Abstract
Soil restoration by exploiting the principles and basics of electrokinetic (EK) has been extended to involve several categories, such as electrokinetic remediation in soil (SEKR), soil consolidation, the prevention of soil pollution, reclaiming salt-affected soil, the dewatering/dryness of wet soils, water reuse, seed germination, sedimentation, etc. As an extension of our recently published review articles on the soil electrokinetic (SEK) process intensification/optimization, the present review illustrates the effect of a reverse-polarity mode (RPM) on the efficiency of the SEK. Based on several searches of six database search engines, we did not find any relevant reviews focused on SEK improvements using the RPM. The influences of the RPM are described by various features, including (a) pollutant removal (organic, inorganic, and mixed pollutants) and (b) integration with other processes (phyto/bioremediation and Fenton oxidation), geosynthetics (consolidation, stabilization, and sedimentation), SEK operation conditions, and soil properties. Most of the RPM studies have focused on the remediation of organic pollutants. Several benefits can be gained from applying the RPM, such as (a) controlling the soil’s temperature, pH, and moisture values at desirable levels, (b) reducing a large number of chemical additives, (c) high remediation efficiency, (d) maintaining the indigenous fungal community’s appropriate diversity and abundance, (e) a stable and higher electric current, (f) enhancing microbial growth, etc. However, the hindrances to applying the RPM are (a) reducing the electroosmosis flow, (b) relatively high energy consumption, (c) reducing the diversity of soil microbes with a prolonged experiment period, (d) providing oxygen for a microbial community that may not be desirable for anaerobic bacteria, etc. Finally, the RPM is considered an important process for improving the performance of the SEK, according to experimental endeavors.
1. Introduction
The pollution of soil with potentially toxic elements has risen recently, owing to rapid economic development, which ultimately leads to a soil productivity reduction, in addition to creating threats to human well-being and sustainable agriculture [1]. The damage rates of soil pollution with potentially toxic elements over the past two decades reached 94.7, 77.4, and 68.4% in plants, humans, and animals, respectively, [1]. There has been a concern since 1900 about the elevating release of inorganic pollution (heavy metals) because of the rapid progress of urbanization and industrialization [2]. Human health can be affected by inorganic pollution, owing to metalloids and heavy metals that are considered not to be biodegradable [3]. The release of organic pollutants into the environment is also considered a threat to human life because the existence of organic pollutants simultaneously with their degradation metabolites may cause several harmful impacts/diseases for human beings (e.g., genetic mutation, distortion, and cancer) [4,5]. Not only does pollution with inorganic and organic elements affect the environment, but the environment is also subject to pollution with microplastics [6], anions [7], and radioactive materials [8].
Several approaches have been proposed to reduce the harmful impact of polluted soils [9,10,11,12,13]. The remediation methodologies may be classified into four classes to be appropriated for different pollutant-containing soils (i.e., chemical, physical, biological, and coupled/integrated methods) [14]. The SEKR is a physiochemical method [15] that is integrated with other chemical [16], physical [17], and phyto/bioremediation approaches [18,19,20]. The SEKR is based on imposing an electric field (direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC)) between electrodes that eventually results in movements of charged and uncharged elements from one location to another, as well as stimulating the bio/phytoremediation [17,21]. The application of DC and AC may be carried out individually or simultaneously [20,22].
The mechanism of the SEKR relies on four approaches that are created once the electrical field is applied (i.e., electromigration, electroosmosis (EO), diffusion, and electrophoresis) that create physiochemical and hydrological changes inside the treated media [23,24]. The basics and principles of the SEKR were introduced by several scientists at the beginning of the 1990s [25,26,27,28,29]; consequently, various articles were published in different fields of interest [11,21,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. Several processes were introduced to guarantee the optimization and intensification of the SEKR, such as modifying the SEK apparatus design [17,21], chemical additives for increasing the desorption and dissolvability of elements [16], continuously reoriented/rotating, reciprocating, and rotational electric fields [37,38,39], approaching/movement electrodes [40], incorporating perforated electrodes, pipes, and nozzles [41], etc. According to the electrode installation technique, the design of the SEK can be categorized into three sections, including vertical design, horizontal design, and mixed design [17,21]. The application of an electric field is responsible for removing bulk elements (heavy metals, cations, anions, etc.) [42,43,44,45] and other materials (organic pollutants) [46,47,48,49]. Accordingly, soil polluted with inorganic and organic pollutants can be remediated simultaneously [50,51]. The removal of heavy metals from polluted soil and catholyte can be carried out simultaneously using the SEKR [52]. The RPM was integrated with the pulsed mode of an electric field to remediate soils containing inorganic and organic contaminants [51,53,54,55,56,57,58,59].
There are several books, reviews, book chapters, and conference papers published on the enhancement approaches for optimizing the efficiency of the SEK; however, based on several searches in six database search engines, we did not find any relevant reviews focused on the integrated SEKR-RPM except for a book chapter published by Inman et al. [60]. This book chapter, entitled “Electrokinetic Soil Remediation Using Novel Electrodes and Modulated Reverse Electric Fields,” focused on modulating the RPM, and it did not discuss its role in depth from different perspectives. The present review depended on a survey of published articles relevant to the SEKR-RPM during the past 31 years (1993–2023). Six search engines were exploited to collect the relevant articles. The roles of the RPM were investigated from different points of view, including (a) pollutant removal (organic, inorganic, and mixed pollutants), (b) integration with other processes (phyto/bioremediation and Fenton oxidation), (c) electrokinetic geosynthetics (consolidation, stabilization, and sedimentation), and (d) operation conditions and soil properties.
2. Data Collection Methodology
The published articles relevant to the SEK research were downloaded from six search engines, including those of Elsevier, Springer, the American Chemical Society, MDPI, Taylor & Francis, and Hindawi, via a search for the following relevant words: “soil & electrokinetic.” More than one thousand articles published during the past 31 years (1993–2023) were downloaded; subsequently, the materials and methods sections were carefully examined for the RPM’s application. The role of the RPM (the topic of the present review) was compared with the lists of published books, book chapters, reviews, and conference papers (mentioned in our published review series) to avoid the repetition of topics [16,17,21].
3. Utilizing the Reverse-Polarity Mode (RPM) during the SEKR
3.1. The SEK-RPM Connection Mechanisms
Serval methods were proposed to ensure the proper application of the RPM during the SEK operation. In the case of the long-term interval period of the RPM (i.e., after the 10th day [61]), polarity reversal may be carried out manually. However, with the short RPM intervals’ periods (i.e., every 5 min [62]), a control unit is utilized to precisely ensure the performance of the RPM.
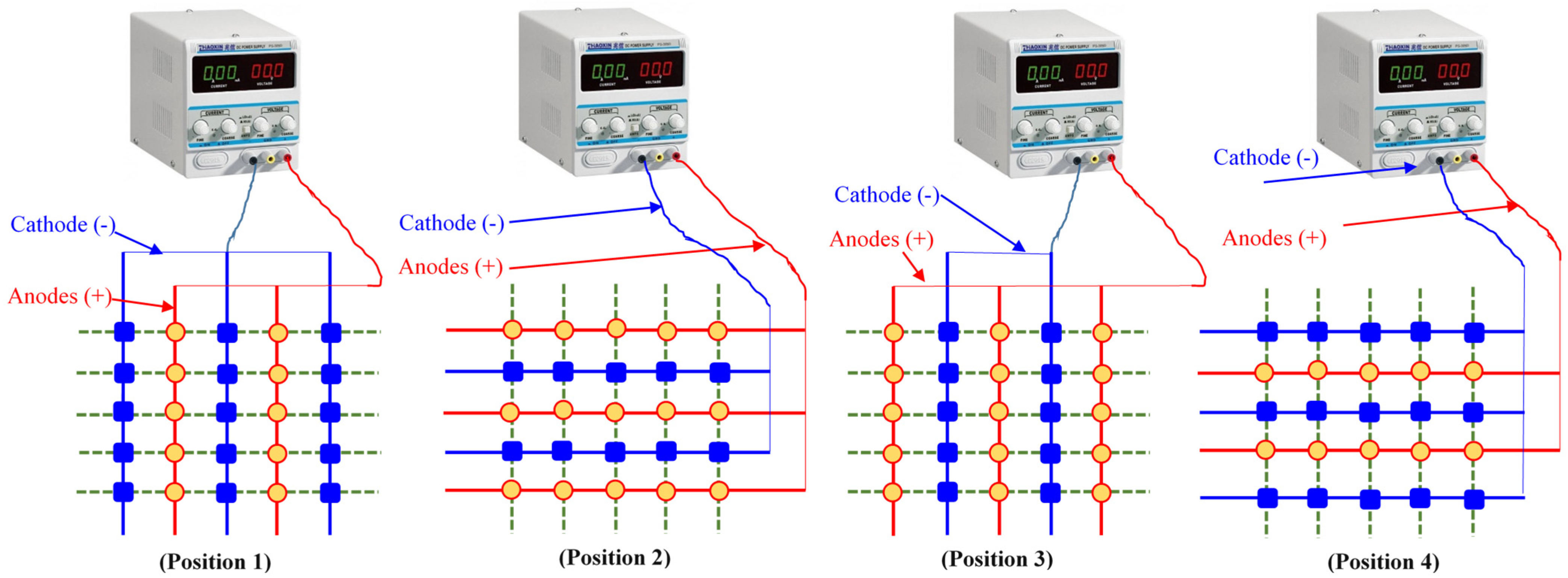
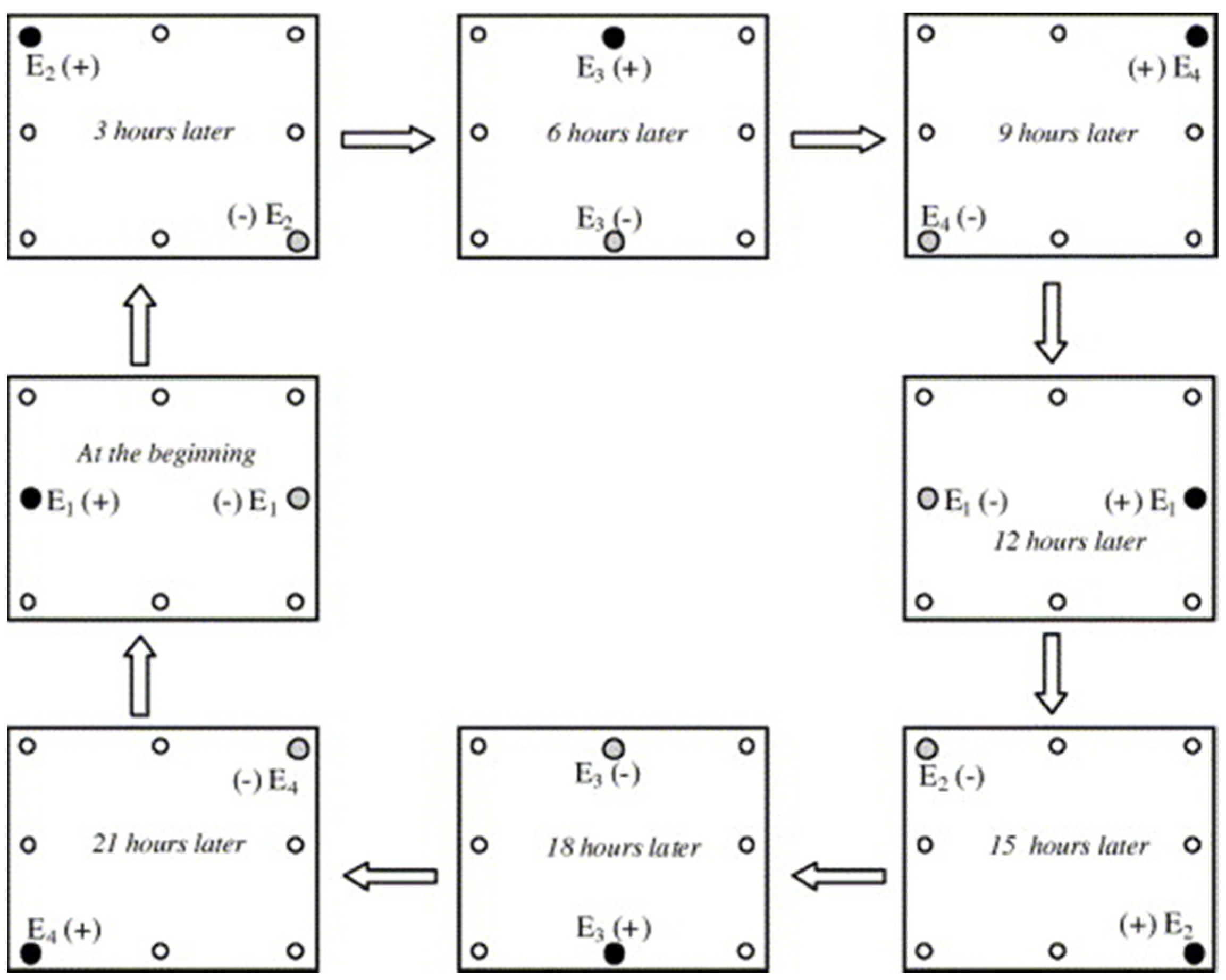
The electrode installation approach plays an important role in implementing the SEK-RPM. Guo et al. introduced an electrode matrix strategy for the proper application of the SEK-RPM at any location of equal distance from fixed electrodes, as shown in Figure 1 [63]. The remediation of sandy loam soil artificially contaminated with phenol using in situ SEKR–bioremediation was investigated by applying the electrode matrix, and a rotational approach as shown in Figure 2 [39]. In this study, the RPM was first optimized, and subsequently, the electrode configuration was optimized for the in situ remediation of phenol using the SEKR–bioremediation. Three RPM intervals were investigated for 10 days (1.5, 3, and 12 h in a clockwise direction with an applied voltage of 1.0 V cm−1).
