Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
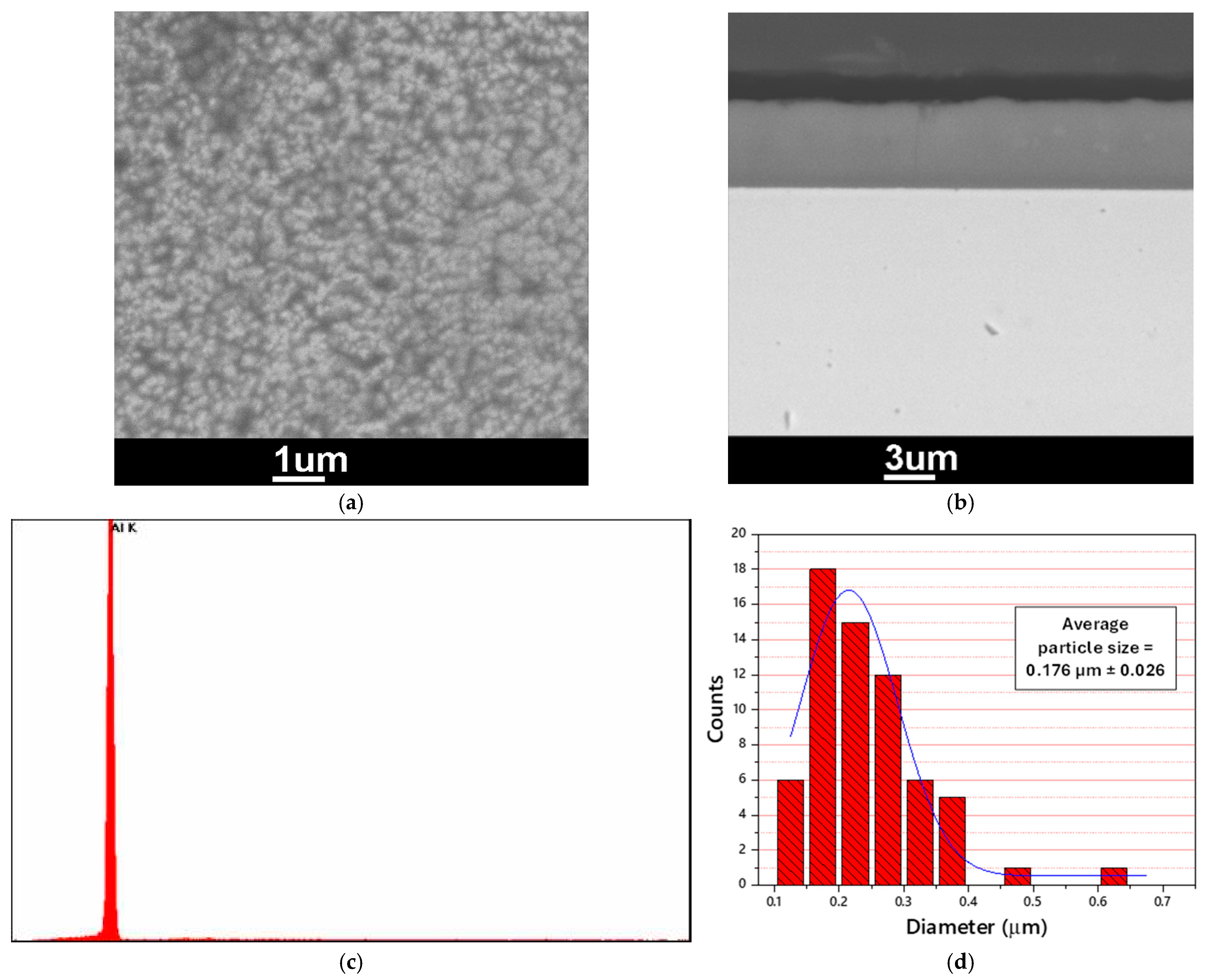
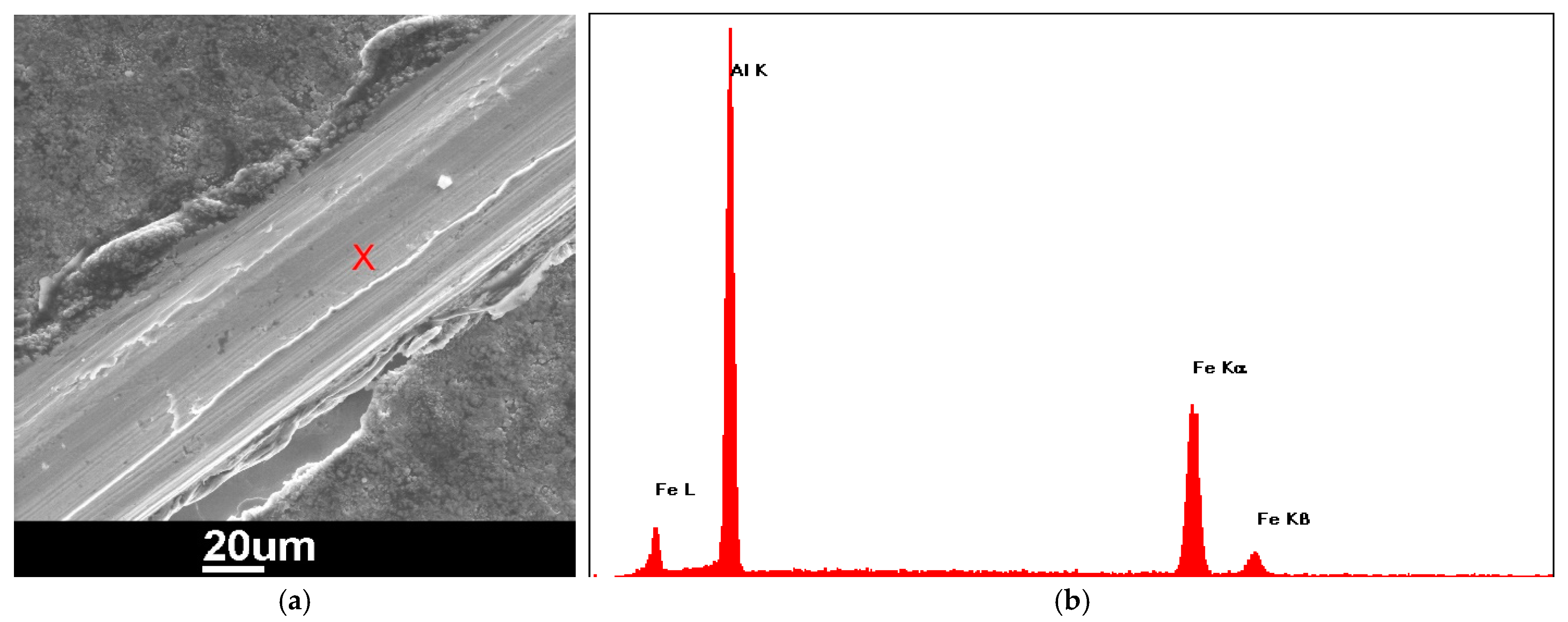
3.1. Electrodeposition of Aluminum
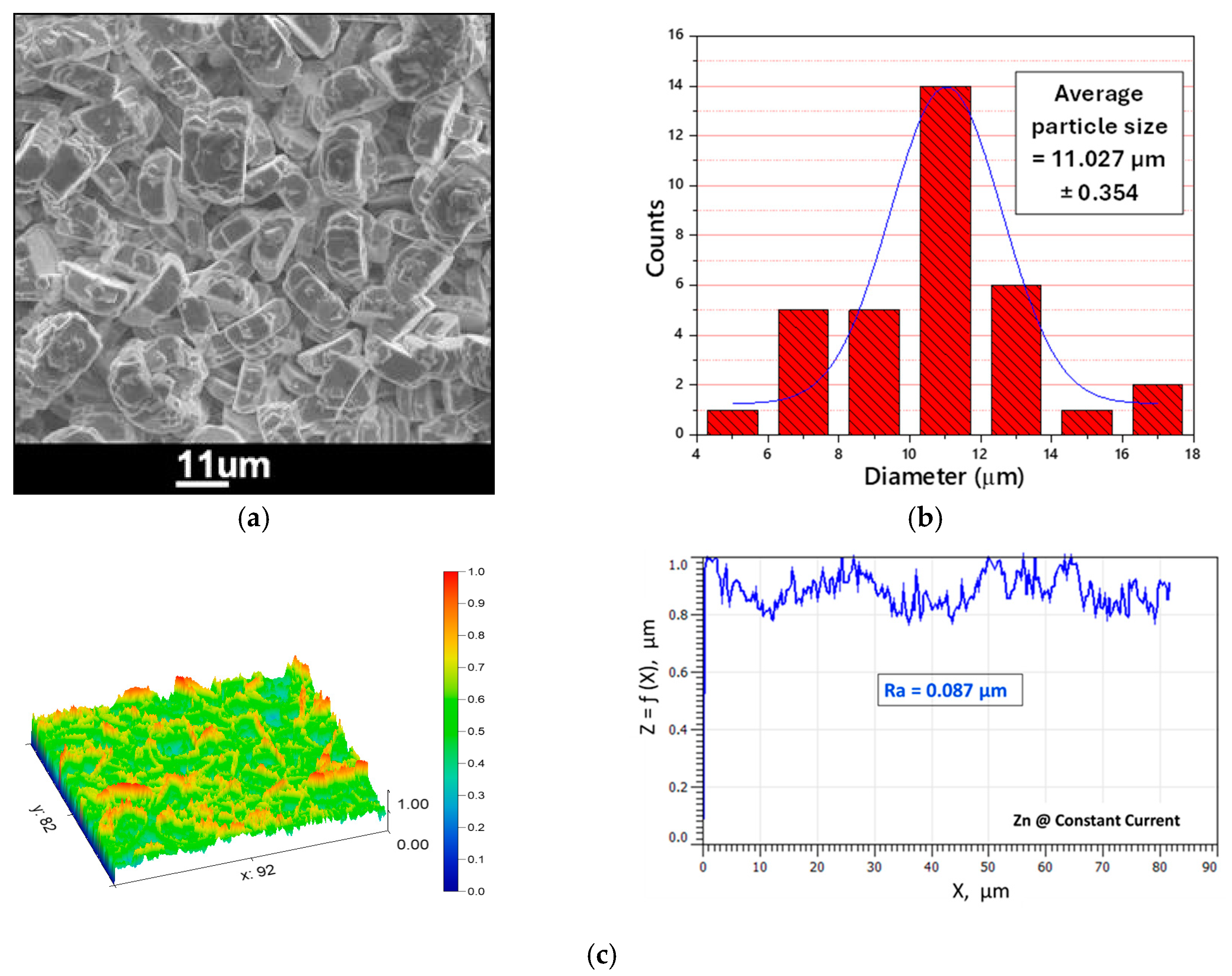
3.2. Electrodeposition of Chromium
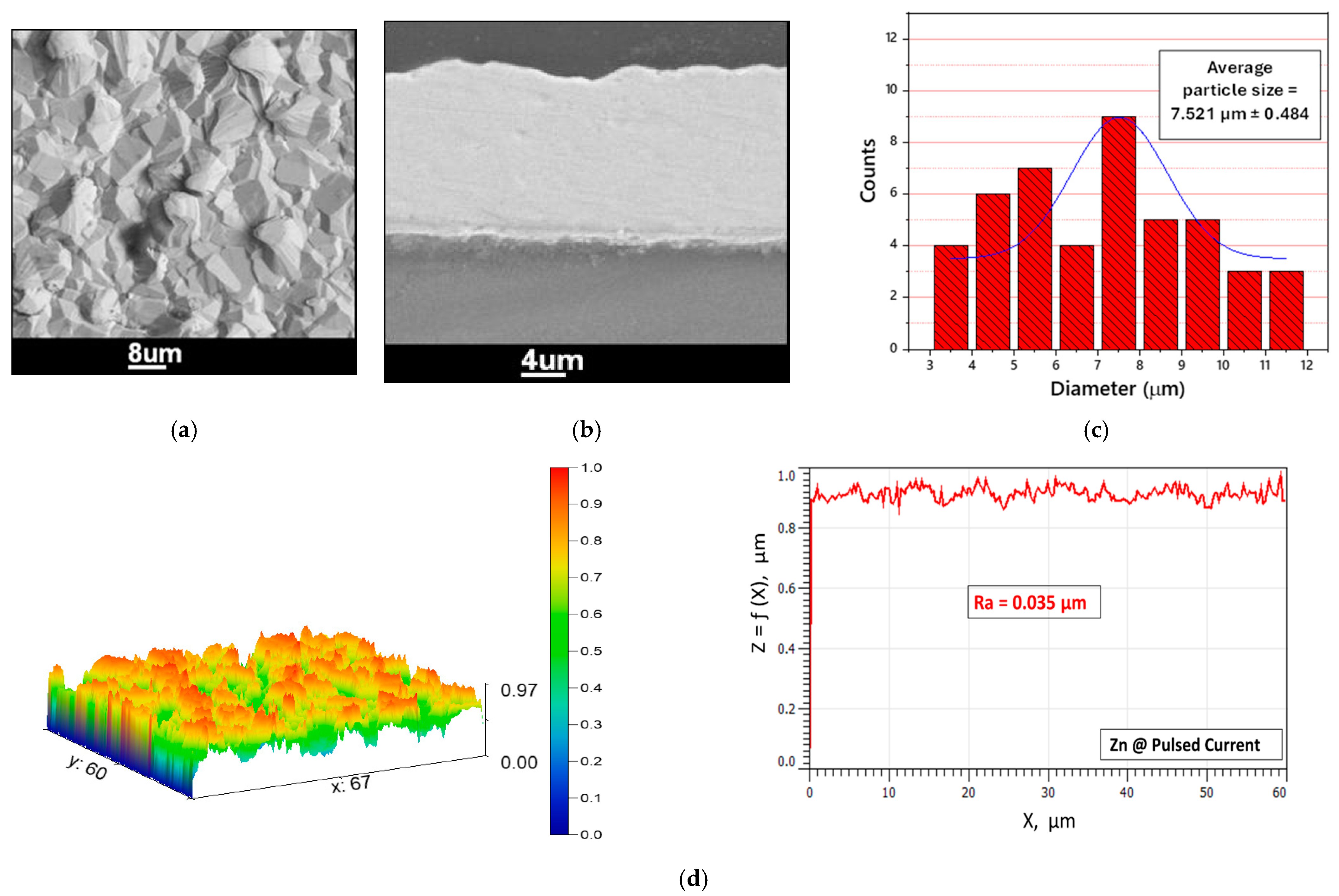
3.3. Electroplating of Magnesium as a Water-Sensitive Substrate
4. Conclusions
- -
- Uniform, adherent, and shiny pure aluminum layers were successfully electrodeposited from a highly hygroscopic chloroaluminate ionic liquid “AlCl3/EMIC (60/40 mol%)” outside a glove box in ambient atmosphere, after protecting the chloroaluminate IL with a decane layer. The electrodeposition process was also successfully preceded for Al plating of Ag-coated polymer fibers.
- -
- The successful electrodeposition of dense and crack-free chromium layers was achieved using a green DES “1 ChCl:2 CrCl3·6H2O + 10%LiCl”, which contains chromium as an environmentally friendly cation “Cr(III)”.
- -
- An air and water-stable DES “1 ChCl:2 urea” was successfully used to electrodeposit adherent zinc layers on RE-Mg alloys. The Zn coats deposited at pulsed current densities were smooth, compact and free of crevices, and thus were protective against corrosion in Cl-containing aqueous solutions.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids—Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniam, K.K.; Penot, C.; Paul, S. Influence of electrolyte choice on zinc electrodeposition. Materials 2024, 17, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, W.; Zanatta, M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Corvo, M.C.; Cabrita, E.J. Revisiting ionic liquid structure-property relationship: A critical analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, F. Ionic liquids: Promising solvents for electrochemistry. Z. Phys. Chem. 2004, 218, 255–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.G.d.R.d.; Costa, J.M.; Almeida Neto, A.F.d. Progress on Electrodeposition of Metals and Alloys Using Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes. Metals 2022, 12, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein El Abedin, S.; Endres, F. Electrodeposition of metals and semiconductors in air- and water-stable ionic liquids. