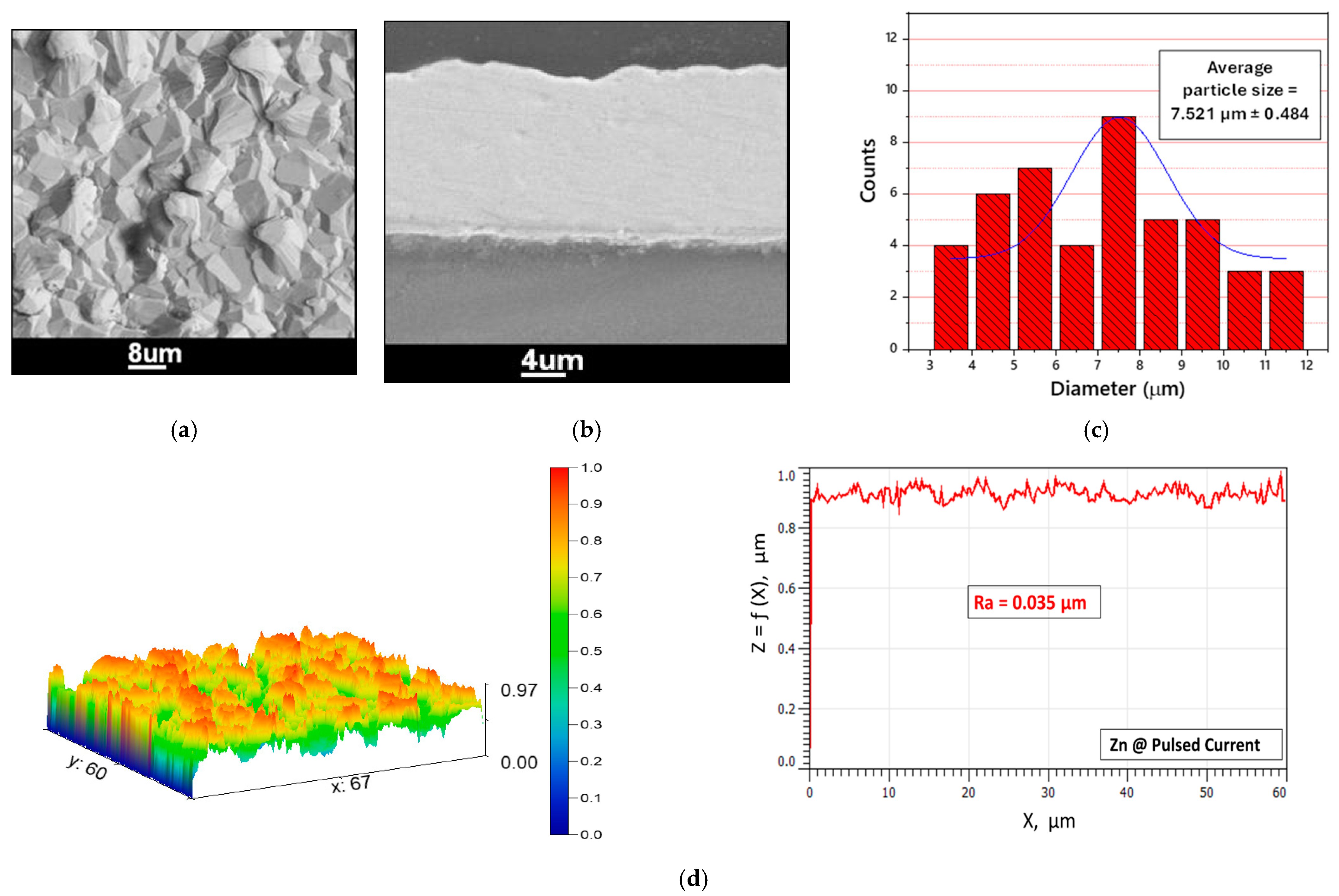
3.3. Electroplating of Magnesium as a Water-Sensitive Substrate
4. Conclusions
- -
- Uniform, adherent, and shiny pure aluminum layers were successfully electrodeposited from a highly hygroscopic chloroaluminate ionic liquid “AlCl3/EMIC (60/40 mol%)” outside a glove box in ambient atmosphere, after protecting the chloroaluminate IL with a decane layer. The electrodeposition process was also successfully preceded for Al plating of Ag-coated polymer fibers.