Figure 1.
Design of an electrode matrix with polarity switching to produce the same intensity of an electric field at any point of equal distance from the electrodes, redrawn from the work of Guo et al. [63].
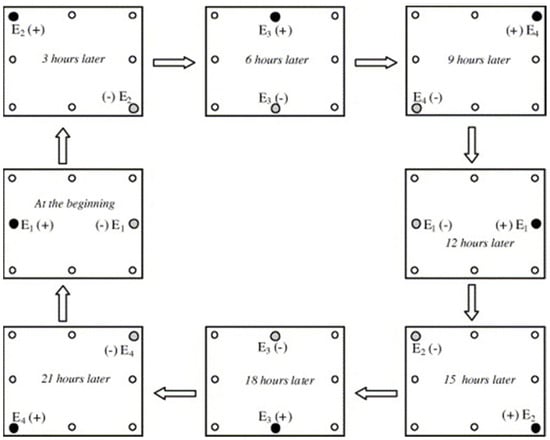
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the rotational operation at an interval of 3 h through an electrode array with four couples for one operation cycle, after Luo et al. [39] (Elsevier Copyright—License Number 5824280357745). The electrified anode ( ●), cathode ( ), and un-electrified electrodes (○) are shown.
), and un-electrified electrodes (○) are shown.
 ), and un-electrified electrodes (○) are shown.
), and un-electrified electrodes (○) are shown.
The integrated SEK–bioremediation and in situ capping were examined for the PAHs’ remediation from abandoned industrial soil. In this study, the anode was located at the bottom of the SEK apparatus to provide a mode that eventually increases the degradation rates of the PAHs’ chemical oxidation (owing to supplying more oxygen via water electrolysis) located in deep soil compared to the equal time intervals of the RPM [64].
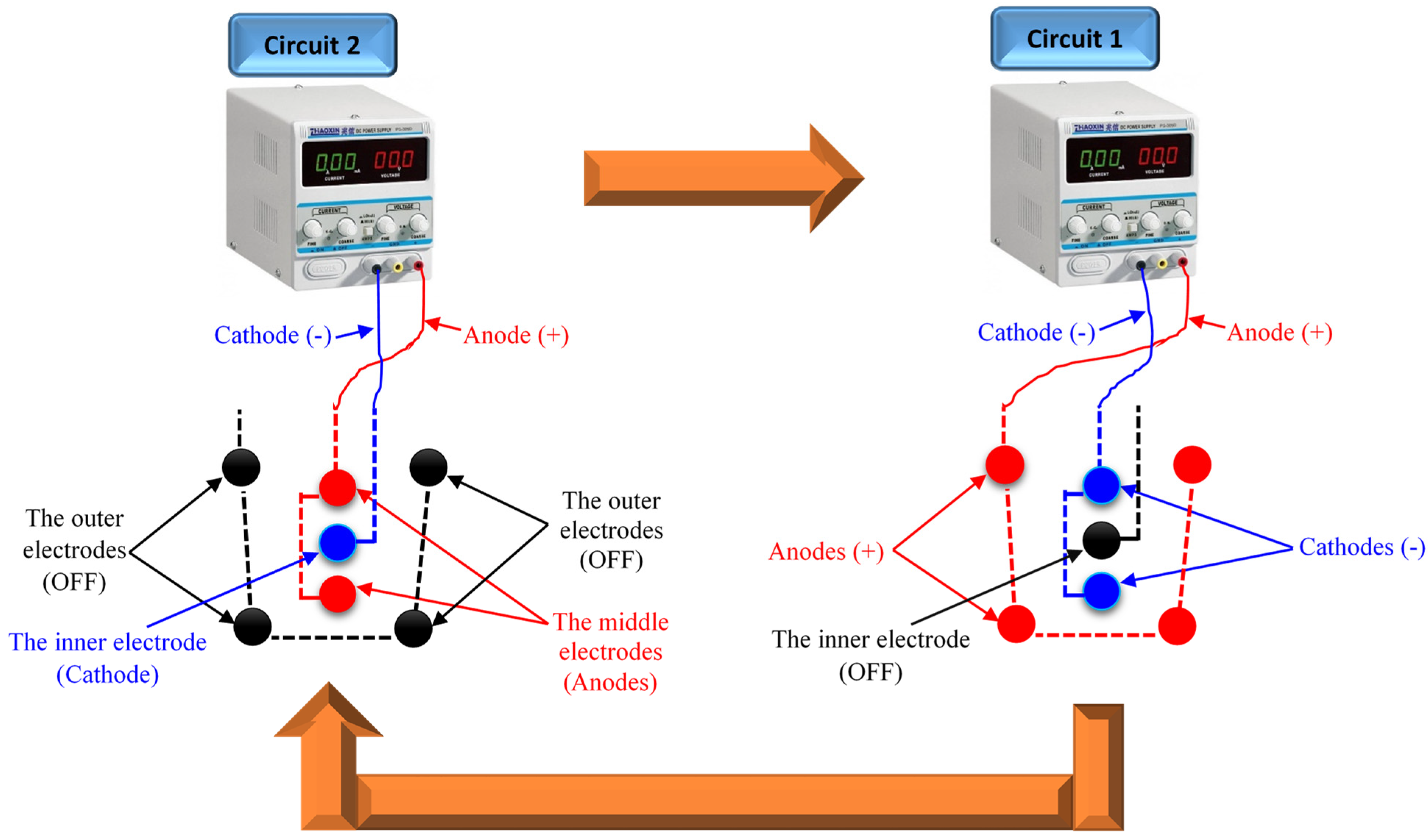
Sun et al. introduced a novel cyclic and progressive EO (CPE) method for soft clay consolidation using EK geosynthetics (EKG) [65]. The CPE basically depends on the RPM application. The CPE is proposed to impose the EO flow toward one direction for the final converging at a certain electrode to avoid the obstacles of the traditional RPM, as presented in Figure 3. The CPE operation mechanism is based on the installation of three electrode layers (outer, middle, and inner) that are connected/linked with the same electric wire. The first circuit was created by connecting the outer electrodes with the positive pole (anodes) and the middle electrodes with the negative pole (cathodes). The second circuit was created by connecting the middle electrodes with the positive pole (anodes) and the inner electrode with the negative pole (cathode). The first and second circuits were not connected simultaneously with a power source. The electrification mode was started with the second circuit, followed by the first circuit, for a certain period. By repeating the electrification mode of the second and first circuits several times, the soil pore water can be moved toward the inner electrode [65].
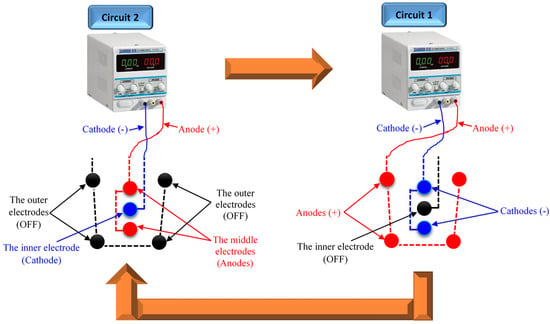
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the cyclic and progressive electroosmosis (CPE) approach, redrawn from the work of Sun et al. [65].
3.2. Applying the SEK-RPM to Remediate Soil Contaminated with Organic Pollutants
The studies that were carried out on applying the RPM to remediate organic pollutants using the SEKR are listed in Table 1. The majority of research utilized an applied voltage of 1 V cm−1, which is considered the most appropriate value for performing SEKR research [16,17], whereas some studies utilized lower and higher values (e.g., 0.4, 0.5, 0.8, 1.3, 1.5, 1.6, and 2 V cm−1) [49,64,66,67,68,69,70,71]. Choosing the appropriate applied voltage was based on trials and errors or according to previous investigations to achieve the exact purpose of the SEKR. The RPM interval periods differed from one study to another, according to the main objectives. The short interval periods of the RPM were 1, 5, 10, and 30 min [64,72], whereas the long interval periods were 5, 10, 14, and 15 days [61,71,73,74]. The experimental SEKR periods ranged between 1 and 168 days [39,70,75].
The effects of applying the RPM during the SEKR of diesel-polluted soils were investigated [66,76]. Ramírez et al. performed a comparison of different approaches during the integrated SEKR–bioremediation in situ (bioremediation, integrated SEK–flushing and bioremediation (SEKF-Bio), daily RPM for SEKF-Bio (RPM-SEKF-Bio), and SEK–flushing (SEKF), combined with a permeable reactive biological (SEKF-PRB)). A daily RPM of 1 V cm−1 that lasted for 14 days was examined with SEKF-Bio (Table 1). The results highlighted the role of the RPM in controlling temperature, pH, and moisture at desirable levels. Both treatments, RPM-SEKF-Bio and SEKF-PRB, reduced the large number of buffer additives for biological activity by improving the transport processes and creating adequate operating conditions [76]. The remediation of diesel-spiked soil for the same period (14 days) was also investigated using the daily RPM during SEK–bioremediation, whereas different applied voltages were examined (0.5, 1, and 1.5 V cm−1), as listed in Table 1 [66]. Compared to traditional SEK–bioremediation, the application of the RPM did not require chemical additives to regulate pH variations; in addition, it represented more efficient remediation. The removal of diesel was 35.10% with an applied voltage of 1.5 V cm−1, whereas this value was reduced by 10.5% with the single bioremediation. The EO flow achieved low values via the application of the RPM [66]. Another study for the same group focused on the influences of the RPM and voltage gradients on the SEKF for the remediation of insoluble organics (diesel hydrocarbons) from clayey soil integrated with the PRB using identical operation parameters (Table 1) [67]. The results confirmed the positive role of the RPM in maintaining the soil pH and temperature at desirable levels to stimulate organic biodegradation, whereas the EO flow was affected. The highest diesel removal efficiency was achieved (36%) with an applied voltage of 1.5 V cm−1 [67].