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Levisky, J.A.; Wilson, R.A.; Hussey, C.L. Dialkylimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: A new class of room-temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm. 1992, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudaev, P.A.; Chistyakov, E.M. Ionic liquids as components of systems for metal extraction. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhote, P.; Dias, A.P.; Papageorgiou, N.; Kalyanasundaram, K.; Grätzel, M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Rodríguez, H.; Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Pernak, J.; Grisel, J.E.; Carliss, R.D.; Soutullo, M.D.; et al. The third evolution of ionic liquids: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, S.; Gardas, R.L. History and development of ionic liquids. In Handbook of Ionic Liquids: Fundamentals, Applications, and Sustainability, 1st ed.; Rajkhowa, S., Singh, P., Sen, A., Sarma, J., Eds.; WILEY-VCH GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Ionic liquid analogues formed from hydrated metal salts. Chemistry 2004, 10, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the nature of eutectic and deep eutectic mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, A.; Moody, N.R.; Husanu, E.; Mezzetta, A.; D’Andrea, F.; Pomelli, C.S.; Bernaert, N.; Paradisi, F.; Guazzelli, L. Challenging DESs and ILs in the valorization of food waste: A case study. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1270221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Raymond, K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R. Ionic liquids based upon metal halide/substituted quaternary ammonium salt mixtures. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.M. An eco-friendly ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent-based liquid–phase microextraction method for enrichment and quantification of nickel in environmental samples. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appll. Sci. 2022, 8, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadr, G.; Awad, M.I.; Haji, K.; Jumaa, J.A.; Abdallah, H.H. Nickel electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents containing copper ions at a high temperature. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 378, 121584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, V.; Bakkar, A. Process for the Galvanic Deposition of at Least One Metal or Semiconductor and Apparatus Therefore. European Patent EP 2599896, 1 December 2011. Available online: https://register.epo.org/application?number=EP12191555&tab=main (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Tsai, R.Y.; Wu, S.T. Phase stability of chromium plating from chromic acid electrolyte containing formic acid. J. Electrochem. Society 1990, 137, 3057–3060. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1149/1.2086159 (accessed on 5 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Archer, J.; John, C. Electrodeposition of chromium black from ionic liquids. Trans. IMF 2004, 82, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protsenko, V. Using deep eutectic solvent-assisted plating baths to electrodeposit composite coatings: A review. Coatings 2024, 14, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. Electrodeposition onto magnesium in air and water stable ionic liquids: From corrosion to successful plating. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tabish, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Enhanced corrosion resistance of layered double hydroxide films on Mg alloy: The key role of cationic surfactant. Materials 2022, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diederichs, S.; Nugmanov, D.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Kerscher, E. Corrosion activity of ultrafine-grained pure magnesium and ZK60 magnesium alloy in phosphate buffered saline solution. Materials 2024, 17, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, E.M.; Zein El Abedin, S.; Shkurankov, A.; Zschippang, E.; Saad, A.Y.; Bund, A.; Endres, F. Electrodeposition