- -
- The successful electrodeposition of dense and crack-free chromium layers was achieved using a green DES “1 ChCl:2 CrCl3·6H2O + 10%LiCl”, which contains chromium as an environmentally friendly cation “Cr(III)”.
- -
- An air and water-stable DES “1 ChCl:2 urea” was successfully used to electrodeposit adherent zinc layers on RE-Mg alloys. The Zn coats deposited at pulsed current densities were smooth, compact and free of crevices, and thus were protective against corrosion in Cl-containing aqueous solutions.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids—Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniam, K.K.; Penot, C.; Paul, S. Influence of electrolyte choice on zinc electrodeposition. Materials 2024, 17, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, W.; Zanatta, M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Corvo, M.C.; Cabrita, E.J. Revisiting ionic liquid structure-property relationship: A critical analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, F. Ionic liquids: Promising solvents for electrochemistry. Z. Phys. Chem. 2004, 218, 255–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.G.d.R.d.; Costa, J.M.; Almeida Neto, A.F.d. Progress on Electrodeposition of Metals and Alloys Using Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes. Metals 2022, 12, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein El Abedin, S.; Endres, F. Electrodeposition of metals and semiconductors in air- and water-stable ionic liquids. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Levisky, J.A.; Wilson, R.A.; Hussey, C.L. Dialkylimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: A new class of room-temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm. 1992, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudaev, P.A.; Chistyakov, E.M. Ionic liquids as components of systems for metal extraction. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhote, P.; Dias, A.P.; Papageorgiou, N.; Kalyanasundaram, K.; Grätzel, M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Rodríguez, H.; Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Pernak, J.; Grisel, J.E.; Carliss, R.D.; Soutullo, M.D.; et al. The third evolution of ionic liquids: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, S.; Gardas, R.L. History and development of ionic liquids. In Handbook of Ionic Liquids: Fundamentals, Applications, and Sustainability, 1st ed.; Rajkhowa, S., Singh, P., Sen, A., Sarma, J., Eds.; WILEY-VCH GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Ionic liquid analogues formed from hydrated metal salts. Chemistry 2004, 10, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the nature of eutectic and deep eutectic mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, A.; Moody, N.R.; Husanu, E.; Mezzetta, A.; D’Andrea, F.; Pomelli, C.S.; Bernaert, N.; Paradisi, F.; Guazzelli, L. Challenging DESs and ILs in the valorization of food waste: A case study. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1270221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Raymond, K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R. Ionic liquids based upon metal halide/substituted quaternary ammonium salt mixtures. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.M. An eco-friendly ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent-based liquid–phase microextraction method for enrichment and quantification of nickel in environmental samples. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appll. Sci. 2022, 8, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadr, G.; Awad, M.I.; Haji, K.; Jumaa, J.A.; Abdallah, H.H. Nickel electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents containing copper ions at a high temperature. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 378, 121584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, V.; Bakkar, A. Process for the Galvanic Deposition of at Least One Metal or Semiconductor and Apparatus Therefore. European Patent EP 2599896, 1 December 2011. Available online: https://register.epo.org/application?number=EP12191555&tab=main (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Tsai, R.Y.; Wu, S.T. Phase stability of chromium plating from chromic acid electrolyte containing formic acid. J. Electrochem. Society 1990, 137, 3057–3060. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/1.2086159 (accessed on 5 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Archer, J.; John, C. Electrodeposition of chromium black from ionic liquids. Trans. IMF 2004, 82, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protsenko, V. Using deep eutectic solvent-assisted plating baths to electrodeposit composite coatings: A review. Coatings 2024, 14, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. Electrodeposition onto magnesium in air and water stable ionic liquids: From corrosion to successful plating. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tabish, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Enhanced corrosion resistance of layered double hydroxide films on Mg alloy: The key role of cationic surfactant. Materials 2022, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederichs, S.; Nugmanov, D.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Kerscher, E. Corrosion activity of ultrafine-grained pure magnesium and ZK60 magnesium alloy in phosphate buffered saline solution. Materials 2024, 17, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, E.M.; Zein El Abedin, S.; Shkurankov, A.; Zschippang, E.; Saad, A.Y.; Bund, A.; Endres, F. Electrodeposition of Al in 1-Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide and 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide Ionic Liquids: In situ STM and EQCM studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4693–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniam, K.K.; Paul, S. A Review on the Electrodeposition of aluminum and aluminum alloys in ionic liquids. Coatings 2021, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Wiemer, M.; Schulz, S.E. Process development of aluminum electroplating from an ionic liquid on 150 mm wafer level. Micromachines 2024, 15, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. A new method for practical electrodeposition of aluminium from ionic liquids. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 51, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. Electrodeposition and corrosion characterisation of micro- and nano-crystalline aluminium from AlCl3/1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid. Electrochimica Acta 2013, 103, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nablo, G.R.; Dela Pena, E.M. A black chrome plating process using trivalent chromium and water-tolerant, ethaline-based ionic liquid baths. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 4887–4897. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:235234616 (accessed on 5 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, C.; Tong, C.; Gou, J.; Wang, X.; Tu, J. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Cr and Cr–P alloy coatings electrodeposited from a Cr(iii) deep eutectic solvent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71268–77127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusas, J.R.B.; Dela Pena, E.M. An environment-friendly chromium electrodeposition process using additive-laden deep eutectic solvent. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Bakkar, A.; Ahmed, E.; Selim, A. Effect of additives and current mode on zinc electrodeposition from deep eutectic ionic liquids. Electrochimica Acta 2016, 191, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhold, V.; Höhlich, D.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Influence of the current regime during electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-containing Fe-Cr-Ni electrolyte on the near-surface pH, Alloy composition, and microcrack behavior. Coatings 2022, 12, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahton, Y.; Kamde, M.A.; Saha, P.V. Influence of Cu addition on the microstructure, and corrosion behavior of electroless Ni-Cu-P coating on squeeze-cast Al-Cu-Mg alloy. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2024, 494, 131544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahallawy, N.; Harhash, M. Recent studies on coating of some magnesium alloys; anodizing, electroless coating and hot press cladding. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 533, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Electrolyte | Icorr (µA/cm²) |
|---|---|
| Classical aqueous acid chloride Zn plating solution (150 g/L KCl and 23 g/L H3BO3), 25 °C | 3711.17 |
| “1 M ChCl:2 M urea” DES, 60 °C | 0.48 |
| Alloy | Nominal Chemical Composition, wt.% | Quality of Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Cp Mg | 99.99 Mg | PD 1 |
| AZ31 | 3 Al, 1 Zn, 0.2 Mn | PD |
| AZ61 | 6 Al, 3 Zn, 0.15 Mn | PD |
| AZ91 | 8.7 Al, 0.7 Zn, 0.13 Mn | PD |
| AS41 | 4.37 Al, 0.93 Si, 0.35 Mn | PD |
| WE43-T6 | 4 Y, 3.4 RE | AL 2 |
| QE22 | 2.5 Ag, 2.1 RE | AL |
| MgGd5Sc1 | 4.64 Gd, 0.26 Sc, 1.53 Mn | AL |
| MgY4Sc1 | 3.88 Y, 0.73 Sc, 1.11 Mn | AL |
| AE42 | 4 Al, 2.5 RE, 0.1 Mn | PD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakkar, A. Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016
Bakkar A. Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakkar, Ashraf. 2025. "Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes" ChemEngineering 9, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016
APA StyleBakkar, A. (2025). Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes. ChemEngineering, 9(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016