A rotatory 2D SEKR was investigated in treating the total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPHs) through the coupling of SEK–bioremediation [62]. The applied voltage was set to 1 V cm−1, and it was rotationally reversed each row and column every 5 min for 100 days (Table 1). The results highlighted the effective role of electric intensity on the degradation of TPHs, which was obvious with SEK–bioremediation compared to bioremediation or the SEKR alone, owing to the superimposed effects of biological degradation and electrochemical stimulation. The synergistic effect was concurrent with the changes in the microbial community structure and could be expressed during the later phase of the experiment. Applying the electric field associated with the RPM caused a reduction in the diversity of soil microbes by prolonging the experimental period. Applying or not applying an electric field associated with the RPM did not influence the temperature between the soil chambers, whereas the soil pH was uniform during the experimental process. The microbial community’s composition and bacterial numbers did not significantly shift spatially [62]. The RPM period of 2 h was investigated during SEK–bioremediation for petroleum-contaminated soil with an applied voltage of 1 V cm−1 for 105 days (Table 1) [77]. The integrated SEK–bioremediation and SEK–bioremediation-RPM improved the petroleum degradation because of the soil’s organic carbon utilization enhancement and maintenance (i.e., P/S value). The electric field stimulated the soil’s organic carbon and petroleum-derived carbon degradation in biological oxidation zones. The metabolism of the soil’s organic carbon enhanced the “abundance of functional bacteria and the alpha diversity of microorganisms over a certain period and maintained similarity to the original microbial community,” which was clear with the SEK–bioremediation–RPM [77].
It was favorable to run the SEKR-RPM to stimulate bacterial growth and preserve soil properties uniformly in order to remediate heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) [48]. Applying the RPM (altered directional operation) at 1 V cm−1 enhanced the removal of PAHs compared to the control experiment, in addition to maintaining the indigenous fungal community’s appropriate diversity and abundance. The uniform distribution of fungal communities was more conducive with the RPM compared to the unidirectional approach [49]. The application of the RPM during the remediation of soil contaminated with a PAH (pyrene) using SEK–bioremediation was investigated, and the results revealed that the pH values stayed close to neutral (7.2, avoiding soil-pH changes) and the electric current was relatively stable and five times higher than that observed with traditional SEK–bioremediation. The SEKR-RPM–bioremediation of pyrene enhanced the degradation rate (SEK oxidation and biological metabolism), as well as microbial counts (microbial growth) [78,79,80]. Applying the RPM increased pyrene removal percentages and bacterial counts adjacent to the electrodes compared to the middle of the apparatus, which highlights the role of discrepancies in electrical intensity at different electrode positions. Non-polar organic contaminants’ degradation may be compatible with the RPM [80]. Applying the RPM during the isolation and characterization of bacteria that degrade heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) highlighted that P. fluorescens and Kocuria sp. could be exploited for the remediation of PAH using integrated SEKR–bioremediation [81].


Table 1.
Summary of the reverse-polarity operation mode during the SEKR of organic pollutant-contaminated soils.
Table 1.
Summary of the reverse-polarity operation mode during the SEKR of organic pollutant-contaminated soils.
| No. | Organic Pollutant-Contaminated Soil | Applied Voltage | Reverse-Polarity Mode | Experimental Period | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diesel-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [76] |
| 2 | Diesel-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [66] |
| 3 | Diesel-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [67] |
| 4 | Total petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [62] |
| 5 | Petroleum-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [77] |
| 6 | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [48] |
| 7 | PAH-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [49] |
| 8 | PAH (pyrene)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [78] |
| 9 | Pyrene-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [79] |
| 10 | Pyrene-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [80] |
| 11 | PAH-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [81] |
| 12 | Heavily PAH-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [64] |
| 13 | Soil contaminated with contaminants of emergent concern |
|
|
| [47] |
| 14 | Cycloparaffinic-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [68] |
| 15 | Chronically hydrocarbon-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [74] |
| 16 | PAH-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [72] |
| 17 | Crude oil-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [82] |
| 18 | Pentachlorophenol-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [61] |
| 19 | Pentachlorophenol-containing unsaturated soil |
|
|
| [83] |
| 20 | Phenanthrene-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [84] |
| 21 | Phenol-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [39] |
| 22 | Herbicide (oxyfluorfen)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [85] |
| 23 | Oxyfluorfen-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [86] |
| 24 | Oxyfluorfen-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [87] |
| 25 | Oxyfluorfen-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [75] |
| 26 | Oxyfluorfen- and atrazine-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [88] |
| 27 | Organochlorine herbicide (clopyralid)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [89] |
| 28 | Soils contaminated with herbicides (2,4 chlorsulfuron (CLSF) and dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)) |
|
|
| [46] |
| 29 | Antibiotic-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [69] |
| 30 | Antibiotic resistance in soil |
|
|
| [70] |
| 31 | Tetracycline-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [90] |
| 32 | Soil contaminated with herbicide |
|
|
| [91] |
| 33 | Phthalates ester-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [71] |
| 34 | Hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [92] |
| 35 | Hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [73] |
Li et al. highlighted several advantages associated with applying the RPM, including (a) decreasing an electric field’s negative impact on degrading microorganisms and soil properties, (b) stimulating contact between microorganisms, contaminants, and nutrients, (c) avoiding the accumulation of ions surrounding electrodes, (d) making the soil pH stable through the contaminated soil, (e) elevating the numbers of bacteria in the bio-barrier and soil, (f) increasing the content of moisture adjacent to the bio-barrier, (g) making the relative abundance of dominant degrading genera more uniform, and (h) modifying the structure of the microbial community [64]. The low applied voltage (0.8 V cm−1) presented a limited influence in promoting the degradation of PAHs, whereas applying a high voltage (1.6 V cm−1) resulted in the penetration of PAHs through the bio-barrier, and they ultimately migrated to the soil’s clean part. An intermitted voltage (1.2 V cm−1) improved the bio-barrier’s microbial quantity and eventually achieved removal efficiency for PAHs; however, the effective migration of PAHs was blocked [64].
Guedes et al. showed that the effect of electro-polarization reversal did not enhance the removal of any contaminants of emergent concern; the removal of caffeine and triclosan was lower compared to the unidirectional EKR approach. The output of that study is not coincident with the results revealed from the other investigations focused on organic contaminants (e.g., hydrocarbons) [47]. Applying the RPM enhanced the dynamic processes of the biodegradation of cycloparaffinic more than the application of the traditional SEKR. The application of an electric field did not change the cyclododecane degradation pathway. The cyclododecane degradation rate was 87.0% when the RPM was applied; however, 79.9% was achieved with the regular SEKR. Electric field application stimulated the ring-breaking of cyclododecane and increased the linear concentrations of substances that are more susceptible to degradation via microorganisms [68]. The removal of hydrocarbons (TPHs and PAHs) was increased by applying the SEKR-RPM [74]. Based on the quantitative PCR of 16S rRNA genes and the function of the community, the RPM exerted a negative impact on the abundance of bacteria (transient impact). The coupling of SEKR–bioaugmentation resulted in the highest degradation of TPHs (76%) and PAHs (78.6%). The RPM can enhance nutrient distribution and mitigate differences between remediation rates surrounding the anode and cathode [74]. Wang et al. also confirmed the role of high frequencies of the RPM on PAH degradation (especially with high PAHs), which was associated with an elevation of the current intensity to the overall electrification time. The SEKR–bioremediation associated with 10 and 30 min of the RPM resulted in the maximum degradation percentages. The elevation of frequencies of the RPM enhanced the physicochemical properties of soil, which ultimately ensured the effective performance of SEKR–bioremediation/degradation and electrochemical oxidation [72]. Prolonging the electric field simultaneously with the RPM’s application delayed the attenuation of the soil’s microbial abundance (especially for high-ring PAH-degrading bacteria and the total PAH-degrading bacteria) in addition to preserving the initial community structure and microbial alpha diversity [72].
Applying the RPM to remediate crude oil-containing saline soil effectively stimulated bacterial abundance (two times), which may be owing to much more uniform nutrient distribution, water, elements, and hydrocarbon oxidization into organic compounds [82]. The uniform distribution of soil pH was observed during the coupled SEKR and permeable reactive barrier (PRB) to remediate pentachlorophenol-contaminated soil [61]. Harbottle et al. illustrated that the constant electric currents caused great variation in both moisture content and pH values during the remediation of pentachlorophenol-containing unsaturated soil, owing to the direct effect of electroosmotic flow and water electrolysis that ultimately caused negative influences on biodegradation parameters (contaminant mineralization and enzyme activity). However, applying the RPM resulted in little variation in the values of moisture content and pH, which eventually increased both contaminant mineralization and soil enzyme activity, as well as reducing the contaminant concentration in the majority of the microcosms except for soil located immediately adjacent to the anode [83]. The highest removal of phenanthrene was achieved with applying the RPM, owing to the better injection and distribution of nutrients. The circulation of the mixed electrolyte could control soil pH well, rather than applying the RPM [84].
The effect of the non-uniform SEKR method on phenol and dichlorophenol mobilization was investigated in unsaturated soils (kaolin and a natural sandy loam soil) [93]. Applying the RPM every 6 h did not present a significant accumulation of phenol or 2,4-DCP inside EK cells. The RPM arbitrarily reversed the directions of 2,4-DCP and phenol. The application of a non-uniform electric field was capable of enhancing the movement and desorption of 2,4-DCP and phenol in unsaturated soils. The driving forces for the remediation of 2,4-DCP and phenol were the electromigration and EO flow that were influenced by soil pH variation [93]. Luo et al. carried out another study that exploited the non-uniform approach with the RPM for improving the phenol bioremediation in situ [94]. The results highlighted that applying the non-uniform electric field method enhanced the phenol movement, as well as in situ biodegradation. The biodegradation of phenol was carried out more effectively in a bidirectional mode than in a unidirectional mode. The removed phenol was increased (more uniform and higher removal) with the application of the smaller interval of the RPM. The RPM was associated with an elevation of the consumed energy while maintaining soil moisture and pH [94]. The RPM intervals stimulated phenol bioremediation, and the more uniform and higher phenol removal was achieved at smaller intervals (the RPM intervals that did not exceed 3 h in this study are the more suitable value) [39]. The efficiency of bioremediation was elevated to ~5 fold, achieving maximum phenol removal (58%) during ten days with a three-hour reversal interval. The larger intervals may result in the accumulation of bacteria or phenols in the specific zone, whereas the smaller/optimal intervals can force the movement back and forth of the bacteria and phenol to primary positions. The bacteria and phenols can migrate inside the soil, back and forth, under the effect of the RPM. Although the smaller intervals of reverse polarity achieved the most desired remediation (uniform high removal), they consumed more energy [39].
It was reported that increasing the RPM frequencies during the remediation of oxyfluorfen negatively affected the EO flow, whereas it controlled the soil’s pH, temperature, conductivity, and moisture content [85]. Applying the RPM maintained a uniform microbial distribution in the soil after the experiment was terminated, indicating the remaining microbial activity throughout the soil. The microbial degradation of oxyfluorfen in soil without applying an electric field was negligible, although it reached 100% for oxyfluorfen-containing water. Applying the periodic RPM enhanced species’ transportation (promoting interactions between nutrients and microbial cultures), ultimately achieving oxyfluorfen removal rates of 5–15%. The optimal values of the periodic RPM were observed between 2 and 3 days. The incorporation of the PRB simultaneously with in situ SEK–bioaugmentation may be considered a successful alternative for oxyfluorfen remediation; however, to achieve higher removal efficiencies, higher retention times are required [75,86,87]. The SEK-RPM integrated with the adsorption barrier achieved a higher removal of herbicides and a lower evaporation loss compared to SEK–flushing [88].