of Al in 1-Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide and 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide Ionic Liquids: In situ STM and EQCM studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4693–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniam, K.K.; Paul, S. A Review on the Electrodeposition of aluminum and aluminum alloys in ionic liquids. Coatings 2021, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Wiemer, M.; Schulz, S.E. Process development of aluminum electroplating from an ionic liquid on 150 mm wafer level. Micromachines 2024, 15, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. A new method for practical electrodeposition of aluminium from ionic liquids. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 51, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. Electrodeposition and corrosion characterisation of micro- and nano-crystalline aluminium from AlCl3/1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid. Electrochimica Acta 2013, 103, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nablo, G.R.; Dela Pena, E.M. A black chrome plating process using trivalent chromium and water-tolerant, ethaline-based ionic liquid baths. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 4887–4897. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:235234616 (accessed on 5 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, C.; Tong, C.; Gou, J.; Wang, X.; Tu, J. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Cr and Cr–P alloy coatings electrodeposited from a Cr(iii) deep eutectic solvent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71268–77127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusas, J.R.B.; Dela Pena, E.M. An environment-friendly chromium electrodeposition process using additive-laden deep eutectic solvent. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Bakkar, A.; Ahmed, E.; Selim, A. Effect of additives and current mode on zinc electrodeposition from deep eutectic ionic liquids. Electrochimica Acta 2016, 191, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhold, V.; Höhlich, D.