Rodrigo et al. highlighted that the RPM gained the best clopyralid retention in the PRB (activated carbon); however, the SEKR-RPM–adsorption barrier achieved the higher removal of clopyralids compared to the SEKR–adsorption barrier [89]. Souza et al. also studied the role of the SEKR integrated with the RPM and adsorption barrier to remediate soil artificially polluted with herbicides (chlorsulfuron (CLSF) and dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)). The properties of the two herbicides were (a) very different adsorption properties and volatility (2,4-D > CLSF in volatility) and (b) high water solubility [46]. The SEKR-RPM–adsorption barrier reduced the 2,4-D and CLSF by 40% and 60%, respectively via carbon bed retention, positively affecting pH regulation, avoiding soil salts’ washing, and reducing evaporation to the minimum values [46]. Compared to the traditional SEKR system, applying the SEKR-RPM over 6-h periods enhanced the remediation efficiency of 2,4-D up to 94.5% [95].
H. Li et al. illustrated that the RPM mitigated abrupt pH changes, keeping it appropriate for biological and EK remediation and avoiding soil-quality alterations while reducing heavy metal contents and modifying heavy metal speciation (i.e., the reactive forms increased; however, the residual forms decreased). The SKE removed 65.4–66.7% of antibiotics, whereas 18.6–21.9% removal was achieved with indigenous microorganisms [69,70]. Resistance to the electric field was observed with the anti-sulfamethoxazole bacteria compared to anti-oxytetracycline bacteria. This may be owing to the “greater constraints on their resistance enzymes.” The spread of antibiotic resistance genes was accelerated in the presence of heavy metals (a 3.86-fold increase for sul1 and a 2.67-fold increase for tetG). There was a significant correlation between Cu and antibiotic resistance genes “consistent with the relatively stronger toxicity of Cu and its high potential to induce the SOS response” [70]. The imposition of the electric field was capable of degrading tetracyclines, owing to the increased concentrations of in electrolytes and soils, and the SEKR-RPM removed 22–84% of tetracyclines [90]. Electrolysis can generate oxidative radicals participating in tetracyclines’ degradation [90]. The removal of chloridazon reached 100% and 63% for the traditional SEKR and the SEKR-RPM, respectively. The traditional SEKR stimulated pesticide desorption; however, the SEKR-RPM favors pesticide re-adsorption, owing to the continuous changing of the migration process. Although the traditional SEKR achieved good removal rates, ultimately, it caused physicochemical alterations in the soil (e.g., pH, electrical conductivity, and moisture). The SEKR–alternate polarity overcame the undesirable alteration of properties [91].
The SEKR improved the phthalates esters’ (PAEs) removal, owing to the organic pollutants desorption rendered via the EO flow that eventually augmented the bioavailability. The microbial growth was not improved enough in the case of oxygen-releasing compound injection into the anode compartment, owing to the negative impact of the SEKR transportation that ultimately caused an oxygen-releasing compound loss [71]. Elevating the applied voltage affected the soil’s conductivity, pH value, and electrolytes during the remediation of hexachlorocyclohexane; however, this effect was less evident with the application of 1 V cm−1 operated with the RPM [92]. Fernández-Cascán et al. observed that applying an electric field to polluted soil (silt) was not very effective in remediating aged hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil, and both the EK fluxes and the EO flow-dragging forces are ineffective, owing to the strong pollutant–soil interaction. The chlorine substitution average number in the chlorinated organic compounds was reduced, which was associated with the basic front that was enhanced by applying the RPM [73]. Kim and Han utilized the RPM to solve the problem of nonuniform injection through the excessive growth of microbes. Applying the RPM distributed ions containing target soil more uniformly, as well as achieving better ion injection to enhance microbiological degradation. The biofouling problem was avoided when the RPM was applied, owing to microorganisms’ excessive growth, inherent ion migration, and organic matter adsorption. The distribution of ions after the RPM relies on the injection period and direction after the RPM is applied [96]. The removal of perchloroethylene was significantly enhanced via the application of the RPM using the integrated SEKR-PRB [97]. The Lasagna process also utilized the SEKR-RPM to remediate organic pollutants (p-nitrophenol- and trichloroethylene-contaminated soils) [98,99,100]. A recent study also utilized the RPM in investigating the degradation of chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol during integrated SEKR–soil washing using an anionic surfactant [101].
3.3. Applying the SEK-RPM to Remediate Soil Contaminated with Inorganic Pollutants
The remediation of inorganic pollutants (heavy metals) using the improved SEK via the application of the RPM is shown in Table 2. The applied voltage of 1 V cm−1 was tested in the majority of experiments; however, other research utilized higher voltages (e.g., 2 and 3 V cm−1) [102,103] and lower voltages (e.g., 0.2, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, and 3 V cm−1) [53,103,104]. The interval periods of the SEKR-RPM for inorganic pollutants ranged between 30 min [105] and 10 days [106]. The experimental periods lasted for 1–21 days, according to the experimental endeavor and the SEKR apparatus design [107,108].
The integrated EK and cork-based PRB to avoid the pollution of groundwater was studied using kaolinite that was artificially contaminated with Cr (hexavalent) as a case study [109]. This study highlighted that applying the RPM (Table 2) caused high Cr accumulation in soil, which may have been owing to the reciprocal migration of Cr [109]. Another study showed that the RPM achieved the highest energy consumption (62 W h−1) during a lab-scale study of the SEKR of a Cr-contaminated aquifer (natural fine sand) compared to other approaches (the SEKR–pulsed/intermittent mode and the traditional SEKR) [110]. The application of the RPM (every 24 and 84 h) represented a slighter variation in soil pH (the best results were observed with the RPM every 24 h); however, a reduction in the removal efficiency of Cr was observed, owing to the repeated migration [111]. Zhou et al. revealed that applying the RPM enhanced the Cr removal rate, particularly for Cr(III), which may have been owing to an improvement in the electrical current and a reduction in the focusing phenomena [55]. Liu and Zhuang revealed that applying the RPM adjusted the pH of an electrolyte solution to below 7; in addition, 69.20% removal efficiency for Cr(VI), associated with less energy consumption, was achieved within 4 h of the RPM [105]. The removal rates for Cr and Cd from abandoned industrial sites were observed with the application of the RPM compared to the traditional SEKR. Applying the RPM controlled the soil pH, keeping it between 5 and 7; in addition, either installing complex equipment or chemical additives were not required [112]. The integrated RPM and installation of the array adsorption zone optimized the removed Cd to 83%. It was also reported that “the reciprocating motion of Cd caused by polarity exchange is no longer a side effect,” owing to the installation of the array adsorption zone [104]. The concentrations of Cd in wheat after the integrated remediation processes of the SEKR-RPM–array adsorption zone were reduced as follows: root (86%), stem (93%), and leaf (95%) [104]. Applying the RPM resulted in Cd migration from the two ends of the target soil toward the apparatus’s middle, especially the exchangeable form of Cd. The moisture content should be controlled so that it is above 0.35 g g−1 with soil pre-acidification using citric acid [53]. Under the best operation conditions of the SEKR-RPM (0.47 V cm−1, reverse polarity of 19.77 h, and Cd concentrations of 65.44 mg kg−1), 86% of Cd could be removed [103]. Also, the RPM was utilized during the integrated SEKR–adsorption for Cd remediation using double-group electrodes [113]. The removal percentages of Cd and Pb were slightly enhanced by applying the RPM, whereas the removed nitrate was not enhanced [114].
Applying the RPM (48-h intervals) achieved the maximum removal of Pb (87.7%), whereas a 61.8% was achieved in the case of the traditional SEKR. The application of RPM was capable of avoiding the “focusing effect” phenomena associated with the traditional SEKR; in addition, chemical additives were excluded, which is considered an economic merit. Applying the RPM prevented Pb precipitation, as well as the re-dissolution of precipitates [107]. Han and Kim revealed that applying the RPM after the addition of an anionic surfactant and citric acid reduced the Pb precipitation (three times) compared to the SEKR unenhanced system [115].
Rojo et al. examined the SEKR of Cu mine tailings using high-frequency sinusoidal electric fields [22]. The results showed that polarization could be reduced by applying the RPM. The EKR process was enhanced by applying the high-frequency sinusoidal electric field, and the remediation action was improved by increasing the effective voltage, particularly in the presence of the RPM. More details about the application of sinusoidal electric fields are presented in the literature [22]. During the remediation of Cu-contaminated soil using carbonized foods as a PRB, the density of the electric current after performing the RPM was lower than previous values. The RPM was capable of completely removing precipitated heavy metals located surrounding the cathode. The PRB was also capable of adsorbing the majority of Cu before the RPM was applied. The existence of heavy metal close to the PRB required a longer removal time, even when the RPM was applied. The farthest transport of Cu was achieved close to the cathode after 10 days of operation and after the application of the RPM. During the elapsed operating time (beyond the RPM), heavy metals containing PRB were migrated toward the soil. The interpretation of this phenomenon may be owing to the excess adsorption capacity of PRB [106].
The feasibility of the SEKR for spiked kaolin containing heavy metal (Mn) was investigated by applying the RPM to overcome metal precipitation, owing to the negative effect of OH- production surrounding the cathode [102]. Reducing the pH adjacent to the cathode electrode is the key factor in the repeated dissolution of Mn, which could be achieved by applying the RPM since it produces H+ ions in the alkaline zone adjacent to the cathode. Once the dissolution of Mn occurs, the original position of polarity is returned, which ultimately encourages Mn transportation toward the desired direction. The traditional SEKR achieved 14% removal percentages for Mn during 7.6 days, whereas 72% was obtained by applying the RPM. The application of the RPM may achieve the complete decontamination of polluted soil, whereas the consumed energy will be moderately elevated [102].


Table 2.
Summary of reverse-polarity operation mode during the SEKR of inorganic pollutant-contaminated soils.
Table 2.
Summary of reverse-polarity operation mode during the SEKR of inorganic pollutant-contaminated soils.
| No. | Inorganic Pollutant-Contaminated Soil | Applied Voltage | Reverse-Polarity Mode | Experimental Period | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cr-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [109] |
| 2 | Cr-contaminated aquifer |
|
|
| [110] |
| 3 | Cr-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [111] |
| 4 | Cr-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [55] |
| 5 | Cr-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [105] |
| 6 | Cr and Cd-containing abandoned industrial sites |
|
|
| [112] |
| 7 | Cd-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [104] |
| 8 | Cd-contaminated paddy soil |
|
|
| [53] |
| 9 | Cd-contaminated saline–sodic soil |
|
|
| [103] |
| 10 | Inorganic contaminants |
|
|
| [114] |
| 11 | Pb-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [107] |
| 12 | Pb-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [115] |
| 13 | Cu-contaminated mine tailings |
|
|
| [22] |
| 14 | Cu-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [106] |
| 15 | Heavy metal (Mn)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [102] |
| 16 | Hg-contaminated clayey soil |
|
|
| [108] |
| 17 | Arsenic-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [116] |
| 18 | Heavy metal-contaminated mine tailings |
|
|
| [117] |
Based on the ANOVA, the most contributing factors for the remediation of Hg from clayey soil were applied voltages > concentrations of Hg > reverse polarity. Applying the RPM every 4 h with an applied voltage of 0.2 V cm−1, and an initial concentration of Hg of 100 mg kg−1, were the optimal circumstances for maximizing the SEKR (99.5% removal of Hg and decreased consumed energy) [108]. Jiang et al. studied the remediation of arsenic-contaminated paddy soil using the SEKR-RPM enhanced with ascorbic and fulvic acid additives (to increase As mobility) [116]. The removal of As was 29.1% associated with the addition of fulvic acid, which was higher than the control experiment (5.5%). The mechanism of As removal in this study was because of “the reductive dissolution of iron oxides and the activation of residual arsenic.” The removal efficiency of the associated heavy metals (Cu, Pb, and Zn) reached 31.7% (highest removal) [116]. Acosta Hernández et al. examined the SEKR of heavy metal-contaminated mine tailings integrated with in situ bioleaching through two series of experiments [117]. The RPM was examined through the first stage of the two series of experiments. The purpose of the first series was to stimulate metal sulfides’ biological dissolution, whereas the second stage was proposed to ensure the removal of leached metals. The results showed that the applied voltage (AC) is considered the best choice compared to the RPM performed within the first series of experiments [117].
3.4. Simultaneous Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants Using the SEKR-RPM
Utilizing the RPM during the simultaneous remediation of mixed pollutants (organic and inorganic) using the SEK was investigated in two studies [50,118]. The two studies utilized the applied voltage of 1 V cm−1, with RPM interval periods (4, 12, and 24 h), and the experiments lasted for 10.5 and 20 days, as listed in Table 3. Ma et al. evaluated the integrated SEKR-RPM and activated bamboo charcoal for the simultaneous removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) and Cd from polluted soils [118]. The RPM applications at 12 and 24 h achieved removal percentages of 40.13% and 24.98% for Cd and 2,4-DCP and ~ 75.97% and 54.92% for Cd and 2,4-DCP, respectively (i.e., applying the RPM every 24 h was more effective). Under the two RPMs, a significant reduction in water content was observed, but it was evenly distributed spatially. In addition, the RPM maintained a pH level close to the initial value (7.2 to 7.4). The RPM of 24 h consumed less electricity compared to the RPM of 12 h [118]. The results of the SEKR for soil artificially co-contaminated with cadmium–pyrene showed that applying the RPM-preserved soil pH values within 7.27–7.67 was appropriate for microbial growth [50]. The electric field application increased the activity and growth of microorganisms that are reasonable for pyrene degradation; however, the solubility of Cd near electrodes is considered a restricting factor (a certain inhibitory effect). The synergistic effect of pyrene-degrading microorganisms and an electric field near the electrode achieved a pyrene removal rate of 56.38%. The efficiency of the removed pyrene was positively correlated with the number of pyrene-degrading microorganisms far from the electrodes [50].

Table 3.
Summary of reverse-polarity operation mode during the SEKR of soils contaminated with mixed pollutants (inorganic and organic).
3.5. The SEKR-RPM Integrated with Phytoremediation
Based on the data presented in Table 4, most of the experiments that exploited the integrated SEKR-RPM–phytoremediation utilized an electric field of 1 V cm−1, which is considered the most coincident value for the SEKR. However, one study carried out by Li et al. investigated the effect of an applied voltage of 2 V cm−1 on remediating uranium-contaminated soil [119]. The low values of the electric field (0.2–0.8 V cm−1) were also examined for the germination experiment and remediation of atrazine-polluted soils [51,120]. The interval periods of the RPM varied between 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h, according to the experimental endeavor (Table 4). The experimental periods were relatively longer than others of the above-mentioned integrated processes.
3.5.1. Removal of Inorganic Pollutants
Bi et al. investigated the effects of different types of electrical fields (DC and AC) on decontaminating metal-polluted soils using phytoremediation by growing tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) and rapeseed (Brassica napus), as presented in Table 4 [20]. Applying the RPM-DC field eliminated the variation of pH-adjacent electrodes. Applying the AC increased the rapeseed biomass, whereas the DC application did not present a negative effect. Under the application of AC, no improvements were achieved in the tobacco biomass, whereas under the application of the DC field, the biomass production of tobacco plants was negatively influenced. The application of AC improved the Cd content in tobacco and rapeseed grown in soil section No. 2 compared to the control experiment. Applying the AC enhanced the uptake of Cu, Cd, Pb, and Zn via rapeseed plant shoots in all soils [20]. The increased accumulation of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn) in Lolium perenne L. was observed with the application of an applied voltage (AC) of 1 V cm−1 compared to the control, whereas no significant increases in heavy metal uptake via the plant were achieved when using the applied voltage (DC) associated with the RPM. Applying the AC improved the heavy metals’ mobilization compared to the DC, although the negligible role of electromigration and electroosmosis [121]. A recent study also utilized the RPM for the enhanced remediation of multi-metal-polluted soil using integrated electro-bio-chemical phytoremediation (sunflower and maize) [122].
The SEKR prompted the bioavailability of uranium in soils (water-soluble and exchangeable fractions of uranium), which ultimately enhanced the uptake of uranium via ryegrass, as well as its bioaccumulation. The RPM adjusted the high pH values surrounding the cathode to neutral values [119]. Applying the AC electric field enhanced the Solanum nigrum growth and biomass compared to the control; however, applying the DC electric field associated with the RPM did not present a significant impact. The SEKR (DC and AC) elevated the concentration of Cd significantly in S. nigrum, and optimal results were achieved with the DC-RPM [123]. Applying the SEKR with amendment additives (EDTA, humic acid, and pig manure compost) significantly increased Cd phytoextraction. Applying the RPM avoided the pH variation surrounding electrodes without harmful effects on shoot biomass production. The SEK increased the concentrations of soil DTPA-extractable Cd [54]. The RPM preserved the stability of the soil pH. Applying an electric field improved the efficiency of the phytoremediation of Pb, which was obvious with the improved growth of plants. Moreover, the RPM increased the enrichment coefficient of Pb in tall fescue and wheat seedlings. During the first 18 days of the electric field connection, the Pb transportation from wheat roots to shoots was significantly increased, whereas after passing 18 days, the transportation of Pb in tall fescue and wheat was restrained [124].
3.5.2. Removal of Organic Pollutants
Huang et al. examined the SEKR of crude oil integrated with phytoremediation/rhizoremediation by planting ryegrass, and the results highlighted the increased removal of total petroleum hydrocarbon content (TPH) using the integrated SEKR and ryegrass compared to other tests [19]. Elevations of 16 S rDNA, Nah, AlkB, dehydrogenase activity, and Phe were reported. The integrated SEKR and phytoremediation improved microbial activity, and the rhizosphere microorganisms were enlarged successfully [19]. Applying the RPM improved plant germination and growth; in addition, high biomass production and the removal of TPHs were achieved after the experiment had been terminated (20 days). The RPM was more efficient for TPH removal, owing to its being capable of avoiding the progress of alkaline and acidity fronts, which enhanced the microbial degradation rate and the transportation of organic compounds. The RPM can effectively participate in water evaporation flux reduction and mobilization, as well as the good distribution of pollutants and nutrients inside soil [125]. Compared to the phytoremediation treatments and natural attenuation, the coupled SEKR-RPM and phytoremediation improved atrazine removal by 7% and 27%, respectively. Applying the electric field 24 h per day (continuously) increased the atrazine accumulation inside ryegrass plants, particularly in shoot biomass. The application of SEKR-RPM for 2 h caused a soil-pH reduction of less than one unit [126]. Sánchez et al. highlighted that it is not easy to sufficiently expect the efficiency of upscaling electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation using data obtained from reduced-scale investigations [120]. The integrated SEKR-RPM–phytoremediation (Ophiopogon japonica) improved the phytoremediation efficiency; the removal rates of phenanthrene and pyrene were increased. Applying an electric field also stimulated the release of root exudate, encouraged root growth, enhanced enzyme activity, and improved phenanthrene and pyrene accumulation. This effect was clearer with an electric field application of 4 h per day (low voltage) compared to 12 h per day [127].
3.5.3. Simultaneous Removal of Inorganic and Organic Pollutants
Acosta-Santoyo et al. studied the effect of EK on the improvement of ryegrass cultures (the germination of seeds and development) in inorganic (heavy metals) and organic (PAHs) pollutant-containing soils [51]. The germination of ryegrass seeds was improved by 75% in clean soil when applying a voltage of 0.2 V cm−1. The ryegrass germination and growth were negatively affected by the existence of contaminants in the soil, whereas an electric field application overcame this obstacle. Anodes made of stable materials are highly recommended to avoid toxic ions’ release, and it is recommended to use anodes made of graphite, owing to no toxicity being generated, as well as a low price. The integrated SEKR and phytoremediation for multi-contaminated soil achieved good outputs, particularly with the application of an AC electric field. Applying the AC electric field for 1 month maximized biomass production, therefore increasing the removal percentages of PAHs and heavy metals from polluted soil [51].
3.6. The SEKR-RPM Integrated with Phytoremediation and Bioremediation Simultaneously
The sustainability of SEK for n-hexadecane degradation was investigated by examining the integrated phytoremediation-assisted EK-bioremediation [18]. The RPM of 1 V cm−1 mode was applied every 2 h, and the results showed the enhancement of the EK sustainability integrated with ryegrass. In the rhizosphere zone, a harmonious micro-environment was constructed that eventually optimized the remediation of organically polluted soil using the integrated EK-Bio technology [18]. Lohner et al. cited that applying the RPM provided oxygen for a microbial community that may not be desirable for anaerobic bacteria, which may be one of the RPM’s disadvantages (“electrokinetic remediation seems not to be a feasible approach for the sequential anaerobic/aerobic bioelectro process”) [128]. The germination rates of sunflower seeds were increased (60–80%) in the case of adding solutions of citric acid and NaNO3 to catholyte simultaneously with the application of the SEKR-RPM. However, a germination reduction was significantly observed surrounding the cathode and anode when the cathodic solutions contained EDTA and NaNO3 simultaneously to applying the traditional SEKR [129].


Table 4.
Summary of reverse-polarity operation mode during the integrated SEKR–phytoremediation of inorganic and organic pollutant-contaminated soils.
Table 4.
Summary of reverse-polarity operation mode during the integrated SEKR–phytoremediation of inorganic and organic pollutant-contaminated soils.
| No. | Pollutant-Contaminated Soil | Applied Voltage | Reverse-Polarity Mode | Experimental Period | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Metal-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [20] |
| 2 | Heavy metal-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [121] |
| 3 | Uranium-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [119] |
| 4 | Cd-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [123] |
| 5 | Cd-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [54] |
| 6 | Pb-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [124] |
| 7 | Crude oil-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [19] |
| 8 | Petroleum-contaminated soils |
|
|
| [125] |
| 9 | Pesticide (atrazine)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [126] |
| 10 | Atrazine-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [120] |
| 11 | PAH (phenanthrene and pyrene)-contaminated soil |
|
|
| [127] |
| 12 | Soils contaminated with inorganic (heavy metals) and organic (PAHs) pollutants |
|
|
| [51] |
3.7. The Utilization of the SEK-RPM during Soil Consolidation, Stabilization, and Sedimentation
The EO flow’s unidirectional movement under the influence of an electric field (DC) is considered a problem that arose in previous research (e.g., “seriously uneven strength and difficult drainage collecting”), and it is mainly limited to EO practical engineering applications [65]. Sun et al. introduced a novel cyclic and progressive EO (CPE) method for soft clay consolidation using EKG [65]. The CPE basically depends on the RPM. The CPE is proposed to impose the EO flow toward one direction for the final converging at a certain electrode in order to avoid the obstacles of the traditional RPM, as previously presented in Figure 3 (Section 3.1). The utilization of the CPE using kaolin clay as target media revealed the omnidirectional enhancement of soil’s geotechnical properties. The EO was enhanced by filling cracks better than sodium chloride-solution additives, although a sodium chloride solution improved the voltage potential and current. Applying the CPE increased the bearing capacity of fine-particle soil [65]. Keykha et al. studied soft soil’s EK stabilization using the carbonate-producing bacteria; the RPM was utilized to ensure CaCO3’s homogeneous distribution. The produced from the bacterial activity was injected for four days into the chamber of the cathode using regular polarity and four days of the RPM [35]. The utilization of the RPM every 10–60 min was capable of removing the calcareous deposits surrounding the cathode [128].
The effect of integrated SEKR–sedimentation on the remediation and dewatering of artificially contaminated sediments was investigated [36]. The applied voltages were 10, 20, and 30 V; however, the experiment periods lasted for 17, 20, 24, 42, 44, and 55 h. In this study, the investigations were carried out in two stages, as follows: (a) sedimentation and (b) consolidation/remediation. The sedimentation was carried out by imposing an applied voltage in an upward direction (the cathode was positioned at the top, whereas the anode was at the bottom). Under the effect of electrophoreses, clay particles will migrate downward. In the second stage, the electrode positions (the anode was at the top, whereas the cathode was at the bottom cathode) stimulate the movement of water and organic substances downward via electroosmosis. In the second stage, the RPM was utilized while opening the channels for bottom drainage [36].