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Influence of the current regime during electrodeposition in a Cr(III)-containing Fe-Cr-Ni electrolyte on the near-surface pH, Alloy composition, and microcrack behavior. Coatings 2022, 12, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahton, Y.; Kamde, M.A.; Saha, P.V. Influence of Cu addition on the microstructure, and corrosion behavior of electroless Ni-Cu-P coating on squeeze-cast Al-Cu-Mg alloy. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2024, 494, 131544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahallawy, N.; Harhash, M. Recent studies on coating of some magnesium alloys; anodizing, electroless coating and hot press cladding. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 533, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Electrolyte | Icorr (µA/cm²) |
|---|---|
| Classical aqueous acid chloride Zn plating solution (150 g/L KCl and 23 g/L H3BO3), 25 °C | 3711.17 |
| “1 M ChCl:2 M urea” DES, 60 °C | 0.48 |
| Alloy | Nominal Chemical Composition, wt.% | Quality of Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Cp Mg | 99.99 Mg | PD 1 |
| AZ31 | 3 Al, 1 Zn, 0.2 Mn | PD |
| AZ61 | 6 Al, 3 Zn, 0.15 Mn | PD |
| AZ91 | 8.7 Al, 0.7 Zn, 0.13 Mn | PD |
| AS41 | 4.37 Al, 0.93 Si, 0.35 Mn | PD |
| WE43-T6 | 4 Y, 3.4 RE | AL 2 |
| QE22 | 2.5 Ag, 2.1 RE | AL |
| MgGd5Sc1 | 4.64 Gd, 0.26 Sc, 1.53 Mn | AL |
| MgY4Sc1 | 3.88 Y, 0.73 Sc, 1.11 Mn | AL |
| AE42 | 4 Al, 2.5 RE, 0.1 Mn | PD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakkar, A. Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016
Bakkar A. Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakkar, Ashraf. 2025. "Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes" ChemEngineering 9, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016
APA StyleBakkar, A. (2025). Examples of the Superiority of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents over Aqueous Solutions in Electrodeposition Processes. ChemEngineering, 9(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9010016