Feijoo et al. studied the enhanced SEK for porous materials’ consolidation [130]. Utilizing commercial products for consolidation faces some limitations, including (a) toxic compounds’ release, owing to solvent evaporation, (b) low penetrability, and (c) no chemical and mineralogical affinity with the material to treat. In this study, the RPM was associated with EK–consolidation through two stages. In the first stage, anions () migrate from the cathode compartment toward the anode, whereas cations (Mg2+) migrate toward the cathode. Precipitation occurs when Mg2+ and concentrations exceed the limit of saturation, which ultimately causes the clogging of pores (total or partial). In the second stage, the RPM is applied; the locations of poultices and solutions are changed. Also, the migration of Mg2+ and is reversed, which eventually causes MgCO3 precipitation within the stone’s superficial area (the surface is more vulnerable to process alteration). Following these two stages, satisfactory results were obtained based on the penetrability and durability with the merit of avoiding an extreme pH in the treated media [130]. Applying the RPM resulted in shear strength’s symmetrical distribution, which improved across the electrodes, particularly when the short-duration mode of the RPM was applied [131]. The RPM caused a fairly uniform distribution of plastic limits and liquid in the electrodes’ gap. The shorter duration of the RPM caused a more even distribution of water content in the electrodes’ gap [131]. Increasing the duration of the RPM and applied voltages reduced the EO consolidation time. The application of the RPM during electroosmotic consolidation was recommended to achieve a more soil-uniform development in the gap between electrodes [131]. Bergado et al. cited that applying the RPM reduced the corrosion of electrodes and avoided excessive desiccation, and it also stimulated a more uniform distribution of shear strength and water content because of the enhanced pore pressure development and a more uniform effective stress elevation [131]. Utilizing the prefabricated vertical drains during electroosmotic consolidation was examined for soft Bangkok clay in which different applied voltages (60, 80, and 120 V) and RPM durations (every 12, 24, and 48 h) were investigated [131].
Mwandira et al. studied the stabilization of clay using EK–biocementation in the presence of carbonic anhydrase-producing bacteria [132]. In this study, the RPM was utilized to preserve pH values, in addition to avoiding the unconducive conditions for biocementation and the precipitation of calcite [132]. Malekzadeh et al. cited that the RPM in time intervals is much more effective compared to the utilization of the RPM at the end of the EK, owing to the RPM intervals avoiding complete anode corrosion in addition to losses in soil conductivity. The RPM reduced the soil settlement rate, it did not influence the draining water amount, and it consumed more energy compared to the unidirectional approach [133]. Zhuang studied the utilization of the EKG approach for the consolidation of large-scale soft ground, and the RPM was applied simultaneously with an elevating voltage [134]. Utilizing an indigenous microorganism through coupled SEK–biocementation (injected via EK or mixed with soil) is a feasible approach in terms of unconfined compressive strength [135].
3.8. The SEKR-RPM Integrated with Fenton Oxidation
Oonnittan et al. investigated the influence of the RPM to remediate hexachlorobenzene using integrated SEKR–Fenton oxidation [136]. The experiments were operated under an applied voltage of 30 V, remediation periods of 10 and 20 days, and the RPM after 5 and 10 days. In experiments run with the RPM, the electrolyte compartments were emptied and cleaned before they were re-filled with catholyte and anolyte solutions. The H2O2 addition was also performed using injection wells that were kept undisturbed throughout the experimental period. Applying the RPM is considered an effective approach to oxidant reachability through contaminated soil within a shorter period. Applying the RPM enhanced the removed hexachlorobenzene from 10 to 33% over 10 days (better and more uniform hexachlorobenzene degradation was achieved). It was noticed that adding hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to the chamber of the anode was crucial for the degradation of hexachlorobenzene, which suggested the integration with another oxidant-delivery approach. Prolonging the RPM did not achieve the highest degradation of hexachlorobenzene [136]. The remediation of iron-rich soil contaminated with phenanthrene using the SEKR–Fenton process with anionic surfactant was examined by switching electrode polarity and the introduction direction of reagents [137]. The applied voltage was set to 30 V. Five experiments were investigated; two of them were run with the RPM and the direction of reagents’ introduction (exchanged at 240 h). The results showed that applying the RPM and the introduction direction of reagents resulted in the regeneration of EO flow because of electric-field redistribution. After the electrode polarity and the introduction direction of reagents were switched, the residual phenanthrene was degraded homogeneously (~70%) [137]. Yang et al. studied the degradation of phthalate esters and acetaminophen in samples collected from river sediments by applying the integrated in situ SEKR–Fenton-like process in which schwertmannite (nanoscale) was used as a catalyst [138]. The applied voltage was 1.5 V cm−1, and the RPM was applied after 7 and 14 days for experimental periods that lasted for 14 and 28 days, respectively. The sole SEKR (1.5 V cm−1) can remove both phthalates and acetaminophen from river sediments; however, applying the RPM can maintain pH values close to neutrality. The SEKR was time-dependent (i.e., prolonged experimental period from 14 to 28 days enhanced removal efficiency) [138].
3.9. Effect of the SEKR-RPM on Electrokinetic Operation Parameters and Soil Properties
The SEKR–adsorption process for treating saline–sodic soil was studied using the response surface modeling in terms of fluids’ replenishing processing [139]. In this study, the experimental condition was the RPM every 0, 24, and 48 h, an applied voltage of 0.2, 0.6, and 1 V cm−1, and pollutant (heavy metals and kerosene) concentrations (20, 60, and 100 mg kg−1). The results revealed that applying higher voltages (0.6 or 1 V cm−1) was associated with long interval periods of the RPM; some trials increased the volume of EO flow significantly. The occurrence of zeta-potential reversal during the application of the RPM was negligible. Increasing the RPM time intervals increased the catholyte replacement [139]. Kaniraj and Yee studied the EO consolidation of organic soil by evaluating the effect of drainage (drainage at the bottom and drainage tubes), the pumping interval (3, 6, and 12 h), and the RPM (0, 8, 12, and 24 h) [140]. The results highlighted that applying the RPM reduced the EO flow significantly, and a lesser increase in undrained shear strength was achieved. The EO consolidation incorporated with the RPM was not based on the intervals of the RPM. Applying the RPM increased the water content post-consolidation; in addition, the undrained strength distributions were increased. Operating experiments without applying the RPM reduced the content of water after the EO consolidation from the end of the cathode to the end of the anode, which eventually increased the undrained strength in the same location. It is recommended to perform the EO process not associated with the RPM and apply shorter pumping intervals if a minimum target for strength is achieved [140]. Hamdi et al. cited that utilizing the RPM can overcome the electric double-layer accumulation during electrokinetic practices, in addition to the capability of an energy-consumption reduction [11]. The RPM was recommended to avoid the dryness of the adjacent anode that ultimately causes cracks’ appearance, reducing the EO flow and reducing the current’s passing as a result of a loss in soil–electrode contact [133]. The RPM reduced the long-term operation complications of the unidirectional EK in the soil matrix, including the high, non-uniform potential and distribution of pH [141].
4. Conclusions
The present review has focused on the roles of the RPM during SEK operation for different purposes. Data were collected from six search engines covering the past 31 years (1993–2023). The roles of the SEKR-RPM were illustrated from eight perspectives, including (a) pollutant removal (organic, inorganic, and mixed pollutants), (b) integration with other processes (phyto/bioremediation and Fenton oxidation), (c) geosynthetics (consolidation, stabilization, and sedimentation), and (d) SEK operation conditions and soil properties. Several positive outputs could be gained from utilizing the SEKR-RPM, as follows (Figure 4):
- (a).
- Controlling the soil temperature, pH, and moisture values at desirable levels;
- (b).
- Reducing the large number of chemical additives;
- (c).
- High remediation efficiency;
- (d).
- Maintaining the indigenous fungal community’s appropriate diversity and abundance;
- (e).
- Stable and higher electric current passing, owing to avoiding a loss in soil–electrode contact;
- (f).
- Enhancing microbial growth;
- (g).
- Decreasing the electric field’s negative impact on degrading microorganisms;
- (h).
- Stimulating the contact between microorganisms, contaminants, and nutrients;
- (i).
- Enhancing the nutrient distribution and mitigating differences between remediation rates surrounding the anode and cathode;
- (j).
- Increased soil enzyme activity;
- (k).
- Smaller/optimal intervals can force the movement back and forth of the bacteria and phenol to primary positions;
- (l).
- Increasing reactive forms of heavy metals; however, decreasing residual forms;
- (m).
- Distributing ion-containing soil more uniformly;
- (n).
- Enhancing the Cr removal rate, particularly for Cr(III), which may be owing to improving the electric current and reducing the focusing phenomena;
- (o).
- Preventing Pb precipitation and the re-dissolution of precipitates;
- (p).
- Reducing polarization;
- (q).
- The RPM can completely remove the precipitated heavy metals located around the cathode;
- (r).
- Improving plant germination and growth, in addition to high biomass production and the removal of TPH;
- (s).
- The RPM can effectively participate in water evaporation flux reduction and mobilization;
- (t).
- Reducing the corrosion of electrodes and avoiding excessive desiccation;
- (u).
- Stimulating a more uniform distribution of shear strength and water content because of the enhanced pore pressure development and a more uniform effective stress elevation;
- (v).
- The occurrence of zeta potential reversal during the application of the RPM is negligible;
- (w).
- Avoiding the dryness of the adjacent anode, which ultimately causes cracks’ appearance.

Figure 4.
The positive influences of the reverse-polarity mode (RPM) on various factors during the application of soil electrokinetics.
Figure 4.
The positive influences of the reverse-polarity mode (RPM) on various factors during the application of soil electrokinetics.

On the other hand, ten hindrances appeared with the application of the RPM that could be summarized as follows (Figure 5):
- (a).
- Reducing the electroosmosis flow;
- (b).
- Relatively high energy consumption;
- (c).
- Reducing the diversity of soil microbes by prolonging the experimental period;
- (d).
- The RPM does not enhance the remediation of the contaminants of emergent concern;
- (e).
- The circulation of mixed electrolytes could control the soil pH well, rather than the application of the RPM;
- (f).
- The larger intervals may result in the accumulation of bacteria or phenol in a specific zone;
- (g).
- Cr accumulates in soil, which may be owing to the reciprocal migration of Cr;
- (h).
- in some cases, no significant increases in heavy metal uptake via plants were achieved;
- (i).
- Applying the RPM provides oxygen for a microbial community that may not be desirable for anaerobic bacteria;
- (j).
- Prolonging the RPM does not achieve the highest degradation of hexachlorobenzene.
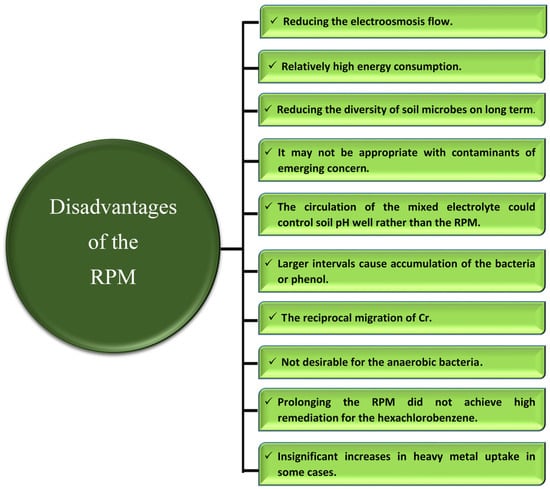
Figure 5.
The negative influences of the reverse-polarity mode (RPM) on various factors during the application of soil electrokinetic.
Figure 5.
The negative influences of the reverse-polarity mode (RPM) on various factors during the application of soil electrokinetic.
Finally, the RPM is considered an important process for improving the performance of SEK research, according to experimental endeavors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.-S.; methodology A.A.-S.; software, A.A.-S.; validation, A.A.-S.; formal analysis, A.A.-S.; investigation, A.A.-S. and H.E.-A.; resources, A.A.-S. and H.E.-A.; data curation, A.A.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.-S.; writing—review and editing, A.A.-S. and H.E.-A.; visualization, A.A.-S.; supervision, A.A.-S.; project administration, A.A.-S.; funding acquisition, A.A.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STIFA); project number: 39369.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, H.; Pu, M.; Li, H.; Lu, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, C.; Pu, W.; Liu, R.; Guo, K.; et al. Progress and prospects for remediation of soil potentially toxic elements pollution: A state-of-the-art review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Shi, C.; Tu, W.; Li, L.; Li, Q. Recent developments in modification of biochar and its application in soil pollution control and ecoregulation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Ai, X.; Wang, B.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Single atom catalysts for organic pollutant degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, J.; Huang, X.; Qiu, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Qu, J.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J. Organic pollutants removal from aqueous solutions using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as adsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yang, J.; Xing, Y.; Ling, W.; Liu, K.; Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Pei, Z.; Wu, T.; et al. The fate of microplastic pollution in the Changjiang River estuary: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Iqbal, M.; Mehmood, K.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, H. Challenges of fluoride pollution in environment: Mechanisms and pathological significance of toxicity—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, A.; Hartmann, P.; Urso, L.; Vives i Batlle, J.; Gonze, M.A.; Calmon, P.; Steiner, M. Approaches to modelling radioactive contaminations in forests—Overview and guidance. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 178–179, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; He, R.; Tian, C.Y.; Song, J. Utilization of halophytes in saline agriculture and restoration of contaminated salinized soils from genes to ecosystem: Suaeda salsa as an example. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Jiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, F. A review of functions and mechanisms of clay soil conditioners and catalysts in thermal remediation compared to emerging photo-thermal catalysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, F.M.; Ganbat, N.; Altaee, A.; Samal, A.K.; Ibrar, I.; Zhou, J.L.; Sharif, A.O. Hybrid and enhanced electrokinetic system for soil remediation from heavy metals and organic matter. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 424–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D. Combination of electrochemical advanced oxidation and biotreatment for wastewater treatment and soil remediation. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 150, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaleh, H.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y.; Sun, Q.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; AbdElgawad, H. Soil flushing coupled with aminated-nanocellulose/MOF hydrogel nanocomposites adsorbents: A novel sustainable remediation strategy for Cr(VI)-contaminated agricultural soils. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Xu, D.; Yue, J.; Ma, Y.; Dong, S.; Feng, J. Recent advances in soil remediation technology for heavy metal contaminated sites: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, J.D.; Raimondo, E.E.; Saez, J.M.; Costa-Gutierrez, S.B.; Álvarez, A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Polti, M.A. The current approach to soil remediation: A review of physicochemical and biological technologies, and the potential of their strategic combination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Ismail, S.; Yossif, T.M.H.; Yassin, S.A.; Ali, M.E.A.; Habib, A.A.M.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Tag-Elden, M.A.; Emam, T.M.; Mahmoud, A.A.; et al. Comprehensive review of progress made in soil electrokinetic research during 1993–2020, part II. No.1: Materials additives for enhancing the intensification process during 2017–2020. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 45, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Ali, M.E.A.; Ismail, S.; Abd-Elmottaleb, O.; Kotp, Y.H.; Osman, M.A.; Hegab, R.H.; Habib, A.A.M.; Saudi, A.M.; Eissa, D.; et al. Comprehensive review of progress made in soil electrokinetic research during 1993–2020, Part I: Process design modifications with brief summaries of main output. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 44, 156–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, F.; Guo, P.; Guo, S. Enhancement of electrokinetic-bioremediation by ryegrass: Sustainability of electrokinetic effect and improvement of n-hexadecane degradation. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Tang, J.; Niu, Z.; Giesy, J.P. Interactions between electrokinetics and rhizoremediation on the remediation of crude oil-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, R.; Schlaak, M.; Siefert, E.; Lord, R.; Connolly, H. Influence of electrical fields (AC and DC) on phytoremediation of metal polluted soils with rapeseed (Brassica napus) and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Chemosphere 2011, 83, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Yu, W. Recent advances in electrokinetic methods for soil remediation. A critical review of selected data for the period 2021–2022. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, A.; Hansen, H.K.; Agramonte, M. Electrokinetic remediation with high frequency sinusoidal electric fields. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Peng, C. New process for ex situ electrokinetic pollutant removal. I: Process evaluation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 2162–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, E.-M.M.; Abou-Shady, A.; Ghoniem, A.E.; Abdelhamied, A.S. Enhancement of the electrokinetic removal of heavy metals, cations, anions, and other elements from soil by integrating PCPSS and a chelating agent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 134, 104306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, Y.B.; Gale, R.J.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Marks, R.E.; Puppala, S.; Bricka, M.; Parker, R. Electrokinetic remediation: Basics and technology status. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 40, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, Y.B.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Gale, R.J. Fundamentals of extracting species from soils by electrokinetics. Waste Manag. 1993, 13, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, Y.B.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Principles of electrokinetic remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 2638–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probstein, R.F.; Hicks, R.E. Removal of contaminants from soils by electric fields. Science 1993, 260, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.P.; Probstein, R.F. Removal of contaminants from saturated clay by electroosmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, M.; Chen, L.; Gong, Z.; Hu, J.; Ma, D. Electrokinetic remediation for the removal of heavy metals in soil: Limitations, solutions and prospection. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 165970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhao, P.; Khare, A.; Patil, M.; Kumar, A.R. Roles of surfactant, oxidant and activator on enhanced electrokinetic-persulfate technique for the removal of hydrophobic organic compounds in soil: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulpoto, I.A.; Yu, Z.; Qazi, M.A.; Ndayisenga, F.; Yang, J. A comprehensive study on microbial-surfactants from bioproduction scale-up toward electrokinetics remediation of environmental pollutants: Challenges and perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Wen, F.; Ren, Y.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X. An overview of bioelectrokinetic and bioelectrochemical remediation of petroleum-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 16, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Shady, A.; El-Araby, H. Electro-agric, a novel environmental engineering perspective to overcome the global water crisis via marginal water reuse. Nat. Hazards Res. 2021, 1, 202–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keykha, H.A.; Huat, B.B.K.; Asadi, A. Electrokinetic stabilization of soft soil using carbonate-producing bacteria. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2014, 32, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.I. Dewatering and decontamination of artificially contaminated sediments during electrokinetic sedimentation and remediation processes. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 10, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Almeira, J.O.; Abou-Shady, A. Enhancement of ion migration in porous media by the use of varying electric fields. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeira, J.; Peng, C.; Abou-Shady, A. Enhancement of ion transport in porous media by the use of a continuously reoriented electric field. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2012, 13, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Fan, X.; Qian, Y. In situ bioelectrokinetic remediation of phenol-contaminated soil by use of an electrode matrix and a rotational operation mode. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Shady, A.; El-Araby, H.; El-Harairy, A.; El-Harairy, A. Utilizing the approaching/movement electrodes for optimizing the soil electrokinetic remediation: A comprehensive review. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 50, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A. A critical review of enhanced soil electrokinetics using perforated electrodes, pipes, and nozzles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Eissa, D.; Abdelmottaleb, O.; Hegab, R. New approaches to remediate heavy metals containing polluted soil via improved PCPSS. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.M.; Eissa, D.T.; Abdelmottaleb, O.M.; Hegab, R.H. Effect of electrokinetic pollutant removal on the status of some macro and micro elements in saline soil. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2018, 39, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.M.; Eissa, D.T.; Abdelmottaleb, O.M.; Hegab, R.H. Behavior of V, Cr, Li, and Ba during electrokinetic pollutant removal: Comparison of PCPSS and VA-PCPSS. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2018, 39, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A. Reclaiming salt-affected soils using electro-remediation technology: PCPSS evaluation. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 190, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.L.; Sáez, C.; Lanza, M.R.V.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Removal of chlorsulfuron and 2,4-D from spiked soil using reversible electrokinetic adsorption barriers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 178, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, P.; Lopes, V.; Couto, N.; Mateus, E.P.; Pereira, C.S.; Ribeiro, A.B. Electrokinetic remediation of contaminants of emergent concern in clay soil: Effect of operating parameters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Guo, S.; Hartog, N. Electrokinetics-enhanced biodegradation of heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil around iron and steel industries. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 85, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S. Effects of electrokinetic operation mode on removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and the indigenous fungal community in PAH-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2013, 48, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q. Insights into the remediation of cadmium-pyrene co-contaminated soil by electrokinetic and the influence factors. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Santoyo, G.; Cameselle, C.; Bustos, E. Electrokinetic—Enhanced ryegrass cultures in soils polluted with organic and inorganic compounds. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeira, O.J.; Peng, C.-S.; Abou-Shady, A. Simultaneous removal of cadmium from kaolin and catholyte during soil electrokinetic remediation. Desalination 2012, 300, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Han, F.; Wang, K.; Lv, Y. Migration and removal of labile Cadmium contaminants in paddy soils by electrokinetic remediation without changing soil pH. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Li, D.; Ye, X.; Xu, H.; Yao, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Gao, N. Enhancement of Cd phytoextraction by hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii using electrical field and organic amendments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5060–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H. Exchange electrode-electrokinetic remediation of Cr-contaminated soil using solar energy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Duan, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhu, X.; Shi, X.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, M.; Xiong, J.; Li, T. Lead dissociation and redistribution properties of actual contaminated farmland soil after long-term EKAPR treatment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 45, 9507–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, A.; Hansen, H.K.; Cubillos, M. Electrokinetic remediation using pulsed sinusoidal electric field. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 86, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, A.; Hansen, H.K.; del Campo, J. Electrodialytic remediation of copper mine tailings with sinusoidal electric field. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, A.; Hansen, H.K.; Monárdez, O. Electrokinetic remediation of mine tailings by applying a pulsed variable electric field. Miner. Eng. 2014, 55, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, M.E.; Jennings Taylor, E.; Myers, D.L.; Zhou, C. Electrokinetic Soil Remediation Using Novel Electrodes and Modulated Reverse Electric Fields. In Emerging Technologies in Hazardous Waste Management 8; Tedder, D.W., Pohland, F.G., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 21–28. ISBN 978-0-306-46921-3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, S.; Wan, J.; Long, H.; Tong, M. A combination of electrokinetics and Pd/Fe PRB for the remediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soil. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Fan, R.; Li, T.; Hartog, N.; Li, F.; Yang, X. Synergistic effects of bioremediation and electrokinetics in the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, G.; Wu, B.; Tai, P. Study on Remediation Technologies of Organic and Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils BT. In Twenty Years of Research and Development on Soil Pollution and Remediation in China; Luo, Y., Tu, C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 703–723. ISBN 978-981-10-6029-8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Tong, M.; Guo, S. Treatment of PAHs contaminated soil in abandoned industrial site using combined method of improved in situ capping and electrokinetic enhanced-bioremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, T.; Yao, K.; Kasu, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Gong, J. Consolidation of soft clay by cyclic and progressive electroosmosis using electrokinetic geosynthetics. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, E.; Villaseñor, J.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Effect of electric field on the performance of soil electro-bioremediation with a periodic polarity reversal strategy. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, E.; Villaseñor, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. Electrokinetic remediation of soil polluted with insoluble organics using biological permeable reactive barriers: Effect of periodic polarity reversal and voltage gradient. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 299, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Wu, B.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Coupling electrokinetics with microbial biodegradation enhances the removal of cycloparaffinic hydrocarbons in soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Ma, J.; Ye, J.; Guo, P.; Li, L. Fate of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in the electrokinetic treatment of antibiotic-polluted soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tian, Y.; Liu, W.; Long, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, B.; Li, N.; Yan, M.; Zhu, C. Impact of electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal contamination on antibiotic resistance in soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.C.; Huang, S.-C.; Jen, Y.-S.; Tsai, P.-S. Remediation of phthalates in river sediment by integrated enhanced bioremediation and electrokinetic process. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Shao, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X. Insights into electro-bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soil under polarity reversal conditions: Effect of effective current intensity and soil properties on microbial function. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cascán, J.; Isidro, J.; Guadaño, J.; Sáez, C.; Rodrigo, M.A. Electrochemically-assisted remediation of silt polluted with aged HCHs. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 464, 142934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crognale, S.; Cocarta, D.M.; Streche, C.; D’Annibale, A. Development of laboratory-scale sequential electrokinetic and biological treatment of chronically hydrocarbon-impacted soils. New Biotechnol. 2020, 58, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, S.; Villaseñor, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. Can electro-bioremediation of polluted soils perform as a self-sustainable process? J. Appl. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, E.M.; Camacho, J.V.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. Combination of bioremediation and electrokinetics for the in-situ treatment of diesel polluted soil: A comparison of strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Guo, S. Effects of soil organic carbon metabolism on electro-bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Effect of polarity-reversal on electrokinetic enhanced bioremediation of Pyrene contaminated soil. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Tian, H.; Wu, Q.; Yi, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, B. Mechanism of bio-electrokinetic remediation of pyrene contaminated soil: Effects of an electric field on the degradation pathway and microbial metabolic processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Guo, S.; Li, T.; Wu, B. Coupling interactions between electrokinetics and bioremediation for pyrene removal from soil under polarity reversal conditions. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, S.; Hartog, N.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, X. Isolation and characterization of heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria adapted to electrokinetic conditions. Biodegradation 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Novel Bacillus cereus strain from electrokinetically remediated saline soil towards the remediation of crude oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26351–26360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbottle, M.J.; Lear, G.; Sills, G.C.; Thompson, I.P. Enhanced biodegradation of pentachlorophenol in unsaturated soil using reversed field electrokinetics. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H. A laboratory feasibility study on a new electrokinetic nutrient injection pattern and bioremediation of phenanthrene in a clayey soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, S.; Villaseñor, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. Effect of the polarity reversal frequency in the electrokinetic-biological remediation of oxyfluorfen polluted soil. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, S.; Villaseñor, J.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Strategies for the electrobioremediation of oxyfluorfen polluted soils. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 297, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, S.; Ocaña, H.; Villaseñor, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. Electrobioremediation of oxyfluorfen-polluted soil by means of a fixed-bed permeable biological barrier. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira dos Santos, E.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Rodrigo, M.A. Reversible electrokinetic adsorption barriers for the removal of atrazine and oxyfluorfen from spiked soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, S.; Saez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Reversible electrokinetic adsorption barriers for the removal of organochlorine herbicide from spiked soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, H. Electrokinetic remediation of antibiotic-polluted soil with different concentrations of tetracyclines. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8212–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, J.; Báez, M.E.; Calzadilla, W.; Aranda, M.; Salazar, R. Removal of chloridazon and its metabolites from soil and soil washing water by electrochemical processes. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 425, 140682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller de Melo Henrique, J.; Isidro, J.; Sáez, C.; López-Vizcaíno, R.; Yustres, A.; Navarro, V.; Dos Santos, E.V.; Rodrigo, M.A. Enhancing soil vapor extraction with EKSF for the removal of HCHs. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Qian, Y. Mobilization of phenol and dichlorophenol in unsaturated soils by non-uniform electrokinetics. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Qian, Y. The use of non-uniform electrokinetics to enhance in situ bioremediation of phenol-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 121, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Vizcaíno, R.; Yustres, A.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Navarro, V. Effect of polarity reversal on the enhanced electrokinetic remediation of 2,4-D-polluted soils: A numerical study. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Han, S.J. Application of an enhanced electrokinetic ion injection system to bioremediation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 146, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebria, D.Y.; Taghizadeh, M.; Camacho, J.V.; Latifi, N. Remediation of PCE contaminated clay soil by coupling electrokinetics with zero-valent iron permeable reactive barrier. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.V.; Sheridan, P.W.; Athmer, C.J.; Heitkamp, M.A.; Brackin, J.M.; Weber, D.; Brodsky, P.H. Integrated In Situ Soil Remediation Technology: The Lasagna Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2528–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.V.; Athmer, C.; Sheridan, P.W.; Hughes, B.M.; Orth, R.; McKenzie, D.; Brodsky, P.H.; Shapiro, A.; Thornton, R.; Salvo, J.; et al. The Lasagna Technology for In Situ Soil Remediation. 1. Small Field Test. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.V.; Athmer, C.; Sheridan, P.W.; Hughes, B.M.; Orth, R.; McKenzie, D.; Brodsky, P.H.; Shapiro, A.M.; Sivavec, T.M.; Salvo, J.; et al. The Lasagna Technology for In Situ Soil Remediation. 2. Large Field Test. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Báez, M.E. Behavior of chlorpyrifos and 3, 5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP) in a sodium-dodecyl sulphate-electrokinetic soil washing system. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 445, 141936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.A.; Cameselle, C. Improvement in electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal spiked kaolin with the polarity exchange technique. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukman, S.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Essa, M.H.; Usman, A. Optimal removal of cadmium from heavily contaminated saline–sodic soil using integrated electrokinetic-adsorption technique. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ma, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X. Electrokinetic remediation of Cd-contaminated soil using low voltage gradients coupled with array adsorption zone and polarity exchange. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhuang, Y. Removal of Chromium from Contaminated Soil by Electrokinetic Remediation Combined with Adsorption by Anion Exchange Resin and Polarity Reversal. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2024, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-G.; Hong, K.-K.; Kim, Y.-W.; Lee, J.-Y. Enhanced electrokinetic (E/K) remediation on copper contaminated soil by CFW (carbonized foods waste). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; van Doren, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, W. Improvement in electrokinetic remediation of Pb-contaminated soil near lead acid battery factory. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3088–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, M.H.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Lukman, S.; Bukhari, A. Application of box-behnken design to hybrid electrokinetic-adsorption removal of mercury from contaminated saline-sodic clay soil. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2015, 24, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, D.C.; Đolić, M.B.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; dos Santos, E.V.; Silva, T.F.C.V.; Vilar, V.J.P. Coupling electrokinetic with a cork-based permeable reactive barrier to prevent groundwater pollution: A case study on hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 429, 140936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Bai, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yao, M.; Zhao, Y. Lab scale-study on the efficiency and distribution of energy consumption in chromium contaminated aquifer electrokinetic remediation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Gong, W.; Chen, Y.; Hong, J.; Wang, Y. Influence of polarity exchange frequency on electrokinetic remediation of Cr-contaminated soil using DC and solar energy. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 153, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Feng, Q.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, T. Electrokinetic remediation of chromium- and cadmium-contaminated soil from abandoned industrial site. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 98, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Song, C.; Zhang, F.; Jia, X.; Ma, D. New-style electrokinetic-adsorption remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil using double-group electrodes coupled with chitosan-activated carbon composite membranes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Guo, X.; Fu, R. Inhibition characteristics of the electrokinetic removal of inorganic contaminants from soil due to evolution of the acidic and alkaline fronts. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Kim, S.S. Application of enhanced electrokinetic extraction for lead spiked kaolin. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2003, 7, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Luo, H.; Luo, J.; Liu, F. Effect of ascorbic acid and combination with fulvic acid on the electrokinetic remediation of paddy soil contaminated by arsenic-containing acid mine drainage. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 152, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta Hernández, I.; Muñoz Morales, M.; Fernández Morales, F.J.; Rodríguez Romero, L.; Villaseñor Camacho, J. Removal of heavy metals from mine tailings by in-situ bioleaching coupled to electrokinetics. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.W.; Wang, F.Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, H. Simultaneous removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol and Cd from soils by electrokinetic remediation combined with activated bamboo charcoal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Larson, S.L.; Ballard, J.H.; Ma, Y.; Su, Y.; Han, F.X. Coupling Electrokinetics and Phytoremediation to Remove Uranium from Contaminated Soil: A Laboratory Pilot-Scale Study. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 3448–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, V.; López-Bellido, F.J.; Cañizares, P.; Villaseñor, J.; Rodríguez, L. Scaling up the electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation of atrazine-polluted soils using reversal of electrode polarity: A mesocosm study. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Díaz, H.L.; López-Bellido, F.J.; Alonso-Azcárate, J.; Fernández-Morales, F.J.; Rodríguez, L. Comprehensive study of electrokinetic-assisted phytoextraction of metals from mine tailings by applying direct and alternate current. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 445, 142051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrazi, A.; Ghasemi-Fasaei, R.; Mojiri, A.; Shirazi, S.S. Investigating an electro-bio-chemical phytoremediation of multi-metal polluted soil by maize and sunflower using RSM-based optimization methodology. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 211, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, H.; Skuza, L.; Wei, S. The effects of different electric fields and electrodes on Solanum nigrum L. Cd hyperaccumulation in soil. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulati, H.; Mamat, A.; Ailijiang, N.; Jiang, L.; Li, N.; Hu, Y.; Su, Y. Electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation of pb-contaminated soil: Influences of periodic polarity reversal direct current field. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.M.V.; Silva, K.N.O.; Silva, D.R.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Santos, E. V Coupling electrokinetic remediation with phytoremediation for depolluting soil with petroleum and the use of electrochemical technologies for treating the effluent generated. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 208, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, V.; Francisco; López-Bellido, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Rodríguez, L. Enhancing the removal of atrazine from soils by electrokinetic-assisted phytoremediation using ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Chemosphere 2019, 232, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Johnson, D.M.; Xi, Y. Enhancement of electrokinetic-phytoremediation by Ophiopogon japonicus: Stimulation of electrokinetic on root system and improvement of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 97591–97600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohner, S.T.; Becker, D.; Mangold, K.-M.; Tiehm, A. Sequential Reductive and Oxidative Biodegradation of Chloroethenes Stimulated in a Coupled Bioelectro-Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6491–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, K.N.O.; Paiva, S.S.M.; Souza, F.L.; Silva, D.R.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Santos, E. V Applicability of electrochemical technologies for removing and monitoring Pb2+ from soil and water. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 816, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, J.; Ottosen, L.M.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Rivas, T.; de Rosario, I. An improved electrokinetic method to consolidate porous materials. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergado, D.T.; Balasubramaniam, A.S.; Patawaran, M.A.B.; Kwunpreuk, W. Electro-osmotic consolidation of soft Bangkok clay with prefabricated vertical drains. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Improv. 2000, 4, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwandira, W.; Mavroulidou, M.; Satheesh, A.; Gunn, M.J.; Gray, C.; Purchase, D.; Garelick, J. An electrokinetic-biocementation study for clay stabilisation using carbonic anhydrase-producing bacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 104916–104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, M.; Lovisa, J.; Sivakugan, N. An Overview of Electrokinetic Consolidation of Soils. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y. Large scale soft ground consolidation using electrokinetic geosynthetics. Geotext. Geomembranes 2021, 49, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.U.; Mavroulidou, M.; Gunn, M.J.; Purchase, D.; Payne, I.; Garelick, J. Electrokinetic biocementation of an organic soil. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonnittan, A.; Isosaari, P.; Sillanpää, M. Effect of polarity reversal on hexachlorobenzene removal during electrokinetic Fenton process. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Switching effects of electrode polarity and introduction direction of reagents in electrokinetic-Fenton process with anionic surfactant for remediating iron-rich soil contaminated with phenanthrene. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 8094–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.C.; Huang, S.-C.; Wang, C.-L.; Jen, Y.-S. Degradation of phthalate esters and acetaminophen in river sediments using the electrokinetic process integrated with a novel Fenton-like process catalyzed by nanoscale schwertmannite. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu’azu, N.D.; Essa, M.H.; Lukman, S. Response surface modeling of rate of replenishing processing fluids during hybrid electrokinetics-adsorption treatment of saline-sodic soil. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniraj, S.R.; Yee, J.H.S. Electro-Osmotic Consolidation Experiments on an Organic Soil. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2011, 29, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.V.; Athmer, C.J.; Sheridan, P.W.; Shapiro, A.P. Scale-up aspects of the LasagnaTM process for in situ soil decontamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 1997, 55, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).